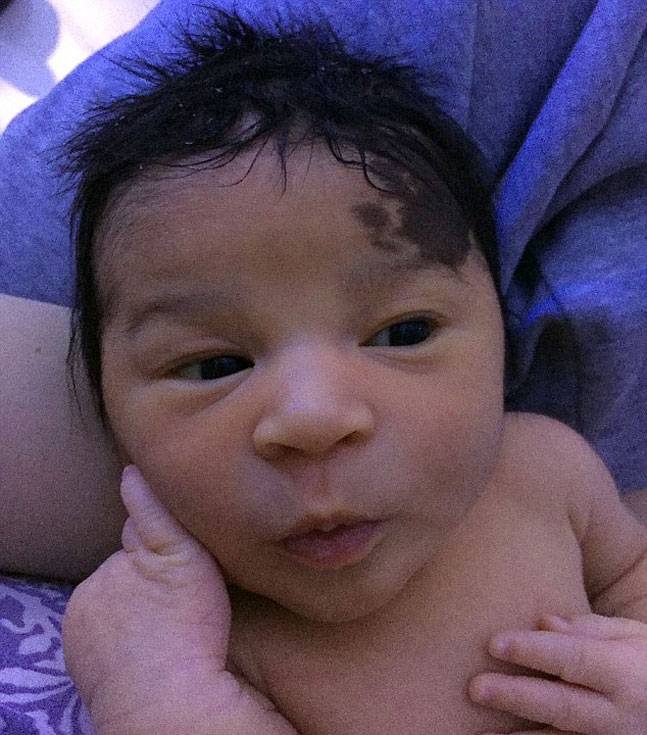
Birthmark on baby's back
Birthmarks in Infants | Johns Hopkins Medicine
A baby's skin coloring can vary greatly, depending on the baby's age, race or ethnic group, temperature, and whether or not the baby is crying. Skin color in babies often changes with both the environment and health. Some of these differences are just temporary. Others, such as certain birthmarks, may be permanent.
Birthmarks are areas of discolored and/or raised skin that are present at birth or within a few weeks of birth. Birthmarks are made up of abnormal pigment cells or blood vessels.
Although the cause of birthmarks is not known, most of them are harmless and do not require treatment. Babies with birthmarks should be examined by your child's health care provider, especially if they are:
-
Located in the middle of the back, along the spine (may be related to spinal cord problems)
-
Large birthmarks on the face, head or neck
-
Interfering with movement of activity, for example a birthmark on the eyelid that may interfere with vision
Some common birthmarks include:
| Birthmark | What it looks like |
|---|---|
| Stork bites, angel kisses, or salmon patches | These are small pink or red patches often found on a baby's eyelids, between the eyes, upper lip, and back of the neck. |
| Congenital dermal melanocytosis (also known as Mongolian spots) | Congenital dermal melanocytosis refers to areas of blue or purple-colored, typically on the baby's lower back and buttocks. These can occur in darker-skinned babies of all races. The spots are caused by a concentration of pigmented cells. They usually disappear in the first 4 years of life. |
| Strawberry hemangioma | This is a bright or dark red, raised or swollen, bumpy area that looks like a strawberry. Hemangiomas are formed by a concentration of tiny, immature blood vessels. Most of these occur on the head. They may not appear at birth, but often develop in the first 2 months. Strawberry hemangiomas are more common in premature babies and in girls. These birthmarks often grow in size for several months, and then gradually begin to fade. They may bleed or get infected in rare cases. Nearly all strawberry hemangiomas completely disappear by 9 years of age. Most of these occur on the head. They may not appear at birth, but often develop in the first 2 months. Strawberry hemangiomas are more common in premature babies and in girls. These birthmarks often grow in size for several months, and then gradually begin to fade. They may bleed or get infected in rare cases. Nearly all strawberry hemangiomas completely disappear by 9 years of age. |
| Port-wine stain | A port-wine stain is a flat, pink, red, or purple colored birthmark. These are caused by a concentration of dilated tiny blood vessels called capillaries. They usually occur on the head or neck. They may be small, or they may cover large areas of the body. Port-wine stains do not change color when gently pressed and do not disappear over time. They may become darker and thicker when the child is older or as an adult. Port-wine stains on the face may be associated with more serious problems. Skin-colored cosmetics may be used to cover small port-wine stains. The most effective way of treating port-wine stains is with a special type of laser. This is done when the baby is older by a plastic surgery specialist. The most effective way of treating port-wine stains is with a special type of laser. This is done when the baby is older by a plastic surgery specialist. |
| Congenital moles | These common moles (less than 3 inches in diameter) occur in about 1 out of every 100 newborns. They increase in size as the child grows, but usually don't cause any problems. Your child's health care provider will watch them closely as rarely they can develop into a cancerous mole. |
Birthmarks (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Are Birthmarks?
Birthmarks are marks on the skin that a baby can develop before birth or soon after. Birthmarks can be flat or raised, have regular or irregular borders, and have different shades of coloring from brown, tan, black, or pale blue to pink, red, or purple.
Most birthmarks are harmless and many even go away on their own or shrink over time. Sometimes birthmarks are associated with other health problems.
Sometimes birthmarks are associated with other health problems.
What Causes Birthmarks?
Doctors don't know what causes most birthmarks. They can't be prevented and they're not caused by anything done or not done during pregnancy. Most aren't related to trauma to the skin during childbirth. Some kinds may run in families, but a genetic cause hasn't been found.
What Are the Types of Birthmarks?
There are two main types of birthmarks, which have different causes:
- Vascular birthmarks happen when blood vessels don't form correctly. Either there are too many of them or they're wider than usual.
- Pigmented birthmarks are caused by an overgrowth of the cells that create pigment (color) in skin.
The most common vascular (blood vessel) birthmarks are macular stains, hemangiomas, and port-wine stains:
Macular stains. Also called salmon patches, angel kisses, or stork bites, these faint red marks are the most common type of vascular birthmark.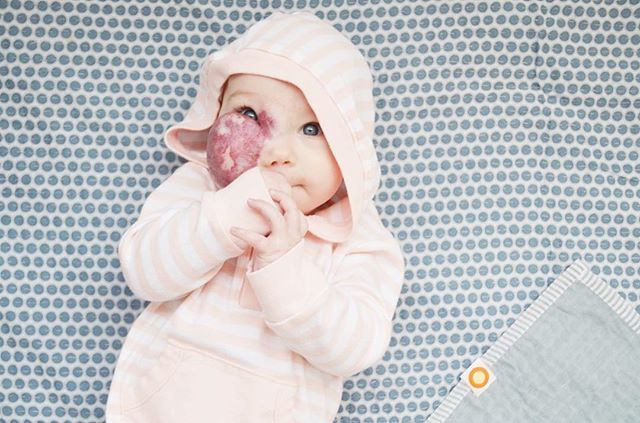 Macular (MA-kyuh-ler) stains typically are on the forehead or eyelids; the back of the neck; or on the nose, upper lip, or back of the head. They may be more noticeable when the baby cries. Most often they fade on their own by the time a child is 1 to 2 years old, although some last into adulthood.
Macular (MA-kyuh-ler) stains typically are on the forehead or eyelids; the back of the neck; or on the nose, upper lip, or back of the head. They may be more noticeable when the baby cries. Most often they fade on their own by the time a child is 1 to 2 years old, although some last into adulthood.
Hemangiomas. Hemangiomas are superficial when they're on the surface of the skin ("strawberry marks"), deep when found below the skin's surface, and compound when they affect both layers. A hemangioma (hee-man-jee-OH-muh) can be slightly raised and bright red, and usually won't be visible until a few days or weeks after a baby is born. Deep hemangiomas might look bluish because they involve blood vessels in deeper layers of the skin.
Hemangiomas grow quickly during the first 6 months or so of life, then usually shrink and disappear by the time a child is 5 to 10 years old. Some, particularly larger ones, may leave abnormal skin as this happens. Surgery can fix this. Others may leave red pigmented skin, which can be helped with special laser treatment. Although they can be anywhere on the body, most hemangiomas are on the head or neck. They can cause problems if they interfere with sight, feeding, breathing, or other body functions.
Surgery can fix this. Others may leave red pigmented skin, which can be helped with special laser treatment. Although they can be anywhere on the body, most hemangiomas are on the head or neck. They can cause problems if they interfere with sight, feeding, breathing, or other body functions.
Port-wine stains. These discolorations look like wine was spilled on an area of the body, most often on the face, neck, arms, or legs. Port-wine stains can be any size, but grow only as the child grows. They tend to darken over time, and can thicken and feel like pebbles in middle adulthood unless treated. They never go away on their own. Doctors will watch ones near the eye to make sure they don't cause problems. When port-wine stains involve certain parts of the face, other tests (such as an MRI) might be needed.
Pigmented BirthmarksThe most common pigmented birthmarks are café-au-lait spots, Mongolian spots, and moles:
Café-au-lait spots. These very common spots are the color of coffee with milk, which explains the name. They can be anywhere on the body and sometimes increase in number as a child gets older. One alone is not a problem. But call your doctor if your child has 6 or more spots that are larger than a pencil eraser (for a younger child), or larger than a dime (for an older child). Having many café-au-lait spots can be a sign of neurofibromatosis (a genetic disorder that causes abnormal cell growth of nerve tissues).
These very common spots are the color of coffee with milk, which explains the name. They can be anywhere on the body and sometimes increase in number as a child gets older. One alone is not a problem. But call your doctor if your child has 6 or more spots that are larger than a pencil eraser (for a younger child), or larger than a dime (for an older child). Having many café-au-lait spots can be a sign of neurofibromatosis (a genetic disorder that causes abnormal cell growth of nerve tissues).
Mongolian spots. These flat, bluish-gray patches are often found on the lower back or buttocks. They are most common on darker skin, such as on children of Asian, American Indian, African, Hispanic, and Southern European descent. They usually fade — often completely — by school age without treatment.
Moles (congenital nevi, hairy nevus). Mole is a general term for brown spots called nevi (NEE-vye). Most people get moles at some point in life. A mole that's there at birth is called a congenital nevus (NEE-viss) and will last a lifetime. Although the risk is still low, large or giant congenital nevi are more likely to develop into skin cancer (melanoma) later in life. Smaller congenital nevi may have a slight increase in risk. Moles can be tan, brown, or black; flat or raised; and may have hair growing out of them.
Although the risk is still low, large or giant congenital nevi are more likely to develop into skin cancer (melanoma) later in life. Smaller congenital nevi may have a slight increase in risk. Moles can be tan, brown, or black; flat or raised; and may have hair growing out of them.
How Are Birthmarks Treated?
Macular stains usually fade away on their own. Ones at the back of the neck may last longer, but are not very noticeable. Most other vascular birthmarks can be treated.
Port-wine stains and some hemangiomas can be disfiguring and upsetting for children. Small hemangiomas in less visible locations usually don't need treatment, as most shrink back into themselves by the time a child is 10. Doctors can treat larger or more visible hemangiomas with medicine put directly into the hemangioma, given into a vein (with an IV), or taken by mouth (oral).
Laser (highly concentrated light energy) treatment can help kids with port-wine stains. Most stains get lighter after several treatments with a "pulsed-dye" laser. Some can return and need re-treatment. Laser treatment often starts in infancy when the stain and the blood vessels are smaller. Marks on the head and neck react well to laser treatment. Special makeup also can hide a port-wine stain.
Some can return and need re-treatment. Laser treatment often starts in infancy when the stain and the blood vessels are smaller. Marks on the head and neck react well to laser treatment. Special makeup also can hide a port-wine stain.
Pigmented birthmarks usually are left alone, with the exception of congenital moles and, occasionally, café-au-lait spots. Doctors can remove moles — particularly large or giant congenital nevi — with surgery, though larger ones may be harder to remove. Laser treatment can remove café-au-lait spots, but these often return.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
A doctor should check a birthmark when it first appears to see what type it is, and to decide what monitoring or treatment it needs, if any.
Call the doctor if a birthmark ever bleeds, hurts, itches, or gets infected. Like any injury where there is bleeding, clean the wound with soap and water and, using a gauze bandage, place firm pressure on the area until the bleeding stops. If the bleeding doesn't stop, call the doctor.
Open sores sometimes form with hemangiomas and can get infected. Pigmented birthmarks rarely cause other problems, but moles should be checked throughout life for changes in size, color, or texture.
What Else Should I Know?
It can be a shock at first to see a birthmark on your newborn. If the birthmark is clearly visible, people might ask questions or stare, which can feel rude. It helps to have a simple explanation ready to handle this. Most people mean no harm, but it's also OK to let them know if they've gone too far.
Even at a young age, kids watch how their parents respond to such situations. This is where they learn how to cope with others' reactions. Talking simply and openly about a birthmark with kids makes them more likely to accept one as just another part of themselves, like hair color. Practice simple answers they can use if asked about it, like "It's just a birthmark. I was born with it." It's also helps kids emotionally to be around supportive family and friends who treat them normally.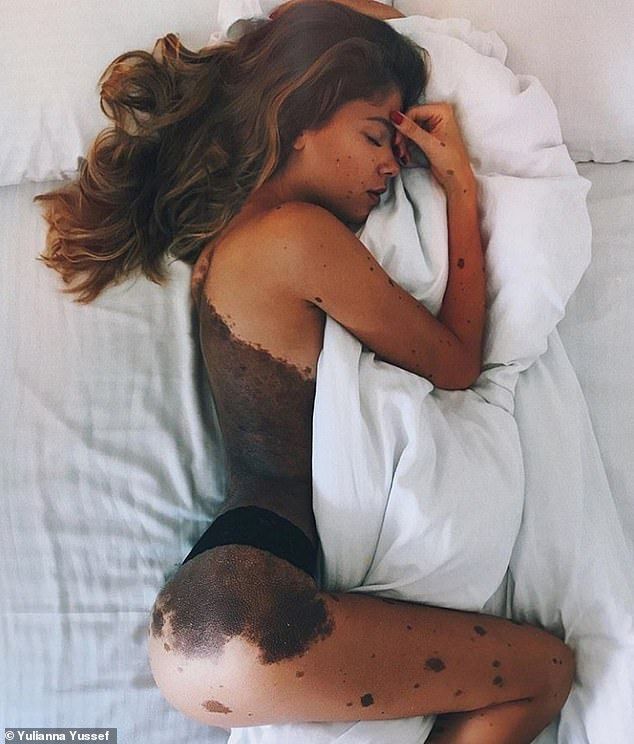
Reviewed by: Steven M. Andreoli, MD
Date reviewed: January 2021
What do moles on a child's body mean? moles are transmitted from moms and dads, this is a kind of DNA-programmed connection with relatives. Due to hormonal changes, moles can either suddenly appear or disappear. Therefore, the picture that parents see in a five-year-old will definitely become different by adolescence. But regardless of the number and location, each mole must be treated carefully: do not pull out the hair, do not comb, do not scratch - irreversible consequences are possible. nine0003
Types of moles
The most harmless moles are pigment moles, they are called lentigo . They look almost like freckles, they are very easy to confuse. Such moles are formed due to the accumulation of melanocytes under the skin, cells responsible for pigmentation.
All other types of birthmarks can cause trouble to their owner. These are epidermal-dermal nevi - moles that can rise above the surface of the skin, usually located on the palms, feet or in the groin area. nine0017 Intradermal nevi - raised, often covered with hair. Dysplastic nevi - irregularly shaped tubercles with indistinct borders, are more than a centimeter in size.
nine0017 Intradermal nevi - raised, often covered with hair. Dysplastic nevi - irregularly shaped tubercles with indistinct borders, are more than a centimeter in size.
One of the most dangerous is giant nevus . This is a congenital spot that can cover large areas of the skin. It is usually removed early, as it looks scary, and the risk that it will degenerate into a malignant formation is quite high.
Which moles are not dangerous, but require a mandatory consultation with a doctor
Blue nevus is a dark blue, black or gray spot, nodule or nodule up to 1 cm in size. The color is due to a large number of cells with melanin in the dermis. Such moles of dense consistency are located more often in the scalp, on the back surface of the hands and feet. Blue nevi usually appear in early childhood, more often in girls, grow slowly.
Spitz's nevus is a reddish-pink or yellowish nodule, most commonly found on the face and extremities in preadolescent children, and grows rapidly. May be a sign of malnutrition, problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Usually it needs to be removed. nine0003
May be a sign of malnutrition, problems with the gastrointestinal tract. Usually it needs to be removed. nine0003
Halonevus makes itself felt in people with reduced immunity and severe autoimmune diseases. A white rim appears in place of the mole. It occurs more often in childhood and adolescence.
Spotted nevus is a light brown café-au-lait macule ranging in size from 1 to 15 cm or more. Against its background are small dark brown spots or nodules 2-3 mm. The lesions usually develop before the onset of puberty. The reason is a failure in the structure of pigment cells containing melanin. nine0003
Mongolian spot - a grayish-blue pigmentary disorder, usually located in the lumbar region, sacrum, buttocks, less often - on the head under the hair. In newborn Mongols, it occurs in 90% of cases, in representatives of other nationalities - no more than 0.5%. It usually disappears in early childhood.
Nevus of Ota is a gray or blue patch around the eye caused by genetic neurological factors.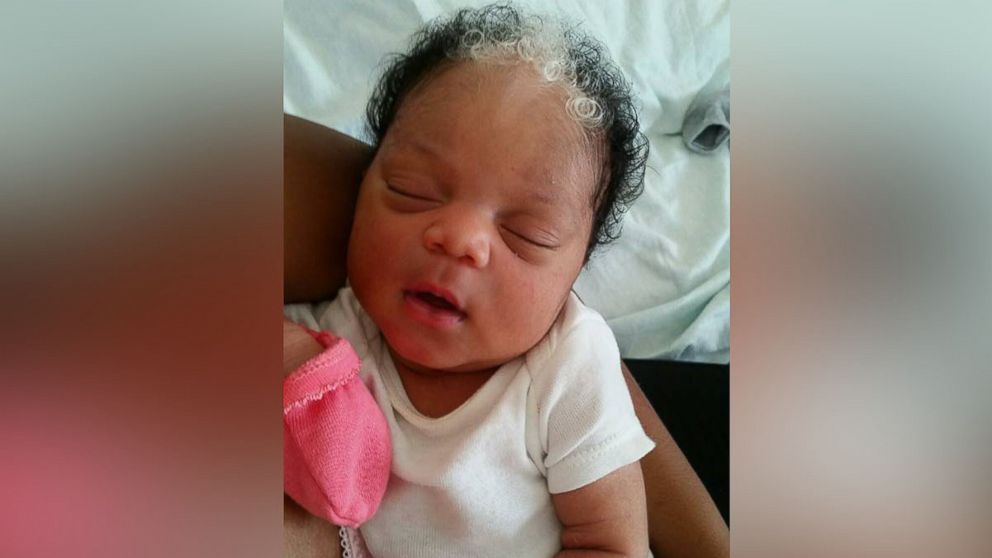 May be subtle or bright. Mostly found in Asian peoples. nine0003
May be subtle or bright. Mostly found in Asian peoples. nine0003
Flaming (wine) nevus looks like an irregularly shaped red or purple spot. Arises from birth, is formed from dilated capillaries. As the child grows, it increases and becomes lumpy, never resolves on its own. The exception is Unna's nevus . A red spot (sometimes called a "stork bite" or "angel kiss") is located on the back of the neck, sometimes on the eyelids and bridge of the nose. There is about a third of newborns, disappears by 3-5 years. nine0003
Anemic nevus Irregular white patches on the chest or back. Causes - a violation of the development of blood vessels in a certain area of \u200b\u200bthe skin. In infants, it is practically not noticeable, it manifests itself brighter at school age.
Interpretation of moles - moleosophy - even in ancient times was one of the ways to predict fate. So, for example, the owners of moles on the face were considered exalted persons.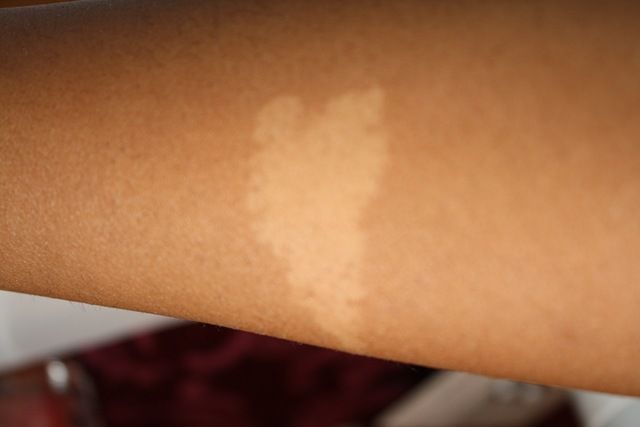 A mole on the right on the chest of the representatives of the strong half is a sign of an easy character, on the left - loving; on the right breast of a woman - a sign of material well-being, on the left - to the first-born boy. nine0003
A mole on the right on the chest of the representatives of the strong half is a sign of an easy character, on the left - loving; on the right breast of a woman - a sign of material well-being, on the left - to the first-born boy. nine0003
The main danger of moles is that some of their types can degenerate into melanoma, a malignant neoplasm with an aggressive course. It occurs in both young people and children, and the frequency of detection is increasing year by year. For more than half a century, the prevalence of pathology has quadrupled. Among all malignant tumors, melanoma accounts for less than 10%, but is the cause of 80% of deaths from oncology.
- Photo
- Anadolu Agency / Anadolu Agency / Getty Images
Why it happens
According to some studies, 75-80% of the total amount of solar radiation that a person receives in a lifetime occurs for up to 20 years. To stay healthy, doctors recommend following these simple rules: do not go to the solarium under the age of 25 or over 55; do not ignore sunscreen, especially in areas with intense ultraviolet load; do not spend much time in the sun if the skin is not prone to tanning. nine0003
To stay healthy, doctors recommend following these simple rules: do not go to the solarium under the age of 25 or over 55; do not ignore sunscreen, especially in areas with intense ultraviolet load; do not spend much time in the sun if the skin is not prone to tanning. nine0003
Ultraviolet radiation increases risk factors if a child or adult:
-
Light type of skin,
-
Nevovs (moles) on body areas,
-
Genetic predisposition,
-
growing moles ;
-
sunburn with blisters (a child under 5 years of age has an 80-fold increased risk of developing melanoma!).
By the way, a large number of moles on the baby's body does not mean anything bad. On the contrary, there is a belief that the more of them, the happier fate will be. According to statistics, a malignant neoplasm occurs in 70% of cases on “clean” skin and only in 30% develops from a congenital nevus. nine0003
Area of special attention
The transformation of a benign formation into a malignant one can occur slowly, over several months or years, or it can happen suddenly, in a very short time. But if trouble comes, dangerous cells will begin to divide rapidly, so it is important not to miss the moment, to regularly undergo preventive medical examinations. Please note: in these cases, a dermatologist should be run as fast as possible.
But if trouble comes, dangerous cells will begin to divide rapidly, so it is important not to miss the moment, to regularly undergo preventive medical examinations. Please note: in these cases, a dermatologist should be run as fast as possible.
-
Pigmentary formations of asymmetric, irregular shape and shape, similar to a geographical map. nine0003
-
Multicolored moles with shades of brown, red, gray and blue.
-
Nodules of regular shape, but unevenly colored.
-
Abruptly growing moles.
-
Disturbing - itchy, sore, or bleeding.
-
Eight spots larger than 6 mm.
-
Multiple scattering (from 50 pieces) larger than 2 mm.
Large - under the knife! nine0015
Melanoma can manifest itself as a change in the color of the nail to brown or black, the appearance of spots on the palms and soles. To monitor for atypical nevi, the patient usually has a dermatoscopy every 3 to 12 months. A biopsy is taken from suspicious lesions and a histological examination is performed to establish the diagnosis.
A biopsy is taken from suspicious lesions and a histological examination is performed to establish the diagnosis.
All congenital moles larger than 2 cm must be under the constant supervision of a doctor - in any case, they will have to be removed. If necessary, the baby will get a skin passport to control the number, growth dynamics and identify any changes in moles. Usually, the operation is performed shortly before the onset of puberty. Especially often cells are reborn on giant congenital nevus (more than 15 cm in diameter) in adolescence.
How to recognize dangerous moles in time
What skin neoplasms in most cases turn into a malignant tumor, why it happens and how to save your life.
Melanoma is the most dangerous skin cancer. Under different guises, she is born from a nevus (mole, birthmark). In the process of development, the tumor rapidly grows through the skin, then, by lymph and blood, it is transferred to other organs.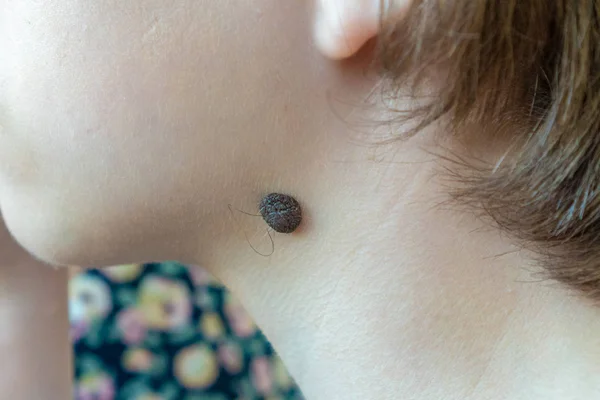 There, new foci appear. The result is death. None of the patients with late-detected melanoma passed the five-year survival limit. Elena Ivannikova, head physician of the Nadzha clinic, tells how to use the life-giving sun rays correctly. nine0158
There, new foci appear. The result is death. None of the patients with late-detected melanoma passed the five-year survival limit. Elena Ivannikova, head physician of the Nadzha clinic, tells how to use the life-giving sun rays correctly. nine0158
- Elena Nikolaevna, everyone knows that the sun is the basis of life, it gives us strength. Warm days have come and the northerners, hungry for the revitalizing rays of the sun, are taking sunbaths. Tell me, maybe the talk about the insecurity of spending time on the beach is greatly exaggerated?
- Of course, in moderate doses, sunlight gives us not only joy and good mood, but also health. It is also a good preventive and therapeutic agent for rickets, stimulates the production of vitamin D, strengthens the immune system, and is beneficial in some chronic skin diseases. Ultraviolet for 10-15 minutes a day is useful. nine0003
However, the danger to health lies in excessive solar radiation. And thermal burns, heat strokes, high blood pressure and photoaging are not the biggest problem.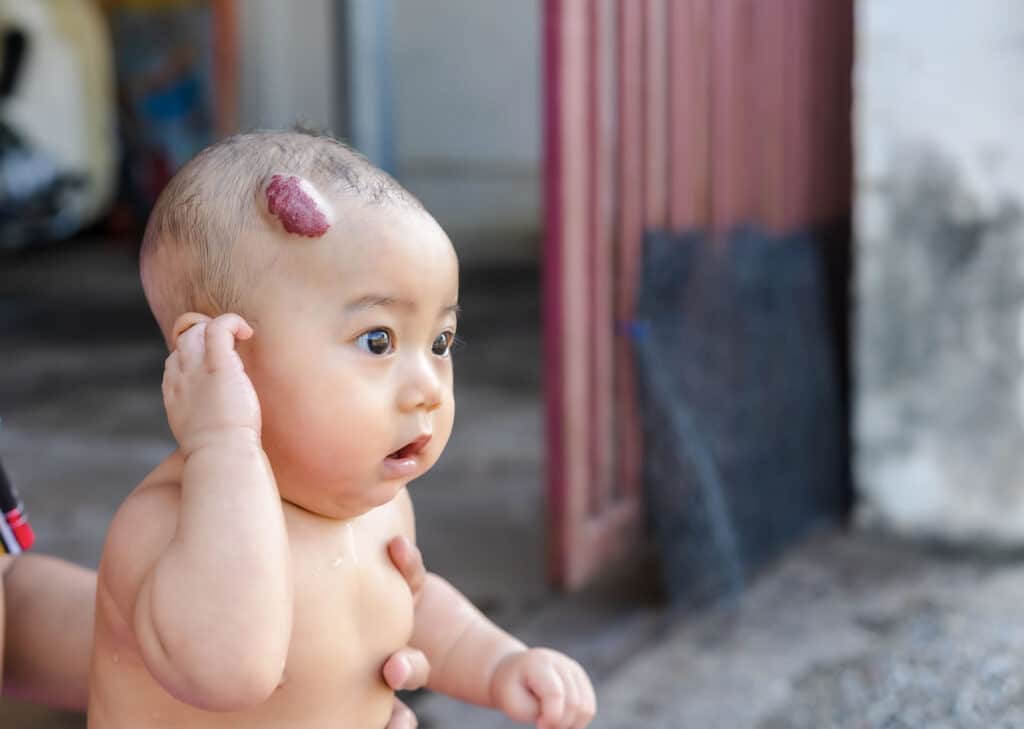
According to the Moscow Scientific Research Institute of Oncology. P. A. Herzen, in the 21st century, the incidence of melanoma in Russia has increased and continues to grow. The incidence of melanoma ranks third among all cancer incidence in Russia. On the first and second lines are lung cancer and breast cancer in women. Meanwhile, this type of skin cancer is often the reverse side of a beautiful tan. nine0003
— Now many people know that skin cancer can grow from a particular mole. How to distinguish such a dangerous mole?
There are no people without moles. If a mole suddenly changes shape, becomes asymmetrical, has jagged edges, is mottled, or turns black, show it to your doctor. If she began to hurt, itch or bleed - this is also a cause for concern. During life, nevi change during life. If a nevus appeared in childhood and at the age of 30-40 it has not changed, you should show it to the doctor. nine0003
A harmless spot is distinguished from melanoma by five signs that are encrypted in the word "ACORD":
- A is asymmetry.
 With an imaginary axis, a safe mole will be divided into two identical parts.
With an imaginary axis, a safe mole will be divided into two identical parts. - K - edge, normally smooth and even.
- Oh, coloring. There shouldn't be any bitterness.
- R is the size. If the mole is larger than 5 mm, observe carefully. The danger increases if it is located on an open area of the body. nine0088
- D - dynamics. If there are wounds, an increase in size and other changes, consult a doctor.
The presence of hair in a mole rather speaks of good quality, but if their loss is suddenly noted, it is worth hurrying to a dermatologist - an oncologist.
In men, "bad" nevi are more often localized on the back. The women are on their feet. Moles located on the palms, feet and in places of friction with shoes and clothes are dangerous. nine0003
— What is the most common cause of a mole turning into cancer? And who is more at risk of getting sick?
- A pigmented formation can become cancer after an injury or a sunburn of radiation. The presence of such a terrible diagnosis in relatives increases the risk.
The presence of such a terrible diagnosis in relatives increases the risk.
Moles turn into a tumor, under the influence of ultraviolet light, in those who have:
- light skin (weak adaptation)
- bright eyes
- blonde and red hair
- many moles (over 50) and freckles
- elderly age.
The risk of getting melanoma in adulthood increases in those who burned under the sun in childhood or more than three times during their lives.
— How to stop melanoma?
“Everyone should be oncologically vigilant about themselves. nine0003
Protect exposed skin from the sun. Once every 3-6 months, examine the moles with the help of mirrors and a camera, remember their appearance. If suspicious moles are found, immediately contact a dermatologist to examine the formation using dermatoscopy.
A dermatoscope is an optical device that magnifies the image tenfold. The doctor examines the mole with the help of this optics and assesses the degree of danger.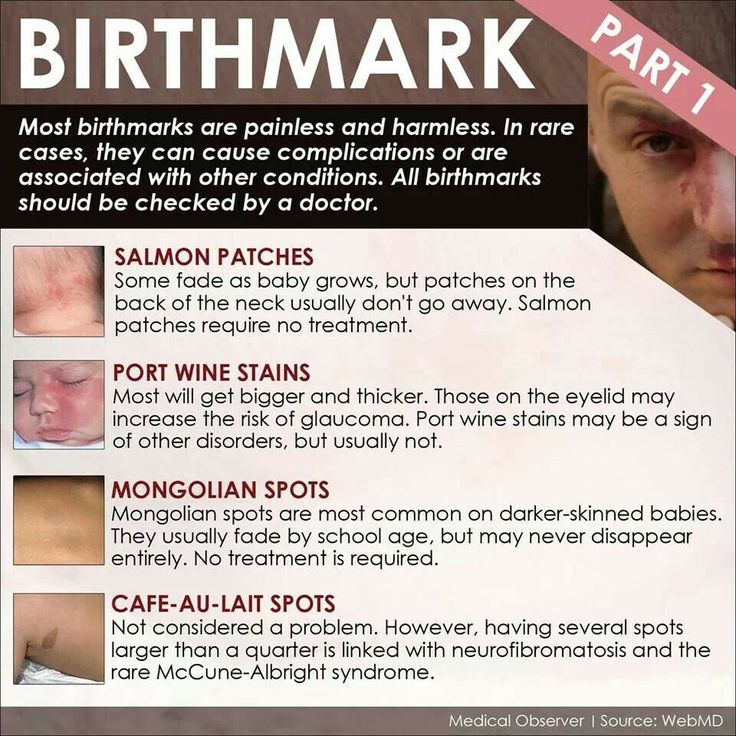 And in its conclusion gives recommendations for treatment or removal. The study is non-traumatic. Safely. It is carried out within 10-15 minutes. Timely dermoscopic examination of moles and detection of melanoma at an early stage in most cases help to prevent further development of the tumor and save human life. nine0003
And in its conclusion gives recommendations for treatment or removal. The study is non-traumatic. Safely. It is carried out within 10-15 minutes. Timely dermoscopic examination of moles and detection of melanoma at an early stage in most cases help to prevent further development of the tumor and save human life. nine0003
— Doctors do not recommend sunbathing from noon to 4 pm. But the northern sun is not as active as the southern one. Perhaps you will give more specific recommendations for our readers?
“Our fellow citizens joke that June is not yet summer in our city, August is no longer summer, and July is as lucky. Indeed, sunny days in our region do not happen as often as we would like, but there are no concessions for us. Sun exposure during peak hours should be avoided. nine0003
- Elena Nikolaevna, I know that you worked as a dermatologist for many years. Your spouse is also a doctor. Does your family like to sunbathe? Tell me, probably, you don’t allow your children to sunbathe and avoid beach holidays?
- Not at all. After all, we are ordinary people. Sometimes, like everyone else, we rest in the south. But never forget about protection. Being in the sun, we put on hats with wide brim or "visors", sunglasses, light light clothes made from natural materials. We do not visit the beach from 11.00 to 16.00. And if you happen to spend time on the beach, then we apply protective agents to open areas of the skin. And children from childhood know the rules of caring for their health. Therefore, they are rather surprised why so many people neglect the simple rules of being on the beach. nine0003
After all, we are ordinary people. Sometimes, like everyone else, we rest in the south. But never forget about protection. Being in the sun, we put on hats with wide brim or "visors", sunglasses, light light clothes made from natural materials. We do not visit the beach from 11.00 to 16.00. And if you happen to spend time on the beach, then we apply protective agents to open areas of the skin. And children from childhood know the rules of caring for their health. Therefore, they are rather surprised why so many people neglect the simple rules of being on the beach. nine0003
— What should be the signal in order to understand that it is worth hiding in the shadows?
- Any change in normal well-being is a reason to stop sun exposure and seek medical help.
- Pharmacy counters, like television advertising, are full of a large number of skin protection products from UV rays. How to choose the right product that is suitable for your skin? nine0003
- It is better to use sunscreens that contain both UVA and UVB filters. In the first days, it is necessary to select a filter that will protect the skin as much as possible from the harmful effects of the sun (SPF 90+, 60+, 50+). Next, choose a sun protection factor that matches your skin type (SPF 30+, 15+).
In the first days, it is necessary to select a filter that will protect the skin as much as possible from the harmful effects of the sun (SPF 90+, 60+, 50+). Next, choose a sun protection factor that matches your skin type (SPF 30+, 15+).
Remember to apply the product 30 minutes before sun exposure and additionally during prolonged sun exposure, as well as after bathing and drying. nine0003
The SPF number does not indicate the quality of protection, but the time that you can stay in the sun without burning.
I would like to add that a reasonable attitude to the sun preserves not only health, but also youthfulness of the skin. After all, skin aging in 80% of cases is premature aging (photoaging). Intensive sunburn is a damaging factor for the skin, leads to dehydration,
coarsening, loss of elasticity and the appearance of spots, which are not easy to get rid of later. nine0003
Basic rules for skin cancer prevention:
- don't be a tanner
- always protect your skin from the active sun
- do not injure moles
- visit a dermatologist-oncologist once a year
- Examine and remove suspicious skin lesions as directed by your doctor.