Can i eat sweets during pregnancy
Sugar in Pregnancy: How Much is Too Much?
Healthy diet Foods to avoid Carbs Fibre Dairy Protein Meat Fish Shellfish Eggs Superfoods Spicy food Salt SugarRead time: 4 minutes
If you have a sweet tooth, sugary foods can be hard to resist. But with very little nutritional value, sugar and sugary foods have few benefits for you or your baby. Find out how sugar affects you during pregnancy and discover healthy alternatives to satisfy sweet cravings.
Free 'Eating for 2' recipe e-book
Healthy, tasty recipes by chef Lorraine Pascale and our team of nutritionists
Join now for FREE
What happens if I eat too much sugar when I’m pregnant?
Most sugary foods and drinks are made with sucrose, otherwise known as table sugar. This form of sugar releases energy quickly, causing blood glucose to spike, triggering a rapid release of insulin to absorb it. You’ve probably experienced the boost of a sugar rush, which is generally followed by a dramatic slump in energy. Rather than keeping you going throughout the day, eating too much sugar when you’re pregnant can leave you feeling even more tired1.
A low-sugar intake helps to keep your blood sugar more stable, along with your resulting energy levels2 and is more likely to result in healthy pregnancy weight gain. Eating too much sugar when you’re pregnant may increase your risk of gestational diabetes3 and pre-eclampsia4 and increases the risk of your baby becoming overweight later in life2.
But how much sugar is too much during pregnancy?
The government recommends that free sugars – sugars added to food or drinks, and sugars found naturally in honey, syrups, and unsweetened fruit and vegetable juices - should not make up more than 5% of the calories you get from food and drink each day5. Pregnant women should have no more than 30g of free sugars a day, which is roughly equivalent to seven sugar cubes5. For instance, one can of cola can have up to nine sugar cubes which is more than the daily allowance5.
For instance, one can of cola can have up to nine sugar cubes which is more than the daily allowance5.
Free sugars are found in sweets, cakes, biscuits, chocolate, and some fizzy drinks and juice drinks. These are the sugary foods pregnant women should try to cut down on as part of a healthy pregnancy diet5.
This doesn’t mean you can’t enjoy anything sweet. A healthier approach is to limit free sugars in your diet and replace them with naturally sweet, nutritious alternatives.
Understanding gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes specific to pregnancy that tends to develop sometime after 20 weeks. It occurs when the body can’t produce enough insulin to regulate the level of glucose in the blood3.
The condition has been connected to a higher birth weight in babies, and pregnancy or birth complications3. Maintaining a healthy pregnancy weight with a low-sugar diet and regular exercise can help minimise your likelihood of developing this condition1.
Factors that can increase your risk for gestational diabetes include
6:- Previously giving birth to a baby weighing more than 9.9lbs
- Having gestational diabetes in the past
- Having a sibling, parent or grandparent with diabetes
- Being of south Asian, black Caribbean or Middle Eastern origin
Low sugar foods for pregnancy
While sweet, sugary foods can be tempting, cakes, pastries, biscuits and sugary drinks should ideally be reserved for occasional treats. It’s better for both you and your baby to avoid eating too much sugar when you’re pregnant and find healthier alternatives instead.
There are many low sugar foods to eat when you’re pregnant. Fruits such as mango, pineapple and berries are good ways to satisfy a sweet craving while still providing a variety of vitamins, minerals and fibre. Fresh, frozen and tinned options are all good, just remember to choose tinned fruit in natural juice or water without any added sugar7.
Dried fruit like apricots or prunes are also good and they give an extra dose of iron8, too. When buying dried fruit, check it doesn’t contain any added sugar, as well. Lastly, try to spread out your fruit intake during the day for a steadier release of natural sugars9.
Simple low sugar swaps
- Replace biscuits with something savoury like carrots with hummus
- Chop fresh fruit into your cereal or porridge, instead of using sugar
- Munch on homemade popcorn, instead of a shop-bought sweet variety
- Snack on dried nuts, instead of sweets
- Drink carbonated water with added fresh juice, instead of cola
- Swap ice cream for a bowl of Greek yogurt and berries
Want to learn more? Find out which foods to avoid when you’re pregnantand why salt is important in pregnancy.
View references
- Murrin C et a.. Maternal macronutrient intake during pregnancy and 5 years postpartum and associations with child weight status aged five.
 Eur J Clin Nutr 2013;67(6):670-679.
Eur J Clin Nutr 2013;67(6):670-679. - Walsh JM et al. The association of maternal and fetal glucose homeostasis with fetal adiposity and birthweight. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2011;159(2):338-341.
- NHS. Gestational diabetes [Online]. 2016. Available at: www.nhs.uk/conditions/gestational-diabetes/pages/introduction.aspx [Accessed February 2020]
- Borgen I et al. Maternal sugar consumption and risk of preeclampsia in nulliparous Norwegian women. Eur J Clin Nutr 2012;66(8):920-5.
- NHS. How does sugar in our diet affect our health [Online]. 2017. Available at https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/how-does-sugar-in-our-diet-affect-our-health/ [Accessed February 2020]
- NHS. Diabetes and pregnancy [Online]. 2015. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Conditions/pregnancy-and-baby/pages/diabetes-pregnant.aspx [Accessed February 2020]
- NHS. 5 a day – What counts? [Online]. 2015. Available at: www.nhs.
 uk/Livewell/5ADAY/Pages/Whatcounts.aspx [Accessed February 2020]
uk/Livewell/5ADAY/Pages/Whatcounts.aspx [Accessed February 2020] - NHS. Iron-deficiency anaemia - treatment [Online]. 2016. Available at: www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Anaemia-iron-deficiency-/Pages/Treatment.aspx [Accessed February 2020]
- Diabetes UK. Fruit and diabetes [Online]. Available at: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/enjoy-food/eating-with-diabetes/food-groups/fruit-and-diabetes [Accessed February 2020]
Read next
- Aptaclub home
- Pregnancy
- Diet & nutrition
- Understanding food groups
- The role of sugar in pregnancy
The Effects Of Sugar During Pregnancy On Your Baby, Your Body And Your Mouth
Top Articles
More Articles
Published date field Last Updated:
Medically Reviewed By Colgate Global Scientific Communications
Ever since you got pregnant, you've probably been dealing with some crazy cravings. Perhaps you find yourself reaching for a jar of peanut butter and some pickles. Or, maybe you've noticed that you're craving candy and sweet treats like never before.
Perhaps you find yourself reaching for a jar of peanut butter and some pickles. Or, maybe you've noticed that you're craving candy and sweet treats like never before.
Should you worry that eating sugar during pregnancy will have a lasting effect on your health or the health of your child? Just as eating an excessive amount of sugar affects your overall health when you're not pregnant, it can have an effect on your health and your baby's health during pregnancy.
Does Sugar Consumption Affect Developing Babies?
When you're pregnant, anything you eat is also consumed by your developing baby. There is some concern that eating a lot of sugar during pregnancy can have an effect on a child's cognition later in life. One study, published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, found an association between mothers drinking certain sweetened beverages (including diet sodas) during pregnancy and reduced cognitive skills in children. While this study doesn't prove having a sugary treat here and there will severely and negatively impact your child's health, it suggests that it's important to think consciously about what you eat when you're pregnant.
While this study doesn't prove having a sugary treat here and there will severely and negatively impact your child's health, it suggests that it's important to think consciously about what you eat when you're pregnant.
Effects of Sugar on Pregnant Women
Consuming a lot of sugary or sweetened foods during pregnancy may also have an effect on your physical health. About 7 in every 100 pregnant women in the U.S. develop a condition known as gestational diabetes, as the National Institutes of Health notes. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and often goes away after delivery. However, it can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes later on, as well as increase your child's risk. If you are diagnosed with gestational diabetes, reducing the number of sweet foods you eat, including fruits, and limiting starchy foods can help you keep your blood sugar levels under control, as UCSF Health points out.
How Sugar During Pregnancy Impacts Your Dental Health
Even when you aren't pregnant, sugar can affect the health of your teeth, leading to decay and cavities.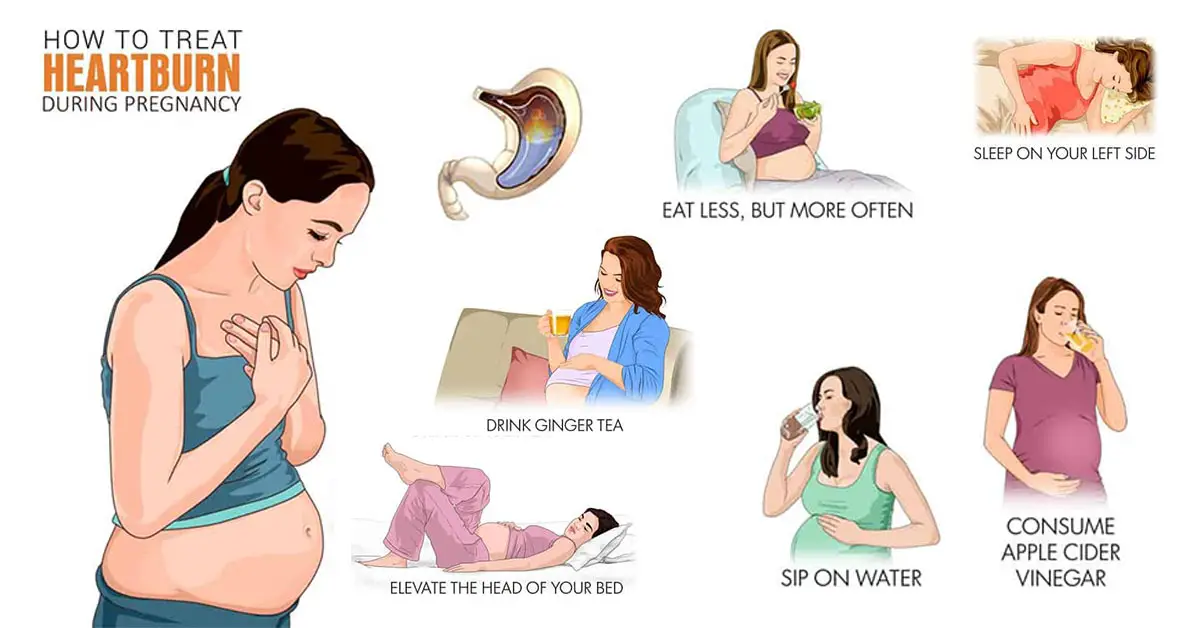 During pregnancy, you might have a slightly higher risk of developing tooth decay, particularly if your diet is high in carbohydrates or if you're dealing with morning sickness, as the American Dental Association (ADA) notes.
During pregnancy, you might have a slightly higher risk of developing tooth decay, particularly if your diet is high in carbohydrates or if you're dealing with morning sickness, as the American Dental Association (ADA) notes.
One way to protect your teeth and overall health while pregnant is to stick to a regular oral care routine. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss every day.
Some women may be concerned about seeing their dentist for a checkup and teeth cleaning during pregnancy — but they don't have to be. An article published in The Journal of the American Dental Association states that both the ADA and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists believe that oral healthcare during pregnancy is safe and that delaying any treatment or preventative care isn't a good idea. The next time you're at the dentist, just let them know you're pregnant, and they'll take things from there.
Tips for Healthy Eating While Pregnant
While cutting back on sugar while pregnant is a healthy choice for you and your baby, those cravings can be really intense. When you need a bite to eat, the ADA recommends choosing low-sugar snacks, such as vegetables, cheese and unsweetened yogurt. Reading food labels can also help you determine if a snack is high in sugar.
When you need a bite to eat, the ADA recommends choosing low-sugar snacks, such as vegetables, cheese and unsweetened yogurt. Reading food labels can also help you determine if a snack is high in sugar.
The occasional chocolate bar or cookie isn't likely to hurt you or your child, but if you're concerned that your pregnancy diet has too much sugar in it, your OB-GYN can help. At your next prenatal visit, ask them for guidance and advice on putting together a healthy, low-sugar diet plan.
Oral Care Center articles are reviewed by an oral health medical professional. This information is for educational purposes only. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your dentist, physician or other qualified healthcare provider.
Like
Neutral
Thank you for submitting your feedback!
If you’d like a response, Contact Us.
Sweet during pregnancy | Is it possible to have sweets and sugar during pregnancy, consumption rate
So, where does the increased need for sweets during pregnancy come from?
First, the craving for sweets during pregnancy may be due to a lack of endorphins - the hormones of happiness and pleasure. On the one hand, this assumption looks strange during the period of expectation of the baby, on the other hand, hormone surges, followed by mood swings - a classic picture. Frustrated or anxious? The hand itself reaches for the chocolate bar. nine0003
Alternative solution:
Take up an interesting hobby, spend more time with friends, watch positive films - use inedible ways to improve your mood.
Secondly, such a craving can be explained by the needs of the body. Energy costs have increased, and they need to be replenished. The fastest way is to eat something sweet. Marmalade, sugar, cookies are all simple carbohydrates that are digested at a high speed. They give a quick feeling of fullness, however, very short-lived. nine0003
They give a quick feeling of fullness, however, very short-lived. nine0003
Alternative solution:
switch to fractional meals - eat more often, but in small portions. Make adjustments to the diet itself: buckwheat, oats, brown rice, beans, pasta from durum wheat varieties are also carbohydrates, but complex. They are also suppliers of sugar, but do not lead to its sharp jump in the blood. And, what is especially important, these substances are digested more slowly than sweets, marshmallows, jams and retain a feeling of satiety for a long time.
And, finally, a deficiency of minerals and trace elements can provoke an increased need for sugar. nine0003
Alternative solution:
Eat more calcium-rich foods (natural yogurt, herbs, cottage cheese, etc.) in your diet - this simple measure can often help reduce sugar cravings during pregnancy. And prepare healthy snacks - berries, cheesecakes, vegetable chips and bars - this will help you quickly “kill” your appetite without harm to weight and health.
What is the danger of sugar in the diet of a pregnant woman?
If you lean too much on sugar and sweets during pregnancy, then weight gain will increase faster and more actively than you would like. And this can cause not only aesthetic discomfort, but also become a serious burden on the spine and joints. In addition, calcium will begin to be washed out and vitamin B1 will be lost, and, as a result, problems with teeth and liver may occur. nine0003
Also, if there are prerequisites, eating too much sweets during pregnancy can provoke diabetes mellitus in pregnant women, arterial hypertension and digestive disorders, including bloating and pain in the left hypochondrium.
And, finally, with the abuse of chocolate, there is a risk of congenital food allergies in the baby!
It turns out that sweets in the diet of pregnant women are an absolute evil? But no! If you really want sweets and it’s simply impossible to calmly walk past a bar of chocolate, you don’t need to restrain yourself. Just choose chocolate with a high cocoa content and try to limit yourself to 2-3 pieces. nine0003
Just choose chocolate with a high cocoa content and try to limit yourself to 2-3 pieces. nine0003
And, finally, the most important question - rolls, cakes, pastries are not allowed, but what sweets can you eat during pregnancy?
- Dried fruits - dried apples, raisins, prunes, figs, dried apricots, dates.
- Honey, but only for those who are not allergic to bee products.
- Natural marmalade and marshmallows - ideally homemade.
- Berries, fruits and vegetables are a great alternative to confectionery. However, this advice does not apply to juices and smoothies, it is recommended to focus on products in their natural form. nine0036
- Jelly from fruit compotes and juices without added sugar.
The norm of sugar consumption during pregnancy - what is it?
The daily intake of carbohydrates in a pregnant woman ranges from 325 to 450 grams, the rate of sugar intake during pregnancy should not exceed 40-50 grams.
Is it possible to sugar during pregnancy or is it better to replace it with special additives, what is more harmful and what is more useful?
Expectant mothers address this question to their gynecologist quite often. In the modern world, there are a huge number of various sweeteners, the effect of most of which on the fetus has not been studied. Therefore, it is definitely not worth abusing them. When choosing an alternative to sugar during pregnancy, it is recommended to give preference to natural supplements, such as stevia. nine0003
In the modern world, there are a huge number of various sweeteners, the effect of most of which on the fetus has not been studied. Therefore, it is definitely not worth abusing them. When choosing an alternative to sugar during pregnancy, it is recommended to give preference to natural supplements, such as stevia. nine0003
Thus, the answer to the question “is it possible to have sweets during pregnancy” is yes! The main thing is to choose the right desserts and remember that this is a great end to the meal, and not a complete replacement for it!
- Pediatrician
- Author of the books “First aid for children”, “Medicines. Big Encyclopedia" and articles about children's health.
- Project consultant for HealthMail.ru, Baby.ru and Babyblog.ru
Others author articles
Is it possible to have sweets during pregnancy?
(5.00 out of 5 based on 1 ratings)
While waiting for a baby, every woman reviews her diet. And perhaps the most difficult is the question of the need to exclude sweets. After all, you don’t want to part with them for many months! And you don't need to. As a rule, pregnancy only in rare cases requires a complete and categorical rejection of your favorite sweets, cakes, chocolate, cakes, pastries, gingerbread and other goodies. nine0003
And perhaps the most difficult is the question of the need to exclude sweets. After all, you don’t want to part with them for many months! And you don't need to. As a rule, pregnancy only in rare cases requires a complete and categorical rejection of your favorite sweets, cakes, chocolate, cakes, pastries, gingerbread and other goodies. nine0003
And yet, in this sense, you must strictly adhere to the doctor's recommendations, because he gives them based on your body characteristics and analyzes.
- Sweets are most often banned completely or almost completely if a pregnant woman has diabetes, is very overweight or has allergies.
- If the doctor has allowed you to eat desserts, it is still necessary to observe a reasonable measure so that the weight does not increase too quickly and does not harm the baby's health. nine0036
- The number of sweets consumed is usually recommended to be gradually reduced in the second and third trimester.
- If we talk about the time of day, then it is preferable to eat desserts in the first half of the day so that they have time to digest.
 However, this is not a strict rule.
However, this is not a strict rule. - Like all other food in the diet of a future mother, cakes, sweets and pastries should, if possible, consist of natural, high-quality ingredients.
- If you decide to eat cake or pastry, then be careful with those that contain nuts. So, hazelnuts and peanuts can be eaten literally 3-5 pieces a day, no more. Nuts, in principle, belong to the category of heavy food, and these 2 types especially. The sweetness itself is already high in calories, so it is better to refuse desserts with nut filling. nine0036
In general, if the doctor does not forbid, then your favorite treats will remain with you throughout the entire exciting period of waiting for the baby. Their undoubted benefit is that it is desserts that help to cope with stress and nervousness, fatigue, because they are a source of carbohydrates and contribute to the production of endorphins. In addition, the substances and vitamins contained in dark chocolate are involved in the formation of the child's body, in particular bones and teeth.