Baby eye infection drops
Eye Infections in Infants & Children
Log in | Register
Health Issues
Health Issues
Listen
Español
Text Size
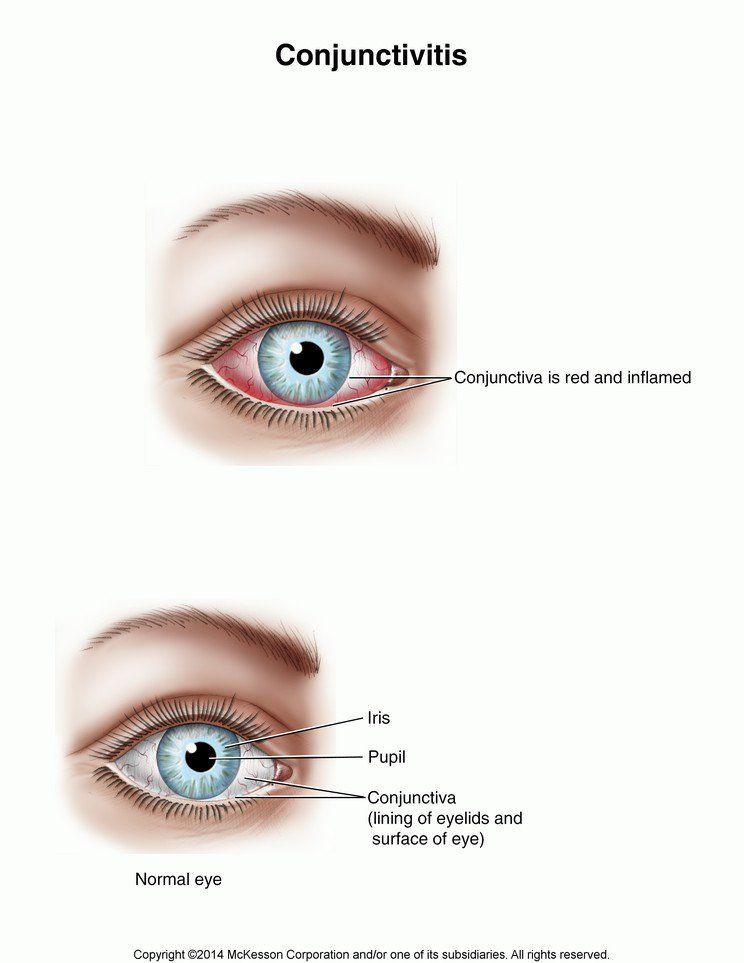
If the white of your child's eye and the inside of his lower lid become red, he probably has a condition called conjunctivitis. Also known as pinkeye, this inflammation, which can be painful and itchy, usually signals an infection, but may be due to other causes, such as an irritation, an allergic reaction, or (rarely) a more serious condition. It's often accompanied by tearing and discharge, which is the body's way of trying to heal or remedy the situation.
If your child has a red eye, he needs to see the pediatrician as soon as possible. Eye infections typically last seven to ten days. The doctor will make the diagnosis and prescribe necessary medication if it is indicated.
Never put previously opened medication or someone else's eye medication into your child's eye. It could cause serious damage.
In a newborn baby:
Serious eye infections may result from exposure to bacteria during passage through the birth canal—which is why all infants are treated with antibiotic eye ointment or drops in the delivery room. Such infections must be treated early to prevent serious complications.
Eye infections that occur after the newborn period:
These infections may be unsightly, because of the redness of the eye and the yellow discharge that usually accompanies them, and they may make your child uncomfortable, but they are rarely serious. Several different viruses, or bacteria, may cause them. If your pediatrician feels the problem is caused by bacteria, antibiotic eye drops are the usual treatment. Conjunctivitis caused by viruses should not be treated with antibiotics.
Eye infections are very contagious!
Except to administer drops or ointment, you should avoid direct contact with your child's eyes or drainage from them until the medication has been used for several days and there is evidence of clearing of the redness. Carefully wash your hands before and after touching the area around the infected eye. See How to Give Eye Drops and Eye Ointment.
Additional Information:
- Pinkeye (Conjunctivitis)
- Children & Contact Lenses: Tips for Parents
- Sties
- Eyelid Problems
- Last Updated
- 2/2/2016
- Source
- Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5, 6th Edition (Copyright © 2015 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Eye - Pus or Discharge
Is this your child's symptom?
- Yellow or green discharge (pus) in the eye
- The eyelids are stuck (matted) together with pus after sleep
- After being wiped away, the pus comes back during the day
- Often caused by a bacterial eye infection
Causes of Eye with Pus
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis. This is a bacterial infection of the eye. The main symptom is eyelids stuck together with pus after sleep. Can be present in 1 or both eyes. A few viruses can cause pus in the eyes, but most don't.
- Viral Conjunctivitis. This is a viral infection of the eyes. Main symptom is pinkness of the white parts of the eyes. The eyes are also watery. Most often, there is no pus. Usually on both sides.
- Normal Discharge. A small amount of dried mucus only in the corner of the eye.
 It may not even be pus. A collection of mucus can be cream colored. Often due to an irritant that got in the eye from dirty hands. Needs no treatment except wiping it away with warm water.
It may not even be pus. A collection of mucus can be cream colored. Often due to an irritant that got in the eye from dirty hands. Needs no treatment except wiping it away with warm water. - Blocked Tear Duct. Present in 10% of newborns. Main symptom is a constant watery eye. Tears fill the eye and run down the face. This happens even when not crying. The eye is not red and the eyelid is not swollen. The wet eye may get secondary infections. This will cause the eyelids to become matted with pus.
- Foreign Object in Eye (Serious). Small particles such as sand, dirt or sawdust can be blown into the eyes. The grit often gets stuck under the upper eyelid. If not removed, the eye reacts by producing pus. The main clue is an eye infection that does not respond to antibiotic eyedrops. Older children complain of feeling something in the eye.
- Eyelid Cellulitis (Serious). This is a deep infection of the eyelid and tissues around it.
 The main symptom is a red, swollen, very tender eyelid. The eye can be swollen shut. Usually only on one side. This can be a problem caused by bacterial conjunctivitis. The eye infection spreads inward. More commonly this is caused by an ethmoid sinus infection. That type occurs without any pus in the eye.
The main symptom is a red, swollen, very tender eyelid. The eye can be swollen shut. Usually only on one side. This can be a problem caused by bacterial conjunctivitis. The eye infection spreads inward. More commonly this is caused by an ethmoid sinus infection. That type occurs without any pus in the eye.
Symptoms of Bacterial Eye Infection
- Yellow or green discharge or pus in the eye
- Dried pus on the eyelids and eyelashes
- The eyelashes are more likely to be stuck together after sleep
- The whites of the eye may or may not be red or pink
- The eyelids are often puffy
When to Call for Eye - Pus or Discharge
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Eyelid is very red or very swollen
- Vision is blurred
- Eye pain or discomfort is more than mild
- Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old. Caution: do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Pus in the eye, but none of the symptoms above.
 Reason: you may need antibiotic eyedrops to treat it.
Reason: you may need antibiotic eyedrops to treat it. - Using antibiotic eye drops more than 3 days and pus is still there
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Pus In the Eye
- What You Should Know About Bacterial Eye Infections:
- Bacterial eye infections are common with colds.

- They respond to home treatment with antibiotic eye drops which need a prescription.
- They are not harmful to vision.
- Until you get some antibiotic eye drops, here is some advice that should help.
- Bacterial eye infections are common with colds.
- Remove Pus:
- Remove all the dried and liquid pus from the eyelids. Use warm water and wet cotton balls to do this.
- Do this whenever pus is seen on the eyelids.
- Also, remove the pus before the antibiotic eye drops are put in. Reason: they will not work if you don't.
- The pus can spread infection to others. So, dispose of it carefully.
- Wash your hands well after any contact with the pus.
- Antibiotic Eye Drops: How to Use
- For a cooperative child, gently pull down on the lower lid. Put 1 drop inside the lower lid. Then ask your child to close the eye for 2 minutes. Reason: so the medicine will get into the tissues.
- For a child who won't open his eye, have him lie down.
 Put 1 drop over the inner corner of the eye. If your child opens the eye or blinks, the eye drop will flow in. If he doesn't open the eye, the drop will slowly seep into the eye.
Put 1 drop over the inner corner of the eye. If your child opens the eye or blinks, the eye drop will flow in. If he doesn't open the eye, the drop will slowly seep into the eye.
- Contact Lenses:
- Children who wear contact lenses need to switch to glasses until the infection is gone.
- Reason: to prevent damage to the cornea.
- Disinfect the contacts before wearing them again.
- Discard them if they are disposable.
- Return to School:
- Your child can return to school when the pus is a small amount.
- Antibiotic eye drops should be used for 24 hours before going back.
- What to Expect:
- With treatment, the pus discharge should clear up in 3 days.
- The red eyes may last up to a week.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Eyelid gets red or swollen
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 12/05/2022
Last Revised: 01/13/2022
Copyright 2000-2022. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Drops for the treatment of eye diseases in infants "Ochkov.net"
The immune system of newborns is very weak, so they are quite susceptible to the effects of various infections. Parents need to carefully monitor the hygiene of the baby. Children often suffer from inflammatory and infectious eye diseases. What effective remedies can be used to treat them?
Inflammatory diseases often occur in babies during the first year of life. A child can become infected through contact with a sick person, when passing through the birth canal of a sick mother, when visiting a clinic. At six months, he already begins to actively crawl, tries to grab all the objects available to him, and then rubs his eyes with dirty hands. Bacteria enter the mucous membrane, causing infectious diseases. This immediately manifests itself outwardly: the eyes turn red, swell, there is increased lacrimation, often with the release of pus. The child, trying to get rid of uncomfortable sensations, scratches his eyes, aggravating the inflammatory processes. Here are some ophthalmic pathologies experts call the most common in infants:
Bacteria enter the mucous membrane, causing infectious diseases. This immediately manifests itself outwardly: the eyes turn red, swell, there is increased lacrimation, often with the release of pus. The child, trying to get rid of uncomfortable sensations, scratches his eyes, aggravating the inflammatory processes. Here are some ophthalmic pathologies experts call the most common in infants:
If signs of infection appear, parents should immediately contact a doctor for a diagnosis. He will prescribe the necessary medicines. In no case should you look for advice on Internet forums.
The fact is that different diseases may have similar external manifestations, but drugs for their treatment will require different ones, depending on the pathogen. Incorrectly selected remedy will cause even more harm to the health of the baby. During the first year of life, a child's vision is actively developing, he acquires new skills and functions, and careless actions can only harm him. After a competent diagnosis, a specialist will select a medicine taking into account the age of a small patient, because not all drugs that can be prescribed to adults are suitable for babies. Consider which drops can be used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in infants.
After a competent diagnosis, a specialist will select a medicine taking into account the age of a small patient, because not all drugs that can be prescribed to adults are suitable for babies. Consider which drops can be used to treat infectious and inflammatory diseases in infants.
Eye drops for the treatment of conjunctivitis
It can be of several types - allergic, bacterial, viral, etc. Therapy should be started as soon as possible, because running conjunctivitis can go into an acute stage. To determine the etiology, the doctor will take a smear from the conjunctival cavity, and then determine its sensitivity to various antibiotics. Only after that you can prescribe eye drops to the baby.
Bacterial (purulent) conjunctivitis
The cause of this type of disease is the contact with the eyes of gonococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus and other pathogenic microorganisms. The disease is dangerous because it develops quite rapidly, therefore, it requires prompt treatment and compliance with all doctor's recommendations, as well as careful hygiene. With bacterial conjunctivitis, pus is released from the eyes, tears flow profusely, the eyelids swell greatly, and the baby is anxious. Infection can occur when bathing in dirty water, contact with a sick adult, scratching the eyes with dirty hands, when passing through the birth canal of the mother, if the infection is present in her genitourinary system. Conjunctivitis usually develops in both eyes at once. For its treatment, ointments and drops with antibiotics are prescribed.
With bacterial conjunctivitis, pus is released from the eyes, tears flow profusely, the eyelids swell greatly, and the baby is anxious. Infection can occur when bathing in dirty water, contact with a sick adult, scratching the eyes with dirty hands, when passing through the birth canal of the mother, if the infection is present in her genitourinary system. Conjunctivitis usually develops in both eyes at once. For its treatment, ointments and drops with antibiotics are prescribed.
Drugs approved for infants have no side effects - they act only in the area of inflammation and are not absorbed into the mucous structures.
So, here are the medicines for the treatment of purulent conjunctivitis that are allowed for children under the age of one year.
Vigamox
The main active ingredient is moxifloxacin 0.5%. This is a drug from the group of fluoroquinolones, which has a broad spectrum of bactericidal properties. It is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens.
It is active against most Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens.
Albucid
The most common and highly effective antibacterial eye drops for children of all ages, from birth. The composition of the drug contains sulfanilamide, which destroys the course of active processes in infected cells. Thus, the reproduction of bacteria is inhibited, and they die. "Albucid" is also prescribed for the treatment of blennorrhea, purulent ulcers. Infants need to inject 2-3 drops into the conjunctival cavity 6 times a day.
Tobrex
The main active ingredient is tobramycin. It is a strong antibiotic that inhibits protein synthesis in affected cells and disrupts the normal functioning of microorganisms. Effective against most pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis. When using "Tobrex" adverse allergic reactions, urinary disorders are possible. In the case of such manifestations, you need to contact a specialist to replace the medicine with another one.
If a child has a large amount of purulent discharge, the doctor may prescribe additional antibacterial ointments, for example, Erythromycin 1%. The tool has good results in the treatment of various forms of infection - fungal, gonococcal, diphtheria and others. The ointment should be used after the introduction of all drops three times a day for 7-10 days, after which you should see a specialist.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
This type is usually transmitted to a child at birth from a mother with chlamydia in almost 70% of cases, and the disease is quite severe. In the eyes of a newborn, abundant purulent discharges form, films appear on the lower eyelids. The disease can manifest itself in the period from one to three weeks after birth.
Chlamydial conjunctivitis can cause other complications: otitis, pneumonia, fever. To eliminate it, use eye drops, ointments, and, if necessary, prescribe injections.

Moxifloxacin has a good effect on chlamydial form. As a local therapy, eye ointments with gentamicin are used. In severe cases, intravenous injections of erythromycin are prescribed. Treatment of this form of conjunctivitis should be carried out only in a clinic under the supervision of a physician.
Viral conjunctivitis
The viral type usually develops in diseases of the upper respiratory tract. It is dangerous because it is transmitted everywhere in any way - through physical contact, common items (hygiene products, dishes), airborne droplets. A child can become infected even while walking with his mother, in a store or clinic. When viral conjunctivitis appears in a baby, treatment should be carried out at home, carefully observing the rules of hygiene. For this, there are also a number of drugs.
"Ophthalmoferon"
Eye drops contain recombinant interferon 2-alpha and diphenhydramine - thus, there is a directed antiviral and antihistamine effect at the same time. They inhibit the activity of bacteria and eliminate inflammation, itching, redness of the eyes. An adverse reaction may be burning after instillation.
They inhibit the activity of bacteria and eliminate inflammation, itching, redness of the eyes. An adverse reaction may be burning after instillation.
Zovirax
The active ingredient in this ointment is acyclovir. Zovirax is a powerful antiviral agent that inhibits viral DNA synthesis without damaging cellular material. The medicine is used for three days, usually after that the results are noticeable.
If antibiotics are used, the eyes should improve within three days of starting treatment - this applies to children and adults. If there is no visible result, then you should visit a doctor - he will prescribe another medicine.
With prolonged use of antibiotics, there is a risk of developing superinfection - the growth of other types of microorganisms that are resistant to the drug, including fungi.
Infant drops for dacryocystitis
Human tear fluid contains antibodies and antimicrobial agents. A tear wets the mucous membrane of the visual organs, preventing them from drying out and creating a protective film on the surface. In a healthy state of the body, a tear is secreted almost constantly from the lacrimal gland, which is located under the upper eyelid.
A tear wets the mucous membrane of the visual organs, preventing them from drying out and creating a protective film on the surface. In a healthy state of the body, a tear is secreted almost constantly from the lacrimal gland, which is located under the upper eyelid.
It happens that after the birth of a child, his tear ducts are clogged with particles of embryonic tissue, which prevents the free outflow of fluid. As a result, inflammation of the tubules begins, since the tear does not remove microorganisms that have entered the palpebral fissure. This disease is called dacryocystitis. It is characterized by increased discharge of pus from the eyes. Parents try to wash them with a decoction of chamomile or tea infusion, but this only helps to remove external secretions. The formation of purulent secretions will continue all the time while the lacrimal canal is clogged.
In the treatment of dacryocystitis in infants, eye drops "Levomycetin" 0.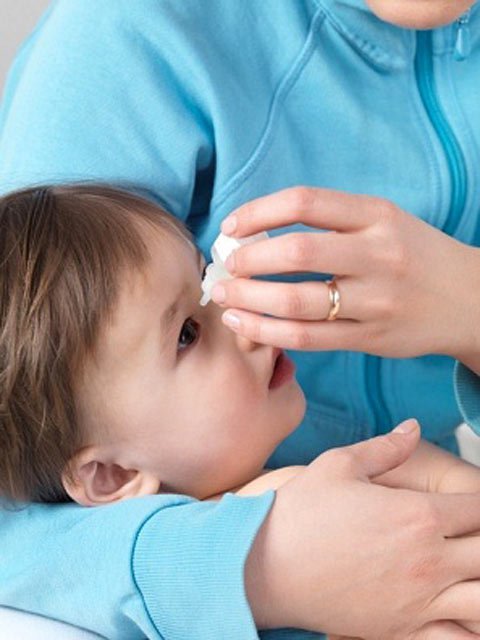 25% have a good result. If the pus does not decrease in two or three days, the doctor may prescribe stronger remedies - Tobrex, Albucid or Floxal. Before the introduction of the drug, it is necessary to massage the lacrimal sac, which is located at the inner corner of the eye. With gentle pressure on the lower eyelid, pus is released from it. Residues should be removed with a cotton swab and the baby's eyes should be washed with a solution of furacilin. After these procedures, you can drip the drug or apply an ointment.
25% have a good result. If the pus does not decrease in two or three days, the doctor may prescribe stronger remedies - Tobrex, Albucid or Floxal. Before the introduction of the drug, it is necessary to massage the lacrimal sac, which is located at the inner corner of the eye. With gentle pressure on the lower eyelid, pus is released from it. Residues should be removed with a cotton swab and the baby's eyes should be washed with a solution of furacilin. After these procedures, you can drip the drug or apply an ointment.
How to administer eye drops for infants
Before administering the drug, it is recommended to flush the eyes with antiseptic solutions to remove residual pus. For this, penicillin diluted in pure water is suitable, which you can buy at any pharmacy in the form of a powder. Attention: it should be used with caution in case of individual intolerance. Also, to eliminate traces of pus, you can use a solution of furacilin or an infusion of chamomile flowers.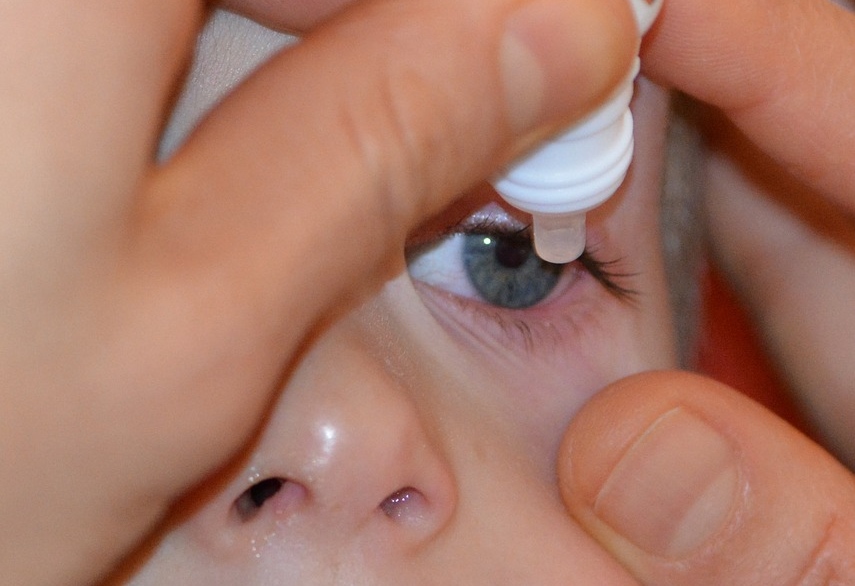 For each eye you need to use a separate cotton pad.
For each eye you need to use a separate cotton pad.
Hygiene must be observed during procedures. Wash and dry hands thoroughly before injecting drugs into the eyes. When instilled, make sure that the tip of the bottle does not touch the mucous membranes and skin around the eyes. The number of drops should strictly comply with the recommendations of the doctor - do not inject too much liquid. After completing the instillation, you need to gently blot the area around the eyes with a clean cloth and wash your hands again to avoid infection yourself.
Ophthalmologists advise - if one of the adults becomes infected with conjunctivitis, it is better to limit contact with the baby as much as possible so that he does not catch the infection. Protective masks should be worn, therapeutic measures should be taken as soon as possible to eliminate the infection.
Antibacterial eye drops are an effective treatment for eye problems in infants. The components of the drug have a local effect and do not penetrate into the bloodstream. If they are chosen correctly, then the course of therapy usually takes 7-10 days. In case of violation of hygiene rules or improper use of ointments and drops, the disease can take a complex course, therefore, strict adherence to all doctor's prescriptions is required.
The components of the drug have a local effect and do not penetrate into the bloodstream. If they are chosen correctly, then the course of therapy usually takes 7-10 days. In case of violation of hygiene rules or improper use of ointments and drops, the disease can take a complex course, therefore, strict adherence to all doctor's prescriptions is required.
Drops for redness, inflammation and irritation of the eyes - choosing the best
Redness of the eyes is an unpleasant situation both from an aesthetic and physiological point of view. It may be accompanied by itching, burning and pain in the visual organs, photophobia, sensation of a foreign body in the eye.
As a rule, redness occurs with the expansion of small vessels on the surface of the sclera (the white of the eye). In itself, it is not a disease, but it can be both a consequence of overwork due to increased visual load, and a symptom of the disease. Redness of the eyes occurs not only in adults, but also in children. The disease often accompanies people who spend a lot of time at a computer or with mobile devices.
The disease often accompanies people who spend a lot of time at a computer or with mobile devices.
Drops from redness of the eyes will help get rid of discomfort and restore clarity of vision. However, it should be borne in mind that this disorder occurs for various reasons. Therefore, drops should be selected, focusing on the cause of redness. And do not forget about the need for to consult an ophthalmologist . The specialist will determine what provokes redness, and prescribe treatment taking into account the characteristics of your health.
Contents
- Causes of redness of the eyes
- General Tips for Choosing Drops
- Selection of drops depending on the causes of redness
- How to choose drops for children
Causes of eye redness
There are a number of reasons that provoke vasodilation on the surface of the sclera. This is first of all:
- eye strain caused by prolonged paperwork, reading in poor light, or long hours in front of a monitor;
- external irritants - wind in the face, ultraviolet radiation, low temperature;
- eye contact with dust, sand, any foreign bodies;
- a long stay in a room in which the air conditioner is working - it dries the air, resulting in itching and burning in the eyes may be due to the fact that the mucous membrane is not sufficiently moistened;
- allergic reactions - to plant pollen, house and office dust, animal hair;
- prolonged driving at night;
- use of low-quality cosmetics, mascara, eye shadow or use of cosmetics in too much quantity;
- exposure to tobacco smoke;
- alcohol abuse;
- various eye diseases such as glaucoma, scleritis or conjunctivitis.

Mobile gadgets can cause red eyes
Separately, it is worth noting the redness of the eyes that occurs when wearing contact lenses. This symptom is especially characteristic for those who have just started using lenses - this is how the body reacts to a foreign body in the eye. As you get used to the problem will disappear, but if you wear lenses for a long time, and the redness does not go away, this is a serious reason to seek medical help.
Redness also appears in cases where you do not properly care for the lenses, do not pay enough attention to cleaning them and do not replace them on time. Prolonged wearing of contact lenses during the day can also cause vasodilation, which is manifested by redness. Take breaks and let your eyes rest from the lenses.
Eye drop recommendation
What drops to choose for the treatment of itching or burning in the eyes? Most importantly, the remedy for redness of the eyes is selected in accordance with the specific cause, due to which the vessels of the sclera expand. This means that you can not do without contacting an ophthalmologist. Only he can make an accurate diagnosis and say why your eyes are red and itchy. The specialist conducts not only a visual examination, but also biomicroscopy - an examination using a special microscope. If necessary, he does additional tests to evaluate the work of the lacrimal glands.
This means that you can not do without contacting an ophthalmologist. Only he can make an accurate diagnosis and say why your eyes are red and itchy. The specialist conducts not only a visual examination, but also biomicroscopy - an examination using a special microscope. If necessary, he does additional tests to evaluate the work of the lacrimal glands.
In addition, many drops have contraindications. For example, not all products are suitable for children and pregnant women. Individual intolerance to the components included in their composition is also possible.
If the drops recommended by your doctor seem too expensive for you, do not look for a budget replacement on your own, discuss a possible alternative with a specialist.
The ophthalmologist will find the cause of the redness of the eyes and prescribe the appropriate treatment with drops
Perhaps you need not just one drop, but several of their varieties. In this case, they need to be instilled into the eyes alternately, with an interval of at least 10 minutes.
If there is no suspicion of a serious pathology, and the discomfort is not permanent, you can independently choose moisturizing drops for redness of the eyes. They mimic natural tears and help get rid of dryness.
Even if you do not have a serious eye disease, you should use drops if you:
- spend a lot of time in front of a computer screen;
- read a lot;
- make up often;
- wear contact lenses.
There are manufacturers who produce solutions in disposable dropper tubes. They are simple and convenient to use, and you can always carry them with you, take them on trips, so that if redness caused by overwork occurs, the problem is quickly solved.
What kind of drops are there
Eye redness drops are an ophthalmic solution, the composition of which is chosen in such a way as to solve vascular problems caused by specific causes. Therefore, all funds are divided into several groups.
Drops "Gilan" imitate a natural tear
Moisturizing compositions are necessary for constant visual work, especially with a high load, as well as when wearing contact lenses. As mentioned above, they mimic natural tears and moisturize the surface of the eyes, helping to get rid of burning and itching, reducing the negative impact of external factors. Moisturizing drops can be used as needed, daily, up to 5-6 times a day.
Drops that constrict blood vessels and help relieve swelling are also recommended for increased visual stress. Thanks to them, the small capillaries in the albuginea narrow, and the redness disappears, and the eye looks white again. Vasoconstrictor drops can be used no more than 1-2 times a week. Regular use of such drugs can lead to undesirable consequences, for example, malnutrition of the structures of the eye and increased intraocular pressure. In addition, drugs in this group are addictive.
Preparations "Systane Ultra" and "Systeine Ultra Plus" allow you to quickly remove redness
An ophthalmologist prescribes antihistamine and anti-inflammatory solutions if the cause of redness of the eyes is an allergic reaction.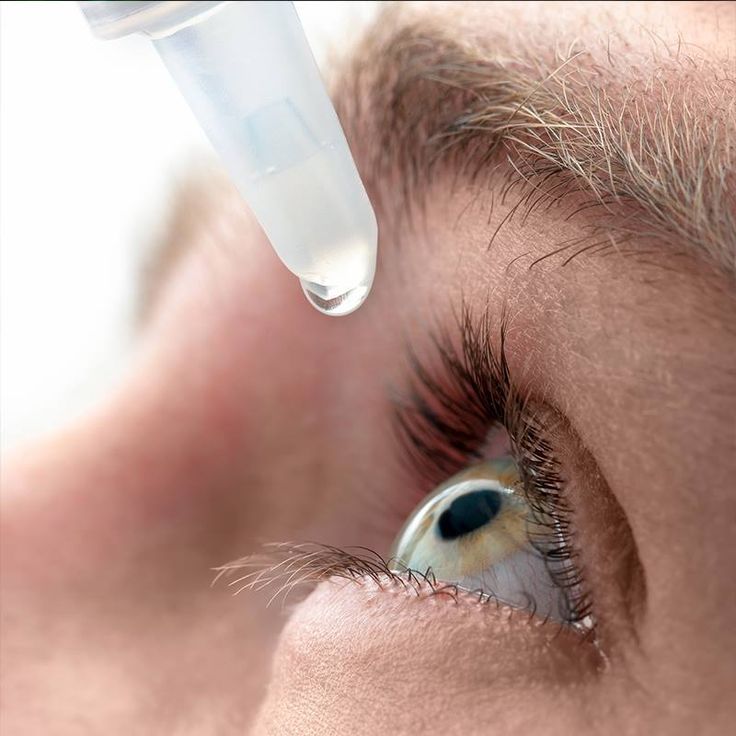 They help to cope with vasodilation, as well as itching and increased tearing. In severe cases of allergies, hormonal solutions help.
They help to cope with vasodilation, as well as itching and increased tearing. In severe cases of allergies, hormonal solutions help.
Often the cause of redness of the eyes is an infection. In this case, it is necessary to use antibacterial drugs.
Eye drops "Artelak Splash" effectively fights dry eyes
With SARS, influenza and the herpes virus, antiviral drops may be prescribed. Vitamin complexes are used to maintain eye health. These are general tonic drugs that can be used for preventive purposes. But they won't help if your eyes are already red.
To combat redness of the eyes, the following preparations are used:
- "Systane Ultra", "Gylan" and "Artelak Splash" - drops that mimic the natural tear fluid. This type of drug is prescribed in cases where redness is due to dry eyes;
- "Okumetil" and Innoxa - drops that have a vasoconstrictive and decongestant effect. Recommended in cases where redness is caused by high visual stress;
- "Dexa-Gentamicin" - an antibiotic prescribed for infections of the anterior segment of the eye, allergies accompanied by bacterial infection, and for prophylactic purposes after operations on the visual organ;
- "Floxal" - antimicrobial therapeutic drops that are used for infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eye.