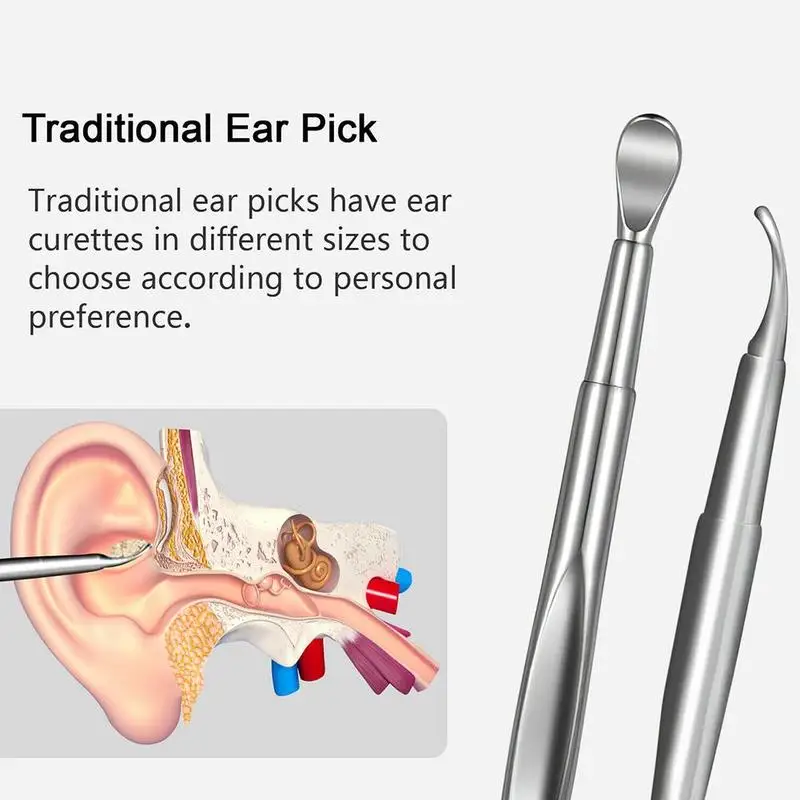
Ear wax removal for infants
Dealing With Earwax (for Parents)
Why Do Ears Make Wax?
Earwax is made in the outer ear canal, the area between the fleshy part of the ear on the outside of the head and the middle ear. The medical term for earwax is cerumen (seh-ROO-mun).
Earwax has some important jobs. It:
- acts as a waterproof lining of the ear canal, protecting it and the eardrum from germs that can cause infection
- traps dirt, dust, and other particles, keeping them from injuring or irritating the eardrum
The wax makes its way through the outer ear canal to the opening of the ear. Then it either falls out or comes out during bathing. In most people, the outer ear canal makes earwax all the time, so the canal always has enough wax in it.
Does Earwax Need to Be Removed?
Usually, there's no need to remove earwax because it comes out by itself. Sticking anything into a child's ears raises the risk of infection or damage to the ear canal or eardrum. Cotton swabs are handy for a variety of grooming needs, but should not be used to remove earwax. In most cases, regular bathing is enough to keep it at healthy levels.
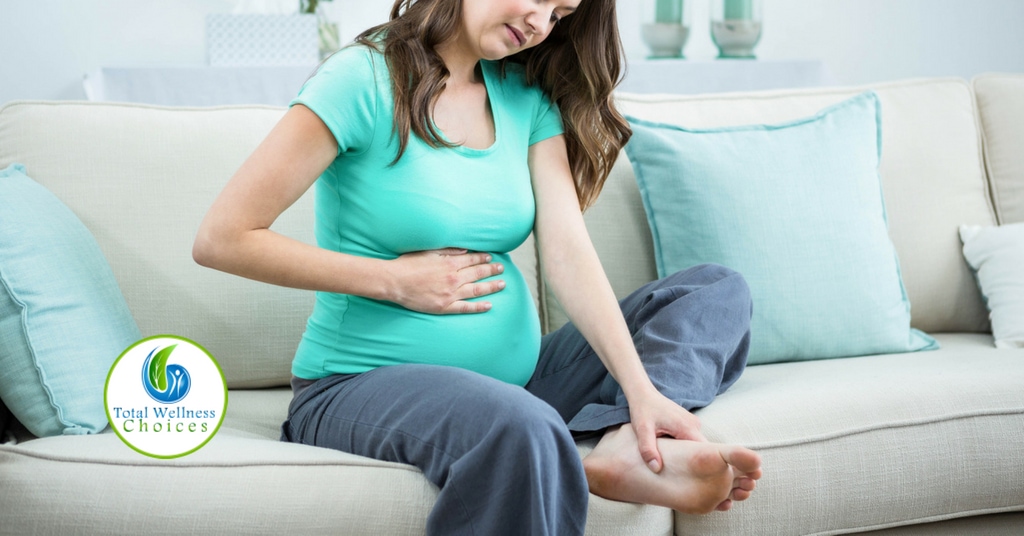
While some people have more earwax than others, in general the ear makes as much wax as it needs. Rarely, kids' ears do make too much earwax. And sometimes earwax can build up and block the ear canal, especially when pushed in by a finger, cotton swab, or other object. This is called "impaction." If it affects hearing or causes pain or discomfort, a doctor can remove it.
Parents — and kids — shouldn't attempt to remove earwax at home, even with remedies that promise to be safe and effective. Doing so risks damage to the ear canal and, possibly, a child's hearing.
What Can Parents Do?
If your child complains of ear discomfort and you see earwax in the ear, it's OK to wipe the outside of the ear with a washcloth. But don't use a cotton swab, a finger, or anything else to poke inside the ear. It could damage the delicate ear canal and eardrum, or pack the wax in even further.
Check with your doctor before using an over-the-counter earwax removal treatment.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
Call the doctor if your child has:
- ear pain, itchiness, or discomfort (like a blocked feeling in the ears)
- hearing problems
In infants and toddlers, tugging at the ears can be sign of an ear problem.
Sometimes doctors will remove earwax:
- if it's painful, itchy, or uncomfortable
- if affects hearing
- to get a better view of the eardrum to check for problems
Earwax removal usually is done in the doctor's office. There might be a little discomfort but it isn't painful. If a child can't sit still or cooperate, the doctor can remove it in an operating room while the child is under general anesthesia.
Doctors can remove earwax in different ways, including:
- scooping it out, pulling it out, or suctioning it out with special instruments designed for this purpose
- flushing it out with warm water.
 Sometimes a doctor will put drops into the ear canal to soften the wax and break it down. Or they might ask you to do this at home and then return to the doctor for wax removal.
Sometimes a doctor will put drops into the ear canal to soften the wax and break it down. Or they might ask you to do this at home and then return to the doctor for wax removal.
Removal takes only a few minutes. If there's a sign of infection, the doctor may prescribe antibiotic ear drops.
What Else Should I Know?
Ear candling has gained a lot of attention as a home remedy for earwax removal. But it hasn't been proved to be safe or effective, and can be dangerous.
In ear candling, one end of a cone-type device is inserted into the ear canal and the other end is set on fire. The idea is that the fire and the cone form a vacuum and extract the wax. But trying this at home carries a high risk of:
- burning the ear canal
- punching a hole in the eardrum, which can cause permanent hearing damage
Whenever you have any concerns about your child's ears or hearing, call your doctor.
Earwax Buildup
Is this your child's symptom?
- Earwax (cerumen) buildup or blockage
- Questions about earwax removal
Symptoms of Earwax Buildup
- Too much earwax can cause rubbing of the ear or poking in the canal.

- A piece of ear wax can become dry and hard in the ear canal. This creates a feeling that an object is in the ear.
- Complete blockage (plugging) of the ear canal by wax causes more symptoms. These include decreased or muffled hearing.
- A large piece of earwax may be seen inside the ear canal.
Causes of Earwax Buildup
- Cotton Swabs. Earwax buildup is usually from using cotton swabs. They push the wax back in and pack it down.
- Fingers. A few children (perhaps 5%) normally produce more wax than others. It usually will come out if it's not pushed back by fingers.
- Ear Plugs. Wearing ear plugs of any type can also push wax back.
Earwax is Normal
- Everyone has earwax. Earwax is normal and healthy. Earwax is not dirty or a sign of poor hygiene.
- Earwax is also called cerumen.
- Earwax is made by special glands in the outer third of the ear canal.
- Earwax has a purpose.
 It protects the skin lining the ear canal. It is a natural water-proofing agent.
It protects the skin lining the ear canal. It is a natural water-proofing agent. - Earwax also has germ-killing properties.
- New earwax is soft and a golden-yellow color.
- Older earwax becomes dryer and turns to a brown or black color.
Ear Canals are Self-Cleaning
- Ear canals are designed to clean themselves.
- The ear canal skin slowly moves out of the ear canal. It carries the earwax along with it. The wax dries up and becomes flaky. It falls out of the ear on its own.
- There are some people who produce much more earwax than others. For such people periodic ear cleaning may be needed.
- Earwax only needs to be removed from inside the ear if it causes symptoms. Examples of symptoms are decreased hearing, discomfort, fullness or blockage.
Problems from Using Cotton-Tipped Swabs
- The cotton-tipped swab pushes the wax back in. The earwax builds up and causes symptoms.
- Ear canal blockage
- Decreased or muffled hearing.
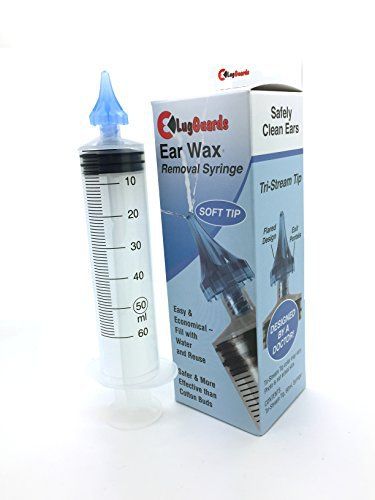
- Trapped water behind the wax (can lead to Swimmer's Ear).
- Itchy or painful canals, especially in teens who often use Q-tips. A dry ear canal is always itchy.
- Sometimes, bleeding or damage to the eardrum.
- Cotton swabs cause more than 10,000 ear injuries each year in the US. More than 2,000 are punctured ear drums. Never allow young children to play with cotton swabs.
Prevention of Blocked Ear Canals
- Never put cotton swabs (cotton buds or Q-tips) into the ear canal.
- Cotton swabs just push the earwax deeper into the ear canal. Reason: Cotton swabs are usually wider than a child's ear canal.
- Earwax doesn't need any help getting out. You can't hurry the process.
- Never try to dig out pieces of earwax with toothpicks, match sticks or other devices. Usually, doing this just pushes the wax back in.
- These objects can also scratch the ear canal and cause an infection.
- If all of the ear wax is removed (as with cotton swabs), the ear canals become itchy.
 They also become more prone to swimmer's ear. This can occur in teens when cotton swabs are smaller than the ear canal.
They also become more prone to swimmer's ear. This can occur in teens when cotton swabs are smaller than the ear canal. - Limit the use of ear plugs.
When to Call for Earwax Buildup
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Ear pain or bleeding after object (such as cotton swab) was inserted into ear canal
- Ear pain after ear canal flushing to remove wax and it's severe
- Walking is very unsteady
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Ear pain after ear canal flushing and it lasts more than 1 hour
- Pus (yellow or green discharge) from the ear canal
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- History of ear drum perforation, tubes or ear surgery. Reason: don't remove wax at home.
- Complete hearing loss in either ear
- Age less than 6 years with earwax problems
- Earwax problems not better after using Care Advice
- You don't want to try to remove earwax at home
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Questions about earwax removal
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Earwax Buildup
- What You Should Know About Earwax Buildup:
- Earwax is good.
- In general, leave earwax alone.
- It will come out and fall away on its own.
- If you see some wax right at the opening, you can flick it away. Use something that won't push it back in, such as a paper clip.
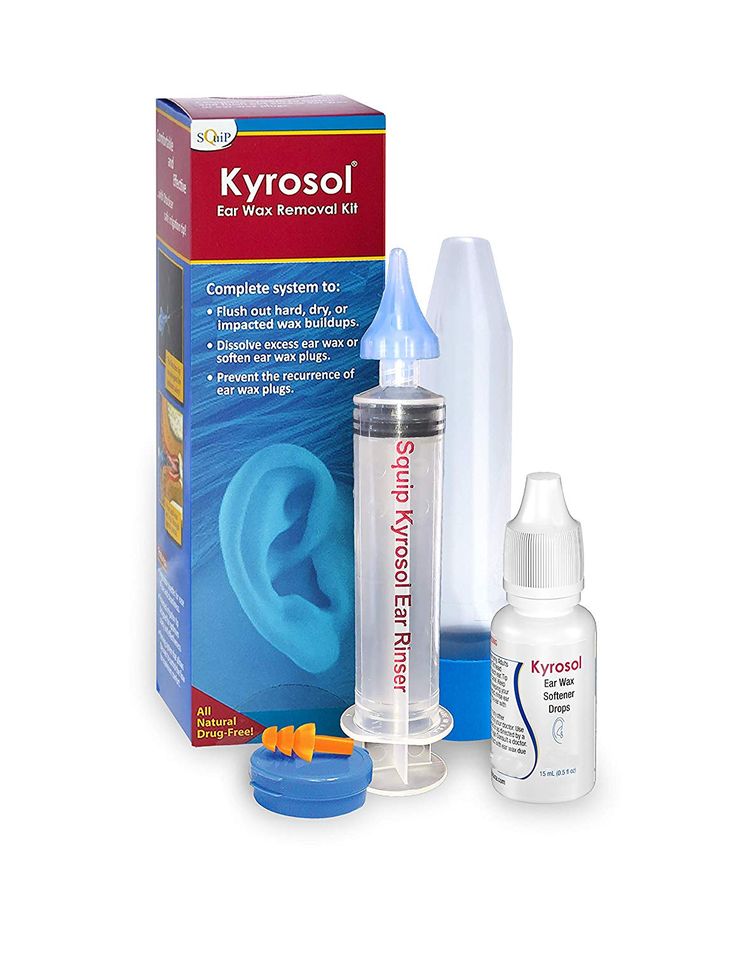
- Reasons to Flush out the Ear Canal:
- Earwax is completely blocking an ear canal and can't hear on that side.
- If the hearing seems normal on that side, the blockage is only partial. You can leave it alone.
- Earwax is completely blocking an ear canal and can't hear on that side.
- Age 6 Years and Older - Ear Canal Flushing with Water:
- Under age 6, use only if advised by your child's doctor.
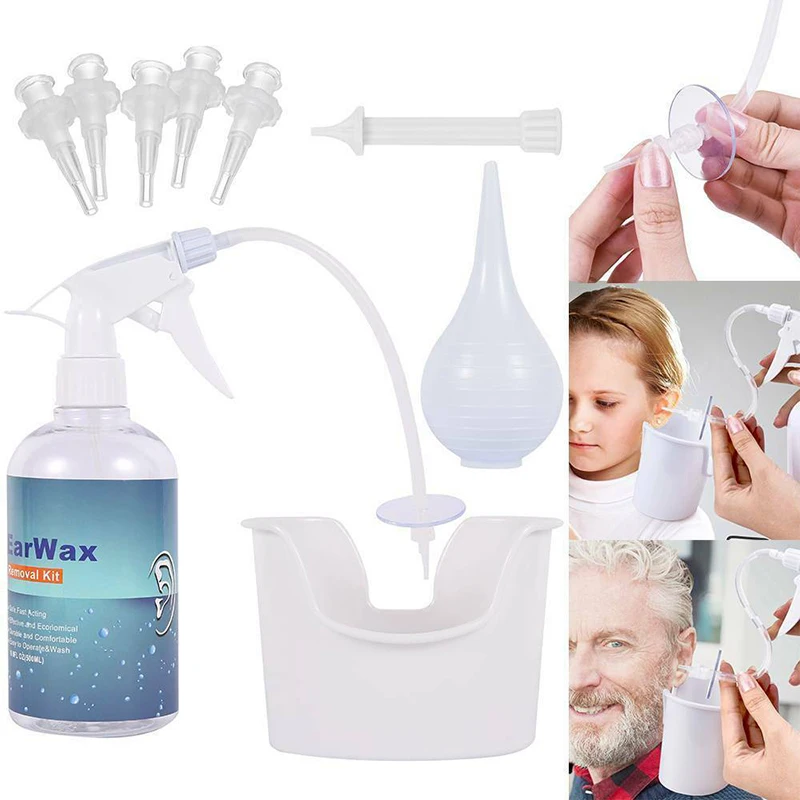
- Buy a soft rubber ear syringe or bulb from the pharmacy. No prescription is needed.
- Have your child lean over the sink. Reason: To catch the water.
- Use lukewarm water (body temperature). Reason: To prevent dizziness.
- Gently squirt the water into the ear canal. Then tilt your child's head and let the water run out. You may need to do this several (3-4) times.
- If the earwax does not seem to be coming out, tilt the head. Then, flush it with the head tilted. Have the ear with the wax in it facing downward. Gravity will help the water wash it out (the waterfall effect).
- Endpoint: Flush until the water that comes out is clear of wax. Also, the ear canal should be open when you look in with a light.

- Afterwards dry the ear thoroughly. You can do this by putting a drop of rubbing alcohol in the ear canal. Or you can set a hair dryer on low. Hold it a foot away from the ear for 10 seconds.
- Caution - Ear Canal Flushing:
- Do not perform flushing if your child has a hole in the eardrum or ear tubes.
- Stop flushing if it causes pain or dizziness.
- Do not use a water jet tooth cleaner (such as a WaterPik) for ear flushing. Reason: The force of the jet can cause pain.
- Ear Drops - Use for 4 Days to Soften the Earwax:
- If the earwax is hard, soften it before flushing the ear canal. Use ear drops to break up the earwax.
- Homemade ear drops: 15% baking soda solution. Make it by adding ¼ teaspoon (1.25 mL) of baking soda to 2 teaspoons (10 mL) of water.
- Other option for homemade ear drops: hydrogen peroxide and water solution. Mix equal parts of each.
- Drug store option: Earwax removal ear drops (such as Debrox).
 No prescription is needed.
No prescription is needed. - Use 5 drops in affected ear, 2 times daily, for 4 days.
- How to Put in Ear Drops:
- Lie on the side with blocked ear upward.
- Place 5 drops into ear canal.
- Keep drops in ear for 10 minutes by continuing to lie down.
- Then lie with the blocked side down. Let the ear drops run out onto some tissue.
- Use twice daily for up to four days.
- Then flushing should be able to get everything out.
- Cautions for Ear Drops:
- Do not use ear drops if your child has a hole in the eardrum. Also do not use them for children with ear tubes.
- Stop using ear drops if pain occurs.
- Earwax Removal Before 6 Years Old:
- Earwax removal in this age group can be hard.
- Removal may not be needed. The ear wax should come out on its own. Don't use cotton swabs.
- Do not use eardrops or ear flushes unless it is advised by your child's doctor.
 This also can be done in your doctor's office.
This also can be done in your doctor's office.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Flushing out the ear canal doesn't return the hearing to normal
- Earache occurs
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 11/09/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Sulfur plug in children: description of the disease, causes, symptoms, cost of treatment in Moscow
Wax plug in a child is a common problem when an excessive amount of earwax accumulates in the ear canal, which thickens and forms a dense lump that causes discomfort and impairs hearing. It can appear at any age, even a year or earlier. Despite the fact that the violation is not considered severe, if not properly and timely treated, it can easily lead to the development of serious complications. It is better to entrust the removal of the cork to a specialist.
Despite the fact that the violation is not considered severe, if not properly and timely treated, it can easily lead to the development of serious complications. It is better to entrust the removal of the cork to a specialist.
Earwax in its composition is a mixture of secretion of sulfuric, sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as dead cells of the epithelium located in the ear canal. This substance contains immunoglobulins that suppress the development of pathogenic microflora, and bacteria necessary for the body.
The development of a secret occurs constantly, as it is necessary to cleanse the ear canal from harmful bacteria, viruses and dust. Normally, sulfur itself is removed from the ear canal to the outside during chewing. If, due to something, the process of sulfur outflow is disturbed, it begins to accumulate inside and, gradually compacting, forms a plug of a larger or smaller size. Significant plugs completely block the ear canal and cause severe hearing loss.
Causes
The formation of accumulation of ear secretions can occur for many reasons, which is why the disease is widespread. As the main reasons for the appearance of a pathological condition, doctors call the following:
-
individual structural features - sometimes the ear canal turns out to be rather narrow, due to which sulfur from it, even with slightly increased thickening, loses the ability to fully stand out, and its compaction begins;
-
errors when cleaning the ears - if cotton swabs or similar items are used, they cannot remove the secret, but only tamp it. This mishandling technique is one of the main reasons why children have a problem;
-
inflammation of the ear canal due to trauma - in this case, local edema disrupts the process of sulfur release and causes it to compact and dry out. Injuries are most often obtained by improper cleaning of the ear, as well as swimming in open water;
-
excessively frequent cleaning of the ears - with it, the ear canals turn out to be catastrophically overdried.
 To moisturize their epithelium, the body begins to actively produce sulfur, which, due to the large amount, does not have time to stand out in sufficient volume and accumulates, thickening;
To moisturize their epithelium, the body begins to actively produce sulfur, which, due to the large amount, does not have time to stand out in sufficient volume and accumulates, thickening; -
long stay in a room with dry air - in such conditions, the tissues in the ear begin to dry out, and sulfur is required in large quantities to moisturize them. The process of violation is similar to the previous cause of the problem;
-
the presence of a foreign body - it mechanically blocks the channel and does not allow the secret to stand out. At the same time, its production does not stop, and it begins to quickly thicken, forming large plugs, which can cause particularly severe discomfort. This cause of the disease, as a rule, occurs in preschool children, who, out of curiosity, can put an object in their ear.
Whatever caused the appearance of pathology, it must be eliminated competently. It is also important to make sure that the problem is related to the accumulation of sulfur, and not to any tumor process, the symptoms of which at first are almost the same. A sulfur plug in the ear of a child can also sometimes be similar in manifestations to a large foreign body.
A sulfur plug in the ear of a child can also sometimes be similar in manifestations to a large foreign body.
Is it possible to determine by eye
If the plug is not deep, you can see it when examining the ear. In this case, it will be noticeable that the auditory canal is completely blocked by a black, brown, gray or yellowish formation. When an inflammatory process is attached, purulent discharge or blood can be seen. Trying to pick such plugs is strictly prohibited. From such an attempt to help the child will only harm. To eliminate education, you need to consult a doctor or, in extreme cases, use the funds purchased at the pharmacy at home.
What a sulfur plug looks like in children is useful for all parents to know. In the photo you can look at the accumulation of sulfur in the ear of an infant and an older child.
Species
Doctors distinguish three types of traffic jams, depending on the consistency of the secret of which they consist. This partly determines how the foreign object will be removed from the ear canal. It is important that there is no tissue damage during treatment, otherwise there is a high risk of infection. Sulfur plugs in children can be:
This partly determines how the foreign object will be removed from the ear canal. It is important that there is no tissue damage during treatment, otherwise there is a high risk of infection. Sulfur plugs in children can be:
-
pasty - their color is from light yellow to rich yellow with an orange tint. They are soft, so removing such a foreign body is quite simple. It cannot damage tissue and does not cause pain when removed;
-
plasticine-like - denser dark brown, they can cause pain when removed, and in case of careless manipulation - injure tissues. Such corks develop from pasty ones if they are not removed in time;
-
hard - black in color, they are particularly dense and easily cause damage even with the most careful removal. In some cases, local anesthesia may be required before they are removed. They are most often formed if the pathology was not promptly paid attention and treatment was not carried out.
The type of formation that takes place in a particular case is determined by the otolaryngologist after examining the patient.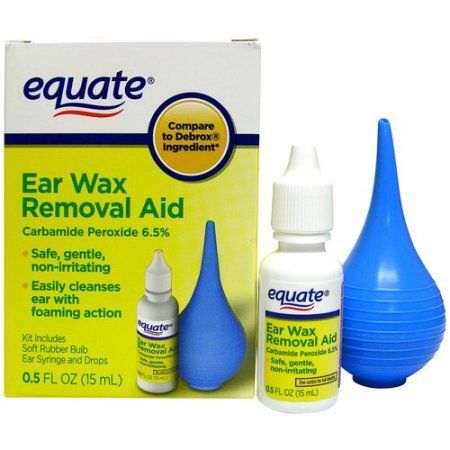 Also, on the basis of the examination, it is also determined how the object will be removed from the ear, as well as whether there are any local complications of the pathology.
Also, on the basis of the examination, it is also determined how the object will be removed from the ear, as well as whether there are any local complications of the pathology.
Who treats
To get rid of the sulfur plug in the ear of a child, you need to contact an otolaryngologist. He has all the necessary skills and tools for treatment. A general practitioner can help in such a situation, but only as a last resort, if there is no way to get help from an ENT.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology is not difficult. In young children, plugs are often found by chance by a pediatrician during a general examination. Parents may not be aware of the problem because the child is not yet talking and cannot show that he or she has a disorder. Usually, after the pediatrician on the same day, it is recommended to visit an otolaryngologist to clean the ear and check for the presence of pathological complications.
A profile specialist conducts an examination of the patient, in which not only the presence of sulfur accumulation is diagnosed, but the density of the lump and the general hearing loss are determined. Inspection with an otoscope allows you to determine the size of the plug and the presence of local effects from it. With the help of a special probe, the density of the accumulation is determined. Also, the otolaryngologist necessarily establishes whether there are tumor formations or foreign objects in the ear canal, due to which the secretion accumulates.
Inspection with an otoscope allows you to determine the size of the plug and the presence of local effects from it. With the help of a special probe, the density of the accumulation is determined. Also, the otolaryngologist necessarily establishes whether there are tumor formations or foreign objects in the ear canal, due to which the secretion accumulates.
In cases where the presence of complications is detected, the doctor prescribes the necessary therapy after removal of the sulfur plug. It can be general or local. Hospitalization is usually not required for the patient. Only with the appearance of severe consequences of pathology at an early age, a specialist can recommend leaving the child under medical supervision.
Prophylaxis
In order to protect the child from ear problems, it is necessary to remember about preventive measures against the accumulation of sulfur. Ear cleaning is carried out once a week, not more often. To do this, use exclusively special cotton swabs designed to clean the ears of children.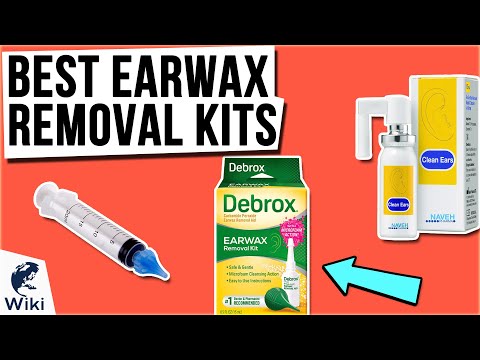 Movement during the procedure should be circular without pressure. If it is noticed that the sulfur began to separate poorly, it is necessary to use special drops for caring for the ear cavity in children. They have a mild effect and dissolve the thickened secret, allowing it to easily flow out. Which particular drug is better to choose, you need to consult a pediatrician or an otolaryngologist, since not all remedies are equally harmless.
Movement during the procedure should be circular without pressure. If it is noticed that the sulfur began to separate poorly, it is necessary to use special drops for caring for the ear cavity in children. They have a mild effect and dissolve the thickened secret, allowing it to easily flow out. Which particular drug is better to choose, you need to consult a pediatrician or an otolaryngologist, since not all remedies are equally harmless.
Also, preventive measures include careful bathing of the child. It is important that water does not get into the ear. Because of it, the sulfur will begin to increase in volume, and blockage of the auditory canal will occur. If water does get in, then you need to remove it with a cotton turunda.
A child has cerumen | 1DMC
What is earwax? What to do if a sulfur plug has formed in the ear of a child?
Each person has a special secret in the ears - earwax. This secret protects us from the effects of dust, dirt, bacteria on the ear. Normally, dust particles settle on the ear wax, it thickens, dries up and is gradually removed from the ear. When chewing and talking, the wall of the external auditory canal shifts and the earwax moves closer to the exit from the ear. Thus, the outer ear is cleansed. However, in the cleaning of the outer ear, violations can occur, and then a sulfur plug forms. The sulfur plug is a conglomerate consisting of earwax, dust and epidermal cells.
Normally, dust particles settle on the ear wax, it thickens, dries up and is gradually removed from the ear. When chewing and talking, the wall of the external auditory canal shifts and the earwax moves closer to the exit from the ear. Thus, the outer ear is cleansed. However, in the cleaning of the outer ear, violations can occur, and then a sulfur plug forms. The sulfur plug is a conglomerate consisting of earwax, dust and epidermal cells.
What are the causes of sulfur plugs in children?
Excessive secretion of sulfur, changes in its consistency, anatomical features of the ear canal may predispose to the formation of sulfur plug in a child.
Increased formation of earwax can provoke foreign bodies of the ear, otitis media in children, water getting into the ears, eczema, dermatitis, wearing a hearing aid, frequent use of headphones. A special role in the hypersecretion of the ear glands and the formation of sulfuric plug belongs to overzealous attempts to clean the child's ears with cotton swabs. This leads to irritation of the sulfur glands, an increase in sulfur production, as well as pushing, tamping and fixing the already existing secret in the bone section of the ear canal. In addition to an increased risk of sulfur plug formation, such “hygiene” is fraught with injury to the ear canal and damage to the eardrum.
This leads to irritation of the sulfur glands, an increase in sulfur production, as well as pushing, tamping and fixing the already existing secret in the bone section of the ear canal. In addition to an increased risk of sulfur plug formation, such “hygiene” is fraught with injury to the ear canal and damage to the eardrum.
The anatomical narrowness and tortuosity of the external auditory canal, which can be hereditary in a child, can contribute to the accumulation of sulfur, as well as the problem of sulfur plugs. The recurrent formation of dry sulfur plugs in a child may be due to insufficient air humidity in the children's room.
Initially, the earwax conglomerate does not completely cover the ear canal and therefore cannot be detected in any way. Gradually increasing in size, it blocks the ear canal, and thereby contributes to hearing loss.
Children with wax plugs often complain of hearing loss. Also, the appearance of reduced hearing can cause water to enter the ears. In this case, the sulfur plug swells, increases in size and completely blocks the ear canal.
In this case, the sulfur plug swells, increases in size and completely blocks the ear canal.
How can they remove the wax plug in a child?
If all these symptoms appear, you should contact an ENT doctor so that he can correctly diagnose and treat. Similar symptoms can be observed with sensorineural hearing loss, when hearing loss is observed with inflammation in the middle ear. Direct examination of the cavity of the outer ear allows you to accurately establish the diagnosis. ENT - the doctor examines the cavity of the outer ear, where he detects a sulfur plug. In color, it can be from yellow-brown to black. With a long stay of the sulfuric plug in the cavity of the auditory canal, it can cause the appearance of bedsores.
It is not allowed to attempt to independently remove the cerumen from the ear canal, as this can lead to damage to the epidermis of the external auditory canal and even the eardrum, while the cerumen will not be removed, but will move deep into the ear canal into the bone section, from which it is quite heavy extract.
Remove cerumen in children by flushing the external auditory canal. For washing, water heated to body temperature is used, since a jet of cold liquid, hitting the eardrum, can cause disturbances in the activity of the vestibular apparatus and then the child may feel dizzy, nausea, headache, and even lose consciousness.
Sulfur plugs are sometimes very dry and difficult to separate when washed. In this case, it is recommended to instill 3% hydrogen peroxide into the ear for 2-3 days or apply Levomekol ointment. When instilling hydrogen peroxide, it must be remembered that it is a liquid that causes swelling and softening of the sulfur plug. In this regard, hearing loss can often occur due to the blockage of the ear canal with swollen cerumen. There is no need to be scared here, after washing the cavity of the ear canal, hearing will be restored completely.
After the removal of the sulfur plug, the child's hearing is usually restored immediately, and unpleasant subjective sensations disappear.