Baby stopped growing at 7 weeks
Why did my fetus stop growing at seven weeks of pregnancy?
Why did my fetus stop growing at seven weeks of pregnancy?Press Enter
to Search
iCliniq / Answers / Obstetrics and Gynaecology / Intrauterine Growth Restriction / Why did my fetus stop growing at seven weeks of pregnancy?
Answered by
Dr. Maneesha
and medically reviewed by
iCliniq medical reviewteam.
This is a premium question & answer published on Oct 27, 2021
Patient's Query
Hello doctor,
When I was 7 weeks pregnant, I visited my gynecologist, and my next appointment was fixed four weeks after that visit. But, two weeks later, I noticed a brown discharge and consulted my doctor to check my baby's heartbeat, and the doctor said there was no heartbeat. And upon further clinical investigation, the doctor confirmed that my baby stopped growing after 7 weeks and 3 days. Would you please clarify for me the reason for this?
Thanks.
Answered by Dr. Maneesha
#
Hello,
Welcome to icliniq.com.
I understand your concern, and I am sorry for the miscarriage that happened. You had an abortion which was diagnosed by the absence of fetal heartbeat. A missed abortion is caused by chromosomal anomalies, uterine anomalies, and undiagnosed maternal illness. The exact cause of abortion cannot be known.
Thanks.
Patient's Query
Hello doctor,
Thanks for the reply.
Kindly explain to me about my miscarriage in detail.
Thanks.
Answered by Dr. Maneesha
#
Hello,
Welcome back to icliniq.com.
You had missed abortion. Let me explain what a missed abortion and the causes of a missed abortion are. A healthy egg has to meet a healthy sperm within 24 hours for fertilization. And if the fertilization happens after 24 hours, it forms an embryo with few chromosome damage. When the fertilized egg reaches the uterus, the endometrium should have been properly ripened and nurtured by proper hormones to provide adequate blood supply to the baby. Uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension can cause harm to the fetus.
And if the fertilization happens after 24 hours, it forms an embryo with few chromosome damage. When the fertilized egg reaches the uterus, the endometrium should have been properly ripened and nurtured by proper hormones to provide adequate blood supply to the baby. Uncontrolled diabetes and hypertension can cause harm to the fetus.
I suggest you do the following tests to rule out the cause for your miscarriage;
1) Fasting and postprandial blood sugar level.
2) Ultrasound of pelvis to rule out uterine fibroids or polyps.
3) Thyroid function test.
4) Serum Prolactin.
5) PTT (partial thromboplastin time) test.
I hope you understand my answer.
Take care.
Was this answer helpful?
|
Same symptoms doesn’t mean you have the same problem. Consult a doctor now!
Dr. Maneesha
Experience: 8 + Yrs
Obstetrics And Gynaecology
Related Questions:
I have brown discharges after my period and felt a big chunk of something inside my vagina. Why?
Why?
.. seen the picture (attachment removed to protect patient identity) you have posted. I want to assure you that you are fine, but a few things need to be evaluated. As your gynecologist has already felt and examined you, there is nothing much to worr... Read full
Could vaginal brown discharge be a sign of cervical cancer?
If they are less than 21 g/dL, then you may need to be placed on cyclical progesterones to avoid such episodes of intermenstrual bleeding ... Also other causes can be endometrial polyp, fibroid or even sometimes ovulation mid... Read full
Is it advisable to take Tranlok-E during pregnancy?
I have checked my pregnancy test on the 8th of this month and my last LMP was on the 5th of last month ... I have consulted the doctor, he confirmed my pregnancy and prescribed me capsule Gestaf. .. Read full
.. Read full
Also Read Answers From:
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction
- Brown Discharge
- Fetal Heart Rate
- Spotting In Pregnancy
Comprehensive Medical Second Opinion.Submit your Case
Also Read
Dengue Fever: Common Questions Answered
Dengue fever is a self-limiting mosquito-borne viral illness that has taken a massive toll on public health. Read below ... Read more»
Listeriosis - Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Listeriosis is a bacterial infection, that can result in severe complications like meningitis, sepsis, and even death. R... Read more»
Myositis - Types, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment, and Prognosis
The term "myositis" refers to a set of uncommon diseases. To know more about myositis, read the full article below. Read more»
Read more»
Ask your health query to a doctor online?
Ask an Obstetrician & Gynaecologist Now* guaranteed answer within 4 hours.
- New User
- Existing User
Password
Show
Forgot your password?
Disclaimer: No content published on this website is intended to be a substitute for professional medical diagnosis, advice or treatment by a trained physician. Seek advice from your physician or other qualified healthcare providers with questions you may have regarding your symptoms and medical condition for a complete medical diagnosis. Do not delay or disregard seeking professional medical advice because of something you have read on this website. Read our Editorial Process to know how we create content for health articles and queries.
Fetal growth restriction (Intrauterine growth restriction)
Babies are sometimes called small for gestational age (SGA) or small for dates (SFD). Most babies that are smaller than expected will be healthy. But up to 10% of pregnancies will be affected by FGR and will need close monitoring during pregnancy. In some cases, you may need to give birth earlier than expected.
Most babies that are smaller than expected will be healthy. But up to 10% of pregnancies will be affected by FGR and will need close monitoring during pregnancy. In some cases, you may need to give birth earlier than expected.
What causes FGR?
FGR can happen when the placenta is not working well enough to provide the baby with the nutrients they need to grow normally. However, we don’t always know why FGR happens.
Sometimes it can be caused by other conditions, such as chromosomal problems or infections, such as cytomegalovirus or toxoplasmosis.
Is there anything that increases the risk of FGR?
There are several things that can increase the risk of FGR. The most common risks are:
- if you have previously had a small baby, pre-eclampsia or stillbirth
- if you have had complications earlier in this pregnancy, particularly heavy bleeding
- having a pre-existing medical problem such as high blood pressure, kidney problems, diabetes or heart disease
- smoking, drinking alcohol or using illegal or recreational drugs
- being over 35 years of age.

If you have any bleeding during your pregnancy, with or without pain, it’s very important to get it checked out.
What does FGR mean for my baby?
If your baby has FGR, there is an increased risk of complications in pregnancy. Sadly, this can include stillbirth. But your healthcare team will monitor the baby’s growth and wellbeing closely to reduce the risk of this happening. They will also talk to you about the best time for you to give birth. This is likely to be earlier than your due date.
Being born early and small can also lead to complications after birth. This includes a higher risk of high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes and thyroid disease in later life. Some babies may need to spend time on a specialist baby unit (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit or NICU).
However, after your baby is born, their growth will not be typically different from other children. Having FGR does not mean they will be smaller than other children when they are school age.
Can I do anything to reduce the risk?
We don’t know why some pregnancies are affected by FGR and some are not. But it is unlikely to be related to anything you have done before or during pregnancy. It is important not to blame yourself.
“I was told by well-intentioned but not medically trained friends to eat more calories, sleep as much as I could and stop worrying, because the worry would be having an impact on my baby’s personality and growth! To my knowledge these comments offer no real help to anyone experiencing this. The best thing to do is to listen to the medical professionals in charge of your care.”
Laura
Some things that increase your risk of having a small baby can’t be changed. But there are some things you can do to reduce the risk, including:
- stopping smoking
- taking vitamin D
- eating a healthy, balanced diet
- not drinking alcohol
- not using illegal/recreational drugs, especially cocaine.

If you are overweight, you are more likely to develop high blood pressure, which can cause complications leading to problems with the baby’s growth. It can help to maintain a healthy weight before and during pregnancy.
High levels of caffeine in pregnancy has been linked to low birthweight, as well as miscarriage. Try to limit your caffeine to 200 milligrams (mg) a day. This is about the same as 2 mugs of instant coffee. Use our caffeine calculator to check your caffeine intake.
If you are considered at risk of FGR
If you are considered at risk of being affected by FGR , your healthcare team may recommend that you take low-dose aspirin (150mg) at night from 12 weeks of pregnancy until 36 weeks.
How will I know if my baby isn’t growing well?
If you have no risk factors for FGR identified in early pregnancy, your midwife will start to measure your bump from 24 weeks, during your routine antenatal appointments, to check that your baby is growing well. This is a simple test using a tape measure. They will measure your bump from the top of the uterus (womb) to your pubic bone. The measurement should then be plotted on a growth chart in your personal maternity record. If your midwife has any concerns about the baby’s growth from this measurement, you will be referred for an ultrasound scan within 72 hours. This does not necessarily mean something is wrong. The scan is just a more accurate way of assessing the baby's growth.
This is a simple test using a tape measure. They will measure your bump from the top of the uterus (womb) to your pubic bone. The measurement should then be plotted on a growth chart in your personal maternity record. If your midwife has any concerns about the baby’s growth from this measurement, you will be referred for an ultrasound scan within 72 hours. This does not necessarily mean something is wrong. The scan is just a more accurate way of assessing the baby's growth.
If you have any risk factors for FGR, the growth of your baby will be monitored by ultrasound scans instead of using a tape measure.
Depending on your medical and pregnancy history, you may also be referred for an ultrasound scan to measure the blood flow to your placenta (this is known as the uterine artery Doppler). This measurement is done at 20–24 weeks of pregnancy. It will determine how often you will need to have ultrasound scans during your pregnancy.
What do I do if I’m worried that my bump isn’t getting bigger?
Baby bumps come in all different shapes and sizes. Although it can be difficult, try not to compare your baby bump to anyone else’s. No two women or two pregnancies are the same. If you are concerned, you can call your midwife at any time.
Although it can be difficult, try not to compare your baby bump to anyone else’s. No two women or two pregnancies are the same. If you are concerned, you can call your midwife at any time.
What happens if my baby is small or not growing?
If your midwife or doctor thinks your baby might have FGR, you will be referred for an ultrasound scan to assess the growth of your baby. During this scan, there will be other tests to check the wellbeing of your baby. These include an assessment of the blood flow through the umbilical cord between the placenta and the baby (umbilical artery Doppler) and an assessment of the fluid around the baby (liquor volume).
Following this assessment, you will be advised how your baby is growing. If it is confirmed that your baby has FGR, you will need further scans to monitor the pregnancy more closely until your baby is born. The frequency of these scans will depend on the size of your baby and blood flow measurements in the umbilical artery. You may also be asked to have a tracing of your baby’s heart rate, known as a cardiotocograph (CTG). Your healthcare team may also discuss the benefit of delivering your baby before your estimated due date (EDD).
You may also be asked to have a tracing of your baby’s heart rate, known as a cardiotocograph (CTG). Your healthcare team may also discuss the benefit of delivering your baby before your estimated due date (EDD).
If the umbilical artery Doppler test is abnormal, you may also be referred for a more detailed scan with a fetal medicine specialist.
Monitoring your baby’s movements
It’s very important to monitor your baby’s movements during pregnancy. Most women usually begin to feel their baby move between 16 and 24 weeks of pregnancy. A baby’s movement can be described as anything from a kick, flutter, swish or roll. There is no set number of normal movements. If you think that your baby’s movements have slowed down or stopped, it is important that you contact your maternity unit immediately. There is always a midwife available 24 hours a day. Do not wait until the next day to seek advice. This is particularly important if there are concerns about your baby’s growth during pregnancy.
Find out more about your baby’s movements in pregnancy.
Will FGR affect how I give birth?
The majority of women who want one will be able to try for a vaginal birth, if there are no other complications. But it is likely that you will be advised to give birth early. This may just be a week earlier than your expected date of delivery or it may be several weeks before, depending on how your baby is. Some babies may be too small to go through labour and a vaginal delivery, so you may be advised to have a caesarean section. Your healthcare professional will talk to you about what they think is best.
You may be advised to have your baby in a hospital where there is a specialist baby unit (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit or NICU). This is because your baby may need extra care, especially if they are very small and born early (prematurely). Not all small babies will need to go to NICU.
Depending on when and how you are going to have your baby, you may be offered steroids to help your baby’s lung development and reduce the chance of breathing problems after birth. You may also be offered magnesium sulphate, which is a medicine given before delivery to reduce the risk of cerebral palsy.
You may also be offered magnesium sulphate, which is a medicine given before delivery to reduce the risk of cerebral palsy.
Will FGR affect my next pregnancy?
If you get pregnant again, the risk of having a small baby again is slightly higher. But you may be able to reduce your risk by trying to live a healthy lifestyle. It can help to:
- not smoke
- eat a healthy, balanced diet
- not drink alcohol
- not use illegal drugs or recreational drugs, especially cocaine
- work with your healthcare professional to make sure any long-term conditions, such as diabetes, are managed well.
In your next pregnancy, your doctor may recommend that you take low-dose aspirin (150mg) at night from 12 weeks of pregnancy.
Try not to worry too much if you want to get pregnant again. Your care will likely depend on what risk factors you have, but if you’ve had a small baby before, your healthcare team will monitor you closely during your next pregnancy.
If you need someone to talk to, call our midwives pregnancy line on 0800 014 7800 (Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm), or email [email protected]
FETUS GROWTH REST | Shchelkovsky perinatal center
1. What is fetal growth retardation?
Fetal growth retardation (FGR) is a complication of pregnancy, as a result of which a lag in growth, fetal weight and other fetometric parameters from the average normative for a specific gestational age is observed.
There are three degrees of severity of IUGR.
- I — fetometric indicators 2 weeks behind.
- II - delay in fetometric indicators by 3-4 weeks. nine0010
- III - delay in fetometric indicators by 4 weeks or more.
Children born with IUGR are not premature. They are just small in stature and weight—much smaller than they should be.
2. Why do placental insufficiency and IUGR occur?
There are many trigger factors for the development of placental insufficiency leading to IUGR. These can be placental (defects of the umbilical cord and placenta), environmental (adverse environmental conditions, work in hazardous industries, etc.) and hereditary (gene and chromosomal disorders, congenital malformations) causes. An extremely important aspect is the state of the mother's body before conception: with various diseases and a deterioration in the health of a woman, the formation of an embryo can occur incorrectly, with violations of cellular and tissue processes, which ultimately can cause IGR and even death of the fetus. nine0003
These can be placental (defects of the umbilical cord and placenta), environmental (adverse environmental conditions, work in hazardous industries, etc.) and hereditary (gene and chromosomal disorders, congenital malformations) causes. An extremely important aspect is the state of the mother's body before conception: with various diseases and a deterioration in the health of a woman, the formation of an embryo can occur incorrectly, with violations of cellular and tissue processes, which ultimately can cause IGR and even death of the fetus. nine0003
Sometimes the cause of IUGR can be the mother's social unhappiness when a pregnant woman eats an unbalanced diet or simply malnourished.
Risk factors for IUGR
- Maternal age 40 years or older.
- Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs).
- ZRP from mother or father.
- Past pregnancies with IUGR (25% risk of recurrence).
- Pregnancy with history of stillbirth.
 nine0010
nine0010 - Severe preeclampsia.
- Chronic arterial hypertension.
- Diabetes mellitus with vascular complications.
- Renal and liver failure.
- Iron deficiency anemia.
- Obesity.
- Sexually transmitted infections.
- Gynecological diseases (endometritis and other infectious and inflammatory diseases, PCOS, benign tumors of the uterus). nine0010
- Surgical abortion.
3. Why is RRP dangerous?
IGR is not only low weight and height, placental insufficiency is fraught with terrible complications for the fetus and newborn. It is known that the mortality rate of full-term children born with growth retardation is 3–8 times higher than that of normal-weight children and ranks second in the structure of perinatal losses after prematurity. In a third of children born with low weight and height, deviations in physical development persist up to 1 year. Children with growth retardation are at risk for lesions of the central nervous system, and the number of infants with severe neuropsychiatric disorders can reach 12-19%. They often observe adaptive breakdowns, weakened immunity, which means that they are prone to colds and infectious and inflammatory diseases. IGR can also have consequences in adult life as a risk factor for various pathological conditions:
They often observe adaptive breakdowns, weakened immunity, which means that they are prone to colds and infectious and inflammatory diseases. IGR can also have consequences in adult life as a risk factor for various pathological conditions:
- obesity
- type 2 diabetes mellitus
- hypertension
- cardiovascular diseases
- high blood cholesterol
- mental disorders; cognitive impairment
IGR affects not only the condition of the fetus and newborn, but also the future health of a person. That is why it is important to diagnose placental insufficiency in a timely manner.
4. How can FGR be detected?
IUGR is usually asymptomatic. In order to diagnose the condition, different methods are used - biometric (determining the height of the fundus of the uterus and measuring the circumference of the abdomen, ultrasonic fetometry from 20 weeks of gestation) and monitoring the condition of the fetus (its biophysical profile and Doppler study of the rate of utero-placental-fetal blood flow).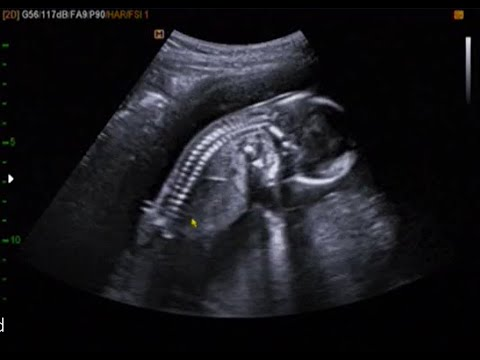 However, such examinations are prescribed and performed by specialists. nine0003
However, such examinations are prescribed and performed by specialists. nine0003
As a mother-to-be, there are some signs that you should look out for when you suspect fetal growth retardation.
- Small weight gain of the pregnant woman.
- Small abdominal circumference.
- Too active or, on the contrary, rare movements of the child (may indicate a lack of oxygen).
The volume of the abdomen begins to increase sharply from the 16th week of pregnancy - it is at this time that it is recommended to start measuring. Typically, the circumference of the abdomen increases by 1-1.5 cm per week. nine0003
How to correctly measure the circumference of the abdomen?
- To avoid measurement errors, it is advisable to have another person take measurements.
- Empty your bladder before taking a measurement.
- Lie on a hard couch with your stomach up, stretch your arms along the body.
- Use a measuring tape to measure the circumference of your abdomen at the level of your navel.
- Check that the tape does not compress the skin.
- Measure the abdominal circumference at the end of exhalation. nine0010
Any alarming changes in your condition should be reported to your doctor!
5. Can FGR be cured?
In most cases, IGR develops in the early stages of pregnancy, however, it is most often diagnosed only in the II-III trimesters, when the unfavorable process is started and treatment and diagnostic measures will no longer have an effect. In modern medicine, there are no drugs that selectively improve uteroplacental or placental-fetal blood flow. It is almost impossible to cure FGR or at least reduce the severity of the disorder after 22 weeks of pregnancy. The only way to prevent fetal death is timely delivery. However, do not panic: experts make such a decision in order to save the life of the child and preserve his health. If early delivery is unavoidable (especially with a period of up to 34 weeks and a fetal weight of less than 2000 g), doctors will prepare the baby for the birth and carry out all the necessary rehabilitation measures. nine0003
nine0003
!!! There is no effective treatment for RRP. Important aspects in the management of such a pregnancy are a clear assessment of the condition of the fetus and timely delivery.
If complications develop (such as preeclampsia or placental abruption), doctors may choose to have an early delivery. This allows you to reduce the risk of serious illness and death of a child by 4-5 times!
6. Prevention is the way out!
It turns out that FGR cannot be cured, but it can be prevented! It is very important to prevent placental insufficiency in women before pregnancy and in its early stages. Ideally, the prevention of this condition should be a continuation of the preconception preparation of every expectant mother. So, what should you pay attention to? It is important to change your lifestyle to include health promotion activities. Run a full check-up. When planning a pregnancy, the doctor will prescribe the necessary examinations and tests. Examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist, laboratory blood and urine tests, ultrasound, consultations of related specialists - all this will help the attending physician to draw a conclusion about the health status of the expectant mother and prescribe a correction for the identified violations. In particular, it is important to cure all infectious and inflammatory processes and minimize the risk of exacerbations and complications of chronic diseases. nine0003
Examination by an obstetrician-gynecologist, laboratory blood and urine tests, ultrasound, consultations of related specialists - all this will help the attending physician to draw a conclusion about the health status of the expectant mother and prescribe a correction for the identified violations. In particular, it is important to cure all infectious and inflammatory processes and minimize the risk of exacerbations and complications of chronic diseases. nine0003
Change your lifestyle.
First of all, it is important to give up bad habits, if any - quit smoking and not drinking alcohol, which negatively affect the possibility of conception, gestation and pregnancy outcome. It is equally important to normalize the daily routine, provide sufficient physical activity, avoid stress and neuro-emotional overstrain.
Eat right.
A balanced diet will provide the body of the future mother with the necessary vitamins and minerals for successful conception and full development of the fetus. nine0003
nine0003
Take special complexes.
In addition to the diet, it is important to additionally take special multivitamin complexes that will help replenish the deficiency of nutrients (folic acid, iodine, iron, vitamin D, etc.) and reduce the risk of pregnancy complications and dangerous consequences for the fetus. In particular, folate deficiency during pregnancy is associated with congenital malformations, fetal growth restriction, and disease programming later in life. In this regard, without exception, all women who want to become mothers should take folates for 3 months before conception and at least during the first trimester of pregnancy. The required dose is determined by the doctor! Remember, an excess of folic acid is just as dangerous as a deficiency! nine0003
Special components in the composition of multivitamin complexes can reduce the likelihood of congenital malformations of the fetus and other complications.
Individual recommendations:
Every pregnancy is unique and requires specific approaches.
Fetal growth restriction (FGR)
Gynecology
It happens that expectant mothers hear a frighteningly incomprehensible abbreviation - ZRP at the appointment with the attending physician or in the ultrasound room. Its decoding is even more frightening: "delayed fetal development." A pregnant woman faced with a similar diagnosis is tormented by many questions. How dangerous is this condition? How will it affect the health of the baby? Will he be able to catch up? nine0003
Adult people are not alike, and among the many external differences they differ in height and weight. Even the same person at different periods of his life can lose weight or gain weight, and this does not cause alarm in anyone. Very young children are another matter: clear criteria are calculated for them, a deviation from which indicates that something is wrong with the baby. And the smaller the child, the more important is the correspondence of his physical development to certain norms. And to assess the state of intrauterine development of the fetus, its size is the most objective criterion. nine0003
nine0003
The weight of a child at birth is very important for his development, especially in the first year of life, and affects his health in the future. Children born with low body weight (up to 2500 grams) are more prone to obstetric complications: they tolerate childbirth worse, they develop hypoxia and even asphyxia more often than children with normal weight, and neurological disorders also occur.
As a result, these babies do not adapt well to a new life. In infancy, they suffer from hyperexcitability, increased or, conversely, decreased muscle tone, sluggishly suck and often spit up food, gain weight poorly, and may lag behind their peers in psychomotor development. Even at the age of 7-8 years, such children are hyperactive, clumsy and do not know how to concentrate on the necessary subject for a long time. The difference between healthy babies and small babies only blurs by 9-10 years, although in height and weight they catch up with their peers by the age of two. However, the consequences of the transferred condition can “come around” already in adulthood. Recent studies have shown an association between low birth weight and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes mellitus and elevated blood lipids, all of which are associated with congenital endocrine disorders seen in low birth weight infants. Therefore, such a pathology as Fetal growth retardation (IUGR or fetal malnutrition) deserves special attention.
However, the consequences of the transferred condition can “come around” already in adulthood. Recent studies have shown an association between low birth weight and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes mellitus and elevated blood lipids, all of which are associated with congenital endocrine disorders seen in low birth weight infants. Therefore, such a pathology as Fetal growth retardation (IUGR or fetal malnutrition) deserves special attention.
FGR can be symmetrical, when all organs are evenly reduced, and asymmetric, when the brain and skeleton correspond to the gestational age, and the internal organs lag behind in development. The reasons for this are smoking, alcohol consumption, chromosomal abnormalities, infections, but most often - fetoplacental insufficiency and other conditions that lead to circulatory disorders: high or low blood pressure, toxicosis of the second half of pregnancy, diabetes mellitus with vascular damage, kidney disease, etc. nine0003
nine0003
Maternal age affects the development of fetal malnutrition . The fact is that the body of too young mothers (16-18 years old) is simply not yet ready for the upcoming stresses, while older mothers (32-40 years old) most often already have a “baggage” of chronic diseases. Smoking, addiction to alcohol and any drugs clearly contribute to the development of malnutrition, as they cause pronounced vasoconstriction and reduce uteroplacental blood flow. Alas, quite often hypotrophy is observed during multiple pregnancies, since two or even three twins have to share, literally brotherly, the nutrients received from the mother. nine0003
One of the simplest methods of monitoring fetal development is to measure the size of the uterus. As soon as it can be easily felt above the womb - approximately at the fourth month of pregnancy, at each visit, the doctor will measure the height of the fundus of the uterus, and in the second half of pregnancy, the circumference of the abdomen at the level of the navel.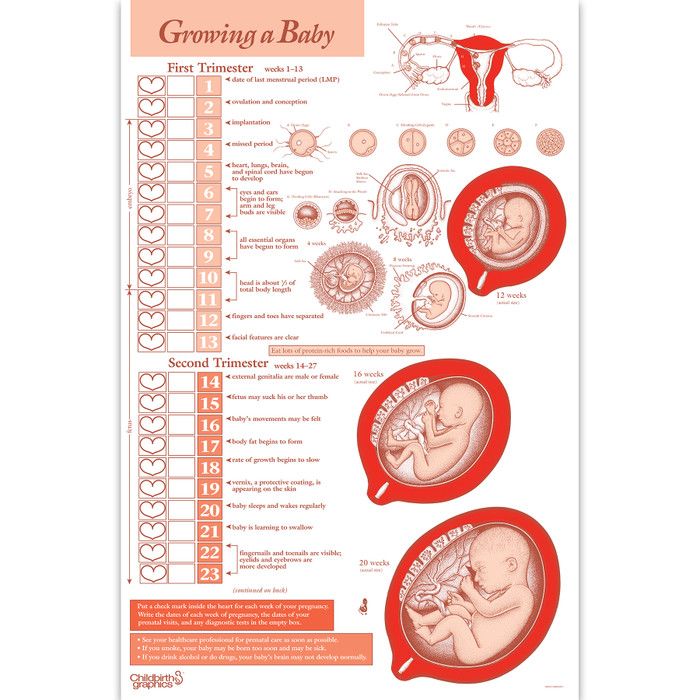 This will allow the doctor to roughly judge the size of the fetus. Obviously, these indicators are not objective enough, because their value is influenced by the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall, the amount of amniotic fluid, and the physique of the woman. nine0003
This will allow the doctor to roughly judge the size of the fetus. Obviously, these indicators are not objective enough, because their value is influenced by the thickness of the anterior abdominal wall, the amount of amniotic fluid, and the physique of the woman. nine0003
The most accurate diagnostic method is the ultrasound biometry used in our Clinic , which measures and evaluates several fetal parameters. The most traditional is the measurement of the head, tummy and femur, but if the doctor has doubts, he will also take additional measurements. The accuracy of the diagnosis is ensured by the high qualification of the doctor conducting the study, the excellent resolution of our Sonix OP ultrasound scanner and the possibility of conducting a Doppler study. Ultrasound also controls the amount of amniotic fluid, reveals signs of placental dysfunction, as well as changes in blood flow in it, which helps the doctor to accurately make a preliminary diagnosis and begin treatment. The first signs of IGR can be detected in such a study as early as 24-26 weeks, and its symmetrical form is more often noted. The occurrence of malnutrition after 32 weeks is more typical for the asymmetric form, and fetal hypoxia usually also joins it. Identified fetal growth retardation should be treated. Depending on the severity of the condition of the fetus, the treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, for example, in our day hospital, or in the maternity hospital. The method and timing of delivery largely depend on the condition of the fetus. If the treatment of FGR is successful and the baby is growing, then it makes no sense to rush things, because by the end of pregnancy it can reach quite a decent size. If, despite all efforts, the child does not gain weight or has any other problems, then they resort to early delivery.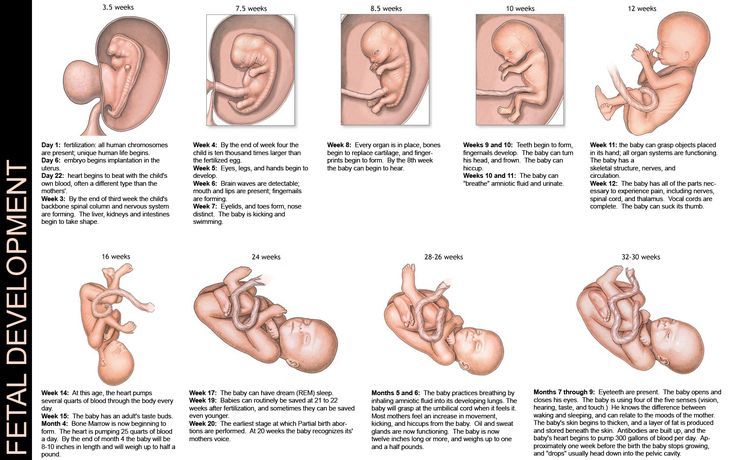 To clarify the diagnosis, we carry out Doppler study of the vessels of the placenta, umbilical cord and large vessels of the fetus, as well as cardiotocography (CTG), which allows you to register the fetal heartbeat and the nature of changes in the frequency of its heartbeats in response to movements or uterine contractions. It is important that normal Doppler and CTG data - even in the presence of low weight, indicate the well-being of the baby. If the examination did not reveal any deviations, then it becomes clear that we are talking about a healthy, low-weight fetus. In this case, we simply observe the woman without any therapy. nine0003
To clarify the diagnosis, we carry out Doppler study of the vessels of the placenta, umbilical cord and large vessels of the fetus, as well as cardiotocography (CTG), which allows you to register the fetal heartbeat and the nature of changes in the frequency of its heartbeats in response to movements or uterine contractions. It is important that normal Doppler and CTG data - even in the presence of low weight, indicate the well-being of the baby. If the examination did not reveal any deviations, then it becomes clear that we are talking about a healthy, low-weight fetus. In this case, we simply observe the woman without any therapy. nine0003  The goal of treatment in this case is not to “fatten the baby”, but to normalize metabolic processes and support the vital functions of the fetus. Of course, the success of treatment largely depends on how timely it is started. A large arsenal of medicines is used to treat malnutrition. It should be individual, taking into account the cause that caused IGR in this particular case and aimed at treating both the woman's diseases and pregnancy complications. For expectant mothers who are carrying a small child, it is very important to have a good diet rich in vitamins and animal proteins, as well as a regimen with limited physical activity. Although you should not overeat, remembering that excesses in the diet do not at all lead to a proportional increase in the amount of nutrients taken by the placenta for the fetus. nine0003
The goal of treatment in this case is not to “fatten the baby”, but to normalize metabolic processes and support the vital functions of the fetus. Of course, the success of treatment largely depends on how timely it is started. A large arsenal of medicines is used to treat malnutrition. It should be individual, taking into account the cause that caused IGR in this particular case and aimed at treating both the woman's diseases and pregnancy complications. For expectant mothers who are carrying a small child, it is very important to have a good diet rich in vitamins and animal proteins, as well as a regimen with limited physical activity. Although you should not overeat, remembering that excesses in the diet do not at all lead to a proportional increase in the amount of nutrients taken by the placenta for the fetus. nine0003  Although, as you know, houses and walls help, but in severe cases it is better not to refuse hospitalization. In the hospital, it is easier to monitor the condition of the mother and baby, and therefore provide more effective assistance. The effect of therapeutic measures must be constantly monitored using ultrasound and CTG, which are usually prescribed at intervals of 2 weeks, and if necessary, more often. FGR treatment almost always produces good results. In most cases, it is possible to observe adequate fetal growth: for example, in 7-10 days, the size of the fetus increases accordingly, and does not lag even further, which is considered a completely satisfactory result. nine0003
Although, as you know, houses and walls help, but in severe cases it is better not to refuse hospitalization. In the hospital, it is easier to monitor the condition of the mother and baby, and therefore provide more effective assistance. The effect of therapeutic measures must be constantly monitored using ultrasound and CTG, which are usually prescribed at intervals of 2 weeks, and if necessary, more often. FGR treatment almost always produces good results. In most cases, it is possible to observe adequate fetal growth: for example, in 7-10 days, the size of the fetus increases accordingly, and does not lag even further, which is considered a completely satisfactory result. nine0003