Surgical procedures for abortion
Abortion - surgical: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
URL of this page: //medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002912.htm
To use the sharing features on this page, please enable JavaScript.
Surgical abortion is a procedure that ends an undesired pregnancy by removing the fetus and placenta from the mother's womb (uterus).
Surgical abortion is not the same as miscarriage. Miscarriage is when a pregnancy ends on its own before the 20th week of pregnancy.
Surgical abortion involves dilating the opening to the uterus (cervix) and placing a small suction tube into the uterus. Suction is used to remove the fetus and related pregnancy material from the uterus.
Before the procedure, you may have the following tests:
- A urine test checks if you are pregnant.
- A blood test checks your blood type. Based on the test result, you may need a special shot to prevent problems if you get pregnant in the future.
The shot is called Rho(D) immune globulin (RhoGAM and other brands).
- An ultrasound test checks how many weeks pregnant you are.
During the procedure:
- You will lie on an exam table.
- You may receive medicine (sedative) to help you relax and feel sleepy.
- Your feet will rest in supports called stirrups. These allow your legs to be positioned so that your doctor can view your vagina and cervix.
- Your health care provider may numb your cervix so you feel little pain during the procedure.
- Small rods called dilators will be put in your cervix to gently stretch it open. Sometimes laminaria (sticks of seaweed for medical use) are placed in the cervix. This is done the day before the procedure to help the cervix dilate slowly.
- Your provider will insert a tube into your womb, then use a special vacuum to remove the pregnancy tissue through the tube.
- You may be given an antibiotic to reduce the risk of infection.
After the procedure, you may be given medicine to help your uterus contract. This reduces bleeding.
This reduces bleeding.
Reasons a surgical abortion might be considered include:
- You have made a personal decision not to carry the pregnancy.
- Your baby has a birth defect or genetic problem.
- Your pregnancy is harmful to your health (therapeutic abortion).
- The pregnancy resulted after a traumatic event such as rape or incest.
The decision to end a pregnancy is very personal. To help you weigh your choices, discuss your feelings with a counselor or your provider. A family member or friend can also be of help.
Surgical abortion is very safe. It is very rare to have any complications.
Risks of surgical abortion include:
- Damage to the womb or cervix
- Uterine perforation (accidentally putting a hole in the uterus with one of the instruments used)
- Excessive bleeding
- Infection of the uterus or fallopian tubes
- Scarring of the inside of the uterus
- Reaction to the medicines or anesthesia, such as problems breathing
- Not removing all of the tissue, requiring another procedure
You will stay in a recovery area for a few hours. Your providers will tell you when you can go home. Because you may still be drowsy from the medicines, arrange ahead of time to have someone pick you up.
Your providers will tell you when you can go home. Because you may still be drowsy from the medicines, arrange ahead of time to have someone pick you up.
Follow instructions for how to care for yourself at home. Make any follow-up appointments.
Problems rarely occur after this procedure.
Physical recovery usually occurs within a few days, depending on the stage of the pregnancy. Vaginal bleeding can last for a week to 10 days. Cramping most often lasts for a day or two.
You can get pregnant before your next period, which will occur 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure. Be sure to make arrangements to prevent pregnancy, especially during the first month after the procedure. You may want to talk with your provider about emergency contraception.
Suction curettage; Surgical abortion; Elective abortion - surgical; Therapeutic abortion - surgical
- Abortion procedure
Katzir L. Induced abortion. In: Mularz A, Dalati S, Pedigo R, eds. Ob/Gyn Secrets. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Leeman L, Godfrey E. Pregnancy termination: first-trimester suction aspiration. In: Fowler GC, ed. Pfenninger and Fowler's Procedures for Primary Care. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 113.
Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A. Abortion. In: Magowan BA, Owen P, Thomson A, eds. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2019:chap 20.
Rivlin K, Westhoff C. Family planning. In: Lobo RA, Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2017:chap 13.
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
In-Clinic Abortion Procedure | Abortion Methods
In This Section
- In-Clinic Abortion
- What happens during an in-clinic abortion?
- What can I expect after an in-clinic abortion?
- How safe is an in-clinic abortion?
- How do I get an in-clinic abortion?
In-Clinic Abortion | Planned Parenthood Video
In-Clinic Abortion | Planned Parenthood VideoWhat is an abortion?
Abortion is a medical procedure that ends a pregnancy. In-clinic abortion procedures are safe and effective. In-clinic abortions are sometimes called surgical abortions, though they're generally an in-office procedure, not surgery.
In-clinic abortion procedures are safe and effective. In-clinic abortions are sometimes called surgical abortions, though they're generally an in-office procedure, not surgery.
What are the types of in-clinic abortions?
In-clinic abortion works by using suction to take a pregnancy out of your uterus. There are a couple of kinds of in-clinic abortion procedures. Your doctor or nurse will know which type is right for you, depending on how far you are into your pregnancy.
Suction abortion (also called vacuum aspiration) is the most common type of in-clinic abortion. It uses gentle suction to empty your uterus. It’s usually used until about 14-16 weeks after your last period.
Dilation and Evacuation (D&E) is another kind of in-clinic abortion procedure. It uses suction and medical tools to empty your uterus. You can get a D&E later in a pregnancy than aspiration abortion -- usually if it has been 16 weeks or longer since your last period.
How effective are in-clinic abortions?
In-clinic abortions are extremely effective. They work more than 99 out of every 100 times. Needing to get a repeat procedure because the abortion didn’t work is really rare.
They work more than 99 out of every 100 times. Needing to get a repeat procedure because the abortion didn’t work is really rare.
When can I get an in-clinic abortion?
How early you can get an abortion depends on where you go. In some places, you can get it as soon as you have a positive pregnancy test. Other doctors or nurses prefer to wait until 5-6 weeks after the first day of your last period.
How late you can get an abortion depends on the laws in your state and what doctor, abortion clinic, or Planned Parenthood health center you go to. It may be harder to find a health care provider who will do an abortion after the 12th week of pregnancy, so it’s best to try to have your abortion as soon as possible.
Why do people choose an in-clinic abortion?
Which kind of abortion you choose all depends on your personal preference and situation. Some people choose in-clinic abortion because they want to to have their procedure done at a health center, with nurses, doctors, and trained support staff there the whole time. (With the abortion pill, you have the abortion at home.)
(With the abortion pill, you have the abortion at home.)
In-clinic abortions are also much faster than the abortion pill: most in-clinic abortions only take about 5-10 minutes, while a medication abortion may take up to 24 hours to complete.
Your nurse, doctor, or health center counselor can help you decide which kind of abortion is best for you.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Abortion Clinics Near You
View Planned Parenthood health centers that provide abortion care and get the information you need to schedule an appointment.
Your information is private and anonymous.
Find Abortion ServicesAsk us anything. Seriously.
Between our trained sexual health educators or chat bot, we can answer your questions about your sexual health whenever you have them. And they are free and confidential.
Chat NowWe couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
Your information is private and anonymous.
I'm not sure This field is required.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
Preparation for medical and surgical abortion. Indications and pre-indications
Before the abortion procedure, the patient is required to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and pass the prescribed tests. This is necessary to identify possible pathologies that will affect the patient's condition during surgery. At the appointment, the doctor determines the gestational age and determines the appropriate method for terminating the pregnancy.
Artificial interruption is done at the request of the patient at a gestational age of up to 12 weeks. As an exception, the legislation takes into account abortions for medical or social reasons.
- For medical reasons, pregnancy is terminated regardless of the term.
- According to social indications, abortion is done at a period of up to 22 weeks.
 The list of social indications is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
The list of social indications is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
Indications for medical abortion:
- the patient's desire to terminate an unplanned pregnancy up to 9 weeks: up to 63 days from the first day of the last menstruation;
- the presence of medical indications for termination of pregnancy, including frozen pregnancy up to 63 days from the first day of the last menstruation.
Contraindications for medical abortion:
- infection of the genital and digestive organs;
- tumors of the reproductive organs;
- the presence of an intrauterine device;
- abnormal position of the ovum;
- scars on the uterus;
- pregnancy disorders while taking hormonal contraceptives;
- tuberculosis;
- diabetes mellitus in a dangerous stage;
- severe mental disorders;
- heart defects;
- acute autoimmune diseases;
- blood diseases.
Surgical abortion
The procedure is done under general anesthesia so that the girl does not feel pain. The doctor removes the fetal egg from the uterus and scrapes the walls with surgical instruments. To avoid complications, the girl remains under medical supervision until her condition stabilizes. If the patient's health is not in danger, then the discharge takes place on the same day.
The World Health Organization has recognized surgical termination of pregnancy as an outdated method, but the method remains popular in Russia. It is used when the deadline for medical abortion is missed.
Preparation for surgical abortion
Surgical abortion is equated to an operation, so a consultation and examination by a gynecologist is required before the procedure. It is advisable to contact the doctor in the clinic where you plan to have an abortion. At the appointment, the doctor collects an anamnesis, learns about chronic diseases, what medications the girl takes, and asks about previous pregnancies. Next, the patient is prescribed tests and sent for an ultrasound. This is necessary to determine the pathologies of the reproductive system, in which abortion is contraindicated.
Next, the patient is prescribed tests and sent for an ultrasound. This is necessary to determine the pathologies of the reproductive system, in which abortion is contraindicated.
Curettage of the fetus remains the fastest and most reliable method, because the mucous layer of the uterus is completely removed. In addition, the gestation period for surgical abortion is longer than for other methods - up to 12 weeks.
Medical abortion
The method consists in taking pharmacological drugs that stop the development of the fetus. Pill abortion is a modern alternative to surgical intervention. The gestational age for medical abortion is no longer than 7 weeks from the last menstrual cycle. Pharmacological abortion at a later date leads to the development of pathologies.
The drugs artificially stimulate a miscarriage in the body: the uterus contracts, accelerates the hatching of the egg and does not allow to gain a foothold. Within 10 days, the patient has bleeding similar to menstruation.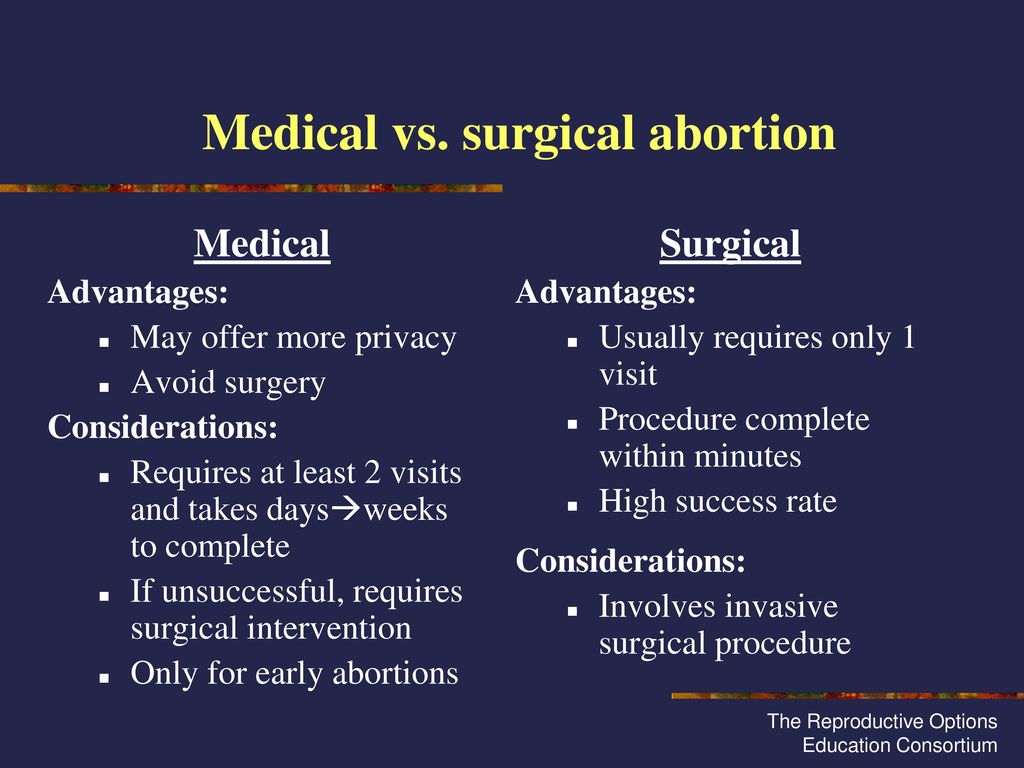 After that, it is necessary to do an ultrasound to monitor the state of the reproductive system.
After that, it is necessary to do an ultrasound to monitor the state of the reproductive system.
Preparation for medical abortion
The procedure does not require serious preparation. It is necessary to consult with your doctor, undergo a pelvic ultrasound, pass the prescribed smears and tests. 5 days before the procedure, it is recommended to give up alcohol and intimacy, avoid stress and physical activity. When the pregnancy is terminated, it is necessary to refrain from sexual intercourse for 3 weeks.
Psychological preparation for abortion
When contacting a antenatal clinic to terminate a pregnancy, a girl will have an open conversation with a doctor or psychologist. The patient will have to weigh the arguments again and make a final decision. If the slightest doubt remains, then time is given to rethink the intention. Before an abortion, it is important to overcome internal doubts in order to avoid depression later. However, you should not delay making a decision, as an increase in terms increases the risk of complications.
Social stigma is often present and a girl may attempt to terminate a pregnancy on her own without consulting a doctor. Such attempts cause damage to the reproductive system and pose a danger to life. Therefore, it is necessary to cope with fear and remember that the doctor will help you make the right decision.
The information presented in the material is of a general nature. Check with your doctor for personal recommendations for terminating a pregnancy.
What you need to know about the surgical method of abortion (Temporarily not carried out) - GBUZ VO "City Clinical Hospital No. 5 of Vladimir"
|
| What do you need to know? |
Until what gestational age can an abortion be performed?
Artificial termination of pregnancy (abortion) is carried out for up to 20 days of delay in the menstrual cycle (mensis).
Abortion is always a difficult decision and a real test for a woman. Before taking such a responsible step, you must carefully read the information about this procedure. One of the main issues is the gestational age until which an abortion is possible.
There are three types of abortion, each of which is used at a certain stage of pregnancy.
For up to 7 weeks, abortion is carried out medically. For this, special drugs are used that provoke a miscarriage. The drug for the procedure can be taken only after examination by a gynecologist and under his control.
For up to 20 days of delay in the menstrual cycle in a day hospital, a so-called mini-abortion is carried out, which is carried out using a special vacuum device.
At later terms up to 12 weeks, abortion is carried out in a specialized hospital.
Vladimir City Clinical Hospital No. 5 is a state healthcare institution that has all the conditions for performing an abortion - an equipped operating room, a day hospital, and anesthetic equipment.
An anesthetist is always present when choosing anesthesia.
Before deciding on such a procedure, it is imperative to consult a specialist.
The procedure for providing medical care to women
in case of artificial termination of pregnancy is determined by the order of the Ministry of Health of Russia dated November 1, 2012 No. 572n (as amended on January 12, 2016) “On approval of the Procedure for the provision of medical care according to the profile” obstetrics and gynecology (with the exception of the use of assisted reproductive technologies )".
P. 106. Order - Before referral for artificial termination of pregnancy for up to twelve weeks, it is recommended to microscopic examination of the discharge of female genital organs, determination of the main blood groups (A, B, 0) and Rh accessories, ultrasound of the pelvic organs. In order to preserve pregnancy, during an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, a pregnant woman is shown an image of the embryo and its heartbeat (if there is a heartbeat).