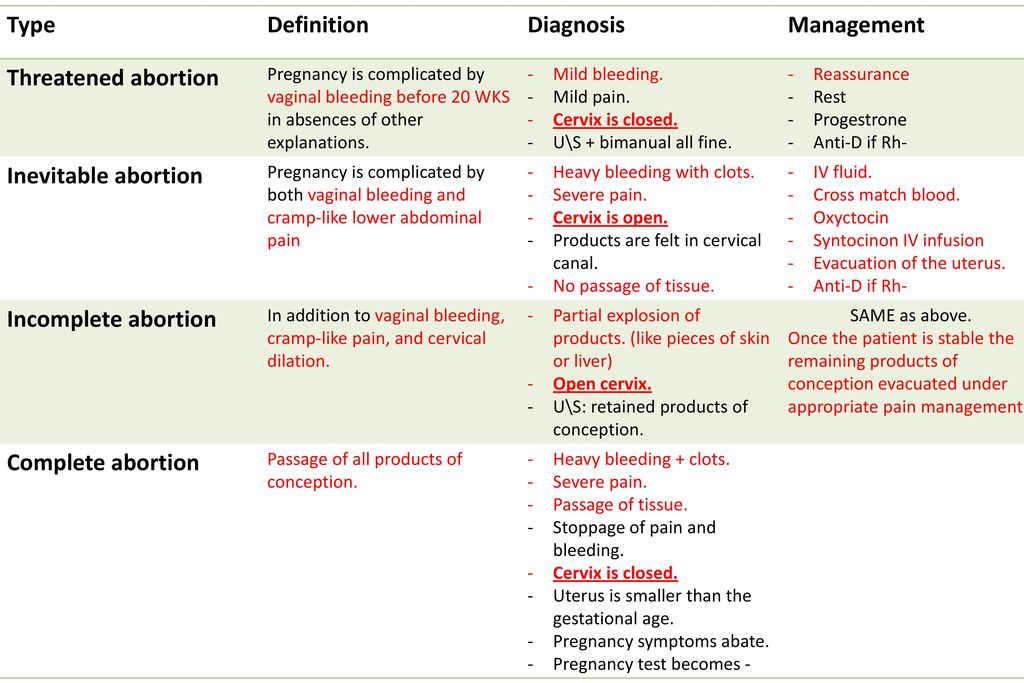
Bleeding in last month of pregnancy
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
One out of 10 women will have vaginal bleeding during their 3rd trimester. At times, it may be a sign of a more serious problem. In the last few months of pregnancy, you should always report bleeding to your health care provider right away.
You should understand the difference between spotting and bleeding:
- Spotting is when you notice a few drops of blood every now and then on your underwear. It is not enough to cover a panty liner.
- Bleeding is a heavier flow of blood. With bleeding, you will need a liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your clothes.
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
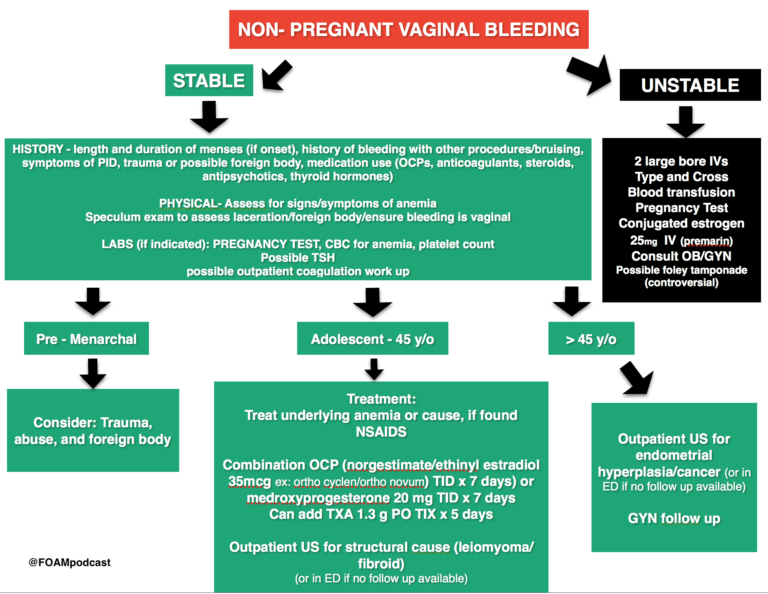
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home. To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.

- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae.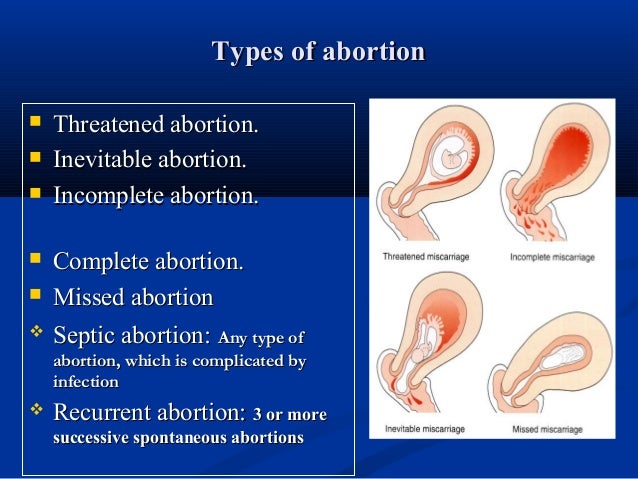 In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Updated by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Browse the Encyclopedia
Vaginal bleeding in late pregnancy Information | Mount Sinai
What Causes Bleeding Later in Pregnancy?
When labor begins, the cervix starts to open up more, or dilate. You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
You may notice a small amount of blood mixed in with normal vaginal discharge, or mucus.
Mid- or late-term bleeding may also be caused by:
- Having sex (most often just spotting)
- An internal exam by your provider (most often just spotting)
- Diseases or infections of the vagina or cervix
- Uterine fibroids or cervical growths or polyps
More serious causes of late-term bleeding may include:
- Placenta previa is a problem of pregnancy in which the placenta grows in the lowest part of the womb (uterus) and covers all or part of the opening to the cervix.
- Placenta abruptio (abruption) occurs when the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before the baby is born.
What to Tell Your Health Care Provider
To find the cause of your vaginal bleeding, your provider may need to know:
- If you have cramping, pain, or contractions
- If you have had any other bleeding during this pregnancy
- When the bleeding began and whether it comes and goes or is constant
- How much bleeding is present, and whether it is spotting or a heavier flow
- The color of the blood (dark or bright red)
- If there is an odor to the blood
- If you have fainted, felt dizzy or nauseated, vomited, or had diarrhea or a fever
- If you have had recent injuries or falls
- When you last had sex and if you bled afterward
What Should Happen Next?
A small amount of spotting without any other symptoms that occurs after having sex or an exam by your provider can be watched at home.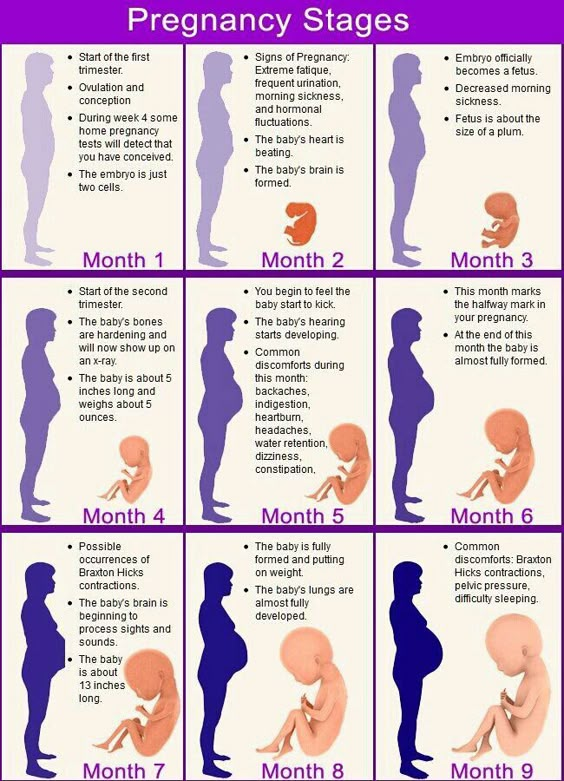 To do this:
To do this:
- Put on a clean pad and recheck it every 30 to 60 minutes for a few hours.
- If spotting or bleeding continues, call your provider.
- If the bleeding is heavy, your belly feels stiff and painful, or you are having strong and frequent contractions, you may need to call 911 or your local emergency number.
For any other bleeding, call your provider right away.
- You will be told whether to go to the emergency room or to the labor and delivery area in your hospital.
- Your provider will also tell you whether you can drive yourself or you should call an ambulance.
Baeseman ZJ. Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy. In: Kellerman RD, Rakel DP, eds. Conn's Current Therapy 2021. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier 2021:1227-1229.
Francois KE, Foley MR. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 18.
Hull AD, Resnik R, Silver RM. Placenta previa and accreta, vasa previa, subchorionic hemorrhage, and abruptio placentae. In: Resnik R, Lockwood CJ, Moore TR, Greene MF, Copel JA, Silver RM, eds. Creasy and Resnik's Maternal-Fetal Medicine: Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 46.
Salhi BA, Nagrani S. Acute complications of pregnancy. In: Walls RM, Hockberger RS, Gausche-Hill M, eds. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 178.
Last reviewed on: 10/5/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. D.A.M. Editorial team.
D.A.M. Editorial team.
Pathological and physiological causes of bleeding during early pregnancy
The gestation period is a complex process that does not always go well. Every second woman has various complications. Most often, women go to the doctor with complaints of spotting. Why does bleeding occur during early pregnancy, how dangerous is it?
Causes of bleeding in pregnancy
Blood in the first trimester of pregnancy in the vaginal secretion is observed in 30% of expectant mothers. Bleeding can be weak, spotting, plentiful.
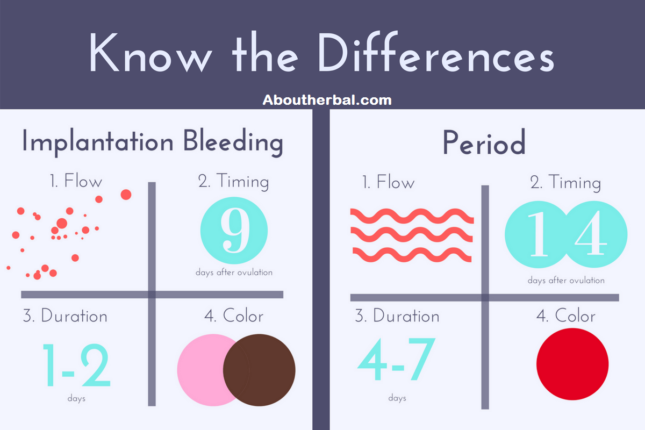
Most often, blood during pregnancy in the early stages is observed during implantation of the fetal egg. When the egg is attached, the vessels are often damaged, which leads to the appearance of blood secretions. They are similar to menstruation, last 1-2 days. This process is considered natural, does not indicate any pathologies.
Any spotting during early pregnancy is a reason for an urgent appeal to a gynecologist. Even if there is no additional discomfort. At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
Even if there is no additional discomfort. At a remote consultation, our doctor will collect an anamnesis, draw up a clinical picture in order to identify the cause of bleeding. And he will select effective methods to eliminate the problem.
Blood during pregnancy - other common causes
In addition to the main ones, there are some other reasons why pathology can develop.
| No. | Cause |
| one | Excessive exercise, deep penetration during intercourse. If the cervix is damaged, slight red discharge occurs, which disappears within two hours. |
| 2 | Progesterone deficiency. With a low level of the hormone, the body starts the process of menstruation. Bloody discharge during pregnancy appears when the uterine mucosa is exfoliated. |
| 3 | Miscarriage - occurs in 2-8% of pregnant women. It is characterized by pain in the lower abdomen, which is rapidly increasing, bloody discharge at the beginning of pregnancy. The causes of the pathological condition can be different - infectious diseases, fetal malformations that are incompatible with life, dehydration, abdominal trauma, taking certain drugs. |
| four | Ectopic pregnancy. Dangerous condition, urgent hospitalization is required. |
| 5 | A failed miscarriage. Blood discharge during pregnancy, abdominal pain are the main manifestations of intrauterine development of the fetus. |
| 6 | Infections. To avoid dangerous complications, it is necessary to treat diseases. Parents of both sexes should be tested. |
| 7 | Full or partial hydatidiform mole. Pathology of the chorion, in which the size of the villi increases, bubble expansions form. The risk group includes women with ovarian dysfunction, inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system, and a history of cystic mole. Bleeding is profuse and constant, characteristic blisters are present. The symptoms of early toxicosis are very pronounced, the size of the uterus, the hCG indicators do not correspond to the gestational age. |
| eight | Cervical cancer. Pregnant women are rarely diagnosed. The risk group includes women with a large number of abortions and childbirth, often changing sexual partners. |
| 9 | Subchorionic hematoma. Hemorrhage around the placenta most often resolves on its own. But it increases the risk of preterm birth and other complications. |
| ten | Cervical erosion. |
Bleeding in the first trimester can be caused by causes that appear at any gestational age. These are fibroids, polyps in the uterus and cervical canal, cardiovascular pathologies that are associated with a weakening of the endothelium.
Physiological or pathological bleeding during gestation - differences
Clinical manifestations of bleeding in pregnant women depend on the causes. Physiological discharge of blood from the genital tract in the early stages of gestation proceeds without deterioration in well-being. With bleeding caused by erosion, fibroids and polyps, there are also no additional discomfort. In this case, only a few drops of blood are released, it bleeds for a short time.
Abundant bleeding, similar to menstruation, against the background of a general satisfactory condition, occurs with a deficiency of progesterone.
Bleeding with spontaneous interruption is accompanied by constant or periodic pain in the lumbar region, abdomen. Disturbed by nausea, bouts of dizziness, slightly increased body temperature. Bleeding can be weak or intense, and clots are often observed in the discharge.
When a fertilized egg is fixed outside the uterus, internal bleeding often occurs, and discharge from the genital tract may appear much later. Characteristic manifestations - acute pain in the abdomen radiates to the anal region, right or left side, blood pressure decreases, cold sweat appears, fainting is possible. Significant blood loss leads to the development of a state of shock with a high probability of death.
Learn more about implantation bleeding
Why does it bleed at the initial stages of gestation? Most often, the appearance of spotting during pregnancy is associated with the implantation of the embryo. They occur 6-12 days after conception and are often one of the first signs of conception.
Usually, the appearance of spotting at the beginning of pregnancy coincides with the time of the onset of menstruation, if the cycle is regular. But discharge in pregnant women is not as abundant as menstrual bleeding. Duration - from several hours to three, with the first pregnancy up to 5 days.
How does implantation bleeding manifest?
- weak, pulling pain in the lower abdomen;
- headache, dizziness;
- sudden change of mood;
- bouts of nausea;
- increased sensitivity, swelling of the mammary glands;
- fatigue, drowsiness.
Important! When the embryo is implanted, little blood is released, usually these are small spots. The discharge may be pink, brown, orange, and there should be no clots.
Possible causes of early bleeding by week
The first months of pregnancy are the most difficult and dangerous. It is in the early stages that various pathologies and complications often appear.
Why blood may appear in the early stages during pregnancy:
- At the 4th week of pregnancy, discharge with an admixture of blood may appear - this is implantation bleeding. Excessive bleeding is a dangerous sign, most often indicates a miscarriage. Spontaneous abortion can be caused by exercise, fever, infections, drugs or alcohol. Such bleeding is profuse, painful, blood clots are present.
- The appearance of sanious discharge at the 5th week of pregnancy may be a sign of a missed pregnancy. The reasons are overwork, Rh conflict, bad habits, bacterial and viral diseases of the reproductive system, genetic disorders in the embryo. Symptoms - causeless fever, severe pain in the lower back and lower abdomen, the disappearance of signs of toxicosis.
- Blood in the secretions at the 6th week of pregnancy appears with an ectopic attachment of the fetal egg, fetal fading, Rhesus conflict. Discharge with blood at 6 weeks of pregnancy is a reason for an urgent visit to the gynecologist.

- At the 7th week of pregnancy, discharge with blood is not the norm. May indicate a miscarriage, missed or ectopic pregnancy.
- From the 8th week of pregnancy, one of the most dangerous periods of pregnancy begins. The formation of the placenta begins, the hormonal background changes. Bloody discharge appears with the threat of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion. Pregnancy is often not saved.
Pay attention! In the second trimester, bleeding occurs only in 5-10% of women. Most often this is associated with late spontaneous abortion, isthmic-cervical insufficiency. The appearance of blood in the III trimester mainly occurs with presentation, placental abruption.
Early bleeding after IVF
The appearance of blood discharge during pregnancy on the 8-10th day after IVF is not considered a pathology, provided that the woman feels normal. After the introduction of the embryo into the uterine cavity, minor damage to the small uterine vessels often occurs. Brown, dark cream, pale pink, odorless discharge most often indicates a successful transplant, pregnancy.
Brown, dark cream, pale pink, odorless discharge most often indicates a successful transplant, pregnancy.
If spotting after IVF is observed for 1-2 days, slight pulling pains in the lower abdomen are disturbing, this may be due to a progesterone deficiency. After the examination, the doctor will adjust the hormonal maintenance therapy.
Pink discharge on the 16th day after the transfer is a dangerous symptom. It may be a sign of detachment of the fetal egg, the threat of termination of pregnancy.
According to studies, uterine bleeding in the first trimester is a common occurrence in pregnancy after IVF. Discharge does not affect the incidence of adverse reproductive outcomes. The number of embryo rejections in women with and without uterine bleeding is approximately the same. Consult with our doctors by phone for more details.
Diagnostics
If blood has gone from the genitals of a pregnant woman, the doctor conducts an external and gynecological examination.
Analyzes and examinations:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- general urine analysis;
- tests for hCG, other hormones;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- CTG is performed to assess the vital activity of the fetus.
Treatment
Methods of treatment depend on the results of the examination.
Bloody discharge in the first trimester - causes and therapeutic measures:
| The reasons | Treatment |
| Miscarriage | Cleansing the uterus. |
| Ectopic pregnancy | Diagnostic laparoscopy, removal of residual fetal tissues, antibiotic therapy. |
| Risk of miscarriage | Hospitalization, bed rest, prescribing drugs to maintain pregnancy, sedatives and tocolytics to reduce uterine tone. |
| bubble skid | Curettage of the uterine cavity. |
| Cervical cancer | Operational intervention. |
| Polyp injury, cervical erosion | Expectant management, if the condition does not worsen, removal and cauterization is carried out after childbirth. |
| progesterone deficiency | hormone therapy. |
| Damage to the uterus | Complete bed rest. |
| Infectious pathologies | Depending on the type of pathogen - antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs. |
Complications and consequences
It is impossible to ignore bloody impurities in vaginal discharge during pregnancy. Without proper and timely assistance, the following complications may occur:
- miscarriage;
- intrauterine fetal death;
- the development of an infectious process, sepsis due to the remainder of dead tissues in the uterine cavity;
- profuse blood loss can lead to death.

Important! Urgent medical attention is needed in case of heavy bleeding, discharge of bright scarlet blood, presence of blood clots in the discharge. In life-threatening and fetal conditions, severe pain in the abdomen, lower back, convulsions, profuse cold sweat, and loss of consciousness are disturbing.
Methods of prevention
If there is blood in the first trimester, it is important to remain calm. Stress and anxiety will only exacerbate the situation. But any health problem is easier to prevent than to treat.
How to avoid bleeding during childbearing - recommendations from a gynecologist:
- eat right and balanced, give up junk and junk food, eat more fresh vegetables and fruits;
- observe the drinking regime;
- in the absence of contraindications, moderate physical activity is indicated - yoga, swimming, special gymnastics for pregnant women;
- more time to walk in the fresh air;
- avoid stress, overwork, observe the daily routine, get enough sleep;
- give up bad habits, do not be in smoky rooms;
- timely visit a gynecologist;
- according to the doctor's prescription, take vitamin complexes for pregnant women;
- do not self-medicate.

The prognosis for bleeding during gestation depends on the causes and timely visit to the doctor. Properly provided medical care can save the life of the fetus and the woman.
FAQ
Why is there blood from the genital tract during gestation?
+
The causes of bleeding in early pregnancy are different. Most often, spotting appears when the fetal egg is fixed, progesterone deficiency, with erosion of the cervix and polyps. Dangerous causes - ectopic, molar, miscarriage, miscarriage.
What to do if there is bleeding during pregnancy?
+
Much depends on the amount of blood released, general well-being. If the bleeding is not strong, not for long, the general condition is normal, it is enough to lie down and rest. Write down the date of the attack, inform the doctor at the next visit. But if even slight spotting during early pregnancy lasts more than 72 hours, is accompanied by cramping or acute pain, fever, you should immediately visit a gynecologist or call an ambulance.
How can you recognize a miscarriage?
+
With the threat of interruption, spotting is scanty, pain in the lower abdomen is absent or may be dull, aching. The condition is considered reversible, with timely treatment, pregnancy can be saved. If a miscarriage has begun, bleeding intensifies, cramping pain appears. The general condition is satisfactory. Urgent hospitalization is required, the probability of maintaining pregnancy is decided on an individual basis.
Expert opinion:
Bleeding during pregnancy is a dangerous symptom. Sometimes spotting can be caused by physiological reasons. But often such a symptom appears in life-threatening conditions for the woman and the fetus.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Articles 46
Specialist with extensive practical experience. He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
He has a certificate of a mammologist, a certificate of professional certification. Participates in foreign business trips and individual training programs (Los Angeles).
- 1982 - 1986 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1987 - 1989 VNITs OZMIR - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1989 - 1992 departmental polyclinic st. Moscow - Kurskaya - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 1992 - 2001 NPO MONIIAG - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2007 - 2008 NP KMIKM - doctor administrator
- 2009 - 2013 Pereslavl Central District Hospital, women's consultation - obstetrician-gynecologist
- 2020 to present Teledoctor24 LLC - doctor - consultant (gynecologist)
The question is asked by Anya, - a question-answer from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
23.10.2014
Hello! I have a second pregnancy (my son is 1 year 2 months), the term is 13-14 weeks. At the 11th week, heavy bleeding began (until that time, nothing bothered) and I was admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of “beginning miscarriage. ” Heavy bleeding lasted from 13.00 to 16.00, then it bled a little all the next day, and on the third day the discharge began to darken and disappeared. The next morning after admission, I had an ultrasound scan (06/04/05), which showed: The uterus in anteflexio, with clear, even contours, rounded, enlarged due to pregnancy and according to its duration. Meometrium of normal structure and echogenicity, without nodules and retrochorial hematomas, in which one live embryo is visualized. The placenta is formed on the right side with the transition to the anterior wall of the uterus, up to 1.2 m thick. The amount of water is normal. The internal os of the uterus is completely closed. The results of the analyzes: Cl. blood test: Er - 4, 15; Hb - 124; Ht - 35, 8; L-9, four; P - 6; C - 73; L - 18; M-3; E-0; ESR - 22. General analysis of urine: Specified weight -1010, PH - Neutral; Protein, Glucose, erythrocytes - neg; L - 1-2-1; epithelium singly. Biochem. blood test: Common. Protein - 65.0; Urea - 3, 2; Creatinine - 76; Bilirubin - 12-0-12; Alat - 23; AsAt - 59; Glucose - 3, 4.
” Heavy bleeding lasted from 13.00 to 16.00, then it bled a little all the next day, and on the third day the discharge began to darken and disappeared. The next morning after admission, I had an ultrasound scan (06/04/05), which showed: The uterus in anteflexio, with clear, even contours, rounded, enlarged due to pregnancy and according to its duration. Meometrium of normal structure and echogenicity, without nodules and retrochorial hematomas, in which one live embryo is visualized. The placenta is formed on the right side with the transition to the anterior wall of the uterus, up to 1.2 m thick. The amount of water is normal. The internal os of the uterus is completely closed. The results of the analyzes: Cl. blood test: Er - 4, 15; Hb - 124; Ht - 35, 8; L-9, four; P - 6; C - 73; L - 18; M-3; E-0; ESR - 22. General analysis of urine: Specified weight -1010, PH - Neutral; Protein, Glucose, erythrocytes - neg; L - 1-2-1; epithelium singly. Biochem. blood test: Common. Protein - 65.0; Urea - 3, 2; Creatinine - 76; Bilirubin - 12-0-12; Alat - 23; AsAt - 59; Glucose - 3, 4.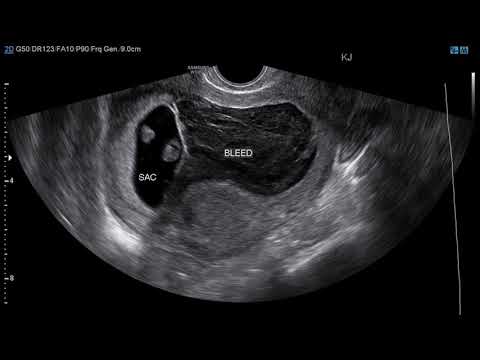 Gr. Blood A (II) Rh - factor positive. RW, HIV, HBs Ag - negative, DHA - 1.88. Treatment was prescribed: No-shpa 2, 0-3 times / m, papaverine 2 times, utrozhestan 1 t - 2 times, Vite 1-3 times, dicynone 2, 0 - 2 times / m, valerian 1 - 3 times, dexamethasone ½ tab. H night, magneB6 2-3 times, Materna 1. a day. While I was in the hospital, I bled a little bit a couple of times, and every day there were periodically pulling pains and tingling in the lower abdomen. She was discharged after 2 weeks, the medications were the same (except for decinone). The next day after discharge, dark brown discharge appeared again, on the same day I did a new ultrasound (06/20/05) results: Pregnancy 14 weeks, One live embryo is determined in the uterine cavity, the size of the fetus is proportional and corresponds to a period of 12 weeks. Rhythmic heartbeat 10 beats/min. Motor activity is determined by malformations not identified. Chorion along the anterior wall of the uterus On the degree of maturity.
Gr. Blood A (II) Rh - factor positive. RW, HIV, HBs Ag - negative, DHA - 1.88. Treatment was prescribed: No-shpa 2, 0-3 times / m, papaverine 2 times, utrozhestan 1 t - 2 times, Vite 1-3 times, dicynone 2, 0 - 2 times / m, valerian 1 - 3 times, dexamethasone ½ tab. H night, magneB6 2-3 times, Materna 1. a day. While I was in the hospital, I bled a little bit a couple of times, and every day there were periodically pulling pains and tingling in the lower abdomen. She was discharged after 2 weeks, the medications were the same (except for decinone). The next day after discharge, dark brown discharge appeared again, on the same day I did a new ultrasound (06/20/05) results: Pregnancy 14 weeks, One live embryo is determined in the uterine cavity, the size of the fetus is proportional and corresponds to a period of 12 weeks. Rhythmic heartbeat 10 beats/min. Motor activity is determined by malformations not identified. Chorion along the anterior wall of the uterus On the degree of maturity. The thickness of the placenta is 16 mm. The tone of the myometrium is slightly increased along the anterior wall. The cervix is not shortened. The cervical canal is closed. I have a few questions: How might such a threat affect a child's development? What additional tests should be taken to clarify the cause of the threat? How long to take the prescribed medication in this amount? Could the short period between pregnancies be the cause of the threat? Thank you for your advice
The thickness of the placenta is 16 mm. The tone of the myometrium is slightly increased along the anterior wall. The cervix is not shortened. The cervical canal is closed. I have a few questions: How might such a threat affect a child's development? What additional tests should be taken to clarify the cause of the threat? How long to take the prescribed medication in this amount? Could the short period between pregnancies be the cause of the threat? Thank you for your advice
Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo:
01/27/2021
The presence of short-term bleeding during pregnancy with normal blood tests and ultrasound data (adequate fetal development, absence of detachment of the placenta) does not have a negative effect on the fetus. In such cases, it is necessary to exclude inflammation of the vagina, a decidual polyp of the cervical canal, when spotting does not occur from the uterus, but is external in nature and is not associated with problems of the fetal egg.
 The situation may adversely affect the implantation of the fetal egg.
The situation may adversely affect the implantation of the fetal egg. 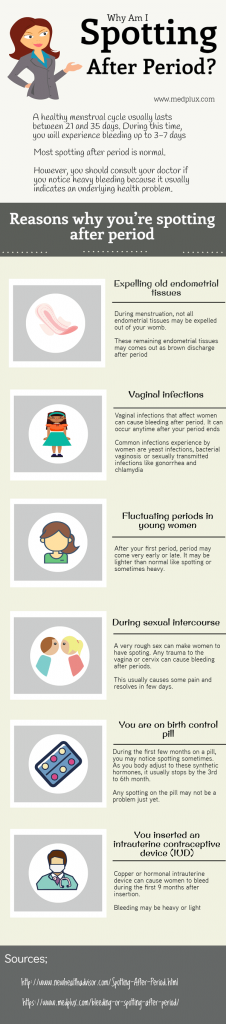
 Detected in 50% of women. For pregnant women, the disease is not dangerous, but constant medical supervision is needed.
Detected in 50% of women. For pregnant women, the disease is not dangerous, but constant medical supervision is needed.