Eat healthy during pregnancy
Eat Healthy During Pregnancy: Quick tips - MyHealthfinder
Pregnancy
When you are pregnant, you need more of certain nutrients like protein, iron, folic acid, and iodine. It’s also important to get enough calcium.
Making smart food choices can help you have a healthy pregnancy and a healthy baby. Here are some ideas to help you eat healthy during pregnancy.
Follow a healthy eating pattern.
Eating healthy means following a healthy eating pattern that includes a variety of nutritious foods and drinks.
- Eat a variety of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, fat-free or low-fat dairy products, and protein foods.
- Choose foods and drinks with less added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium (salt).
- Limit refined grains and starches, which are in foods like cookies, white bread, and some snack foods.
- If you are feeling sick, try eating a piece of whole-grain toast or whole-grain crackers.
Learn more about eating healthy.
Get the right amount of calories for you.
Being pregnant doesn't mean you need to eat twice as much food.
- First trimester (first 12 weeks) – Most women don’t need any extra calories.
- Second trimester (13 to 26 weeks) – Most women need about 340 extra calories a day.
- Last trimester (after 26 weeks) – Most women need about 450 extra calories a day.
Ask your doctor or midwife how many calories you need during pregnancy.
Create a personalized Daily Food Plan.
Make healthy snack choices.
Examples of healthy snacks include:
- Low-fat or fat-free yogurt with fruit (look for options with no added sugar)
- Whole-grain crackers with fat-free or low-fat cheese
- Carrots with hummus
Take a prenatal vitamin with folic acid, iron, and iodine every day.
- Folic acid helps prevent some birth defects of the brain and spine.
- Iron and iodine help keep you and your baby healthy.

Talk with your doctor or nurse about a prenatal vitamin that’s right for you.
Eat 8 to 12 ounces of seafood each week.
Fish and shellfish have healthy fats that are good for you and your baby. But some fish is high in mercury, a metal that can hurt your baby’s development. It’s a good idea to eat seafood that is high in healthy fats but lower in mercury.
Best choices
These choices are lower in mercury, so you can eat 8 to 12 ounces a week.
- Canned light tuna
- Catfish
- Cod
- Herring
- Oysters
- Salmon
- Shad
- Shrimp
- Tilapia
- Trout
Good choices
You can eat 4 ounces of these fish a week if you don’t eat any other seafood that week.
- Canned or fresh white (albacore) tuna
- Chilean sea bass or striped bass
- Grouper
- Halibut
- Mahi-mahi
- Snapper
- Yellowfin tuna
Fish to avoid
Don’t eat bigeye tuna, king mackerel, marlin, orange roughy, shark, swordfish, or tilefish. They are high in mercury.
They are high in mercury.
Learn more about choosing fish that is healthy and safe to eat [PDF - 308 KB].
Don’t eat certain foods.
These foods may have bacteria in them that can hurt your baby. Stay away from:
- Raw (uncooked) or rare (undercooked) fish or shellfish, like sushi or raw oysters
- Soft cheeses (like feta, Brie, and goat cheese), unless they are pasteurized
- Raw or rare meats, poultry, or eggs
- Unpasteurized juices or milk
- Lunch or deli meats, smoked seafood, and hot dogs – unless they are heated until steaming hot
- Prepared salads like ham salad, chicken salad, or seafood salad
- Raw sprouts, including alfalfa, clover, radish, and mung bean sprouts
Learn more about foods to avoid during pregnancy.
Limit drinks with caffeine and added sugars.
- If you drink coffee or tea, choose decaf. Pick unsweetened options and don’t add sugar.
- Drink water or seltzer instead of drinks with added sugars like soda, fruit drinks, and energy or sports drinks.

Don’t drink alcohol.
No amount of alcohol is safe during pregnancy.
Content last updated June 1, 2022
Reviewer Information
This information on healthy eating during pregnancy was adapted from materials from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Office on Women’s Health, and the National Institutes of Health Weight-control Information Network (WIN).
Reviewed by:
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services and the U.S. Department of Agriculture Dietary Guidance Review Committee
For more information on healthy eating during pregnancy, visit:
- http://www.choosemyplate.gov/moms-pregnancy-breastfeeding
- https://www.womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/staying-healthy-and-safe
Healthy eating before having a baby
Eating nutrient-dense foods that contain a variety of vitamins and minerals can help you be healthy before and during pregnancy.

Getting to a healthy weight before becoming pregnant can improve your chances of conceiving and having a healthy pregnancy and baby.
Taking 400 mcg of folic acid before pregnancy can help protect your baby from birth defects.
Substitute sodas that are sweetened with sugar for water and other low or non-sugary drinks. This may help reduce the risk for gestational diabetes.
It’s best to limit caffeine to no more than one or two 6-ounce cups of coffee each day. Some studies show that too caffeine may affect your chances of getting pregnant.
What can you eat to help you have a healthy pregnancy?
It’s common for women to look for information about how to be as healthy as possible before pregnancy. This includes what foods are best to eat and which foods to avoid. For example, you may wonder how the foods you eat can affect a chronic health condition or your fertility.
The foods you eat provide nutrients that are important to help you be healthy before and during pregnancy. Nutrients are parts of food, like vitamins and minerals that help your body stay healthy.
Nutrients are parts of food, like vitamins and minerals that help your body stay healthy.
Eat a balanced diet including:
- Products made from whole grains including corn tortillas, oatmeal, brown rice, bread, pasta, and cereals
- Fruit of all types, including raw, frozen, or canned without added sugar, and juice that is 100% fruit juice
- Vegetables of all colors, including raw, frozen, or “low sodium” canned and 100% vegetable juice
- Lean protein from meat, poultry, fish, eggs, beans, peas, peanut butter, soybeans and tofu
- Low-fat or fat-free dairy, including milk, cheese, and yogurt
- Healthy fats from avocados, nuts, seeds, vegetable oil, and olive oil
The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s choosemyplate.gov website can help you plan healthy meals before and during pregnancy.
Any meat that you eat should be cooked thoroughly. Toxoplasmosis is an illness caused by a parasite in food. A parasite is a plant or an animal that lives in or on another plant or animal. Toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma gondii is found in raw and undercooked meat; unwashed fruits and vegetables; contaminated water; dust; soil; dirty cat litter boxes; and outdoor places where cat poop can be found. If you get toxoplasmosis right before getting pregnant, this can be harmful to you and your baby.
Toxoplasmosis is caused by the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Toxoplasma gondii is found in raw and undercooked meat; unwashed fruits and vegetables; contaminated water; dust; soil; dirty cat litter boxes; and outdoor places where cat poop can be found. If you get toxoplasmosis right before getting pregnant, this can be harmful to you and your baby.
Avoid touching your mouth with your hands after cleaning the litter box or gardening, and make sure that the meat that you eat is cooked properly.
How much folic acid do you need before getting pregnant?
Folic acid is a vitamin that every cell in your body needs for healthy growth and development. If you take folic acid before pregnancy and during early pregnancy, it can help protect your baby from birth defects of the brain and spine called neural tube defects (NTDs) and birth defects of the mouth called cleft lip and palate.
To help prevent birth defects, take a vitamin supplement with 400 mcg of folic acid in it every day at least 1 month before pregnancy through the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Later in pregnancy, you need 600 mcg of folic acid each day to help your baby grow and develop. Take a vitamin supplement with 400 mcg of folic acid each day, even if you're not trying to get pregnant.
Later in pregnancy, you need 600 mcg of folic acid each day to help your baby grow and develop. Take a vitamin supplement with 400 mcg of folic acid each day, even if you're not trying to get pregnant.
If you’re at high risk for having a baby with an NTD, take 4,000 mcg of folic acid each day to help prevent an NTD. Start taking 4,000 mcg 3 months before you get pregnant through 12 weeks of pregnancy.
You also can get folic acid in food. When folic acid is naturally in food, it’s called folate. Foods that are good sources of folate are:
- Beans, like lentils, pinto beans, and black beans
- Leafy green vegetables, like spinach and Romaine lettuce
- Asparagus
- Broccoli
- Peanuts
- Citrus fruits, like oranges and grapefruit
- Berries
- Orange juice (100% juice is best)
Folic acid is the manmade form of folate that is in fortified foods and vitamin supplements. Fortified and enriched means a food has added nutrients, like folic acid. Look for the word “fortified” or “enriched” on labels on foods like:
Look for the word “fortified” or “enriched” on labels on foods like:
- Bread
- Breakfast cereal
- Cornmeal
- Flour
- Pasta
- Products made from a kind of flour called corn masa, like tortillas, tortilla chips, taco shells, tamales and pupusas
- White rice
Should you watch how much sugar you eat?
Eating or drinking too much sugar may raise your risk of developing heart disease, high blood pressure, chronic inflammation, diabetes and fatty liver disease. It also can make you gain too much weight.
Sugar occurs naturally in all foods that contain carbohydrates. This includes fruits, vegetables, grains and dairy. Your body digests foods that contain natural sugar slowly. This provides a steady supply of energy to your cells. Make sure you eat enough fresh fruits and vegetables. They may help you reduce the risk of getting a chronic health condition like diabetes, heart disease or some types of cancer.
Added sugars are sugars that aren’t found naturally in foods. It is sugar that is added to foods and drinks to make them taste better. Drinks are the most common source of added sugars. Soft drinks, fruit drinks, sports and energy drinks, coffee and tea drinks (not black coffee or tea), flavored yogurts, cereals, cookies, cakes, candy, and most processed foods also have added sugar. It also can be found in foods you may not think are sweet, like soups, bread, cured meats like bologna, and ketchup.
Find added sugars in your foods by checking the food label. Some names for added sugars in foods include honey, high fructose corn syrup, maple syrup, fruit juice concentrate and dextrose. The American Heart Association (also called AHA) recommends that women limit added sugar to no more than 6 teaspoons a day. That is no more than 25 grams of added sugar per day.
Most adults eat or drink about 77 grams of sugar a day. That is 3 times more sugar than a woman should have. One can of soda contains 8 teaspoons of added sugar. Fresh fruits have natural sugar, but they also have fiber, vitamins and minerals. It is much healthier to eat a piece of fresh fruit or to drink a glass of water than any candy or soda with added sugar.
Fresh fruits have natural sugar, but they also have fiber, vitamins and minerals. It is much healthier to eat a piece of fresh fruit or to drink a glass of water than any candy or soda with added sugar.
Food labels will soon include the amount of added sugar in each product. This will make tracking how much added sugar you eat easier.
How much caffeine is safe to drink when trying to get pregnant?
Studies show that women who drink more than 2 cups of coffee or 5 cans of soda that contain caffeine may have a harder time getting pregnant.
Caffeine is found in:
- Coffee
- Coffee-flavored products, like yogurt and ice cream
- Tea
- Some soft drinks
- Energy drinks
- Chocolate and chocolate products, like chocolate syrup and hot cocoa
You may have heard that too much caffeine may cause miscarriage (when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy). Some studies say this is true, and others don’t. Until we know more about how caffeine can affect pregnancy, it’s best to limit the amount you get to 200 milligrams each day. This is about the amount in one 12-ounce cup of coffee or two 6-ounce cups of coffee. Be sure to check the size of your cup to know how much caffeine you’re getting.
Until we know more about how caffeine can affect pregnancy, it’s best to limit the amount you get to 200 milligrams each day. This is about the amount in one 12-ounce cup of coffee or two 6-ounce cups of coffee. Be sure to check the size of your cup to know how much caffeine you’re getting.
The amount of caffeine you get from food and drinks throughout the day adds up. If you have a cup of coffee in the morning, you may want to limit having other foods and drinks during the day that have caffeine. Try drinking water, fruit juice, or decaffeinated tea or coffee instead.
What other nutrients are important before pregnancy?
It is important to eat nutrient-dense foods that contain a variety of vitamins and minerals, including:
Calcium. Calcium is important for having healthy bones. It is recommended that women get 1,000 milligrams of calcium a day. Good sources of calcium include milk, cheese, yogurt, broccoli, kale, sardines, and orange juice that has calcium added to it. Three servings of food or drinks that contain calcium each day equal about 1,000 milligrams of calcium.
Three servings of food or drinks that contain calcium each day equal about 1,000 milligrams of calcium.
Choline. Choline will help your baby’s brain and spinal cord develop correctly. It’s recommended that women get 425 milligrams a day before getting pregnant, and 450 milligrams a day while pregnant. Without enough choline, your baby may develop NTDs or cognitive issues. Some prenatal vitamins contain choline, but is only a small amount, about 55 mg of choline, so you will need to eat foods with choline to get enough. Sources of choline include egg yolks, lean red meat, fish, milk, poultry, pork, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, broccoli, Brussels sprouts, beans, and nuts.
Fiber. Eating a high-fiber diet with cereals, fruits, and vegetables can lower your risk of developing gestational diabetes. Sources of fiber include fruit, vegetables, beans, bran cereal, and whole-grain bread and pasta.
Iodine. Iodine is a nutrient that your body needs during pregnancy to make thyroid hormones that help your baby’s bones and nerves develop. It is recommended that women get 150 micrograms of iodine a day before getting pregnant and 220 micrograms of iodine during pregnancy. Not all prenatal vitamins contain iodine, so make sure you eat foods that have iodine in them. Without enough iodine, you may develop hypothyroidism (a condition when the thyroid doesn’t make enough hormones) or an enlarged thyroid. Risks to your baby include brain damage. Sources of iodine include table salt (with iodine added to it), seaweed, saltwater fish, seafood, some dairy products, and fortified cereal and bread.
It is recommended that women get 150 micrograms of iodine a day before getting pregnant and 220 micrograms of iodine during pregnancy. Not all prenatal vitamins contain iodine, so make sure you eat foods that have iodine in them. Without enough iodine, you may develop hypothyroidism (a condition when the thyroid doesn’t make enough hormones) or an enlarged thyroid. Risks to your baby include brain damage. Sources of iodine include table salt (with iodine added to it), seaweed, saltwater fish, seafood, some dairy products, and fortified cereal and bread.
Iron. Iron is a mineral your body uses to make hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein that helps carry oxygen from your lungs to the rest of your body. You will need twice as much iron during pregnancy than you did before pregnancy. It is recommended that women get 15 to 18 micrograms of iron a day. When you get pregnant, you will need 27 micrograms a day. Most prenatal vitamins will provide enough iron. Other sources include lean red meat, chicken, turkey, sardines, anchovies, clams, mussels, oysters, dried beans, peas, nuts, raisins, dried fruit, prune juice, spinach, broccoli, kale, turnip greens, collard greens, whole-grain breads and iron-enriched white bread, pasta, rice, and cereals.
Vitamin D. Vitamin D may help protect your body from infection and will help your baby’s bones and teeth grow. All women, including pregnant women, need 600 international units (IU) of vitamin D a day. Good sources are fatty fish like salmon and milk and cereal that has vitamin D added to it. Your body also makes vitamin D when your skin is in the sunlight.
Zinc. Zinc will help your baby grow and develop properly. Not enough zinc has been linked to preterm birth and a higher rate of infection. It is recommended that women get 8 milligrams while trying to conceive and 11 milligrams during pregnancy. Good sources of zinc include oysters, beef, crab, lobster, pork, baked beans, fortified breakfast cereal, dark meat chicken, and pumpkin seeds.
Most of your nutrients should come from the foods you eat. Taking prenatal vitamins can help you get all of the nutrients you need to be ready for pregnancy. Prenatal vitamins are multivitamins made just for pregnant women. Compared with a regular multivitamin, they have more of some nutrients that you need during pregnancy. You can start taking prenatal vitamins before you get pregnant.
Compared with a regular multivitamin, they have more of some nutrients that you need during pregnancy. You can start taking prenatal vitamins before you get pregnant.
Can what you eat affect fertility?
Women trying to become pregnant naturally will benefit from a healthy diet with plenty of folic acid, vitamin B12, and omega-3 fatty acids These nutrients were linked to a higher rate of fertility. Fertility is a woman’s ability to get pregnant or a man’s ability to get her pregnant.
Eating a lot of fast food, red meat, processed meats, potatoes, sweets, and sugar-sweetened beverages (especially sodas or energy drinks) may cause fertility issues.
Women who are seeing a health care provider for help getting pregnant may be more likely to conceive with folic acid supplements or eating a diet high in isoflavones (a natural type of the hormone estrogen found in plants).
Talk to your doctor about what diet and supplements are right for you.
How does weight can affect your pregnancy?
Being overweight can make it more difficult to conceive. It also increases your risk of certain issues during pregnancy, including high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm birth, having a stillbirth, having a long delivery, and having a higher chance of needing a cesarean delivery. Losing weight before becoming pregnant can improve your chances of conceiving and delivering a healthy baby.
It also increases your risk of certain issues during pregnancy, including high blood pressure, gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, preterm birth, having a stillbirth, having a long delivery, and having a higher chance of needing a cesarean delivery. Losing weight before becoming pregnant can improve your chances of conceiving and delivering a healthy baby.
It’s not healthy to try to lose weight while you are pregnant, so it’s important to take steps before conceiving. To lose weight, you need to use more calories than you eat or drink. The number of calories you need each day depends on your age, height, weight, and the amount of physical activity you get. Most women need to eat or drink 1,600 to 2,400 calories a day. Eating and drinking fewer calories and being more physically active is a safe way to lose weight.
Being underweight when you get pregnant also can be unsafe. Being underweight increases your risk of having a low-birthweight baby or preterm birth. Low birth weight is when a baby is born weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces. These babies may have medical or behavioral problems later in life.
These babies may have medical or behavioral problems later in life.
Being overweight can increase your risk of developing gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes is a kind of diabetes that some women get during pregnancy. Getting to a healthy weight and exercising more now can reduce the chance that you will get gestational diabetes while pregnant.
Talk with your health care provider about what weight is healthy for you before and during pregnancy.
It’s a good idea to have a preconception checkup. A preconception checkup is a medical checkup you get before pregnancy. It helps your health care provider make sure you’re healthy and that your body is ready for pregnancy. The checkup helps your provider treat and sometimes prevent health conditions that may affect your pregnancy. Your health care provider also will talk to you about what you should eat to help you have a healthy pregnancy.
Last reviewed: July, 2020
Nutrition of a pregnant woman
So, your plans and decisions to give birth to a child have come true - you are pregnant! But this news causes you a double feeling: - on the one hand, a feeling of joy, and on the other hand, a feeling of certain fear and even fear of unknown trials for your life and the fate of the unborn baby. What will he be like? - healthy, beautiful, happy?...
What will he be like? - healthy, beautiful, happy?...
And this largely depends on the woman herself, on what lifestyle she will lead during pregnancy and, most importantly, how she will eat. nine0003
Nutrition of a woman in different periods of pregnancy
The main thing in the menu of a future mother is variety. She should consume foods from all food groups: meat, fish, vegetables and fruits, dairy products, bread and cereals.
A woman's nutrition during pregnancy can be roughly divided into three periods (trimesters).
If before pregnancy a woman ate normally, felt comfortable, did not experience allergies to any products, then it is not worth changing her diet at an early stage of the first trimester of pregnancy. nine0003
During this period, all organs and systems in the child's body are formed, tissues are formed. The body needs complete proteins and vitamins: lean meat (rabbit, chicken, turkey), fish and seafood, dairy products. Be sure to eat rice, fresh or frozen vegetables, seasonal fruits. In the first trimester, many expectant mothers are still working. No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch. nine0003
In the first trimester, many expectant mothers are still working. No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch. nine0003
In the first trimester of pregnancy, there is an active restructuring of the body and adaptation to a new state. During this period, it is recommended to switch to a low-calorie diet, which includes more fruits, juices, decoctions of dried fruits, including rose hips. At the very beginning of pregnancy, especially if toxicosis torments, more frequent, but less plentiful meals are recommended.
Always keep a hematogen, a bag of nuts or dried fruit in your pocket to have a snack on the street. If your condition does not allow you to eat regular food, you should pay attention to baby food. Baby products literally save expectant mothers suffering from severe toxicosis. These are boxed cereals, children's curds, cookies and fruit purees. nine0003
In the first trimester, special attention must be paid to the quality of products. Gradually abandon sauces, semi-finished products and canned food containing harmful chemical additives. Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs. nine0003
Gradually abandon sauces, semi-finished products and canned food containing harmful chemical additives. Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs. nine0003
According to nutritionists, the diet of pregnant women should be 300 kcal / day higher than that of non-pregnant women, but in the first trimester there is no need to increase the energy value of the diet at all; in the second trimester, an additional 340 kcal / day is required; in the third trimester - 452 kcal / day. Pregnant women generally get enough calories, and more than 80% of women achieve and even exceed the required weight gain. These extra calories benefit the fetus. An underweight woman should gain 16–20 kg during her entire pregnancy, an overweight woman about 7 kg, and a normal body weight of 11–12 kg. nine0003
nine0003
In the second trimester there are active jumps in the height and weight of the baby and uterus, so the caloric content of the diet needs to be increased. It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
Very often in pregnant women in the second trimester hemoglobin drops, this is a normal physiological phenomenon, if it is not threatening to health. You can increase hemoglobin by eating red meat, chicken, fish, dried fruits, pomegranates, green vegetables and fresh herbs, buckwheat, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, pomelo, lemons), rosehip and berry infusions. nine0003
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman should limit the intake of smoked and fried foods, as well as salt in her diet. In no case should you limit the liquid. Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism. nine0003
Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism. nine0003
During this period, you can increase the calorie content of food. Childbirth must be approached physically strong. It is better to eat meat and fish in the morning, for breakfast and lunch, and for dinner, prepare dairy and vegetable dishes: cheesecakes, stewed vegetables, cottage cheese and vegetable casseroles. It is necessary to minimize the intake of canned food, smoked meats, pickles and marinades, hot spices and fatty foods. Frequent walks in the air, physical activity are recommended.
In the third trimester, it is necessary to reduce the calorie content of foods at the expense of confectionery and flour products, eat less fatty meat, as well as cheese and sour cream. nine0003
By the end of this period, many experts advise pregnant women to give up meat altogether in order to increase tissue elasticity and prevent ruptures.
During the entire period of pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the combination of products. If you combine foods wisely, you can ensure more efficient absorption of food. If the food is digested poorly, then this can lead to rotting and fermentation of products and the formation of substances harmful to the body of the mother and child. In addition, the fermentation process is accompanied by gas formation, which can lead to flatulence (bloating) and discomfort. This is especially harmful in the last stages of pregnancy. nine0003
Try not to take the first, second and third course at the same time; this overflows the stomach and presses on the fetus, the food is poorly digested and poorly absorbed. Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat only when you are hungry, try not to snack on the go. Follow the diet, eat at about the same time. nine0003
Proper preparation of food will help to maximize the useful substances contained in the products. Do not overcook food, try not to reheat the same dish several times, it is better to set aside only the portion that will be used. Cook in the most gentle way: baking, steaming, stewing. Avoid frying, boiling in large amounts of water, with this method of processing products, many useful substances are lost. If possible, do not cook for several days at once. Do not use aluminum cookware when cooking. Remember that for a pregnant woman, it is not calories that are important, but the quality of food, its naturalness, primarily a “living cell” (whole cereals, raw vegetables and fruits, fresh meat and dairy products). nine0003
nine0003
What can harm the pregnant woman and the fetus
Smoking and alcohol – quit smoking from the first days of pregnancy, if you have smoked before, avoid "passive" smoking, and do not consume alcoholic beverages in any doses.
Lack of vitamins and microelements in the body - their absence or deficiency can lead to irreparable consequences. So, for example, iodine deficiency can lead to mental retardation of a child, folic acid deficiency - to severe fetal deformities, calcium deficiency - to a violation of the formation of the child's skeleton, iron deficiency - to anemia and a delay in the physical and neuropsychic development of the child. It is necessary to consult a doctor, perhaps he will recommend switching to iodized salt, as well as supplementing your diet with a vitamin-mineral complex and folic acid. nine0003
Excess weight is the risk of having a large child, which means the risk of complications during childbirth and the child's tendency to become obese at an older age.
The use of food additives (sauces, seasonings such as vegeta, bouillon cubes), exotic fruits, semi-finished products, carbonated drinks - the risk of allergies and anomalies in a child, unfortunately, increases.
Recommended for pregnant women:
- Do not eat hot dogs and other snacks containing meat that has not been heated on fire or boiled in boiling water. nine0058
- Avoid soft cheeses. Hard cheeses are safe.
- Do not eat raw frozen pies and meat pastes, seafood. Canned analogues are safe.
- Do not consume raw vegetables, unpasteurized juices, liver, meat, poultry and eggs that have not been sufficiently cooked. These products may contain Salmonella taxins.
- Limit sweets.
- In no case do not resort to starvation and various diets. nine0058
- Regularly monitor blood pressure and do not miss visits to the gynecologist.
Remember!
Your child's development and health depend on your diet and lifestyle during pregnancy!
Healthy nutrition during pregnancy
Category: Healthy food.
Happiness, agonizing expectation, anticipation and even fear - all these feelings inevitably accompany pregnant women. And it is very important during this period not to surrender to emotions, but to remember the responsibility that is an integral part of this time. It is during this period that it is important to follow the basics of a healthy lifestyle, taking into account the requirements of pregnancy. Proper nutrition during pregnancy is the most relevant, since what a woman eats largely determines how her child will develop. For example, whether a pregnant woman receives enough protein depends on whether the child will have enough building material. nine0003
It makes sense to take into account one important feature: proper nutrition in early pregnancy will be somewhat different from the diet of a pregnant woman in the last weeks.
Not everyone understands where such differences come from, but understanding the topic will be quite simple. Judge for yourself, important systems of the body are laid in the early stages, but the size of the fetus increases slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like. nine0003
Judge for yourself, important systems of the body are laid in the early stages, but the size of the fetus increases slightly. Therefore, in the early stages, a healthy diet for pregnant women is based on sufficient intake of minerals, vitamins, and the like. nine0003
In the second trimester of pregnancy, nutrition should focus on increased protein intake, since it is now that the active growth of the child and its internal organs begins. All this requires a building material, that is, protein.
Nutrition in the third trimester of pregnancy is, first of all, vitamins and minerals that are necessary for the development of the internal systems of the child's body, especially calcium for bone growth and the development of the nervous system. nine0003
When planning a pregnancy, proper nutrition is also very important. The more healthy, hardy, strong the woman's body is at the time of conception, the greater the chances of successfully fixing the fetal egg in the uterus. And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
And a certain set of vitamins in the body contributes to the proper development of the embryo.
As you can see, the difference in recommendations for proper nutrition of pregnant women by months, and sometimes even by weeks, is quite justified. However, there are, of course, general rules for proper nutrition during pregnancy, which will be discussed further. nine0003
General principles of good nutrition during pregnancy
First of all, it is worth remembering one simple thing: it is better to get up from the table slightly hungry than with heaviness in the stomach from overeating. In this regard, it is better to adhere to the principles of fractional nutrition at all: eat less, but more often. The ideal option would be to eat 5-6 times a day. The last meal should be 3 hours before bedtime. If the feeling of hunger is unbearable, you can drink a glass of milk or yogurt, eat an apple or a pear. It is this diet for pregnant women that will be most optimal. nine0003
nine0003
Proper nutrition during pregnancy, like, in fact, any proper nutrition, involves the exclusion or maximum restriction of fried foods, pickled foods and smoked meats. Steamed, boiled, stewed or baked food will be much more useful. Food for pregnant women should be as fresh and natural as possible, should not contain preservatives, excess salt, and the like.
Obviously, canned foods, various sausages and other long-term storage products, if not banned, then require strict control of their use. nine0003
Of course, it is recommended to give up fast food. However, it is worth noting that if the choice arises - to remain hungry or eat something not very healthy, it is better to choose the latter. A pregnant woman should not starve. Another thing is, if you get suspiciously often before such a choice, then you should think about carrying fruit or sandwiches with you.
Of great importance is the balance between such important components of nutrition as proteins, fats, carbohydrates, as well as vitamins and minerals. Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different times implies a different balance of these components, the fact itself remains unchanged. nine0003
Of course, a balanced diet for pregnant women at different times implies a different balance of these components, the fact itself remains unchanged. nine0003
Weekly meals
1-3 weeks pregnant
Gynecologists count pregnancy not from the day of conception, since it is almost impossible to calculate it, but from the first day of the last menstruation. Therefore, the first 2 weeks of the obstetric gestation period falls on the time before conception.
Pregnancy planning is an extremely important period, on which, whatever one may say, both the health of the unborn child and the absence of any complications during pregnancy depend. So it turns out that proper nutrition before pregnancy is of paramount importance. At this stage, it is very important to increase the amount of folic acid. Doctors often recommend drinking it in the form of capsules, but it is much better to get all the vitamins from normal food. Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, lettuce, cabbage, etc.), asparagus, beans and legumes, seeds and nuts, citrus fruits. nine0003
Folic acid is found in green leafy vegetables (spinach, lettuce, cabbage, etc.), asparagus, beans and legumes, seeds and nuts, citrus fruits. nine0003
It is equally useful to consume yellow fruits and vegetables. But it is better to refuse fatty and sweet foods. This will avoid problems with obesity, as well as reduce the risk of early toxicosis.
Approximately on the 10-14th day of the cycle, fertilization occurs and the movement of the fetal egg begins towards the uterus. From this time on, we can talk about the onset of pregnancy.
3rd week
Nutrition at the beginning of pregnancy is a very complicated topic, since literally every week new organs and systems appear in the fetus, which means that the need for vitamins and nutrients is constantly changing. nine0003
In the third week of pregnancy, the egg is implanted and the placenta begins to develop, as well as the fetal membrane. For their full development, calcium is needed, which is found in dairy products, nuts, fish, legumes, fruit juices and cereals; and manganese, it can be obtained from nuts, spinach, beets, mushrooms, animal liver.
4 weeks
For 4 weeks, the nutrition remains the same as for 3, but at this time it is especially important to give up coffee. However, drinking this certainly tasty, but not very healthy drink during pregnancy should be done with extreme caution. Especially coffee is contraindicated in the evening. As you can see, proper nutrition in the first month of pregnancy is not too difficult. Further it will be a little more difficult. nine0003
5 week
As a rule, toxicosis of pregnant women begins around this time. To alleviate this condition, you can slightly change your daily menu. So, meat and eggs, as well as other animal proteins, can be replaced with nuts, soy and other legumes. Instead of milk, you can eat yogurt and cheese. It will not be superfluous to introduce carrots, mangoes, apricots into the diet.
6 week
Toxicosis is in full swing, so the morning should start with crackers or unsweetened crackers. It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink plenty of fluids, at least 8 glasses a day (for example: water with lemon juice or tea with lemon). At night, you can eat a handful of raisins. nine0003
It is better to eat them immediately after waking up, without getting out of bed. At this stage, it is better to drink plenty of fluids, at least 8 glasses a day (for example: water with lemon juice or tea with lemon). At night, you can eat a handful of raisins. nine0003
7 week
At this time, problems with the intestines may arise. Therefore, you should avoid foods that promote gas formation, including cabbage. It will not be superfluous to refuse those products that strengthen. It is better to introduce prunes, fresh kefir and the like into the diet.
8 week
Ginger tea will help to cope with toxicosis, and do not forget about nuts.
nine0002 9-10 weeksGive preference to whole grain cereals and whole grain bread. Brown rice is better than white. In general, the body of a pregnant woman at this stage needs quite a lot of fiber.
11-12 weeks
The first trimester of pregnancy is coming to an end, and nutrition at this time should be special. This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a particular dish, then it is precisely those substances that are contained in it that your baby lacks. Of course, you shouldn't go to extremes. nine0003
This is the most difficult time, and it is very important to listen to yourself, to your body. If you want to eat a particular dish, then it is precisely those substances that are contained in it that your baby lacks. Of course, you shouldn't go to extremes. nine0003
13-16 weeks
Nutrition in the 2nd trimester during pregnancy is characterized, as already mentioned, by abundant protein intake. In addition, it is necessary to increase the total daily caloric intake of food. If in the first trimester it will be enough to eat 2400-2700 kcal, then from this time it is necessary to eat 2700-2900 kcal.
16-24 weeks
Nutrition at 6 months of pregnancy should contribute to the development of the child's vision and hearing. That is, you need vitamin A and beta-carotene. It is better to eat cabbage, yellow peppers, carrots at this time. Keep in mind that vitamin A is absorbed only with fats. nine0003
24-28 weeks
It is at this time that fractional nutrition becomes especially relevant. The uterus is actively growing, taking up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller, and it is difficult for it to contain a large amount of food. Even when eating small meals, a pregnant woman may be bothered by heartburn. It is better to give up carbonated drinks and coffee, they also provoke heartburn. In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow. nine0003
The uterus is actively growing, taking up more and more space in the abdominal cavity, and begins to put pressure on the stomach. Accordingly, the stomach becomes smaller, and it is difficult for it to contain a large amount of food. Even when eating small meals, a pregnant woman may be bothered by heartburn. It is better to give up carbonated drinks and coffee, they also provoke heartburn. In general, the nutrition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester should be as diverse as possible, as the needs of the baby grow. nine0003
29-34 weeks
At the 8th month, bones are actively growing and teeth are being laid, therefore, it is very important to eat as many calcium-containing foods as possible. For brain development, fatty acids are simply necessary, and they contribute to the absorption of calcium. Iron deficiency at this time can lead to the development of anemia, both in the mother and in the child. Fatty fish, nuts, red meat, dark green vegetables and seeds are the foods to eat during this period of pregnancy. nine0003
nine0003
35–40 weeks
Nutrition at the 9th, last month of pregnancy, should contribute to the overall strengthening of the mother's body. After all, she has a very difficult and time-consuming job ahead of her - childbirth. The main source of energy in the body is carbohydrates, and it is their consumption that should become the basis of the nutrition of a pregnant woman before childbirth. Cereals and vegetables are the foods that you should eat during this period.
That's all that can be said about trimester nutrition. An example of a menu for pregnant women by trimesters may also be useful. Based on these menus and explanations for them, you can create a menu for yourself. nine0003
Sample menu for pregnant women for the 1st trimester
1. Breakfast: muesli with yogurt and freshly squeezed pear juice.
2. First snack: salmon sandwich.
3. Lunch: mushroom soup, cabbage salad, herbal tea.
4. Second snack: whole grain bread with cheese.
Second snack: whole grain bread with cheese.
5. Dinner: carrot salad and vegetable risotto. You can drink everything with kefir.
In the first trimester, it is very important that a woman receives a large amount of folate and vitamin B6 from food. nine0003
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 2nd trimester
In the second trimester for pregnant women, the presence of omega-3 acid, calcium, vitamin D and iron in the diet is important.
1. Breakfast: oatmeal in milk with apple and cinnamon, chamomile tea.
2. First snack: almonds with prunes.
3. Lunch: lentil soup, seaweed salad, cranberry juice.
4. Second snack: sandwich with herring. nine0003
5. Dinner: omelet with mushrooms and yogurt.
An example of a menu for pregnant women for the 3rd trimester
Carbohydrates and vitamin K play a special role here.
1. Breakfast: pancakes with cream cheese and curdled milk.
2. First snack: whole grain cheese sandwich.
3. Lunch: fish hodgepodge, tuna and green salad, rosehip broth.
4. Second snack: cheesecake. nine0003
5. Dinner: fish with rice and fermented baked milk.
Special nutrition for pregnant women
But this is not all the nutritional features of pregnant women. In some cases, women develop pathologies during pregnancy that require special nutrition. So, with anemia in pregnant women, special nutrition is simply necessary. A woman who has experienced pregnancy anemia should consult a doctor not only about drug treatment, but also about an appropriate diet. With such a disease, it is very important to increase the intake of foods containing iron. Iron can be obtained from animal products (lean red meat, fish, poultry) and vegetable (nuts, dried porcini mushrooms, spinach, buckwheat, legumes, etc.) origin. In addition, it is important not only to know which foods to use, but also in what combinations, as this affects the absorption of iron in the human body.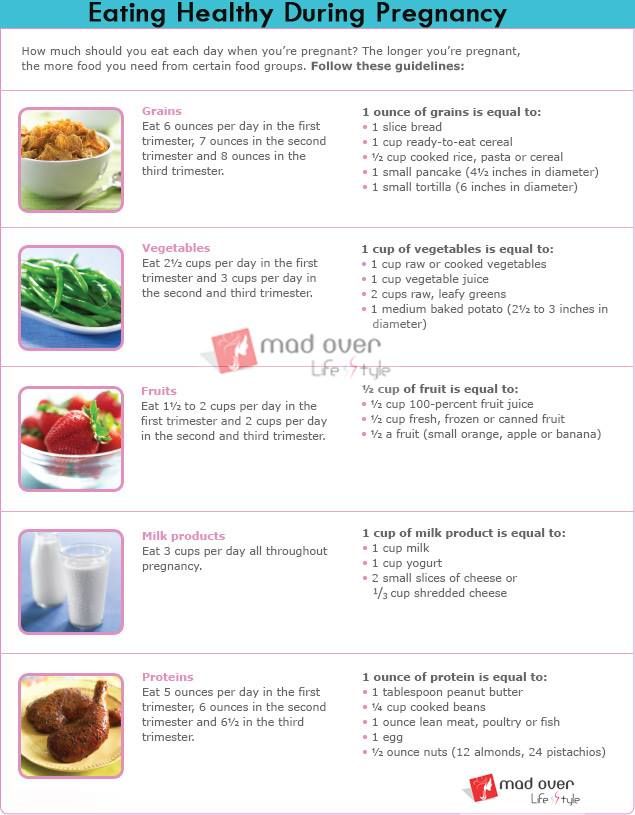 Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated. nine0003
Vitamin C increases the absorption of iron in the body, that is, the combination of products containing iron and vitamin C is favorable. Foods containing calcium (dairy products) and tannin (tea, coffee) prevent the absorption of iron in the intestine. Therefore, their use should be separated. nine0003
With obesity that has developed during pregnancy, there may be a need for dietary nutrition for pregnant women. It is important to remember that without consulting a doctor, a pregnant woman should not choose a diet for weight loss. The risk of developing pathologies and abnormalities is too great, both in the body of the mother and in the body of the child.
Especially harmful are mono-diets and diets that require prolonged fasting. Both contribute to malnutrition and vitamin deficiency. It will take a very long time to restore the state of the body, the supply of nutrients and vitamins, and it is completely impossible to compensate for the harm that such diets cause to a child.