Blocked tear duct baby home remedy
Blocked Tear Duct Baby: At-Home Treatments
Blocked tear ducts in babies
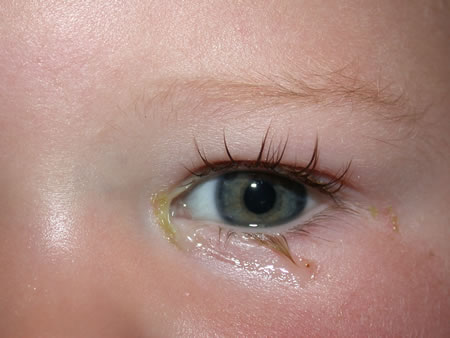
A few days after we brought our son home from the hospital, he woke up with one of his eyes crusted shut with green gunk.
I was horrified that my sweet baby boy’s perfect face was marred, and immediately called our family eye doctor. Visions of pink eye and house-wide infection went through my head. What could it be? Would he be OK? Would he go blind?
Luckily, our eye doctor eased my worries right away and assured me that it wasn’t a life-threatening eye infection, but actually a blocked tear duct.
Luckily, in most cases, blocked tear ducts aren’t serious. The American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus (AAPOS) explains that in most cases, blocked tear ducts clear up on their own without treatment.
In the meantime, there are a few simple ways to help clear up blocked tear ducts at home.
Use a warm compress
Every few hours, when the drainage builds up, warm up a clean and soft washcloth or cotton ball with water and gently clean the eye.
You can apply gentle pressure to the tear duct. Then, wipe from the inside of the duct to the outside so you don’t wipe anything into the eye. The duct is located between the lower eyelid and the nose, and the main opening is on the part of the lower eyelid closest to the nose.
If both of your baby’s tear ducts are clogged, use the clean side of the washcloth or a new cotton ball before wiping the other eye.
Apply tear duct massage
To help open the tear duct and empty it out, you could do a tear duct massage. Essentially, you can apply gentle pressure toward the opening of the duct, alongside the upper nose and along the lower eyelid, to try to help them clear. Ask a doctor to demonstrate how to do this.
You can perform the duct massage up to two times a day. But remember, it’s very important to be as gentle as possible.
Eye drops
If the ducts do get infected, your child’s pediatrician or eye doctor might prescribe antibiotic drops or ointment to put into the eyes. The drops or ointment will clear up the infection.
The drops or ointment will clear up the infection.
Most cases of clogged tear ducts will resolve as your baby gets older — typically by 12 months of age, especially with at-home treatments.
But, if your baby has clogged tear ducts past 1 year of age, your doctor may recommend a simple procedure to help unclog the tear ducts.
What is a blocked tear duct in babies?
Blocked tear ducts, also called nasolacrimal duct obstruction, are relatively common in newborn babies. Around 5–10 percent of babies have a blocked duct, sometimes in both eyes.
One of the most common causes of a blocked tear duct is that the membrane that covers the end of the duct doesn’t open like it should. This causes the duct to become blocked by the tissue of the membrane.
A blocked tear duct could also be caused by:
- the absence of the opening of the duct of the upper or lower eyelid
- a tear duct system that is too narrow
- an infection
- a crooked or misplaced bone blocking the tear duct from the nasal cavity
Other symptoms caused by conditions like a cold can worsen symptoms of a blocked tear duct.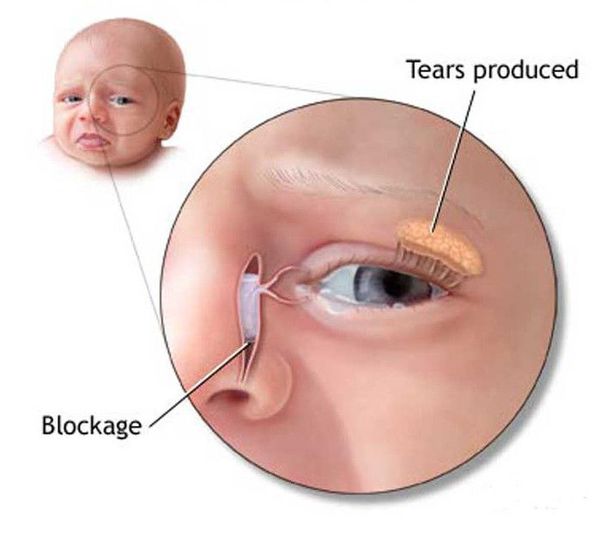
What are the symptoms of a blocked tear duct?
The symptoms of a blocked tear duct can look a lot like an eye infection such as pink eye. The signs of a blocked tear duct usually begin during the first few days or weeks of a newborn’s life. Symptoms might include:
- constant tears
- mildly swollen and red eyelids (the eyes should not be red)
- eyelids that stick together
- green-yellow discharge
In most cases, the discharge is actually tears and normal bacteria, and not a sign of infection. The discharge produced by a blocked tear duct will appear similar to the discharge from an infection, but the eye itself will only become red with an infection.
All of us, babies included, have normal bacteria on our eyelids that get flushed away by our tears.
When the duct system is clogged, the bacteria has nowhere to go and stays on the eyelid. This could cause an infection to develop. You’ll want to watch your baby for any symptoms that the discharge, redness, or swelling is getting worse.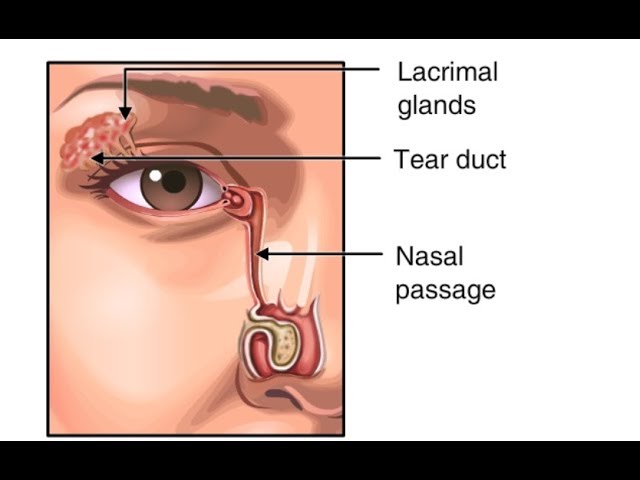
Make sure to have your doctor check your baby for a blocked tear duct. If an infection is causing the symptoms it can be serious.
Can you prevent blocked tear ducts?
In newborns, many times the blocked ducts result from the membrane not opening at birth. There’s no good way to prevent this from happening.
However, you can monitor your baby for symptoms. Be sure to never smoke around your baby or allow smoking in your house. Smoke, and other potential hazards like dry air, can irritate your baby’s nasal passages and make the symptoms of the blockage worse.
The takeaway
If you notice that your newborn has “gunk” in their eyes, don’t panic. If your baby is otherwise OK, it’s probably just a clogged tear duct, which is common in babies.
Have your doctor check your baby to make sure. Watch your baby for symptoms of infection and report them to your doctor. Call your doctor immediately if your baby seems ill or has a fever.
You can also try some at-home remedies, like massage or a warm washcloth, to clear the eyes and help relieve your baby’s discomfort.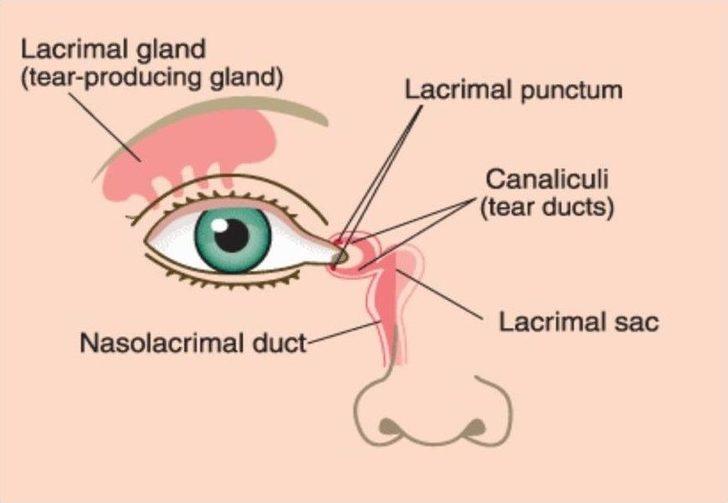
Share on Pinterest
Blocked Tear Duct in Babies
From yellow discharge to eye infections, blocked tear ducts cause discomfort to babies and worry to parents. Tears cannot drain properly when the duct is blocked, and the duct ends up swollen or getting infected. Keep reading to learn more about a blocked tear duct in babies.
What Is a Blocked Tear Duct?
A blocked tear duct is a condition when the tear duct (where tears drain through a small tube in the eyes) gets blocked or doesn’t open up properly. Blocked tear ducts usually reveal themselves during the first two weeks after the baby is born, when the baby starts getting “watery” eyes. A yellow or white discharge often accompanies them, and sometimes this discharge ends up sealing the eyelids shut too.
How Common Is It in Babies?
Almost six out of 100 newborns are affected by blocked tear ducts after birth. They may occur during the baby’s birth year and may not cause any eye problems when they first appear as well.
Causes of Blocked Tear Duct
The common causes of a blocked tear duct in infants are-
- When the tissue at the end of the tear duct is not able to open up
- Eye infections
- When the nasal bone grows abnormally, thus putting pressure on the tear duct and sealing it off
- Partial or underdeveloped openings near the corners of the eyes where the tears drain out
Symptoms of a blocked tear duct usually appear during the first few days to weeks after being born.
- Yellow or white discharge from the corners of the eyes
- Redness and swelling of the eyes
- Watery eyes
- Tears streaming down the cheek
- Epiphora (excessive tearing)
- Tenderness or a bump near the side of the nose
- Swollen blue bump near the inside corner of the eyes (also known as dacryocystocele)
- Eye infections accompanied by fever, mucus or pus in the eyes
Diagnosis and Tests
Most blocked tear duct conditions in babies resolve naturally with time. However, sometimes a little bit of testing and diagnosis never hurts to cross-check if it spurs from underlying causes. The following three tests are used for diagnosing a blocked tear duct –
However, sometimes a little bit of testing and diagnosis never hurts to cross-check if it spurs from underlying causes. The following three tests are used for diagnosing a blocked tear duct –
- Tear Drainage Test– A special dye is applied to your child’s eyes to check whether or not tears drain correctly. If the duct has anything that is blocking its path, then the dye remains on the eye’s surface even after five minutes pass.
- X-Ray Exam – An X-ray or CT scan of the dacryocystogram (tear duct area) is done to check for blocked tear ducts. It is followed up with an MRI to image the location of the blockage and identify its causes.
- Medical Evaluation – Your doctor may evaluate your medical history to ascertain whether tear duct blockages run in the family. A physical examination and an ophthalmic examination are done to check for other plausible reasons for blockage.
How to Treat a Blocked Tear Duct in Your Child
Blocked tear ducts usually open up on their own.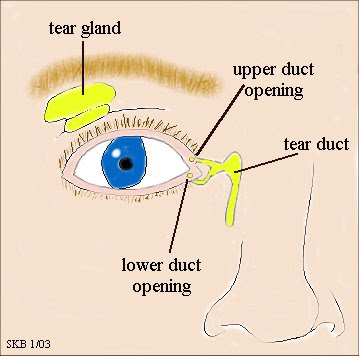 Meanwhile, here are four treatments you can try to help them open up and get those tears draining.
Meanwhile, here are four treatments you can try to help them open up and get those tears draining.
1. Surgical Probing – Surgical probing is a procedure done at the hospital to manually open up the tear ducts through surgery. It’s done on an outpatient basis, and your ophthalmologist will recommend it if your baby has a severe infection and must be admitted to the hospital. The procedure lasts for about 10 minutes.
2. Silicone Tube Intubation – Silicon tubes are inserted into tear ducts to stretch and open them up. The tubes are kept in place for six months and surgically removed afterwards.
3. Balloon Catheter Dilation (DCP) – A balloon is placed into the tear duct by insertion through the corner of the eyes and inflated using a sterile solution to expand the tear duct openings. It is afterwards deflated and removed from the eyes.
4. Antibiotic Eye Drops – If an infection spreads, your baby’s paediatrician may prescribe your little one some antibiotic eye drops or eye ointment. These drops or ointments aid in clearing up infections and eliminate harmful bacteria from blocked tear ducts.
These drops or ointments aid in clearing up infections and eliminate harmful bacteria from blocked tear ducts.
Home Remedies for Baby’s Blocked Tear Duct
Home remedies work just as well as surgical treatment. Try these before you consider surgical procedures for your little one-
1. Breast Milk – Apply a few drops of breast milk to treat blocked tear ducts in your little one’s eyes and watch them recover gradually.
2. Tear Duct Massage – Ask your doctor to demonstrate how to do a massage to help your baby’s blocked tear duct and be gentle. Basically, you apply gentle pressure between the tear ducts along the upper nose area to aid in clearing up the ducts. This can be done up to two times a day, every day.
3. Warm Compress – Take a soft, clean washcloth and dip it in warm water. Gently wipe the insides of the duct and work your way outward so that particles don’t enter the eye. If both your baby’s ducts are blocked, you must use another clean washcloth or a cotton ball to repeat the process.
Prevention
Prevention is better than cure. Here are some ways you can prevent your baby’s tear duct from facing blockage in the first place-
- Wash your hands– Before and after cleaning their eyes, make sure to wash your hands and maintain hygiene.
- Massage regularly – You don’t need to massage your baby’s tear ducts only when there’s a blocked tear duct. By massaging from the start, you’ll prevent those tear ducts from clogging beforehand.
- Environmental factors – Reduce exposure to sunlight, cold, and wind for your infant to prevent tear duct blockage.
- Wipe their eyes – Use small cotton balls or a clean cloth to wipe away any excess drainage from your baby’s eyes regularly, especially the outer parts.
A blocked tear duct is nothing serious or extreme to worry about. It happens to many babies and the above remedies will certainly come in handy. Try these out and watch them heal soon!
Also Read: Remedies for Pink Eyes in Babies
Treatment of blockage of the lacrimal canal | Dobromed
Inflammation of the lacrimal canal (dacryocystitis) is a pathological condition in which fluid cannot pass through the canal of the lacrimal gland. Sometimes the duct is simply clogged. As a result, tears penetrate into the paranasal sinuses and stagnate there, creating ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Inflammation occurs in acute and chronic form.
Sometimes the duct is simply clogged. As a result, tears penetrate into the paranasal sinuses and stagnate there, creating ideal conditions for the development of pathogenic microorganisms. Inflammation occurs in acute and chronic form.
Causes of appearance
Dacryocystitis occurs in the presence of pathologies of a physiological nature, namely congenital narrowing of the duct (stenosis). Sometimes doctors reveal a complete blockage of the lacrimal duct.
- Injury to the eyes or paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammatory process of the nose, which provokes swelling of the tissues around the eye.
- An infectious process caused by bacteria and viruses that leads to clogging of the duct.
- Contact with foreign particles in the eye or work in dusty and smoky areas. As a result, the channel becomes clogged.
- Allergy to exposure to an irritant.
- Decreased protective properties of the body.
- Overheating and subcooling.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
Very often this pathology occurs in newborn babies. This is due to the peculiarity of the structure of the lacrimal ducts. When the baby is in the amniotic fluid, the tear duct is closed by a special membrane that must rupture during or after childbirth. This process does not occur if pathology occurs. Tears collect in the canal and this provokes an inflammatory process. It mainly develops in women. Men are also no exception, but they rarely have this pathology. The reason is the differences in the structure of the lacrimal canal. Women use cosmetics, most of which cause inflammation.
Symptoms of the disease
Tears are necessary for the normal functioning of the organs of vision. They moisturize the cornea of the eye, protect against mechanical irritants, perform an antibacterial function. Sometimes tears stop flowing, this is the first sign of an obstruction of the lacrimal canal. Treatment is one of the ways to cope with the problem and prevent the development of canaliculitis.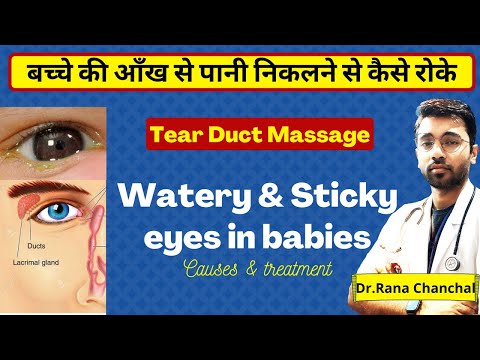 Sometimes lacrimal canal massage helps.
Sometimes lacrimal canal massage helps.
- painful and unpleasant sensations in the region of the eye;
- redness of the skin around the eye;
- feeling of constriction and fullness;
- swelling of the skin;
- lacrimation;
- edema;
- vision problems;
- increased secretion of mucus that smells bad;
- pus formation;
- high body temperature;
- intoxication of the body.
The acute stage of dacryocystitis appears as an inflammatory process affecting one eye. In the chronic stage, the lacrimal canal swells, the eye turns red and the number of tears increases.
Seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms. Blockage can occur in both acute and chronic stages. The accumulation of tear fluid increases the likelihood of infectious processes.
Diagnosis
Dacryocystitis is detected without much difficulty. At the appointment, the doctor conducts a visual assessment of the eye and palpation of the lacrimal sac.
- Paint test. The eye is instilled with a dye solution. If pigment appears in the eye after a few minutes, this indicates a blockage of the lacrimal canals.
- Probing. Using a probe with a needle, the ophthalmologist is introduced into the duct, which contributes to its expansion and getting rid of the problem.
- Dacryocystography. X-ray examination with the introduction of a dye. In the picture, you can see the structure of the eye system and identify the problem.
- Patency can also be checked by the West test. A cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage, from the side of the lesion. Collargol is instilled into the eye. The state is considered normal when, after 2 minutes, the tampon turns dark. If the tampon remains clean or stains after 10 minutes, there is a problem.
Treatment
The eyes are the mirror of the soul. When there is a problem with the eye, it is not worth the risk. Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor after a preliminary diagnosis. The method of treatment is selected depending on the form and cause of the pathology that provoked it, age characteristics.
The method of treatment is selected depending on the form and cause of the pathology that provoked it, age characteristics.
- Eye wash with antibacterial and disinfectant solutions.
- Application of special drops and ointments.
- Massage treatments and compresses to help clear the canal.
Wash eyes with antiseptic solutions several times a day. The procedure is performed by an ophthalmologist in a hospital setting.
Antibacterial ointments and drops:
- Floxal is a broad-spectrum antibacterial preparation. Fights the inflammatory process. The course of treatment is 10 days, two drops twice a day.
- Dexamethasone - drops with antibacterial effect. Effective in infectious processes. Bury 5 times a day. The required dosage and course of treatment are selected by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Levomycetin is a hormonal drug. It is used for allergic reactions and inflammation.
- Ciprofloxacin - is prescribed for infections of the lacrimal canal.
 Buried every three hours.
Buried every three hours.
Means have contraindications and side effects. Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of the attending physician.
If the treatment does not have a positive effect, bougienage is performed - cleaning the lacrimal canal from purulent contents; It is possible to quickly cope with the disease only with timely treatment. With negative symptoms, you need to visit an ophthalmologist.
Radical methods of struggle
In the absence of a positive effect from drug treatment, and also if the cause is a tumor or cyst, surgical treatment is performed.
Surgery is possible:
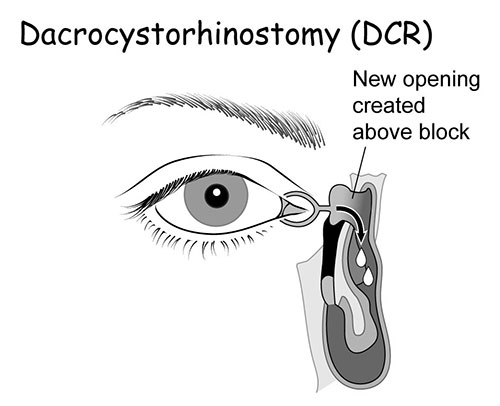
- Endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy. An apparatus with a camera is inserted into the duct. With the help of an endoscope, a puncture or incision is made. A special valve is created, the main purpose of which is drainage. The recovery period is 7 days. In parallel, antibiotic therapy is carried out to prevent the risk of developing an inflammatory process.
 The main advantage is the absence of visible traces after the operation.
The main advantage is the absence of visible traces after the operation. - Balloon dacrycytoplasty is an intervention that, due to its safety, is performed even for newborns. A conductor with a reservoir filled with liquid is inserted into the channel. Allows you to achieve the expansion of the site, thereby punching it. The procedure is carried out under local anesthesia. During the rehabilitation period, special drops and antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Massage
Prepare hands before the procedure: wash, disinfect or wear gloves.
Massage scheme:
- Press on the outer corner of the eye, turn your finger to the bridge of the nose.
- Gently press and massage the lacrimal sac, removing purulent masses from it.
- Instill a warm solution of furacilin and remove the discharge.
- Carry out pressure-massaging movements along the lacrimal ducts.
- Jerky movements along the nasolacrimal sac with some effort to open the canal and extract the discharge.
- Instill a solution of chloramphenicol.
Folk remedies
After prior approval with a doctor, traditional medicine is successfully used at home.
Folk remedies:
- Aloe. In case of inflammation, it is good to instill freshly prepared aloe juice, half diluted with saline.
- Eyebright. Prepare in the same way. Use for instillation of eyes and applying compresses.
- Chamomile. Has an antibacterial effect. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. collection, boil in a glass of boiling water and insist. Apply as an eye wash.
- Thyme. Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, the infusion is used for dacryocystitis.
- Kalanchoe. Natural antiseptic. Cut the leaves and keep in the refrigerator for two days. Next, extract the juice and dilute in a 1: 1 ratio with saline. This tool can be used to treat children. Adults can instill 2 drops of concentrated juice into the nose. The person begins to sneeze, during which the lacrimal canal is cleared of pus.
- Rose leaves. Only those flowers that are grown on their own plot are suitable. It will take 100 gr. collection and a glass of boiling water. Boil for five hours. Use in the form of lotions.
- Ivy Burda. Boil a tablespoon of herbs in a glass of boiling water, boil for 15 minutes. Apply for washes and compresses.
- Sweet pepper. Drink a glass of sweet pepper fruit every day. adding a teaspoon of honey.
Conclusions
Preventive measures directly depend on the causes of obstruction. You can reduce the risk of spreading the infection by observing the rules of personal hygiene. Avoid rubbing your eyes with dirty hands. Do not come into contact with people with conjunctivitis. Have personal decorative cosmetics. Proper use of compact lenses.
Blockage of lacrimal ducts | CooperVision Russia
If you've seen a crying baby or the latest sentimental Hollywood movie recently, you're well aware that tears run down your face
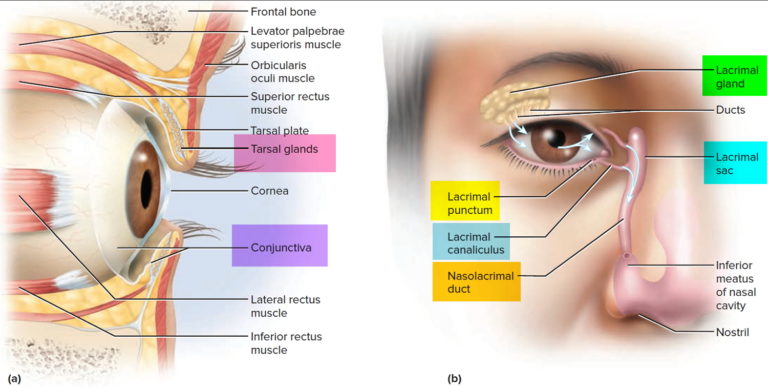
However, we also have a tear duct (also called "nasolacrimal duct" and "tear duct").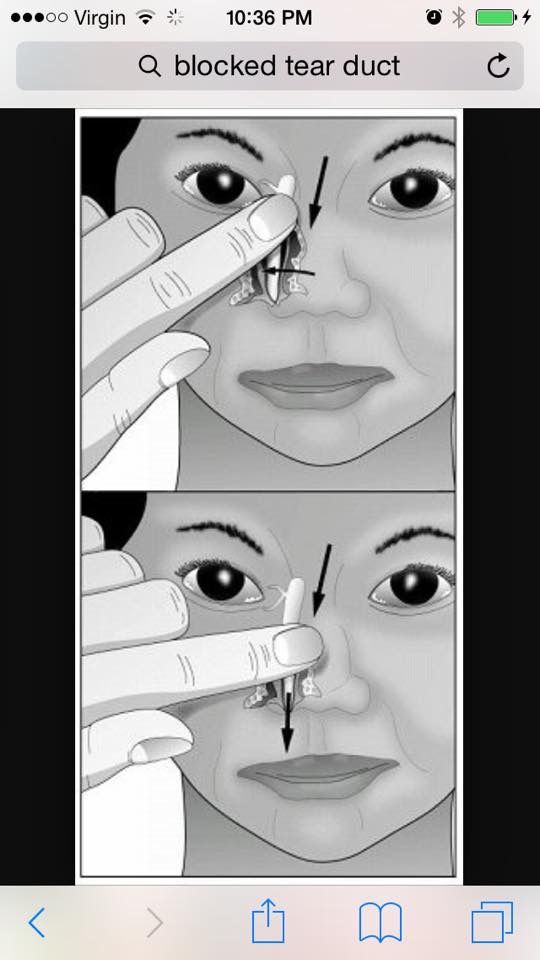 through which tears pass through the nose. These drainage tubes lead to a runny nose while crying or an allergic reaction in the eyes.
through which tears pass through the nose. These drainage tubes lead to a runny nose while crying or an allergic reaction in the eyes.
When the tear duct becomes blocked, problems arise. Let's look at the causes of blocked tear ducts, how it happens and how to get rid of it.
Why does tear duct blockage occur?
Blockage of the tear ducts occurs for many reasons.
Congenital blockage: One fifth of all babies are born with blocked tear ducts. It may be caused by an underdeveloped or abnormal canal or developmental problems in the structure of the face and skull.
Age-related narrowing of the tear ducts: In adults, there may be a narrowing of the entrance of the lacrimal duct, which increases the likelihood of blockage of the lacrimal duct.
Infections and inflammations: Infections and inflammations of the tear duct, eyes and nose can also cause blockage of the tear duct. Blockage of the tear duct itself can lead to infection and inflammation.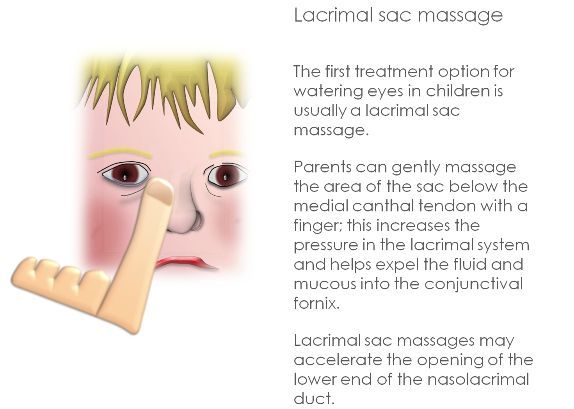
Bruises and injuries of the face: Any bruises that affect the lacrimal ducts and the bone structure around them can lead to blockage of the lacrimal duct.
Tumors, cysts and calculi: Blockage of the tear duct can be caused by tumors and other growths.
As you can see, while the blockage of the lacrimal canal produces many symptoms, it can also indicate a primary disease. Always consult your ophthalmologist for eye problems so that he can provide timely assistance.
Symptoms of blocked tear ducts
Blocked tear ducts or an infection caused by blockage can be characterized by a number of symptoms. These include:
- Watery eyes and excessive tearing
- Recurrent inflammations and infections (infections may be caused by blockage or lead to blockage)
- Accumulation or secretion of mucus
- Pain and swelling in the corners of the eyes
- Blurred vision
- Bloody Tears
Your ophthalmologist will be able to assess the function of the drainage of the lacrimal duct and decide on the treatment options.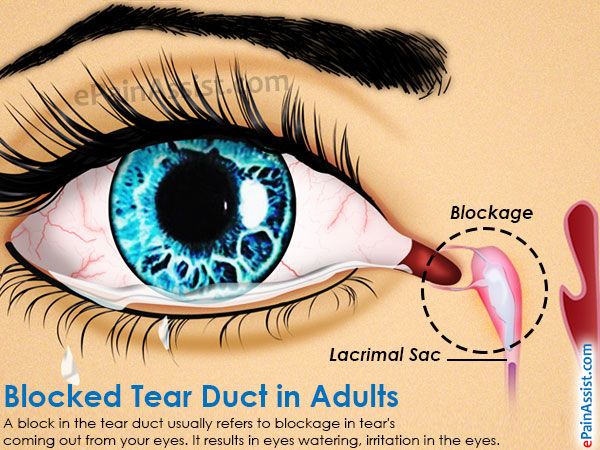
Treatment of blocked tear ducts
The best treatment for blocked tear ducts is determined by its cause. Your ophthalmologist will recommend trying the least invasive method first and then choosing what works for you and when you need to switch to other treatments.
The following are common treatments for blocked tear ducts.
Blocked tear ducts in infants
In many newborns, blocked tear ducts resolve within the first year of life. However, there are cases when treatment is necessary. The first treatment for blocked tear ducts in infants includes dilatation (gentle widening of the duct), probing, and lavage. If this does not help, the ophthalmologist will sometimes insert a dilating probe to further widen the canal.
Blockage of lacrimal ducts in adults
Blockage of the tear ducts in adults usually indicates a narrowing or other problem that does not go away on its own. The first stage of treatment is the same as for infants: dilation, probing and lavage.