Baby has hard poop
Symptoms, Treatment and When to Call a Doctor
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Constipation (con-sta-PA-shun) in infants can worry parents. Most of the time, your baby is not really constipated. They may not have developed a routine for pooping yet. Some babies do not develop a bowel movement (BM) pattern for a while.
An infant’s BM pattern can change if their diet changes, like switching from breastmilk to formula, starting solid foods, or drinking less formula than usual. If your baby’s stool (poop) is not soft or easily passed, then they may be constipated.
In rare cases, constipation may be caused by a lack of nerves going to the intestines or by a problem with the way the intestine formed at birth. Your baby can be tested for these conditions if your health care provider feels it is needed.
Signs of Constipation
- less stools than their usual pattern
- straining more than normal to have a bowel movement
- a change in how the stool looks from soft and mushy to:
- small, hard pebbles, or like a large, round golf ball
- loose and watery
- abdomen (belly) bloated or swollen with gas
- painful cramps
Treatment
- If your baby is not eating baby food yet, you may give 1 to 2 ounces of 100% fruit juice (pear, prune, cherry, or apple) once a day.
Stop the juice if their stools become too loose.
- If they are old enough to eat baby foods, feed them pureed pears, peaches, or prunes instead of giving them juice.
- If your baby eats cereal, it may help to give oatmeal, wheat, or barley cereal. Rice cereal can cause constipation in some children.
- Sometimes giving your baby a warm bath to relax them or exercising their legs, like riding a bicycle, will help stimulate the bowels to move (Picture 1).
- If it has been a few days since your baby has pooped and the juice or pureed food has not worked, then you can try a glycerin suppository. Place your baby on their back. Gently push the suppository into their anus (bottom). Suppositories are meant for occasional use.
- Contact your baby’s health care provider before giving them laxatives, baby mineral oil, or enemas to treat constipation.
Medical Therapy
Your child’s health care provider may order the following treatments:
- Give your child medication.

- Check your child’s temperature using a digital, rectal thermometer. Put a small amount of petroleum jelly (Vaseline®) on its tip before inserting into the rectum. Taking a rectal temperature may stimulate the baby to pass stool.
When to Call the Health Care Provider
Call the health care provider if any of the following occurs:
- Your baby is irritable and seems to be having stomach pain. Infants will pull their legs up to their stomach and cry when they are in pain.
- Your baby has constipation and develops vomiting, and their belly looks like it is bloated or filled with gas.
- You see blood in their stool.
- Their constipation does not get better with treatment.
If you have any questions or concerns, call your baby’s health care provider.
Constipation: Infant (PDF), Spanish (PDF), Somali (PDF), Arabic (PDF), Nepali (PDF)
HH-I-14 ©Copyright 1984, Revised 2022, Nationwide Children’s Hospital
You Might Also Be Interested In
Blog
The Pee Palette: What Do All of Those Colors Mean?
Blog
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy: How It Can Help
Podcast
PediaCast 503 Your Childs Stomach Part 1
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
What is constipation?
Constipation is when your baby’s poo is hard and dry, making it difficult for them to poo. Sometimes, doing a hard poo can be painful. It’s common for babies to have constipation when they are changing from formula or breast milk to solid foods.
Sometimes, doing a hard poo can be painful. It’s common for babies to have constipation when they are changing from formula or breast milk to solid foods.
What is normal?
All babies are unique, and this includes how often they poo. There is a very wide range of ‘normal’. Some babies poo after every feed. Others will only poo once every few days. When it comes to how often they poo, once in 7 days, or 7 times in one day are both fine, so long as your baby is happy and well. But while the number of poos is not critical, if your baby seems to have pain when trying to poo or has a very hard, dry poo, you can speak with their doctor or child health nurse for advice.
Why is my baby constipated?
One of the main causes of constipation in babies is a change in diet. A change in diet may include:
- changing from being formula-fed
- changing from being breastfed
- exposure to new foods and flavours
- not drinking enough liquids (breastmilk, formula or water)
It is more common for bottle (infant formula) fed babies to have constipation than breast-fed babies.
If your baby has started eating solid food, a lack of fibre in their diet may also potentially cause of constipation. Some babies simply have a natural tendency towards constipation, even when they have a good diet and drink enough fluids. This doesn’t mean they are unhealthy or unwell.
In extreme cases, rare illnesses can cause constipation such as:
- problems with nerve endings in the bowel
- problems relating to the spinal cord
- thyroid deficiency
- other metabolic disorders
Baby poo guide
Learn more about your baby's poo.
All babies are checked for these conditions, so this is usually not something you need to be concerned about. But if you are worried about your baby or are notice that pooing is painful for them, seek medical advice.
How to recognise the signs of constipation
The main signs of constipation are hard, dry poos. The following are other signs of constipation:
- Your baby may show signs of straining when trying to pass a poo.

- Your baby may be unsettled, may seem fussy or irritated.
- Your baby may be eating less or feeding less well than usual.
- A tear or crack might appear in the skin around the anus, which may at times bleed.
In some cases, if your child is constipated, they may look bloated or their stomach may appear larger than usual. It can be possible to feel their poo (hard, solid lumps) while pressing softly on their stomach.
How to treat constipation at home
Try these tips to help babies who have difficulty passing poos:
- If your baby has infant formula, always measure the water first before adding the formula powder — this helps ensure that the ratio of water-to-formula is correct.
- If your baby is old enough to drink water, offer extra drinks (boiled and cooled first).
- Gently rub their stomach to help stimulate the bowel — your baby might also feel better with gentle massage to help manage the pain of constipation.
- A warm bath can help calm and settle your baby and relieve discomfort.

If your baby is older than 6 months, add some extra fruit and vegetables to their diet to boost their fibre intake.
If your child is older than 9 months, adding stewed prunes or apricots to their meal may help. They can have up to 3 tablespoons, 3 times a week. Cereal that has bran may also help mild constipation. Older babies can try prune juice diluted with water (half prune juice and half water). Start slowly, with 10 millilitres. Increase as needed until they can do a soft poo.
Does my child need to see a doctor?
Constipation is common. Often it will pass without intervention, or with the help of the strategies listed above. If you are worried that your baby has constipation, is uncomfortable or is in pain, their doctor can assess them and recommend baby-safe strategies. There are medical treatments for constipation that your doctor may consider, based on your baby’s circumstances.
If your baby was previously treated for constipation but still struggles to poo, it is important to go back to your doctor for a review. There are several treatments they can try.
There are several treatments they can try.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne (Kids Health Information 2020 - Constipation), Queensland Health (Constipation in children), Perth Children’s Hospital (Constipation in children)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Your child's health
- Poos and wees
- Baby poo guide
Need more information?
Constipation in babies and children | Raising Children Network
Children with constipation have hard poo that’s difficult to push out. A high-fibre diet and regular toileting usually helps. Some children need laxatives.
A high-fibre diet and regular toileting usually helps. Some children need laxatives.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Colic in infants - MyDr.com.au
Colic is a pattern of unexplained, excessive crying in an otherwise healthy and well-fed baby and happens to 1 in 5 Australian babies.
Read more on myDr website
All about baby poo
Babies poo! Some poo after every feed, while others can go for days without a dirty nappy. But what you do find in the nappy can say something your baby's health - learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Common myths about babies
Find out about some of the common myths you may hear or read about young babies.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Constipation and children - Better Health Channel
A healthy diet, plenty of fluids, exercise and regular toilet habits can help relieve constipation in children
Read more on Better Health Channel website
When can babies drink water?
You may wonder when it is safe to start giving your baby water. Whether you are breastfeeding or formula-feeding, learn how and when to get started.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Poos and wees
Babies have very delicate skin and need changing soon after they wet themselves or passed a stool (poo) to prevent nappy rash and stop them from smelling.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breast feeding your baby - MyDr.com.au
Breast milk has long been known as the ideal food for babies and infants. Major health organisations recommend that women breast feed their babies exclusively until they are 6 months old, and continue breast feeding, along with solids, until they are 12 months old or more. Breast milk has many benefits.
Read more on myDr website
What's in the nappy? - video
It may not sound like fun, but checking your baby's poos and wees will help monitor their health and wellbeing.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breastfeeding... Is it for me? | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Before your baby is born, you should decide whether you wish to breastfeed your baby or not
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Constipation in a child: what to do?
Constipation disrupts the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. The main manifestation of constipation is a rare stool, difficulty in emptying the intestinal tract. If emptying occurs every three days, but there is no swelling and discomfort, and the feces have a normal consistency, this is not considered constipation.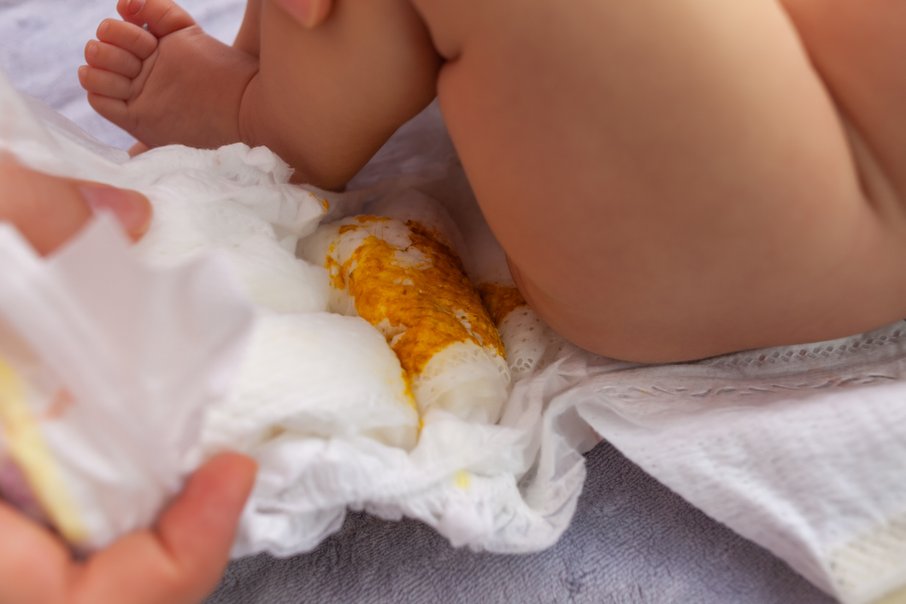
If your child is constipated, a specialist should be consulted. Initially, you should seek help from a gastroenterologist. The First Children's Medical Center employs the best pediatric gastroenterologists in Saratov: here you can get qualified medical care!
Symptoms of constipation
The main symptoms of constipation include:
- infrequent bowel movements;
- if the child pushes hard trying to go to the toilet;
- if there is pain during bowel movements;
- stools look like balls.
When the baby is breastfed, he can empty himself up to seven times a day, after each meal. During the first week, the frequency of emptying is three times a day.
When the baby is one month old, the stool will be daily. At two months of age and when complementary foods begin, stools can be once every two days. If the baby has a soft stool, he feels good, but at the same time he defecates once every few days, this is the norm.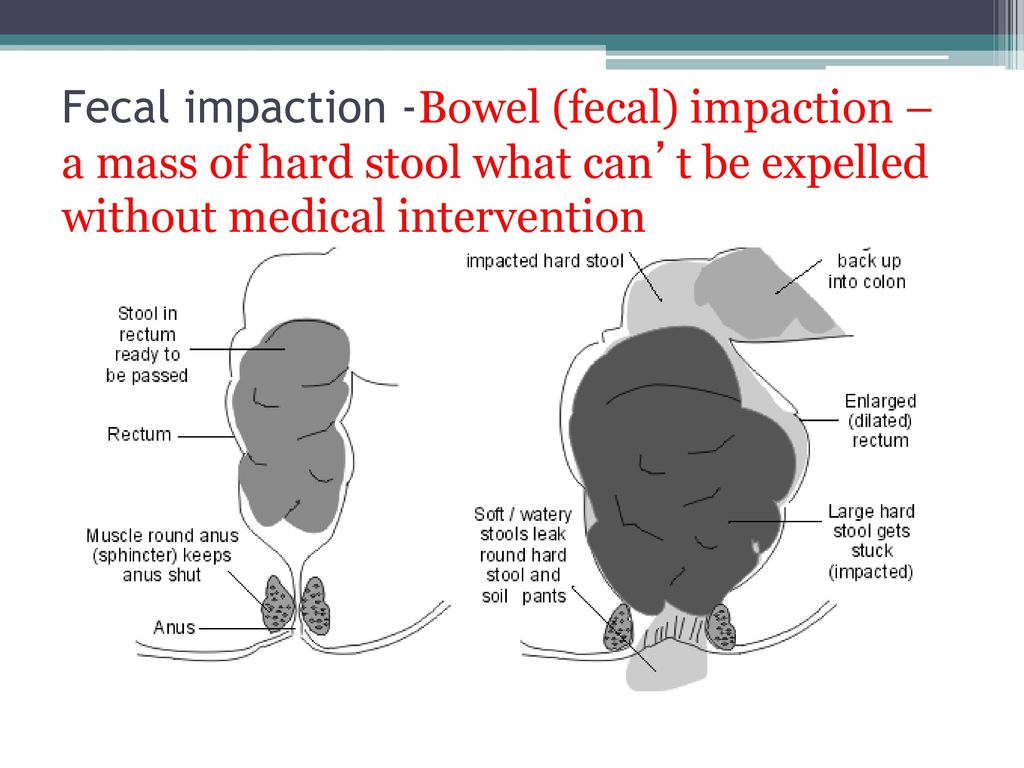
Signs of constipation include: discomfort during bowel movements, moodiness, very hard stools. If this situation persists, you should contact your pediatrician.
It is important to adjust the feeding regimen. Do not overfeed the child, do not transfer to artificial feeding if the mother has little milk. The first step is to try to fix the situation. A nursing mother should drink more fluids, stop eating foods that cause flatulence, reduce intestinal motility. Only in extreme cases should be transferred to artificial mixtures.
If the baby is formula-fed, he should empty himself once a day. The main mistake in this case is that parents often change mixtures, try others. Mixtures should be adapted, sour-milk, which contain probiotics and prebiotics. It is also necessary to strictly follow the instructions, properly dilute the mixture, taking into account all proportions. The introduction of complementary foods should be on time. The diet should contain foods that contain a large amount of fiber.
After the introduction of complementary foods, the stool becomes formed, hard, less frequent. Until the age of three, bowel movements should be daily. After three years, the frequency of defecation should be at least three times a week.
Why constipation occurs
There are two types of constipation - organic and functional. The causes of organic constipation are:
- Hirschsprung's disease;
- anomalies in the development of the gastrointestinal tract;
- pathology of the endocrine system;
- violations of metabolic processes.
In a newborn child, this symptom may indicate a narrowing, lengthening or expansion of the intestinal tract.
The causes of functional constipation include:
- psychological problems, such as being in an unfamiliar environment;
- lactose deficiency;
- lack of fluid in the body;
- errors in the diet;
- negative reaction of the body to taking antibacterial drugs, drugs for the treatment of anemia, anticonvulsants;
- congestion of bile in the gallbladder and its ducts;
- Intestinal worms.

In newborns, the nervous system is immature, it is just being formed. Therefore, children are unable to control the movements of their muscles during bowel movements. You can help them by gently bending the legs, pressing them to the tummy. With these movements, the pelvic muscles relax, the bowel is released much faster.
How the therapy works
The treatment of constipation requires a holistic approach. Treatment is prescribed in each case individually, depending on the cause of constipation.
To ensure the normal functioning of all organs, it is necessary to adjust the stool in children. You will need to adjust your diet and lifestyle, do not abuse laxatives, as they only help temporarily.
The main principles of therapy include:
- Diet correction. Requires elimination of foods that can cause constipation. Among them are fermented milk products, rice, muffins, bakery products, pasta. The menu is recommended to include vegetable fiber, which is found in fresh fruits and vegetables.
 You should also abandon fast carbohydrates - flour products, sweets. You need to add to the menu more foods that contain potassium, for example, figs, dried apricots, prunes.
You should also abandon fast carbohydrates - flour products, sweets. You need to add to the menu more foods that contain potassium, for example, figs, dried apricots, prunes. - Observe the drinking regimen. It is important to drink clean drinking water. During the day, the child should drink at least 40 milliliters of water per kilogram of his weight.
- According to the doctor's prescription, the baby should be given medicines, homeopathic remedies. These include drugs for the outflow of bile, drugs that restore the intestinal microflora. You can use antihelminthics, laxatives, drugs with lactulose in the composition. Your doctor may also prescribe medications that contain polyethylene glycol. They retain moisture in the intestines, thin the stool.
- In case of prolonged constipation, the child can be given a glycerine suppository, a microclyster as a stimulant.
- Undergo physiotherapeutic procedures prescribed by the doctor, massage, do therapeutic exercises.

- Provide a calm environment, help the baby psychologically so that he is not afraid to empty his intestines. You can read fairy tales, play with your child.
- Train the intestines, after eating, put the child on the potty for a few minutes.
First you need to get rid of constipation and only then potty training. If constipation is not treated in a timely manner, this will entail unpleasant consequences for the health of the child.
Pediatric gastroenterologist: where to turn for help?
To get rid of such a problem, it is necessary to visit a pediatric gastroenterologist. First you need to find out why constipation occurs, adjust the diet, after which, depending on the cause, competent therapy is prescribed.
Contact the First Children's Medical Center: we employ pediatric gastroenterologists who have experience working with children of all ages. We monitor the constant improvement of staff qualifications and offer the services of only highly qualified doctors.
You can sign up for a consultation from 8.00 to 20.00 by calling (8452) 244-000. Reception is by appointment.
Constipation in children. Prevention. Diet therapy
home
Articles
Health
Sabitova Vasily Ilyasovna Gastroenterologist
06/21/2019
Constipation is widespread among both adults and children (5-30% depending on the diagnostic criteria). Symptoms become chronic in more than 30% of patients, not only cause discomfort and pain to the child himself, but also disrupt the quality of life of his family.
CONSTIPATION - a condition manifested by an increase in the intervals between bowel movements (compared to the individual norm) or systematically slow, difficult and / or insufficient bowel movements. Constipation also includes stools with “gruel”, but after defecation was absent for up to 3 days.
Constipation can be related to functional or organic causes (abnormalities, inflammation). In children, 90-95% of constipation is functional. The peak incidence of functional constipation falls on 2-4 years, when they begin to accustom the child to the potty / toilet.
In children, 90-95% of constipation is functional. The peak incidence of functional constipation falls on 2-4 years, when they begin to accustom the child to the potty / toilet.
Main causes of functional constipation
- Pain
- Fever
- Dehydration
- Wrong diet of a nursing mother
- Insufficient drinking regime of a child with artificial feeding
- Insufficient drinking regimen of a breast-fed child with the introduction of complementary foods
- Early transition of the child to artificial feeding
- Fast transition of the baby from one mixture to another (less than 7 days)
- Irrational nutrition of the child (for a long time the child receives food with a large amount of proteins, fats and insufficient dietary fiber, abuse of drinks containing a large amount of astringents - tea, coffee, cocoa)
- Excessive use of baby hygiene products or the development of an allergic reaction of the skin of the perianal area
- Consequences of perinatal injuries of the nervous system
- Rickets, vitamin D deficiency
- Anemia
- Impaired thyroid function (deficiency - hypothyroidism)
- Food allergy, especially cow's milk protein allergy
- Forced potty training, period of adaptation to new conditions (nursery, kindergarten)
- Physical inactivity - a sedentary lifestyle
- Mental trauma or stress
- Systematic suppression of the urge to empty the bowels, associated, for example, with the beginning of attending a kindergarten, school, etc.
- Taking certain drugs
- Constipation in family members
Frequency of defecation in children of different ages
| Age | Number of bowel movements per week | Number of bowel movements per day |
| 0 – 3 months breastfeeding artificial feeding | 5 - 40 5 - 20 | 2.9 2.0 |
| 6 - 12 months | 5 - 28 | 1.8 |
| 1 - 3 years | 4-21 | 1.4 |
| 4 years and older | 3 - 14 | 1.0 |
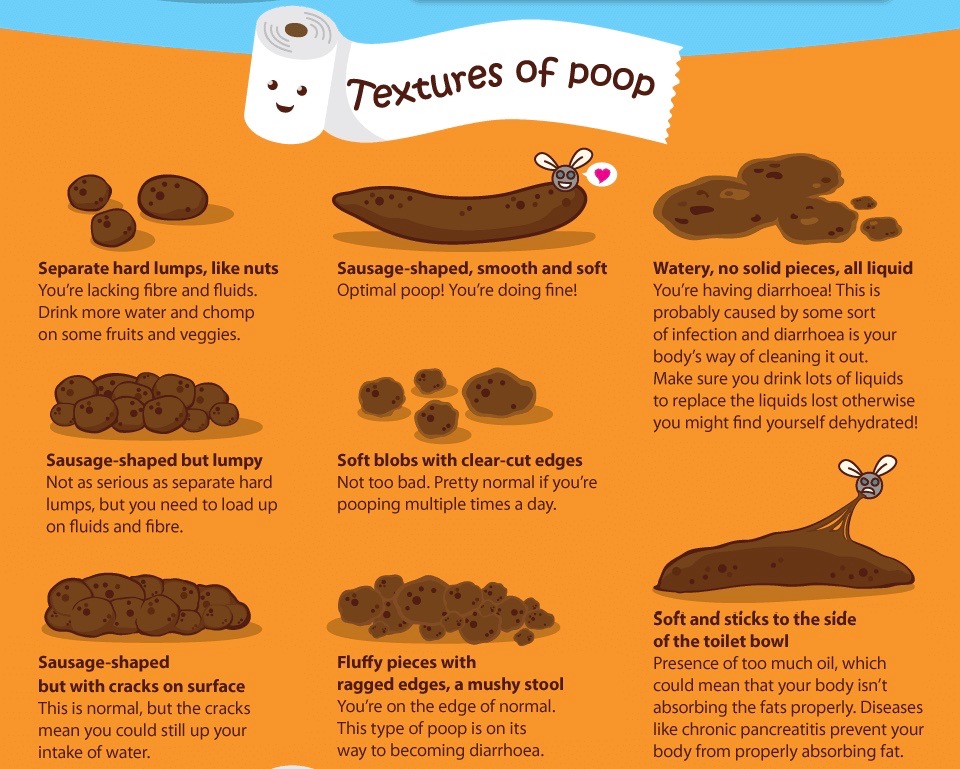
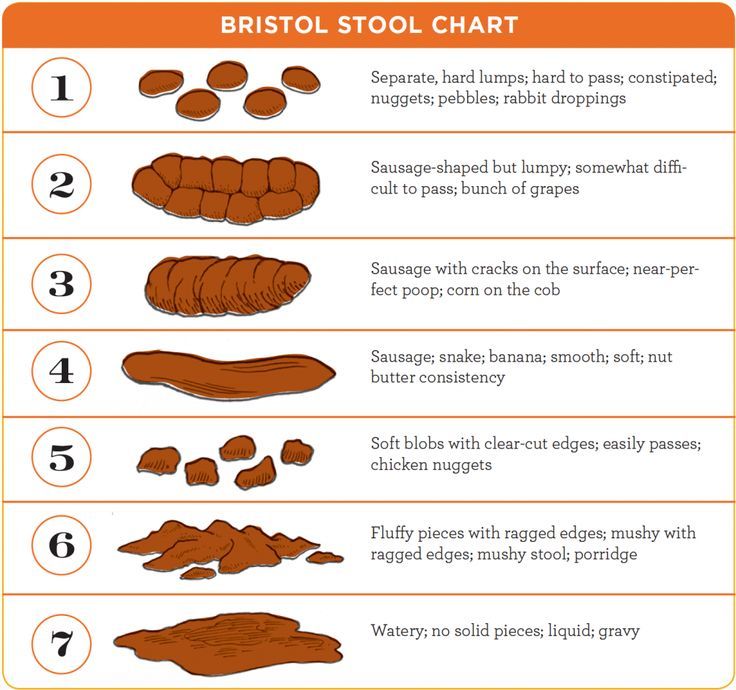
In addition to the frequency of the chair, you should pay attention to its nature. For a more objective assessment, the “Bristol fecal shape scale” is convenient, since it is the shape of the feces, and not the frequency of the stool, that is more consistent with the time of intestinal transit.
Bristol stool scale
In accordance with this scale, 3 and 4 form of feces is regarded as normal, and 1 and 2 indicate delayed transit (constipation). Quite often, in practice, there are situations when a child has a bowel movement frequency within the normal range, but the stool is dense, fragmented, in a meager amount. These signs indicate incomplete emptying of the bowels and are considered as manifestations of constipation.
The consistency of the stool in newborns and infants should be mushy. From 6 months to 1.5 - 2 years, feces can be both formalized and mushy. From the age of two, the chair must be decorated.
Signs and symptoms of constipation
- abdominal pain, often bursting, aching, sometimes colicky
- bloating
- change in the shape and consistency of the stool
- excessive flatulence
- unpleasant smell of flatus and stool
- may have pain during bowel movements
- straining to defecate
- there may be blood in the stool - on the surface of the feces or in the form of traces on a napkin (indicates an anal fissure)
If you do not eliminate constipation and do not establish bowel movements, then there is a risk of coprostasis (formation of fecal stones) and fecal intoxication:
- loss of appetite
- lack of energy
- general malaise
- depression, irritability
- nausea, vomiting
- skin symptoms - dryness, rash, peeling
- fecal incontinence, stool spotting
- urinary retention and incontinence due to pressure from a crowded bowel on the bladder
- bleeding from fissures, hemorrhoids
The treatment of constipation involves the following goals:
1. Normalization of stool consistency (soft, painless stools)
Normalization of stool consistency (soft, painless stools)
2. Regularity of bowel movements (prevention of re-accumulation of feces)
The treatment of constipation is a sequential, complex, individual process and consists of several stages:
- child and parent education
- correction of nutrition and drinking regimen
- elimination of existing coprostasis with the help of medications
- maintenance therapy
It is necessary to exclude factors that provoke and contribute to constipation (normalization of motor and nutritional regimen, discontinuation of medications that can cause constipation, identification of a food allergen, exclusion or confirmation of neuromuscular disease, celiac disease, etc.).
Lifestyle normalization includes:
- development of a conditioned reflex
- active lifestyle
- gymnastics
- light abdominal massage training
- for small children - laying out on the stomach, bending the legs to the stomach.

Education is the first step in the treatment of functional constipation. It must be remembered that episodes of fecal smearing and encopresis (fecal incontinence) are not arbitrary and should not be blamed on the child, who may already be frightened and disoriented. In some cases, when the intra-family situation is difficult, the help of a family psychologist may be needed.
It is important to understand that the treatment of functional constipation can be lengthy, based on trust, partnership and requires patience. Modern laxatives that are legal in children will not make the intestines “lazy”, will not cause “addiction”, they enter the bloodstream in minimal amounts or are not absorbed at all and are safe for long-term use.
Correction of the behavior of a child with constipation is based on the development of a routine of visiting the toilet, in order to achieve regular defecation. Defecation should be every time at the same time. The urge to defecate is based on the gastrocecal reflex, which manifests itself in the morning 1 hour after eating. A child with constipation needs to spend 3-10 minutes in the toilet (depending on age). It is necessary to plant the child on a potty or offer to visit the toilet after each meal.
A child with constipation needs to spend 3-10 minutes in the toilet (depending on age). It is necessary to plant the child on a potty or offer to visit the toilet after each meal.
A prerequisite for effective defecation is to provide a good support for the legs (a low bench on which the child can put his feet), which helps to increase intra-abdominal pressure.
If the defecation is not successful, the child should never be punished and vice versa. The daily frequency of bowel movements can be noted in a diary, which can be analyzed at a scheduled visit to the doctor.
Treatment of constipation should begin with lifestyle changes, which include dietary modification, drinking regimen and physical activity.
Calculation of fluid volume for healthy children
Children under 1 year of age should drink at least 100 ml of water per day.
For healthy children weighing 10 to 20 kg the water requirement is calculated using the formula:
100 ml (volume of water for children under 1 year old) + 50 ml per kg for body weight over 10 kg.
For example, with a mass of 12 kg: 100 ml + 2 x 50 ml = 200 ml.
A child weighing 20 kg should drink water: 100 ml + 50 x 10 = 600 ml
For children weighing over 20 kg the following formula is suggested for calculation:
600 ml (volume of water for a child weighing 20 kg) + 20 ml for each kg over 20 kg.
For children over 3-5 years old you can use the calculation of the amount of water: 30ml / kg of weight
Principles of Dietary Therapy for Constipation:
- meeting physical needs for nutrients and energy
- exclusion of excessive consumption of proteins and fats, which can inhibit intestinal motility
- enrichment of the diet with dietary fiber
- normalization of intestinal microflora with pro- and prebiotics
If the child is breastfed, then the mother's nutrition is corrected (restriction of products that promote gas formation). With artificial feeding, special mixtures are shown.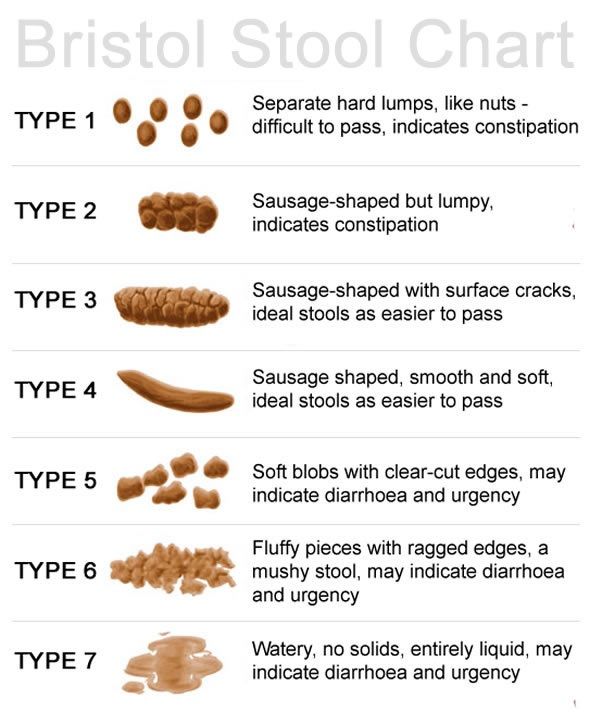 For constipation associated with an allergy to cow's milk protein, therapeutic mixtures are prescribed if the child is bottle-fed. If the child is breastfed, cow's milk and products based on it are completely excluded from the mother's diet.
For constipation associated with an allergy to cow's milk protein, therapeutic mixtures are prescribed if the child is bottle-fed. If the child is breastfed, cow's milk and products based on it are completely excluded from the mother's diet.
After the introduction of “thick” complementary foods, boiled water is necessary for all children, regardless of the type of feeding.
For older children, it is recommended to eat foods rich in vegetable fibers. It is not recommended to “smear food”, puree, “snacks”, “eating on the go”. Food should be crumbly, meat / poultry / fish - “piece”. A “bulk” breakfast is required to stimulate the “gastrocecal reflex”.
The main source of coarse-fiber vegetable fiber, containing a large amount of dietary fiber, is cereal bran, rye bread, as well as a number of vegetables and fruits. According to the principles of evidence-based medicine, a statistically significant increase in stool frequency and improvement in its consistency was demonstrated with the use of fiber compared with placebo.
Bran, as the main source of vegetable fiber, is recommended to be added to the second and third courses, after pouring boiling water over it and settling for 20 minutes. Bran can also be used in between meals, drinking plenty of fluids. For school-age children, the total amount of fluid when taking bran should be at least 1.5-2 liters per day, otherwise they mainly act as sorbents, absorbing fluid from the intestines, thereby increasing constipation. The dose is selected individually, it is recommended to start with 1 teaspoon 2-3 times a day, with a gradual increase to 40 g per day. When the effect is achieved, the dose is reduced and limited to one dose.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (2009) recommends a fiber intake of 0.5 g/kg/day (maximum 35 g/day) for all children. Fiber intake below the minimum recommended value has been shown to be a risk factor for chronic constipation in children.
However, long-term intake of a large amount of plant fibers due to fermentation by intestinal microflora is naturally accompanied by bloating and flatulence.
Children with constipation are shown to take cool liquids on an empty stomach (drinking and mineral water, juice, compotes, kvass), to enhance the laxative effect, it is possible to add honey, xylitol or sorbitol. It is very beneficial for bowel function to increase the intake of juices containing sorbitol/sorbitol, such as juice from plums, pears, apricots, peaches and apples,
With “sluggish” bowel function (hypomotor constipation), cool mineral water of medium and high mineralization is used, such as Essentuki 17, Batalinskaya, Arzni, Donat Magnesium, etc.; with spastic constipation (hypermotor constipation, stool form more often type 1) - warm and low mineralization (Essentuki 4). Calculation of mineral water - 3-5 ml / kg per day.
It is necessary to limit milk in its pure form and in dishes, as flatulence may occur with the appearance or intensification of abdominal pain. It is better to replace whole milk with sour-milk products - kefir, acidophilus, yogurt, yogurt, etc.
The diet of children with constipation includes dishes rich in vegetable fiber - salads from fresh vegetables, greens 2-3 times a day, baked apples, stewed vegetables, diluted vegetable and fruit juices with pulp. Food is cooked mostly unground, steamed or boiled in water.
It is preferable to take raw vegetables and fruits (in the absence of contraindications). Especially recommended are tomatoes, zucchini, pumpkin, carrots, beets, lettuce, cauliflower, apples. Dried fruits (prunes, dried apricots, figs) are given in soaked form and as part of cooked dishes. White cabbage, young green beans, green peas are allowed with good tolerance. Parsley, dill, celery are good to add to various dishes and salads.
If after reading the article you still have questions or you do not understand how to apply the recommendations in your particular case, we invite you and your child to be examined by a pediatric gastroenterologist at the DDC. For the convenience of parents, you can make an appointment with a pediatric gastroenterologist at the Children's Diagnostic Center on a weekday and on Saturdays.