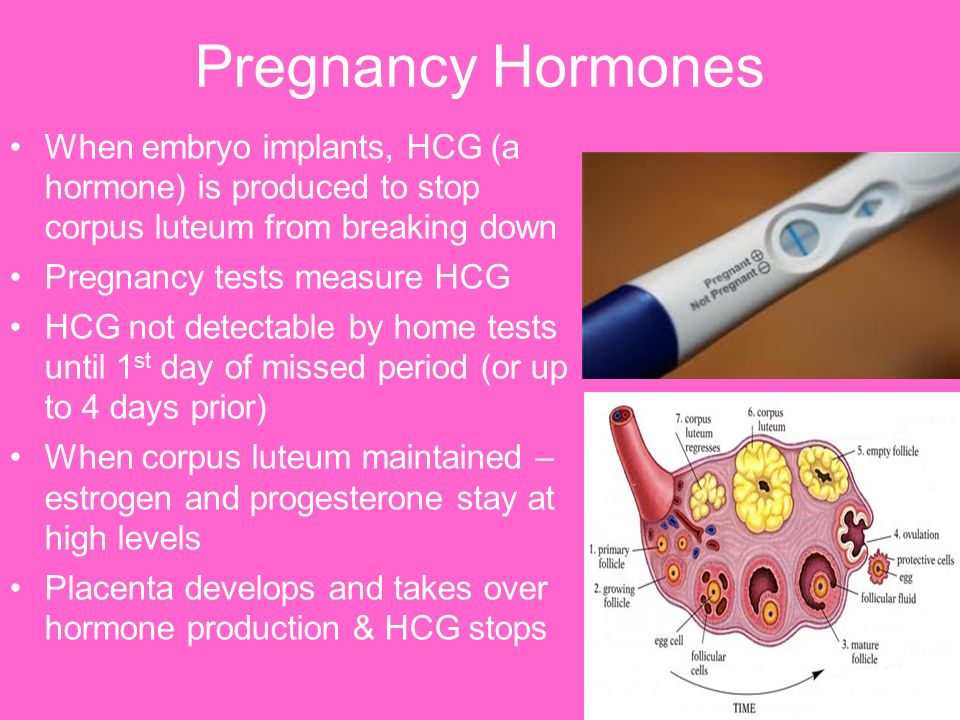
Measuring hcg levels
HCG Levels in Pregnancy & hCG Levels Chart by Week
Human chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG for short, is often referred to as “the pregnancy hormone” because it’s present in large quantities during pregnancy. And it is, after all, the hormone that many at-home pregnancy tests are designed to detect! Find out more about what hCG is, when it’s detectable by at-home pregnancy tests, and what the typical hCG levels are for each of the early weeks of pregnancy.
What Is hCG and When Does Your Body Start Producing It?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is known as the pregnancy hormone, as your body produces it in large amounts when you’re pregnant.
Although you can have low levels of hCG in your body at any time, the levels of this hormone tend to rise sharply early on in your pregnancy for two reasons:
About 10 days after conception, the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of your uterus and your body starts to make hCG.
Over the next week or so, hCG levels will increase.
At about 4 weeks pregnant, the egg—now called an embryo—implants further into the uterus and begins to produce even more hCG, which triggers increased productions of other hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
Together, these hormones help build the lining of the uterus and send signals to the ovaries to stop releasing eggs, ultimately stopping your period.
During these early weeks of pregnancy, you may not show any outward signs of being pregnant and you may not even suspect that you’re pregnant! You may, however, experience implantation bleeding when the fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus (as described above). This is normal and may resemble spotting or a light period.
When Can Pregnancy Tests Detect hCG?
Home pregnancy tests often work by detecting hCG in your urine. All of these over-the-counter pregnancy tests work a little differently, so check the instructions in or on the box.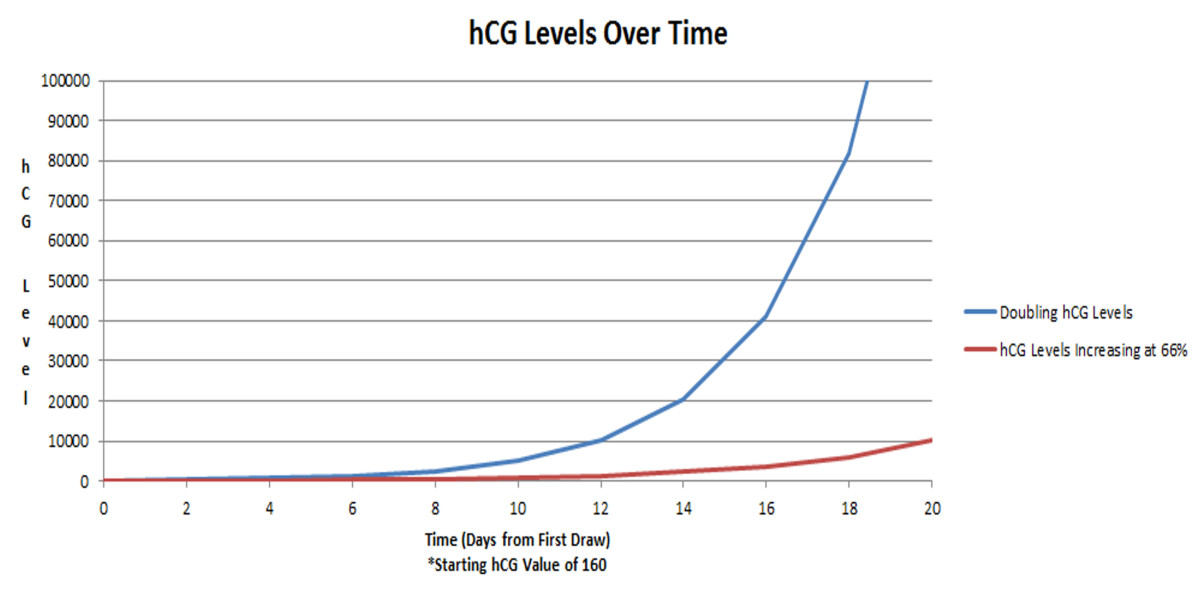 Keep in mind that hCG levels increase over time, so at-home tests are more accurate as your pregnancy progresses. Therefore, a home-pregnancy test that’s taken too early might not detect low levels of hCG and could produce a false negative, meaning the result is negative when you’re actually pregnant.
If you’re wondering when to take an at-home pregnancy test, try one of the following timelines:
Keep in mind that hCG levels increase over time, so at-home tests are more accurate as your pregnancy progresses. Therefore, a home-pregnancy test that’s taken too early might not detect low levels of hCG and could produce a false negative, meaning the result is negative when you’re actually pregnant.
If you’re wondering when to take an at-home pregnancy test, try one of the following timelines:
You might try taking a pregnancy test about three to four weeks after the first day of your last period, as this is when the levels of hCG in your urine will have increased enough to be detectable.
You could wait until around the time you miss your next period, which could be the initial clue that you may be pregnant anyway! By then, the levels of hCG are detectable.
A blood test is the most accurate way to detect hCG levels, because more of the pregnancy hormone is present in the blood than in the urine. Plus, blood tests need less of the hCG hormone to detect a pregnancy, as explained below:
Blood tests.
 Pregnancy blood tests can detect hCG hormone levels as low as 5 to 10 mIU/mL.
Pregnancy blood tests can detect hCG hormone levels as low as 5 to 10 mIU/mL.
Urine tests. At-home urine tests require higher levels of hCG to detect a pregnancy, typically at least 20 mIU/mL.
If your home pregnancy test is positive, your healthcare provider may offer a blood test to check your hCG levels. The results can help your provider confirm your pregnancy and determine how far along you are.
If you’ve just found out you’re pregnant, you can get an estimate of your due date with our Due Date Calculator using either the date of conception or the date of the first day of your last menstrual period!
hCG Levels Chart by Week
The week-by-week chart below will give you an idea of how your hCG levels may rise during the first trimester, and then dip slightly during the second trimester. Keep in mind that, if you want your hCG blood test results explained in more detail, your healthcare provider is the best person to ask.
What Does It Mean if You Have High or Low hCG Levels?
It’s important to remember that every pregnancy is different, and you may have lower or higher levels of hCG hormone than what’s indicated in the week-by-week chart above. Most likely, there’s no cause for concern, but your healthcare provider will help you understand what these levels mean.
Low Levels of hCG
Low levels of hCG are normal for non-pregnant women and men. Normally, hCG levels would be less than 5 mIU/mL and less than 2 mIU/mL, respectively, for these groups. If you’re pregnant and experience low hCG levels, it’s important to look at your entire pregnancy as a whole. Your healthcare provider will consider all the factors of your pregnancy to determine why you might be experiencing lower-than-normal levels of hCG. If your provider suspects anything like an ectopic pregnancy, they may perform additional tests to rule it out.
High Levels of hCG
Likewise, high levels of the hCG hormone might not indicate anything out of the ordinary. However, a higher-than-normal level of hCG may be a sign that you’re having twins or triplets! Again, your healthcare provider will work with you to determine an appropriate course of action, if any is needed.
Lower- or higher-than-normal levels of the hCG hormone during your pregnancy might not indicate anything unusual. However, it’s always a good idea to follow up with your healthcare provider as a precaution, regardless of any questions or concerns you have. Read more about other pregnancy symptoms not to ignore.
However, a higher-than-normal level of hCG may be a sign that you’re having twins or triplets! Again, your healthcare provider will work with you to determine an appropriate course of action, if any is needed.
Lower- or higher-than-normal levels of the hCG hormone during your pregnancy might not indicate anything unusual. However, it’s always a good idea to follow up with your healthcare provider as a precaution, regardless of any questions or concerns you have. Read more about other pregnancy symptoms not to ignore.
The Bottom Line
The hCG hormone plays an important role in your pregnancy, and the changing levels of this hormone are just one of many transformations your body will experience as your baby develops.
Although hormonal changes can make you feel a little off from time to time during your pregnancy, try to take these as reassurance that your baby is growing, and you’re getting closer and closer to the day you finally get to meet them.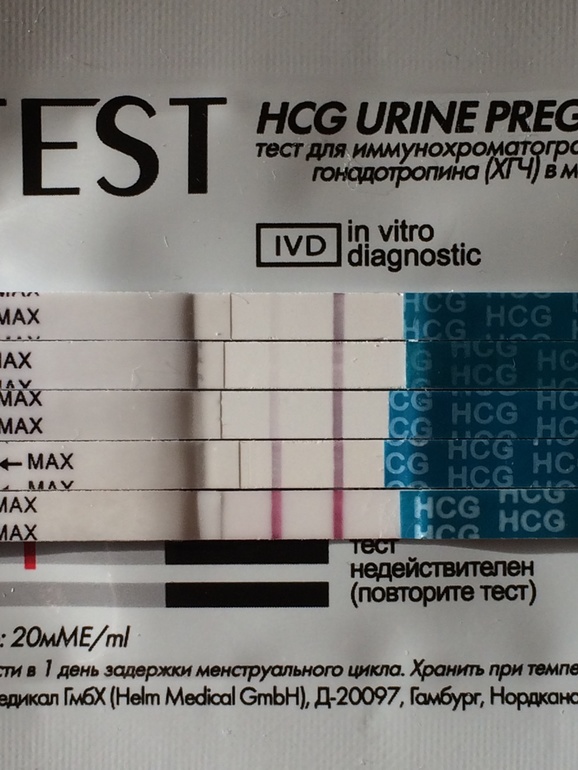 In the meantime, prepare for your baby’s arrival and get rewards on all your diapers and wipes purchases with the Pampers Club app!
Ready to share your pregnancy news with friends and family? Get creative pregnancy announcement ideas in the video below!
In the meantime, prepare for your baby’s arrival and get rewards on all your diapers and wipes purchases with the Pampers Club app!
Ready to share your pregnancy news with friends and family? Get creative pregnancy announcement ideas in the video below!
HCG blood test - quantitative Information | Mount Sinai
Serial beta HCG; Repeat quantitative beta HCG; Human chorionic gonadotropin blood test - quantitative; Beta-HCG blood test - quantitative; Pregnancy test - blood - quantitative
A quantitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) test measures the specific level of HCG in the blood. HCG is a hormone produced in the body during pregnancy.
Other HCG tests include:
- HCG urine test
- HCG blood test -- qualitative
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
How the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed. This is most often taken from a vein. The procedure is called a venipuncture.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain.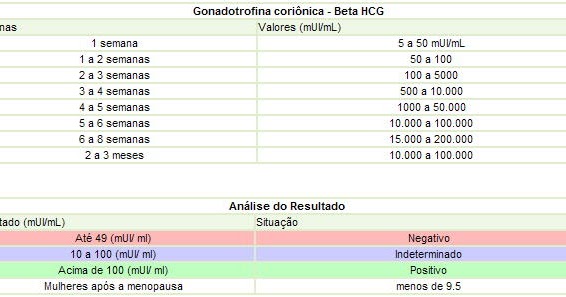 Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Others feel only a prick or stinging sensation. Afterward, there may be some throbbing.
Why the Test is Performed
HCG appears in the blood and urine of pregnant women as early as 10 days after conception. Quantitative HCG measurement helps determine the exact age of the fetus. It can also assist in the diagnosis of abnormal pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancies, molar pregnancies, and possible miscarriages. It is also used as part of a screening test for Down syndrome.
This test is also done to diagnose abnormal conditions not related to pregnancy that can raise HCG level.
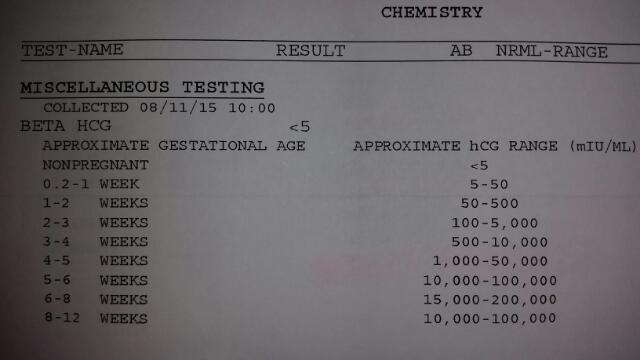
Normal Results
Results are given in milli-international units per milliliter (mUI/mL).
Normal levels are found in:
- Non-pregnant women: less than 5 mIU/mL
- Healthy men: less than 2 mIU/mL
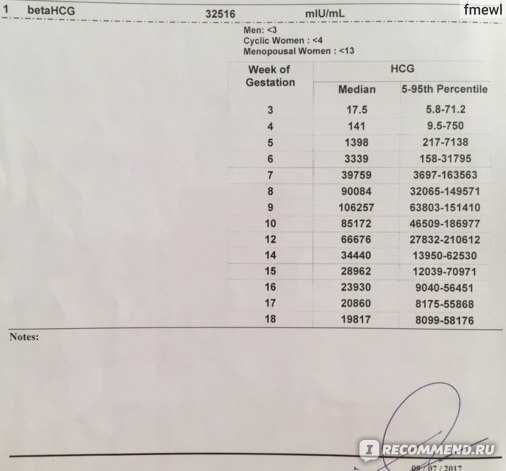
In pregnancy, HCG level rises rapidly during the first trimester and then declines slightly. The expected HCG ranges in pregnant women are based on the length of the pregnancy.
- 3 weeks: 5 - 72 mIU/mL
- 4 weeks: 10 -708 mIU/mL
- 5 weeks: 217 - 8,245 mIU/mL
- 6 weeks: 152 - 32,177 mIU/mL
- 7 weeks: 4,059 - 153,767 mIU/mL
- 8 weeks: 31,366 - 149,094 mIU/mL
- 9 weeks: 59,109 - 135,901 mIU/mL
- 10 weeks: 44,186 - 170,409 mIU/mL
- 12 weeks: 27,107 - 201,165 mIU/mL
- 14 weeks: 24,302 - 93,646 mIU/mL
- 15 weeks: 12,540 - 69,747 mIU/mL
- 16 weeks: 8,904 - 55,332 mIU/mL
- 17 weeks: 8,240 - 51,793 mIU/mL
- 18 weeks: 9,649 - 55,271 mIU/mL
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your provider about the meaning of your specific test result.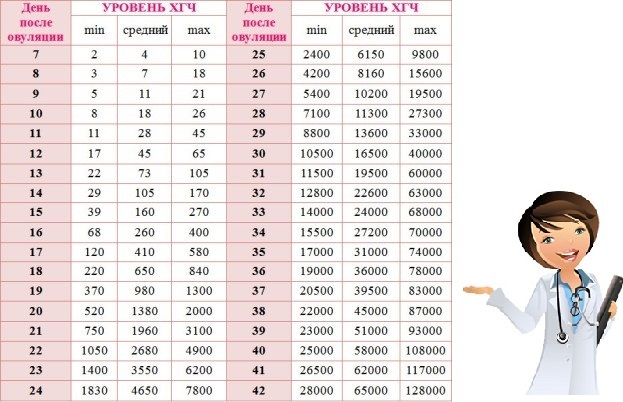
What Abnormal Results Mean
Higher than normal level may indicate:
- More than one fetus, for example, twins or triplets
- Choriocarcinoma of the uterus
- Hydatidiform mole of the uterus
- Ovarian cancer
- Testicular cancer (in men)
During pregnancy, lower than normal levels based on the gestational age may indicate:
- Fetal death
- Incomplete miscarriage
- Threatened spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)
- Ectopic pregnancy
Risks
Risks of having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Blood accumulating under the skin (hematoma)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Jain S, Pincus MR, Bluth MH, McPherson RA, Bowne WB, Lee P. Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Diagnosis and management of cancer using serological and other body fluid markers. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 74.
Jeelani R, Bluth MH. Reproductive function and pregnancy. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 23rd ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2017:chap 25.
University of Iowa Diagnostic Laboratories. Test directory: HCG - serum, quantitative. www.healthcare.uiowa.edu/path_handbook/rhandbook/test446.html. Updated February 10, 2022. Accessed March 11, 2022.
Yarbrough ML, Stout M, Gronowski AM. Pregnancy and its disorders. In: Rifai N, ed. Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. 6th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2018:chap 69.
Last reviewed on: 12/3/2020
Reviewed by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 03/11/2022.
how to pass, explanation of indicators, whether it is possible to take it in early pregnancy, cost .
But it will come in handy in some other cases.
What is hCG
Human chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by placental cells during pregnancy. A small amount of hCG is also produced in the pituitary gland.
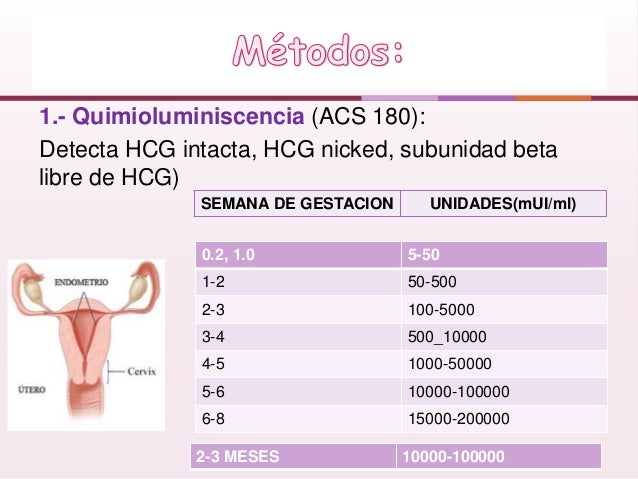
Most commonly, hCG levels are measured using one of two blood tests.
Free beta-hCG is taken during prenatal screenings of the first and second trimesters: at 11-14 and 15-20 weeks of pregnancy. This is one of the ways to diagnose chromosomal pathologies, which we will return to later.
Another test for free beta-hCG is prescribed for the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms:
- in women - choriocarcinoma, hydatidiform mole;
- in men - testicular cancer.
Generic beta hCG. To diagnose pregnancy, it is the total beta-hCG, which is often called simply hCG or hCG analysis, that is used. Any laboratory will understand what you mean if you say that you need an hCG analysis for pregnant women.
Total beta-hCG begins to be produced 6-8 days after ovulation. It promotes the production of progesterone, supports the growth of the placenta, promotes the growth of the fetus.
/pregnancy/
How much does it cost to carry a baby
There are two more types of hCG hormones, but they are not of great importance for diagnosis:
- Hyperglycosylated hCG, which is synthesized in the second or third week of pregnancy.
- Pituitary hCG that mimics the action of luteinizing hormone during the menstrual cycle.
Men also have hCG hormones, albeit in a minimal amount, so calling hCG a pregnancy hormone, although beautiful, is not quite right. In the male body, hCG performs an important function - it causes the testicles to produce testosterone.
In the male body, hCG performs an important function - it causes the testicles to produce testosterone.
Further in the article we will mainly talk about the analysis for total hCG in the body of a woman, because it is taken most often.
How hCG levels are determined
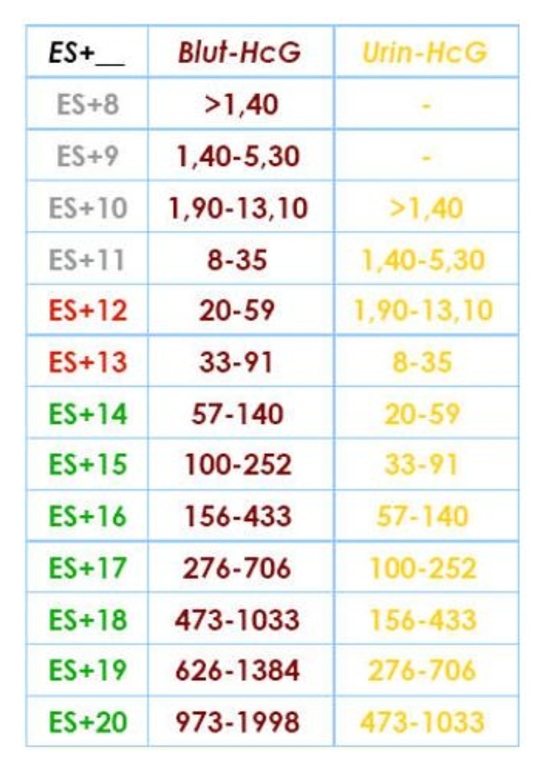
HCG levels are determined using tests that show the concentration of the hormone in urine or blood. If it is below 5 mIU / ml, the analysis is negative, within 5-25 mIU / ml it is doubtful, and a concentration above 25 mIU / ml indicates pregnancy.
Human chorionic gonadotropin - Medscape
HCG levels can be measured using test strips, digital urine tests sold in supermarkets, and a blood test for hCG from a vein that is done in a laboratory.
Strips and digital tests are convenient for home use: no special knowledge or reagents are needed to perform the test and evaluate the result. It is important to remember that pregnancy test strips often do not show it until a missed period.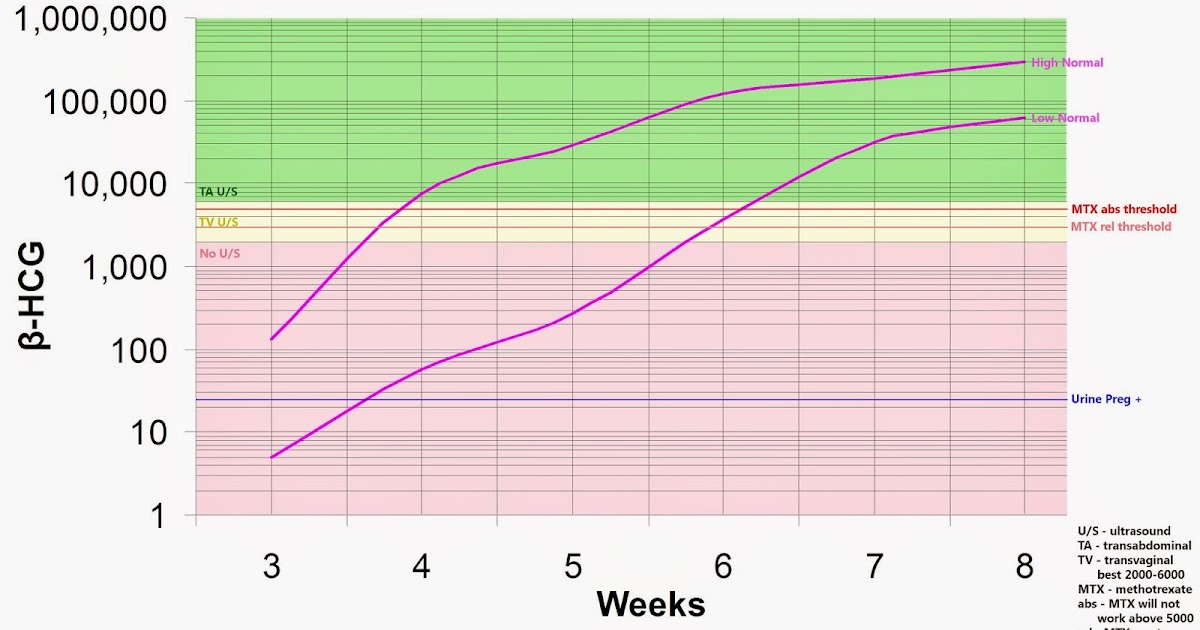 The reason is that in the urine the level of the hormone increases later than in the blood.
The reason is that in the urine the level of the hormone increases later than in the blood.
Test strips usually do a qualitative analysis for hCG: they answer “yes” if the hormone detection threshold is exceeded, and “no” if the hormone level in the blood has not reached the threshold level. Their sensitivity starts from 20-50 mIU / ml, and this is written in the instructions. But some digital tests can show the approximate duration of pregnancy in weeks: one, two or three, or three or more weeks. There is little benefit from this: anyway, only a blood test gives accurate data.
A blood or urine test in the laboratory is always quantitative and allows you to find out the exact concentration of hCG. For such an analysis, you will need venous blood or the first portion of morning urine.
What to do? 12.12.19
In the clinic they force you to buy a container for tests
The sensitivity threshold of the Clearblue Plus test is 25 mIU / ml The sensitivity of the Evitest tests is 20 mIU / mlHow to donate blood for an hCG test
When to take an hCG test. It makes sense to take an analysis for hCG no earlier than the first day of missed menstruation. In some cases, it is possible even 2-3 days earlier: if, according to the terms from intercourse, pregnancy is already possible.
It makes sense to take an analysis for hCG no earlier than the first day of missed menstruation. In some cases, it is possible even 2-3 days earlier: if, according to the terms from intercourse, pregnancy is already possible.
Where to get tested for hCG. In Russia, a blood test for total hCG to check for pregnancy is accepted by most commercial laboratories. It can also be taken in private clinics that do tests on their own equipment or send them to a specialized laboratory.
Before testing for hCG, no examination or referral from a doctor is needed: it can be taken at any laboratory for a fee.
How to prepare. Before taking hCG, different laboratories give different recommendations: from "preferably in the morning and on an empty stomach" to "strictly on an empty stomach, do not drink or smoke an hour before the analysis." In Europe and the USA, there are no restrictions before surrender at all. At the same time, if you plan to take the analysis several times, it makes sense to do it at the same time of day - this way the result will be more objective.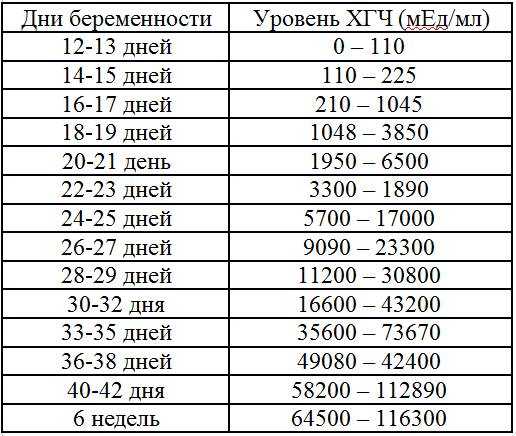
HCG blood test - Walk-In Lab, USA
Cost of analysis
Prices valid in Moscow at the time of publication and include blood sampling from a vein.
In the laboratory:
- "Invitro" - 810 R;
- "Hemotest" - 760 R, called b-hCG;
- CMD - 685 R.
In a private clinic:
- Chaika - 1400 R;
- "Family" - 1100 R;
- "TsIR" - 770 R.
A blood test for hCG to check for pregnancy can be taken according to compulsory health insurance. To do this, you need to get a referral from a gynecologist at a clinic or antenatal clinic. But there is no point in this saving.
/analiz/
You are entitled to free tests under CHI
The queue for tests can stretch for two weeks, waiting for results - for a week or more. Outdated by three weeks - yes, at least for three days, because the level of hCG during pregnancy is constantly growing - the analysis for hCG for pregnant women is useful only to a medical institution for reporting.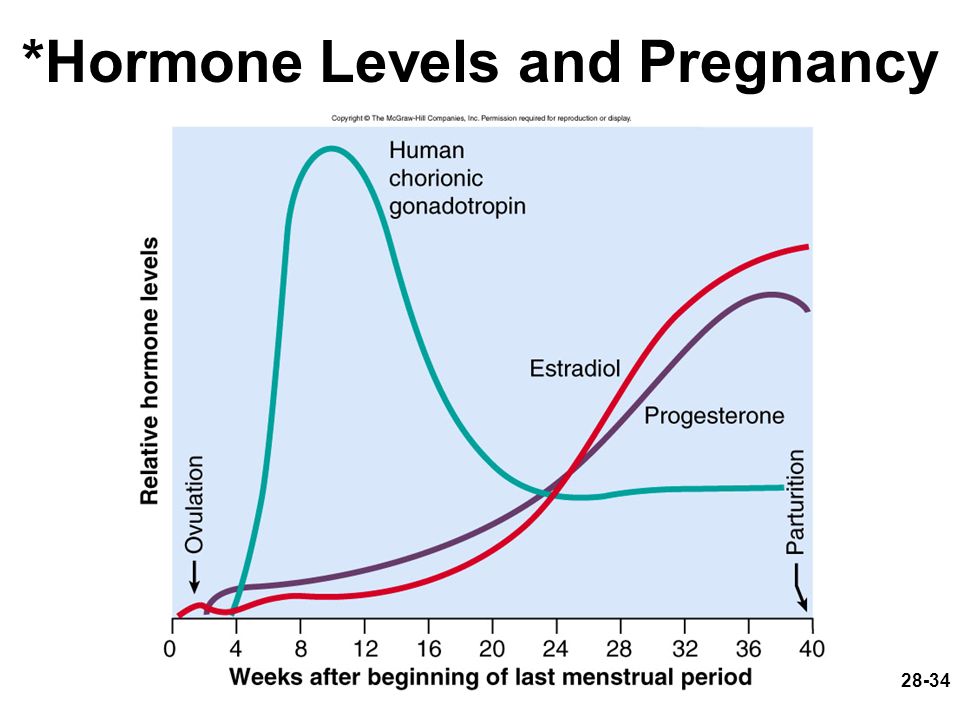
Obtaining and interpretation of a blood test for hCG
Analysis accuracy. During pregnancy, the level of hCG in the blood increases by 2 times every 1.4-2.1 days until at least 10 weeks of pregnancy. Therefore, tests taken at different times on the same day will show different numbers.
Physiology of Pregnancy - MSD Handbook
HCG levels between 5 and 25 mIU/mL are considered questionable and should be retested.
Test results are reported with an accuracy of 1 milliunit per milliliter or nanogram per milliliter. Error in the results is possible, but it is usually associated with incorrect analysis or expired reagents.
In the analyzes of different laboratories, there may be different units of measurement of hCG. The most common are mIU/ml = mU/ml = mIU/ml = mU/ml. All of them are equal to each other:
- mIU / ml is the milliinternational unit per milliliter;
- mU/ml - milliunit per milliliter;
- miU/ml — Million International Unit per milliliter in English spelling;
- mU/ml is a milliunit per milliliter in English spelling.
If IU/l, U/l, IU/ml are found in the analysis, they mean the same thing, but not in milliunits per milliliter, but in units per liter. To convert one unit to another, a calculator is useful.
/babytest/
Are you ready to have a baby?
HCG norms by week. The reference values themselves in laboratories may also differ slightly. This may be due to test manufacturers and analysis standards. The main indicator is an increase in the level of hCG up to 11 weeks of pregnancy.
When evaluating the results, it is important to remember that hCG is calculated by weeks of pregnancy from conception - the embryonic period. It is 2-3 weeks less than the obstetric period, counted from the first day of the last menstruation.
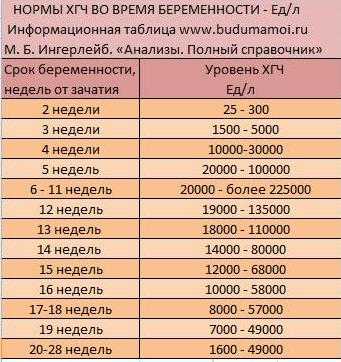
HCG norms by week in different laboratories
| Pregnancy from conception | Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml | Invitro, honey/ml |
|---|---|---|
| Not pregnant | Less than 5 | Less than 5 |
| 2 weeks | 9. 5-750 5-750 | 25-300 |
| 3 weeks | 217-7138 | 1500-5000 |
| 4 weeks | 1580-31 795 | 10,000-30,000 |
| 5 weeks | 3697—163 563 | 20,000-100,000 |
| 6 weeks | 32065-149571 | 20,000 - 225,000 up to 11 weeks |
| 7 weeks | 63 803—151 410 | - |
| 8 weeks | 46509-186977 | - |
| 9 weeks | 27,832—210,612 | - |
| 10 weeks | 13,950—62,530 | - |
| 11-12 weeks | 12,039—70,971 | 19,000-135,000 (12 weeks) |
| 13-14 weeks | 9040—56,451 | 18,000-100,000 (13 weeks) 14,000-80,000 (14 weeks) |
| 15 weeks | 8175—55 868 | 12000-68000 |
| 16 weeks | 8099—58,176 | 10,000-58,000 |
| 17-18 weeks | - | 8000-57,000 |
| Male | Less than 5 | Less than 5 |
NOT PREATED
HEMOTEST, Helix, MME/ml
less than 5
Invitro, Med/ml
less than 5
Pregnancy from conception - 2 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
9. 5–750
5–750
Invitro, MLUST/ML
25-300
3 weeks
Hemothest, Helix MME/ml
217-7138
Invitro, Med/ml
1500-5000
4 weeks
Hemetest, Helix, MME/ML
1580–31 795
Invitro, IU/ml
10,000—30,000
5 weeks
Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml
3697-163 563
Invitro, Med/ml
20 000-100 000
6 weeks
Helix, MME/ML
32 065-149 571
Invitro, Med/ml
20 000-225 000 to 11 weeks
7 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
63 803–151 410
Invitro, Medary /ml
—
8 weeks
Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml
46509–186 977
Invitro, medical/ml
-
9 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
27 832–210 612
Invitro, ML
-
10 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
13 950-62 530
Invitro, ML
-
11-12 weeks
Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml
12,039—70,971
Invitro, mU/ml
19 000-135 000 (12 weeks)
13-14 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
9040-56 451
Invitro, Med/ml
18 000 —100,000 (13 weeks)
14,000–80,000 (13 weeks)
15 weeks
Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml ml
12000-68000
16 weeks
Hemotest, Helix, mIU/ml
8099-58176
Invitro, Med/ml
10 000-58 000
17-18 weeks
Hemothest, Helix, MME/ml
-
Invitro, MLUST/ML
8000-57 000
Male
HEMOTEST, Helix, MME/ml
less than 5
Invitro, Med/Ml
less than 5
Enlargia increases in multiple pregnancy several times compared to pregnancy with one child. For example, when carrying twins in the early stages, the level of hCG can be three times higher than in the case of a singleton pregnancy. If one of the fetuses dies, the hCG level drops.
For example, when carrying twins in the early stages, the level of hCG can be three times higher than in the case of a singleton pregnancy. If one of the fetuses dies, the hCG level drops.
Indicators after IVF do not differ from hCG values during normal pregnancy. But the hormone level is checked daily from the fifth to the twenty-first day after the transfer of the embryo into the uterus. This is necessary in order to track the success of in vitro fertilization. If the hCG values are below the norm by more than 20%, the woman is given hCG injections. If the level of the hormone does not increase at all, then the embryo did not take root.
/guide/eko/
How much does IVF cost
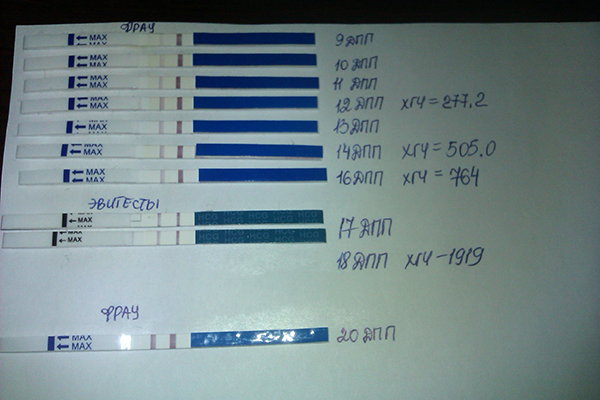
An example of an analysis for hCG by week. I will share my personal experience gained in 2009.
Possible discrepancies
The analysis is positive, the pregnancy test is negative. This happens if you first use the strip, and then donate blood in the laboratory. In this case, it is worth trusting a blood test for hCG to diagnose pregnancy. In urine, the concentration of hCG increases with a lag behind blood, in addition, the test may be of poor quality or have a too high sensitivity threshold. The probability of error in a laboratory test for hCG is minimal.
In this case, it is worth trusting a blood test for hCG to diagnose pregnancy. In urine, the concentration of hCG increases with a lag behind blood, in addition, the test may be of poor quality or have a too high sensitivity threshold. The probability of error in a laboratory test for hCG is minimal.
How much we spent on pregnancy management in a private clinic
Pregnancy test positive, analysis negative. Most likely, the defective test strip is to blame and there is actually no pregnancy. It may be that the pregnancy came and ended almost immediately. In most cases, women are not even aware of it, taking a few days of delay for a small cycle failure.
Causes of an increase in hCG
Pregnancy is the main reason for an increase in hCG. At the same time, if ovulation, and then pregnancy, occurred earlier than the middle of the cycle, the hCG level will be higher than the reference values. An ultrasound can be done to clarify the date.
Taking hormonal preparations containing human chorionic gonadotropin as an active substance. Their full list is in the Register of Medicines of Russia. Common trade names: Horagon, Pregnil, Profazi.
Trophoblastic tumors are the result of genetic disorders of pregnancy, the general name for tumors derived from elements of the placenta. They can appear both during pregnancy and after it ends with an abortion or miscarriage. If the level of hCG is elevated, and the woman is no longer pregnant, she needs to be examined by an oncogynecologist.
Trophoblastic tumors. Clinical Guidelines - Medi-ru
Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - MSD Handbook
Causes of low hCG during pregnancy
Ectopic or ectopic pregnancy. If the embryo develops outside the uterus, the hCG level will rise slowly and lag behind normal reference values. To diagnose an ectopic pregnancy, it is also necessary to do an ultrasound scan.
Ectopic Pregnancy - MSD Manual
Anembryonic. In the absence of an embryo in the uterine cavity, hCG levels continue to rise until spontaneous or medical abortion. Lagging behind the norms of concentration in the first trimester of pregnancy - up to 8 times, but the hormone level does not stop growing. Anembryony is dangerous for a woman, but the diagnosis must be confirmed by several ultrasounds and only after that an abortion should be performed.
Illegal pregnancy. In this case, the hCG level will rise normally while the embryo is developing. If the pregnancy has stopped, the growth of hCG will slow down, and after a miscarriage or abortion it will gradually decrease.
Child developmental delay. An analysis for hCG in this situation is not a basis for making a diagnosis: it is necessary to do an ultrasound scan to determine the cause of the fetal lag in development from the gestational age.
Threat of miscarriage.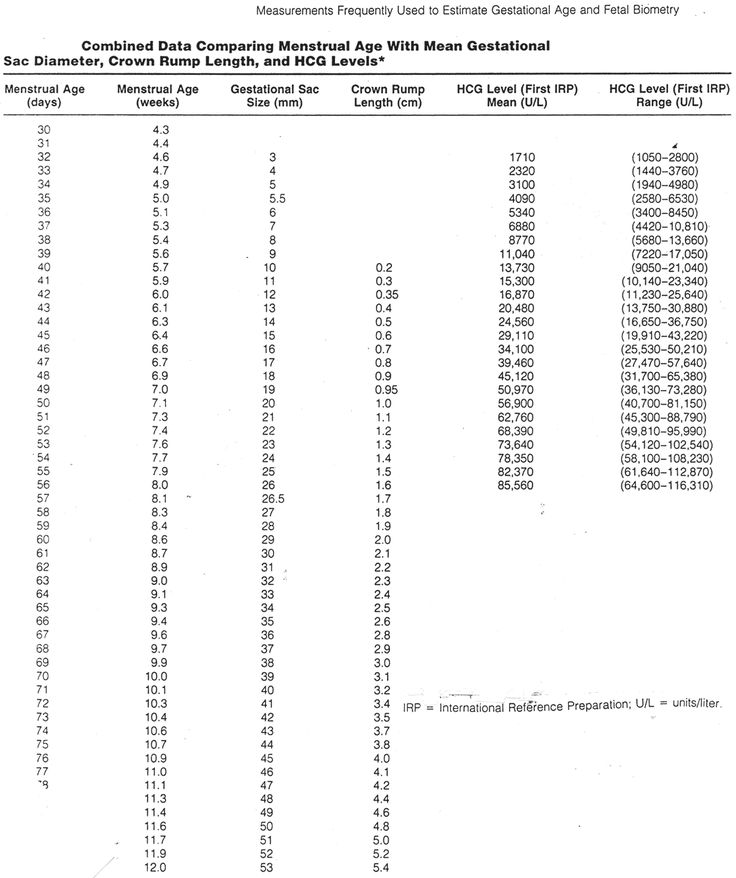 The growth of hCG begins to slow down 5-6 days before a possible miscarriage.
The growth of hCG begins to slow down 5-6 days before a possible miscarriage.
Placental dysfunctions. In this case, hCG is growing more slowly than usual. To detect placental insufficiency, together with hCG, PAPP-A, a plasma pregnancy-associated protein-A, is taken at the first screening.
Incorrect determination of the gestational age. If ovulation and then pregnancy occurred later than the middle of the cycle, the hCG level will be below the reference values. An ultrasound can be done to clarify the date.
/sonography-rocks/
How much does a pelvic ultrasound cost
Causes of an increase in free beta-hCG
This test for another type of hormone is taken during screening of the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. It indicates possible chromosomal pathologies of the child.
Violation of the number of chromosomes:
- Down syndrome is a pathology of the 21st pair of chromosomes.
 Such children have features of physical and mental development;
Such children have features of physical and mental development; - Edwards syndrome is a pathology of the 18th pair of chromosomes. They weigh less than normal newborns and have multiple malformations. Only 5-10% of children with Edwards syndrome survive to a year. They all have serious problems with learning and with general development;
- Patau syndrome is a pathology of the 13th pair of chromosomes. Such children are also born with lower weight, multiple malformations and rarely live to be a year old.
Change in the number of sex chromosomes:
- polysomy — extra X or Y chromosomes. People with polysomy sometimes have intellectual disabilities and health problems;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome is the absence or defect of the X chromosome in girls. They differ from their peers in shorter stature, external features, such as low-set ears, often have problems with the heart, kidneys, and delayed sexual development;
- polyploidy - two or three sets of chromosomes instead of one.
 According to some reports, polyploidy is the cause of every tenth miscarriage.
According to some reports, polyploidy is the cause of every tenth miscarriage.
Remember
- HCG is an important pregnancy hormone that allows you to determine it in the early stages, as well as to make sure that it is proceeding normally.
- The level of hCG in urine rises later than the level of hCG in the blood, so home test strips will show that pregnancy has occurred later than a blood test.
- The level of hCG in the body of a pregnant woman doubles every 1.4-2.1 days until 10-11 weeks of pregnancy.
- Lagging hCG levels from reference values may indicate problems with pregnancy, or may be a sign of an incorrect calculation of the gestational age.
- An increase in the level of hCG at times may be a sign of multiple pregnancy, chromosomal abnormalities, or an incorrect calculation of the gestational age.
- In some cases, the hCG blood test is used to diagnose serious illnesses in women outside of pregnancy and in men.
hCG, human chorionic gonadotropin, indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
I confirm More
- INVITRO
- Library
- Lab...
- HCG, Chorionic...
ECO
Miscarriage
Pregnancy
1183 29July
We remind you that independent interpretation of the results is unacceptable, the information below is for reference only.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, β-hCG, beta-hCG, Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and normal indicators.
Chorionic gonadotropin is a hormone produced by the outer shell of the embryo, and is normally determined in the blood and urine of a woman only when pregnancy occurs.
Chorionic gonadotropin consists of two subunits - alpha and beta. The beta subunit (β-hCG) used for the immunometric determination of the hormone is unique. To monitor the course of pregnancy, the determination of the beta subunit of hCG is used. The level of beta-hCG in the blood as early as 6-8 days after conception makes it possible to diagnose pregnancy (the concentration of β-hCG in the urine reaches the diagnostic level 1-2 days later than in the blood serum).
HCG has a multifaceted effect on the body of a pregnant woman: it affects the development of the embryo and fetus, stimulates the synthesis of estrogens and androgens by ovarian cells, promotes the functional activity of the chorion and placenta, and ensures the successful course of pregnancy.
The introduction of hCG into the body of non-pregnant women stimulates ovulation and the synthesis of sex hormones necessary for conception. In men, this hormone enhances the formation of seminal fluid, activates the production of gonadosteroids.
In early pregnancy and up to the 2nd trimester, β-hCG supports the production of hormones necessary to maintain pregnancy, and in male fetuses it stimulates cells responsible for the formation and development of the male reproductive system.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG, beta-hCG, b-hCG, Human Chorionic)
Synonyms: Beta-hCG general. Human Chorionic Gonadotropin; hCG; Pregnancy Quantitative hCG; Beta hCG; Total beta hCG. Brief description of the analyte Human chorionic gonadotropin ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with home visit
RUB 685
Add to cart
Indications for determining the level of hCG in women
- Absence of menstruation (amenorrhea).
- Exclusion/confirmation of pregnancy, including ectopic (ectopic).
- Diagnosis of the state of the fetus at different stages of pregnancy.
- Assessment of the state of the placenta at different stages of pregnancy.
- Dynamic monitoring of fetal development during pregnancy, including in the diagnosis of malformations.
- Suspicion of the presence of neoplastic diseases of the reproductive system, such as hydatidiform mole (a rare pathology of the fetal egg, in which instead of developing the embryo, chorionic villi grow), chorionepithelioma (a malignant tumor that develops from the epithelium of the villi of the fetal egg).
- Performing artificial termination of pregnancy.
Indications for determining the level of hCG in men:
The presence of suspicion of tumors of the testicles.
Deadline for this test is 1 working day, excluding the day of taking the biomaterial.
Rules for preparing for a blood test to determine the level of hCG
non-specific: it is enough to refrain from smoking and drinking alcohol on the eve of the procedure, limit stress and intense physical activity for a week; blood donation is carried out on an empty stomach.
The determination of hCG in the blood is possible already on the 6-8th day after conception. The use of urinary test systems (rapid pregnancy tests) will be informative starting from the 7th day after the fertilization of the egg. To confirm the result, it is recommended to re-determine the level of the hormone a few days after the first analysis.
You can take a blood test for hCG (thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin, Thyroid StimulatingHormone, TSH) at the nearest INVITRO medical office. The list of offices where biomaterial is accepted for laboratory testing is presented in the "Addresses" section.
Reasons leading to high levels of β-hCG
- Multiple pregnancy.
- Incorrect timing of pregnancy.
- Pathological pregnancy: the appearance of edema, increased blood pressure, loss of protein in the urine (preeclampsia), convulsions (eclampsia), toxicosis.
- The presence of a pregnant woman with chronic diseases (for example, diabetes mellitus).
- Multiple fetal malformations (in such a situation, the determination of the level of β-hCG is used together with other indicators, the so-called "triple test". This study is used as a screening, and not for diagnosis.).
Reasons for fixing a decrease in the level of β-hCG
- Incorrectly established terms of pregnancy.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Frozen pregnancy.
- Threat of miscarriage.
- Fetal or placental disorders (including placental insufficiency).
- Intrauterine fetal death (in this case, it is informative to determine the level of the hormone in the first and second trimesters).
During abortions, the level of β-hCG is also monitored, the dynamics of growth / fall of which can be used to judge the completeness of the manipulation.
Determining the level of hCG, in addition to establishing the fact of pregnancy in the early stages, is part of the screening examination of pregnant women in the first trimester, along with ultrasound.
2 040 RUB
Add to cart
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 3,090 Sign up
In gynecological practice, human chorionic gonadotropin is used to treat infertility, stimulate ovulation, and synthesize sex steroids. In urology, it is used in the treatment of cryptorchidism (undescended testicles) and infertility associated with impaired spermatogenesis.
Quantitatively, β-hCG is determined in the blood, for a qualitative determination, special test systems (pregnancy tests) are used, and in this case, urine serves as a biomaterial.
Quantitative determination of the level of hCG allows you to monitor the course of pregnancy in dynamics. To do this, obstetrician-gynecologists have developed tables for increasing the level of hCG, depending on the duration of pregnancy in weeks. The sensitivity of the determination is in the range of 1.2-1125000 mU/ml.
Reference values of hCG levels in dynamics by gestational age
| Pregnancy (weeks from conception) | HCG level (mU / ml) |
| 2 | 25–300 |
| 3 | 1500–5000 |
| 4 | 10000–30000 |
| 5 | 20000–100000 |
| 6–11 | 20000–>225000 |
| 12 | 19000–135000 |
| 13 | 18000–110000 |
| 14 | 14000–80000 |
| 15 | 12000–68000 |
| 16 | 10000–58000 |
| 17–18 | 8000–57000 |
| 19 | 7000–49000 |
| 20–28 | 1600–49000 |
| Men and non-pregnant women | 0–<5 mU/ml |
Values ranging from 5 to 25 mU / ml do not allow unambiguous confirmation or denial of pregnancy, therefore, a second study is required after two days.
Since the hormone is produced by the placenta, during normal pregnancy, with placental pathology (for example, with fetoplacental insufficiency - a violation of the development of the fetus and placenta), with multiple pregnancies, the values of β-hCG will differ. With a normal pregnancy until the fifth week, the level of the hormone rises exponentially: every two days its concentration doubles, reaching a peak by the 11th week of gestation. Accordingly, in a multiple pregnancy, the level of β-hCG will be even higher than in a single pregnancy.
If the indicator deviates from the norm, additional ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, appendages) is required.
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs (uterus, adnexa) (US examination of pelvic organs (uterus, adnexa))
Ultrasound scanning of the organs of the female reproductive system to assess the shape and size, as well as exclude pathology.
RUB 2,590 Sign up
However, with a normal hCG value, additional examinations may also be needed:
- Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy (required to confirm pregnancy, clarify the term).
Ultrasound diagnosis of pregnancy
Examination to confirm pregnancy and determine the place of attachment of the ovum (to exclude ectopic pregnancy).
RUB 2,390 Sign up
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to assess the characteristics and confirm the normal development of the fetus.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination necessary to monitor the growth and development of the fetus in the first trimester of pregnancy.
RUB 3,090 Sign up
- Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days) - to confirm the presence of several fetuses, determine their characteristics; It is necessary for planning the subsequent actions of the doctor and the management of pregnancy.
Screening ultrasound of the 1st trimester of multiple pregnancy (11-13 weeks 6 days)
Examination to assess the growth and development of fetuses, their position in the uterus, and make a plan for further pregnancy management.
RUB 3,990 Sign up
- Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week) - performed in case of suspected ectopic pregnancy.
Fetal ultrasound according to indications (before the 20th week)
Additional ultrasound, which is prescribed in the presence of concomitant pathologies to monitor the condition of the fetus.
RUB 2,790 Sign up
- Lab tests to be performed in the first trimester are collected in the Pregnancy: 1st trimester (1-13 weeks) profile.
For professional assistance in interpreting the results, contact
obstetrician-gynecologist
.
Sources:
- www.invitro.ru
- Clinical guidelines "Ectopic (ectopic) pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Premature birth". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians-Gynecologists, Association of Obstetric Anesthesiologists-Resuscitators. – 2020.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Recommendations
-
PSA (prostate specific antigen) test
6719 may 13
-
Human papillomavirus
12961 04 May
-
Alkaline phosphatase
12749 16 April
Show more
Similar articles
Pregnancy
Abnormalities of the kidneys
Anencephaly
Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP, alfa-Fetoprotein)
Alpha-fetoprotein: indications for prescription, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Infertility
Varicocele
ECO
Spermogram in INVITRO
Sperm analysis is an integral part of infertility diagnostics and monitoring of diseases of the male genital area. The analysis of the ejaculate includes the determination of the quantitative and qualitative morphological composition of spermatozoa using visual counting in the Goryaev chamber and special staining.
More
ECO
Thrombophilia
Pregnancy
Thrombosis: extended panel 114GP
Thrombosis, extended panel: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of results and norm indicators.
More
Malabsorption syndrome
Pregnancy
Vegetarianism
Celiac disease
Crohn's disease
Osteoporosis
Tuberculosis
25-OH vitamin D
25-OH vitamin D: indications for prescribing, rules for preparing for the test, interpretation of the results and norm indicators.
More
Heredity
Pregnancy
ECO
Research to determine biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood
You can perform molecular genetic tests that reveal a predisposition to various diseases, and now also undergo research to establish biological relationship in the family: paternity and motherhood.