Can morning sickness start in second trimester
Pregnancy - morning sickness - Better Health Channel
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- Around half to two-thirds of all pregnant women will experience morning sickness.
- Possible causes include high levels of hormones, blood pressure fluctuations and changes in carbohydrate metabolism.
- Severe morning sickness, called hyperemesis gravidarum, may require hospitalisation.
- Symptoms of morning sickness may be relieved by eating a few dry crackers before you get up in the morning, avoiding foods and smells that make you nauseous, drinking plenty of fluids and choosing high-carbohydrate and high-protein foods.
What is morning sickness?
Around half to two-thirds of all pregnant women will experience morning sickness to some degree, particularly in the first trimester. The symptoms include nausea and vomiting. Morning sickness is typically at its worst early in the day, hence its name, but it can strike at any point during the day or night.
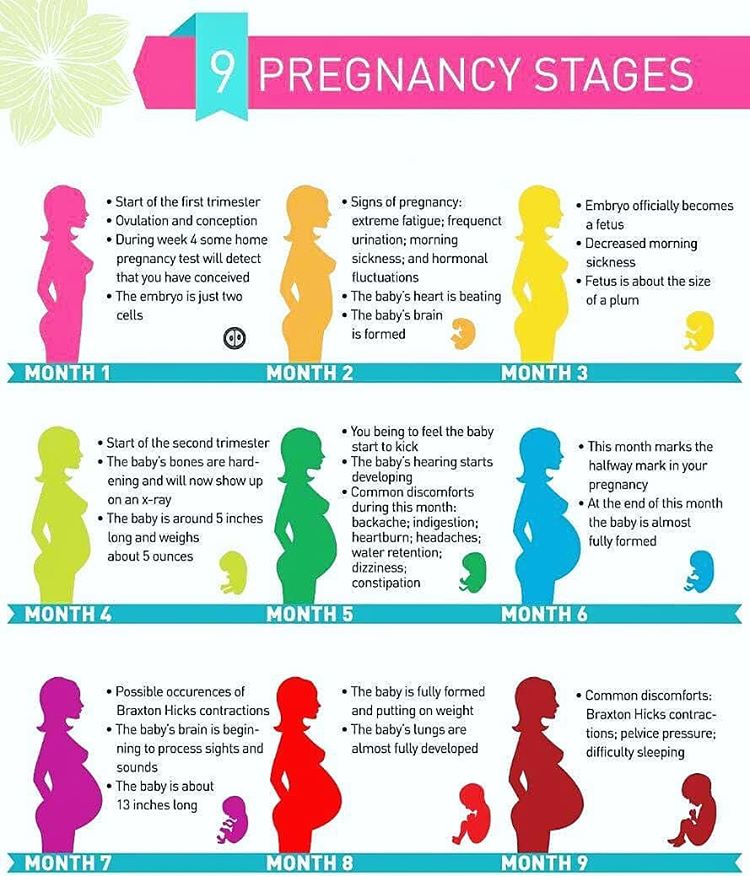
For most women, morning sickness begins around the fourth week of pregnancy and resolves by weeks 12 to 14. However, 1 in 5 women endures morning sickness into their second trimester, and an unfortunate few experience nausea and vomiting for the entire duration of their pregnancy.
In most cases, morning sickness doesn’t harm the woman or the unborn child. However, severe morning sickness that includes weight loss and dehydration needs prompt medical attention.
Symptoms of morning sickness
Symptoms of morning sickness can include:
- nausea
- loss of appetite
- vomiting
- psychological effects, such as depression and anxiety.
The myth of hysteria and morning sickness
Unrelenting morning sickness can have a profound effect on your quality of life, preventing you from working, socialising and looking after your other children.
Pregnant women enduring morning sickness report higher levels of psychological stress, including anxiety and depression. This prompted the false belief that morning sickness is purely psychosomatic, which means that the woman’s fears and anxieties trigger her physical discomfort. However, there is no research to support these claims.
This prompted the false belief that morning sickness is purely psychosomatic, which means that the woman’s fears and anxieties trigger her physical discomfort. However, there is no research to support these claims.
Possible causes of morning sickness
The cause of morning sickness remains a mystery, but it is thought a combination of physical and metabolic factors play a significant role, including:
- high levels of hormones, including oestrogen
- fluctuations in blood pressure, particularly lowered blood pressure
- altered metabolism of carbohydrates
- the enormous physical and chemical changes that pregnancy triggers.
Morning sickness and your baby
Some women are concerned that the action of vomiting may threaten their unborn baby. Vomiting and retching may strain the abdominal muscles and cause localised aching and soreness, but the physical mechanics of vomiting won’t harm the baby. The fetus is perfectly cushioned inside its sac of amniotic fluid.
Numerous studies have discovered that moderate morning sickness is associated with a reduced risk of miscarriage. However, prolonged vomiting (that leads to dehydration and weight loss) can deprive your child of proper nutrition and increase the risk of your baby being underweight at birth.
If you have nausea and vomiting that will not stop, contact your GP (doctor) or midwife.
Severe morning sickness (hyperemesis gravidarum)
Severe morning sickness is known as hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), and can affect around one in 1000 pregnant women. The symptoms of HG include repeated vomiting, weight loss and dehydration. Treatment usually involves hospitalisation, and the administering of intravenous liquids and nutrition.
The possible complications of untreated hyperemesis gravidarum include:
- electrolyte imbalances
- extreme depression and anxiety
- malnourishment of the fetus
- excessive strain on vital organs, including the liver, heart, kidneys and brain.

Managing morning sickness
Suggestions for coping with morning sickness include:
- Don’t take drugs of any kind, unless your doctor knows you are pregnant and has prescribed specific medications.
- Eat a few dry crackers or plain sweet biscuits before getting out of bed in the morning.
- Don’t eat anything that you suspect will make you nauseous. In general high-carbohydrate meals are well tolerated.
- Eat small meals regularly, as an empty stomach tends to trigger nausea.
- It may help to avoid cooking or preparing foods.
- Drink as much as you can manage. Sometimes sips of flat lemonade, diluted fruit juice, cordial, weak tea, ginger tea, clear soup or beef extract drinks are helpful. If none of these are bearable, try sucking on ice cubes.
- Vitamin B6 supplements can be useful, but doses above 200 mg per day can actually be harmful. Follow your doctor’s advice.
- Consider acupressure or acupuncture on the wrist.

- Wear loose clothes that don’t constrict your abdomen.
- Moving around may aggravate morning sickness. Rest whenever possible.
Seeing your doctor about morning sickness
Always seek medical advice if your morning sickness is severe, if you have lost a lot of weight quickly, or if you feel depressed or anxious. Treatment options can include medication that won’t harm your developing baby.
Where to get help
- Your GP (doctor)
- Midwife
- Obstetrician
- Maternal and Child Health Line (24 hours, 7 days) Tel. 13 22 29
- Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy, The Royal Women’s Hospital.
- Chan RL, Olshan AF, Savitz DA, et al., 2010, ‘Severity and duration of nausea and vomiting symptoms in pregnancy and spontaneous abortion’, Human Reproduction, vol. 25, no. 11, pp. 2907–2912.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
What to expect in your second trimester | Conditions, Treatments & Specialty
Hooray – you’re almost half way through your pregnancy! Some mamas say the second trimester is the easiest. For many women, the second trimester is a time of preparation for baby’s arrival. Your energy levels are up, you’re feeling great post-morning sickness and the fatigue of your first trimester is subsiding. During these three months, you’ll notice a lot of changes going on with and in your body, all to support the growth of your little one!
For many women, the second trimester is a time of preparation for baby’s arrival. Your energy levels are up, you’re feeling great post-morning sickness and the fatigue of your first trimester is subsiding. During these three months, you’ll notice a lot of changes going on with and in your body, all to support the growth of your little one!
When is the second trimester?
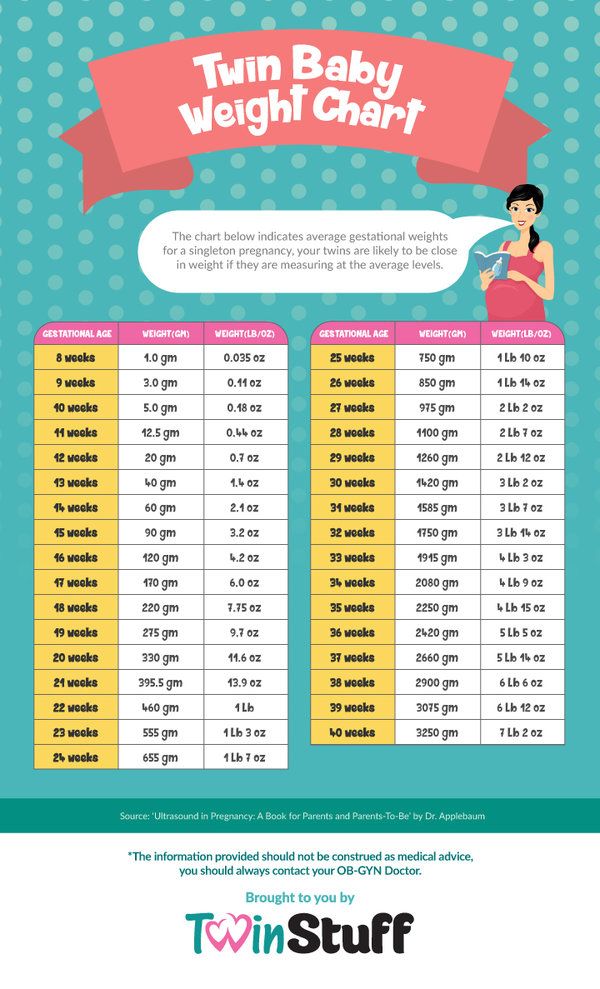
The second trimester of your pregnancy spans weeks 14 through 27, or months four through six. Your first semester nausea has probably passed (yay!), but you may have started experiencing some of the second trimester’s symptoms. Pregnancy heartburn and constipation, anyone?During these weeks, your baby and your belly are really starting to grow! At the beginning of your third trimester, your baby hardly weighs one pound, but by the end, they’ll weigh in at around two pounds.
What is happening to your body?
As your baby starts to grow, you’ll start noticing some changes in your own body, too. Your breasts will continue to grow because of enlarging milk glands and deposits of fat, which means your body is getting ready to produce milk for your baby.
Your breasts will continue to grow because of enlarging milk glands and deposits of fat, which means your body is getting ready to produce milk for your baby.
As your belly grows, your doctor will measure your belly from your pubic bone to the top of your belly to measure your baby’s growth. This growth will cause some skin changes, including stretch marks and dry, itchy skin.
Other symptoms you may experience during your second trimester may include:
- Body aches
- Darker skin on your face
- Dizziness or lightheadedness from lower blood pressure
- Growing breasts and belly
- Heart burn
- Increased appetite
- Leg cramps
- Swelling hands or ankles
Creams and lotions can help with your skin symptoms, and light exercises such as walking can help to alleviate leg cramps.
You’ll start to feel your baby move during the second trimester, and you’ll hear his or her heartbeat for the first time around week 16! During your second trimester, you’ll have the option to undergo genetic testing to test your child for genetic or chromosomal conditions.
Pregnancy symptoms to call your doctor about
Not every symptom is cause for alarm; in fact, most are normal. However, if you experience anything that worries you, you can always reach out to your doctor. They are there to support you through your journey!
If you experience any of these symptoms, reach out to your doctor immediately:
- Blurred vision
- Extreme swelling
- Fever over 100°F
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Rapid weight gain
- Severe or unusual abdominal cramping or pain
- Severe diarrhea
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes (jaundice)
You’ll likely see your doctor every two to four weeks throughout your second trimester but follow your instincts. Call your doctor if you need to see them sooner than a scheduled appointment.
How is your baby growing?
Your second trimester is a great time to enroll in prenatal education, breastfeeding, infant CPR and parenting classes. Your doctor can recommend and help you chose classes, too. As you start to join classes and make some great strides towards motherhood, your baby hits some incredible milestones in the second trimester.
Your doctor can recommend and help you chose classes, too. As you start to join classes and make some great strides towards motherhood, your baby hits some incredible milestones in the second trimester.
At the beginning of the second trimester, your baby has all their facial features, which you’ll start to see at your ultrasound appointments. You can also find out the sex of your baby at around week 18! If you don’t want to know, make sure you say so at your ultrasound appointments.
Your baby’s organs fully develop in the second trimester. They can also begin to hear and grow some of their hair. They’ll develop a layer of fat to help with their metabolism, and you’ll even notice that your appetite will increase to support their growth. Towards the end of your second trimester, your baby can stick out their tongue and “dance” to music. The nerves in their ears will form enough so that they can recognize the difference between your and your partner’s voices, too.
You may also notice that your child begins to develop their sleep cycle—you’ll be able to feel their movement and stillness as they sleep and wake!
Talk to our team today to schedule an appointment
Call 800-275-6401 and say “women’s services. ”
”
Call for an appointment
2022 Geisinger Health
- Developer
- Terms & conditions
- HIPAA (new)
- Privacy policy
- Non-discrimination notice
- Social media guidelines
- Corporate compliance reporting
- Report fraud
- Employee login
- Provider resources
- Geisinger company stores
Geisinger Health Plan may refer collectively to Geisinger Health Plan, Geisinger Quality Options Inc., and Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, unless otherwise noted. Geisinger Gold Medicare Advantage HMO, PPO, and HMO D-SNP plans are offered by Geisinger Health Plan/Geisinger Indemnity Insurance Company, health plans with a Medicare contract. Continued enrollment in Geisinger Gold depends on annual contract renewal. Geisinger Health Plan Kids (Children’s Health Insurance Program) and Geisinger Health Plan Family (Medical Assistance) are offered by Geisinger Health Plan in conjunction with the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services (DHS). Geisinger Health Plan is part of Geisinger, an integrated health care delivery and coverage organization.
Continued enrollment in Geisinger Gold depends on annual contract renewal. Geisinger Health Plan Kids (Children’s Health Insurance Program) and Geisinger Health Plan Family (Medical Assistance) are offered by Geisinger Health Plan in conjunction with the Pennsylvania Department of Human Services (DHS). Geisinger Health Plan is part of Geisinger, an integrated health care delivery and coverage organization.
Second trimester of pregnancy (from 13 to 28 weeks)
The beginning of the second trimester is traditionally considered one of the calmest. Walk more. Walking is very helpful. Sit down to rest only when you are tired. Movement in the fresh air improves the supply of oxygen to the fetus, which is very necessary for its normal development.
Nausea disappears, appetite improves. Do not eat a lot of salty, refuse marinades, smoked meats, if you have not done this before. The increased need of the child's body for proteins and vitamins begins. The daily diet should include meat or fish (boiled or stewed), dairy products, especially cottage cheese, eggs. Do not forget about vegetables, fruits, greens. An excellent source of vitamin C is sauerkraut (rather than salted) cabbage. Salads from carrots, cabbage, beets, apples, green radish should be on your table every day.
Do not forget about vegetables, fruits, greens. An excellent source of vitamin C is sauerkraut (rather than salted) cabbage. Salads from carrots, cabbage, beets, apples, green radish should be on your table every day.
At 17-20 weeks you will feel your baby's first kicks. From them you can determine how comfortable the baby feels. Intense tremors are a signal of lack of oxygen. Maybe you haven’t walked for a long time or, on the contrary, you are engaged in hard physical labor. Get out into the fresh air or lie down to rest and you will immediately feel how the child has calmed down.
But the lack of movement is an alarm. See a doctor immediately!
The fetal need for calcium sharply increases - intensive growth of the skeleton has begun. If you don't have enough free calcium in your body right now, you could lose your teeth. To prevent this from happening, start taking calcium supplements in consultation with your doctor.
At this time, toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy may occur, the child suffers greatly from it. Therefore, if the doctor suggests hospitalization, do not refuse. Toxicosis can, if not be avoided, then at least reduce its manifestations. Be sure to follow your diet. Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Therefore, if the doctor suggests hospitalization, do not refuse. Toxicosis can, if not be avoided, then at least reduce its manifestations. Be sure to follow your diet. Completely exclude salty, smoked, fried, spicy, canned food, chocolate. Do not eat a lot of grapes and drink fresh milk. Limit flour and rich products. As before, your diet should include boiled meat and fish, oatmeal and buckwheat porridge, vegetables and fruits
Periodically, once a week, check for fluid retention in the body. It is allowed to release liquid 200-300 ml less than what was drunk. If little urine is released, this is a signal of latent edema and the onset of toxicosis.
It is very good if you can measure your blood pressure at home. Show the results of measurements at the next visit to the doctor. Both high and too low pressure should alert. With low pressure, blood sluggishly crosses the placenta, and the baby does not receive enough nutrients.
Do not neglect blood tests - it is important not to miss the development of anemia. In this case, you will be prescribed iron supplements and multivitamins. The diet should include beef liver, tomato juice, buckwheat porridge, apples, preferably Antonovskie (they contain more iron than other varieties).
In this case, you will be prescribed iron supplements and multivitamins. The diet should include beef liver, tomato juice, buckwheat porridge, apples, preferably Antonovskie (they contain more iron than other varieties).
Women who are at risk of giving birth to a child with a genetic pathology (those who have severe hereditary ailments in their families), as well as women over 35 years old (they have an increased likelihood of having a child with Down syndrome) are referred for a consultation by a geneticist.
In case of a normal pregnancy at 20-22 weeks of pregnancy, a second scheduled ultrasound examination is prescribed.
Why do you feel sick during pregnancy in the early stages, at what time can pregnancy be determined. What helps with nausea
Every second woman feels sick during pregnancy. An unpleasant symptom appears even before a woman finds out that she is in a position. We tell you why the malaise begins, how many months it lasts and how you can cope with unpleasant symptoms.
What is toxicosis?
Morning (and sometimes afternoon and evening) ailments, along with sore breasts and the absence of menstruation, are considered the main signs by which a woman understands that she is pregnant. But from what day of pregnancy does she start to feel sick? The period at which toxicosis begins varies.
Nearly a third of women experience nausea approximately 4 weeks after the end of their last period. In the remaining 70%, toxicosis occurs at week 8. At the same time, in addition to nausea, half of the women also experience vomiting. In the vast majority of pregnant women, all unpleasant symptoms disappear by the 14th week.
However, in the third trimester, nausea may return. Most often, nausea during pregnancy occurs after eating for a long time.
This is due to the fact that the growing uterus and the child in it begin to squeeze the stomach, which causes a feeling of overeating and nausea. But it also happens that this is a sign of preeclampsia, which must be treated.
Most often, morning sickness and vomiting occur. Unpleasant odors, being in a stuffy room, motion sickness in transport, as a reaction to a certain type of food, and other factors can also provoke an attack. However, discomfort can occur unexpectedly or in cases where everything was normal before.
Among the risk factors that lead to the development of toxicosis are migraines, overweight, endocrine disorders, bronchial asthma, depression, eating disorders, underweight, multiple pregnancy. However, these factors do not mean that a pregnant woman will definitely have toxicosis.
Nausea is not only an unpleasant symptom that overshadows the joy of future motherhood. It can lead to serious consequences. Among them are weight loss, insomnia, fluid and electrolyte imbalance, multiple organ failure, and spontaneous abortion.
Important! Be sure to tell the gynecologist in charge of the pregnancy if any meal causes vomiting, you have begun to significantly reduce body weight
Causes of toxicosis
Almost every woman is faced with the question of what causes nausea during pregnancy? Several factors play a role in the etiology of toxicosis. What exactly provokes its development in a particular woman is impossible. Among the main reasons are the following:
What exactly provokes its development in a particular woman is impossible. Among the main reasons are the following:
| Factors | Description |
| Genetic factors | If the mother had severe nausea, then the daughter may experience the same symptoms. |
| immune factors | With nausea and vomiting, the body reacts to antigens that arise in response to foreign genes of the fetus. |
| Toxic factors | There is a hypothesis according to which normal excretory processes are disrupted during pregnancy, which causes poisoning. |
| Nervous Factors | In women with identified vegetovascular dystrophy and somatotrophic disorders, nausea develops due to dysfunction of the nervous system. |
| Psychological factors | Identified depression, neurosis, increased anxiety, eating disorders and other disorders lead to gastrointestinal dysfunction. |
| Hormonal factors | A relationship has been found between the level of the hormone hCG and estradiol and the symptoms of toxicosis. It is also confirmed by the fact that the symptoms of toxicosis decrease along with a decrease in the level of these hormones. |
However, it is important to distinguish the symptoms of toxicosis from other diseases. Nausea and vomiting can also be a sign of other illnesses, such as kidney failure or peptic ulcers. Therefore, with severe toxicosis, it is imperative to undergo examinations to exclude other pathologies.
Usually, a general and biochemical blood test, a blood test for infections, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and urinary system, as well as fibrogastroduodenoscopy and consultations with specialized specialists are prescribed.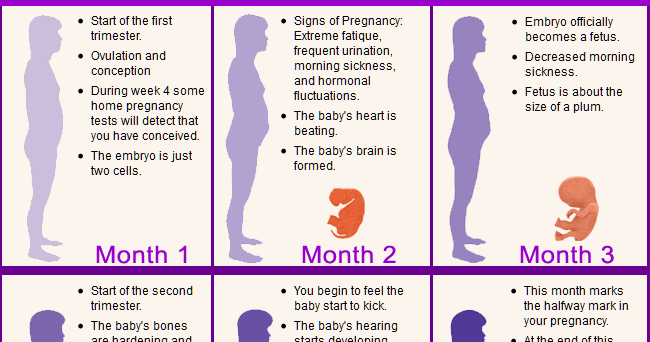 Treatment and examinations are carried out with care so that it does not harm the child.
Treatment and examinations are carried out with care so that it does not harm the child.
Be sure to consult a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist and nephrologist if the symptoms of toxicosis persist after the 14th week of pregnancy so that this does not pose a danger to the baby. Our doctors will answer all your questions by phone at any time of the day.
What to do in order not to feel sick
You can prevent the development of nausea and toxicosis even during preparation for it. It is necessary to undergo examinations and treat all pathologies found. Particular attention should be paid to diseases that are a risk factor in the development of discomfort.
Another important point is adjusting the diet. In general, it is recommended to give up fried, fatty and spicy foods, as well as start eating often and in small portions. Food should be at room temperature. In addition, it is recommended to drink more.
Plain water and tea can be replaced with mineral water and herbal infusions of mint, lemon balm, chamomile, cranberry and ginger. However, you should not get carried away with herbs, as they may have an impact on the course of pregnancy.
If these methods do not help, the gynecologist may recommend taking antiemetics, vitamin preparations, isotonic solutions, and sedatives. Consultation with a psychologist is also recommended to exclude psychogenic factors.
In severe cases and with signs of exhaustion, the pregnant woman is placed in a hospital where more intensive therapy is carried out. If the woman's condition does not improve, termination of the pregnancy may be recommended as a last resort.
If toxicosis does not cause trouble, it is not treated in any way. They only offer to slightly adjust the diet and try folk methods of dealing with toxicosis. These include a few sips of mineral water, saltine crackers, or a lemon wedge right after waking up.
Case study:
The patient went to the gynecologist with complaints of severe nausea, persistent vomiting and weight loss. The gynecologist did not write off everything for pregnancy and conducted a full examination. FGDS with a biopsy revealed the presence of Helicobacter pylori and signs of gastritis in a woman. After treatment of the underlying disease, the symptoms of toxicosis also decreased.
FAQ
At what time can pregnancy be determined?
+
A blood test for chorionic gonadotropin can show pregnancy as early as 6–8 days after conception. However, it is more reliable to carry it out 3-5 days after the delay or on the 12th day after conception.
How many days after conception does it start to vomit?
+
Nausea can develop from 4 to 7 weeks after the last menstruation, that is, even before the delay appears. Symptoms of toxicosis usually disappear by 12-14 weeks. Also, unpleasant symptoms may return in the third trimester.
Also, unpleasant symptoms may return in the third trimester.
What to do if the chest stops hurting during pregnancy?
+
If the chest stops hurting at any stage of pregnancy, this may indicate hormonal disorders in the expectant mother. It can lead to problems with gestation, so any changes in well-being must be reported to the gynecologist.
After how many weeks can you find out about pregnancy?
+
The first signs of pregnancy appear at least 4 weeks after the end of the last menstruation, even before the delay. They will fail in the form of nausea, mood changes, tearfulness. In addition, in the early stages of pregnancy, the breast hurts and enlarges.
How to distinguish toxicosis from ordinary nausea?
+
By external signs, it is almost impossible to distinguish them from each other. But there is a slight difference.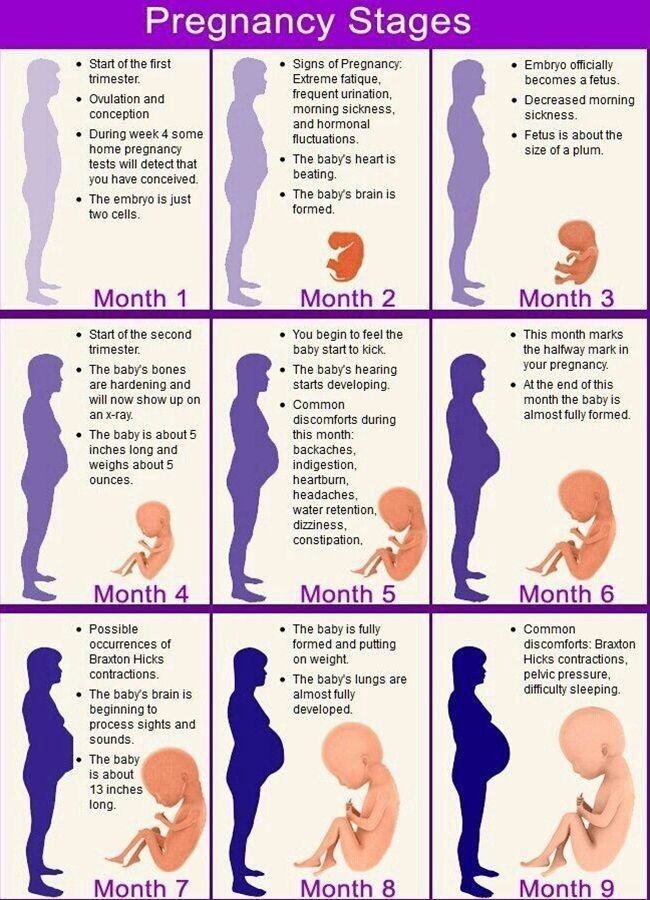 Toxicosis usually manifests itself in the morning, and nausea - at any time of the day, including in the evening. If nausea is not complicated by vomiting, but does not go away within a few days, it is recommended to do a home pregnancy test or donate blood for hCG.
Toxicosis usually manifests itself in the morning, and nausea - at any time of the day, including in the evening. If nausea is not complicated by vomiting, but does not go away within a few days, it is recommended to do a home pregnancy test or donate blood for hCG.
Expert opinion
Nausea in the later stages may indicate the development of preeclampsia. This complication affects all organs and leads to the development of severe multiple organ failure. In addition to nausea and vomiting, a pregnant woman is worried about swelling, severe headaches, rapid weight gain, high blood pressure and visual impairment.
Preeclampsia has the most serious consequences for both the mother and the unborn baby. Therefore, if late toxicosis is suspected, a woman is placed under the constant supervision of a doctor in the department of pregnancy pathology.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience.