Chlamydia women pictures
Herpes, Genital Warts, Gonorrhea, STD Symptoms, & Testing
Medically Reviewed by Traci C. Johnson, MD on August 16, 2021
You don't have to have sex to get an STD. Skin-to-skin contact is enough to spread HPV, the virus family that causes genital warts. Some types cause warts and are usually harmless, but others may lead to cervical or anal cancer. Vaccines can protect against some of the most dangerous types.
Signs: Pink or flesh-colored warts that are raised, flat, or shaped like cauliflower. Often there are no symptoms.
"Crabs" is the common term for lice that set up shop in pubic hair. The term comes from the shape of the tiny parasites, which look very different from head or body lice. The creatures crawl from one person to another during close contact. Pubic lice can be killed with over-the-counter lotions.
Symptoms: Intense itching, tiny eggs attached to pubic hair, or crawling lice.
Scabies is an itchy infestation caused by a tiny mite that burrows into human skin to lay eggs. It is not always an STD, as it can spread through any skin-to-skin contact. But among young adults, the mites are often acquired during sex. Scabies is treated with prescription creams.
Symptoms: Intense itching especially at night and a pimple-like rash. It may take 2-6 weeks for symptoms to appear.
Gonorrhea spreads easily and can lead to infertility in both men and women, if untreated. Antibiotics stop the infection.
Symptoms: Common symptoms are burning during urination and discharge, but often there are no early symptoms. Later, the infection may cause skin rashes or spread to the joints and blood.
In Men: Discharge from the penis, swollen testicles.
In Women: Vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, spotting. Symptoms may be mild and are easily confused with a urinary tract or vaginal infection.
Most people don't notice the early symptoms of syphilis. Without treatment, it can lead to paralysis, blindness, and death. Syphilis can be cured with antibiotics.
Signs and Symptoms: The first sign is usually a firm, round, painless sore on the genitals or anus. The disease spreads through direct contact with this sore. Later there may be a rash on the soles, palms, or other parts of the body (seen here), as well as swollen glands, fever, hair loss, or fatigue. In the late stage, symptoms come from damage to organs such as the heart, brain, liver, nerves, and eyes.
Chlamydia is a common STD that can lead to infertility if left untreated. It clears up quickly with antibiotics. But it often goes unnoticed because symptoms are vague or absent. Chlamydia can also infect the rectum and throat.
Symptoms in Men: Burning and itching at the tip of the penis, discharge, painful urination.
Symptoms in Women: Vaginal itching, discharge that may have an odor, pain during sex, painful urination.
That painful cold sore you get on your lip every now and then? It's probably caused by a type of herpes virus called HSV-1. This virus is usually not an STD; it spreads easily among household members or through kissing. But it can be spread to the genitals through oral or genital contact with an infected person. Though there is no cure, drugs can shorten or prevent outbreaks.
This virus is usually not an STD; it spreads easily among household members or through kissing. But it can be spread to the genitals through oral or genital contact with an infected person. Though there is no cure, drugs can shorten or prevent outbreaks.
Signs and Symptoms: Occasional cold sores or "fever blisters" on the lips. Small blister or sores on the genitals are also possible.
Most cases of genital herpes are caused by a virus called HSV-2. It's highly contagious and can spread through intercourse or direct contact with a herpes sore. As with HSV-1, there is no cure. But antiviral drugs can make outbreaks less frequent and help clear up symptoms more quickly.
Symptoms: Fluid-filled blisters that form painful, crusted sores on the genitals, anus, thighs, or buttocks. Can spread to the lips through oral contact.
Hepatitis B is a stealthy virus that can cause severe liver damage. It spreads through contact with blood and other body fluids. People can be infected through sex, needle sharing, and at birth, as well as by sharing razors and toothbrushes. There is no cure, but drugs can keep the virus in check. There's also an effective vaccine to prevent hepatitis B.
People can be infected through sex, needle sharing, and at birth, as well as by sharing razors and toothbrushes. There is no cure, but drugs can keep the virus in check. There's also an effective vaccine to prevent hepatitis B.
Symptoms: People may develop nausea, belly pain, dark urine, fatigue, and a yellowing of the skin or eyes with acute infection. Chronic infection can lead to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. Many people have no symptoms for years.
The HIV virus weakens the body's defense against infections. HIV spreads through unprotected sex, needle sharing, or being born to an infected mother. It may cause no symptoms for years, so a blood test is the best way to learn your status. Timely treatment is important to help prevent serious illnesses.
Early symptoms of HIV Infection: Many have no symptoms, but some people get temporary flu-like symptoms one to two months after infection: swollen glands (seen here), a fever, headaches, and fatigue. Canker sores in the mouth can occur, too.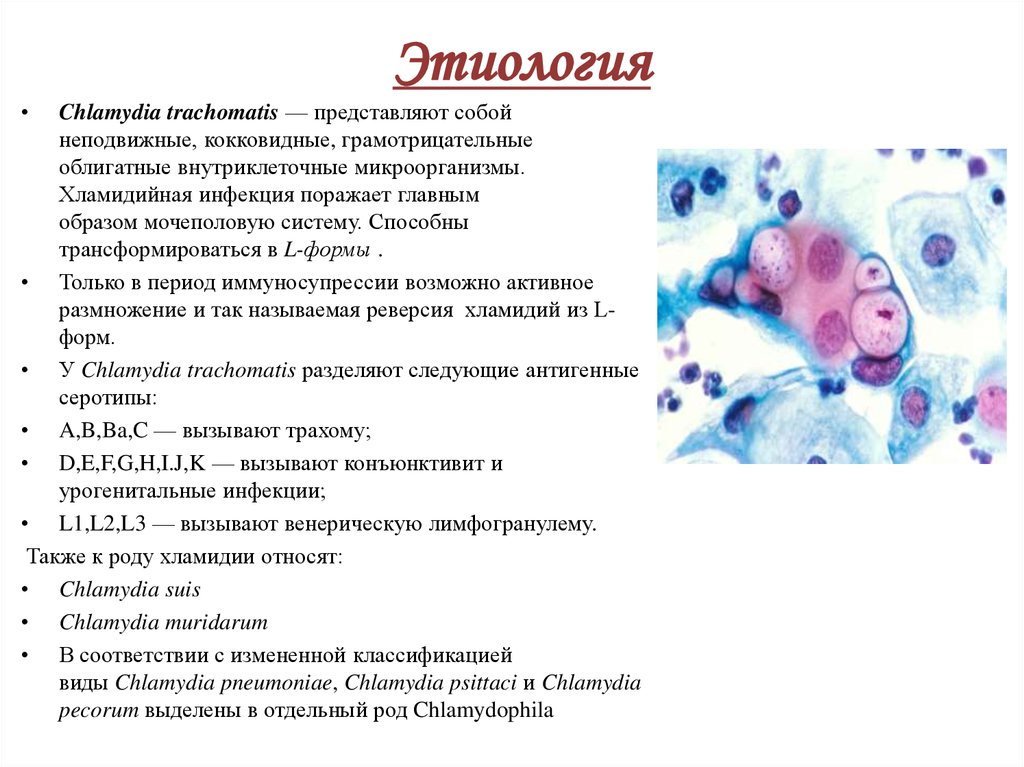
Reliable HIV tests can be done in a clinic or at home with the FDA-approved Home Access brand test kit. Anonymous tests use only a number to identify you. One limitation is the "window period" of up to six months after exposure to HIV when these antibody tests sometimes do not find the virus. You can pass HIV to others during that time.
If You Suspect HIV/AIDS: If you've been exposed to HIV, starting medications immediately can help prevent infection. If you have the virus, treatments can help prevent HIV from turning into AIDS.
While there is no cure for HIV, there are medications that can suppress the amount of virus multiplying inside the body. People take a combination of antiviral drugs in hopes of preventing the infection from advancing to AIDS. Additional treatments can help prevent or fight off serious infections, if the immune system has weakened.
Trichomoniasis is caused by a parasite that spreads during sexual contact. It can be cured with prescription drugs.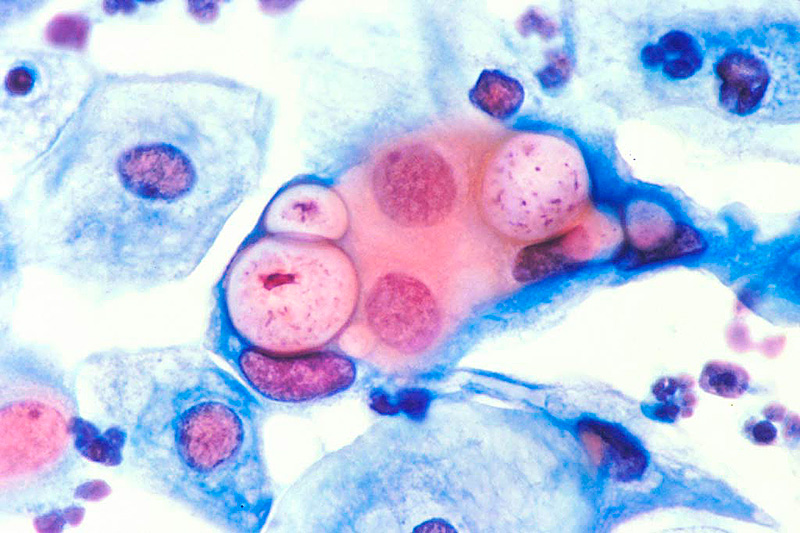
Signs and Symptoms in Men: Most men have no obvious symptoms. Some develop a mild discharge or slight burning during urination.
Signs and Symptoms in Women: Women may develop a yellow-green discharge with a strong odor, vaginal itching, or pain during sex or urination. Symptoms usually begin five to 28 days after acquiring the parasite.
Chancroid is a bacterial STD that is common in Africa and Asia but rare in the U.S. It causes genital sores that can spread the bacteria from one person to another. Antibiotics can cure the infection.
Symptoms in Men: Painful bumps on the penis that may develop into pus-filled open sores, pain in the genitals and groin.
Symptoms in Women: Painful bumps in the genital area that can develop into open sores, swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
LGV is caused by a type of chlamydia that is usually rare in the U.S. But it's becoming more common in men who have sex with men. Like other forms of chlamydia, it can be cured with antibiotics.
Symptoms: Open sores on the genitals or anus, headache, fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph glands in the groin (seen here). If acquired through anal sex, LGV may cause rectal bleeding or discharge.
Not an STD itself, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is a serious complication of untreated STDs, especially chlamydia and gonorrhea. It happens when bacteria spread to infect the uterus and other female reproductive organs. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent damage to a woman's fertility.
Signs and Symptoms: Lower abdominal pain, fever, unusual discharge, painful intercourse, painful urination, and spotting. However, there are often no warning signs.
Anyone who is sexually active is at risk for an STD, regardless of gender, race, social class, or sexual orientation. That said, teenagers and young adults acquire STDs more easily than older people. By age 25, half of sexually active adults get an STD. Having multiple sex partners also raises the risk. The CDC has noted that some STDs are on the rise in men who have sex with men, including syphilis and LGV.
The CDC has noted that some STDs are on the rise in men who have sex with men, including syphilis and LGV.
Yes, they can. Many STDs spread through any type of sexual activity, including skin-to-skin contact and oral sex. This is especially true of STDs that produce genital lesions or sores.
The best ways to avoid getting an STD are to abstain from any sexual contact and be in a monogamous, long-term relationship with an uninfected partner. To reduce the odds of getting STDs:
- Ask your partner if they have an STD.
- Ask partners to be tested before sexual activity.
- Use condoms.
- Avoid sexual activity if your partner has signs of an STD.
- Be aware of symptoms and get regular checkups with your health care provider.
While condoms are effective in preventing the spread of some STDs, they are not perfect. Condoms are better at protecting against gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, and trichomoniasis. But they offer less protection against herpes, syphilis, and genital warts. These infections can spread through contact with skin lesions that are not covered by a condom. Finally, condoms offer virtually no protection against crabs and scabies.
These infections can spread through contact with skin lesions that are not covered by a condom. Finally, condoms offer virtually no protection against crabs and scabies.
If you think you have an STD, tell your partner(s) as soon as possible. You may be able to spread the infection even if you have already begun treatment or are using condoms. With some STDs, doctors recommend treating both partners at the same time. This may be a difficult conversation. Some people find it helpful to write a script ahead of time. Be sure to let your partner ask questions and express their feelings.
It is important for pregnant women to be checked for STDs. They can cause women to go into labor too early and may complicate delivery. Many STDs can be passed from mother to baby during pregnancy, childbirth, or after the baby is born. STDs' effects on babies can include stillbirth, low birth weight, neurologic problems, blindness, liver disease, and serious infection. But there are treatments to minimize these risks. Treatment during pregnancy can cure some STDs and lower the risk of passing the infection to your baby.
Treatment during pregnancy can cure some STDs and lower the risk of passing the infection to your baby.
Most STD treatments do not protect you from getting the same infection again. A course of drugs may cure gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia or trichomoniasis, but a new exposure can start a new infection. If your partner is not treated, you can continue to pass infections back and forth. And if you're not taking the right precautions to protect yourself, you can be re-infected quickly or even pick up a second STD.
IMAGES PROVIDED BY:
1) Science Source, Dr P. Marazzi, Dr. Harout Tanielian, Biophoto Associates / Photo Researchers Inc.
2) London Scientific Films
3) Dr. P. Marazzi / Photo Researchers, Inc.
4) Juergen Berger / Photo Researchers, Interactive Medical Media LLC , Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
5) Science Source/Photo Researchers, Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
6) BSIP/Photo Researchers Inc
7) Interactive Medical Media LLC
8) Interactive Medical Media LLC, Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology, Dr. Harold Fisher/Visuals Unlimited
Harold Fisher/Visuals Unlimited
9) Eye of Science/Photo Researchers Inc
10) Dr. M.A. Ansary / Photo Researchers, Inc., Science Source, Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology
11) Bildagentur RM/Tips Italia
12) Bruce Forester/Photographer's Choice
13) IMA / Photo Researchers Inc
14) Dr. M.A. Ansary / Photo Researchers, Inc., David M. Phillips / Photo Researchers, Inc, Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas & Synopsis of Clinical Dermatolog
15) Dr. M.A. Ansary / Photo Researchers, Inc.
16) Judith Glick / Phototake
17) Clarissa Leahy/Photographer's Choice
18) Christoph Martin/Lifesize
19) George Diebold/Photographer's Choice
20) Michael Winokur/Workbook Stock
21) John Lamb/Stone
22) UHB Trust/Stone
23) Alan Powdrill/Stone
REFERENCES:
American Social Health Association.
American Social Health Association's National Herpes Resource Center.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention web site.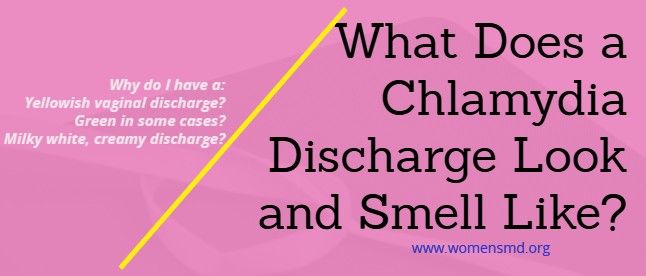
FDA web site.
Fleming, et al. The New England Journal of Medicine, Oct. 16, 1997.
March of Dimes web site.
Merck Manual, 17th edition.
National HIV Testing Resources.
National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
National Institutes of Health.
The Nemours Foundation's Kids Health web site.
U.S. Dept. of Health and Human Services.
© 2021 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. View privacy policy and trust info
Most Common STDs, Pictures and Descriptions
This article contains images of STD infected genitalia sourced from top medical sites. Not all STDs will present as displayed in each image. In order to have an STD diagnosed you must receive STD testing and consult with a doctor.
STD Pictures and Descriptions
Sexually transmitted diseases, or STDs, are infections that are spread from one person to another during vaginal, anal, and oral intercourse.
Without treatment, STDs can lead to serious health problems. Let’s take a look at the most common STDs and the symptoms that appear on both males and females.
Let’s take a look at the most common STDs and the symptoms that appear on both males and females.
Book an STD screening appointment
Oral Herpes
Oral herpes is an infection also known as herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1).
The virus is transmitted through oral secretions or sores on the skin, and can be spread through oral sex, kissing or sharing objects such as toothbrushes or eating utensils, during an outbreak.
Oral herpes symptoms start as an itch and tingle before a blister appears. The fluid-filled blister erupts and the small and shallow ulcer on a red base becomes crusted, scabbed, dry and yellow.
Read: What Are The Herpes Stages?
The symptoms will usually appear on the lips, gums, nose, cheeks, throat, roof of the mouth, chin, or neck.
HSV-1 is a lifelong infection and has infected an estimated 3.6 billion people under the age of 50 (67%) globally.
PlushCare’s board certified doctors can help with symptom management and even prescribe oral herpes treatment following an online appointment.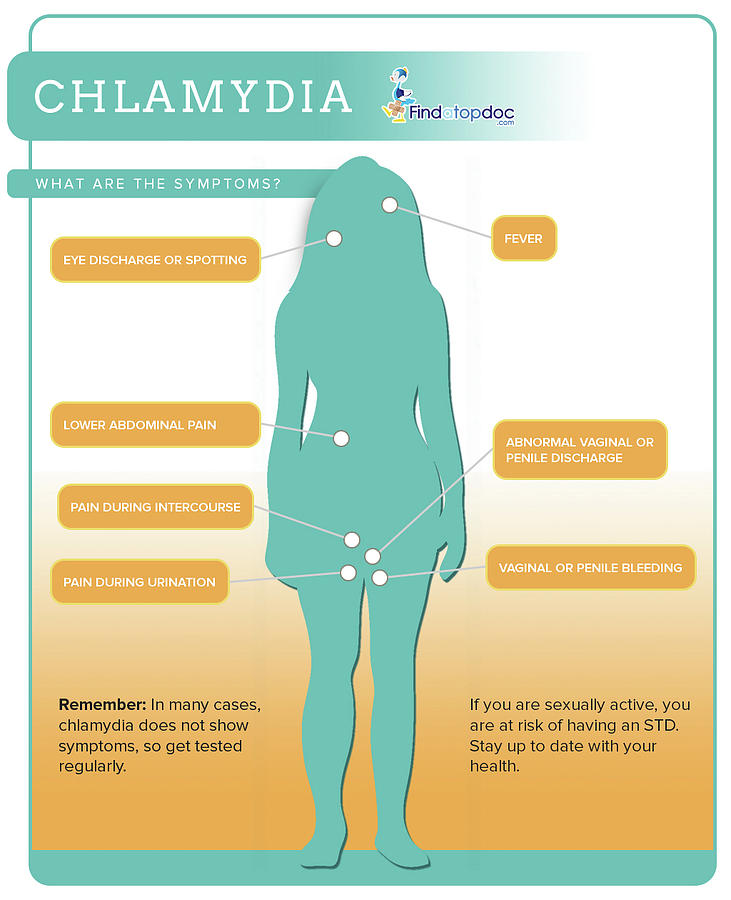 The average appointment lasts just 15 minutes. Our doctors can send your prescription to your preferred pharmacy.
The average appointment lasts just 15 minutes. Our doctors can send your prescription to your preferred pharmacy.
Common prescriptions our doctors write for oral herpes include:
- acyclovir (Zovirax)
- famciclovir (Famvir)
- valacyclovir (Valtrex)
Get Oral Herpes Treatment Online >>
Genital Herpes: Women
Genital herpes, mostly caused by herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2) is widespread throughout the world. More women are infected than men however, the infection is more easily spread from men to women than from women to men.
Genital herpes symptoms in women may begin to show 2 to 4 weeks after being exposed to the infection.
Some women may have no symptoms or signs of the infection, or may not have an outbreak for months or even years after they were first infected.
Initial symptom outbreaks to look out for may include:
- Fever and flu-like symptoms
- Pain or discomfort during urination
- Vaginal discharge
- Pain in the vagina, buttocks, or legs
- Swollen lymphnodes
After a couple days, you can develop painful sores in your genital region including your vagina, anus, inside the vagina, thighs, buttocks, cervix or urinary tract.
Genital herpes is lifelong and incurable however, symptoms can be managed so that outbreaks are controlled and shortened.
If you think you have herpes simplex virus 2, book an appointment with a PlushCare doctor. Our doctors can place an order for a herpes test and prescribe you antiviral medications that can help your sores heal sooner.
Genital Herpes in MenApproximately two-thirds of men with genital herpes, known as herpes simplex virus 2, do not experience symptoms.
It is also common for mild genital herpes symptoms in men to be confused with other skin conditions.
HSV-2 is lifelong and incurable. Fortunately, symptoms can be managed during an outbreak using antiviral medication.
Our PlushCare physicians can order you a herpes test and prescribe you with antiviral medications for herpes outbreaks.
Initial genital herpes symptoms in men may include:
- Body aches
- Headaches
- Fatigue
- Fever and flu-like symptoms
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Raw or cracked skin around the genital area
- Pain itching or tingling around the genital region
- Blisters or sores on the penis or scrotum
Herpes sores appear as small, red bumps or white blisters that can pop up on your penis, anus and/or around the thighs and buttocks.
When the blisters rupture, you may notice a painful ulcer forming in its place. It will ooze fluid and eventually heal and form a scab.
Resist the urge to pick the scab so the infected area can heal.
If left untreated or you are touching the infected area you can spread the virus andHSV-2 can lead to eye infections, eczema herpeticum, encephalitis or meningitis.
Time between outbreaks can be months to years and can be triggered by trauma, illness, and intercourse.
Get Genital Herpes Treatment Online >>
Genital Herpes Stages for Male and Female
There are six different stages to the development of genital herpes:
Stage one: Prodrome – This stage is highly contagious. You may experience pain, tingling or itching in the infected area as the herpes virus becomes active inside the skin and heads towards the surface to begin the outbreak.
Stage two: Skin Redness – The infected genital region may turn red and sensitive, lasting from a few hours to a few days.
Stage three: Formation of lesions – Lesion or sores begin to rise on the skin. Sores may appear around the anus or genitals in clusters or individually. The sores fill up with fluid and become painful. This stage may last a few days.
Stage four: Development of Lesions – This stage will be the most contagious. The lesions or herpes sores will grow until they are ready to burst to release a build up of fluid. The wound will stay open and runny for a few days.
Stage five: Scabbing – Once the herpes sore has drained its fluid build up, it will dry out and begin to scab over a few days.
Stage six: Healing – Once the scab falls off, the sore will be healed.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in Women
Genital Human Papillomavirus, or genital HPV, is a sexually transmitted disease spread through vaginal, oral or anal sex. It is extremely common and in many cases will go away on its own without displaying symptoms.
42% of US population aged 18-59 had genital herpes , most in their late teens and early 20’s, are infected with HPV. There are over 100 varieties of HPV, some strains cause warts while others may lead to an increased risk of certain cancers. The HPV vaccine can help prevent more serious and high risk strains of HPV.
HPV symptoms in women may appear as small bumps or warts, individually or in groups over the infected genital area. They can grow on the vulva, the walls of the vagina, or in and around the anal canal. They can be small or large, elevated or flat, and may be shaped like cauliflower.
That said, many women do not experience symptoms and can be diagnosed with a regular Pap test by a doctor.
Unfortunately, HPV cannot be cured but the body is typically able to fight it off and in most cases symptoms will go away on their own. When HPV does not go away, it can cause more serious health problems including:
- Cervical cancer
- Genital warts
- Oropharyngeal cancer
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis
If you think you have HPV, schedule an appointment with a PlushCare physician who can order you an HPV test.
Get HPV Treatment Online >>
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in Men
HPV is so prevalent that nearly all sexually active people will get it at some time in their life, if they don’t get the HPV vaccine. And even if you’ve had the vaccine there are many strains of HPV you are not protected against, though they are generally low risk strains.
HPV infection is transmitted through anal, vaginal, and oral sex or skin-to-skin contact.
Most men with human papilloma virus produce little to no symptoms. The infection tends to resolve on its own without any long-term effects.
HPV symptoms in men include warts on your penis, scrotum, and/or anus.
The small bumps or group of bumps appear small or large, risen or flat, and can be shaped as a cauliflower. Warts rarely cause pain or discomfort, though they may feel itchy or tender.
If you think you’ve been exposed to HPV, book an appointment with a PlushCare physician who can diagnose your condition and give you a treatment plan.
Get HPV Treatment Online >>
Chlamydia in Women
Chlamydia is a common STD that is caused by the bacteria Chlamydia trachomatis. It is easily spread by having vaginal, oral or anal sex with someone who has chlamydia.
Chlamydia survives in moist and soft tissues not covered by skin such as the genitals, mouth and throat.
Chlamydia can easily be cured using antibiotics. It can also cause serious damage to a woman’s reproductive system, if left untreated.
Read: How to Get Rid of Chlamydia
It is common for someone with chlamydia to have no symptoms. . Symptoms may not appear until several weeks after you have sex with an infected person.
Chlamydia symptoms in women include:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge with an odor
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Pain when having sex
- Itching or burning
- Bleeding between periods
- Abnormal pain with fever
You should be examined by a doctor if you notice any of these symptoms or if your partner has an STD or symptoms of an STD.
A chlamydia test requires a urine sample or a cotton swab from the cervix or infected area. Our doctors can provide you with a lab order for testing and prescribe you with any necessary antibiotics.
Get Chlamydia Treatment Online >>
Chlamydia in Men
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease that affects both men and women.
Most men with Chlamydia show no symptoms; 50% of men with chlamydia do not exhibit symptoms.
The infection is spread through semen and vaginal fluids, but the transmission of the disease is not dependent on ejaculation. If symptoms do appear, they can show up several weeks after having sex with an infected person.
Chlamydia symptoms in men may include:
- Clear or cloudy discharge from the tip of the penis
- Painful urination
- Burning or itching around the opening of the penis
- Pain and swelling around the tesitcles
- Pain, discharge, bleeding around the anus
If you think you have chlamydia, book an appointment with an online doctor at PlushCare. The doctor will provide you with a lab order to test for the STD. The test is typically a swab from the urethra.
The doctor will provide you with a lab order to test for the STD. The test is typically a swab from the urethra.
If your results come back positive, your doctor will prescribe you oral antibiotics such as azithromycin or doxycycline. Contact one of our doctors today if you are experiencing symptoms of chlamydia.
Get Chlamydia Treatment Online >>
Gonorrhea in Women
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted disease sometimes called “the clap” or the drip.
It has been estimated that the United States sees about 550,000 new cases of gonorrhea every year. About 90% of those are from sexually active people between the age of 15 to 44.
This bacteria survives on mucous membranes that are moist, soft tissues not covered by skin. Thus, this infection can be found inside the vagina, cervix, uterus, fallopian tubes, urethra, rectum, as well as the lining of the eyes, mouth or throat.
Read: Is Gonorrhea Curable?
Gonorrhea symptoms in women include:
- Painful urination
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Vaginal bleeding after intercourse
- Painful lower abdominal area
Gonorrhea is easily treated with antibiotics which kill the bacterial infection in a matter of days.
Book an appointment with PlushCare to get a lab order for Gonorrhea testing. If your results come back positive our doctors will write you a prescription for antibiotics.
Get Gonorrhea Treatment Online >>
Gonorrhea in Men
Gonorrhea is a very common infection, especially among young people ages 15 through 24 years. Gonorrhea, also known as the “clap” or the drip, is a sexually transmitted infection that is transmitted through semen or vaginal fluids.
Gonorrhea tends to infect warm, moist areas of the body including the urethra, throat, and anus.
It cannot be passed through casual contact such as kissing, holding hands, hugging, or sneezing.
Not all infections cause symptoms, that said symptoms may appear several days after being infected.
Common gonorrhea symptoms in men include:
- Painful urination
- Pus-like discharge from the tip of the penis in yellow, green or white
- Pain or swelling in one testicle
- A persistent sore throat
Gonorrhea in men, if left untreated, can cause painful condition in the tubes attached to the testicles and can spread to your blood and joints.
Most of the time urine can be used for a gonorrhea test. If you think you think you have gonorrhea consult a doctor about your treatment options.
A PlushCare doctor can write you a lab order and if you test positive can provide you with the necessary antibiotics.
Get Gonorrhea Treatment Online >>
Syphilis in Women
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease that is highly contagious.
Around 19 of every 200,000 men and women in the United States report contracting syphilis.
This bacteria can enter your body through vaginal, anal or oral sex from the partner`s sores.
Like other STDs, if syphilis is left untreated it can cause long-term problems such as arthritis, brain damage, and blindness.
Read: What to Do if You Think You Have Syphilis
Syphilis symptoms can take months or even years to appear, so it is possible to acquire or transmit the disease without knowledge of its existence.
Syphilis sores or syphilis chancres may be painless and can heal in about three to six weeks on its own if left untreated.
Since it is a bacterial infection, syphilis is completely curable with correctly prescribed antibiotic medication.
That said, if left untreated syphilis can advance to later stages that can cause lasting damage. A mother can pass it to the child during pregnancy.
If you think you have syphilis book an appointment with a PlushCare doctor. They will order you a syphilis test if necessary. If your results come back positive the doctor will prescribe you antibiotics to treat your infection.
Get Syphilis Treatment Online >>
Syphilis in Men
Syphilis is a common bacterial infection that’s spread through sexual intercourse.
Syphilis is easily cured with antibiotic medication, but can cause permanent damage if you are not treated immediately.
Untreated syphilis can lead to permanent problems like brain damage, paralysis, and blindness.
Syphilis is easily transmitted during sex when one partner have a syphilis sore in the anus or genitals or through kissing with an oral sore. The infection cannot be spread through casual contact, such as sharing foods, hugging, holding hands, coughing, or sitting on a toilet seat.
Syphilis symptoms in men appear as chancres or sores and most likely develop on the penis head or top of the shaft or on the scrotum.
The infection can be diagnosed with a syphilis test which includes drawing blood and swabbing fluid from an open sore.
You can book an appointment with a PlushCare doctor who can write you a lab order for testing and give you a treatment plan, including any necessary antibiotics, following a positive diagnosis.
Get Syphilis Treatment Online >>
Stages of syphilis in Men and Syphilis Symptoms in Women
If left untreated syphilis will advance from its primary stage and get worse over time leading to complicated health problems.
The stages of syphilis are:
- Primary stage – Sores or chancres appear at the site of infection (mouth, lips, anus, rectum, vagina, cervix for women or mouth, lips, anus, rectum, scrotum, and penis for men). These appear 3 to 6 weeks after infected, and heal if left untreated.
- Secondary stage – Red or reddish brown rash on the trunk, palms of the hands and soles of the feet may appear. You may experience sore throat, patchy hair loss, swollen lymph nodes, or headaches and fever.
- Latent stage – During this phase, the bacteria are still alive in your body but you may experience no symptoms. The infection can affect your heart, brain, and nerves and can last for years. Not everyone who has syphilis will enter this stage. Some will go directly into the tertiary stage.
- Tertiary stage – Post secondary stage symptoms, the infection remains latent in the body if left untreated.
 This stage is not contagious, but the infection may have started to damage organs, such as your brain, nerves, eyes, etc. Symptoms of tertiary stage include numbness, problems controlling muscle movements, vision loss and dementia.
This stage is not contagious, but the infection may have started to damage organs, such as your brain, nerves, eyes, etc. Symptoms of tertiary stage include numbness, problems controlling muscle movements, vision loss and dementia.
Get STD Testing and Treatment Online
If you’ve been exposed to an STD or are experiencing symptoms of an STD you should see a doctor about STD testing.
This can be done online through PlushCare. Our top doctors are able to write STD testing orders and will refer you to your local lab for testing. Once your results come back the doctor will reach out for a follow up appointment.
Your PlushCare doctor will work with you to create a treatment plan including any necessary prescription medications, such as antibiotics or antiviral medication.
Book an appointment to talk to a doctor and get a lab order for STD testing.
Read More About STDs
- STD Testing Online
- What’s Included in an STD Panel?
- Where to get Tested for STDs
symptoms and treatment, causes, first signs and manifestations of chlamydia
What is it?
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease affecting the pelvic organs.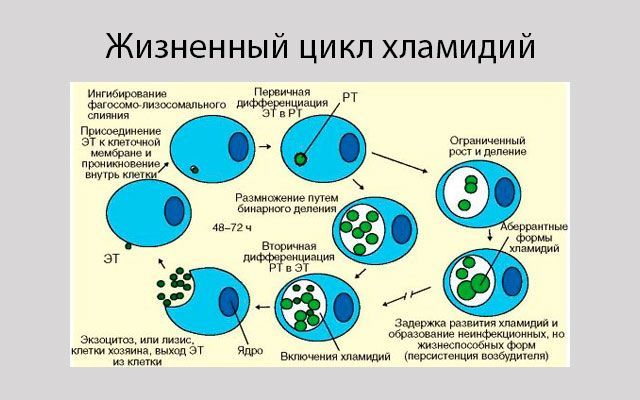 In women, chlamydial infection can cause chronic inflammation in the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
In women, chlamydial infection can cause chronic inflammation in the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
Causes, causative agent
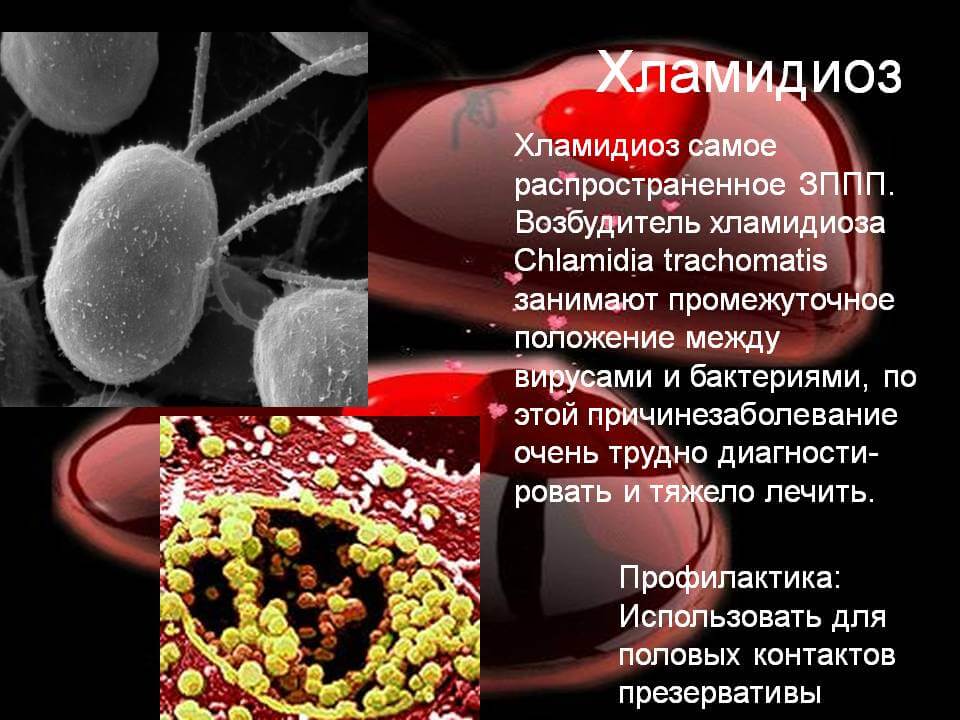
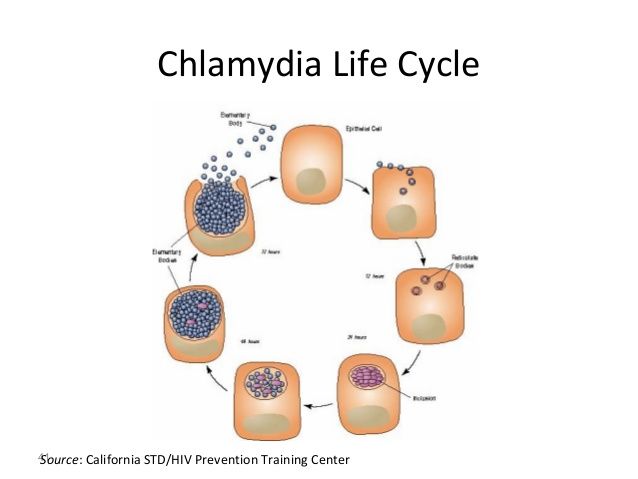
The cause of chlamydia (chlamydiasis) is infection with special microbes - chlamydia. Bacteria of this group are extremely widespread. Microorganisms that cause infectious diseases in humans include, among others: Chlamydia trachomatis (Fig. 1), Chlamydophila psittaci, Chlamydophila pneumoniae . The first of them is the most unpleasant, it affects the reproductive system, intestines and urinary tract. Other types of chlamydia can multiply in the cells of the mucous membranes of the eyes, respiratory tract, and lungs.
Figure 1. Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria. Source: CC0 Public DomainChlamydia transmission
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted disease. Genital infection is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria, the disease is especially common among young people under the age of 24 years of both sexes.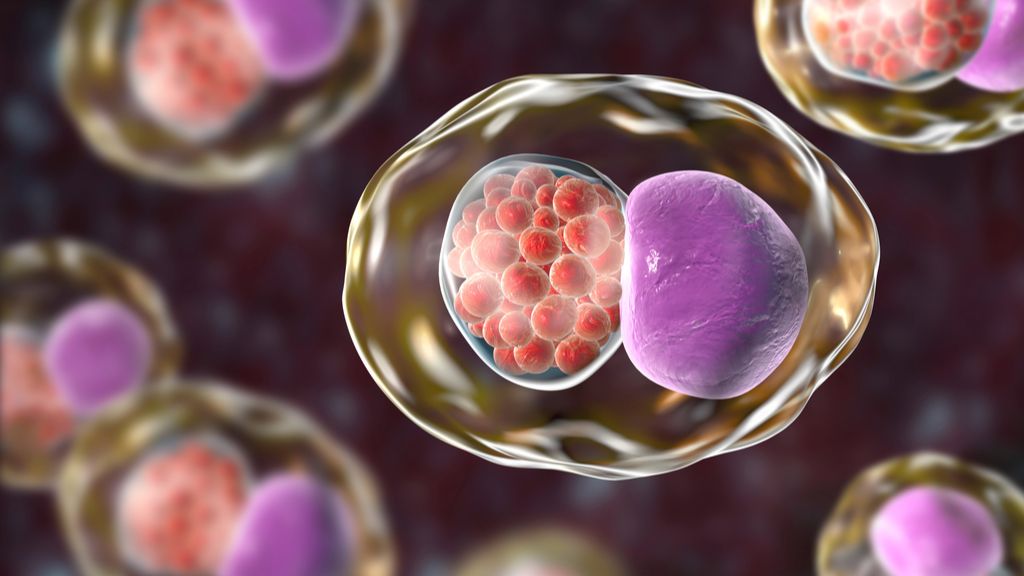 Once on the vulva, in women, the bacteria can cause an ascending infection that spreads through the genitourinary tract. First, the cervix is infected, from where the bacteria settle into the urethra, uterus, fallopian tubes, and internal organs. In this case, the infection of the sexual partner and the newborn during childbirth in case of pregnancy is inevitable (vertical transmission).
Once on the vulva, in women, the bacteria can cause an ascending infection that spreads through the genitourinary tract. First, the cervix is infected, from where the bacteria settle into the urethra, uterus, fallopian tubes, and internal organs. In this case, the infection of the sexual partner and the newborn during childbirth in case of pregnancy is inevitable (vertical transmission).
A feature of chlamydial infections is their frequent combination with infection by other bacteria (for example, pathogens of gonorrhea or candidiasis), as a result of which mutual pathogenicity may increase.
It is not uncommon for chlamydia to be transmitted through the household, especially among members of the same family. In a family where parents are ill with chlamydia, this infection often occurs in children. If parents have a sexually transmitted infection, their children may suffer from conjunctivitis, an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes. However, these bacteria can be "picked up" in any public place: in a bathhouse, a sports center, etc. Wherever a person shows negligence in hygiene, he can become infected with dangerous bacteria - the pathogenicity of chlamydia on household surfaces lasts up to two days at room temperature.
Wherever a person shows negligence in hygiene, he can become infected with dangerous bacteria - the pathogenicity of chlamydia on household surfaces lasts up to two days at room temperature.
How infections associated with other members of the genera Chlamydia and Chlamydophila are transmitted, as well as the course of chlamydia in men and children, can be read here.
Who is at risk?
Among the main risk factors for chlamydia:
- age under 24,
- unprotected vaginal, anal, oral sex,
- frequent change of sexual partners,
- presence of other sexually transmitted infections,
- depressed immune system.
Important! If one of the partners is diagnosed with chlamydia, the probability of the same diagnosis in his couple is about 40-60%. The risk of infection of a child from an infected mother during childbirth is 50%.
The danger of chlamydia for women: complications
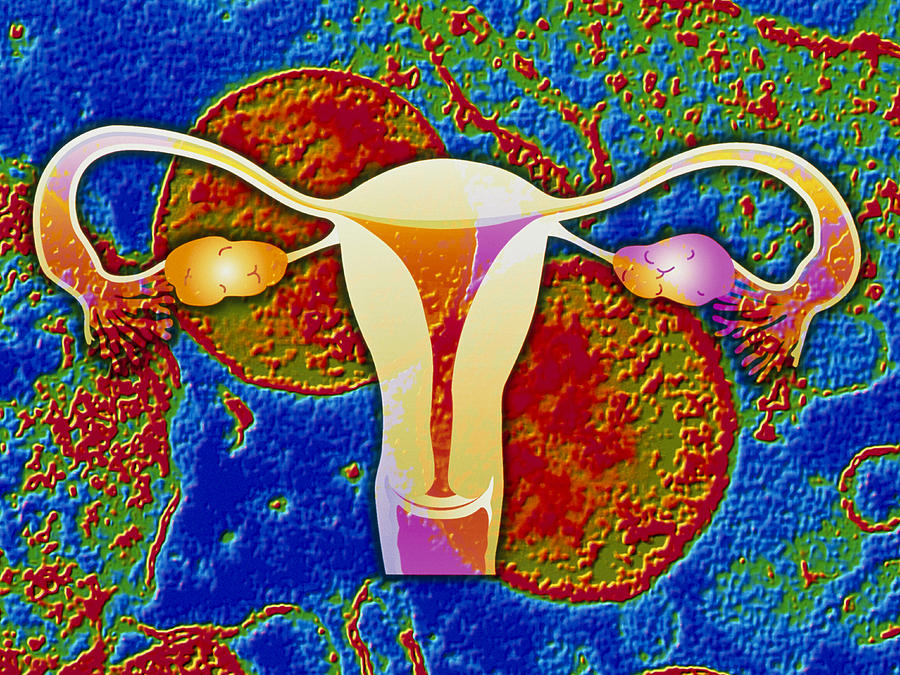
Female chlamydia is especially insidious, as it is asymptomatic in almost 80% of cases. Lack of timely treatment allows the disease to go into a chronic stage. Even if there are no external manifestations of infection, chlamydia can cause inflammation of the pelvic organs - the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, peritoneum (PID). Due to the adhesive process, with prolonged inflammation, the fallopian tubes can become blocked. Because of this, the eggs lose their ability to move towards the uterus, and infertility develops (Fig. 2). Chlamydia causes about half of all infertility cases in women.
Lack of timely treatment allows the disease to go into a chronic stage. Even if there are no external manifestations of infection, chlamydia can cause inflammation of the pelvic organs - the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, peritoneum (PID). Due to the adhesive process, with prolonged inflammation, the fallopian tubes can become blocked. Because of this, the eggs lose their ability to move towards the uterus, and infertility develops (Fig. 2). Chlamydia causes about half of all infertility cases in women.
Chlamydia in pregnancy: risks
In pregnant women, chlamydia is associated with an increased risk of preterm birth, miscarriage, stillbirth, and other complications. If the pregnancy is successful, chlamydia can be passed on to the newborn from the mother.
What happens if chlamydia is not treated?
Lack of timely treatment allows the disease to become chronic. In this case, inflammation can affect all organs of the small pelvis and spread to other body systems. Among the complications of untreated chlamydial infection:
In this case, inflammation can affect all organs of the small pelvis and spread to other body systems. Among the complications of untreated chlamydial infection:
- endometritis (inflammation of the endometrium),
- perihepatitis (inflammation of the lining of the liver),
- cervical cancer, ectopic pregnancy,
- lymphogranulomatosis (disease of lymphoid tissue),
- diseases of the eyes and joints.
Symptoms of chlamydia in women
More than 20 different clinical syndromes and conditions can be associated with chlamydia, including:
- cervicitis,
- pneumonia,
- vulvovaginitis,
- endometritis,
- reactive arthritis,
- endocarditis and others.
That is, the infection manifests itself in inflammatory diseases of various organs, but mainly in the pelvic region. However, the first manifestation of the disease should be expected only after a long time after infection, sometimes after many years.
Common complaints of chlamydia in women include:
- abnormal vaginal discharge,
- burning when urinating,
- rectal pain and bleeding (when infected through anal sex).
Important! Women who frequently change sexual partners and "priestesses of love" are recommended to be screened for genital infections at least once a year. In this case, a test for chlamydia is necessarily included due to the wide prevalence and danger of these bacteria.
Diagnosis of chlamydial infection
Modern effective methods for diagnosing chlamydia include polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and enzyme immunoassay (ELISA). In the first case, the DNA of the infectious agent is detected in the laboratory, that is, its presence in the body at any stage of the disease. ELISA is aimed at detecting the body's antibodies to bacteria, that is, the manifestation of an immune response to an infection that has a certain duration of the course.
To perform PCR on chlamydia DNA, it is necessary to donate biological material. It is necessary to obtain a scraping of epithelial cells from the cervical canal, urethra, conjunctiva of the eyes, posterior pharyngeal wall, to separate the joint fluid - depending on the symptoms and referral of the doctor. The success of the test depends on how well the samples are taken.
Photo: freepik.comPreparation for the study is required. The patient should not take antibiotics for 2 weeks, sexual intercourse is prohibited a day before the scraping. If the scraping is made from the urethra, you need to refrain from urinating for 3 hours. When scraping from the vagina per day, douching or the use of any intravaginal drugs is prohibited. The biomaterial of the conjunctiva of the eye is taken by an ophthalmologist.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay will require taking blood samples from the sick person, as this is where antibodies to the causative agent of the disease appear. IgA antibodies responsible for local immunity are detected several days after infection. After 3-4 weeks, the body begins to produce IgM antibodies. At the same time, IgG antibodies may appear, indicating a chronic course of the disease. It should be understood that the presence of antibodies to chlamydia in the blood does not always indicate the presence of an infection, it is a response to the pathogen, antibodies can remain in the blood for many years after treatment. ELISA is an auxiliary diagnostic method for infertility (a positive result may serve as an indication for checking the patency of the fallopian tubes) and in itself cannot be the reason for starting chlamydia therapy.
IgA antibodies responsible for local immunity are detected several days after infection. After 3-4 weeks, the body begins to produce IgM antibodies. At the same time, IgG antibodies may appear, indicating a chronic course of the disease. It should be understood that the presence of antibodies to chlamydia in the blood does not always indicate the presence of an infection, it is a response to the pathogen, antibodies can remain in the blood for many years after treatment. ELISA is an auxiliary diagnostic method for infertility (a positive result may serve as an indication for checking the patency of the fallopian tubes) and in itself cannot be the reason for starting chlamydia therapy.
Preparation for ELISA takes a little time. Its task is to ensure the "quality" of the blood so that it does not clot before it reaches the laboratory. Come to donate blood on an empty stomach - no earlier than 8 hours after the last meal. It is also recommended not to abuse heavy food on the evening before. 1-2 hours before the test, you can not smoke, be subjected to serious mental or physical stress.
1-2 hours before the test, you can not smoke, be subjected to serious mental or physical stress.
Important! If a patient is diagnosed with chlamydia, it is necessary to conduct an examination of her sexual partner and cohabiting relatives or prescribe them prophylactic treatment without examination. Both partners should undergo therapy, only in this case the risk of re-infection is excluded.
Treatment of chlamydia infection in women
Chlamydia is treated with tetracycline antibiotics (eg doxycycline) and/or macrolides (azithromycin, erythromycin, etc.). Less often antibiotics from the group of fluoroquinolones. β-lactam preparations are not effective. A few weeks after the course of treatment, an additional examination is carried out - a control test, since relapses of chlamydia are possible.
In addition to systemic antibiotics, in severe infections, topical treatment with antibacterial or antifungal drugs is additionally prescribed. Immunomodulators are sometimes used as maintenance therapy.
Immunomodulators are sometimes used as maintenance therapy.
Treatment during pregnancy
Chlamydia infection is best eliminated before pregnancy. The ectopic pregnancy that occurs with chlamydia is extremely life-threatening. If harmful microbes are found in a pregnant woman, more gentle medications are used for treatment. Antibiotics necessary to suppress the causative agent of the disease are often dangerous to the fetus. In particular, pregnancy is a contraindication for the use of tetracyclines.
Prevention of infection
Since chlamydia transmission occurs more frequently through intimate contact between people or through another person's secretions (saliva, etc.), it is clear that the best way to prevent chlamydia is to limit such unprotected contact. Protection from genital infection involves the constancy of sexual preference with a reliable permanent partner.
Photo: fongbeerredhot / freepik.com Using a condom can also prevent bacteria from entering the genitals.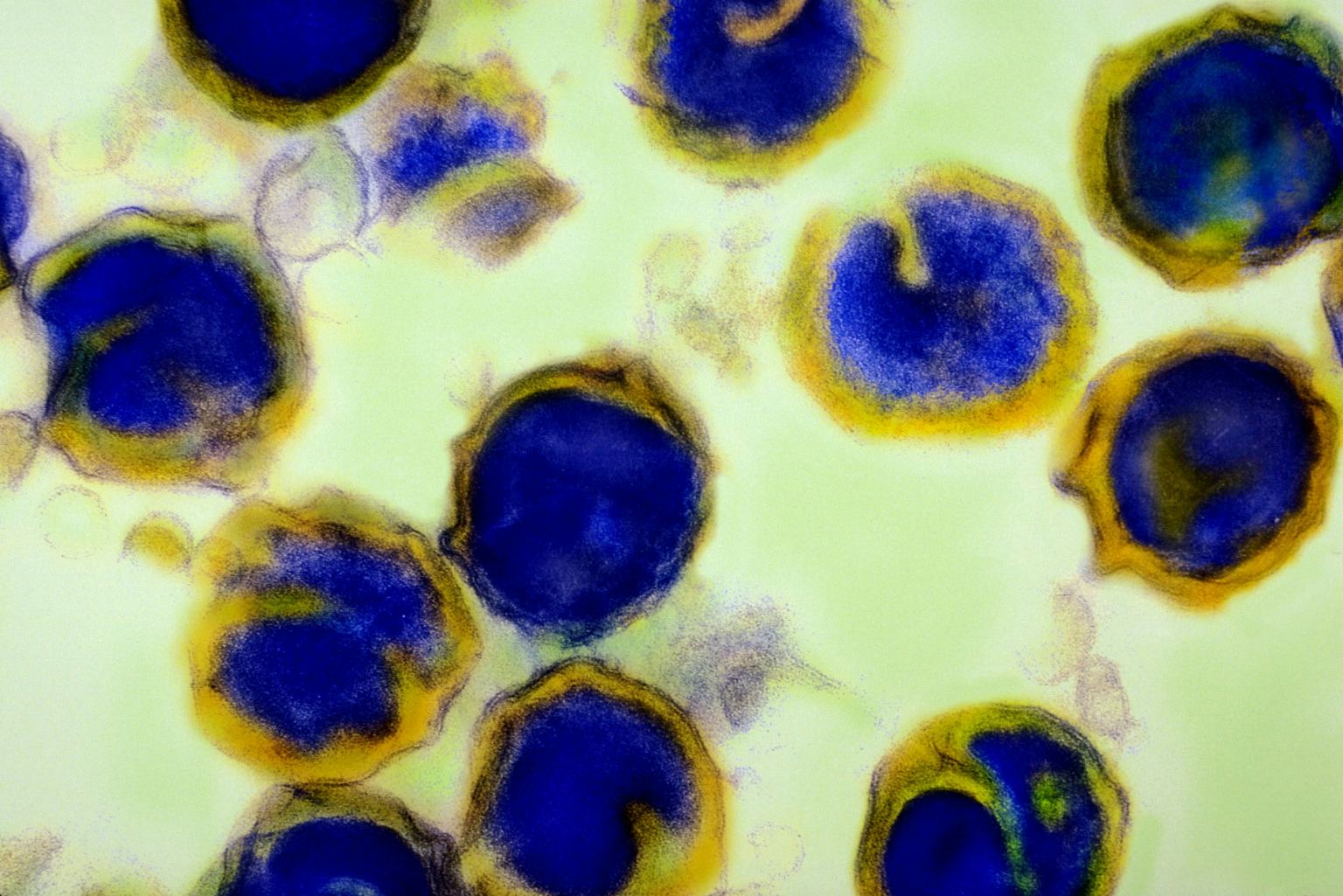 If there was sexual contact with an unreliable partner, after it it is desirable to be examined for sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia.
If there was sexual contact with an unreliable partner, after it it is desirable to be examined for sexually transmitted infections, including chlamydia.
Preventing accidental introduction of chlamydia into the eyes can be done by following normal hygiene practices, including individual use of household and personal hygiene items. In those who have had chlamydia, a very weak and short-term immunity is formed, so re-infection is possible. Even if the patient has been ill and cured, the rules for preventing infection should be followed.
Conclusion
Chlamydia is an insidious and dangerous infection that is one of the main causes of female infertility. The disease is transmitted both sexually and domestically, so it often affects how many generations of blood relatives. Simple prevention, timely diagnosis and treatment are ways to combat chlamydia.
Sources
- Ilyin I.I., Delektorsky V.V. Chlamydia and mycoplasmal diseases of the genitourinary organs: Skin and venereal diseases.
 A guide for doctors in 4 volumes / Ed. Yu. K. Skripkina. - M.: Medicine, 1996. - S. 219-262.
A guide for doctors in 4 volumes / Ed. Yu. K. Skripkina. - M.: Medicine, 1996. - S. 219-262. - Chlamydial Infections In: "2015 Sexually Transmitted Diseases Treatment Guidelines". CDC. June 4, 2015
- Chlamydiosen (Teil 1): Erkrankungen durch Chlamydia trachomatis - RKI-Ratgeber für Ärzte. (Nicht mehr online verfügbar.) In: Website des Robert Koch-Instituts (RKI). December 21, 2010
symptoms, photos, treatment. How to treat Chlamydia
Chlamydia: symptoms in women and treatment regimen
Genital chlamydia is an insidious disease that often causes female infertility and pregnancy failure among women. Gram-negative bacteria, chlamydia, provoke the occurrence of a sexually transmitted disease. The disease is transmitted more often sexually, less often - household. For example, through linen, hygiene items, bath accessories, provided that they are used by a sick person.
The symptoms of the disease in women are different from those in men. However, they can be very different. Often the disease proceeds without any symptoms, which leads to its complication. Women who care about their health need to know about chlamydia.
However, they can be very different. Often the disease proceeds without any symptoms, which leads to its complication. Women who care about their health need to know about chlamydia.
What is it?
Chlamydia is an infectious disease caused by intracellular parasites - chlamydia, affecting the organs of the genitourinary system.
Causes and risk factors
Chlamydia infections in women are caused by the intracellular organism Chlamydia trachomatis. These bacteria can stay in the human body for a long time without causing clinical manifestations, but in the event of a weakening of the body's defenses, chlamydia begin to increase vitality and growth, causing signs of chlamydia in women. The most common way of transmission of chlamydia is sexual - both with traditional and non-traditional types of unprotected intercourse.
In addition, transmission of chlamydia can occur in utero or during childbirth from mother to child when the fetus passes through the birth canal. There is also a contact-household route of transmission of the disease - through hands contaminated with infected secretions, personal hygiene items, bed linen, etc. Such cases of infection are rare, since chlamydia quickly die outside the body. Cases of transmission of chlamydia during blood transfusions are known.
There is also a contact-household route of transmission of the disease - through hands contaminated with infected secretions, personal hygiene items, bed linen, etc. Such cases of infection are rare, since chlamydia quickly die outside the body. Cases of transmission of chlamydia during blood transfusions are known.
First signs
More often than not, chlamydia infection causes no symptoms, but in some cases certain complaints are observed.
The first signs of chlamydia in women:
- Feeling a little soreness and discomfort when urinating;
- Sensation of excessive moisture in the genitals;
- Burning sensation in the vulva and itching in the urethra;
- Mucopurulent vaginal discharge. On examination, the discharge appears with pressure on the affected area;
- Drawing pains in lower abdomen;
- Defect in the form of erosion in the area of the cervix;
- Heaviness and pain in the lumbar spine;
- Menstrual disorders;
- General weakness and fever.

Chlamydial conjunctivitis can also occur when the eyes are involved in the pathological process.
Symptoms of chlamydia in women
This disease can be asymptomatic for many years, signs of the disease are found in only 30-40% of women. However, the latent course of the process is not at all safe: chlamydia, even if it occurs without any symptoms, can cause many complications, including infertility. The incubation period of the disease is 2-4 weeks, so the appearance of any symptoms is often not associated with sexual intercourse that took place in the past.
Depending on the organ affected by the infection, various diseases occur and obvious symptoms appear.
- Urethritis - chlamydia infection of the urethra with the development of burning and pain during the management of small needs.
- Bartholinitis - inflammatory processes in the Bartholin gland, which is located on both sides at the entrance to the vagina. It is manifested by pain, swelling and redness on the side of the lesion, fever.
- Erosion and inflammation of the cervix (endocervicitis), accompanied by pulling pains in the lower abdomen, the appearance of mucopurulent discharge, often spotting after intercourse.
- Salpingitis and adnexitis - inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries (often a combined pathology). Pain in the right or left side, menstrual irregularities, fever - these symptoms make it possible to suspect chlamydia appendages in women.
- Endometritis (inflammation of the inner layer of the uterus) - characteristic symptoms: high body temperature, uterine bleeding, mucopurulent discharge, severe pain behind the pubis.
- Chlamydial pharyngitis - occurs when infected during oral sex. It is characterized by sore throat, pain when swallowing.
- Pelvioperitonitis is a lesion of the peritoneum in the pelvic area. In this case, there are quite sharp pains in the abdomen, constipation, bloating, tension of the abdominal wall.
- Arthritis (Reiter's syndrome) - chronic chlamydia in women can lead to autoimmune inflammation of the joints.
- Chlamydial proctitis - inflammation of the rectal mucosa (after unprotected anal contact) with the appearance of pain, mucopurulent discharge from the anus.
- Inflammation of the lungs - the first signs of chlamydial inflammation are characterized by cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, fever.
- Conjunctivitis - eye damage with the development of lacrimation, redness, burning. It develops when the infection enters the eyes with dirty hands, when sharing towels.
In itself, the infection can proceed latently - the first symptoms will appear along with the diseases provoked by the infection!
Diagnosis
Methods to help diagnose chlamydia:
- Bacteriological culture of microflora. The presence of bacteria is determined. Blood, urine, genital secretions can be used for it.
- PCR. A polymerase chain reaction for several hours will help to identify the causative agent of the disease even by one small fragment, if it was in the original material.
- RIF. Analysis of the immunofluorescence reaction by staining the material with a special reagent. A fluorescent microscope in the presence of chlamydia will highlight them.
- ELISA. With the help of an enzyme immunoassay, antibodies to chlamydia are determined. The stage of the disease is specified.
- Swab. A small amount of discharge from the urethra, the vagina is examined with a microscope.
Laboratory tests are of great importance for making the correct diagnosis, since the existing chlamydia: unexpressed symptoms in women are very common, occur in a latent form. A blood test, a smear from the vagina is taken in several stages - at the beginning of treatment and a control one at the end.
What does chlamydia look like: photo
The photo below shows how the disease manifests itself in women.
What happens if you don't treat?
Complications of chlamydia in women:
- The adhesive process leads to chronic pain in the pelvic area.
- Salpingo-oophoritis is complicated by pelvioperitonitis - inflammation of the pelvic peritoneum. The acute phase of the disease proceeds with high body temperature and severe pain in the lower abdomen. With the transition of the disease to the chronic phase of the course, the severity of clinical symptoms is smoothed out.
- When the infection spreads to the upper abdominal region, severe pain appears in the right hypochondrium, which indicates damage to the liver capsule (Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome). The development of a powerful adhesive process leads to chronic pain in the upper floor of the abdominal cavity.
- Chronic inflammatory disease of the cervix, pelvic organs, abdominal cavity organs - formidable complications of chlamydia in women. Multiple adhesions are the cause of the development of pathology of pregnancy and infection of the fetus either during pregnancy or during childbirth.
- Some chlamydia have been found to have a heat shock protein capable of inducing autoimmune reactions.
 Such patients develop Reiter's syndrome, in which inflammation of the vagina is combined with reactive arthritis of one or more joints and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctivitis). The syndrome develops 20 times more often in men.
Such patients develop Reiter's syndrome, in which inflammation of the vagina is combined with reactive arthritis of one or more joints and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctivitis). The syndrome develops 20 times more often in men.
Most often, chlamydia in women often occurs with smoothed symptoms and takes a chronic form with a minimum number of external manifestations, having a significant impact on the human reproductive system. [adsen]
Should my sexual partner (husband, boyfriend) be treated?
Be sure to tell your sexual partner if you have chlamydia. He needs to see a urologist and get tested for venereal infections.
Even if your partner does not have chlamydia, he still needs to be treated.
Treatment of chlamydia in women
The problem of complex treatment of chlamydial infection in women should be solved taking into account the clinical picture of the patient. There are no ready-made algorithms, general treatment regimens for chlamydia in women, since in each case it is worth considering the state of immunity, concomitant diseases, and the state of the intestinal microflora.
Any bacterial infection, including chlamydia, requires the use of antibiotics. Since the infectious agent parasitizes intracellularly, the choice of antibiotics in the treatment of chlamydia should be limited only to such antimicrobial agents that can destroy the infection inside the cells:
The presence of concomitant sexually transmitted infections must be taken into account in order to ensure that the choice of antibiotic is most effective in the presence of a mixed infection.
There are European recommendations for the treatment of chlamydia, according to which it is prescribed:
- Azithromycin 500 mg 2 tab.
 once, or Doxycycline 0.1 twice a day for 7 days.
once, or Doxycycline 0.1 twice a day for 7 days. - With this scheme, the effectiveness of treatment reaches 97%.
Second line:
- Erythromycin 500 mg 4 times a day every 6 hours 7 days
- Ofloxacin 300 mg twice daily every 12 hours for 7 days
- Roxithromycin 150 mg twice a day after 12 hours 7 days
- Spiramycin 3 million units every 8 hours for 7 days
Pregnant:
- Erythromycin 500 mg every 6 hours 4 times a day for 7 days
- Josamycin 750 mg 3 times a day after 8 hours 7 days
- Spiramycin 3 million U every 8 hours 3 times a day for 7 days.
All information about drugs and treatment regimens is for informational purposes only. Treatment of chlamydia is carried out only by a qualified specialist based on the results of tests, the patient's history, in dynamics, taking into account the criteria for cure.
Immunomodulators
They are an important part of the effective treatment of chlamydia and are used in acute and chronic chlamydial infections. These include: "Methyluracil", "Timalin", "Takvitin", "Lysozyme", "Viferon", "Polyoxidonium", "Cycloferon".
These include: "Methyluracil", "Timalin", "Takvitin", "Lysozyme", "Viferon", "Polyoxidonium", "Cycloferon".
Recently, for the treatment of female chlamydia, the drug "Polyoxidonium" is very widely used, especially if an atypical form of urogenital chlamydia is present. "Polyoxidonium" helps to increase the production of antibodies, and also reduces the side effects of other drugs, shortens the recovery period, increases the body's resistance to other infections.
But it is worth remembering that self-administration of any drugs, especially immunomodulators, is strictly prohibited.
Treatment regimens for chlamydia in women
Effective treatment of infection in women is based on taking drugs that kill chlamydia or inhibit the growth of microorganisms. The doctor gives a general assessment of the state of the patient's body, identifies concomitant diseases in order to prescribe the correct therapy.
Treatment regimens for chlamydia in women:
- Indolent chlamydia.
 In the first two weeks, immunotherapy, systemic enzyme therapy is carried out. Then the doctor prescribes antibiotics, multivitamins, antifungal agents. To restore and support the body, the gynecologist prescribes physical procedures, local treatment, probiotics, hepatoprotectors. The treatment regimen from the start of antibiotics is identical to that of acute chlamydia.
In the first two weeks, immunotherapy, systemic enzyme therapy is carried out. Then the doctor prescribes antibiotics, multivitamins, antifungal agents. To restore and support the body, the gynecologist prescribes physical procedures, local treatment, probiotics, hepatoprotectors. The treatment regimen from the start of antibiotics is identical to that of acute chlamydia. - Acute chlamydia. Prescribed drugs: the antibiotic doxycycline (3 weeks, 100 mg 2 times a day), an immunomodulator at the doctor's choice, multivitamins. After 7 days, systemic enzyme therapy is performed. If there are fungal infections, the drugs "Fluconazole", "Nystatin" are used. In combination with therapeutic agents, probiotics, hepatoprotectors are prescribed, physical procedures, and local treatment are prescribed.
- Chronic chlamydia. Within two weeks, inductotherapy is carried out, "Amixin" is prescribed for 30 days (every other day). Systemic enzyme therapy is carried out (2 weeks). 10 days after the start of treatment for the infection, antibiotics are prescribed (the amount of the drug is identical to the amount in the treatment of an acute disease), multivitamins.