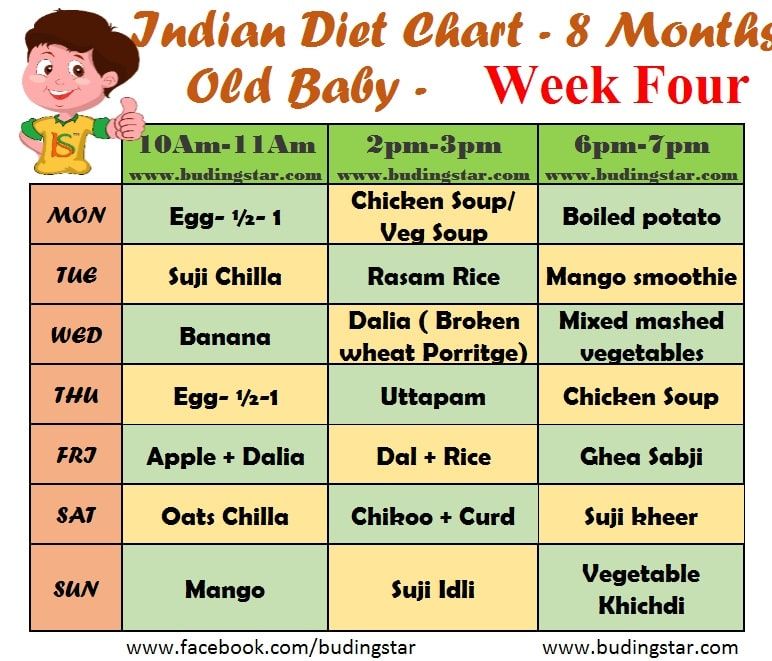
Chances of getting listeria while pregnant
Listeria from Food Safety for Moms to Be
While You're Pregnant Main Page
What Is Foodborne Illness? | Listeria | Toxoplasma
Spanish (Español)
Listeria: Frequently Asked Questions
"What is Listeria monocytogenes?"
It's a harmful bacterium that can be found in refrigerated, ready-to-eat foods (meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy - unpasteurized milk and milk products or foods made with unpasteurized milk), and produce harvested from soil contaminated with L. monocytogenes. Many animals can carry this bacterium without appearing ill, and thus, it can be found in foods made from animals. L. monocytogenes is unusual because it can grow at refrigerator temperatures where most other foodborne bacteria do not. When eaten, it may cause listeriosis, an illness to which pregnant women and their unborn children are very susceptible.
"How could I get listeriosis?"
By eating ready-to-eat meats, poultry, seafood, and dairy products that are contaminated with L. monocytogenes. You can also get listeriosis by eating contaminated foods processed or packaged in unsanitary conditions or by eating fruits and vegetables that are contaminated from the soil or from manure used as fertilizer.
"How could listeriosis affect me?"
The symptoms can take a few days or even weeks to appear and may include fever, chills, muscle aches, diarrhea or upset stomach, headache, stiff neck, confusion, and loss of balance. In more serious cases, listeriosis could also lead to the mother's death.
Most of the time, pregnant women who are infected with listeriosis don't feel sick. However, they can pass the infection to their unborn babies without even knowing it. That's why prevention of listeriosis is very important. In any case, if you experience any of the above symptoms, see your doctor or healthcare provider immediately.
Facts (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) 
"How could listeriosis affect my baby?"
During the first trimester of pregnancy, listeriosis may cause miscarriage. As the pregnancy progresses to third trimester, the mother is more at risk. Listeriosis can also lead to premature labor, the delivery of a low-birth-weight infant, or infant death. Fetuses who have a late infection may develop a wide range of health problems, including intellectual disability, paralysis, seizures, blindness, or impairments of the brain, heart, or kidney. In newborns, L. monocytogenes can cause blood infections and meningitis.
Listeriosis & Pregnant Hispanic Women
Studies show that pregnant Hispanic women may have a higher incidence of listeriosis than pregnant non-Hispanic women. This is most likely because they might make and eat homemade soft cheese and other traditional foods made from unpasteurized milk. "Queso fresco"- a traditional homemade cheese, prepared from unpasteurized milk and widely consumed by Hispanics - has led to miscarriages, death of newborns, and premature delivery caused by L. monocytogenes.
"Queso fresco"- a traditional homemade cheese, prepared from unpasteurized milk and widely consumed by Hispanics - has led to miscarriages, death of newborns, and premature delivery caused by L. monocytogenes.
To prevent the risk of listeriosis, Hispanic pregnant women should not eat homemade soft cheeses and other traditional foods made from unpasteurized milk. Like all other pregnant women, they should follow the food safety precautions outlined below.
"How can I prevent listeriosis?"
The good news is that listeriosis can be prevented! Here's how...
Time to Chill
- Your refrigerator should register at 40° F (4° C) or below and the freezer at 0° F (-18° C). Place a refrigerator thermometer in the refrigerator, and check the temperature periodically. During the automatic defrost cycle, the temperature may temporarily register slightly higher than 40° F. This is okay.
- Refrigerate or freeze perishables, prepared food, and leftovers within two hours of eating or preparation.
 Follow the 2-Hour Rule: Discard food that's left out at room temperature for longer than 2 hours. When temperatures are above 90° F (32° C), discard food after 1 hour.
Follow the 2-Hour Rule: Discard food that's left out at room temperature for longer than 2 hours. When temperatures are above 90° F (32° C), discard food after 1 hour. - Use ready-to-eat, perishable foods, such as dairy, meat, poultry, seafood, and produce, as soon as possible.
Fridge TIPS
- Clean your refrigerator regularly.
- Wipe up spills immediately.
- Clean the inside walls and shelves with hot water and a mild liquid dishwashing detergent; then rinse.
- Once a week, check expiration and "use by" dates, and throw out foods if the date has passed. Follow the recommended storage times for foods.
Refrigerator & Freezer Storage Chart (PDF).
To Eat or Not to Eat?
Don't eat:
- Hot dogs, deli meats, and luncheon meats - unless they're reheated until steaming hot.
- Soft cheeses like Feta, Brie, and Camembert, "blue-veined cheeses," or "queso blanco," "queso fresco," or Panela - unless they're made with pasteurized milk.
 Make sure the label says, "made with pasteurized milk."
Make sure the label says, "made with pasteurized milk." - Refrigerated pâtés or meat spreads.
- Refrigerated smoked seafood - unless it's in a cooked dish, such as a casserole. (Refrigerated smoked seafood, such as salmon, trout, whitefish, cod, tuna, or mackerel is most often labeled as "nova-style," "lox," "kippered," "smoked," or "jerky." These types of fish are found in the refrigerator section or sold at deli counters of grocery stores and delicatessens.)
- Raw (unpasteurized) milk or foods that contain unpasteurized milk.
It's okay to eat:
- Canned or shelf-stable (able to be stored unrefrigerated on the shelf) pâtés and meat spreads.
- Canned or shelf-stable smoked seafood.
- Pasteurized milk or foods that contain pasteurized milk.
Note: See your doctor or healthcare provider if you have questions about listeriosis.
>
Listeriosis During Pregnancy
Pregnant women are told time and again: Don’t eat raw meat, avoid unpasteurized cheese, steer clear of deli counter salads. Why? You can largely blame listeriosis, a foodborne illness that doesn’t pose much risk for mom but can be harmful for baby. Find out what causes listeriosis, what your odds are of contracting it and the steps you can take to prevent it.
Why? You can largely blame listeriosis, a foodborne illness that doesn’t pose much risk for mom but can be harmful for baby. Find out what causes listeriosis, what your odds are of contracting it and the steps you can take to prevent it.
What Is Listeriosis?
Technically speaking, listeriosis is an infection caused by Listeria monocytogenes bacteria. Practically speaking, listeriosis is a type of food poisoning that can cause pregnancy complications.
Listeria bacteria are found in soil, water and sewage, but they can also contaminate food—so if you eat something that’s been contaminated with listeria, you can develop listeriosis. The listeria bacteria is killed with heating and pasteurization, so listeriosis is usually linked to eating uncooked meats or vegetables, raw or unpasteurized milk products, or processed foods (such as hot dogs and deli meat) that become contaminated after being cooked at the food processing facility.
Listeriosis can make people feel sick, but rarely causes severe health problems. What’s scary for moms-to-be, however, is that having it during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and preterm birth. Babies of moms who had listeriosis during pregnancy are also at risk for listeria infection.
What’s scary for moms-to-be, however, is that having it during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and preterm birth. Babies of moms who had listeriosis during pregnancy are also at risk for listeria infection.
How Common Is Listeriosis During Pregnancy?
Wondering what are the odds of getting listeriosis while pregnant? Good news—they’re very low. It’s true that pregnant women have an increased risk of contracting listeriosis, but the real risk is still tiny. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), there are approximately 1,600 cases of listeriosis in the United States each year. But only about one in seven cases—or about 200 cases per year—occur in pregnant women, out of nearly 4 million pregnancies every year.
“You’re much more likely to step outside and slip on ice on your front steps in the winter than you are to contract listeria,” says Kelly Kasper, MD, ob-gyn and associate clinical professor at the Indiana University School of Medicine. And if you do get listeria, baby might not— transmission of listeriosis from mom to baby is not a sure thing. Plus, listeria infections are easily treatable with antibiotics.
And if you do get listeria, baby might not— transmission of listeriosis from mom to baby is not a sure thing. Plus, listeria infections are easily treatable with antibiotics.
How Do You Know If You Have Listeriosis?
“The symptoms of a listeria infection look a lot like a cold or mild flu,” Kasper says. “The most common symptom is a fever. You might also have muscle aches or a sore throat.” Some people also have diarrhea.
Because the symptoms are so nonspecific, it’s impossible to tell if you have listeriosis solely based on symptoms. That’s why doctors tell pregnant women to contact their health care provider if they’re running a fever—not because they’re always worried about listeriosis, but because fever is a symptom of all kinds of ailments, many of which should be diagnosed and treated right away. The only way to figure out if your symptoms pose a threat to you or baby is to have them checked out by a qualified health care provider.
So how do you test for listeria in pregnancy? If your doctor suspects listeriosis—if you have symptoms of listeriosis and have recently eaten some suspect food, for instance—she can order a simple blood test to determine if you have listeriosis or not.
How Does Listeriosis Affect Baby?
Listeriosis increases the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, preterm delivery and listeriosis infection once baby is born, but the odds of anything bad happening to baby are slim. Here’s why:
• Listeria infection can spread from mom to baby through the placenta, but it’s not a sure thing. So even if you get listeriosis, baby might not. The antibiotics used to treat listeriosis during pregnancy can prevent infection of the fetus.
• Antibiotics can also be used to treat (and prevent complications of) listeriosis in newborns. While listeriosis in babies can cause severe blood infections, meningitis, pneumonia and even death, treatment with antibiotics can resolve the infection and usually prevent complications.
How To Prevent Listeriosis During Pregnancy
If you want to decrease your risk of getting listeriosis to almost zero, you can follow the official listeriosis prevention guidelines and avoid eating the following during pregnancy:
- Unpasteurized soft cheeses
- Refrigerated smoked seafood
- Raw or unpasteurized milk products
- Cold (or room temp) deli meats or hot dogs (they’re fine if they’re heated to steaming hot)
- Prepared deli counter salads, such as egg salad, tuna salad and seafood salad
Or you can take a slightly more relaxed approach. Given the extreme improbability of contracting listeriosis from properly handled foods, Kasper suggests eating food you’ve prepared yourself and following common sense guidelines when you prep and store it:
Given the extreme improbability of contracting listeriosis from properly handled foods, Kasper suggests eating food you’ve prepared yourself and following common sense guidelines when you prep and store it:
• Store foods safely. Make sure your refrigerator is set to 40 degrees Fahrenheit or below, and return items to the fridge as soon as possible after using. Don’t let foods sit out for long periods at room temperature.
• Wash fruits and vegetables. Rinse any raw produce thoroughly under running tap water before eating.
• Pay attention to expiration dates. If your lunch meat is past its expiration date (or if it smells or looks funny), throw it away.
“You want to be smart about listeria and keep yourself healthy. But at the same time, you don’t want to quit living,” Kasper says. “There are some things that we know are very important, common and threatening to a pregnancy, like influenza—that’s why we recommend the flu shot. Listeriosis is very uncommon. You don’t have to put yourself in a plastic bubble because you’re afraid of what might happen.”
Listeriosis is very uncommon. You don’t have to put yourself in a plastic bubble because you’re afraid of what might happen.”
What do you do if you have listeriosis? Oral antibiotics can effectively treat listeriosis during pregnancy. Taking the antibiotics can help baby as well. Research shows that treating moms-to-be with high doses of antibiotics during pregnancy decreases the incidence of listeriosis-related preterm births and stillbirths.
Stories From Moms-To-Be Who Have Had Listeriosis
“I know it’s rare but my doula ate a sub and she got so sick from listeriosis she went into labor. Thankfully she was full term. My OB is very strict about [sticking to safe foods]. That says something about the potential dangers. Something to keep in mind—to me [eating certain foods is] not worth the risk.”
“A friend of mine had listeriosis during her first pregnancy—the baby was okay!—and from what she told me, it was constant, uncontrollable vomiting. She said she was puking every five minutes, for a good hour or so. Poor thing!”
Poor thing!”
“A woman who goes to my OB practice did get listeriosis while I was pregnant with my first child and it did not have a good outcome. Even the doctors in the practice were shocked because it is so rare.”
Expert source: Kelly Kasper, MD, ob-gyn and associate clinical professor at the Indiana University School of Medicine.
Please note: The Bump and the materials and information it contains are not intended to, and do not constitute, medical or other health advice or diagnosis and should not be used as such. You should always consult with a qualified physician or health professional about your specific circumstances.
4 main symptoms of listeriosis and how to avoid it
Listeriosis is a foodborne bacterial disease that can lead to devastating consequences in pregnant women and people with weakened immune systems. Listeria is most commonly found in improperly processed and cooked meats and unpasteurized dairy products.
Healthy people rarely experience this infection, but it can be fatal for newborns or unborn babies. Immunocompromised individuals are also at higher risk of life-threatening complications. That is why, at the first suspicion, it is necessary to take an analysis for listeriosis. Timely treatment helps prevent or mitigate the development of complications.
Immunocompromised individuals are also at higher risk of life-threatening complications. That is why, at the first suspicion, it is necessary to take an analysis for listeriosis. Timely treatment helps prevent or mitigate the development of complications.
The peculiarity of this bacterium is the ability to survive and develop in chilled and even frozen foods. For this reason, people who are at higher risk of infection should avoid foods that may contain this bacterium.
If you develop this infection, you may experience the following symptoms:
- Fever,
- Muscle pain,
- Nausea,
- Diarrhea.
Symptoms of listeriosis may appear several days after eating contaminated food. However, for some, a month or even more passes before the first signs of the disease appear.
If listeria spreads to the nervous system, the patient may experience additional symptoms, including:
- Headaches,
- Hardening of the neck muscles,
- Confusion in the mind,
- Loss of balance,
- Seizures.

How does listeriosis manifest itself during pregnancy and newborns?
Compared to other healthy adults, pregnant women are more susceptible to this infection. In most pregnant women, the bacterium causes only mild symptoms. But the consequences for the child can be dire. The baby may die unexpectedly or face a life-threatening infection during the first days after birth. Sometimes miscarriages happen.
As with adults, listeriosis symptoms in newborns may be mild. They include:
- Weak desire to eat,
- Irritability,
- Fever,
- Vomiting.
Listeriosis in people with weakened immunity:
This category of people includes:
- persons over 60 years old,
- AIDS/ AIDS,
- people who are taking place chemotherapy,
- People with kidney disease or diabetes,
- People taking large doses of prednisone or certain drugs for rheumatoid arthritis,
- People taking drugs after organ transplants (immunosuppressants).

Listeria can be found in soil, water or animal feces. Most often people become infected after eating:
- Infected meat,
- Unpasteurized milk or products made from it0012
- Raw vegetables that have been contaminated from soil or manure used as manure
When to run to the doctor?
If you have been eating foods that have since been taken off the market due to Listeria, listen to your body. If the four main symptoms appear, immediately go to the doctor. The same goes for eating foods that may have been contaminated: unpasteurized milk, an undercooked hot dog, or deli meats. If after using them symptoms of listeriosis appear, go get tested.
If you have additional symptoms that affect the nervous system, call an ambulance. These symptoms may indicate the development of one of the life-threatening complications - bacterial meningitis.
In most cases, this infection is so mild that patients may not notice anything. But this does not negate the fact that this disease can lead to life-threatening complications. These include:
But this does not negate the fact that this disease can lead to life-threatening complications. These include:
- Blood poisoning (septicemia),
- Inflammation of the membranes and fluid that surrounds the brain (meningitis),
- Miscarriage in early pregnancy (in 20% of cases),
- The development of a deadly infection in a child during the first days after birth (even if the infection was very mild in the mother).
The most effective way to detect this infection is through a blood test to determine the DNA of the bacterium. By the way, if you live in Kyiv, you can take this test at our medical center in Troyeschina.
In some cases, additional research methods are required - analysis of urine or cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment for listeriosis varies according to the severity of the symptoms. Most people with a mild infection do not need to be treated, but should be monitored by a doctor. In severe cases, antibiotics are prescribed.
Listeriosis during pregnancy must be treated very quickly. The main goal is to prevent the transmission of infection from mother to child. If the baby was born with this infection, he may be prescribed a combination of several antibiotics.
as prevent This ?
To prevent listeriosis infection, follow these simple guidelines:
- Practice good hygiene: always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before and after preparing food. After cooking, wash utensils and surfaces, especially cutting boards. In this case, it is necessary to use detergent and hot water.
- Thoroughly clean the surface of raw vegetables with a peeling brush or a vegetable brush. Do this under strong running water.
- Bring food to full readiness. Check each time that meat and egg dishes have been fully cooked through.
Precautions for people at risk
Recall that this group includes pregnant women and immunocompromised people. In their case, it is necessary to apply additional preventive measures with the following types of products:
In their case, it is necessary to apply additional preventive measures with the following types of products:
- Unpasteurized milk - cut it out completely.
- Soft cheeses. Avoid soft cheeses like feta, brie, camembert and blue cheese unless the label says the cheese was made with pasteurized milk.
- Hot dogs and deli meats. Eat them only if they have been thoroughly cooked under high temperature (until steam appears). Wash your hands thoroughly after preparing hot dogs and charcuterie.
- Chilled or frozen smoked seafood and dried meats. Do not eat these foods. Only canned smoked seafood is acceptable.
Now you know how to reduce your risk of contracting Listeria. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 260 people die from this infection every year in the United States. Therefore, at the first suspicions, it is better to take an analysis for listeriosis and be calm.
Sources:
- Listeria infection, Mayo Clinic,
- What Is Listeria, WebMD,
- Listeria (Listeriosis), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC.

infection
bacterial infection
blood test
gastroenterologist
Our Blog | POLYCLINIC 6
The appeal can be opened by this link
Published
Appeal can be opened at this link
Published
We invite you to read the instructions for using the Talon.by service to order coupons remotely.
Link to instruction: https://blog.talon.by/article/kak-zakazat-talon-na-talonby
Published
Published
Pensioners are one of the most important categories of the population, which is under close attention of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. To ensure safety and reduce the number of "fiery" incidents with their participation, propagandists use various forms of work, one of which is the republican action "Caring for the safety of the small Motherland", the purpose of which is to prevent fires due to careless handling of fire and death on them elderly people.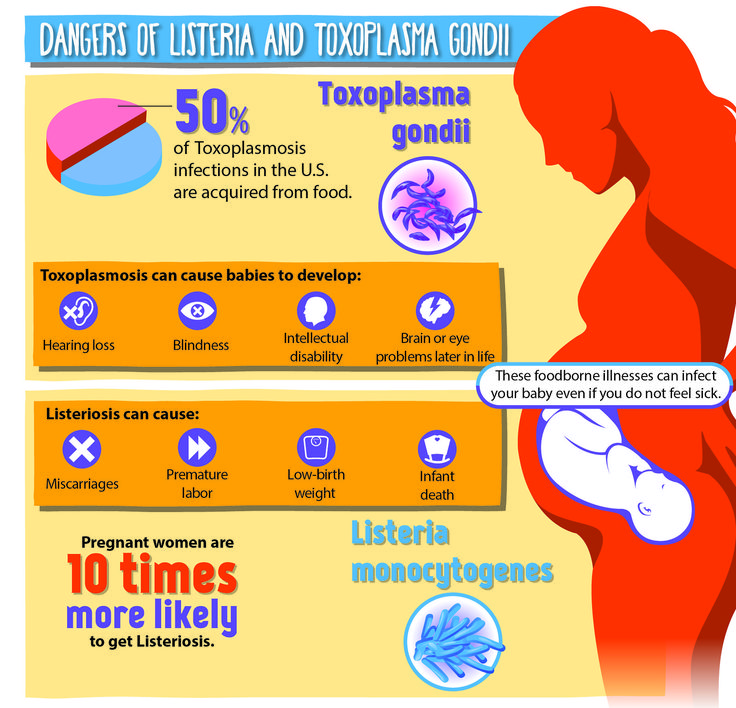
It will be held in two stages: the first - from August 1 to 19, and the second - from September 19 to October 1. A lot of interesting things are planned during the stages.
Published
Published
Today, not only adults have mobile phones, but also every child. These modern gadgets allow you to stay in touch with your family, and can also replace other popular devices: player, TV, computer, camera. All phones have batteries that are charged from the mains. Sometimes improper use of the phone, violation of safety rules can lead to a fire or injury to a person.
Another instructive story from Borisov, in which the whole family almost died due to inattentive handling of electrical appliances.
https://youtu.be/ejvt6mf7Lf4?t=563
Published
Be careful when relaxing on water!
The weekend is ahead and the forecasters promise real summer weather. To escape from the heat of the city, many rush to the reservoirs. Do not forget that water is a source of increased danger, and carelessness can overshadow the rest.
To escape from the heat of the city, many rush to the reservoirs. Do not forget that water is a source of increased danger, and carelessness can overshadow the rest.
Really hot summer weather has set in. To escape from the heat of the city, many rush to the reservoirs. Do not forget that water is a source of increased danger, and carelessness can overshadow your vacation. Listen to the recommendations of the Ministry of Emergency Situations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uLw2xgkyz2s
https://mchs.gov.by/glavnoe/393512/
Published
On the basis of the health care institution "23rd City Polyclinic" a district office was organized to provide gynecological care to women in wheelchairs (hereinafter referred to as the Office) in room No. 306 with a working schedule from 16.00 to 20.00.
To be referred to the Cabinet, you must contact the head of the antenatal clinic of the 6th polyclinic by phone 215 64 22 or in person room.