Can you miscarry and still be pregnant
How to tell if a miscarriage has happened
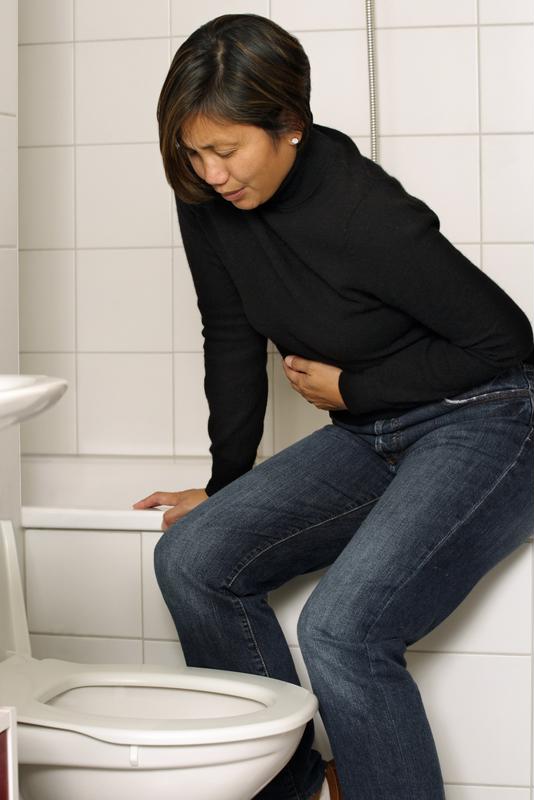
If you’ve heard the term miscarriage, you probably know that it means the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks’ gestation. Miscarriage is something that no one wants to think about during early pregnancy, but 10-20% of all known pregnancies end in miscarriage. Being able to recognize miscarriage symptoms and knowing what to do next can help you be more prepared in case one happens.
Miscarriage symptoms
A miscarriage can happen suddenly or gradually, which means that you may not notice any particularly early symptoms of a miscarriage. But no matter how fast it happens, key symptoms include:
- Pink, red or brown vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Cramps or pain in the lower abdomen
- Passing tissue or blood clots from the vagina
Every miscarriage is different. The heaviest bleeding and cramps may be over within a few hours, but bleeding could continue off and on for as long as three weeks. And although most people experience cramps, a miscarriage isn’t always painful.
Both vaginal spotting and mild cramps are common during early pregnancy, so it’s possible to have a miscarriage and not know it. This is why you should call your care provider if you experience any of the above symptoms once you’ve confirmed your pregnancy.
When do miscarriages happen?
Most miscarriages happen during the first trimester, which is the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. If you’re not tracking your menstrual cycle or fertility, it’s possible to mistake an early miscarriage for a period. And although miscarriages can still happen after the first trimester, the chances drop significantly – to around 3-4%. It’s also possible to have a pregnancy loss after 20 weeks, but this is referred to as a stillbirth. It’s treated differently and is much less common than a miscarriage.
Will a pregnancy test be negative after a miscarriage?
It takes time for your hormones to return to their pre-pregnancy levels after a miscarriage. The amount of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) may still be high enough to trigger a positive result on a pregnancy test for several weeks after a miscarriage.
The amount of the pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) may still be high enough to trigger a positive result on a pregnancy test for several weeks after a miscarriage.
What causes miscarriages?
One of the most important things to know about miscarriages is that they’re often caused by things that you have no control over, including:
- Chromosomal abnormalities: This is when a fertilized egg has too many or too few chromosomes. Chromosomal abnormalities account for around half of all miscarriages and are usually random. They can either prevent the embryo from developing or from forming in the first place.
- Uterine or cervical issues: In some cases, conditions related to the uterus or cervix can interfere with embryo development and lead to miscarriage. This includes conditions that create growths or scar tissue in the uterus like endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, and cervical insufficiency – which is when the cervix opens too early, typically in the second trimester.

- Infections: Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can cause you to miscarry. It’s important to get tested for STIs before you get pregnant, as you can have an infection without symptoms. You may also miscarry if you become infected with listeriosis, which is a type of food poisoning. This is why it’s recommended that you avoid eating certain foods during pregnancy.
In addition to the above, there are other factors that can increase your risk of miscarriage and other pregnancy complications. These risk factors include:
- Age: Pregnancy after age 35 comes with a higher risk of miscarriage. This is because as you age, eggs with extra or missing chromosomes become more common.
- Environmental exposure: Working around or otherwise being exposed to radiation, toxins or contaminants.
- Health conditions: Certain health conditions, like autoimmune disorders, thyroid disorders, severe diabetes and being over- or underweight.

- Lifestyle choices: Smoking, drinking alcohol and using drugs.
- Previous miscarriages: Having two or more miscarriages in a row can be a sign that you have a higher chance of miscarrying in general.
What does NOT cause a miscarriage
Physical activity and sex have not been linked to miscarriage. But if you’re ever unsure about whether something is safe to do during your pregnancy, talk to your care provider.
Some studies have shown that stress or high caffeine intake during pregnancy may increase miscarriage risk. More research is needed, but it’s recommended that you try to manage your stress as best you can, and keep your daily caffeine intake below 200 milligrams.
What to do if you have a miscarriage
Again, if you notice potential symptoms of a miscarriage, call your care provider. They will want to confirm the miscarriage and make sure that you aren’t at risk for heavy blood loss or infection. This is usually done with a pelvic exam and an ultrasound.
Miscarriages frequently resolve on their own without any need for treatment. It may take a few days to pass all of the tissue, and you may have moderate bleeding that lightens over the course of a couple weeks. Seek immediate medical treatment if you have heavy bleeding that does not lighten, fever, weakness or other signs of infection.
Medical treatment for a miscarriage
There’s no treatment that can stop a miscarriage. Instead, miscarriage treatment focuses on preventing excessive blood loss and infection, which can happen if the uterus isn’t completely cleared of tissue. Once a miscarriage has been confirmed, options for treatment may include:
- Medication: Medication can be used to speed up the passing of pregnancy tissue.
- Surgery: If there’s leftover tissue in the uterus or signs of heavy blood loss or infection, a minor surgery called dilation and curettage (D&C) may be performed. In a D&C, the cervix is dilated so that the remaining tissue can be gently removed.
 This option can also be chosen based on preference.
This option can also be chosen based on preference.
Tips for recovering from a miscarriage
- To prevent infection, avoid putting anything in your vagina during a miscarriage, and for two weeks afterwards. This means avoiding sexual intercourse and using pads instead of tampons.
- If you’re having painful cramps during or after a miscarriage, take acetaminophen – follow the label instructions.
- Your iron levels may drop as a result of the bleeding. To offset this and support your body’s blood production, eat a healthy diet that’s high in iron and vitamin C. Iron can be found in red meat, shellfish, beans and leafy green vegetables. Vitamin C can be found in citrus fruit, kiwis, bell peppers and many other vegetables.
- A miscarriage can be an emotionally difficult time, and there’s no right or wrong way to feel. It’s common to experience a variety of emotions, including mood swings, grief, anger and loneliness. Talk with family, friends or a counselor if you’re feeling overwhelmed or need support after a pregnancy loss.

- Be kind to yourself. The physical and emotional toll of a miscarriage can be draining. It’s okay to take a step back from your regular activities if you need to rest and recuperate.
- Once your miscarriage has been confirmed, go to any recommended follow-up appointments, and report new or worsening symptoms to your care provider as soon as possible.
Can you avoid a miscarriage?
After a miscarriage, it’s normal to wonder if you could have done anything differently. Remember, a miscarriage is rarely anyone’s fault, and there’s no sure way to prevent one from happening. That said, there are a few healthy lifestyle choices you can make to minimize your risk:
- If you smoke, drink alcohol or use drugs, quit as soon as possible.
- Get tested for STIs.
- Talk to a medical professional about any health conditions you haven’t had treatment for.
- Stick to any treatment plans or other methods you’ve already been given for managing health conditions.

- Get enough physical activity.
- Eat a balanced diet.
Keep your risk low
If you aren’t pregnant yet, one of the best things you can do to minimize your risk of miscarriage and other complications is to make a preconception appointment. This is an opportunity for your care provider to review your medical and lifestyle histories, and make recommendations that can give your pregnancy the healthiest possible start.
And if you’re already pregnant, stick to your prenatal appointment schedule. Your prenatal appointments ensure that you and your little one are getting all the care you need. Plus, these appointments give your care team the chance to catch signs and symptoms of complications before they affect your pregnancy.
Make a preconception appointment or a prenatal appointment.
Miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
The loss of a baby through miscarriage can be very distressing. A miscarriage generally occurs for reasons outside your control and nothing can be done to prevent or stop it from happening. Most women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have a healthy pregnancy in the future.
Most women who have had a miscarriage will go on to have a healthy pregnancy in the future.
What is a miscarriage?
A miscarriage is the loss of your baby before 20 weeks of pregnancy. The loss of a baby after 20 weeks is called a stillbirth.
Up to 1 in 5 confirmed pregnancies end in miscarriage before 20 weeks, but many other women miscarry without having realised they are pregnant.
Common signs of miscarriage include:
- cramping tummy pain, similar to period pain
- vaginal bleeding
If you think you are having a miscarriage, see your doctor or go to your local emergency department.
Many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester that does not result in pregnancy loss.
What are the types of miscarriage?
There are several types of miscarriage — threatened, inevitable, complete, incomplete or missed.
Other types of pregnancy loss include an ectopic pregnancy, molar pregnancy and a blighted ovum.
Threatened miscarriage
When your body is showing signs that you might miscarry, that is called a 'threatened miscarriage'. You may have light vaginal bleeding or lower abdominal pain. It can last days or weeks and the cervix is still closed.
The pain and bleeding may resolve and you can go on to have a healthy pregnancy and baby. Or things may get worse and you go on to have a miscarriage.
There is rarely anything a doctor, midwife or you can do to prevent a miscarriage. In the past bed rest was recommended, but there is no scientific proof that this helps at this stage.
Inevitable miscarriage
Inevitable miscarriages can come after a threatened miscarriage or without warning. There is usually a lot more vaginal bleeding and strong lower stomach cramps. During the miscarriage your cervix opens and the developing fetus will come away in the bleeding.
Complete miscarriage
A complete miscarriage has taken place when all the pregnancy tissue has left your uterus. Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common — this is the uterus contracting to empty.
Vaginal bleeding may continue for several days. Cramping pain much like labour or strong period pain is common — this is the uterus contracting to empty.
If you have miscarried at home or somewhere else with no health workers present, you should have a check-up with a doctor or midwife to make sure the miscarriage is complete.
Incomplete miscarriage
Sometimes, some pregnancy tissue will remain in the uterus. Vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal cramping may continue as the uterus continues trying to empty itself. This is known as an 'incomplete miscarriage'.
Your doctor or midwife will need to assess whether or not a short procedure called a ‘dilatation of the cervix and curettage of the uterus’ (often known as a ‘D&C’) is necessary to remove any remaining pregnancy tissue. This is an important medical procedure done in an operating theatre.
Missed miscarriage
Sometimes, the fetus has died but stayed in the uterus. This is known as a 'missed miscarriage'.
If you have a missed miscarriage, you may have a brownish discharge. Some of the symptoms of pregnancy, such as nausea and tiredness, may have faded. You might have noticed nothing unusual. You may be shocked to have a scan and find the fetus has died.
If this happens, you should discuss treatment and support options with your doctor.
Recurrent miscarriage
A small number of women have repeated miscarriages. If this is your third or more miscarriage in a row, it’s best to discuss this with your doctor who may be able to investigate the causes, and refer you to a specialist.
A miscarriage can occur suddenly or over a number of weeks. The symptoms are usually vaginal bleeding and lower tummy pain. It is important to see your doctor or go to the emergency department if you have signs of a miscarriage.
The most common sign of a miscarriage is vaginal bleeding, which can vary from light red or brown spotting to heavy bleeding. If it is very early in the pregnancy, you may think that you have your period.
Other signs may include:
- cramping pain in your lower tummy, which can vary from period-like pain to strong labour-like contractions
- passing fluid from your vagina
- passing of blood clots or pregnancy tissue from your vagina
What really happens during a miscarriage?
WARNING — This article contains some graphic descriptions of what you might see during a miscarriage.
What should I do if I think I’m having a miscarriage?
If you are concerned that you are having a miscarriage, call your doctor or midwife for advice and support.
Keep in mind that many women experience vaginal spotting in the first trimester of pregnancy that does not result in a miscarriage.
If you are alone, consider calling your partner or a friend for help and support.
If you have very heavy bleeding, strong pain or feel unwell, call triple zero (000) or have someone take you to your nearest emergency department.
How is a miscarriage managed?
Unfortunately, nothing can prevent a miscarriage from happening once it has begun. What happens now depends on your own health and what is happening to you.
Each approach has benefits and risks. You should discuss these with your doctor.
Expectant or natural management
Also called ‘watch and wait’, expectant management may be recommended in early pregnancy. This involves going home and waiting until the pregnancy tissue has passed from your womb by itself. This can happen quickly, or it may take a few weeks.
Medical management
You may be offered medication that speeds up the passing of the pregnancy tissue. You may be asked to stay in hospital until the tissue has passed, or you may be advised to go home.
Surgical management
You may be advised to have a form of minor surgery called a 'dilatation and curettage' (also called a D&C or a curette). This procedure is often recommended if you have heavy bleeding, significant pain or signs of infection.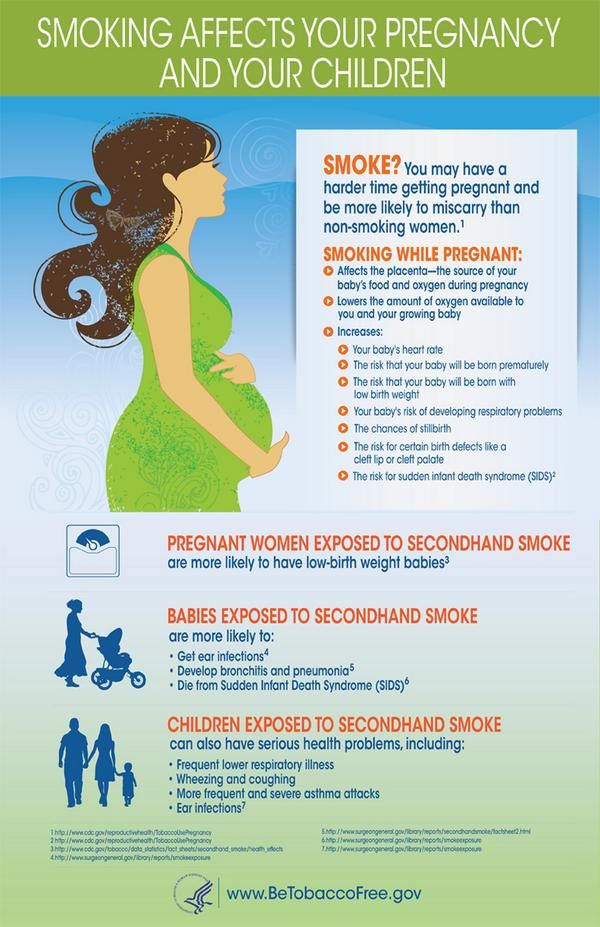 It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
It may also be recommended if expectant or medical management has failed. You may also decide that you prefer this option.
This procedure is done under general anaesthesia in an operating theatre. It takes 5-10 minutes once you are asleep. The doctor opens the cervix and removes the remaining pregnancy tissue.
How is a miscarriage treated?
Once it is confirmed that you are having a miscarriage, your doctor may offer or recommend treatment. There are many options. All have benefits and risks — discuss these with your doctor.
If the miscarriage is complete
If it seems the miscarriage is complete, you should still see your doctor for a check-up. You may be advised to have an ultrasound to make sure your uterus is empty.
If you go to hospital
If you go to your hospital’s emergency department, you will be seen first by a triage nurse, who will assess how urgently you need to be seen by a doctor. Depending on your symptoms, you will either be taken in to see a doctor immediately, or you will be asked to wait.
If you are waiting to be seen and your symptoms become worse or you feel like you need to go to the toilet, let the staff know immediately.
What happens if I miscarry at home?
Some women miscarry at home before they have a chance to see their doctor or get to the hospital.
If this happens, then:
- use pads to manage the bleeding
- if you can, save any pregnancy tissue that you pass, as your doctor may recommend it is tested to see why your miscarriage happened
- take medications such as paracetamol if you have pain
- rest
- call your doctor or midwife
There is a chance you may see your baby in the tissue that you pass, but often the baby is too small to recognise, or may not be found at all. It is normal to want to look at the remains, but you may decide you do not want to. There is no right or wrong thing to do.
Some women miscarry while on the toilet. This can also happen if you are out and about, or in hospital. There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
There is no right or wrong way to handle this.
Why do miscarriages happen?
Many women wonder if their miscarriage was their fault. In most cases, a miscarriage has nothing to do with anything you have or have not done. There is no evidence that exercising, stress, working or having sex causes a miscarriage.
Most parents do not ever find out the exact cause. However, it is known that miscarriages often happen because the baby fails to develop properly, usually due to a chromosomal abnormality that was spontaneous, not inherited.
Occasionally, miscarriage is caused by:
- hormonal abnormalities
- immune system and blood clotting problems
- medical conditions such as thyroid problems or diabetes
- severe infections causing high fevers (not common colds)
- physical problems with your womb or cervix
What are the risk factors for miscarriage?
Women are more likely to have miscarriages if they:
- are older
- smoke
- drink alcohol in the first trimester
- drink too much caffeine in coffee, tea or energy drinks
- have had several previous miscarriages
Can you prevent a miscarriage?
Living healthily — no cigarettes, no alcohol and little to no caffeine — can decrease your risk of miscarriage. It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
It’s a good idea to avoid contact with people who have a serious infectious illness when you’re pregnant.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
Talk to your doctor or midwife for information and advice on what do and how to look after yourself if you experience a miscarriage.
Your hospital should be able to provide details of available support services, such as bereavement support.
SANDS is an independent organisation that provides support for miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn death. You can call them on 1300 072 637 or visit www.sands.org.au.
You can also call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436, 7am to midnight (AET) to speak to a maternal child health nurse for advice and emotional support.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
If the pregnancy is terminated naturally before the fetus reaches gestational age, this is called a spontaneous abortion or miscarriage. More than half of miscarriages occur no later than 12 weeks of gestation due to fetal abnormalities. The rest falls on the period up to 20 weeks and is associated with pathologies of pregnancy. If the pregnancy is terminated in the second half, it is called preterm labor.
Spontaneous abortion, otherwise known as miscarriage, is one of the most common complications during pregnancy, accounting for 10-20% of diagnosed pregnancies, and is the rejection of a fetus weighing no more than 500 grams. and less than 22 weeks. Unfortunately, with such indicators, the fetus is not viable. Usually 80% of the total number of spontaneous abortions occurs before the 12th week of pregnancy.
Types of spontaneous abortion
1. Threat of miscarriage - characterized by mild uterine cramps, pulling pain in the lower abdomen and sometimes mild bloody discharge from the vagina.
2. A miscarriage that has begun - is characterized by more severe pain and profuse bleeding. At the same time, the tone of the uterus is slightly increased, and the internal os is closed.
3. Inevitable miscarriage - accompanied by dilatation of the cervix - a fetal egg can be distinguished - with profuse bleeding and severe cramps in the lower abdomen.
4. Incomplete miscarriage - part of the fetus comes out. The bleeding is so profuse that it can lead to the death of a woman.
5. Completed miscarriage - the fetal egg and the fetus itself are completely out. After that, the bleeding and spasms stop.
The etiology of miscarriage is due to many factors. Among them:
- genetic disorders;
- previous induced abortions;
- too little time has passed since the previous pregnancy;
- inflammatory infections in the mother, endocrine disorders;
- blood conflict between mother and fetus;
- taking hormonal contraceptives and certain medications;
- smoking during pregnancy and drinking alcohol;
- unknown causes.
To prevent miscarriage, it is necessary to give up bad habits, not to have abortions and to be regularly examined by a doctor.
Spontaneous abortion begins with the appearance of cramping, drawing pains, similar to pain during menstruation. Then bleeding from the uterus begins. At first, the discharge is slight or moderate, and then, after detachment of the fetal egg, abundant discharge with bloody clots begins. The appearance of these symptoms requires urgent hospitalization.
After examining a woman in a hospital, having determined the degree of detachment of the embryo, one of the following diagnoses will be made:
- the threat of pregnancy - detachment is only outlined or is completely insignificant. In this case, the pregnancy can be saved;
- a miscarriage that has begun - detachment is already quite decent with a pronounced pain syndrome. And in this case, the fetus can be saved;
- abortion in progress - detachment with displacement progresses, labor-like contractions begin. Pregnancy cannot be saved, cleaning is required;
Pregnancy cannot be saved, cleaning is required;
- incomplete miscarriage - independent exit of a part of the fetus and membranes, curettage is necessary for the final curettage of the uterus;
- late abortion - premature delivery of an unviable baby.
After a spontaneous abortion, it is recommended to take a short break in planning and take preventive measures to avoid recurrence.
In case of repeated miscarriage, a thorough comprehensive examination is necessary to determine the causes of miscarriage and eliminate them.
A miscarriage is a severe psychological trauma, especially during the first pregnancy. But do not give up, with a competent approach to planning and bearing, the next pregnancy will certainly end with the appearance of a long-awaited baby.
Causes of spontaneous abortion
1. Doctors call various chromosomal pathologies one of the main reasons: monosomy, autosomal trisomies, polyploidy. They account for 82-88% of spontaneous miscarriages.
2. The second most common cause is disorders in the female genital area: endometritis - inflammation of the uterine mucosa - preventing the implantation of the fetal egg and its development and polycystic ovaries.
3. Hormonal disorders, namely progesterone deficiency.
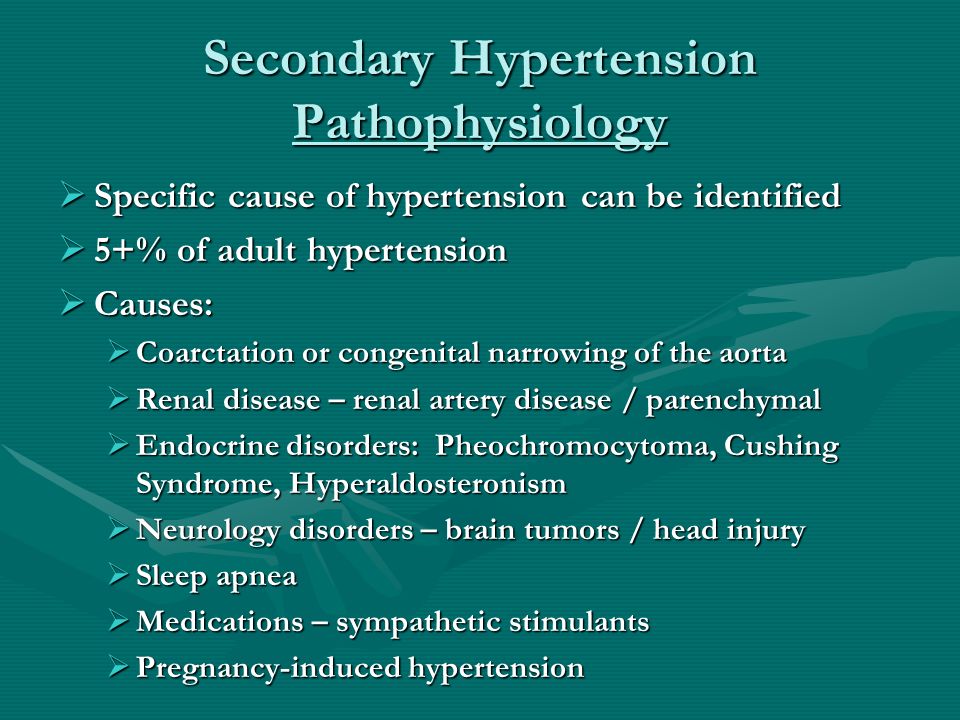
4. Chronic diseases - uncontrolled diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure.
5. Viral infections rubella, chlamydia and others.
Treatment
In case of severe blood loss, ultrasound is performed to determine the viability of the fetus and rule out an ectopic pregnancy. A woman is prescribed bed rest and is treated with antispasmodic drugs to relax the uterine myometrium and stop bleeding.
If doctors still diagnose a spontaneous abortion that has begun, then the actions are reduced either to expectant tactics (within 2-6 weeks the fetal egg should come out by itself), or to prescribing drugs that accelerate the delivery of the fetus, or to vacuum aspiration (medical abortion ).
Pregnancy after abortion
Pregnancy after abortion
Share
It is no secret that termination of pregnancy by abortion always affects the state of a woman's reproductive health. A woman often makes such a decision not of her own free will. There are also medical indications for artificial termination of pregnancy. So, for example, physical pathologies of fetal development, genetic abnormalities, "frozen" pregnancy - when the fetus, at a certain stage of its existence, simply stops growing and developing.
Many, especially women who have not given birth, are concerned about the question: is it possible to get pregnant after an abortion and how will the pregnancy proceed after an abortion? Let's look at the consequences of this procedure for the female body.
Abortion is especially dangerous for nulliparous women. In the process of abortion, the cavity and cervix are injured. After the removal of the fetal egg, the walls of the uterus are scraped.
It is possible to get pregnant after an abortion, but there is a high probability of unwanted deterioration. Abortions are dangerous for subsequent pregnancy with complications such as uterine ruptures. Be sure to consult a gynecologist. If you have had abortions more than once, this will inevitably lead to thinning of the walls of the uterus or the formation of through holes in the walls of the uterus. If the uterine rupture occurs during childbirth, then the danger threatens not only the mother, but also the baby.
Also, in a subsequent pregnancy after an abortion, there is a possibility of miscarriage. It can be triggered by isthmic-cervical insufficiency due to trauma to the cervix. Since during an abortion, the cervix is moved apart with a special device that allows you to remove the fetus.
The cervix weakens as a result of such procedures, and may involuntarily open during pregnancy at any time. What causes a miscarriage.
There is a special procedure for suturing the cervix that your doctor may recommend during your examination. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the suture is removed shortly before delivery. This manipulation will help to significantly reduce the likelihood of miscarriage.
This procedure is performed under local anesthesia, the suture is removed shortly before delivery. This manipulation will help to significantly reduce the likelihood of miscarriage.
In women with poor reproductive function, even after the first abortion, infertility may occur. The same applies to women with serious chronic diseases of the reproductive system.
With a high probability, the question: is it possible to get pregnant after an abortion, it is worth answering - yes! Only you automatically move into the risk group for the threat of abortion.
The surest way to avoid an abortion is to use contraception all the time. You ask, is it possible to get pregnant with protection? Yes, there is such a possibility. When using oral or vaginal contraceptives, it is very important to follow all directions for use. If you violate the sequence of administration or the technique of administration, then the likelihood of pregnancy is very high.
With strict observance of all the rules, the onset of an unwanted pregnancy is unlikely.