Can i take vitamin c if im pregnant
Can You Take Vitamin C While Pregnant? | Nature Made®
Mar 11, 2021 Pregnancy Tips , Vitamin C
Quick Health Scoop
- Vitamin C provides multiple health benefits, including playing a key role in supporting a healthy immune system†
- Vitamin C provides additional pregnancy-related benefits, too
- It is safe to take Vitamin C during pregnancy
Eating a healthy, balanced diet plays a critical role in your well-being, but even more so for pregnant women who need to nourish their developing baby. Plus, during pregnancy, women may need more of certain nutrients. For example, pregnant women need a lot more Folate, Iron, Iodine, and Zinc; a little more Magnesium and Vitamin C; and the same amount of Calcium, Vitamin D and Vitamin E.1, which can be found in a variety of prenatal supplements. (Read More: Magnesium Benefits) But when it comes to taking Vitamin C while pregnant, is it safe and how much Vitamin C per day is safe? What are the benefits of Vitamin C during pregnancy, and how much should moms-to-be take?
Benefits Of Vitamin C During PregnancyIn general, Vitamin C provides multiple health benefits, such as supporting your healthy immune system, working as an antioxidant by helping to neutralize damaging free radicals in your cells, and as an enzyme cofactor, assisting in reactions such as making collagen and carnitine. Vitamin C also aids in the absorption of Iron.2,†
But it’s also important to know that additional benefits of Vitamin C during pregnancy exist, too. As mentioned above, the body needs Vitamin C to produce collagen—a part of skin, blood vessels, tendons, and bone. Vitamin C is also an antioxidant that helps neutralize free radicals before they can damage cells. Finally, pregnant women need significantly more Iron during pregnancy as their blood volume increases.3 Additionally, Vitamin C improves the absorption of Iron from plant-based foods.2,†
Learn More: What are Postnatal Vitamins?
Is Vitamin C Safe For Pregnancy?Typically, women take prenatal multivitamins both before and during pregnancy, because they’re specially formulated to support the development of baby’s brain, nervous system, and eyes.† Among the many important nutrients, these prenatal multis typically contain the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) of Vitamin C for pregnant women. While healthy women need 75 mg of Vitamin C each day, pregnant women require 85 mg of Vitamin C each day, and breastfeeding women need 120 mg per day.2
While healthy women need 75 mg of Vitamin C each day, pregnant women require 85 mg of Vitamin C each day, and breastfeeding women need 120 mg per day.2
As a general rule of thumb, pregnant women should avoid taking more than twice the recommended dietary allowances of vitamins and minerals.4
So, Vitamin C during pregnancy is certainly safe and beneficial for both mom and baby, as long the dosage remains within recommended daily levels.
Learn More: Can You Take Melatonin While Pregnant?
The Bottom LineVitamin C delivers a variety of health benefits, such as supporting a healthy immune system, but it also provides additional pregnancy-related benefits, too. It is safe to take Vitamin C while pregnant, and it’s necessary for both mom-to-be and developing baby. If you are pregnant, eating a healthy, balanced diet, and taking prenatal vitamins, you’re likely getting all the Vitamin C you need each day. As always, you should check with your healthcare provider before taking any medications, vitamins, or herbal supplements during pregnancy.†
As always, you should check with your healthcare provider before taking any medications, vitamins, or herbal supplements during pregnancy.†
Continue to check back on the Nature Made blog for the latest science-backed articles to help you take ownership of your health.
Learn More About Women's Health:
- When Should You Start Taking Prenatal Vitamins?
- What Vitamins Do Women Need?
- Vitamins for Women 50+
† These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
References:
1. Linus Pauling Institute. “Pregnancy in Brief.” August 2016. Accessed on: October 8, 2020. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/health-disease/pregnancy-in-brief
2. National Institutes of Health. “Vitamin C: Fact Sheet for Consumers.” 2019. Accessed on: August 27, 2020. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-Consumer/
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-Consumer/
3. Cardiovascular Journal of Africa. “Physiological changes in pregnancy.” March-April 2016. Accessed on: October 9, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4928162/#
4. Mayo Clinic. “Should women take supplements while pregnant?” January 15, 2020. Accessed on: October 9, 2020. https://www.mayoclinichealthsystem.org/hometown-health/speaking-of-health/should-women-take-supplements-while-pregnant
Lisa Beach
NatureMade Contributor
Sandra Zagorin, MS, RD
Science and Health Educator
You Might Like
Sign Up For More insights From Nature Made
Receive the Latest News and Special Offers
Vitamin C during pregnancy | BabyCenter
Vitamin C is important for a healthy immune system, and during pregnancy it helps you and your baby make collagen for your tendons, bones, and skin. To get enough vitamin C during pregnancy, eat citrus fruits and other fruits and vegetables that are rich in this important nutrient. Because it's fairly easy to get enough vitamin C from your diet and your prenatal vitamin, you probably don't need to take a vitamin C supplement.
To get enough vitamin C during pregnancy, eat citrus fruits and other fruits and vegetables that are rich in this important nutrient. Because it's fairly easy to get enough vitamin C from your diet and your prenatal vitamin, you probably don't need to take a vitamin C supplement.
Photo credit: iStock.com / nautiluz56
Why you need vitamin C during pregnancy
Both you and your baby need vitamin C daily because your bodies use it to make collagen, a structural protein that's a component of cartilage, tendons, bones, and skin. Vitamin C is also important for a healthy immune system.
Also known as ascorbic acid, vitamin C is essential for tissue repair, wound healing, bone growth and repair, and healthy skin. Vitamin C helps your body fight infections and acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage.
Vitamin C also helps your body absorb iron, especially from vegetarian sources.
Signs of a vitamin C deficiency include fatigue, gum inflammation, slow-healing cuts, bruises, and dry skin.
How much vitamin C do pregnant women need?
Pregnant women need more vitamin C than women who aren't pregnant – and breastfeeding women need even more.
Pregnant women ages 18 and younger: 80 milligrams (mg) per day
Pregnant women ages 19 and older: 85 mg per day
Breastfeeding women ages 18 and younger: 115 mg per day
Breastfeeding women ages 19 and older: 120 mg per day
Advertisement | page continues below
Nonpregnant women ages 18 and younger: 65 mg per day
Nonpregnant women ages 19 and older: 75 mg per day
Best foods with vitamin C during pregnancy
Citrus fruits probably jump to mind – they're especially high in vitamin C – but leafy greens and many other fruits and vegetables are also excellent sources. Choose fresh foods as your source of vitamin C because heat can destroy this vitamin. Also, keep in mind that some cereals and juices are fortified with vitamin C.
Vitamin C also helps maximize the amount of iron you get from the other foods you eat. (You need a lot more iron during pregnancy, and it can be hard to get enough.) That's why it's a good idea to try to include a vitamin C-rich food with every meal. This is especially true when eating vegetarian sources of iron, like beans – the vitamin C can help you absorb up to six times more iron.
Foods that provide vitamin C include:
- 6 ounces orange juice: 93 mg
- 6 ounces grapefruit juice: 70 mg
- one medium kiwi: 64 mg
- 1/2 cup raw, sweet green bell pepper: 60 mg
- 1/2 cup broccoli, cooked: 51 mg
- 1/2 cup strawberries, sliced: 49 mg
- 1/2 medium grapefruit: 39 mg
- one medium baked potato: 17 mg
- one raw, medium tomato: 17 mg
- 1 cup spinach, cooked: 9 mg
Do you need a vitamin C supplement during pregnancy?
There's usually no need to take a separate supplement. You can easily get the vitamin C you need from fruits and vegetables, and your prenatal vitamins also contain vitamin C.
It's not a good idea to take large doses of vitamin C when you're pregnant. The maximum daily amount that's considered safe is 1800 mg for women 18 and younger and 2000 mg for women 19 and over. Excessive vitamin C can upset your stomach, and more studies are needed to understand how these supplements could affect pregnancy outcomes.
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Eva Dasher
Eva Dasher writes, researches, and edits content on a wide variety of subjects, including parenting, medicine, travel, natural history, science, business, and the arts. Her favorite pastimes include experimenting with new foods, libations, and restaurants, as well as traveling the world with her two college-age children, husband, extended family, and friends.
Vitamins and pregnancy - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Kurbatskaya Olga Nikolaevna
Obstetrician-gynecologist
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"
One of the most common questions that pregnant women ask their doctor is what vitamins should I take during pregnancy? Let's say right away whether expectant mothers need to drink pharmaceutical vitamins or not - there is no unequivocal answer to this question. Some doctors believe that the necessary nutrients should be obtained from natural products. Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother.
Some doctors believe that the necessary nutrients should be obtained from natural products. Others are in favor of taking pharmaceutical multivitamins. It can only be said unequivocally that vitamins and microelements must necessarily enter the body of a pregnant woman. We will tell you which of them are most important for the expectant mother.
Folic acid
Other names for this vitamin are vitamin B 9 or B with . This vitamin is necessary for cell division and reproduction, so it is especially important in the first trimester of pregnancy, when all organs and systems of the child are being laid. Folic acid plays an important role in the synthesis of hemoglobin, and with its deficiency, anemia can develop. And folic acid also helps to reduce the likelihood of spinal defects in a child, takes care of the correct formation of his psyche and intellect. It is better to start taking folic acid three months before the planned conception, since a small supply of this vitamin will only be useful for both the expectant mother and the baby. If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day.
If the pregnancy has come unplanned, then folic acid must be taken as soon as the woman finds out about her situation. On average, the dosage of this vitamin is from 0.4 to 0.8 mg per day.
Calcium
An expectant mother needs about 1200–1400 mg of calcium daily, while an ordinary woman needs 800–1000 mg of this trace element. Why? During pregnancy, the amount of calcium in the body of the expectant mother is significantly reduced, since it is also spent on the growth and development of the child. Especially a lot of calcium is needed in the third trimester, when the baby's skeleton is calcified. But calcium is needed not only for the growth of bones and teeth of a child - with its help, his nervous system, his heart, muscles, skin tissues, eyes, ears, hair and nails are formed. A pregnant woman needs calcium for the full functioning of the kidneys, the prevention of muscle pain, constipation, osteoporosis, caries and toxicosis. In addition, this trace element protects the expectant mother from stress and nervous overload.
Vitamin E
This vitamin is involved in the process of tissue respiration, it helps oxygen to penetrate into every cell of the body. At the same time, vitamin E is an excellent antioxidant: it protects cells from the formation of free radicals that can provoke various diseases. This protective function is especially important at the stage of embryo formation. In addition, vitamin E helps to normalize the hormonal balance of the body. In the early stages, it participates in the formation of the placenta, and also protects against abortion. The dose of vitamin E during pregnancy is 15 mg.
Vitamin E is found in vegetable oils, not less than this vitamin in lettuce, tomatoes, rose hips, parsley, spinach and peas. Some vitamin E is found in meat, eggs and milk.
Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in all metabolic processes, helps to cope with stress, normalizes the functioning of the cardiovascular system and blood pressure, and keeps blood vessels in good shape. Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed.
Due to a lack of magnesium in the body, cramps in the muscles (usually in the calves) may appear. And since the uterus is also a muscular organ, with a lack of magnesium during pregnancy during gestation, the excitability of the myometrium increases, which leads to active uterine contractions. Therefore, with hypertension and the threat of abortion, magnesium is often prescribed.
Magnesium is rich in whole grains and whole grain breads, figs, almonds, seeds, dark green vegetables, and bananas.
iodine
Iodine is usually prescribed for pregnant women in the first trimester. Up to 16 weeks of pregnancy, the development of the child and the laying of all its organs and systems are "under the protection" of the mother's thyroid gland. And if a woman has little iodine, then this means that some system or organ of the baby may suffer. And even when the child’s own thyroid gland is formed and starts working, she can still take iodine only from the mother’s body. Its daily dose is 250 mg per day.
Its daily dose is 250 mg per day.
Iodine is easiest to get from seafood and sea or iodized salt. A lot of iodine is found in sea fish, seaweed, squid, persimmon, feijoa, dates, dried figs, dairy products and meat. However, iodine is destroyed by temperature effects, which means that after heat treatment, the amount of iodine in the products decreases sharply.
Iron
Iron is necessary primarily for the prevention of anemia. After all, it is part of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen throughout the body of the mother and child. In addition, iron is involved in protein synthesis, which is involved in the formation of muscle tissue. And iron deficiency can lead to increased uterine tone. The average daily dosage of iron is 30–60 mg. In some cases, if the woman's iron supply was initially reduced, the dosage may be higher.
Iron is found in meat, especially a lot of it in veal, turkey, hare, pork and beef. There is iron in plant foods, but from there it is absorbed much worse. Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
Iron is best absorbed when taken together with vitamin C.
If a pregnant woman eats properly and varied, eats a lot of fruits and vegetables, then she may not need an additional complex of vitamins for pregnant women. It may be necessary to drink some vitamins separately, but this should be determined by the doctor. If, before pregnancy, a woman had signs of vitamin deficiency, she eats incorrectly or poorly, then multivitamins cannot be dispensed with.
Inset
Vitamin B 9 (folic acid) is found in animal liver, spinach, asparagus, lentils, Brussels sprouts, beans and wholemeal flour. However, it is absorbed very poorly from food, no more than 50%. That is why it is prescribed to almost all pregnant women.
At one time, our body will not be able to absorb more than 500 mg of calcium. Therefore, you should not try to get the entire daily norm of this trace element in one meal. Try to eat foods containing calcium in small portions several times a day.
To increase the concentration of magnesium in tissues, vitamin B 6 (pyridoxine) is needed, which facilitates its absorption and acts as a conductor of magnesium into the cell. Therefore, magnesium and vitamin B 6 are often prescribed together.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Kurbatskaya Olga Nikolaevna
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"
PregnancyHome birthBirth
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select the clinic
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the prices for programs in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the cost of services by phone / with the managers of the clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Clinic KG "Lapino" in Odintsovo (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" Khodynskoye PoleClinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" Savelovskaya Clinic "Mother and Child" » South-WestClinic "Mother and Child" NovogireevoClinic "Mother and Child" Lefortovo
All directionsSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical studiesTreatment roomTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic studiesUltrasound examinations for adults
01.
Specialist consultations (adults)
02.
Specialist consultations (children)
03.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
04.
General clinical studies
05.
Procedure cabinet
06.
Telemedics for adults
07. 9000 Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Do pregnant women need to take vitamin preparations?
Almost every woman during pregnancy, doctors recommend taking various vitamin preparations. But do pregnant women need to take vitamins? Is a balanced diet not enough?
Almost every woman during pregnancy, doctors recommend taking various vitamin preparations. But do pregnant women need to take vitamins? Is a balanced diet not enough? We asked these and other questions to Ekaterina Aleksandrovna Minchenkova, an obstetrician-gynecologist at Expert Clinic Smolensk.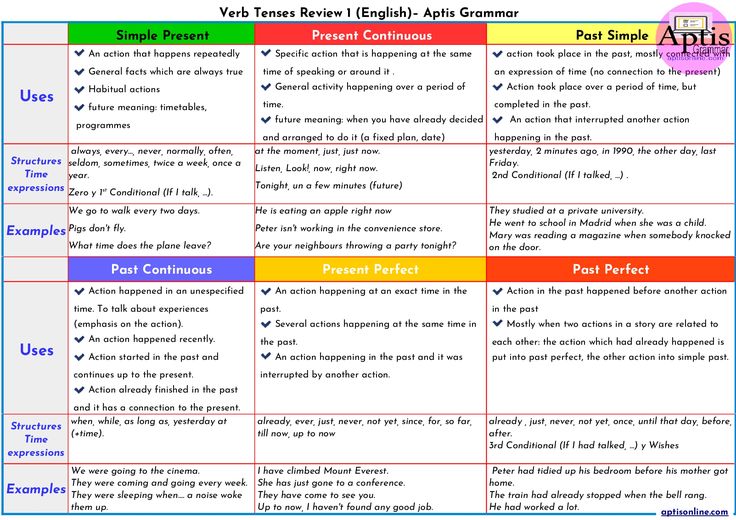
— Ekaterina Alexandrovna, what is the role of vitamins in the body in general and in the body of a pregnant woman in particular?
— Vitamins are special substances that everyone (not only women) need in small amounts for the normal functioning of the body. They are involved in metabolism, they are biological accelerators of chemical reactions occurring in the cells of the body, etc. In a pregnant woman, the need for vitamins and microelements is higher, because the fetus also needs them.
— What vitamins can you get from food?
— Most vitamins are not formed in our body, but come from food. If a pregnant woman eats a full, rational, varied diet, then she does not need an additional intake of vitamins and minerals (with some exceptions). They will be easily obtained with food in sufficient quantities. No vitamin supplement can match the benefits of proper nutrition.
- Speaking of nutrition, you said "with a few exceptions. " That is, despite the correct diet, pregnant women should still take some vitamins? And if so, which ones?
" That is, despite the correct diet, pregnant women should still take some vitamins? And if so, which ones?
Yes. During pregnancy, doctors prescribe some vitamins and minerals, even if the woman eats normally. I will dwell on those that I consider the most important. Vitamin number 1 for pregnant women is vitamin B9, or folic acid. Probably, one could do without additional intake of other vitamins, but without folic acid - in any way. This is because the strongest evidence for the need for vitamin supplementation during pre-pregnancy and the first 12 weeks of pregnancy is only for folic acid. With a lack of this vitamin, the likelihood of neural tube defects in the fetus, as well as some other defects (cleft lip, palate, congenital heart defects, malformations of the urinary tract and extremities, congenital hydrocephalus) may increase.
The recommended dose of folic acid is 400-500 mcg (micrograms) per day, in rare cases it may be more. To cover the daily dose of this vitamin, you need to eat 500 g of liver (chicken, goose, pork, beef, cod, etc. ) or 1 kg of salad. It is difficult to provide the required daily amount of folic acid through food, so the doctor prescribes it in the form of a drug.
) or 1 kg of salad. It is difficult to provide the required daily amount of folic acid through food, so the doctor prescribes it in the form of a drug.
Next is vitamin D. It is formed in the body under the influence of ultraviolet rays (the main way to obtain it), and in some quantities comes with certain foods. All pregnant women may be recommended an additional dose of 600 - 1200 IU / day. But it is better to visit a doctor to decide whether it is necessary or not.
Vitamin B12 supplementation may be indicated for vegans and vegetarians.
I would like to say about trace elements - they are also important for the body of a pregnant woman. All women in the CIS countries are advised to take additional iodine in the form of potassium iodide. Before pregnancy, the dose of iodine is 100–150 mcg per day. With the onset of pregnancy, throughout its entire duration and during breastfeeding, the dose increases to 250 mcg per day. But usually the coverage of the need for iodine is distributed as follows: we get 50 micrograms from food, and take 200 micrograms in the form of a drug. In case of thyroid diseases, consultation with an endocrinologist is mandatory.
In case of thyroid diseases, consultation with an endocrinologist is mandatory.
Calcium 1000 mg per day should be taken daily from food or mineral supplements if the woman does not consume calcium-containing foods.
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). WHO still does not recommend the additional intake of this component during pregnancy and insists on a healthy diet. A sufficient intake of omega-3 is necessary for the proper formation of the organs of vision and the brain of the unborn child. In 2018, a study was conducted in which several thousand pregnant women participated. A diet high in omega-3s has been shown to reduce the risk of preterm birth from 7% to 2%, as well as the risk of having small babies.
An excellent source of omega-3-PUFAs are salmon fish, tuna and seafood. If you use them 2 times a week, then you do not need supplements and dietary supplements with this component. Everyone else should think about changing the diet or taking them additionally (of course, after consulting a doctor).
- You talked about the possible consequences of a lack of folic acid. And what can a deficiency of trace elements lead to in a pregnant woman and an unborn child?
- Children born to mothers with mild to moderate iodine deficiency are more likely to have behavioral disorders in the form of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Severe iodine deficiency in pregnant women is fraught with an increase in the frequency of stillbirth and infant mortality, miscarriage, the birth of underweight children, children with mental retardation.
Lack of calcium also leads to negative consequences: bone density decreases, which leads to the development of osteoporosis in menopausal women and an increased risk of fractures in old age. Possible heart rhythm disturbance, muscle spasms, convulsions. In pregnant women, especially those at risk, the likelihood of developing gestational hypertension (high blood pressure) and preeclampsia (a pathology in which blood pressure rises during pregnancy, edema is formed, and protein appears in the urine) increases.
Calcium is best absorbed from dairy products, 2-3 servings of which will provide the daily intake. 1 serving is equal to 200 ml of milk, kefir, curdled milk, fermented baked milk, or 200 g of yogurt, or 100 g of cottage cheese or 40 g of cheese.
Iron deficiency in the mother's body before pregnancy and in its early stages can "cross out" all subsequent efforts of parents and teachers in teaching children. The developing brain of a future baby is especially sensitive to a lack of iron in the body, including in the case of its hidden deficiency, when hemoglobin is normal, and there are few iron reserves.
Many people know that iron is necessary for the formation of hemoglobin, which is able to bind oxygen. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells, which carry oxygen to the cells. And if there is little oxygen, then the cells suffer. Imagine feeling out of breath. So it is here: the brain cells of a still little man (3-12 weeks of pregnancy), lacking oxygen, divide more slowly, because of which neural connections are simplified, the gray matter suffers, and your baby will no longer become a genius, even if you responsibly began to take iron supplements after 12 weeks of pregnancy.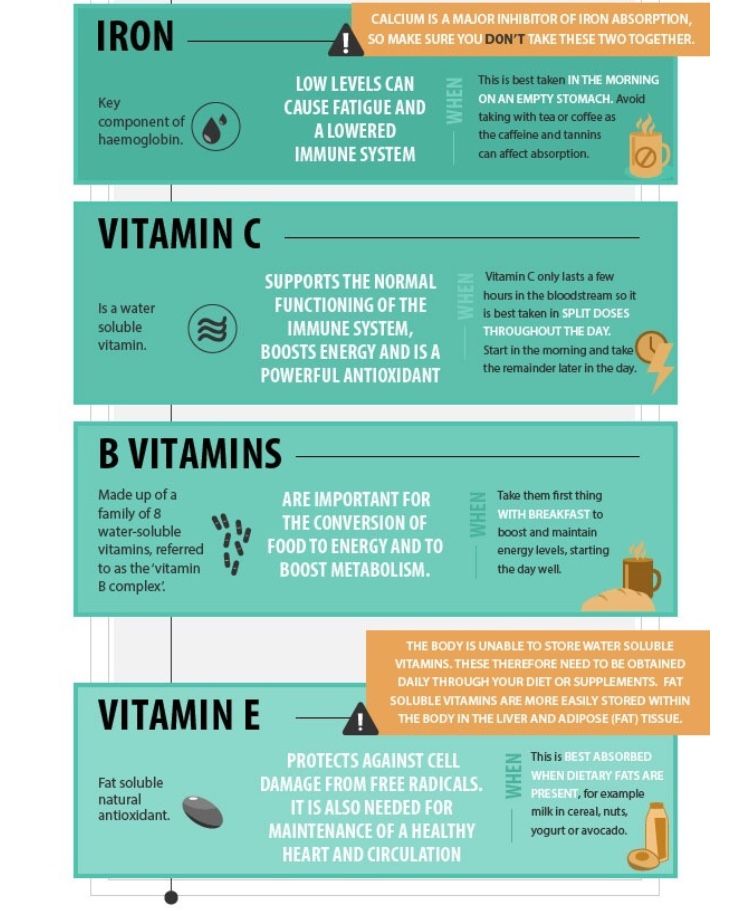
— Can I take prenatal vitamins without a doctor's prescription?
— No. I recommend taking vitamins only after consulting a doctor if they are deficient. Among persons who may be at increased risk of vitamin deficiency:
- obese people;
- vegans;
- having some bowel disease;
- people with low socioeconomic status;
- real hungry
and some others. For these women, an additional intake of vitamins will be justified.
- Can vitamin supplements taken during pregnancy be harmful or useless?
- At the moment there is no evidence that multivitamins prevent the development of any diseases, that they are necessary and useful. That is, they turned out to be ineffective. Vitamins usually contain more than 5 components. And even a very qualified clinical pharmacologist will not calculate all the options for the interaction of active components in a living organism. According to many studies, most multivitamin complexes are not absorbed by the body. They contain components (vitamins and trace elements) that are incompatible with each other: calcium and iron, fat- and water-soluble groups of vitamins, zinc and folate. B1, B6 and B12, although from the same group, are at war with each other or reinforce each other's negative effects. Therefore, if you take vitamins, it is better to take them separately, and only those that are really necessary.
According to many studies, most multivitamin complexes are not absorbed by the body. They contain components (vitamins and trace elements) that are incompatible with each other: calcium and iron, fat- and water-soluble groups of vitamins, zinc and folate. B1, B6 and B12, although from the same group, are at war with each other or reinforce each other's negative effects. Therefore, if you take vitamins, it is better to take them separately, and only those that are really necessary.
Often the dosages of the components do not correspond to the recommended ones (for example, folic acid is recommended at a dose of 400 mcg per day, and in multivitamins it is often contained in an amount of 200 mcg, etc.).
All supplements and vitamin complexes containing vitamin A should be avoided due to its possible teratogenic effect (that is, the ability to cause malformations in a child during pregnancy).
There are no natural vitamins on the modern pharmaceutical market. Without exception, all preparations contain vitamins or their analogues, which are obtained synthetically. The natural ones are found only in foodstuffs.
The natural ones are found only in foodstuffs.
— Do prenatal vitamins have side effects?
— Of course. Firstly, as with any other drugs, they can cause an allergic reaction. Side effects from the gastrointestinal tract are also common: nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, etc. The load on the liver is high. Excess intake of certain vitamins can lead to cancer.
— Is it possible for a pregnant woman to take vitamins with uterine fibroids? And if so, which ones?
— There are no restrictions and peculiarities in terms of taking vitamins.
— Are there any contraindications to taking vitamins for pregnant women?
- Contraindications are the same as for all other drugs. Increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug or their intolerance, hypervitaminosis, severe renal failure and some others. Therefore, only a specialist can appoint them.
I would like to finish with the words of one professor: even by eating a fruit with nitrates, a person will receive more useful vitamins and microelements than by taking one synthetic tablet.