Does the meningitis rash itch
What is the 'meningitis rash'?
When we think of meningitis, we may think of the so-called ‘meningitis rash’ – a red or purple marking on the body which remains present when pressed with a glass. However, the rash does not always appears in cases of meningitis, and the word ‘rash’ itself may be misleading. Information and Support Officer Katherine Carter explains more.
What is the meningitis rash?Meningitis and septicaemia can be caused by many different bugs, including viruses and fungi, but most cases of severe meningitis and septicaemia are caused by bacteria. Meningococcal bacteria in particular are the most common cause of the meningitis rash.
These bacteria can be very common and are mostly harmless, but in some people this bacteria invade the body via the back of the nose and throat, causing severe illness and even death. Sadly we don’t yet understand why some people get ill from a bacteria that is harmless to most of us.
Once the bacteria have invaded the back of the nose and throat, they travel through the bloodstream. As this happens, the bacteria rapidly multiply and produce toxins which travel around the body causing damage to blood vessels and organs. As the blood vessels get damaged, blood starts to ‘leak’ into the surrounding tissue, often causing what looks like a ‘rash’ to appear on the skin. However, this does not always appear.
This rash can be one of the clearest and most specific signs of meningococcal meningitis and septicaemia to recognise – hence why you have probably heard of it. However, meningococcal rashes can be extremely diverse, and look different on different skin types. The rate of progression can also vary greatly.
- A petechial rash looks like pin-prick red or purple spots on the skin, and can resemble flea bites.
- A purpuric rash looks more like bruising, showing up as reddish-purple areas on the skin.
A rapidly evolving petechial or purpuric ‘rash’ is a marker of very severe disease. As part of the MRF helpline team, I have had a parent describe a rapidly evolving rash as “like someone using a biro to draw all over the skin”. If you, or someone you know, appears to be suffering from a rash of this kind, please seek medical help immediately.
As part of the MRF helpline team, I have had a parent describe a rapidly evolving rash as “like someone using a biro to draw all over the skin”. If you, or someone you know, appears to be suffering from a rash of this kind, please seek medical help immediately.
Isolated and dispersed pin-prick spots may first appear, so it is important to search the whole body for small petechiae, or red and purple spots. Petechiae are 1 to 2 mm in diameter and commonly appear in clusters in areas where pressure occurs from elastic in underwear, nappies or stocking. The rash can be more difficult to see on dark skin, but may be visible in paler areas, especially the soles of the feet, palms of the hands, abdomen, or on the inside of the eyelid or roof of the mouth.
The 'glass test' can be used to determine if a rash is or is not a symptom of meningitis.
What does the ‘glass test’ do?
Many people are familiar with the so-called “tumbler test” or “glass test”, whereby a glass or other clear surface is pressed onto the rash. If it disappears when pressed, this is known as a blanching rash. The meningitis “rash” can start as a blanching rash, but nearly always develops into a non-blanching red, purple or brownish petechial rash or purpura, meaning it will not disappear when pressed.
If it disappears when pressed, this is known as a blanching rash. The meningitis “rash” can start as a blanching rash, but nearly always develops into a non-blanching red, purple or brownish petechial rash or purpura, meaning it will not disappear when pressed.
In response to the blood vessels leaking as the disease progresses, the body produces an overwhelming clotting response, which stops oxygen from reaching the extremities. This results in extensive purpuric areas, usually called ‘purpura fulminans’, which look like large bruises over the skin and can be very dark in colour.
The extremities are normally worst affected: often the feet and hands (but can extend over a whole arm or leg) and sometimes the ears, nose or lip. Devastatingly, as the extremities become starved of oxygen, they can become blackened which can lead to scarring and amputation.
What should I do if someone has lots of other meningitis symptoms, but no rash?Most patients with overwhelming meningococcal septicaemia develop a rash - it is one of the clearest and most important signs to recognise. However, in cases of meningitis the rash can be very scanty, blanching, atypical or even absent. When we talk about meningitis, we often think ‘rash’, but it is incredibly important to know that a rash won’t always appear.
However, in cases of meningitis the rash can be very scanty, blanching, atypical or even absent. When we talk about meningitis, we often think ‘rash’, but it is incredibly important to know that a rash won’t always appear.
Please remember that a very ill person needs medical help even if there are only a few spots, a rash that fades, or no rash at all. Trust your instincts, someone who has meningitis or septicaemia could become seriously ill very quickly. Get medical help immediately if you suspect meningitis or septicaemia – rash or no rash!
Meningitis - Symptoms - NHS
Symptoms of meningitis can appear in any order. Some may not appear at all. In the early stages, there may not be a rash, or the rash may fade when pressure is applied.
You should get medical help immediately if you're concerned about yourself or your child.
Trust your instincts and do not wait for all the symptoms to appear or until a rash develops.
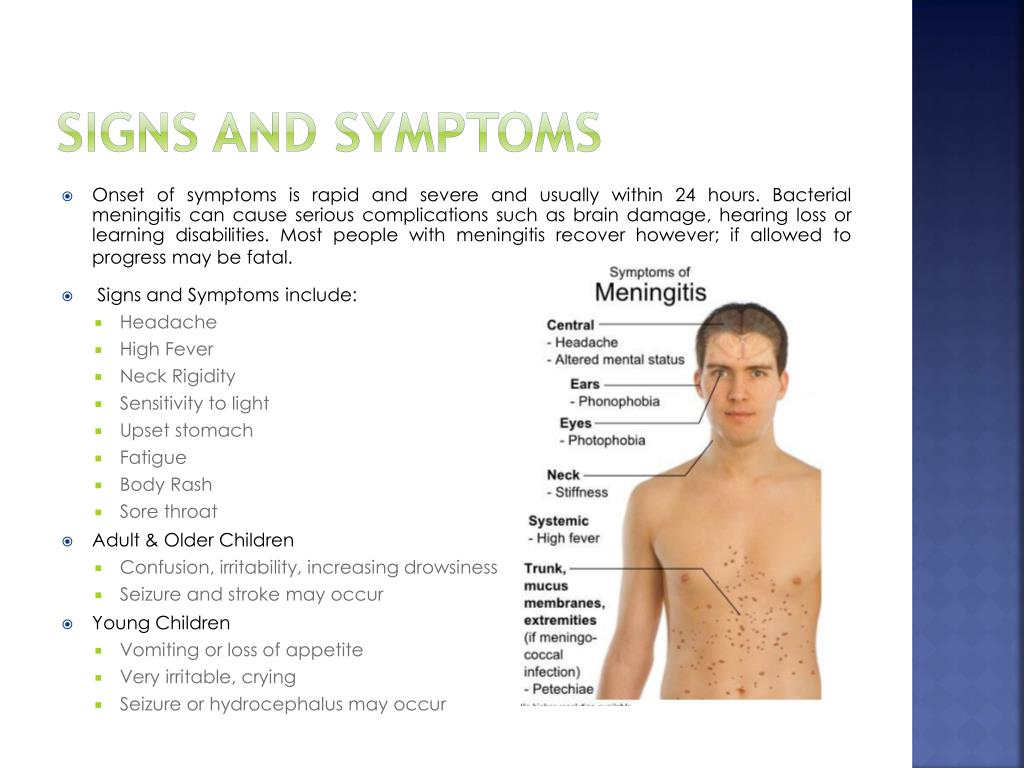
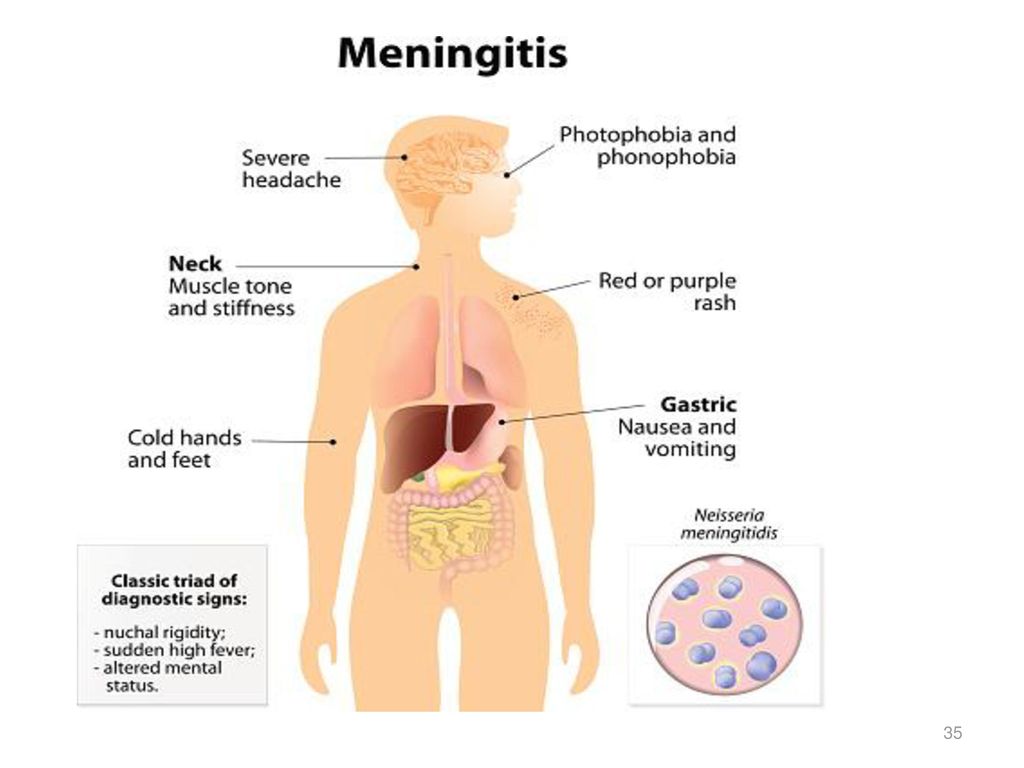
Symptoms of meningitis and sepsis include:
- a high temperature
- cold hands and feet
- vomiting
- confusion
- breathing quickly
- muscle and joint pain
- pale, mottled or blotchy skin (this may be harder to see on brown or black skin)
- spots or a rash (this may be harder to see on brown or black skin)
- headache
- a stiff neck
- a dislike of bright lights
- being very sleepy or difficult to wake
- fits (seizures)
Babies may also:
- refuse feeds
- be irritable
- have a high-pitched cry
- have a stiff body or be floppy or unresponsive
- have a bulging soft spot on the top of their head
Someone with meningitis or sepsis can get a lot worse very quickly.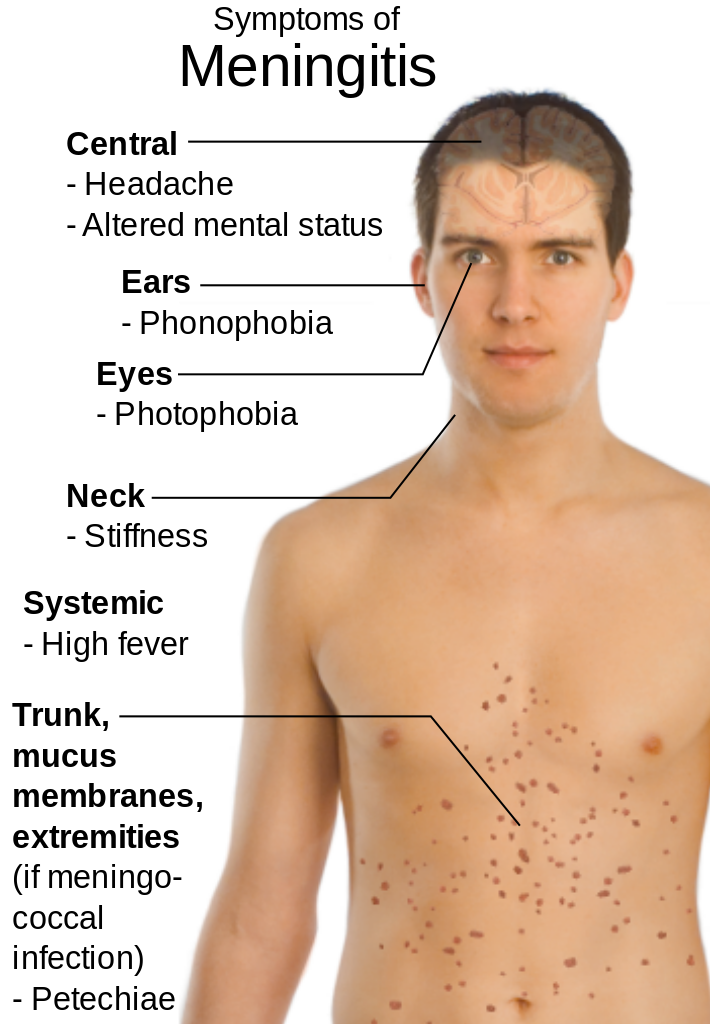
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest A&E immediately if you think you or someone you look after could have meningitis or sepsis.
Call NHS 111 for advice if you're not sure if it's anything serious.
If you’ve had medical advice and are still worried or any symptoms get worse, get medical help again.
The rash usually starts as small, red pinpricks before spreading quickly and turning into red or purple blotches.Credit:
Mediscan / Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/meningococcal-rash-image1683649.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=83D4AFC7-AC4B-4271-B09C-727E90532943&p=17774&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dATB0C2%26qt_raw%3dATB0C2%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d788068%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
It does not fade if you press the side of a clear glass firmly against the skin.
Credit:
Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/testing-of-meningococcal-rash-image589611.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=6C8D2A33-C874-43AF-A58B-398C0D9552AF&p=17774&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dA8FF2B%26qt_raw%3dA8FF2B%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d195878%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
The rash can be harder to see on brown or black skin. Check paler areas, such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, roof of the mouth, tummy, whites of the eyes or the inside of the eyelids.
Check paler areas, such as the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, roof of the mouth, tummy, whites of the eyes or the inside of the eyelids. Credit:
Meningitis Research UK https://hscic365.sharepoint.com/sites/Pilot/NHSUK/Health%20AZ/Forms/AllItems.aspx?id=%2Fsites%2FPilot%2FNHSUK%2FHealth%20AZ%2FHealth%20A%2DZ%2FA%2DZ%20content%20audit%2FM%2FMeningitis%2FImage%20and%20section%20review%2007%202019%2FRe%5FPhotography%20of%20the%20meningitis%20rash%2Eeml&parent=%2Fsites%2FPilot%2FNHSUK%2FHealth%20AZ%2FHealth%20A%2DZ%2FA%2DZ%20content%20audit%2FM%2FMeningitis%2FImage%20and%20section%20review%2007%202019
If a rash does not fade under a glass, it can be a sign of sepsis (sometimes called septicaemia or blood poisoning) caused by meningitis and you should call 999 straight away.
Page last reviewed: 25 October 2022
Next review due: 25 October 2025
Meningococcal infection and its prevention
Meningococcal infection occupies an important place in infectious pathology and continues to be relevant for the Republic of Belarus
Meningococcal infection affects only people. The causative agent - meningococcus - is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as, for example, with the flu. This microbe lives in the nasal cavity and can be transmitted from person to person by sneezing, coughing and even talking. This is a very serious disease that can develop among full health in a matter of hours and minutes. Children are more often ill, and generalized forms of the disease in 80% of cases occur in children under 2 years of age. Sometimes it is not possible to save a sick child. nine0003
The causative agent - meningococcus - is transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as, for example, with the flu. This microbe lives in the nasal cavity and can be transmitted from person to person by sneezing, coughing and even talking. This is a very serious disease that can develop among full health in a matter of hours and minutes. Children are more often ill, and generalized forms of the disease in 80% of cases occur in children under 2 years of age. Sometimes it is not possible to save a sick child. nine0003
The incubation period (the period from the moment meningococcus enters the body until the first signs of the disease appear) can last from several hours to 10 days. It all depends on the age and immune status of the patient.
The microbe itself is relatively unstable in the external environment. Outside of a person, he dies within 30 minutes. Fresh air, direct sunlight, ultraviolet radiation and disinfectants are especially detrimental to meningococcus.
This disease is characterized by a very acute onset, one might say in the midst of full health or after a slight runny nose.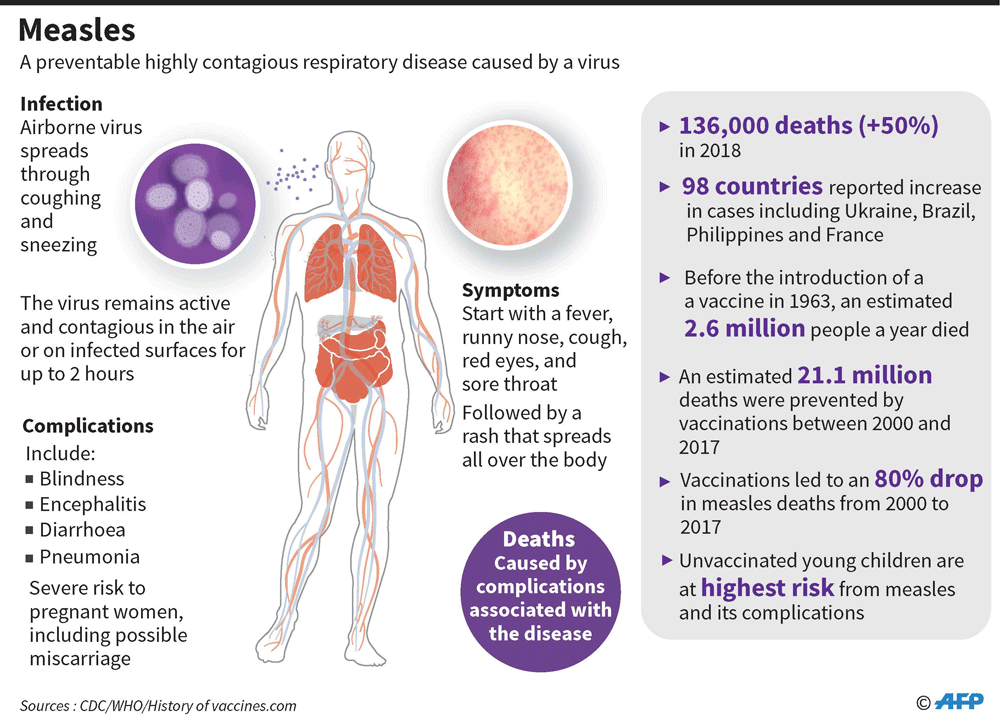 The temperature rises sharply to very high numbers, the child complains of a severe headache, at first a single, and then indomitable vomiting appears. Young children, who cannot yet complain, may have regurgitation, lethargy, refusal of the breast.
The temperature rises sharply to very high numbers, the child complains of a severe headache, at first a single, and then indomitable vomiting appears. Young children, who cannot yet complain, may have regurgitation, lethargy, refusal of the breast.
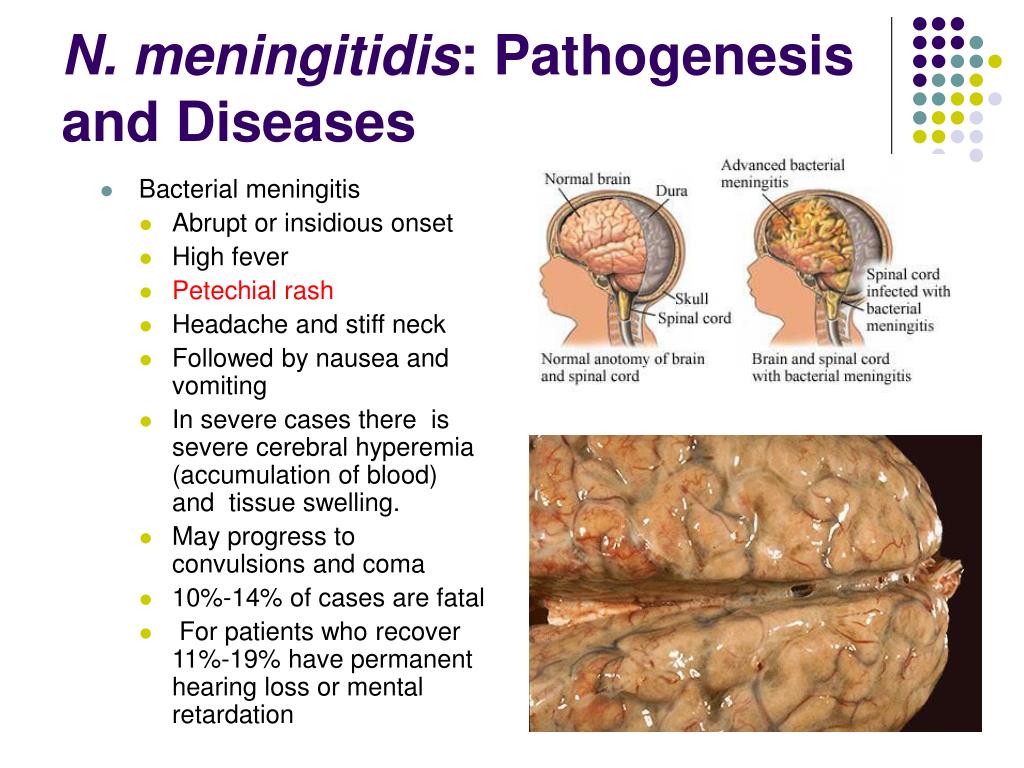
The main symptom of the fulminant form and the appearance of an infectious agent in the blood (meningococcemia) is a rash on the child's skin. Rash with meningitis in children is one of the most characteristic symptoms. Initially, it may be morbilliform in nature - in the form of small red spots and papules. After some time, such a rash disappears and a hemorrhagic rash characteristic of meningococcal infection appears. Pinpoint hemorrhages appear first in the feet and legs of the child, and then spread higher to the trunk and other parts of the body. On pale skin, they resemble a picture of a starry sky. nine0003
- Note that meningococcal rash does not go away with pressure. If a rash appears on the face, eyelids, oral mucosa, auricles, or at the very beginning of the disease, this is an unfavorable factor and is typical for severe forms of the disease.
 The rash will increase. And it is precisely in the presence of it that it is necessary to re-call the doctor, since the primary diagnosis before the rash can be set as an acute respiratory disease.
The rash will increase. And it is precisely in the presence of it that it is necessary to re-call the doctor, since the primary diagnosis before the rash can be set as an acute respiratory disease.
This form of meningitis is dangerous because toxic-septic shock can develop due to hemorrhage in vital organs and, above all, in the adrenal glands. This shock causes death in 5-10 percent of patients. Therefore, the sooner parents seek medical help, and the sooner an appropriate diagnosis is made, the greater the chance of saving the patient. But in any case, hospitalization will be required and parents do not need to refuse it.
- What are the preventive measures for meningococcal disease? nine0016
You just need to carefully monitor the child's condition and, if warning signs appear, immediately seek medical help.
Oddly enough, the best prevention of meningitis is to strengthen the immune system - walks in the fresh air, rational nutrition and hardening. Equally important is personal hygiene. Thorough hand washing is very important to avoid infection. Teach your children to wash their hands frequently, especially before eating, after being in a public place, and after they have touched animals. nine0003
Equally important is personal hygiene. Thorough hand washing is very important to avoid infection. Teach your children to wash their hands frequently, especially before eating, after being in a public place, and after they have touched animals. nine0003
And most importantly, do not try to treat the baby yourself. In many ways, the results of the treatment of meningitis depend on the time that has passed since the onset of the first symptoms and the start of therapy. Only a specialist is able to correctly assess the situation and select treatment tactics.
Prevention of meningitis in children is primarily the prevention of airborne infection of the child. For children aged 1 to 3 years, the main danger is adults, and first of all, relatives. The most dangerous age for meningitis is up to 5 years, and in many respects the health of the child depends on his parents. If one of the older family members has a cough, runny nose, nasal congestion, think about the child - do not approach him, or put on a four-layer gauze bandage, covering both the nose and mouth. nine0003
nine0003
- Meningococcus is one of the weakest microbes, it dies very quickly outside the human body, especially from the action of ultraviolet rays of sunlight. Regular ventilation of the premises and sufficient sunlight can quickly get rid of these microbes in the air. Thus, you need to take care of good lighting in your child's room. The nursery should always be ventilated and washed clean.
Among other preventive measures, it is recommended to have fewer contacts during the period of the seasonal rise in the incidence of influenza and ARVI, to attend social events less frequently. All festive events (christenings) associated with the birth of a child must be carried out outside the apartment where he is. nine0003
And most importantly, don't try to treat yourself. The results of treatment of meningococcal infection largely depend on the time interval between the onset of the first symptoms and the start of therapy. Only a specialist can correctly assess the situation and choose the tactics of treatment.
If hospitalization is suggested by a health worker, do not refuse it, your child's life may depend on it.
A complete and balanced diet enriched with vitamins and microelements, playing sports, hardening the body also contribute to the body's resistance to infection. nineNedved N.V.
what happens, a photo of how it looks in a child and features of the hemorrhagic type
Home → Diseases → Meningitis
Published: 11/27/17
Updated: 11/30/20 Author: Alexandra Ageeva
A rash is an unpleasant symptom that leaves a person with a lot of inconvenience. It can occur for various reasons, one of which is meningitis. nine0003
At the same time, diseases for rashes are characterized by certain features, knowing which, you can seek medical help in time and prevent complications. Read more about it in this article.
All information on the site is presented for informational purposes only and does not replace the need for examination by a doctor. We kindly ask you to contact a medical institution if you have any health problems.
We kindly ask you to contact a medical institution if you have any health problems.
Hide content
nine0014What is this disease? Why does this symptom appear and where is it localized? What does it look like? Photo
Do you itch? How to distinguish a dangerous sign from similar ones? First aid Treatment Are hemorrhagic rashes dangerous in this disease? Bibliography
What is this disease?
WARNING : Meningitis is a dangerous infectious disease that can be spread through the air or through household items. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in preschool children. nine0003
Quite often, the pathological process begins with symptoms of nasopharyngitis, and then vomiting, rash, and headache follow. The rash of meningitis on the first day of illness is very similar to the rash of measles.
Watch a video about the symptoms of meningitis:
Why does this symptom appear and where is it localized?
The causative agent of meningitis produces a toxic substance . It is a poison to the vascular system. The formation of a non-inflammatory rash is associated with the effect of toxins on the blood vessels. nine0003
Their walls become extremely permeable. Rashes often form with generalized forms of meningitis immediately after infection.
With meningitis, the rash always forms on the lower and upper limbs, as well as on the sides of the patient.
What does it look like?
In bacterial meningitis, the rash is most often located on the sides and lower extremities of the child. The shape of the rash is irregular, the color can be from red to dark brown, almost purple.
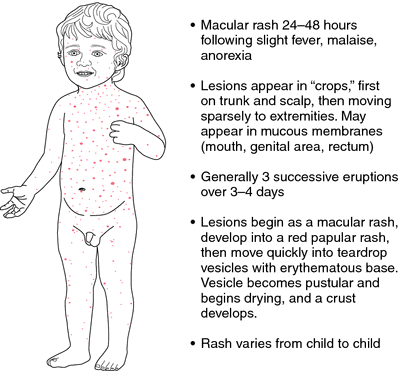
When touched, does not rise above the skin. Especially dangerous is the appearance of rashes on the head. In order to make sure that the rash is caused by meningitis, you should press on it and hold it. If she does not turn pale, urgent medical attention should be sought. nine0003
- As the disease progresses, sepsis may develop.
- The shape is more like "asterisks". With viral meningitis, the rash appears in rare cases, it is not as bright as with a bacterial infection, it can be located on any part of the body, and even on the mucous membranes. It does not have a specific form.
The meningitis rash does not itch, itch, or cause particular discomfort to the child, and cannot be contracted by contact. However, it is important to remember that it is not the rashes themselves that are contagious, but the infection that causes them . Therefore, precautions should be taken when examining a child.
Meningitis is highly contagious and many forms are transmitted by both airborne droplets and contact.
Expert's opinion
Zemlyanukhina Tatyana Vyacheslavovna
Paramedic for emergency and emergency care at Clinical Emergency Hospital #7, Volgograd.
Ask an expert
The disease begins with a small herpetic rash quickly acquiring a large stellate hemorrhagic form, which most often manifests itself together with hemorrhages in the mucous membrane of the eyes as a result of vascular damage. This symptom may last from two hours to two weeks. nine0003
Photo
You can see what the meningitis rash looks like in these photos:
Do they itch?
The peculiarity of this rash is that it does not itch or hurt . It is these symptoms that should alert the patient, because with allergies, for example, rashes itch and hurt very much. With meningitis at the initial stage, the rash is small in size.
IMPORTANT : These are small red spots that look like fresh bruises.
But over time, they increase in size, merge and spread over a large area of the body. nine0003
How to distinguish a dangerous sign from similar ones?
It is important to remember that not only meningitis is manifested by a skin rash . You need to know how to distinguish a dangerous hemorrhagic rash with meningitis, from rashes with allergies, chickenpox, rubella and others. Common childhood diseases that may cause rashes:
- Chicken pox.
- Measles.
- Mononucleosis.
- Various allergies.
- Rubella.
- Scarlet fever. nine0016
- Pyoderma.
- The meningeal rash differs from the chickenpox rash in that it is blistering in smallpox and covers the entire body of the child. It is localized without any pattern, and at first it is small red spots that form papules, and then vesicles containing a clear liquid. After the vesicles burst, crusts form.
In meningitis, the rash is localized in certain parts of the body, has a dark red color, does not have bubbles.
With smallpox, the rash is itchy and itchy, but not with meningitis. nine0003
- A distinctive feature of the measles rash is a rapid transition from red or purple to dark, almost black. Forms papules, which is not typical for meningeal. With measles, the rash is on the face. With meningitis, a rash on the face is very rare.
- In mononucleosis rash there is no itching and irritation, as in meningeal, but mononucleosis rashes turn pale when pressed. The spots are reddish in color and clusters can be located on any part of the body. nine0016
- An allergic rash, as a rule, does not cause a general infectious syndrome in a patient. Infectious rash, on the contrary, is accompanied by fever, weakness, headache. The main difference between an allergic rash and a meningitis rash is itching.
- In children, rubella spots do not merge into a single whole, and the rash appears some time after the onset of the disease. With meningitis, a rash is one of the first symptoms.
Rubella is accompanied by a runny nose, sore throat, and other symptoms that are not characteristic of meningitis. nine0016
- Scarlet fever is caused by streptococci, they can also be the cause of meningitis, but in scarlet fever the rash is accompanied by slight itching, and is often localized in the groin or armpits. The rash is punctate and can cover any skin folds, face, thighs. The meningitis rash does not itch, and looks more like asterisks.
- With pyoderma, the formations spread throughout the body, in the form of vesicles with pus, then they dry up and turn yellow.
First Aid
Since a hemorrhagic rash occurs when blood capillaries break, the first thing to do when it is detected is to limit the child's mobility, and observe bed rest until the doctor arrives. nine0003
Important! If a rash and meningitis-like symptoms appear, immediately call an ambulance and take the patient to a hospital.
Only a doctor, after a general examination and examination of the tests, can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Meningitis is not only a severe disease for the patient himself, but also dangerous for others .
Treatment
If rash manifestations lead to the development of a hyperthermic state, severe pain, then urgent hospitalization and medical assistance are required. If no adequate action is taken in the near future, the consequences can be very sad. nine0003
In the treatment of meningeal infection, antibiotic therapy is prescribed. Using antibiotics, it is possible to stop the pathogenic microflora that led to the development of the disease. The patient after hospitalization is placed in the inpatient department of the hospital. Further, his treatment is reduced to the following :
- The doctor prescribes bed rest with a sparing diet to the patient.
- Antibacterial preparations. Prescribe drugs with low, medium and high permeability. The most effective include: Amoxicillin, Cefuroxime, Ketoconazole, Clindamycin. The dosage is determined individually.
But the duration of therapy should not be longer than 7-10 days, as addiction occurs. nine0016
- In addition to antibiotic therapy, antiviral drugs are prescribed.
- The combination of desensitizing therapy with anti-inflammatory therapy will alleviate the patient's condition, stop unpleasant symptoms.
The therapeutic course for any age category will be at least 10 days. If there are complicated forms, then the duration of treatment may increase. As soon as the patient is discharged from the hospital, he should prepare for long-term home treatment. For some patients with meningococcal pathology, recovery takes 1 year. Read more about emergency care and nursing care for meningitis in this article. nine0003
Meningitis vaccination available . It can prevent the development of this dangerous disease. Vaccination is required in places where a regular outbreak of the disease occurs.
TIP : When a skin rash is accompanied by high fever and severe headache, go to the hospital as soon as possible.
Such a state means that the account of life goes to the clock.
Are hemorrhagic rashes dangerous in this disease?
Complicated variants of the course of the pathological process are often diagnosed. Inflammation that occurs in the meninges almost always goes away. But if the treatment was started at the wrong time or the disease proceeds in a severe form, then this is fraught with the following complications :
- mental retardation of the child;
- mental impairment;
- development of a paretic, paralyzed condition;
- blindness or strabismus;
- hearing loss; nine0016
- the patient becomes asthenic, lethargic, his memory decreases and attention is absent.
If you suddenly find such a rash against the background of a high temperature, especially if new elements of the rash appear one by one in a matter of minutes, URGENTLY call an ambulance. Infectious disease specialist Nekrasova E.
S. 21st city polyclinic, Minsk.
Meningitis is a rather dangerous disease. When an infectious process damages the brain, the work of many systems throughout the human body is disrupted. If treatment is not started in time, the consequences can be extremely unfavorable. The most dangerous complication remains the death of the patient. nine0003
Bibliography
- Pokrovsky V.I., Favorova L.A., Kostyukova N.N. Meningococcal infection.-M.: Medicine, 1976: 272p.
- Vengerov Yu.Ya., Nagibina M.V., Molotilova T.P., Chentsov V.B. et al. // Clinical and pathogenetic significance of lactic acidosis in purulent meningitis "(I National Conference with international participation on neuroinfection - Moscow- 2007: 13 - 15.
- Koroleva I.S., Beloshitsky. G.V., Spirikina L.V., et al. // Actual problems of meningococcal infection and purulent bacterial meningitis. – Epidemiology and vaccination. – 2009; 1:5-8.
- Harisson L.H., Trotter C.L.