Does pregnancy affect milk supply
How will my milk change when I am breastfeeding through pregnancy? • KellyMom.com
- Milk supply during pregnancy
- Changes in milk composition
- Will I produce colostrum?
- Colostrum and stool changes in the older nursling
- Milk changes after birth
- Will I have enough milk for two?
Milk supply during pregnancy
Most mothers who are nursing through pregnancy notice a decrease in milk supply by mid-pregnancy, but sometimes as early as the first month. During pregnancy, the mature milk is also making a gradual change to the colostrum which is present at birth. Supply may increase toward the end of pregnancy as colostrum production kicks in.
Why does milk production usually decrease during pregnancy? Progesterone levels gradually rise during pregnancy. One theory for the cause of decreased milk supply during pregnancy (Flower 2003) is that the progesterone makes the alveoli permeable, or “leaky,” so they can’t store milk well. At birth (the delivery of the placenta) progesterone levels drop dramatically, allowing prolactin to take over. Prolactin makes the alveoli impermeable, thus setting the stage for the return of copious milk production.
.
The production of breastmilk depends upon adequate emptying of the breasts, but the supply and demand regulation of milk supply does not usually hold up when faced with the hormonal changes of pregnancy. The decrease in milk production usually occurs despite continued or increased nursing frequency, although a minority of pregnant mothers do not experience a decrease in milk supply. Obviously if your child does decrease demand, that will further decrease supply.
When your milk supply begins to decrease, your nursling may respond by increasing or decreasing nursing frequency. Your child will most likely make up for decreased milk intake by eating more solids (indeed, increased solid food intake is one way that pregnant moms might track a decrease in milk supply). You can go ahead and encourage increased solid foods – just keep in mind that if your baby is under a year, milk should be his/her primary source of nutrition. As long as your baby is gaining weight adequately and nursing at least 3-4 times a day, he/she is unlikely to need an additional source of milk (see Is my older baby getting enough milk?).
You can go ahead and encourage increased solid foods – just keep in mind that if your baby is under a year, milk should be his/her primary source of nutrition. As long as your baby is gaining weight adequately and nursing at least 3-4 times a day, he/she is unlikely to need an additional source of milk (see Is my older baby getting enough milk?).
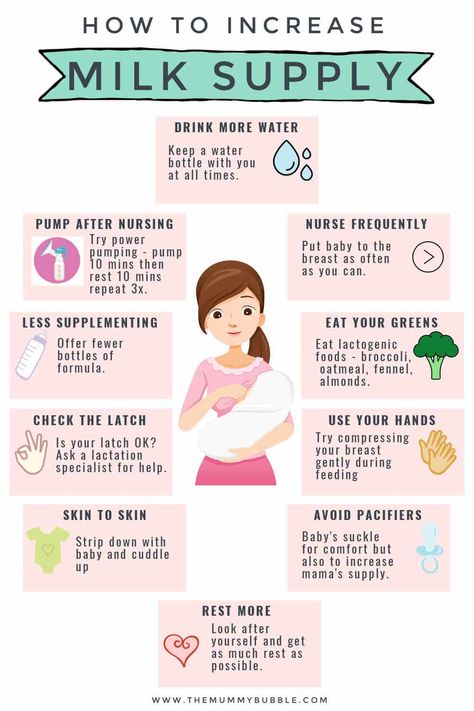
Many moms claim that eating oatmeal once a day helps their milk supply. There are also a number of herbs that can help to increase milk supply, but experts are generally not in agreement when it comes to safe use during pregnancy.
Changes in milk composition
One study compared changes in the milk of two lactating pregnant mothers through the first two months of pregnancy to daily changes in the milk of two women who were gradually weaning (Prosser, Saint & Hartmann 1984). Milk composition and volume changes during pregnancy were similar to those during gradual weaning, but the changes during pregnancy occurred despite continued or increased nursing, rather than in response to a decrease in nursing frequency.
| ||||||||||
The changes that accompany the decrease in milk supply would be expected to affect the taste of the milk, and indeed some nursing toddlers mention the change in taste to mom. Once the milk is mostly/fully colostrum, the taste may change again. Some nurslings don’t like the taste change (particularly when combined with the concurrent reduction in milk supply) and may wean as a result. Some love it. Others either don’t seem to notice the change, continue nursing despite the change, or simply don’t mind.
Once the milk is mostly/fully colostrum, the taste may change again. Some nurslings don’t like the taste change (particularly when combined with the concurrent reduction in milk supply) and may wean as a result. Some love it. Others either don’t seem to notice the change, continue nursing despite the change, or simply don’t mind.
Will I produce colostrum?
Yes. The changeover between mature milk and colostrum production begins, on average, between the 4th and 8th month of pregnancy, but some mothers start producing colostrum somewhat earlier than that. Many mothers who nurse through pregnancy have noted that their milk contains mostly colostrum during the last month before baby is born. You will continue to produce colostrum throughout the latter part of your pregnancy – your older nursling cannot “use it up.”
Colostrum and stool changes in the older nursling
If your older nursling is getting a good quantity of colostrum (either before or after birth), the natural laxative effect of the colostrum may cause him/her to have looser and more frequent stools. The stools should return to normal once your colostrum is completely replaced with mature milk.
The stools should return to normal once your colostrum is completely replaced with mature milk.
Milk changes after birth
At birth, the sudden decrease in progesterone and estrogen levels (and resulting surge in prolactin levels) that occurs with the birth of the placenta causes colostrum production to kick into high gear and signals your milk to “come in.” Once your baby is born, the amount of time you produce colostrum is limited, since your mature milk will begin to come in within a few days.
See also: Does my newborn always need to nurse first?
Will I have enough milk for two?
Both research and anecdotal evidence assure us that a mother breastfeeding two or more children (whether nursing siblings, twins, or more) has the capability to produce large amounts of milk (see Saint, Maggiore & Hartmann 1986). In one study a tandem nursing mother produced a double supply of milk for the entire 7 months that her older child nursed alongside the newborn (see Prosser 1984). As with any nursing relationship, factors like breast reduction surgery or adoption can affect the amount of milk produced, but the only supply concern generally reported by tandem nursing mothers is oversupply, rather than undersupply. See Got Milk? for more information on maintaining and increasing milk supply.
As with any nursing relationship, factors like breast reduction surgery or adoption can affect the amount of milk produced, but the only supply concern generally reported by tandem nursing mothers is oversupply, rather than undersupply. See Got Milk? for more information on maintaining and increasing milk supply.
Breastfeeding During Pregnancy and Tandem Nursing • KellyMom.com
PDF version (great for printing)
By Hilary Flower, author of
Adventures in Tandem Nursing: Breastfeeding During Pregnancy and Beyond, published by La Leche League International in July 2003
You have probably heard most of these common statements circulating about breastfeeding during pregnancy and tandem nursing. I set out to test their veracity, and was surprised by what I found! Test the currency of your own knowledge: which statements are myth, fact, or simply unknown?
.
1. “At 24 weeks gestation, the uterus changes in such a way that breastfeeding goes from being safe to risky.
 ” …MYTH or FACT?
” …MYTH or FACT?Myth. Oxytocin is a hormone released during breastfeeding that causes uterine contractions, usually too mild to notice. This fact has raised concern that breastfeeding could contribute to preterm labor in an otherwise healthy pregnancy. The uterus starts out pregnancy fairly insensitive to oxytocin, and somehow the rumor got started that it increases in sensitivity in mid-pregnancy. Research does not support this. Instead, the first marked increase occurs after the 37th week—with little or nothing happening before that time.
2. “When you are breastfeeding during pregnancy, your body gives first to the fetus, then to the nursling, and then what’s left over goes to your own daily needs and reserves.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. If your body fat is already perilously low, you will want to note that malnourished women yield some body fat to contribute to fetal weight gain. But we have no research to tell us whether the fetus or nursling gets priority in times of shortage. More importantly, we have no reason to believe that anyone needs to come up short unless the mother is malnourished. Follow your appetite, eat enough calories of a basic mixed diet, and gain weight within the same parameters as if you weren’t breastfeeding, and your body will do the rest.
More importantly, we have no reason to believe that anyone needs to come up short unless the mother is malnourished. Follow your appetite, eat enough calories of a basic mixed diet, and gain weight within the same parameters as if you weren’t breastfeeding, and your body will do the rest.
3. “The newborn always needs to nurse first.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. Your newborn may need “first dibs” on colostrum since it is in limited supply in the first day or two. The sensation of your milk “coming in” indicates that your supply has exceeded your children’s demand; you can now count on plenty for both nurslings. Indeed, if you experience engorgement or an overly strong milk flow, your newborn may have an easier time if you nurse your toddler first!
4. “Most mothers experience a significant drop in milk supply during pregnancy.” …MYTH or FACT?
Fact. 70% of mothers notice a significant drop in supply during pregnancy. Still, a minority of mothers continue to produce an abundance of milk throughout pregnancy.
5. “Tandem nursing mothers can make a double supply of milk—just like mothers nursing twins.” …MYTH or FACT?
Fact. In one study a tandem nursing mother made a double supply of milk for the entire seven months that she tandem nursed (and her newborn was well above average in growth!). The only supply concern generally reported by tandem nursing mothers is oversupply.
6. “A majority of children self-wean during their mothers’ pregnancies.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. It is true that a majority of children do wean during their mothers’ pregnancies; the question is: who’s idea is it? In one study of La Leche League mothers breastfeeding during pregnancy, 26% of children self-weaned, 28% of the mothers led weaning, and the other 46% went on to tandem nurse.
7. “If you enjoy nursing your child before pregnancy, there’s no reason to believe that pregnancy would change that.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. It’s important to note that pregnancy does tend to change “breastfeeding as usual” for many mothers. Some mothers find that nursing during pregnancy causes pain, agitation, or nausea, and such problems can affect their feelings about continuing. (Similarly some toddlers don’t like the changes in flavor and supply of milk.)
Some mothers find that nursing during pregnancy causes pain, agitation, or nausea, and such problems can affect their feelings about continuing. (Similarly some toddlers don’t like the changes in flavor and supply of milk.)
8. “Tandem nursing will ensure a smooth sibling adjustment for your older child.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. Your older child may experience a range of emotions, from fear of displacement–to anger at you–to delight in the new baby. And remember that sibling relationships tend to have their own rhythms of bonding and fighting, and both can happen at your breast! Realistic expectations, lots of mama love, open communication and a sense of humor will help you move through any challenges that arise.
9. “Breastfeeding reduces morning sickness.” …MYTH or FACT?
Unknown! This appears to be true for many mothers (myself included) but only a scientific study could tell us whether statistics will bear this out or not. On the other hand, some unlucky moms do experience isolated bouts of nausea specifically during breastfeeding sessions.
10. “Tandem nursing mothers are martyrs.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. It is true that nursing two children is a big commitment. On the other hand, weaning a reluctant child is no easy task either, particularly if you are pregnant or caring for a new baby. Each mother must choose the option she is most prepared to follow through on.
BONUS QUESTION: “Tandem nursing is rare.” …MYTH or FACT?
Myth. Many mothers are careful about whom they tell, but this invisibility masks a common practice. In one study of 179 mothers who had breastfed at least one child for at least six months, 61% had breastfed during pregnancy, and 35% had tandem nursed.
For more information, see Nursing During Pregnancy and Tandem Nursing: The Official FAQ or read a chapter from Adventures in Tandem Nursing.
REFERENCES
- Flower, 2003, pp. 223-230; Kimura T, et al. Expression of oxytocin receptor in human pregnant myometrium. Endocrinology 1996; 137:780-85.
- Flower, 2003, pp.
 248-49; Hamosh M, Dewey KG, Garza C, et al: Nutrition During Lactation. Institute of Medicine, Washington, DC, National Academy Press, 1991.
248-49; Hamosh M, Dewey KG, Garza C, et al: Nutrition During Lactation. Institute of Medicine, Washington, DC, National Academy Press, 1991. - Flower, 2003, pp. 76-78.
- Moscone [sic] SR, Moore MJ. Breastfeeding during pregnancy. J Hum Lact. 1993 Jun;9(2):83-88.
- Flower, 2003, pp. 233-234; Prosser CG, Saint L, Hartmann PE. Mammary gland function during gradual weaning and early gestation in women. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1984 Apr;62 (Pt 2):215-28.
- Flower, 2003, pp. 166; Moscone [sic] IBID.
- Flower, 2003, pp. 39-66.; Moscone [sic] IBID;
- Flower, 2003, pp. 192-199.
- Flower, 2003, 263-64.
- Flower, 2003, pp. 8-10.
- Flower, 2003, p.16; Kendall-Tackett, K. Unpublished Data.
New pregnancy while breastfeeding - what to do?
Number of views: 135 383
You are pregnant while breastfeeding. You are faced with a difficult choice: you do not plan to terminate the pregnancy, and the first-born is still too small to wean him from the breast. How to be? Is it possible to breastfeed during pregnancy? What is it fraught with?
How to be? Is it possible to breastfeed during pregnancy? What is it fraught with?
Breastfeeding pregnancy - heart of the matter
Even 300 years ago there was no question of stopping breastfeeding during pregnancy. The woman had no choice - a small child needs food, and there were practically no alternatives to mother's milk.
Today, a pregnant woman can receive a categorical recommendation from doctors as a matter of urgency to wean the firstborn from the breast. Yes, sometimes the completion of breastfeeding is dictated by the interests of pregnancy . But more often than not, it's overkill. Unless there is a clear medical indication, whether or not to feed during pregnancy, and if so, for how long – decision of parents , not doctors and relatives.
The medical side of the issue
Very cautious The decision to continue breastfeeding during pregnancy is worthwhile for women who have experienced preterm labor, recurrent spontaneous miscarriages, or are currently at risk of preterm labor .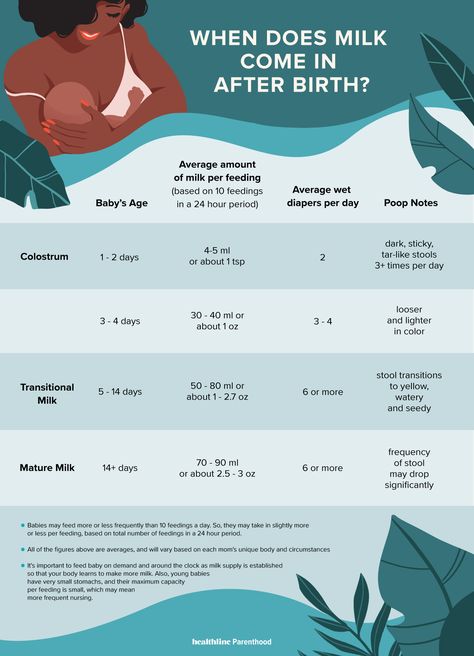 Here it is important to carefully weigh all the pros and cons, listen to the opinion of your doctor.
Here it is important to carefully weigh all the pros and cons, listen to the opinion of your doctor.
Physicians recommending interruption of breastfeeding are afraid that the onset of pregnancy during breastfeeding may end in miscarriage or the fetus will not grow and develop harmoniously.
The reason doctors fear miscarriage or premature delivery is the effect of oxytocin on the uterus. Hormone oxytocin causes milk flushes and uterine contractions . That is, theoretically, each time breastfeeding, a woman can provoke uterine contractions, which will lead to a miscarriage. But in practice, things don't quite work out that way.
Yes, frequent nipple stimulation can trigger labor pains in a full-term woman. And putting the newborn to the chest allows the uterus to contract after childbirth and return to its previous state.
But nature is wise and in most cases breastfeeding does not harm women with normal pregnancies. Once again, we note that we are talking about the norm !
Once again, we note that we are talking about the norm !
The state of the uterus at the beginning of pregnancy is different from the state "before delivery or immediately after". She has low ability to absorb oxytocin. Between the 1st and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy, the number of oxytocin receptors increases 12-fold. The low ability of the uterus to absorb oxytocin at the beginning of pregnancy suggests that 90,005 HBs will not cause 90,006 effective contractions.
One of the reasons recently given by doctors who advocate stopping breastfeeding during pregnancy was the impossibility of prescribing medications . Now the list of drugs allowed for hepatitis B has expanded significantly. Women have the opportunity to receive medical care in the required volume.
Nutrition of the expectant mother
Will the body of a nursing mother be able to provide fetus with all the substances necessary for harmonious development? Good and balanced a feeding woman will have no problem meeting the needs of her baby and unborn child. Of course, she needs a nutritious diet , as well as vitamins that the doctor will prescribe. The problem will arise in case of a lack of nutrients. The deficit will be satisfied at the expense of the resources of the mother's body. The kids will get theirs, but the woman may be emaciated.
Of course, she needs a nutritious diet , as well as vitamins that the doctor will prescribe. The problem will arise in case of a lack of nutrients. The deficit will be satisfied at the expense of the resources of the mother's body. The kids will get theirs, but the woman may be emaciated.
Difficulties to be encountered
The peculiarities of breastfeeding during a new pregnancy are as follows:
- 's nipples become very sensitive. A woman may feel unexpected attacks of pain in the nipples or breasts, they are provoked by hormonal changes in the body. You can solve the issue with lanolin . Due to its viscosity, it blocks the nerve endings on the nipple and reduces sensitivity . Lanolin can be applied a few minutes before feeding in a thin layer.
- Increased fatigue level . In the first trimester, women often feel increased drowsiness , and an actively crawling toddler will not let you relax.
 Mom's fatigue is associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy, and not with breastfeeding. The condition will improve as the pregnancy progresses.
Mom's fatigue is associated with hormonal changes during pregnancy, and not with breastfeeding. The condition will improve as the pregnancy progresses. - Becomes less milk . 7 out of 10 mothers confirm that the volume of breast milk is reduced during subsequent pregnancies.
- Breast milk changes taste . Sometimes the firstborn refuses the breast on his own, because the milk has changed. The onset of pregnancy during breastfeeding leads to hormonal changes in the body. As a result, the amount of lactose in milk is reduced, but the amount of sodium increases. The taste of milk changes.
- A woman may feel uterine contractions while breastfeeding. Most often, they do not pose any threat to the mother or fetus. But at Feeling sore Need to see a doctor immediately !
- In the late term, due to the large belly, it is difficult to find a comfortable position for feeding .
 Sometimes it is difficult for the baby to reach the mother's breast. Here you need to experiment, a suitable option is sure to be found.
Sometimes it is difficult for the baby to reach the mother's breast. Here you need to experiment, a suitable option is sure to be found.
Arguments "for"
Breastfeeding for a child is not only food , but also contact with mother , comfort. There are situations (illness, stress) when the baby is is better left on GV . The ability to suck on his mother's breast has a beneficial effect on his emotional and physical condition. If mommy can organize the feeding of the eldest without harming herself and the unborn baby, this will be the best way out.
Pregnancy while breastfeeding means very little difference between babies. Jealousy and competition for mother's attention are inevitable here. Many women find that tandem feeding helps them cope with the jealousy of an elder and problems with childcare with a slight age difference. An article about tandem feeding will soon appear in the online magazine MamExpert.
Comment of a tandem-feeding mother
One of the mothers of the MamExpert community shared her own experience with us. We gratefully publish her opinion:
“I breastfed during pregnancy and in tandem for over a year. And all this period I had to listen to scoldings, starting from the gynecologist in the LCD consultation and up to the head of the department of the 2nd maternity hospital (from her after the birth). Moreover, in the period from 36 weeks until delivery (41.1), the doctors were glad that I was breastfeeding, hoping that this would stimulate labor early, since the fetus was large. The first contraction really came during feeding, but already at 41.1. The boy was born 57 cm 4375 gr. Then even the dermatologist tried to stick his nose into my breastfeeding. And about pediatricians who strictly say that after a year there is nothing to feed children with breast milk, I generally keep quiet. This is a personal matter for everyone, and sticking your nose into someone else's GV is at least not competent! Only one doctor in the ambulance could explain to me why our doctors demand so much to stop breastfeeding early: to make it easier to treat mothers if they get sick.
If someone would give me some more intelligible argument against breastfeeding after a year, and this applies to both state institutions and adult and pediatric medicine, as well as paid centers.
Both young and experienced mothers have many questions about breastfeeding. Each baby is individual and with him parents can get into a situation that did not arise with older children! MamExpert courses will help you not to succumb to difficulties and find a solution to any issue.
Come to our breastfeeding course! Here you will gain knowledge that will give you a real understanding of what breastfeeding is. You will understand what to do if something goes wrong. Gain self-confidence and be able to enjoy breastfeeding.⠀
Course speaker
-
Inna Shabelnikova - certified lactation consultant, leading lecturer MamExpert and mother of three children - Every day I come across mothers who have been told that they are "not dairy", that their milk is not nutritious enough for the baby and much more .
 . . utter. These are all myths! The limits are only in your head! You will be able to feed, enjoy it and give the child all the best!
. . utter. These are all myths! The limits are only in your head! You will be able to feed, enjoy it and give the child all the best!
Would you like to take a course? Sign up here: https://www.mamexpert.by/ochnye-kursy/ or call +375 44 553 20 50!
Pregnancy while breastfeeding is not uncommon. In a similar situation, according to studies, are up to 40% of women. When deciding whether to feed or not, it is important to take into account the state of oneself and the baby, feelings, relationships in the family. In most cases, this is not a medical issue, but a parental decision.
Author of the article: Daria Sovina
comments powered by HyperComments
Breastfeeding during pregnancy
and in breast milk. And often in such a situation it is possible to hear from a gynecologist that the child needs to be weaned urgently, because stimulation of the nipples can lead to neither more nor less, but to termination of pregnancy (receptors in the uterus will perceive breast sucking as a signal to contract the walls, which can provoke premature birth). Is it so? Let's figure it out.
Is it so? Let's figure it out.
Why do doctors insist on stopping lactation during pregnancy?
In fact, if your doctor recommends that you stop breastfeeding, it is important to understand the reason for the request. If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy due to, say, the tone of the uterus, then TERMINATION OF BREASTFEEDING WILL NOT SOLVE THIS PROBLEM. This will require a comprehensive solution to the problem, perhaps even hospitalization.
If we talk about the reaction of the uterus to oxytocin released during feeding, then it is very small until the last weeks of pregnancy, since the fetus has not yet matured and the time for childbirth has not yet come, and the number of receptors in the uterus that are sensitive to oxytocin is still very small. If the mother retains breastfeeding until the last days, then RECEPTORS IN THE UTERUS DO NOT REACT THIS WAY TO IRRITATION OF THE NIPPLES , since this process continues in the background throughout the pregnancy, that is, it does not represent anything different from the usual state.
When all indicators of mother's health are normal, then THERE IS NO REASON TO STOP NATURAL FEEDING. Mom does not have new responsibilities for caring for a child who is learning to fall asleep without a breast, and the hormonal background does not change. Everything remains the same, which, of course, has a beneficial effect on the well-being of a pregnant woman.
What are the difficulties you may face while breastfeeding during pregnancy?
Nipple sensitivity . This is a fairly common problem and should be taken into account. First of all, you will have to reduce the time of breast sucking and the frequency of attachments. For this child, you can distract with conversations, and it is also recommended to water him more so that the baby does not seek to quench his thirst with breast milk.
Decreased milk supply towards the middle of pregnancy. During this period, lactation is greatly reduced, and for some mothers, milk may even disappear for several days or even weeks. This period can be used for gentle weaning, or you can keep the attachment, thus maintaining contact with the baby. By the third trimester, colostrum most often already appears.
This period can be used for gentle weaning, or you can keep the attachment, thus maintaining contact with the baby. By the third trimester, colostrum most often already appears.
What should mothers pay attention to when breastfeeding during pregnancy?
Complete nutrition. A pregnant and breastfeeding woman simply needs to get a varied diet, complex supplements and vitamins will also be useful. It is important to remember that the body distributes nutrients first to the growing fetus, then to milk, and the rest to the mother herself. The double load - pregnancy and breastfeeding - should be fully compensated by adequate nutrition, rich in all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
More rest. It is important for a future mother to understand that she receives an increased load on her body, comparable to carrying twins, so timely and proper rest is vital for her! Looking for helpers and asking for help from loved ones in such a situation is not a whim, but a necessity.
Carrying on hands. It is impossible to refuse to carry the older child in her arms when a new pregnancy appears, especially if at the time of its onset the baby is less than a year old. The first child also needs mother's warmth and her hugs, just like the second, especially since babies often fall asleep in their arms with their breasts.
Mom's body usually copes with a gradually growing load, because it does not occur overnight. To make it easier for yourself to carry a baby in your arms, you can use the help of physiological carriers - slings, which can be worn so that there is no pressure on the stomach. For example, in a sling with rings it will be very convenient to rock the baby to sleep or wear it on the hip when he needs his mother's arms.
When making a decision to continue or stop breastfeeding during pregnancy, it is important to weigh the pros and cons well, and it is also especially important to understand that the older child is no different from the younger in anything, except for age, so it is worth doing everything possible so that both children were able to get everything they needed.