How much motrin can a child take
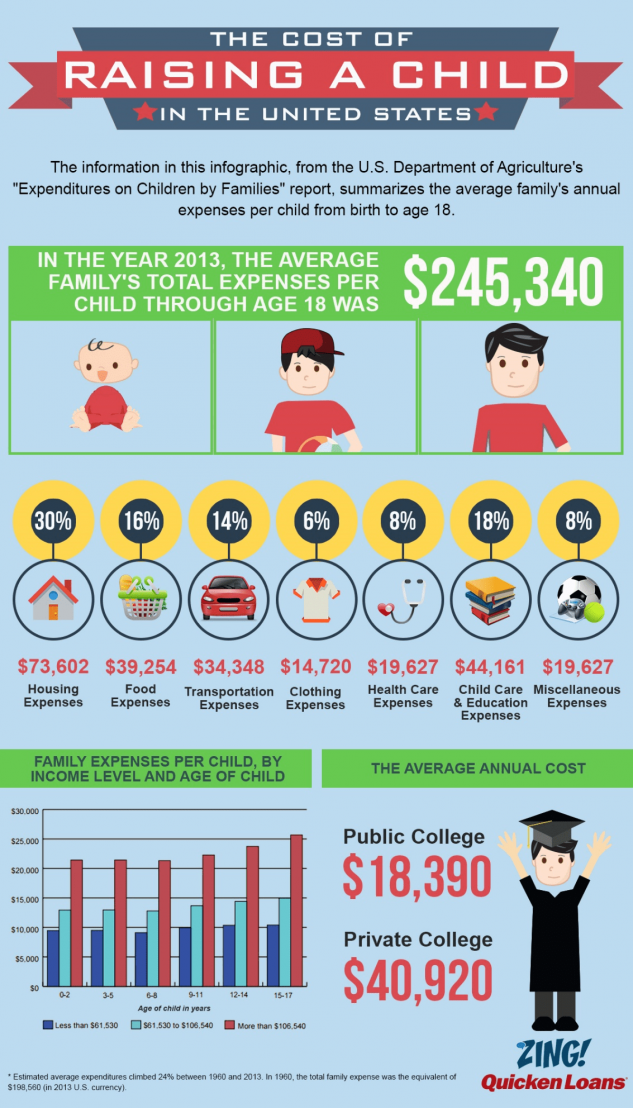
Children & Infants Dosage by Age & Weight
- Home
- Products
- View Dosing Charts for Children & Infants
Use these charts to find the right dose of Children’s MOTRIN® or Infants’ MOTRIN® for your child.
A few reminders:
- When giving any medicine, always read and follow the label carefully.
- Find right dose on chart.
- If possible, use weight to dose; otherwise, use age.
- Only use the dosing device provided with the medicine. Do not use any other dosing device.
- Do not give more than directed.
- If needed, repeat dose every 6-8 hours. But, do not use more than 4 times a day.
- Shake well before using.
- mL = milliliter
- Each 5 mL contains: sodium 2 mg
QA Text:
QA Question:
INFANTS' MOTRIN® ORAL SUSPENSION DROPS 50 mg/1.25mL
| Weight (lb) | Age (mos) | Dose (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Under 6 mos | Ask a doctor | |
| 12-17 lbs | 6-11 mos | 1. |
| 18-23 lbs | 12-23 mos | 1.875 mL |
| Age (mos) Under 6 mos | |
| Ask a doctor | |
| Weight (lb) 12-17 lbs Age (mos) 6-11 mos | |
| 1.25 mL | |
| Weight (lb) 18-23 lbs Age (mos) 12-23 mos | |
| 1.875 mL |
Dispense the liquid slowly into the child's mouth, toward the inner cheek.
Back to top
QA Question:
CHILDREN’S MOTRIN® ORAL SUSPENSION 100 mg/5mL
| Weight (lb) | Age (yr) | Dose (mL)* |
|---|---|---|
| Under 24 lbs | Under 2 years | Ask a doctor |
| 24-35 lbs | 2-3 years | 5 mL |
| 36-47 lbs | 4-5 years | 7. 5 mL 5 mL |
| 48-59 lbs | 6-8 years | 10 mL |
| 60-71 lbs | 9-10 years | 12.5 mL |
| 72-95 lbs | 11 years | 15 mL |
| Weight (lb) Under 24 lbs Age (mos) Under 2 years | |
| ask a doctor | |
| Weight (lb) 24-35 lbs Age (mos) 2-3 years | |
| 5 mL | |
| Weight (lb) 36-47 lbs Age (mos) 4-5 years | |
| 7.5 mL | |
| Weight (lb) 48-59 lbs Age (mos) 6-8 years | |
| 10 mL | |
| Weight (lb) 60-71 lbs Age (mos) 9-10 years | |
| 12.5 mL | |
| Weight (lb) 72-95 lbs Age (mos) 11 years | |
| 15 mL |
*Or as directed by a doctor. Replace the original bottle cap to maintain child resistance.
Replace the original bottle cap to maintain child resistance.
Back to top
QA Question:
CHILDREN'S MOTRIN® CHEWABLES 100mg/chewable tablet
| Weight (lb) | Age (yr) | Dose (chewable tablets) |
|---|---|---|
| Under 24 lbs | Under 2 years | Ask a doctor |
| 24-35 lbs | 2-3 years | 1 |
| 36-47 lbs | 4-5 years | 1 1/2 |
| 48-59 lbs | 6-8 years | 2 |
| 60-71 lbs | 9-10 years | 2 1/2 |
| 72-95 lbs | 11 years | 3 |
| Weight (lb) Under 24 lbs Age (mos) Under 2 years | |
| ask a doctor | |
| Weight (lb) 24-35 lbs Age (mos) 2-3 years | |
| 1 | |
| Weight (lb) 36-47 lbs Age (mos) 4-5 years | |
| 1 1/2 | |
| Weight (lb) 48-59 lbs Age (mos) 6-8 years | |
| 2 | |
| Weight (lb) 60-71 lbs Age (mos) 9-10 years | |
| 2 1/2 | |
| Weight (lb) 72-95 lbs Age (mos) 11 years | |
| 3 |
Back to top
This website contains current product information and may differ from the information on the product packaging you may have. If you have any questions, please contact the Consumer Care Center at 1-877-895-3665.
If you have any questions, please contact the Consumer Care Center at 1-877-895-3665.
Ibuprofen dosing for children Information | Mount Sinai
Motrin; Advil
How Ibuprofen can Help Your Child
Ibuprofen is a type of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It can help:
- Reduce aches, pain, sore throat, or fever in children with a cold or the flu
- Relieve headaches or toothaches
- Reduce pain and swelling from an injury or broken bone
Proper Dosing
Ibuprofen can be taken as liquid or chewable tablets. To give the correct dose, you need to know your child's weight.
You also need to know how much ibuprofen is in a tablet, teaspoon (tsp), 1.25 milliliters (mL), or 5 mL of the product you are using. You can read the label to find out.
- For chewable tablets, the label will tell you how many milligrams (mg) are found in each tablet, for example 50 mg per tablet.
- For liquids, the label will tell you how many mg are found in 1 tsp, in 1.25 mL, or in 5mL. For example, the label may read 100 mg/1 tsp, 50 mg/1.25 mL, or 100 mg/5 mL.
For syrups, you need some type of dosing syringe. It may come with the medicine, or you can ask your pharmacist. Make sure to clean it out after every usage.
If your child weighs 12 to 17 pounds (lbs) or 5.4 to 7.7 kilograms (kg):
- For infant drops that say 50mg/1.25 mL on the label, give a 1.25 mL dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 teaspoon (tsp) on the label, give a ½ tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 2.5 mL dose.

If your child weighs 18 to 23 lbs or 8 to 10 kg:
- For infant drops that say 50mg/1.25 mL on the label, give a 1.875 mL dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a ¾ tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 4 mL dose.
If your child weighs 24 to 35 lbs or 10.5 to 15.5 kg:
- For infant drops that say 50mg/1.25 mL on the label, give a 2.5 mL dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 1 tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 5 mL dose.
- For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 2 tablets.
If your child weighs 36 to 47 lbs or 16 to 21 kg:
- For infant drops that say 50mg/1.25 mL on the label, give a 3.75 mL dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 1½ tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 7.
 5 mL dose.
5 mL dose. - For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 3 tablets.
If your child weighs 48 to 59 lbs or 21.5 to 26.5 kg:
- For infant drops that say 50mg/1.25 mL on the label, give a 5 mL dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 2 tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 10 mL dose.
- For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 4 tablets.
- For junior-strength tablets that say 100 mg tablets on the label, give 2 tablets.
If your child weighs 60 to 71 lbs or 27 to 32 kg:
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 2½ tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 12.5 mL dose.
- For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 5 tablets.
- For junior-strength tablets that say 100 mg tablets on the label, give 2½ tablets.
If your child weighs 72 to 95 lbs or 32.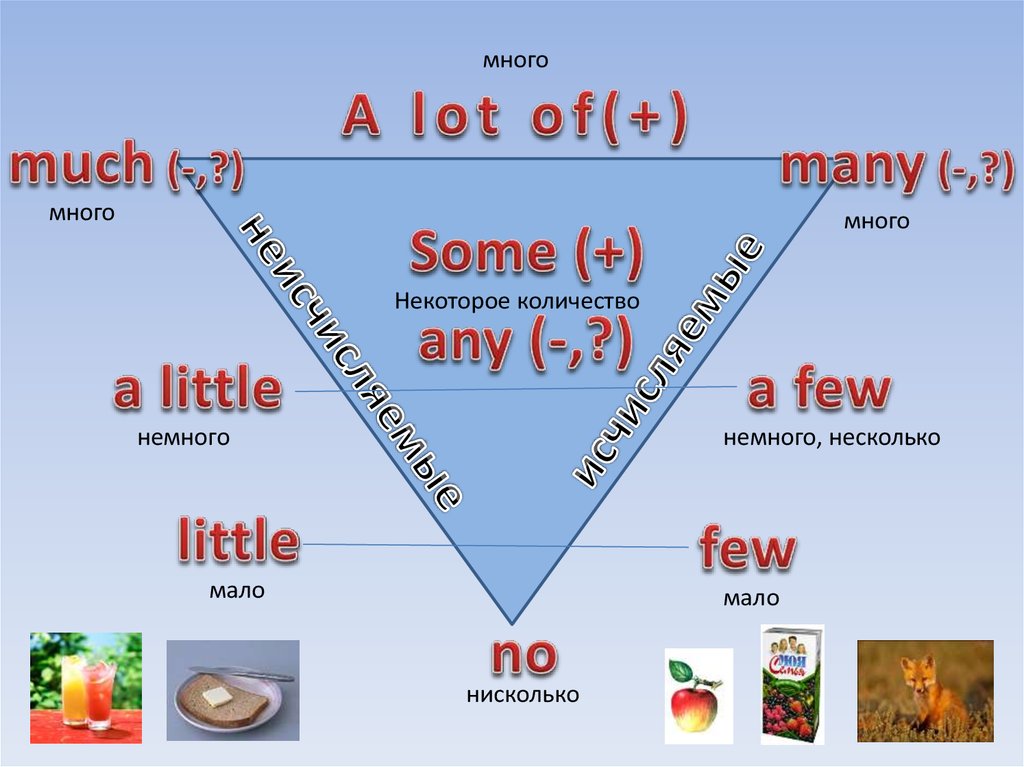 5 to 43 kg:
5 to 43 kg:
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 3 tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 15 mL dose.
- For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 6 tablets.
- For junior-strength tablets that say 100 mg tablets on the label, give 3 tablets.
If your child weighs 96 lbs or 43.5 kg or more:
- For liquid that says 100 mg/1 tsp on the label, give a 4 tsp dose.
- For liquid that says 100 mg/5 mL on the label, give a 20 mL dose.
- For chewable tablets that say 50 mg tablets on the label, give 8 tablets.
- For junior-strength tablets that say 100 mg tablets on the label, give 4 tablets.
Try giving your child the medicine with food to avoid stomach upset. If you are not sure how much to give your child, call your health care provider.
Do not give ibuprofen to children under 6 months of age, unless directed by your provider.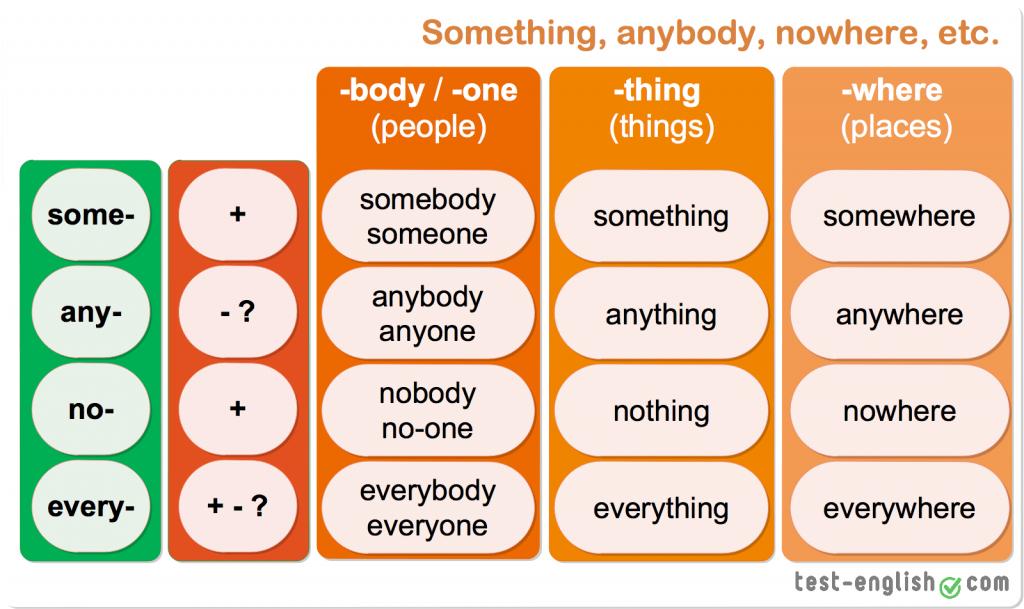 You should also check with your provider before giving ibuprofen to children under age 2 years or less than 12 pounds or 5.5 kilograms.
You should also check with your provider before giving ibuprofen to children under age 2 years or less than 12 pounds or 5.5 kilograms.
Giving Medicine to Children
Make sure you don't give your child more than one medicine with ibuprofen. For example, ibuprofen can be found in many allergy and cold remedies. Read the label before giving any medicine to children. You should not give medicine with more than one active ingredient to children under age 6 years.
There are important child medicine safety tips to follow.
- Carefully read all of the instructions on the label before giving your child medicine.
- Make sure you know the strength of the medicine in the bottle you purchased.

- Use the syringe, dropper, or dosing cup that comes with your child's liquid medicine. You can also get one at your local pharmacy.
- Make sure you are using the right unit of measurement when filling medicine. You may have the option of milliliters (mL) or teaspoon (tsp) dosing.
- If you are not sure what medicine to give your child, call your provider.
Children with certain medical conditions or taking certain medicines should not take ibuprofen. Check with your provider.
If Your Child Takes too Much
Be sure to post the number for the poison control center by your home phone. If you think your child has taken too much medicine, call the poison control center at 1-800-222-1222. It is open 24 hours a day. Signs of poisoning include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
It is open 24 hours a day. Signs of poisoning include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and abdominal pain.
Go to the nearest emergency room. Your child may need:
- Activated charcoal. Charcoal stops the body from absorbing the medicine. It has to be given within an hour. It does not work for every medicine.
- To be admitted to the hospital to be monitored.
- Blood tests to see what the medicine is doing.
- To have his or her heart rate, breathing rate, and blood pressure monitored.
When to Call the Doctor
Call your provider if:
- You are not sure what dose of medicine to give your infant or child.
- You are having trouble getting your child to take medicine.

- Your child's symptoms do not go away when you would expect.
- Your child is an infant and has signs of illness, such as fever.
American Academy of Pediatrics website. Ibuprofen dosage table for fever and pain. Healthychildren.org. www.healthychildren.org/English/safety-prevention/at-home/medication-safety/Pages/Ibuprofen-for-Fever-and-Pain.aspx. Updated May 23, 2016. Accessed January 15, 2021.
Aronson JK. Ibuprofen. In: Aronson JK, ed. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs. 16th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:5-12.
Theobald JL, Kostic MA. Poisoning. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 77.
Last reviewed on: 10/2/2020
Reviewed by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
tablets for body pain have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects
The frequency of adverse reactions (AR) is given as the following classification: very often (≥1/10), often (from ≥1/100 to <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), rare (≥1/10,000 to <1/1000), very rare (<1/10,000), frequency not known (cannot be estimated based on available data) ).
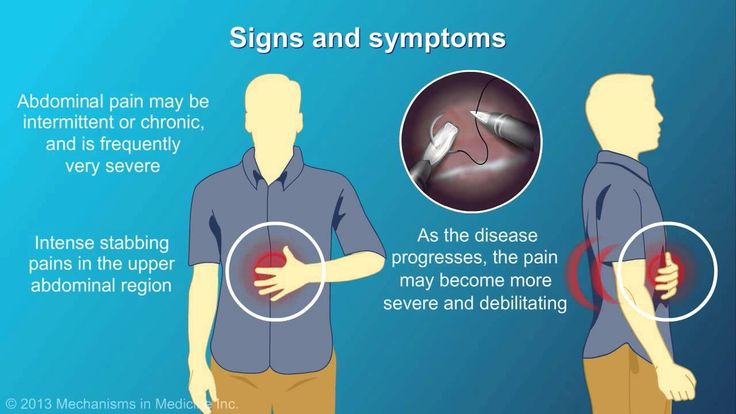
The most frequently observed adverse reactions were from the gastrointestinal tract. It is possible to develop a peptic ulcer, gastric perforation or gastrointestinal bleeding, sometimes fatal, especially in elderly patients (see section "Special Instructions").
Within each group, HPs are listed in descending order of severity.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Uncommon: Eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
Nervous system disorders:
often: headache, vertigo, dizziness, drowsiness;
infrequently: depression, sleep disturbance, impaired concentration, insomnia, malaise.
Visual disturbances:
common: visual impairment.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders:
often : tinnitus, hearing impairment;
infrequently: hearing loss.
Cardiac disorders:
common: swelling, palpitations;
Uncommon: congestive heart failure.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
often : shortness of breath;
infrequently : eosinophilic pneumonia.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
often: constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhoea, stomatitis, flatulence;
infrequently: gastrointestinal bleeding and / or gastric perforation, hematemesis, melena, vomiting;
very rare : relapse or worsening of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease;
frequency unknown : gastritis.
Liver and biliary tract disorders:
infrequently: increased activity of "liver" enzymes, jaundice.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
often : pruritus, skin rash, ecchymosis, purpura;
infrequently : alopecia, photodermatosis;
very rare : bullous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders:
infrequently : myalgia and muscle weakness.
Renal and urinary tract disorders:
Uncommon: glomerulonephritis, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, renal papillary necrosis.
General disorders and administration site disorders:
often : thirst, increased sweating;
infrequently : hypersensitivity reactions, menstrual disorders, hyperthermia (chills and fever).
During therapy with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, edema and symptoms of heart failure, increased blood pressure were reported.
Clinical studies and epidemiological data suggest that the use of certain non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (especially high doses for long-term therapy) may be associated with a slight increase in the risk of arterial thrombosis (eg, myocardial infarction or stroke).
Undesirable effects, the causal relationship of which has not been established with the use of naproxen
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia.
Nervous system disorders: aseptic meningitis, cognitive dysfunction.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: erythema multiforme; photosensitivity reactions like cutaneous porphyria tarda and epidermolysis bullosa; hives.
Vascular disorders: vasculitis.
General disorders and administration site disorders: angioedema, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia.
If you notice these adverse reactions, stop taking the drug and, if possible, consult a doctor.
Top
Ibufen - instructions for use, doses, side effects, reviews of the drug Ibufen: - Encyclopedia of drugs RLS
Description of the drug Ibufen (oral suspension, 100 mg / 5 ml) based on official instructions, approved manufacturing company in 2004
Approval date: 27.07.2004
Content
- Active substance
- ATX
- Pharmacological group
- Nosological classification (ICD-10)
- Composition and form of release
- Description of the dosage form
- Pharmacokinetics
- Indications
- Contraindications
- Dosage and administration
- Side effects
- Interaction
- Overdose
- Precautionary measures
- special instructions
- Storage conditions
- Best before date
- Reviews
Active ingredient
Ibuprofen* (Ibuprofen*)
ATX
M01AE01 Ibuprofen
Pharmacological group
NSAIDs - Derivatives of propionic acid
Nosological classification (ICD-10)
ICD-10 code list
- G43 Migraine
- J02.
 9 Acute pharyngitis, unspecified
9 Acute pharyngitis, unspecified - J06 Acute infections of the upper respiratory tract of multiple and unspecified sites
- J11 Influenza, virus not identified
- K00.7 Teething syndrome
- K08.8.0* Toothache
- M25.5 Joint pain
- M79.
 1 Myalgia
1 Myalgia - M79.2 Neuralgia and neuritis, unspecified
- R50 Fever of unknown origin
- R51 Headache
- T14.3 Dislocation, sprain and injury of capsular-ligamentous apparatus of joint, body region unspecified
- T14.9 Injury, unspecified
- T88.
 1 Other immunization-related complications, not elsewhere classified
1 Other immunization-related complications, not elsewhere classified
Composition and formulation
| Oral suspension | 5 ml |
| ibuprofen | 100 mg |
in 100 g orange glass bottles; in a box 1 bottle (a measure with a scale is attached to the package).
Description of dosage form
Suspension of orange color with an orange smell and sweet taste, with a slightly perceptible burning aftertaste. There may be a separation into a liquid layer and a precipitate, which, after mixing, constitute a homogeneous suspension.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, more than 80% is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. max "> C max in blood plasma is achieved when taken on an empty stomach - after 45 minutes, when taken after meals after 1. 5-2.5 hours. Protein binding - 90%. Slowly penetrates into the joint cavity, but in the synovial fluid creates concentrations greater than in blood plasma (C max in the synovial fluid is reached after 2-3 hours). It is metabolized mainly in the liver. It undergoes pre- and post-systemic metabolism. After absorption, about 60% of the pharmacologically inactive R-form is slowly transformed into active S-form Excreted by the kidneys (60–90% in the form of metabolites and products of their combination with glucuronic acid, to a lesser extent - with bile, unchanged - no more than 1%). It has a two-phase elimination kinetics with 1/2">T 1/2 2-2.5 hours, after administration in a single dose it is completely eliminated within 24 hours. The antipyretic effect of Ibufen develops after 30 minutes and lasts 6-8 hours.
5-2.5 hours. Protein binding - 90%. Slowly penetrates into the joint cavity, but in the synovial fluid creates concentrations greater than in blood plasma (C max in the synovial fluid is reached after 2-3 hours). It is metabolized mainly in the liver. It undergoes pre- and post-systemic metabolism. After absorption, about 60% of the pharmacologically inactive R-form is slowly transformed into active S-form Excreted by the kidneys (60–90% in the form of metabolites and products of their combination with glucuronic acid, to a lesser extent - with bile, unchanged - no more than 1%). It has a two-phase elimination kinetics with 1/2">T 1/2 2-2.5 hours, after administration in a single dose it is completely eliminated within 24 hours. The antipyretic effect of Ibufen develops after 30 minutes and lasts 6-8 hours.
Indications
As an antipyretic: for colds, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza, tonsillitis (pharyngitis), childhood infections accompanied by fever, post-vaccination reactions. 0003
0003
As an analgesic: for toothache, painful teething, headache, migraine, neuralgia, muscle and joint pain, trauma and burns.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs), peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, severe insufficiency of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular system, arterial hypertension, hemophilia, hypocoagulation, hemorrhagic diathesis, glucose deficiency -6-phosphate dehydrogenase, bronchospastic reactions after the use of acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs ("aspirin asthma"), Quincke's edema, nasal polyps, hearing loss, infancy (up to 6 months, with body weight - below 7 kg).
Dosage and administration
Inside , after meals. The average single dose is 5-10 mg/kg of body weight 3-4 times a day. Children aged 6 months - 1 year (7-9 kg) - 2.5 ml (50 mg) 3 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 7.5 ml (150 mg). 1-3 years (10-15 kg) 2.5 ml (50 mg) 3-4 times daily, maximum daily dose 7. 5-10 ml (150-200 mg). 3-6 years (16-20 kg) - 5 ml (100 mg) 3 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 15 ml (300 mg). 6-9 years (21-30 kg) - 5 ml (100 mg) 4 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 20 ml (400 mg). 9-12 years (31-41 kg) - 10 ml (200 mg) 3 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 30 ml (600 mg). Over 12 years (more than 41 kg) - 10 ml (200 mg) 4 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 40 ml (800 mg). The dose can be repeated every 6-8 hours. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose. For children from 6 months to 1 year, the drug is prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor.
5-10 ml (150-200 mg). 3-6 years (16-20 kg) - 5 ml (100 mg) 3 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 15 ml (300 mg). 6-9 years (21-30 kg) - 5 ml (100 mg) 4 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 20 ml (400 mg). 9-12 years (31-41 kg) - 10 ml (200 mg) 3 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 30 ml (600 mg). Over 12 years (more than 41 kg) - 10 ml (200 mg) 4 times a day, the maximum daily dose is 40 ml (800 mg). The dose can be repeated every 6-8 hours. Do not exceed the maximum daily dose. For children from 6 months to 1 year, the drug is prescribed on the recommendation of a doctor.
Side effects
From the side of the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, sleep disturbance, anxiety, drowsiness, depression, agitation, visual impairment (reversible toxic amblyopia, blurred vision or double vision).
From the side of hematopoiesis: heart failure, tachycardia, increased blood pressure; anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia.
From the digestive tract: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, heartburn, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence, abnormal liver function, peptic ulcers, gastric bleeding.
From the urinary system: acute renal failure, allergic nephritis, nephrotic syndrome (edema), polyuria, cystitis.
Allergic reactions: itching, rash, bronchospastic syndrome, allergic rhinitis, angioedema, Steven-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome.
Interactions
Should not be combined with other NSAIDs (acetylsalicylic acid reduces anti-inflammatory effect and increases side effects). When taken simultaneously with diuretics, the diuretic effect decreases and the risk of developing renal failure increases. Weakens the effect of antihypertensive drugs, incl. ACE inhibitors (simultaneously reduces their excretion by the kidneys), beta-adrenergic agents, thiazides. Enhances the effect of oral hypoglycemic agents (especially sulfonylurea derivatives) and insulin, indirect anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics (increases the risk of hemorrhagic complications), the toxic effect of methotrexate and lithium preparations, increases the concentration of digoxin in the blood.
Microsomal oxidation inducers (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, zixorin, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants) increase the risk of developing severe hepatotoxic complications (increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites), microsomal oxidation inhibitors reduce it. Caffeine enhances the pain-relieving effect.
Overdose
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, headache, tinnitus, depression, drowsiness, metabolic acidosis, hemorrhagic diathesis, decreased blood pressure, acute renal failure, abnormal liver function, tachycardia, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation; convulsions, apnea and coma (especially characteristic of children under 5 years of age).
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal, alkaline drink, symptomatic therapy (correction of acid-base balance, blood pressure).
Precautions
Use with caution in cirrhosis of the liver with portal hypertension, hepatic and/or renal failure, heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, hyperbilirubinemia, gastric and duodenal ulcer (history), gastritis, enteritis, colitis, diseases blood (leukopenia, anemia), pregnancy (II-III trimesters), during breastfeeding. In patients with bronchial asthma or other diseases that occur with bronchospasm, there may be an increased risk of developing bronchospasm.
In patients with bronchial asthma or other diseases that occur with bronchospasm, there may be an increased risk of developing bronchospasm.
During long-term treatment, it is necessary to control the picture of peripheral blood and the functional state of the liver and kidneys. When symptoms of gastropathy appear, careful monitoring is indicated (conducting esophagogastroduodenoscopy, a blood test with the determination of hemoglobin, hematocrit, fecal occult blood analysis).
If there is no antipyretic effect within 2 days and no analgesic effect within 3 days, you should consult a doctor. In case of side effects, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Special instructions
Shake the vial before use until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. With prolonged use, NSAIDs can cause damage to the gastric mucosa, peptic ulcers, and gastrointestinal bleeding.
Use with caution in diabetic patients - contains sugar.
If side effects occur, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.