Leg cramps during miscarriage
Signs and Symptoms of Miscarriage at Every Stage of Pregnancy
Miscarriage remains a highly sensitive topic that many Americans avoid talking about—but more women than you may think experience early pregnancy loss, often leaving them with intense emotional and physical symptoms of grief.
Among women who know they are pregnant, roughly 10 to 15 percent experience a miscarriage. However, it's estimated that the actual miscarriage rate may be significantly higher—up to 50 percent, according to March of Dimes, a nonprofit organization that focuses on reducing premature births in the United States. This is due to the fact that many women miscarry before even realizing they're pregnant.
But why does a miscarriage even happen—and are the symptoms always obvious? Here's what you should know.
What causes a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is a pregnancy loss that occurs on its own within the first 20 weeks of gestation. While doctors are sometimes unable to explain why a miscarriage occurs, about half of miscarriages result from an abnormal number of chromosomes in an embryo.
Related Stories
- 6 Early Signs You Might Be Pregnant
- Carrie Underwood Reveals She Had 3 Miscarriages
"Reproduction is not flawless, and nature seeks to eliminate imperfect developing embryos," says Felice Gersh, MD, an obstetrician-gynecologist and director of the Integrative Medical Group of Irvine. Other potential causes can stem from problems with the uterus or cervix (such as large uterine fibroids, for example), or infections like sexually transmitted diseases.
Some women are at a greater risk for miscarrying than others, including those who are older than 35, have a history of two or more miscarriages, use drugs or alcohol, smoke cigarettes, or have been exposed to harmful chemicals.
If you've experienced a miscarriage, it's important to understand that it was in no way your fault, and it's likely that your next pregnancy will go well, explains Dr. Gersh. However, you should definitely seek professional counseling if you're experiencing intense grief. "Having a miscarriage is very emotionally impactful," she says. "But please know things most likely will get better."
Gersh. However, you should definitely seek professional counseling if you're experiencing intense grief. "Having a miscarriage is very emotionally impactful," she says. "But please know things most likely will get better."
Miscarriage symptoms
🚨 If you experience any of the symptoms of miscarriage, see your doctor, who can help stop the bleeding and prevent infection. 🚨
Weeks 2 through 4
In the first few weeks after conception, most women won’t even know they're pregnant, as only a very sensitive pregnancy test will detect a pregnancy so early. A miscarriage during this early period is often referred to as a chemical pregnancy and sometimes goes unnoticed. Chemical pregnancies are often mistaken for a regular menstrual cycle that may arrive earlier or later than expected, with similar bleeding and cramping.
Weeks 4 through 12
Through the first trimester of pregnancy, the symptoms of miscarriage remain the same. "The most typical symptom of impending miscarriage is some degree of bleeding—which can vary from light spotting to heavy bleeding," Dr. Gersh explains. The color of the blood can be brownish, pink, or bright or dark red, and can include some clots. The heavier the bleeding, the more likely it is that a miscarriage has occurred.
"The most typical symptom of impending miscarriage is some degree of bleeding—which can vary from light spotting to heavy bleeding," Dr. Gersh explains. The color of the blood can be brownish, pink, or bright or dark red, and can include some clots. The heavier the bleeding, the more likely it is that a miscarriage has occurred.
You may also feel cramping in your abdominal or pelvic region, as well as a lower back ache. "The degree of discomfort can vary from minimal to quite severe during the actual miscarriage,” says Dr. Gersh, noting that pain can also radiate down the upper legs.
The severity of the bleeding and cramps can sometimes (but not always) correlate with the duration of the pregnancy. "Think of it this way: the more tissue that's built up in the uterus, the more that must be removed," she explains. Hence, there will be more bleeding and cramping as the pregnancy progresses.
After a miscarriage, you may notice that any pregnancy symptoms you've been experiencing—breast tenderness, fatigue, nausea, and more—will disappear once a miscarriage occurs. “If nausea and breast tenderness disappear, that could signify that pregnancy hormone levels are dropping, though this is a very soft sign and without bleeding or cramping, I wouldn’t get too concerned,” says Dr. Gersh. However, she does reiterate that getting checked out is always wise.
Weeks 12 through 20
Once you've entered your second trimester, miscarriage symptoms can include pelvic pressure and mucous discharge; otherwise the main symptoms to look for are still bleeding and cramping.
Types of miscarriage
There are many different ways for a miscarriage to happen, and nearly all types of miscarriage have the same symptoms listed above. This includes:
This includes:
- Blighted ovum: This refers to a fertilized egg that never developed into an embryo.
- Recurrent miscarriage: When a woman has multiple miscarriages, they're described as recurrent miscarriages and often require medical testing to uncover the underlying cause.
- Threatened miscarriage: This common condition causes miscarriage symptoms like abnormal bleeding and pain, but may not actually result in pregnancy loss, according to Dr. Gersh. While the pregnancy is considered a "threatened miscarriage," many of these cases successfully carry to full term with the proper care.
Do these symptoms always point to a miscarriage?
Not necessarily, here are two exceptions to be aware of:
Ectopic (or tubal) pregnancyThis refers to a pregnancy where a fertilized egg implants anywhere outside the womb—usually a fallopian tube, but sometimes on the ovaries, in the cervix, on the liver, or by the bowel. These pregnancies are rarely successful and usually cause internal ruptures, which lead to vaginal bleeding, extreme cramping, dizziness, and fainting. An ectopic pregnancy is a very serious, potentially life-threatening condition and one of the most common causes of maternal mortality. The symptoms can be quite similar to a normal miscarriage, so be sure to contact your doctor if you experience them.
These pregnancies are rarely successful and usually cause internal ruptures, which lead to vaginal bleeding, extreme cramping, dizziness, and fainting. An ectopic pregnancy is a very serious, potentially life-threatening condition and one of the most common causes of maternal mortality. The symptoms can be quite similar to a normal miscarriage, so be sure to contact your doctor if you experience them.
A molar pregnancy occurs when tissue in the uterus develops into a tumor. The placenta doesn't develop properly; instead, that tissue grows into a mass of cysts that grows in a chaotic manner and fills the uterus until heavy bleeding occurs. The symptoms may also include nausea and grape-like cysts that pass through from the vagina. An ultrasound can detect a molar pregnancy, so they rarely grow very large before being surgically extracted. A molar pregnancy almost always results in pregnancy loss, although many women who experience one are able to have a successful pregnancy later on.
A molar pregnancy almost always results in pregnancy loss, although many women who experience one are able to have a successful pregnancy later on.
The bottom line: Miscarriages are more common than many people realize, and while they can be extremely upsetting, they are never a woman's fault. While pregnant, it's important to pay close attention to your body and alert your doctor to any pain or bleeding. Despite having a miscarriage, many women go on to have healthy, successful pregnancies in the future.
Leah GrothContributor
Leah Groth is a freelance writer based in Philadelphia. Her work has appeared in a number of international publications including Glamour, Prevention, Health, VeryWell, Business Insider, and Reader’s Digest. In those rare moments that she isn’t putting words together on her keyboard, you can find her chasing after her two children and hunting dogs, working on her 100-year-old colonial home, or trying out all of the cutting edge gadgets and products she is writing about. She also loves working out and drinking copious amounts of coffee.
She also loves working out and drinking copious amounts of coffee.
Miscarriage Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), miscarriage happens in at least 10 percent of clinically identified pregnancies. (Meaning, you actually knew you were pregnant; some miscarriages happen before you even miss your period.)
When miscarriage happens after you’ve already gotten a positive pregnancy test, it can be a physically and emotionally painful process.
We can’t make miscarriage any easier, but we can help you understand what’s happening. For instance, although abdominal pain is one of the most frequent symptoms of a miscarriage, it’s not the only type of pain or discomfort you might feel.
Here’s a breakdown of seven types of pain you might have during a miscarriage and what you can do to relieve your symptoms.
Cramping with a miscarriage is usually caused by your uterus contracting. Just like during your period, your uterus contracts to push contents out. Since your uterus is mostly a muscle, these contractions feel like muscle cramps (in other words, they hurt).
Since your uterus is mostly a muscle, these contractions feel like muscle cramps (in other words, they hurt).
You’ll usually feel these cramps on both sides of your lower abdomen or pelvic region. The cramps may come and go in waves or your pain may feel more constant. Unless your doctor has told you not to, you can treat your pain with over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like Motrin or Tylenol. You can also use a heating pad to ease cramping.
During a normal menstrual cycle, your uterus builds up lining to prepare for a pregnancy. When the pregnancy can’t continue, the lining needs to be shed.
Because your body has been preparing for pregnancy, there will be more lining and tissue, so your bleeding will be heavier than a period. The further along you are in the pregnancy, the heavier it will be.
To absorb the bleeding, you’ll need to wear a pad. ACOG doesn’t recommend using tampons during a miscarriage. And because the bleeding may last longer and be heavier than a typical period, you may notice some discomfort from moisture accumulation.
Blood loss with a miscarriage
You can lose a significant amount of blood with a miscarriage. Stay in touch with your doctor during the process and call if you experience dizziness or excessive blood loss (e.g., soaking more than two maxi pads per hour for more than 2 hours in a row).
To combat any discomfort, change your pad frequently and clean the area gently with water, avoiding soap.
The change in the vaginal environment from bleeding may also cause a yeast or bacteria overgrowth that could lead to vaginal odor. If you notice any signs of a yeast infection such as itching, or if the discharge becomes very foul smelling, call a doctor.
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can be caused by hormone changes, as well as side effects from any medication you take to manage the miscarriage. Diarrhea can also be caused by the relaxing of the smooth muscle, just like you experience with a period.
To combat nausea symptoms, drink plenty of water and try to eat small meals consisting of bland, gentle-on-the-stomach foods. These can include:
These can include:
- rice
- bananas
- oatmeal
- scrambled eggs
- plain grilled chicken
If your symptoms are making it hard for you to keep food down or stay hydrated, ask your doctor about taking an antinausea or antidiarrheal medication.
Similar to how your period cramps can lead to back pain, the uterine contractions during a miscarriage can cause back pain. This is usually felt in the lower back and the pain can be mild, moderate, or severe.
You can treat it just like you would your cramps — with pain relievers and heating pads — but if it’s really uncomfortable, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor what else you can do.
Shoulder pain is a symptom of ectopic pregnancy and it’s a serious medical emergency. If you have severe, one-sided pain, dizziness or fever, or pain affecting your rectum, pelvis, shoulder, or neck, call your doctor or get urgent medical care right away.
Ectopic pregnancy may not cause bleeding, so it can be a harder type of pregnancy to identify.
It’s normal to feel tired and weak with a miscarriage. You may also have a headache. If you experience excessive dizziness or feel like you may faint, tell your doctor or call your local urgent care center.
It’s also important to rest and drink plenty of water to manage these symptoms. Try to sleep, stay hydrated, and eat nutrient-dense foods.
No matter how far along in your pregnancy you are when you miscarry, you’re allowed to feel grief. Miscarriage emotions can be complicated and messy. You may feel both sad and relieved that it’s over, or you may feel intense and sometimes overwhelming grief.
No matter your situation, you might feel disappointed, hopeless, or scared to conceive again. You might experience anxiety, mood swings and irritability, and even depression.
Talking about your loss can help. Try turning to trusted friends and family members, social media groups, or a mental health professional. Miscarriage can also lead to clinical depression, similar to postpartum depression — so be sure to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms.
The severity of your miscarriage symptoms will depend on how far along you are in your pregnancy and what type of miscarriage you have. Still, a miscarriage at any stage can be difficult because all bodies respond differently.
You may choose expectant management to let your body pass the tissue on its own, you might use medication that can speed up the process, or you may choose a surgical procedure called a dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove the contents of the uterus.
The bleeding that occurs with miscarriage can be different for everyone, too. In general, you can expect menstrual-like bleeding for about a week. After that, spotting can continue for several weeks — sometimes even until your next period. And when is that? Again, it varies: Your menstrual cycle can restart anywhere between 4 to 8 weeks after the miscarriage.
When to seek medical help
If you suspect you’re having a miscarriage, you should always consult with your doctor. Your provider will also stay in touch with you throughout the recovery process.
Depending on the timing of your miscarriage and how it’s managed, it may be 2 or 3 weeks before you’re feeling like yourself again physically. In some cases, your doctor may order an ultrasound to confirm that your uterus is clear of retained tissue.
For some people, the emotional pain of a miscarriage can last much longer. It’s important to remember that the stage of your pregnancy when you miscarried doesn’t matter: You experienced a loss, and loss naturally comes with feelings of grief.
Sometimes that grief can get too big for you to handle on your own. As with postpartum depression after a birth, symptoms of depression can develop after a miscarriage. In fact, according to a 2015 journal article, nearly 20 percent of women report symptoms of depression and/or anxiety after miscarriage.
If you think you might be depressed or are simply struggling to manage your emotional recovery after miscarriage, don’t be afraid or ashamed to reach out for support. A licensed mental health professional can help you process your loss and begin to heal.
You can also look for a miscarriage support group to connect with other people who have shared your experience. You can search or contact any of the following resources for local and online miscarriage support groups:
- Hope After Loss
- Share Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support
- Empty Cradle
- First Candle
- Empty Arms Bereavement Support
- The Compassionate Friends
- The Miscarriage Association (UK)
Miscarriage can be a difficult experience on your body, mind, and heart. You can help ease physical symptoms with rest, fluids, OTC pain relievers — and stay in touch with your doctor if you have any complications.
It’s also important to address the emotional pain of a miscarriage. Talking to a mental health professional or finding support from a local or online pregnancy loss group can help you take steps toward healing.
Convulsions during pregnancy: treatment and prevention
Every woman at least once in her life has come across the concept of convulsions. This is especially unpleasant, and, unfortunately, not uncommon, the phenomenon manifests itself during pregnancy. Should I be scared or worried?
This is especially unpleasant, and, unfortunately, not uncommon, the phenomenon manifests itself during pregnancy. Should I be scared or worried?
Pregnant women often experience convulsions at night when falling asleep or before waking up. The sensations are so painful, strong and unbearable that they do not allow her to fully rest.
In the first trimester, the expectant mother suffers from convulsions against the background of early toxicosis due to a lack of healthy substances. But usually this phenomenon manifests itself in the second or third trimester due to the increased load on the woman's body and the likely nervous displacements.
Causes of sudden seizures during pregnancy
What are the sources of seizures in a pregnant woman and how to deal with them?
As already mentioned above, involuntary muscle contractions can lie in wait for a woman during any period of expectation of a baby. Accordingly, the causes of occurrence are different, they are united by one thing: there are failures and disorders in the body, ranging from a lack of vitamins and trace elements to complications.
According to experts, the main sources of unpleasant painful impulsive muscle contractions can be:
- Deficiency of trace elements such as calcium, potassium, magnesium and vitamin B6. What caused this deficit?
-
- Toxicosis, accompanied by profuse vomiting. Consequently, the female body is deprived of a large number of trace elements (most often in the first trimester of expecting a child).
- Uncontrolled use of diuretics.
- The fetus requires more needs for development (which is observed more in the middle of pregnancy).
- Improper and unbalanced diet, which leads to insufficient intake of nutrients into the body.
- The amount of hemoglobin decreases - that is, the protein that is responsible for delivering oxygen to all organs. During pregnancy, the health of the mother and child depends on the level of hemoglobin.
- If the expectant mother violates the diet, eats a lot of carbohydrates, is fond of sweets, eats rarely, but in large portions - all this can lead to a violation of blood sugar levels.

- Varicose veins, especially if the pregnant woman puts a lot of pressure on her legs.
- Uncountable consumption of caffeinated drinks by a woman. Such abuse is fraught with dehydration of the muscles, their tension. This may result in the development of seizures.
- “Inferior vena cava syndrome” is a condition in which an enlarged uterus presses on the inferior vena cava. A significant additional load is provoked on the work of the heart, blood vessels, blood supply to the fetus, and a violation of the venous outflow from the legs. One result is the development of seizures. This condition occurs in the last term, especially when resting on the back or right side.
- All kinds of diseases and complications of pregnancy.
Leg cramps
Many expectant mothers, when talking to their gynecologist and talking about painful sensations, complain about spasms in the muscles of the legs, more precisely, cramps in the calf muscles. The time of occurrence of these unpleasant symptoms is either in the evening or in a dream, at night.
At night, the body rests, is at rest and relaxed. It is at such moments that women often wake up from the pain of cramps in the muscles of the legs. Therefore, some pregnant women put a pin near them to prick a cramped muscle.
Causes:
- Leg cramps can be triggered by many factors: deficiency of trace elements, primarily magnesium and calcium, vitamins D and B6, and many others. But the main thing is that an additional burden falls on the woman's body.
- Spasms at night are the result of increased stress on the legs during the day. It is worth paying special attention to women in the "position" on the shoes they wear throughout the day. High heels are absolutely not recommended for pregnant women if they have a predisposition to cramps. Therefore, all doctors advise wearing low-speed shoes: the legs will not be overloaded, and, accordingly, there will be less muscle contractions at night.
- If you have a habit of crossing your legs while sitting on a chair or in an armchair, you should stop it.

- Proper healthy nutrition is a must. Starting from 4 months, it is recommended to rest on the left side so that the condition of the “inferior vena cava syndrome” does not appear.
Help:
- If at any time of the day the leg is "crumpled" - use a pin or needle, lightly prick the muscle.
- A good method is to strain and pull the toe of the leg in which the spasm has developed towards you, sometimes helping with your hands. Repeat several times and try to relax while doing it. And then massage in the place where unpleasant painful sensations arose to restore blood circulation. After that, you can slowly walk around or sit, raising your legs to a dais.
Leg cramps
Leg muscle contractions are not the only ones that can disturb a pregnant woman: during this period of life, the expectant mother also experiences discomfort in her arms.
Causes:
- The main sources of pain are the same as described above: improper and irregular nutrition, lack of useful trace elements, overheating, excessive abuse of diuretic drugs, various diseases and complications of pregnancy, prolonged muscle tension.

- Women who have the same type of hand movements for a long time are susceptible to such spasms. For example: office workers, musicians, assembly line workers and others. But housewives should also think about how to take care during pregnancy. After all, a long time to cut vegetables or do other homework can lead to painful sensations.
Help:
- If a pregnant woman works all day, it is imperative to plan the work so that her hands can rest. The best option is to alternate work and rest every 15 minutes. Rest is recommended to be combined with light exercises: waving your arms, clenching and unclenching your fists, rotating your hand, shaking your hands.
- Hand massage is an excellent method. It is quite enough to massage problem areas and the result will please you very soon.
If all the above recommendations do not help, be sure to consult your doctors. The possibility of internal diseases should be excluded. For example, symptoms of neuropathy are frequent cramps in the same place, problems with the cardiovascular system - frequent painful cramps in the left arm.
For example, symptoms of neuropathy are frequent cramps in the same place, problems with the cardiovascular system - frequent painful cramps in the left arm.
Abdominal cramps
Abdominal cramps are usually very frightening for a woman, she becomes very nervous and imagines the worst options for herself. But often all the sensations that a pregnant woman takes for cramps are uterine contractions that are inevitable during pregnancy.
- During any period of pregnancy, you should not worry about the above sensations, provided that there are no concomitant signs: bloody or brown discharge, the general condition of the pregnant woman has not worsened, no sudden weaknesses appear throughout the day.
- If seizures occur shortly after conception, the likely cause is the attachment and implantation of a fertilized egg to the uterus. Further, when the fetus is fixed and begins to grow, this may become a factor in abdominal cramps, although not felt by most women.

Attention!
Starting from the 20th week of pregnancy, expectant mothers may experience mild, non-painful cramps: the uterus is preparing for the upcoming birth and is training contractions in advance.
False contractions (the concept was introduced by an English doctor, after his name they are called “Braxton-Hicks contractions”) - completely safe, they do not cause the opening of the cervix, therefore, do not lead to labor. The main signs of Braxton-Hicks contractions are irregularity, unpredictability, short duration and relative painlessness.
Pre-delivery training contractions also occur at earlier dates, but usually the woman does not identify them.
If a pregnant woman notices that the contraction is regular, repeating at regular intervals, accompanied by pain in the back or abdomen, there is a brown spotting discharge, seek medical help immediately. All of the above signs may indicate an increased tone of the uterus and the risk of miscarriage.
Treatment of seizures during pregnancy
The most important thing that a woman expecting a child must do when seizures appear is to contact her gynecologist. The doctor, after consulting with specialists and excluding serious diseases, will give recommendations to reduce or completely stop muscle spasms.
The main recommendation, which will sound from the lips of doctors, is to review the diet of a pregnant woman. It is necessary to add to the menu more foods that are rich in essential nutrients - potassium, magnesium, calcium.
- Potassium
Every cell in the body contains potassium, which is extremely important. Toxicosis, improper use of drugs, excessive consumption of caffeine lead to a lack of this element.
Potassium deficiency is manifested by:
- Convulsions
- Constipation
- Thirst
- Depression and nervousness
- Tachycardia.
Foods rich in potassium: melon, dried apricots, beans, beef liver, bananas, broccoli, potatoes.
- Calcium
Calcium is one of the most essential minerals for humans.
Calcium deficiency is manifested by:
- Tooth decay
- Cramping
- Insomnia
- Numbness and convulsions
- Nervousness
- Brittle nails.
Sources of calcium - dairy products, asparagus, broccoli, legumes, nuts, cabbage, figs.
- Magnesium
Comprehensive stabilizer of body processes. The need for magnesium during pregnancy increases by 2-3 times.
Magnesium deficiency is manifested by:
- Convulsions
- Decrease in body temperature
- Arrhythmia.
Contained in sunflower seeds, carrots, nuts, legumes, green vegetables.
Painful spasms can be eliminated by massage, a specially selected course of exercises, various ointments and gels. Any medications can be taken only after prescription by specialists.
Prevention of seizures
In order to prevent seizures, doctors advise:
- wear comfortable shoes with low, stable heels;
- with a predisposition to the expansion of the superficial veins of the legs, you should wear special designed stockings;
- rest more often with legs elevated;
- if you have to be on your feet for a long time without moving, it is recommended to do simple exercises: rise in turn on your toes, then lower yourself to the foot;
- late pregnancy, try to lie on the left side;
- take contrast showers;
- Relaxing foot baths with warm water and sea salt are recommended before going to bed.
Miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriage
Diagnosis of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
90302 miscarriage is spontaneous miscarriage0131 for up to 20 weeks. According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus.
According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus. Miscarriage is a fairly common occurrence, but this fact does not make things easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Symptoms of miscarriage .
Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include:
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting (although this is common in early pregnancy)
- Pain or cramps in the abdomen or lower back
- Fluid vaginal discharge or tissue fragments
It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common.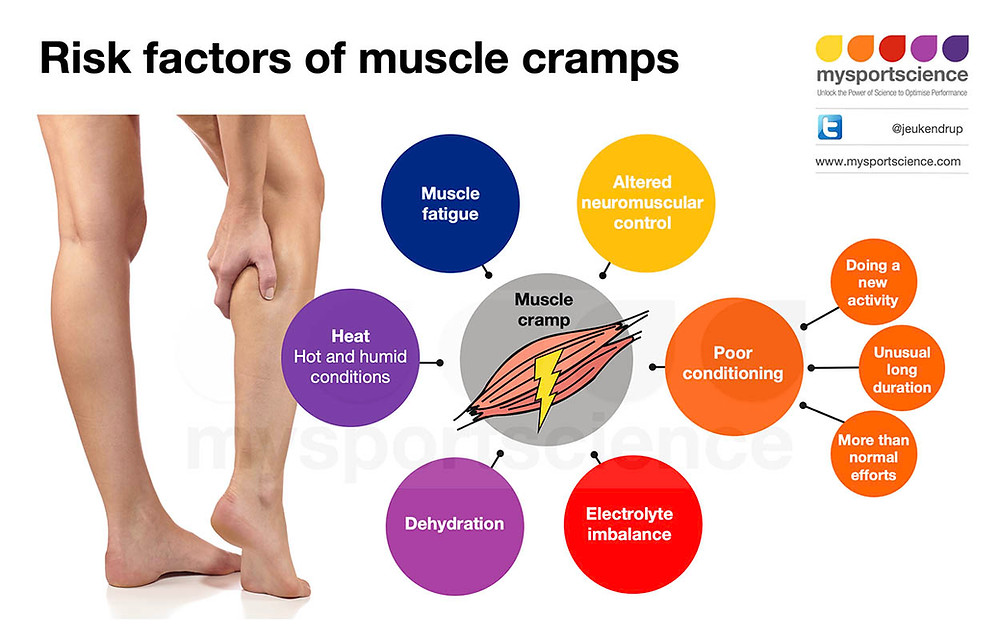 In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage.
Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus. This infection, also called septic miscarriage, can cause:
- Fever (feeling hot, chills)
- Body pains
- Thick, foul-smelling vaginal discharge
When to see a doctor.
Call your doctor if:
- Bleeding, even if only light spotting occurs
- Profuse, liquid vaginal discharge without pain or bleeding
- Isolation of tissue fragments from the vagina
You can place a piece of tissue removed in a clean container and take it to your doctor for examination. It is unlikely that the study will give any accurate results, but if it is determined that the fragments of the excreted tissue are from the placenta, the doctor will be able to conclude that the symptoms that appear are not associated with the presence of a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.