Can you miscarry at 18 weeks
Understanding Second Trimester Loss | Obstetrics and Gynecology
Pregnancy loss in the second trimester can be the result of a very preterm delivery (like a spontaneous miscarriage in the second trimester) or death of the fetus (called a fetal demise). About 2-3% of pregnancies will be lost in the second trimester, a rate that is much lower than in the first trimester. Once a pregnancy gets to about 20 weeks gestation, less than 0.5% will end in a fetal demise.
A loss at this time in pregnancy is most often a hard and sad experience. Many friends and family already know you are pregnant. What do you do? What do you say? For most women and their partners, the process of grieving is no different than losing a person who has been in your life for some time. You often have hopes and dreams about your child before that child is born, and losing the pregnancy in the second or third trimester is certainly a loss for a family.
Why see a UC Davis Health specialist?
Our specialists can evaluate you quickly in an office setting. Any laboratory testing or ultrasound examinations that need to be done can be performed easily and conveniently. We perform our own ultrasound examination in the office and can share the results with you immediately. Treatment of a second trimester loss is very different than early miscarriage, and our specialists can provide all options to you and your family. We understand that losses at this time require both emotional and medical support. We are happy to review all treatment options but also know that you may need some time. It is also important for you to know that a fetal demise in the second trimester is not a medical emergency so treatment is not immediately indicated.
If you are having very heavy vaginal bleeding or are feeling very sick, you should go to the Emergency Room to see our physicians.
Symptoms of a second trimester loss
- Bleeding: Most commonly, bleeding is a sign of a problem with the placenta and does not indicate a fetal demise. But, bleeding can be a sign that the cervix is opening without labor (called cervical insufficiency).
 With cervical insufficiency, the cervix begins to open early without contractions; as the cervix opens more, contractions then follow.
With cervical insufficiency, the cervix begins to open early without contractions; as the cervix opens more, contractions then follow. - Cramping: Pregnancy losses in the second trimester can be due to early labor.
- Loss of fetal movement: This can indicate a fetal demise. Most women can feel the baby moving by the 20th week. If the baby has been moving and you no longer feel that same movement, it is important to contact the doctor’s office immediately to make sure the baby is fine. Decreased fetal movement is more commonly a sign that there is a problem with the pregnancy and only rarely does it mean the fetus has died.
Most women less than 20 weeks of pregnancy do not notice any symptoms of a fetal demise.
The test used to check for a fetal demise in the second trimester is an ultrasound examination to see if the baby is moving and growing. Fetal demise is diagnosed when the ultrasound examination shows no fetal heart activity.
What causes a second trimester loss?
The causes of a pregnancy loss in the second trimester are very different than early pregnancy loss. There are medical conditions that increase the risk for cervical insufficiency or preterm labor before viability which include:
There are medical conditions that increase the risk for cervical insufficiency or preterm labor before viability which include:
- Prior surgery to the cervix
- Use of illicit drugs, especially cocaine
- Fetal abnormalities (genetic or structural problems)
- Uterine infection (this is more common in developing countries and less common in the United States)
- Physical problems with the uterus, including fibroids or abnormalities in the shape of the uterus
There are also some medical conditions that are associated with fetal death in the second trimester which include:
- Fetal abnormalities (genetic or structural problems)
- Poorly controlled maternal cnoditions like thyroid disease, diabetes or hypertension
- Lupus (systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Autoimmune or genetic conditions that increase a woman’s risk of forming blood clots in her legs or her lungs (like antiphospholipid syndrome)
- Very early pre-eclampsia or eclampsia of pregnancy
- Trauma
The specialists at UC Davis Health will review with you what testing is indicated to help learn more about why a second trimester loss occurred. Despite the testing that is available, about half of the time there is no identifiable reason for a second trimester loss. We can work with you to figure out what may be helpful with a next pregnancy or to learn more about medical issues that are important for your future.
Despite the testing that is available, about half of the time there is no identifiable reason for a second trimester loss. We can work with you to figure out what may be helpful with a next pregnancy or to learn more about medical issues that are important for your future.
Treatment of a second trimester loss
It is typically not safe for a woman to wait for the pregnancy to deliver on its own with a second trimester loss. There is a high chance of having significant bleeding when a pregnancy in the second trimester delivers on its own at home. In the case of fetal demise, a dead fetus that has been in the uterus for 4 weeks can cause changes in the body’s clotting system. These changes can put a woman at a much higher chance of significant bleeding if she waits for a long time after the fetal demise to deliver the pregnancy.
Our doctors are committed to providing all available treatment options. Testing to figure out the cause of the pregnancy loss can be performed regardless of the method a woman chooses for termination.
We understand that a second trimester loss is an emotional and stressful time and we want to ensure that the emotional needs of you and your family are met as well. We understand this is a time that you need support and we are sensitive to your wishes for remembrances and religious preferences. We will discuss these issues with you before any treatment.
When a diagnosis of fetal demise in the second or third trimester is made, options include:
- Surgical evacuation: This procedure, called a dilation and evacuation, can be performed in the second trimester, typically up to about 24 weeks. Surgical evacuation is the most common treatment women choose and involves removing the pregnancy through the cervix in the operating room while you are asleep. The cervix needs to be opened about 1-2 inches in diameter. The doctors can use different ways to open the cervix based on how far along the pregnancy is and your individual circumstance. The goal is to provide the safest care for each patient.
 After a surgical evacuation, normal activity can typically be resumed the following day. Opening or preparing the cervix for surgical evacuation of the pregnancy may involve:
After a surgical evacuation, normal activity can typically be resumed the following day. Opening or preparing the cervix for surgical evacuation of the pregnancy may involve: - Medicines (tablets) that are put in the vagina a few hours to one day before the procedure.
- Medicine (tablets) that you hold between your cheek and gums for 30 minutes before swallowing. You would use this medicine a few hours before the procedure.
- Placing thin sticks in your cervix, called osmotic dilators, to absorb water from the cervix which causes the dilator sticks to swell slowly over 4-24 hours. Having the osmotic dilators placed is similar to getting a Pap test.
Labor induction: This treatment uses medicines to cause the uterus to go into labor. For women with pregnancies beyond 24 weeks, this is commonly the only option. If you choose this option, you will be in the Labor and Delivery Unit at UC Davis Medical Center and will have all of the same pain treatments available to you as a woman who is naturally in labor (like IV pain medications or an epidural). The treatment typically starts with swallowing a pill to make the uterus more sensitive to the medications to induce labor. About 24 hours later, you are admitted to the Labor and Delivery Unit and will have medicine (tablets) put in the vagina every few hours to cause labor. Sometimes, women need medicine through an IV to also help get labor started. It may take 1-2 days for the uterus to go into labor and for the delivery to be complete. Up to 5% of women in the second trimester do not go into labor and need a surgical evacuation.
The treatment typically starts with swallowing a pill to make the uterus more sensitive to the medications to induce labor. About 24 hours later, you are admitted to the Labor and Delivery Unit and will have medicine (tablets) put in the vagina every few hours to cause labor. Sometimes, women need medicine through an IV to also help get labor started. It may take 1-2 days for the uterus to go into labor and for the delivery to be complete. Up to 5% of women in the second trimester do not go into labor and need a surgical evacuation.
Your doctor will be able to explain more details about the pros and cons of each treatment.
After treatment of a second trimester loss
Bleeding may continue for several weeks after a labor induction but tends to be much lighter with a surgical evacuation. Any bleeding may change in color from bright red to pink or brown. Lower abdominal cramping in the few days after treatment is also common. You should contact a doctor right away if the bleeding gets heavier instead of lighter over time, if a fever develops, or if vaginal discharge or a strange or unpleasant vaginal odor occurs. Avoid intercourse, douching, or using tampons for one week. Regular activities can be resumed right away, based on how you feel. Importantly, if you want to delay getting pregnant, it will be very important to start an effective method of contraception.
Avoid intercourse, douching, or using tampons for one week. Regular activities can be resumed right away, based on how you feel. Importantly, if you want to delay getting pregnant, it will be very important to start an effective method of contraception.
FAQs about second trimester loss
Q: What is cervical insufficiency?
A: This diagnosis is made when a woman has dilation of the cervix during the second trimester without having any contractions or signs of a uterine infection. Some studies suggest that some types of surgeries performed when women have advanced pre-cancerous changes in the cervix can increase the risk of cervical insufficiency. These surgeries include cervical conization (also known as a “cone biopsy”) or if a patient has had multiple LEEP procedures. With these surgeries, part of the cervix is removed to get rid of the pre-cancerous changes. Having these procedures increases the risk of having a second trimester loss by about 1%. In women who have these types of procedures, the chance of having cervical insufficiency is about 1.5%.
In women who have these types of procedures, the chance of having cervical insufficiency is about 1.5%.
Q: What treatments are available if one of the tests shows I have a medical problem that increased the chance of a second trimester loss?
A: Our specialists will work with you to maximize your health status before you try to get pregnant again. For some women, this may mean treatment of a thyroid condition, improved control of diabetes, or changing medications being used for chronic illnesses. Some conditions may require blood thinners like aspirin or injectable medications that should be started early in the next pregnancy (after a normal pregnancy is seen with an early ultrasound exam).
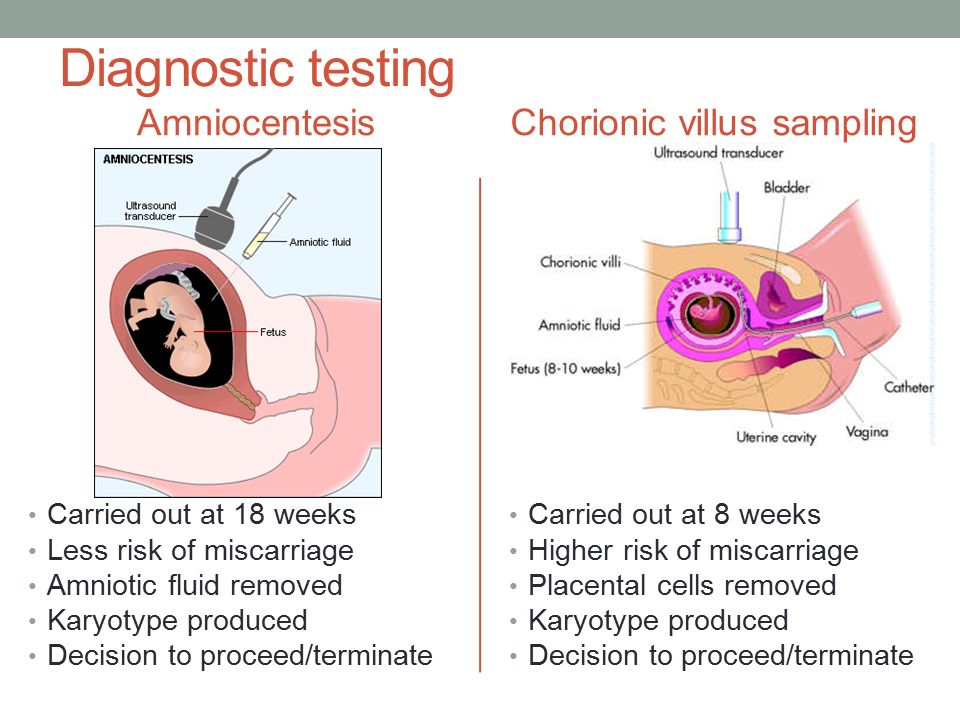
Q: In my last pregnancy, I didn’t get any genetic testing and had a second trimester demise related to a genetic abnormality. What genetic testing is available for my next pregnancy to help figure out if the pregnancy is normal so I can learn earlier if the pregnancy is genetically normal?
A: It will be important to meet with a genetic counselor, if possible, before your next pregnancy, who can also review the details of the available tests. The counselor can also talk with you more about your history and your family history to make sure no genetic or familial medical problems are missed. There are a few different tests, all of which can be performed early in pregnancy, depending on what is right for you. Screening for some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities just from your blood (called NIPT or non-invasive prenatal testing). First trimester screening can be performed between 11 and 14 weeks which involves a blood test and an ultrasound examination. In some situations, chorionic villus sampling (a biopsy of the placenta) or expanded prenatal screening may be indicated. Our specialists and genetic counselors can work with you and your family to help you understand all of these tests and figure out what approach is right for you.
The counselor can also talk with you more about your history and your family history to make sure no genetic or familial medical problems are missed. There are a few different tests, all of which can be performed early in pregnancy, depending on what is right for you. Screening for some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities just from your blood (called NIPT or non-invasive prenatal testing). First trimester screening can be performed between 11 and 14 weeks which involves a blood test and an ultrasound examination. In some situations, chorionic villus sampling (a biopsy of the placenta) or expanded prenatal screening may be indicated. Our specialists and genetic counselors can work with you and your family to help you understand all of these tests and figure out what approach is right for you.
Q: After a second trimester loss, how long should I wait before I try to conceive again?
A: There is really no good information available to show the absolute right answer to that question. First, it may take a month or two to have any testing completed to help figure out why you had a second trimester loss. We know that it takes some time for your uterus and your body to get back to normal. The specialists at UC Davis usually recommend waiting at least 3 months after a second trimester loss before trying again to get pregnant.
First, it may take a month or two to have any testing completed to help figure out why you had a second trimester loss. We know that it takes some time for your uterus and your body to get back to normal. The specialists at UC Davis usually recommend waiting at least 3 months after a second trimester loss before trying again to get pregnant.
Late miscarriage: second trimester loss
Most miscarriages happen in the first 12 or 13 weeks of pregnancy. It is much less common to miscarry after this stage. We provide some information on second trimester loss on this page, and more on the emotional impact here.
Late miscarriage, also called second-trimester or mid-trimester loss, refers to a miscarriage that happens when a baby dies between 14 and 24 weeks of pregnancy.
If a baby dies before 14 weeks but the miscarriage itself happens later, that is usually considered to be a missed or silent first-trimester loss.
If a baby dies at or after 24 weeks of pregnancy, this is called a stillbirth.
(These definitions apply to the UK – they can differ in other countries.)
You may find it very hard to understand why a very late loss is called a miscarriage rather than a stillbirth. The reason is that 24 weeks of pregnancy is the legal age of viability in the UK – the stage at which a baby is thought to stand a good chance of surviving if born alive. Some parents find this distinction very upsetting.
We talk more about the emotional impact of late loss here and you can find people’s stories about late loss here.
Why do late miscarriages happen?
There are several known causes of late miscarriage. Some can cause earlier losses too, while others can cause problems after 24 weeks of pregnancy as well as before. Most miscarriages at whatever stage happen because of an abnormality in the baby.
Causes of late miscarriage
The main causes of late miscarriage are thought to be:
- Chromosome problems: These are usually one-off events, happening out of the blue, but they might be due to a problem that you or your partner have, probably without knowing.
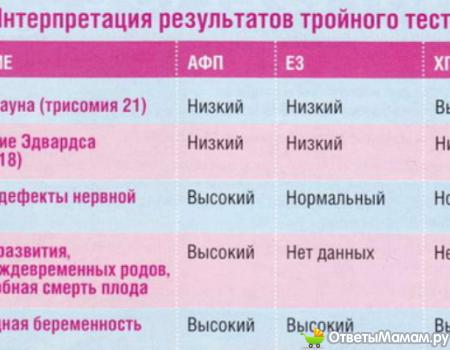
 Examples of chromosome arrangements or differences that can cause miscarriage are Downs Syndrome, Edwards Syndrome and Turners Syndrome.
Examples of chromosome arrangements or differences that can cause miscarriage are Downs Syndrome, Edwards Syndrome and Turners Syndrome. - Genetic: This is when the baby doesn’t develop normally right from the start and cannot survive. This is the cause of more than half of all early miscarriages, but it can cause late loss too.
- Structural: Problems in the baby’s body, for example spina bifida or a congenital heart defect.
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS): APS is a condition that increases blood-clotting. If blood clots too easily during pregnancy, it can cause early or late miscarriage, as well as other pregnancy problems.
- Infection: Some infections can cause a late miscarriage, either by infecting the baby or by infecting the amniotic fluid (the liquid around the baby).
- Anatomical: There are two main anatomical causes of late miscarriage:
- an unusually shaped womb (uterus), especially one that is partly divided in two
- a weak cervix (the neck of the womb), which may start to open as the uterus becomes heavier in later pregnancy and thus cause a miscarriage.
There is more detailed information about causes, management and investigations of late miscarriage here.
Miscarriage
Gynecology
Miscarriage (spontaneous abortion, miscarriage) is the spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the period from conception to the 28th week. Miscarriage up to 28 weeks is referred to as spontaneous miscarriages (abortions), termination of pregnancy in terms of more than 28 weeks - to premature birth. Spontaneous miscarriages are divided into early (up to 16 weeks) and late (from 16 to 28 weeks). There is also habitual miscarriage (termination of pregnancy two or more times in a row).
Unfortunately, today, premature termination of pregnancy is not such a rare occurrence. According to statistics, in the last 40 years, almost every fifth pregnancy ended in miscarriage. Scientific studies say that in fact, more than half of spontaneous miscarriages! But this happens during the first three or four days of pregnancy, and therefore women do not even realize that they were pregnant for some time: after all, the next menstruation came either on time or with a slight delay. Naturally, such cases could not be taken into account by medical statistics. An analysis of reported cases of spontaneous abortions shows that 80% of them occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Naturally, such cases could not be taken into account by medical statistics. An analysis of reported cases of spontaneous abortions shows that 80% of them occur in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy.
The causes of spontaneous miscarriage are numerous. More than half of them are associated with genetic causes - violations of the quantity and quality of chromosomes in the cells of the embryo, as a result of which it becomes unviable, dies and is removed from the uterus. In this case, spontaneous miscarriage is the result of natural selection working against unviable fetuses.
In addition, miscarriage can be caused by various infections, chronic diseases, disorders in the immune system. Gynecological problems also play an important role - inflammatory diseases of the genital organs, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, postoperative scar on the uterus, uterine malformations, cervical insufficiency and various hormonal disorders , of which ovarian hypofunction and hyperandrogenism, genital and general infantilism are the most common.
Miscarriage is practically not affected by light falls and lifting of moderate weights by the mother. The fetus is sufficiently protected, and if the mother's body is healthy and the fetus's genetic program is normal, then the injury must be truly terrible to harm the fetus.
The causes of recurrent miscarriage (i.e., multiple spontaneous abortions) are practically the same, but a violation of the immune system plays a more definite role when the development of maternal sensitization to fetal tissue antigens or erythrocyte and leukocyte sensitization reactions takes place.
The clinical picture of premature termination of pregnancy depends on the stage of miscarriage and the duration of pregnancy. Usually, with the threat of interruption, pregnant women complain of pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, periodic tension (tonus) of the uterus. There are five stages in the course of early abortion: threatening, incipient abortion, ongoing abortion, incomplete and complete abortion. Early abortions are characterized by the birth of the entire fetal egg. The correct regimen and treatment in the first two stages can save the pregnancy. In subsequent stages, the removal of the entire fetal egg or its delayed parts is required. Symptoms of a threatened and incipient abortion are distinguished by the state of the cervix: it is unchanged in a threatened abortion and somewhat shortened with a closed or ajar canal in an incipient abortion. In addition, the intensity of the pain syndrome, the degree of uterine tension and / or the presence of blood discharge are taken into account.
Early abortions are characterized by the birth of the entire fetal egg. The correct regimen and treatment in the first two stages can save the pregnancy. In subsequent stages, the removal of the entire fetal egg or its delayed parts is required. Symptoms of a threatened and incipient abortion are distinguished by the state of the cervix: it is unchanged in a threatened abortion and somewhat shortened with a closed or ajar canal in an incipient abortion. In addition, the intensity of the pain syndrome, the degree of uterine tension and / or the presence of blood discharge are taken into account.
Late miscarriage proceeds according to the type of childbirth: there is an opening of the cervix, then the outflow of amniotic fluid, the birth of the fetus and, finally, the birth of the placenta. Clinically, it is manifested by cramping or aching pain in the lower abdomen, periodic uterine tension and, less commonly, bloody discharge.
If there is a threat of termination of pregnancy, complex treatment is prescribed: medications, especially hormonal ones, are prescribed only according to strict indications and in minimal doses, since the consequences of hormonal treatment on both the fetus and the unborn child can appear even after many years.
In order to determine the cause of miscarriage, the doctors of our Clinic in each case are assigned an individual comprehensive examination: genetic, gynecological, ultrasound, laboratory, etc. If intrauterine pathology and / or endometrial pathology are suspected, separate diagnostic curettage is performed under hysteroscopy control, and if endometriosis is suspected, tubal pathology and adhesive process in the pelvis, with uterine myoma and scleropolycystic ovaries, operative laparoscopy may also be necessary. Such a large volume of examination should be clear to the patient: after all, miscarriage, as a rule, is the result of not one, but several causes that have their effect simultaneously or sequentially. In addition, many women who have experienced a spontaneous miscarriage may need the help of a psychotherapist who can provide professional advice to help eliminate the negative psychological consequences of this phenomenon. After the examination, a set of appropriate therapeutic measures is planned, depending on the identified factors of miscarriage. The patient's partner is also examined, which includes the identification of hereditary diseases, clarification of the presence of previously or currently existing diseases of various organs and systems, semen analysis and examination for infections.
The patient's partner is also examined, which includes the identification of hereditary diseases, clarification of the presence of previously or currently existing diseases of various organs and systems, semen analysis and examination for infections.
Prevention of miscarriage is carried out both before and during pregnancy. Our obstetricians-gynecologists conduct a special examination for all women who have undergone spontaneous abortion and preterm birth, including a targeted history taking, elucidation of the features of menstrual function (by functional diagnostic tests), hysterosalpingography and ultrasound scanning. According to strict indications, a strictly defined bacteriological, virological, immunological and genetic study is prescribed. If deviations from the norm are detected, they are corrected. During pregnancy, we single out a risk group for miscarriage, outline the terms and methods of treatment and preventive measures, recommend the sanitation of foci of chronic infection, which creates optimal conditions for the development of pregnancy. If the next medical examination confirms the presence of a threat of miscarriage, then urgent measures are prescribed to preserve the pregnancy, and most often the treatment we have performed is effective.
If the next medical examination confirms the presence of a threat of miscarriage, then urgent measures are prescribed to preserve the pregnancy, and most often the treatment we have performed is effective.
Miscarriage, how to avoid - Planning and management of pregnancy in the gynecology of the Literary Fund polyclinic after a miscarriage
- Gallery
- News
- Blog
- Reviews
- Jobs
- Licenses
- Insurance partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule of reception of citizens on personal appeals
- What you need to know about coronavirus infection?
- Rules for patients
- Online doctor's consultation
- to corporative clients
- The documents
A miscarriage is always associated with severe consequences for the whole body of a woman and for her reproductive organs in particular, it also affects the family situation, disrupts the woman's work schedule. An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
An unfavorable outcome of pregnancy requires great mental and physical costs on the part of parents. Therefore, contacting doctors to find out the causes of the problem is the very first and correct step towards the birth of a child.
Any competent gynecologist will tell you that the problem of miscarriage can be solved. With proper preparation for pregnancy and its management, the next time you will have a successful pregnancy. Most girls after a miscarriage go to extremes: they try to get pregnant again as soon as possible. And if this succeeds, then the miscarriage is very often repeated. And you need to give the body a rest for 2-3 months, then identify and eliminate the cause. And only then try.
Causes of miscarriage
Many are convinced that miscarriages are due to a fall, injury, or some other physical shock. Any woman who has had a miscarriage can remember that not long before she either fell or lifted something heavy. And I am sure that she lost her unborn child precisely because of this. However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
However, those women whose pregnancy was normal also fall and lift heavy things. Most sudden miscarriages do not occur for this reason. The reason is in violations of the pregnancy itself. Approximately half of miscarriages are due to abnormal genetic development of the fetus, which can be hereditary or accidental. Merciful nature, following the principles of natural selection in everything, destroys the defective and unviable fetus. But you should not be afraid of this. The fact that there is a defect in one embryo does not mean at all that all the others will be the same.
The woman's body is almost always to blame for the other half of miscarriages. They are caused by various known and unknown factors, such as: acute infectious diseases suffered in the first trimester of pregnancy, poor environment or difficult working conditions, excessive psychological or physical stress, abnormal development of the uterus, radiation, alcohol, smoking and certain types of drugs.
The causes of early and late miscarriage may differ, although they may overlap. The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
The most important thing is to find out and eliminate or compensate for your own cause of miscarriage. Having discovered the cause, the gynecologist will tell you how to avoid another loss.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage statistics also include “missed pregnancy”. Sometimes it happens that the embryo dies and lingers in the uterine cavity. Most often, this fact is detected by ultrasound. The dead fetus may begin to decompose, and this, thereby, will lead to poisoning of the mother's body.
Doctors resort to surgical curettage, which is associated with a risk of inflammation and complications. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy is planned after the body is fully restored - not earlier than a year. During this year, you will have to find out the cause of the missed pregnancy and treat it.
Miscarriage up to 6 weeks
The main causes of miscarriage on this line are malformations of the embryo itself. Statistics say that from 70-90% of embryos had chromosomal abnormalities: they are random and will not occur in other pregnancies. You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
You may have been ill, taken medication, or were under the influence of other harmful factors. Fate saved you from a child with malformations.
The human body is perfect and finds a way to correct the situation by miscarriage. Today is a tragedy for you. The real tragedy would be the preservation and birth of a sick, non-viable child. So don’t cry and understand: everything is for the best, you won’t help grief with tears ... And after three months, try again - it will almost certainly turn out to be successful.
It should also be noted that the fact of a miscarriage does not mean that you have lost something. So for a period of 7-8 weeks, the absence of an embryo in the fetal egg is found - "anembryony". It is believed that in 80-90% of cases, miscarriages are undiagnosed non-developing pregnancies.
Miscarriage between 6 and 12 weeks
Miscarriage during this period is also considered early. Its most common causes are:
Endocrine disorders
Endocrine disorders, when the ovaries do not synthesize enough hormones to keep the fetus in the womb, or the amount of male sex hormones is increased, is one of the most common causes of miscarriage and miscarriage.
Hormone imbalance in a woman's body is likely to lead to an early termination of pregnancy. With a lack of the main hormone progesterone produced by the ovaries, this happens most often. Another hormonal problem is an increase in the tone of the uterus, which provokes the expulsion of the fetus.
Progesterone prepares the uterine mucosa for implantation and is the hormone for maintaining pregnancy in the first months. If conception occurs, the fetus cannot properly establish itself in the uterus. As a result, the fertilized egg is rejected. But pregnancy can be saved with the help of progesterone preparations if this problem is detected in time.
An excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogens and progesterone can also be the cause of an early miscarriage. Often, the cause of recurrent miscarriages are androgens that affect the formation and development of pregnancy; as well as thyroid and adrenal hormones. Therefore, a change in the function of these glands can lead to miscarriage.
Undertreated sexual infections
This problem must be solved before conception. Often the cause of miscarriage is sexually transmitted infections: syphilis, trichomoniasis, toxoplasmosis, chlamydia, cytomegalovirus and herpetic infections. Their effect on the fetus and the course of pregnancy is different for each woman and depends on the timing of infection, the activity of the microorganism, the degree of immune protection and the presence of other adverse factors. Depending on the situation, they can lead to the formation of fetal malformations, intrauterine infection, feto-placental insufficiency, early miscarriage or premature birth. Infection of the fetus and damage to the membrane of the fetus leads to miscarriage. To avoid this, infections should be treated before pregnancy. The use of therapy is possible during pregnancy as prescribed by a doctor.
Viral infections and other diseases
Any disease accompanied by intoxication and fever above 38 o C can lead to a miscarriage. Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Rubella, influenza and viral hepatitis occupy a leading position in this list. At a period of 4-10 weeks for pregnancy, ordinary tonsillitis can also become tragic, pneumonia carries a more serious risk. Pyelonephritis and appendicitis can cause early labor. When planning a pregnancy, it is imperative to undergo a medical examination in order to identify and treat foci of infections.
Extremely dangerous during pregnancy rubella - it leads to severe fetal malformations, so infection during pregnancy is an indication for medical abortion.
Any disease during pregnancy can lead to non-viability of the fetus. And the body, through a miscarriage, insures you against unwanted offspring. With such a miscarriage, the next pregnancy has every chance of going well.
Immune causes of miscarriage
Sometimes antibodies that are hostile to the fetus are formed in the blood of a pregnant woman. This cause can be predicted and eliminated in advance. Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Most often, the conflict occurs when the embryo inherits the positive Rh factor of the father, and the negative Rh factor, the mother's body rejects the embryonic tissues that are alien to it. Constant monitoring of antibody titer and the introduction of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins allows you to maintain and maintain pregnancy. In case of an immune conflict, progesterone preparations are also used to prevent miscarriage, which in this case has an immunomodulatory effect.
Reduced immunity
Reduced immunity during pregnancy is also an immune cause. The body is simply not able to grow a new life in itself. You need to take care of yourself and recover before the next conception.
Anatomical causes of miscarriage
Anatomical causes of miscarriage are the most intractable. Malformations of the uterus are a serious reason for miscarriage. Sometimes you just have to deal with it.
Miscarriage between 12 and 22 weeks
Such a miscarriage is considered late. Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
Its causes coincide with the causes of miscarriages in the early stages (anatomical, immune, infectious, endocrine).
At this time, miscarriage also occurs due to isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a weak cervix cannot hold the fetus and opens. For this reason, a miscarriage can occur in the 2nd or 3rd trimester. Isthmic-cervical insufficiency is observed in 15.0-42.7% of women suffering from miscarriage. Careful monitoring of the pregnant woman allows you to identify the problem in time and make surgical correction of the cervix before the onset of childbirth.
In isthmic-cervical insufficiency, there is only one method of treatment - a mechanical narrowing of the cervical canal. To do this, the neck is either sewn up or a special ring is put on it. However, the latter method is less efficient, because the ring can easily slide off the neck, then it will no longer hold back the process of opening it.
After suturing, if necessary, it is possible to use antibiotics and drugs that normalize the microflora of the vagina. The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
The treatment of the vagina and the control of the state of the seams are carried out daily for 5 days. Stitches are removed at 37-38 weeks and with premature onset of labor.
Isthmic-cervical insufficiency may be primary (for no apparent reason), may be the result of abortion or hormonal disorders (increased levels of androgens - male sex hormones or their precursors).
Miscarriage after 22 weeks
Such a loss is hard to forget. Obstetricians talk about premature birth after the 28th week of pregnancy. Traditionally, a child born after this period is considered viable. But medicine knows many cases when it was possible to save the life of earlier children.
We recommend that you be carefully examined for miscarriage, check the above factors. In addition to them, the cause of a miscarriage can be antiphospholipid syndrome, while the woman's body perceives the child as something alien and rejects it. This disease, like the others listed, can be corrected; you have a very real chance of bearing a child.
Miscarriage due to impaired hemostasis
All of the above causes account for only 30-40%. Up to 70% of miscarriages are caused by disorders in the blood coagulation system (hemostasis).
Disorders of the blood coagulation system leading to pregnancy loss can be divided into thrombophilic (increased clotting) and hemorrhagic (a tendency to bleed). Both of these extremes are dangerous to the fetus. Various disorders leading to the formation of small blood clots lead to the fact that the fetus loses sufficient blood supply, development is disturbed and the fetus is rejected.
The main hemorrhagic changes can manifest themselves even in childhood in the form of increased bleeding during cuts, extractions of teeth, the onset of menstruation. But sometimes they declare themselves only during pregnancy and are the cause of a miscarriage. Bleeding in the early stages and detachment of the chorion is difficult to stop.
You may not guess, but incomprehensible headaches, weakness, fatigue, temporary loss of smell or hearing may be symptoms of a blood clotting disorder.