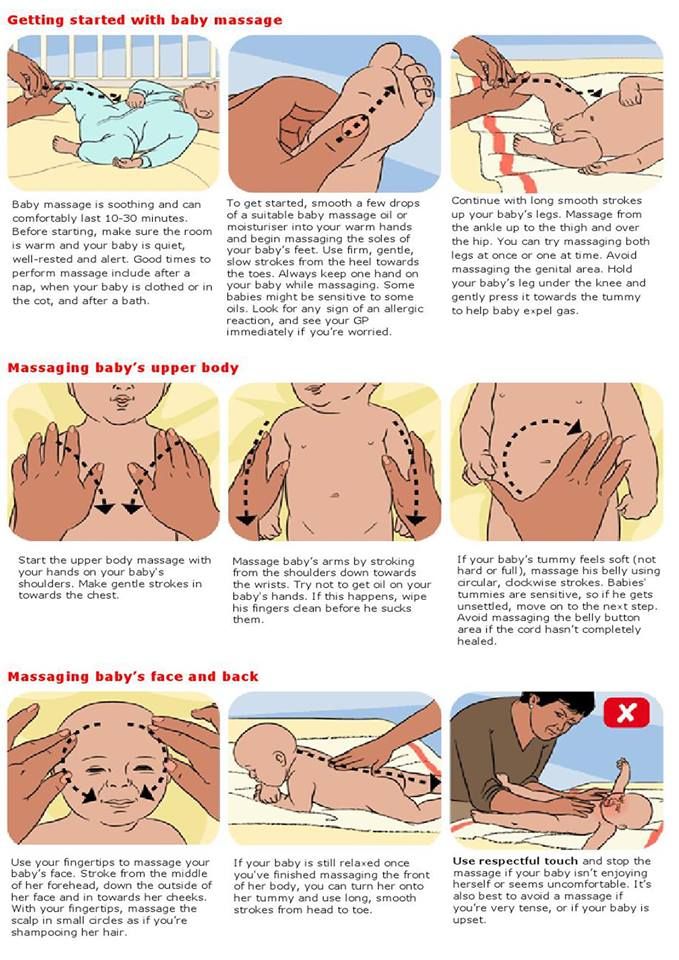
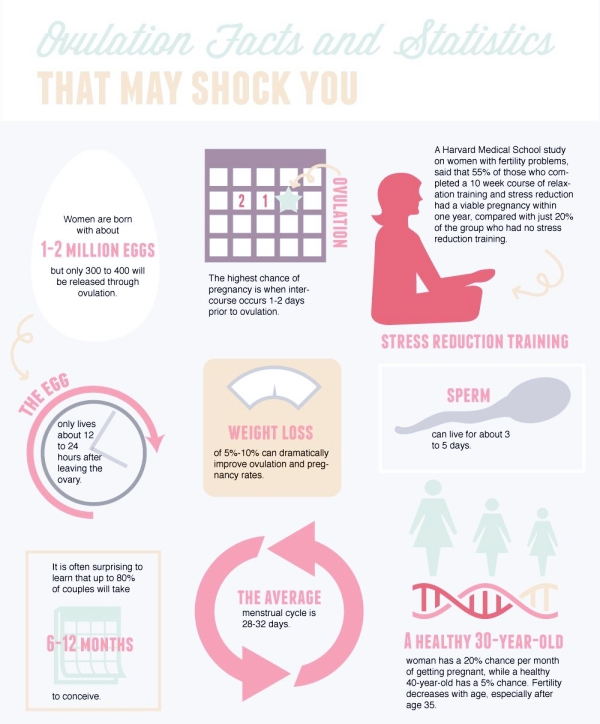
Can you get pregnant few days before ovulation
Ovulation signs – know when you’re most fertile
Ovulation signs – know when you’re most fertile | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- There are signs that can help you track and predict ovulation, including changes to your body temperature and vaginal discharge.
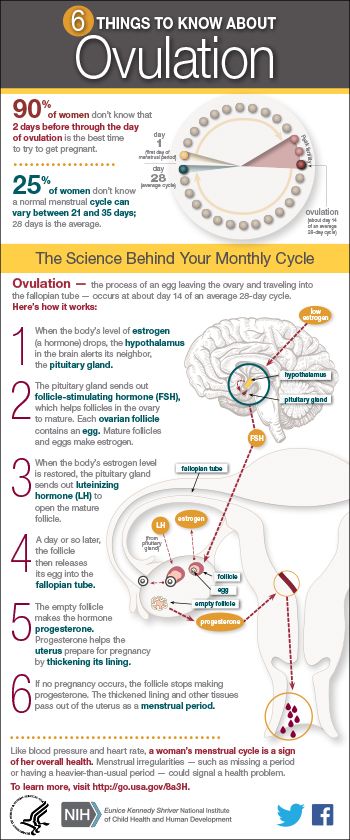
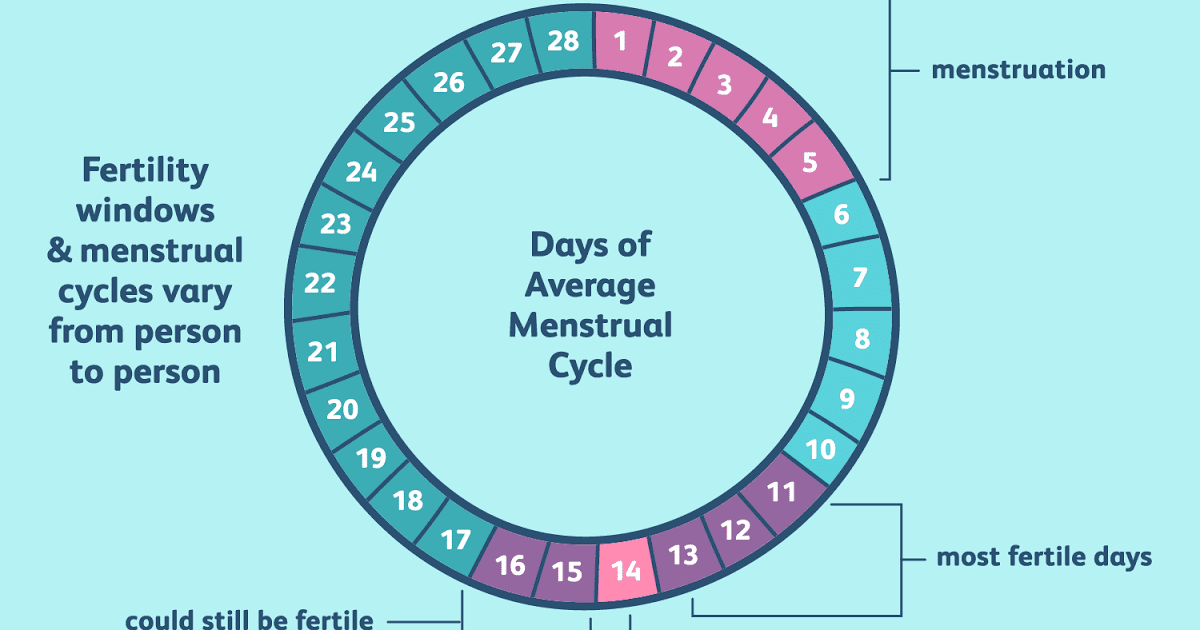
- In a typical 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs at around day 14.
- Ovulation predictor kits detect levels of luteinising hormone (LH) in your urine and can help you know when ovulation is likely to occur.
- Having sex in the days leading up to and the day of ovulation will increase your chance of conceiving.
- If you are trying to get pregnant, see your doctor for a pre-conception health check.
When am I most fertile?
You are most likely to conceive during the 5 days before ovulation, along with the day you ovulate. Sperm can live up to 5 days inside your body, so if you have sex up to 5 days before your egg is released, you can get pregnant.
After ovulation, your egg can only live for 12 to 24 hours. After this time is up, your chance of getting pregnant is virtually zero until your next menstrual cycle.
Your chances of getting pregnant are at their highest in the 3 days leading up to and including ovulation.
How can I predict ovulation?
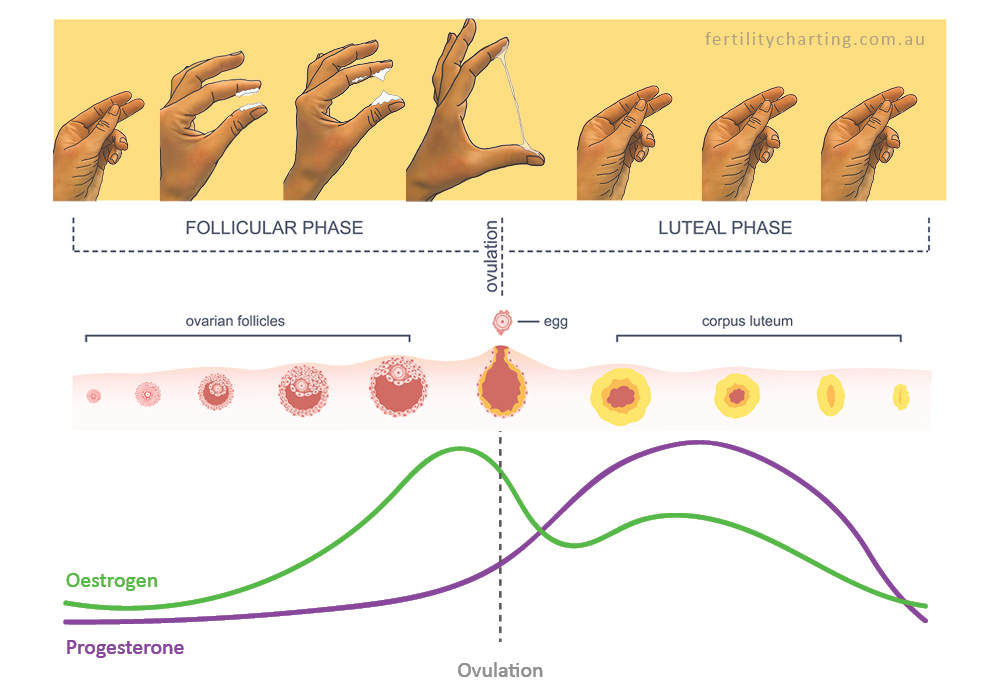
Ovulation usually happens about halfway through your menstrual cycle. This is about 14 days before the first day of your next period in a typical 28-day cycle, but the exact time can vary. Signs that you are about to ovulate can be subtle. However, there are some things you can pay attention to and track over time to help you predict your fertile window.
Changes in mucus
Around the time of ovulation, you may notice your vaginal discharge is clear, stretchy and slippery — similar to egg whites. After ovulation, when the chances of becoming pregnant drop, vaginal discharge tends to become cloudy and thick, or disappear entirely.
After ovulation, when the chances of becoming pregnant drop, vaginal discharge tends to become cloudy and thick, or disappear entirely.
Changes in body temperature
When you’ve just ovulated, your body temperature may increase very slightly, by about half a degree Celsius. If you’re using temperature to keep track of when you are most fertile, you need to use a special thermometer to take your temperature every morning before you get out of bed. If you record the readings every day using a graph or a spreadsheet, it’s possible to learn your pattern over time. The time when you are most fertile is 2 to 3 days before the rise in temperature.
Other signs
There may be other signs that you are near the time of ovulation, such as mild abdominal cramps, breast tenderness or increased sex drive. However, using these signs to predict when you’re fertile is not the most reliable method.
Using ovulation calculators and kits
Ovulation calculators and kits can also help you predict ovulation.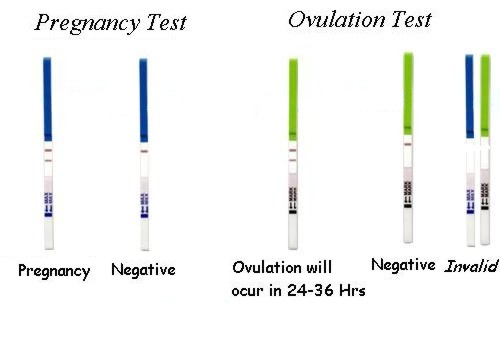
Ovulation calculators are available on websites such as www.yourfertility.org.au. Use the date of your last period and the length of your cycle to predict when you are likely to be most fertile.
Home ovulation predictor kits are available from pharmacies. They test for a rise in the level of a hormone called luteinising hormone (LH) in your urine. You should use the kit a few days before your predicted ovulation day. A positive result indicates you will ovulate within the next 24 to 36 hours.
Your doctor can also arrange a blood test to check your progesterone levels, which can be used to detect ovulation.
What else should I think about if I’m trying to conceive?
If you are trying to get pregnant, there are some other things you should consider, such as:
- taking a folate supplement
- maintaining a healthy diet
- making sure your vaccinations are up to date
Most healthy couples will conceive within a year of trying. If you are under 35 years of age and have been trying to conceive for a year without success, see your doctor to discuss your options.
If you are under 35 years of age and have been trying to conceive for a year without success, see your doctor to discuss your options.
If you or your partner are over 35, you might like to see your doctor after trying to conceive for 6 months, as fertility can decrease with age.
You can find more information from:
- Your Fertility for more information on ovulation and the fertile window.
- Jean Hailes for Women’s Health for more information on things that can be helpful to know, when you start trying for a baby.
- Your doctor
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Your Fertility (Right time for sex), Your Fertility (Understanding ovulation and the fertile window), Family Planning NSW (Maximising Natural Fertility), Jean Hailes (Trying for pregnancy), Your Fertility (Thinking about having a baby?), Australian Prescriber (Fertility testing), Australian Family Physician (Basal body temperature chart)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.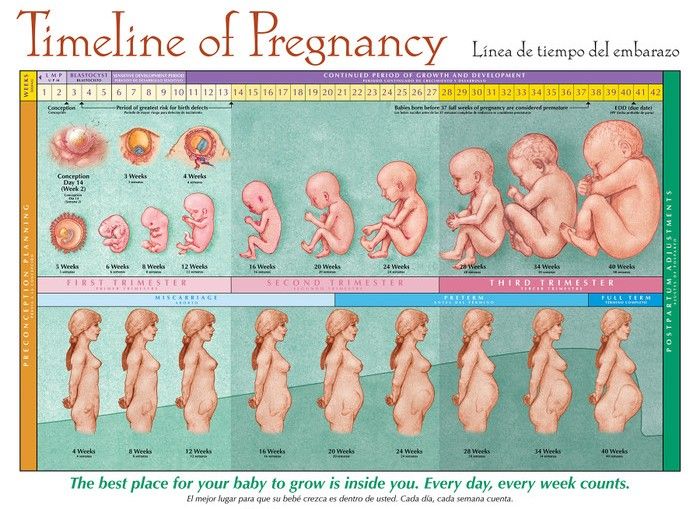
Last reviewed: October 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Planning for pregnancy
- Working out your due date
- Early signs of pregnancy
Need more information?
Understanding ovulation and the fertile window
When you want to have a baby you can improve your chance of getting pregnant if you know about ovulation and the ‘fertile window’ in the menstrual cycle.
Read more on Your Fertility website
Ovulation and fertility - Better Health Channel
The female body shows several signs of ovulation and you may experience some or all of these signs.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ? | Your Fertility
Apart from being healthy, what else can help you get pregnant?
Read more on Your Fertility website
Getting pregnant - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Getting pregnant is easy for some women, but for others it can be a difficult. Women are most fertile between 20 and 24 years of age, after which fertility declines.
Read more on myDr website
Unexplained infertility and chance of pregnancy | Your Fertility
Get your timing right Your window of opportunity to fall pregnant each month is small
Read more on Your Fertility website
The Pink Elephants Support Network - Female Fertility Issues - Pink Elephants
The Pink Elephants Support Network are a not for profit charity, formed to support women through miscarriage, pregnancy loss and beyond.
Read more on Pink Elephants Support Network website
Planning to have a baby | VARTA
Planning ahead If you are thinking about having a baby in future, there are some things you can do to improve your chances.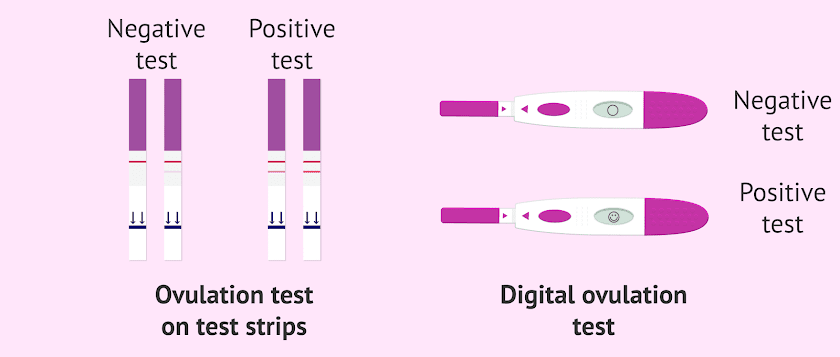 Preconception is the period leading up to getting pregnant. This is a great time for both men and women to focus on ways to improve their health, and increase the chance of pregnancy and having a healthy baby. The earlier you start the conversations about having a baby, the better. Here are some things you and your partner (if any) should start thinking about now: the number of children you would like to have the age at which you would like to have your first and last child improving your health before you try booking a preconception health check with your GP. Your Fertility has practical ideas for how you can improve your preconception health including checklists for men and women. Improving fertility Age is the most important factor affecting a woman’s chance of conceiving. Female fertility starts to decline around age 30 and after age 35 the monthly chance of conceiving decreases more rapidly. Age can also affect a man’s fertility and the chance of having a healthy baby. Certain lifestyle factors for both men and women also affect the ability to conceive, the health of the pregnancy, and the health of the future baby.
Preconception is the period leading up to getting pregnant. This is a great time for both men and women to focus on ways to improve their health, and increase the chance of pregnancy and having a healthy baby. The earlier you start the conversations about having a baby, the better. Here are some things you and your partner (if any) should start thinking about now: the number of children you would like to have the age at which you would like to have your first and last child improving your health before you try booking a preconception health check with your GP. Your Fertility has practical ideas for how you can improve your preconception health including checklists for men and women. Improving fertility Age is the most important factor affecting a woman’s chance of conceiving. Female fertility starts to decline around age 30 and after age 35 the monthly chance of conceiving decreases more rapidly. Age can also affect a man’s fertility and the chance of having a healthy baby. Certain lifestyle factors for both men and women also affect the ability to conceive, the health of the pregnancy, and the health of the future baby. A healthy weight, a nutritious diet and regular exercise can significantly boost fertility, as can quitting smoking, stopping drug use and curbing heavy drinking. When you are ready to try for a baby, it is important to know when conception is most likely to happen. In an average cycle of 28 days, ovulation happens on day 14. However, cycle length varies between women, and it is important to note that ovulation occurs earlier in women with shorter cycles and later in women with longer cycles. However, pregnancy is only possible during the five days before ovulation through to the day of ovulation. These six days are the ‘fertile window’ in a woman’s cycle, and reflect the lifespan of sperm (five days) and the lifespan of the egg (24 hours). Your Fertility’s ovulation calculator can help you work out the fertile window. Medical conditions and fertility PCOS Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal condition affecting up to one in five women of childbearing age. The condition affects two hormones, insulin and testosterone (male-like hormones), which may be produced in higher levels and can impact on fertility.
A healthy weight, a nutritious diet and regular exercise can significantly boost fertility, as can quitting smoking, stopping drug use and curbing heavy drinking. When you are ready to try for a baby, it is important to know when conception is most likely to happen. In an average cycle of 28 days, ovulation happens on day 14. However, cycle length varies between women, and it is important to note that ovulation occurs earlier in women with shorter cycles and later in women with longer cycles. However, pregnancy is only possible during the five days before ovulation through to the day of ovulation. These six days are the ‘fertile window’ in a woman’s cycle, and reflect the lifespan of sperm (five days) and the lifespan of the egg (24 hours). Your Fertility’s ovulation calculator can help you work out the fertile window. Medical conditions and fertility PCOS Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal condition affecting up to one in five women of childbearing age. The condition affects two hormones, insulin and testosterone (male-like hormones), which may be produced in higher levels and can impact on fertility. Women with PCOS are prone to irregular menstrual cycles due to absent or infrequent ovulation. While the majority of women with PCOS become pregnant without fertility treatment, they often take longer to fall pregnant and are more likely to need treatment (ovulation induction or IVF) than women without PCOS. Despite this, studies show little difference between the number of children born to women with PCOS than to those without. Conception may sometimes occur as a result of lifestyle modification or after receiving medication to assist with ovulation (ovulation induction) and advice regarding the timing of sex. The most successful way to treat PCOS is by making healthy lifestyle changes. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly is the best way to reduce symptoms and increase fertility. If you have difficulty conceiving, your GP may refer you to a specialist clinician. Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation (MCHRI) has a list of questions that may be helpful. You can find more information and resources about PCOS at Your Fertility, Jean Hailes for Women’s Health and MCHRI.
Women with PCOS are prone to irregular menstrual cycles due to absent or infrequent ovulation. While the majority of women with PCOS become pregnant without fertility treatment, they often take longer to fall pregnant and are more likely to need treatment (ovulation induction or IVF) than women without PCOS. Despite this, studies show little difference between the number of children born to women with PCOS than to those without. Conception may sometimes occur as a result of lifestyle modification or after receiving medication to assist with ovulation (ovulation induction) and advice regarding the timing of sex. The most successful way to treat PCOS is by making healthy lifestyle changes. Eating a healthy diet and exercising regularly is the best way to reduce symptoms and increase fertility. If you have difficulty conceiving, your GP may refer you to a specialist clinician. Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation (MCHRI) has a list of questions that may be helpful. You can find more information and resources about PCOS at Your Fertility, Jean Hailes for Women’s Health and MCHRI. Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrium, the tissue that normally lines the womb (uterus), grows outside the uterus. Endometriosis may cause fibrous scar tissue to form on the uterus. It can also affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the bowel. Endometriosis may cause very painful periods and reduce fertility or cause infertility. You can find out more about endometriosis at Jean Hailes for Women’s Health and the Better Health Channel.
Endometriosis Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrium, the tissue that normally lines the womb (uterus), grows outside the uterus. Endometriosis may cause fibrous scar tissue to form on the uterus. It can also affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes and the bowel. Endometriosis may cause very painful periods and reduce fertility or cause infertility. You can find out more about endometriosis at Jean Hailes for Women’s Health and the Better Health Channel.
Read more on Victorian Assisted Reproductive Treatment Authority website
Pregnancy testing options - MyDr.com.au
Testing for pregnancy and ovulation is simple using home pregnancy and ovulation test kits, which give results that are about 99% accurate. Find out what pregnancy and ovulation testing kits are available.
Read more on myDr website
All about Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | Jean Hailes
Read about causes, signs and symptoms of PCOS, as well as diagnosis and treatments available to help.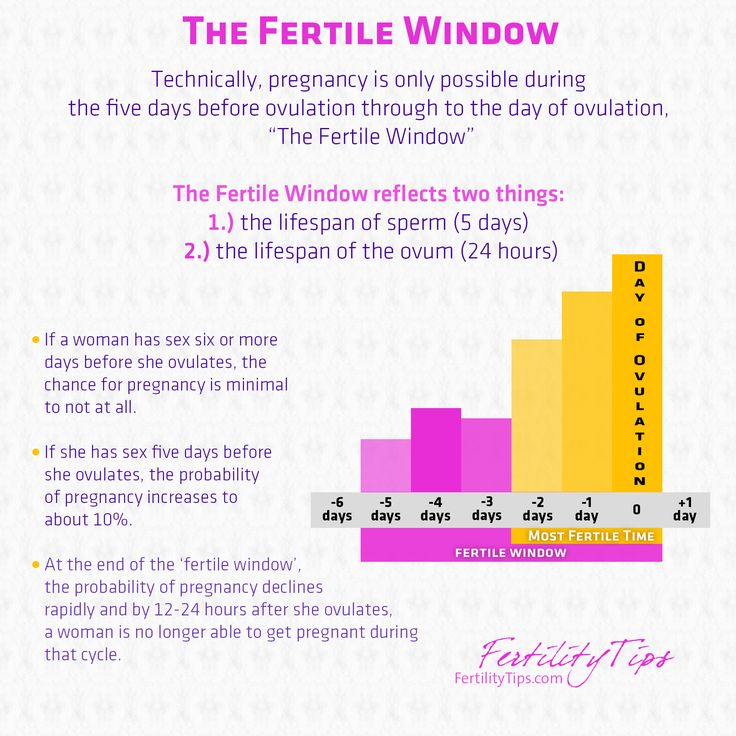 Jean Hailes is Australia's leader in women's health.
Jean Hailes is Australia's leader in women's health.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Four things you didn’t know about periods — Free health… | Jean Hailes
When you first learn about periods and get your first one, there's a lot to take in, and get used to...
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.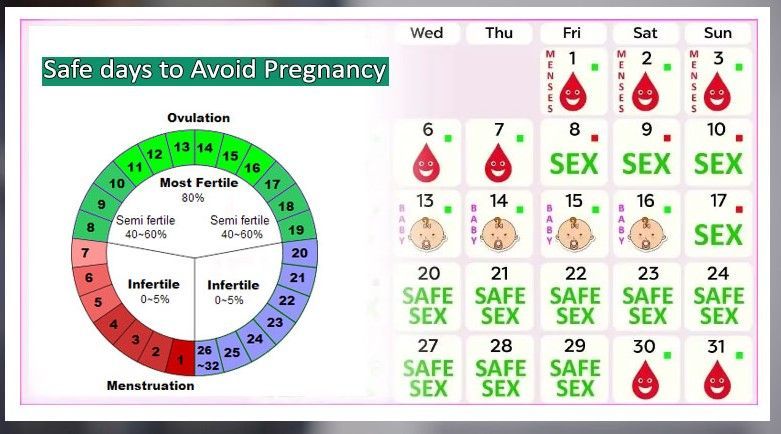
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care.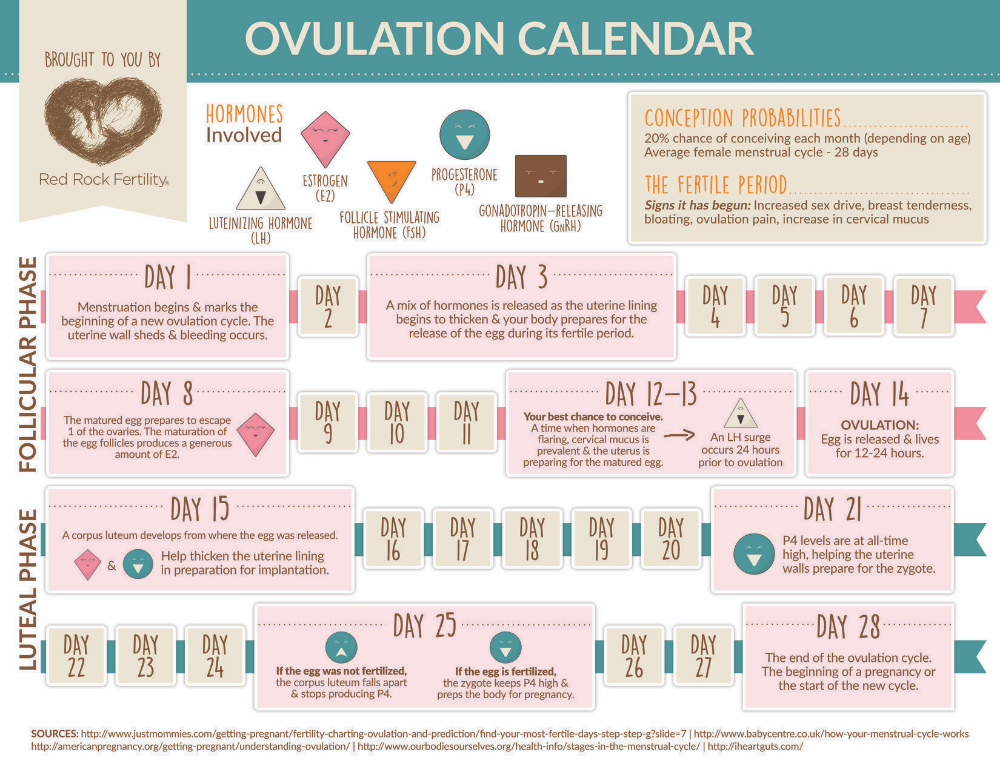 If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Right Time For Sex , When Do You Ovulate ?
When are you more likely to conceive?
We’re talking about the 'fertile window’ – the days in a woman’s menstrual cycle when pregnancy is possible.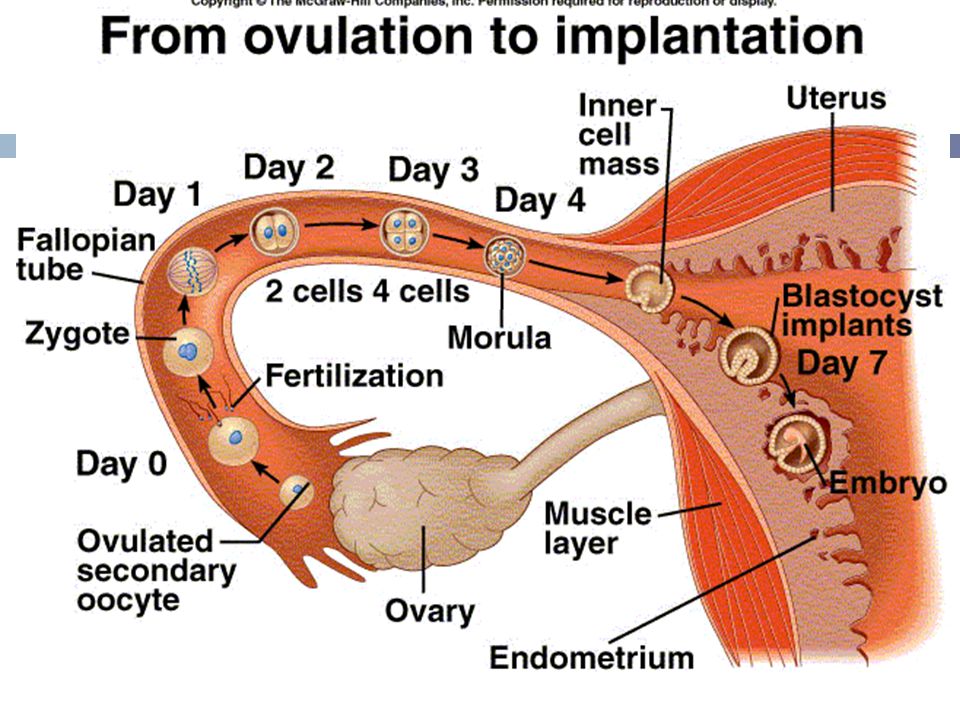 The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ depends on the length of the menstrual cycle, which varies among women.
The ‘fertile window’ is the day an egg is released from the ovary (ovulation) and the five days beforehand. Having sex (intercourse) during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
Ovulation Calculator
What day did you your most recent period start?
Number of days in your cycle Please select20 Days21 Days22 Days23 Days24 Days25 Days26 Days27 Days28 Days29 Days30 Days31 Days32 Days33 Days34 Days35 Days36 Days37 Days38 Days39 Days40 Days41 Days42 Days43 Days44 Days45 Days
Your ovulation day
Most fertile time
-
What is an ovulation calculator and how does it help you get pregnant?
This ovulation calculator or ovulation calendar can help you work out your most fertile time.
 These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.
These are the days you are most likely to get pregnant.It can also estimate your due date if you do become pregnant during your next fertile days.
Others ways to help you work out when you're ovulating:
- Notice changes in vaginal mucus
A few days before ovulation, you may notice your vaginal mucus becomes clear, slick and slippery, and feels a bit like egg white.
This is a sign that ovulation is about to happen. It’s the best time to have sex, as sperm travel more easily in this kind of mucus.
- Use an ovulation predictor kit
You can use a predictor kit from a supermarket or pharmacy, to test your urine for signs of ovulation. If you start testing your urine a few days before the day you next expect to ovulate, a positive result means you are going to ovulate within the next 24 to 36 hours (one to two days).
-
Facts about timing
Ovulation is when a mature egg is released from the ovary. The egg then moves down the fallopian tube where it can be fertilised. If sperm are in the fallopian tube when the egg is released, there is a good chance that the egg will be fertilised, creating an embryo, which can grow into a baby.
Pregnancy is technically only possible if you have sex during the five days before ovulation or on the day of ovulation. But the most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including ovulation. Having sex during this time gives you the best chance of getting pregnant.
By 12-24 hours after ovulation, a woman is no longer able to get pregnant during that menstrual cycle because the egg is no longer in the fallopian tube.
There’s almost no chance of getting pregnant if you have sex before or after the fertile window (but if you’re not trying to get pregnant, don’t rely on this – contraception is your best option!).
-
How to know when you’re ovulating
Knowing when you ovulate can help you plan for sex at the right time and improve your chance of getting pregnant. You can keep track of your menstrual cycles on a chart, in a diary, or on a free period-tracker app on your smartphone.
To work out the length of your menstrual cycle, record the first day you start bleeding (first day of your period). This is day 1. The last day of your cycle is the day before your next period begins.
- What is a ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’?
Some people think the ‘menstrual cycle’ and a ‘period’ are the same thing.
A period is when you bleed (or menstruate).

A menstrual cycle starts on the day when a period starts (day 1) and ends the day before the next period. A cycle’s length is considered normal if it’s between 21 and 35 days. They can vary between women and from one cycle to the next.
- Working out your ‘average’ menstrual cycle length
If your menstrual cycles are different lengths (most women’s cycles are) you can work out your average cycle length.
The number of days in a woman’s menstrual cycle can vary month to month. Periods are not always regular. It can be useful to work out an ‘average’ cycle length, based on the length of three menstrual cycles, to estimate when you’re most likely to be ovulating.
If you add the number of days in three cycles and divide the total number by three, it gives you your average cycle length.
Example
Sarah tracked her last three menstrual cycles by counting the time from the first day of one period, to the day before the next period.
Cycle 1 was 28 days; Cycle 2 was 32 days; Cycle 3 was 27 days
28 + 32 + 27 = 87
87 divided by 3 = 29
So the average length of Sarah’s menstrual cycles is 29 days.
- Working out your most fertile days
When you know your average menstrual cycle length, you can work out when you ovulate.
Ovulation happens about 14 days before your period starts.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 28 days, you ovulate around day 14, and your most fertile days are days 12, 13 and 14.
- If your average menstrual cycle is 35 days ovulation happens around day 21 and your most fertile days are days 19,20 and 21.
- If you have shorter cycles, say 21 days, ovulation happens around day 7 and your most fertile days are days 5, 6 and 7.
Your most fertile days are the three days leading up to and including the day of ovulation.
Some women have very irregular cycles or find it difficult to work out an average cycle length. This can make it hard to work out when ovulation happens. If it’s all too hard, having sex every 2-3 days covers all bases and improves your chance of getting pregnant.
Myth busting
- MYTH
A woman can get pregnant any time of the month.
- FACT
A woman can only get pregnant on a few days during her menstrual cycle.
Why?
Because eggs and sperm only live for a short time:
- Sperm live for around five days.
- Eggs can only be fertilised for around 24 hours (one day) after being released from the ovary.
Eggs and sperm need to come together at the right time for fertilisation to happen to create an embryo.
Getting the timing right
If you're trying to get pregnant, timing is everything. Dr Karin Hammarberg explains how to work out when you are ovulating and the right time to have sex to improve your chance of pregnancy.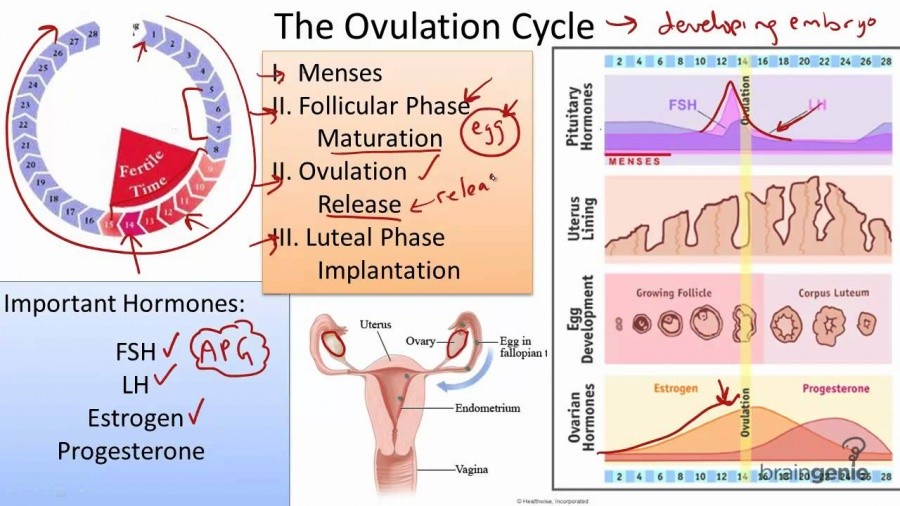
-
What are the chances?
Having sex as close as possible to the time of ovulation increases the chance of pregnancy.
If a woman has sex six or more days before she ovulates, the chance she will get pregnant is virtually zero.
If she has sex five days before she ovulates, her probability of pregnancy is about 10 percent.
If she has sex on the day of ovulation, or the two days before, the chance of getting pregnant is around 30 percent.
These are average figures and depend on a woman’s age.
When does preconception health begin?
Professor Sarah Robertson, Director of Robinson Research Institute, University of Adelaide, highlights the key time before pregnancy that your health is most important to ensure your child has the best start to life.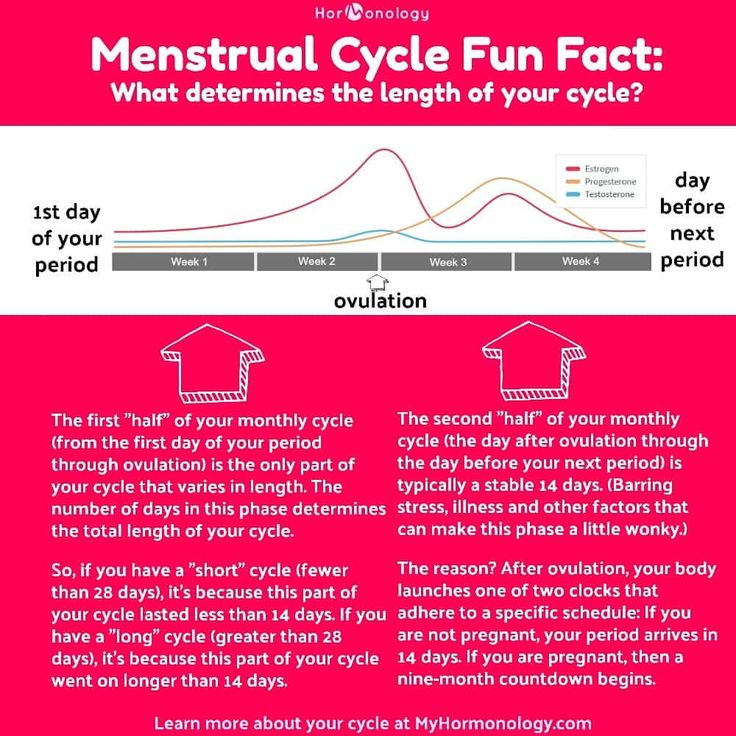
How to know you are ovulating
Kerry Hampton, a registered nurse and fertility specialist, discusses the importance of fertility awareness, and how to determine your fertile window to improve your chances of conceiving.
- References
- American Society for Reproductive Medicine, Optimizing natural fertility, https://www.reproductivefacts.org/news-and-publications/patient-fact-sheets-and-booklets/documents/fact-sheets-and-info-booklets/optimizing-natural-fertility/
- Berglund Scherwitzl, et al. (2015). Identification and prediction of the fertile window using Natural Cycles. The European Journal of Contraception and Reproductive Health Care, 20(5), 403-408. doi:10.3109/13625187.2014.988210
- Ecochard, R., et al. (2015). Self-identification of the clinical fertile window and the ovulation period.
 Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031
Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1319-1325.e1313. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.031 - Pfeifer, S., et al. (2017). Optimizing natural fertility: a committee opinion. Fertility and Sterility, 107(1), 52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2016.09.029
- Stanford, J. B. (2015). Revisiting the fertile window. Fertility and Sterility, 103(5), 1152-1153. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.02.015
- Stanford, et al. (2002). Timing intercourse to achieve pregnancy: current evidence. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 100(6), 1333-1341.
- Stephenson, J., et al. (2018). Before the beginning: nutrition and lifestyle in the preconception period and its importance for future health. The Lancet, 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8 doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30311-8
- Vélez, M. Pet al. (2015). Female exposure to phenols and phthalates and time to pregnancy: the Maternal-Infant Research on Environmental Chemicals (MIREC) Study. Fertility and Sterility.
 doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005
doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.01.005 - Verón, G. L., et al. (2018). Impact of age, clinical conditions, and lifestyle on routine semen parameters and sperm kinematics. Fertility and Sterility, 110(1), 68-75.e64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.03.016
- Waylen, A. Let al. (2009). Effects of cigarette smoking upon clinical outcomes of assisted reproduction: a meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update, 15(1), 31-44.
- Zenzes, M. T. (2000). Smoking and reproduction: gene damage to human gametes and embryos. Hum Reprod Update, 6(2), 122-131.
Page created on: 28/08/2018 | Last updated: 17/03/2023
When is a woman most fertile?
If you are a woman taking precautions to prevent pregnancy, or if you are thinking about pregnancy in some way in the future, the issue of fertility usually remains in the background.
The question of when a woman is most fertile has two aspects.
First, is the menstrual monthly cycle and the period when a woman is most fertile.
To figure out the arithmetic, a fertility calendar or an ovulation calculator will help. The second aspect of the question concerns biological age and the stage of life at which women are most fertile. In our article, we will look at the monthly cycle, the days that are the most fertile during this cycle, and various means of monitoring and predicting ovulation. This makes it possible to predict the time of maximum fertility with some accuracy.
Second , we look at the stages of fertility at various times in a woman's life and their impact on her ability to conceive.
It is well known that fertility peaks at age 20 and begins to decline after age 30; after 35 years, natural conception rates begin to drop sharply. However, in today's society, many women, for understandable financial and social reasons, choose to delay childbearing until the age of thirty. Thus, we are faced with the paradoxical situation where many women, who have long sought to prevent pregnancy in their younger years, find themselves in a situation where they begin to look for ways to increase their chances of conceiving.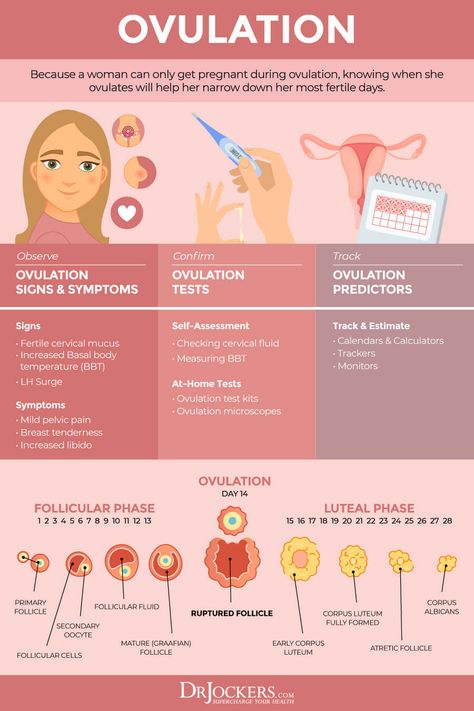
When is a woman most fertile? What does the menstrual cycle show?
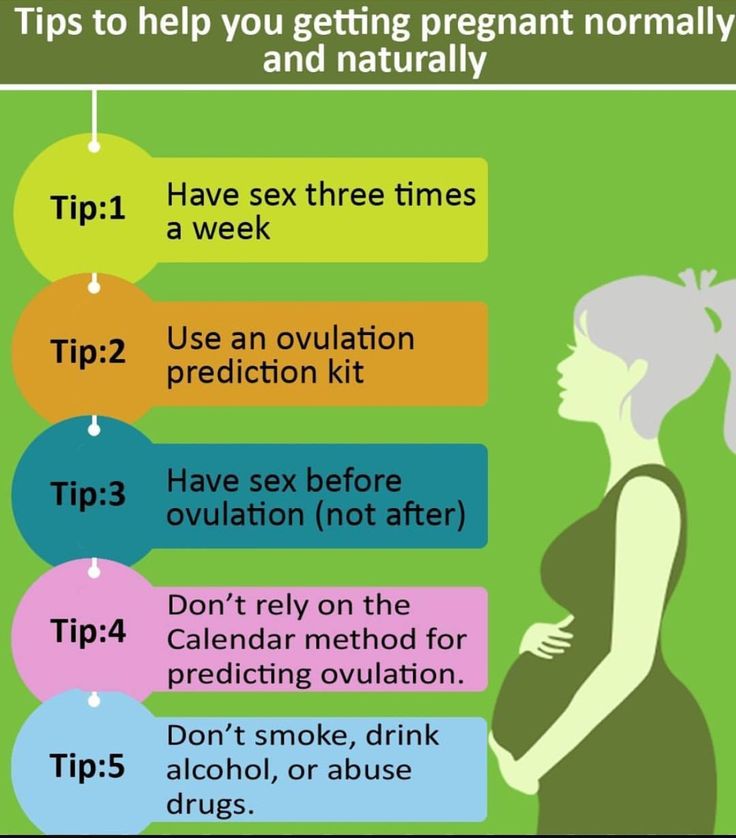
In a woman, the ability to conceive is maximum a day or two before and after ovulation. This is when the egg is released from the ovaries. You can calculate with a reasonable degree of accuracy when ovulation will occur, especially if your cycle is regular, anywhere between 24 and 35 days. Consider the start of your period (bright spotting) as the first day of your cycle, and the day before the next as the end of your cycle. Ovulation usually occurs 12-16 days before the start of the next cycle. Thus, if you have a regular 28-day cycle, then the indicator remains the same: ovulation occurs on the 12th-16th day. However, fertile time is not limited to these few days. Remember that you can get pregnant if you have unprotected sex at any time during the week before ovulation, as sperm can live in a woman's genital tract for up to seven days.
Fertility specialists generally advise that if you are hoping to get pregnant, it is advisable to specifically schedule contacts around this time, as it can be difficult to calculate the exact day of ovulation, and trying to have sex on a schedule can cause unnecessary stress and anxiety.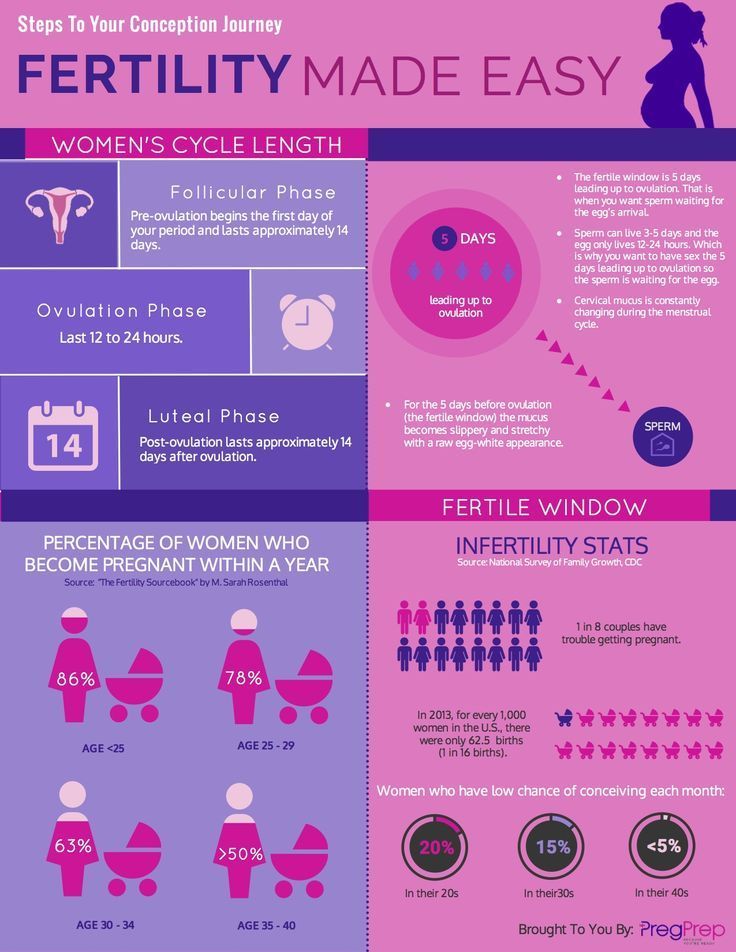 For the best chance of getting pregnant as long as there are no underlying fertility problems, it is recommended to have intercourse every 2-3 days during your cycle. In addition, fertility calendars, an ovulation test, and self-monitoring for signs of ovulation can help predict the ideal time to conceive.
For the best chance of getting pregnant as long as there are no underlying fertility problems, it is recommended to have intercourse every 2-3 days during your cycle. In addition, fertility calendars, an ovulation test, and self-monitoring for signs of ovulation can help predict the ideal time to conceive.
Menstrual calendar
It could be an old-fashioned pen and paper, a spreadsheet, or one of the many online calendars available. They are also known as ovulation calendars or ovulation calculators. They all do the same thing: keep track of your menstrual cycle dates and use the 12-16 day calculation outlined above to determine the days on which you are most likely to conceive.
Ovulation Tests
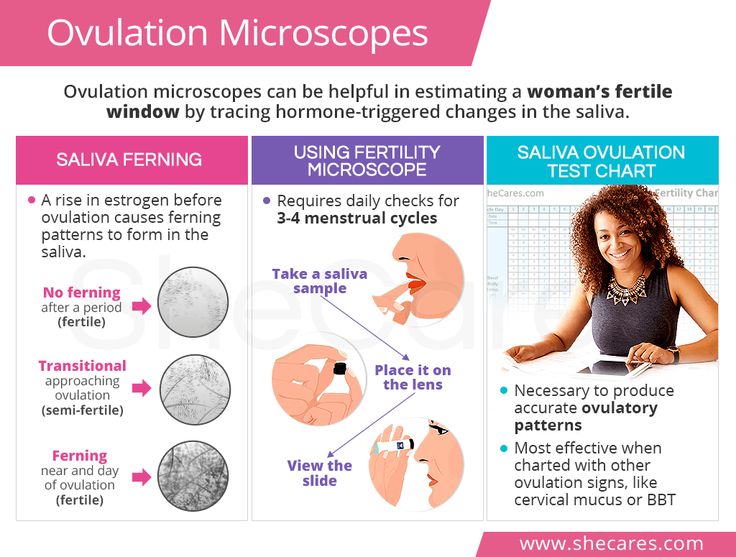
These are test kits that measure the level of luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. The essence of the measurement is to capture the surge in LH levels that occurs during your cycle a couple of days before ovulation. There are also tests that measure the same hormone pulsation but use a saliva sample. In these tests, saliva takes on the appearance of a fern-like pattern when it dries on glass. However, the most accurate analysis that allows you to track the LH peak is a urinalysis (rarely used in routine practice).
In these tests, saliva takes on the appearance of a fern-like pattern when it dries on glass. However, the most accurate analysis that allows you to track the LH peak is a urinalysis (rarely used in routine practice).
Self-monitoring for signs of impending ovulation
Self-monitoring includes taking temperature every morning after waking up, as well as monitoring the quality and consistency of vaginal mucus secretions. This must continue for several months so that ovulation can be tracked. This is the least reliable of the methods, because there can be many different causes of body temperature fluctuations (night rises, colds, blood sugar fluctuations), and in fact, many girls rightly find this procedure tedious and difficult to perform.
Fomin's clinic — a network of multidisciplinary clinics
Today's world is full of information: literally with one click, each of us can open the Universe and learn everything - from string theory to concert posters for the next week.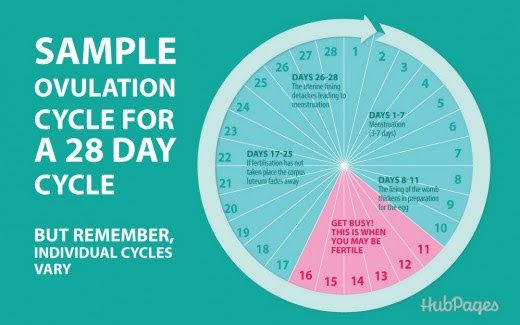 It is all the more interesting that, having unlimited access to knowledge, we still live in myths - and sometimes they arise, including thanks to the Internet, replicating untruth and absurdity.
It is all the more interesting that, having unlimited access to knowledge, we still live in myths - and sometimes they arise, including thanks to the Internet, replicating untruth and absurdity.
We have prepared for you a short “blitz” of six questions or myths about pregnancy and conception, so that you are fully equipped and do not believe the tales on the Internet.
Well... not exactly. Firstly, the idea of a “full examination” is a clear exaggeration, because there is no single list of tests that an expectant mother needs to pass. Ideally, visit a doctor three months before the end of contraception, get tested for STIs and antibodies to rubella. If additional examinations are required, you will be individually prescribed everything you need - including, probably, vaccinations that should be “updated”. As for alcohol and smoking, they are really contraindicated at the stage of pregnancy planning, so if you have these addictions, you will have to give them up.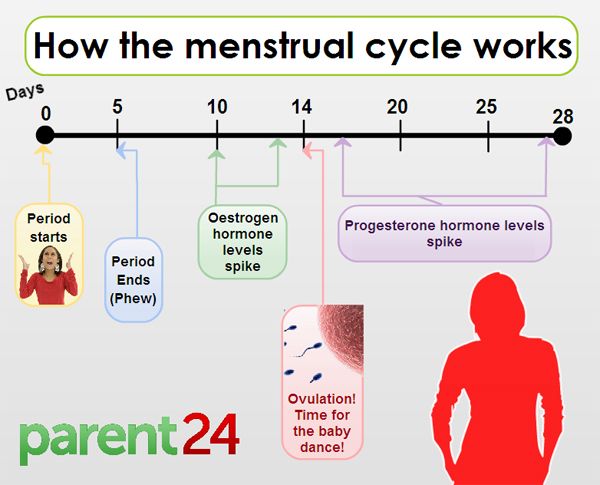 However, it should be remembered that smoking cessation applies to both electronic cigarettes and “passive smoking”, which can lead to dangerous consequences for the fetus.
However, it should be remembered that smoking cessation applies to both electronic cigarettes and “passive smoking”, which can lead to dangerous consequences for the fetus.
Spoiler: no big deal. Do not panic and blame yourself for all mortal sins because of a glass of wine. With the recognized insecurity of alcohol, scientists have proven that a woman drinking 1-2 servings a couple of times a week should not harm the unborn child. For men, the allowable figures are slightly higher - 3-4 doses of alcohol per week. The main thing is to know the measure and not to overdo it.
There is, of course, a simplified formula for calculating the estimated due date: plus 7 days and minus 3 months from the date of the last period, but to be honest, it doesn’t work like that: the fact is that it is very difficult to “program” pregnancy and make sure that the child is born when you want. If you have a plan and are going to stick to it, be prepared for the fact that things can go wrong, if only because:
- the duration of pregnancy is not 40 weeks, but 37-42 weeks, which means that you can easily get into a five-week “loop”, which will reduce the chances of fulfilling the plan to zero;
- with regular sex, the probability of conception is not 1 time per month (exactly when you guessed it), but 1 time per year.
Nothing is impossible... However, it is worth clarifying the question a little: you can get pregnant only during ovulation (more precisely, shortly after it), but you can have sex, which will lead to a long-awaited pregnancy, on different days. Of course, on the days of menstruation, the probability is lower than on the days that precede ovulation, but on none of the days of the menstrual cycle this probability is not zero.
Let's just say that trying multiple times a day is a bad idea. Why? At least because ejaculation more than once a day worsens the quality of sperm, as a maximum - such perseverance and zeal can create tension in the relationship of partners. Doctors advise to have sex every 2-3 days throughout the cycle, and not try to guess the moment and throw all your strength into this short period.
Planning the sex of a child is an extremely prolific topic for myth-makers. Some believe that with the help of a special table that takes into account such indicators as the age of the father and mother, the month of conception, it is possible to accurately calculate the sex of the child. This "method" is anti-scientific and has nothing to do with reality.
Some believe that with the help of a special table that takes into account such indicators as the age of the father and mother, the month of conception, it is possible to accurately calculate the sex of the child. This "method" is anti-scientific and has nothing to do with reality.
Another myth is that you have to get pregnant on the day you ovulate to have a boy. Previously, scientists really believed that X and Y spermatozoa differ from each other (Y are faster), and the sex of the child is formed due to the first one that broke through the defenses of the female egg. If you want to conceive a boy, you need to have sex on the day of ovulation so that the Y-sperms responsible for the "male sex" have more time to get to the egg located farthest from the entrance to the uterus.
However, this myth does not stand up to criticism: the fact is that there is no difference between the X and Y chromosomes, which means that the sex of the child does not depend on which of the sperm reaches the egg first.