Average weight 37 weeks
37 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Ultrasound, Baby Development
Reviewed by
Tanya Tantry, MD
Obstetrician & Gynecologist, Medical Consultant at Flo
Contents
Congratulations on officially becoming 37 weeks pregnant! It’s a big accomplishment to make it this far. Each passing day brings you one step closer to finally meeting your little one. Your baby is now considered ‘at-term’ and can actually arrive at any time now!
37 weeks pregnant in months
When you’re expecting, it’s quite easy to lose track of how many months pregnant you are because you’re so focused on counting weeks. Well, we’re here to tell you that you’ve officially entered the second week of your ninth month of pregnancy.
There are a lot of things going on in there with a baby, and a lot of changes happening in your body as it prepares for labor and delivery. Let’s find out all about it.
Take a quiz
Find out how Flo can help you
How big is your baby at 37 weeks?
The average length of a baby at 37 weeks gestation is 19.1 inches (48.5 cm). Baby likely weighs 6.3 pounds (2.8 kg) and is packing on half an ounce (14 g) per day.
Remember when your little one was the size of a poppy seed? Bet he doesn’t feel so little anymore! Baby is now as long as a head of romaine lettuce.
37 weeks pregnant baby position
When does the baby head turn down? This is usually after 26 weeks. By week 37, your baby should be in this cephalic presentation. If he isn’t, you should consult your doctor as soon as possible.
You might be wondering how to tell if baby’s head is down. You can do this via belly mapping. This lets you know how the baby is positioned in your womb.
Pregnancy week 37 fetal development
At this point, baby is too big to do much kicking and punching. You’re more likely to feel her stretching, rolling, twisting, and turning as it gets more crowded in there.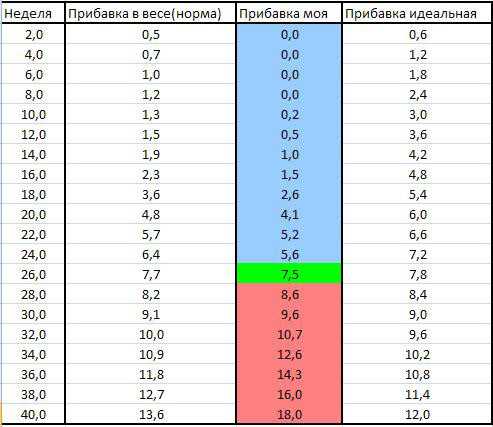 Your uterine wall continues to stretch out, becoming thinner and letting more light through as baby (hopefully) starts to adjust to a more regular schedule.
Your uterine wall continues to stretch out, becoming thinner and letting more light through as baby (hopefully) starts to adjust to a more regular schedule.
Currently, baby is practicing breathing by inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid. The brain and lungs aren’t quite finished growing and developing, although if baby is born this week, everything is likely to be just fine.
Your body at week 37 of pregnancy
37 weeks pregnant belly
“Has baby dropped yet?” As you progress in your ninth month of pregnancy, you’ll probably be hearing this question a lot. It means that baby’s head has descended into your pelvis in anticipation of labor. When this happens, it’s a sign that you’ll be delivering baby within the next four weeks. Your belly will actually look like it’s lower down.
If you have dropped, your lungs will get some much-needed relief. Unfortunately, your bladder will pay the price, and at this point, you may feel a constant need to pee. All that pressure can also cause some other new aches and pains down there.
At this point, you’ll want to lather on that stretch mark cream, because in the next three weeks, you’re likely to see new marks and lines show up as your baby rapidly gains weight.
37 weeks pregnant symptoms
You may be feeling a lot of things at this point in your pregnancy. It all comes with the territory. These are some of the symptoms you may be experiencing in your 37th week of pregnancy.
- Swelling. A little swelling in the extremities is normal at this stage of pregnancy. You may even find that your nose looks bigger!
- Nausea. Nausea is a common symptom of pregnancy often associated with the first trimester, but the last few weeks can bring on some major queasiness! Talk to your doctor if you are vomiting to ensure that you don’t become dehydrated.
- Heartburn. Baby is growing rapidly, which means he’s probably putting some pressure on your digestive system.
- Trouble sleeping.
 Many women experience difficulty sleeping in their ninth month. Whether your bladder, lower back, cramping calves, or general discomfort is keeping you awake, there are things you can do to encourage better sleep. Cut down on caffeine, increase your water intake in the morning and cut down on drinking in the evening, do light exercise during the day, and get yourself a great body pillow for support while sleeping.
Many women experience difficulty sleeping in their ninth month. Whether your bladder, lower back, cramping calves, or general discomfort is keeping you awake, there are things you can do to encourage better sleep. Cut down on caffeine, increase your water intake in the morning and cut down on drinking in the evening, do light exercise during the day, and get yourself a great body pillow for support while sleeping. - Contractions. Braxton-Hicks contractions — or “practice contractions” — may be more frequent now as your body prepares for birth. Braxton Hicks contractions do not result in dilation of the cervix.
- Your abdomen will feel tight, but will likely relax within a minute or two on its own, with a change in position, or when you empty your bladder.
- Spotting. A few drops of blood every now and then — and especially after sex — is normal at this stage of pregnancy. If it’s more than a few drops, call your doctor.
- Vaginal discharge. Your vaginal discharge may increase to the point where you might need to wear a pantyliner (sanitary pads) .
- Stretch marks. These last few weeks of pregnancy are really pushing your body to the limit — your skin may need some love, so apply that stretch mark cream liberally!
- Abdominal pressure. You’re bound to feel pressure here, there, and everywhere in your abdomen. Try getting into an all fours pose to relieve some pressure.
Aside from all the physical symptoms you’re experiencing, there may be a lot of emotional changes going on as well. Excitement, fear, anticipation, and even anxiety may begin to arise as you mentally prepare for this little human’s entrance to the world.
You may find yourself cleaning, organizing, washing, and scrubbing — all part of “nesting”. Baby’s arrival is just around the corner, so who can blame you for wanting to be prepared?
Your ultrasound schedule will vary based on where you live, how your pregnancy is going, and who your doctor is.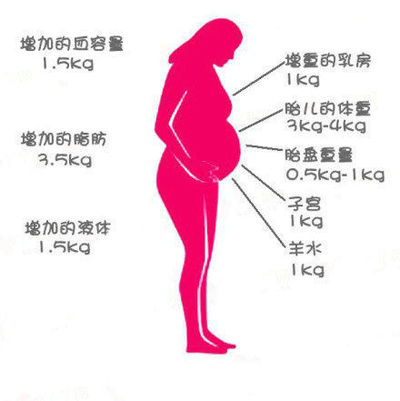 At this stage of pregnancy, most women will have had all their ultrasounds already.
At this stage of pregnancy, most women will have had all their ultrasounds already.
If you suspect that something is wrong, or that baby is moving less than she is supposed to be moving at this point, your doctor may opt to do a quick ultrasound to make sure that everything is okay.
A 37-week ultrasound will help to determine how baby is doing in there, and to ensure that she isn’t in any distress.
You may feel like it’s the last thing you want to do right now, but light exercise is still recommended, even at this very late stage of pregnancy. Grab your partner or a friend and head outside for a stroll around the block. Do light stretches, and maybe even some pregnancy-safe yoga as well.
Don’t forget to drink water during pregnancy — it’s one of the most important things you can do to keep you and baby happy and healthy. Drink plenty of water through the morning and afternoon, and ease up a bit in the evening to prevent too many middle-of-the-night bathroom visits.
You’re in the home stretch. Keep on eating the recommended foods to eat during pregnancy, and stay away from raw meat, raw eggs, raw fish, raw seafood, raw sprouts, smoked fish or meat, and soft cheeses. As soon as that baby is out, you can have all the sushi, pasta carbonara, and smoked salmon you want!
These helpful pregnancy nutrition tips are especially useful during these last few weeks:
- Eat nutrient-dense foods and minimize consumption of simple carbohydrates.
- Make sure you’re getting enough calcium to help build your baby’s nervous system and bones.
- Keep taking your prenatal vitamins which are essential for baby’s development.
- Focus on eating lean meat and poultry and fatty fish for protein.
- You should be getting 27 mg of iron per day.
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of a few large meals.
Sex at week 37 of pregnancy
Sex at 37 weeks is perfectly fine for most pregnancies. Unless told otherwise by your doctor, you and your partner can continue to be intimate until your water breaks or you’re rushing to the hospital due to real labor contractions.
You’ll definitely want to experiment with different positions if your go-to is missionary. For example spooning (lying on the left side in order to reduce pressure on vena cava inferior). At 37 weeks, there can be too much pressure on your belly. Also, it isn’t a good idea to lie flat on your back for too long because it can compromise blood flow to the large blood vessels (abdominal part of the aorta, part of vena cava inferior) behind the uterus.
You may experience contractions after orgasm. That’s completely normal, and nothing to be concerned about. They usually disappear within a few minutes.
Another thing you may experience after having sex at 37 weeks is spotting. Your cervix is very tender now, and there’s a lot more blood flow in that area than usual, so you may get irritated pretty quickly. A little blood is usually not a cause for concern.
Feeling antsy? Week 37 is the perfect time to prepare mentally and physically for baby’s arrival. Here are some things you can do each day of week 37 to better prepare yourself for D-day.
37 weeks 1 day pregnant
Take some photos! Hold up a head of lettuce or a stalk of Swiss chard to indicate how big your baby is at week 37. Measure your belly and write it down. In a few years, you’ll marvel at just how much your belly grew in your last trimester of pregnancy.
37 weeks 2 days pregnant
Time to start packing your hospital bag! Get out your hospital bag checklist and make sure you have everything you need come go-time. If you don’t, make a shopping list so you could order online or head to the store and pick up those useful last-minute items (you know, like witch hazel, disposable undies, magazines, maternity sanitary pads, snacks, etc.).
37 weeks 3 days pregnant
Make an appointment with your doctor for your 38-week prenatal visit if you haven’t already. Sit down and write out a list of questions you would like to ask your doctor. They can include questions about the next few weeks of pregnancy, labor, delivery, after-care, or anything else you may be wondering about.
37 weeks 4 days pregnant
Read about labor and childbirth and make sure you know the signs of active labor. Include your partner in your research, and brush up on techniques and methods that your partner can use to make you more comfortable during contractions and throughout your stay in the delivery room.
37 weeks 5 days pregnant
Read up on baby blues and postpartum depression (PPD). It’s important to know about these things and to acknowledge that 15% of women experience PPD after birth. Learn the signs and make sure your partner can recognize the signs as well.
37 weeks 6 days pregnant
Try a perineal massage. It’s certainly not the most comfortable thing in the world, but a perineal massage may save you from some burning and tearing down there. The idea is to gently stretch the perineum — the area between your vagina and anus — to minimize burning, pain, and tearing during delivery.
Make sure your hands and perineum are well lubricated for the massage.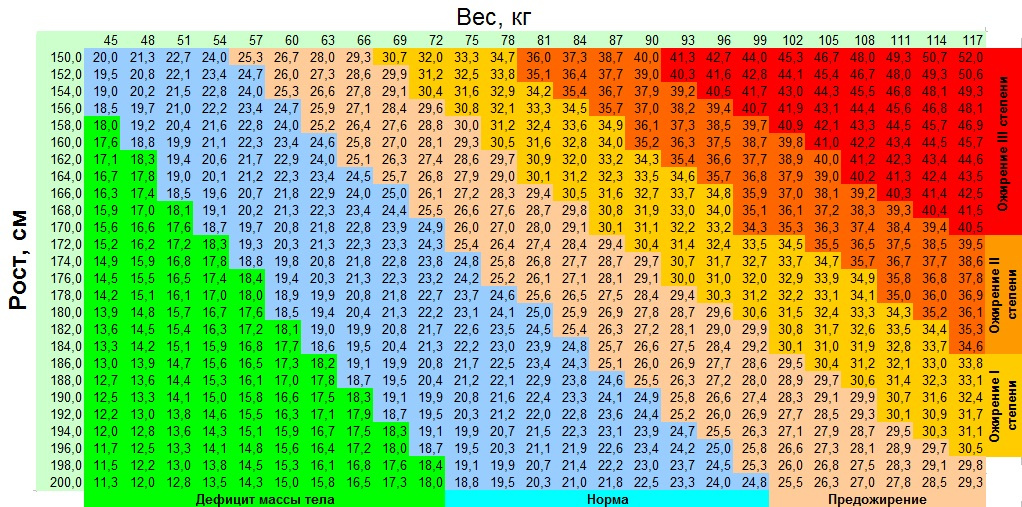 Insert 2 fingers 3-4 cm (1.2-1.6 inches) into your vagina and gently, but firmly apply pressure downward, toward your anus. Slowly pull your two fingers apart so that you are stretching downwards and outwards. When you begin to feel a tingling sensation, it means that you are stretching the skin. You can also stretch the perineum from the outside by gently pulling the skin outward toward your thighs.
Insert 2 fingers 3-4 cm (1.2-1.6 inches) into your vagina and gently, but firmly apply pressure downward, toward your anus. Slowly pull your two fingers apart so that you are stretching downwards and outwards. When you begin to feel a tingling sensation, it means that you are stretching the skin. You can also stretch the perineum from the outside by gently pulling the skin outward toward your thighs.
Get your partner to help you with the perineal massage if you have difficulty doing it yourself.
37 weeks 7 days pregnant
Read about baby grooming basics and newborn care. Immerse yourself in a world of baby poop (How many times a day? What color should it be?), pee (How many wet diapers should a newborn be putting out?), spit up (How much is too much?), cleaning (Do I really need to clean the umbilical cord stump with alcohol every time I change a diaper?), bathing (Wait until the stump falls off!), and more.
What to ask your doctor?
You should feel comfortable asking your doctor about anything having to do with the rest of your pregnancy, labor, delivery, after-care, your next period, and more. Questions about your physical, emotional, and mental well-being are all equally important.
Questions about your physical, emotional, and mental well-being are all equally important.
Here are some questions you can put on your list:
- What happens if I go past my due date?
- Can I walk around during labor?
- Can I eat and drink during labor?
- What are the standard post-birth newborn tests and procedures?
- At what point do you decide if I will need an episiotomy?
- Will I have lochia if the baby is delivered via C-section?
- How long will I bleed after giving birth?
- When should I be expecting my period?
Be sure to go over your birth plan with your doctor and ask about policies regarding induction, pain medication, emergency cesareans, delivery room rules (who is allowed in), and anything else you would like to be briefed on. Make sure you have all the answers you want, because this may be your last appointment before giving birth.
You made it to week 37 of pregnancy, and for that, you should be proud! By this point, baby is feeling crowded in there and each passing day brings him closer to his big debut.
The urge to clean, organize, and get all ready for a newborn is probably very strong, but don’t forget to put your feet up and relax a little before baby comes!
References
https://www.thebump.com/pregnancy-week-by-week/37-weeks-pregnant https://www.healthline.com/health/pregnancy/37-weeks-pregnant#takeaway https://www.huggies.com.au/pregnancy/week-by-week/37-weeks-pregnant https://www.webmd.com/baby/your-15th-prenatal-visit-twins https://www.bellybelly.com.au/pregnancy/perineal-massage/ http://www.baby2see.com/development/week37.html
Continue reading
38
38 week pregnant
39
39 week pregnant
40
40 week pregnant
See all weeksFetus size by week: Your baby's weight throughout pregnancy
Find out how big your baby is during each week of their development with our fetal growth chart. From early in pregnancy, babies grow at different rates, so your baby's actual size by week may vary substantially – but look how they grow! At 20 weeks your baby may be just over 10 inches long and weigh less than 12 ounces, but by 32 weeks they'll reach almost 17 inches and top 4 pounds. At 33 weeks they may be over 17 inches and closer to 5 pounds, and by 37 weeks they'll reach 19 inches and about 6.5 pounds.
From early in pregnancy, babies grow at different rates, so your baby's actual size by week may vary substantially – but look how they grow! At 20 weeks your baby may be just over 10 inches long and weigh less than 12 ounces, but by 32 weeks they'll reach almost 17 inches and top 4 pounds. At 33 weeks they may be over 17 inches and closer to 5 pounds, and by 37 weeks they'll reach 19 inches and about 6.5 pounds.
How do you determine fetus size by week?
There are different methods for estimating how big a fetus is, which is why you'll find different numbers depending on the source.
Experts have formulas they use to come up with the estimated fetal weight (EFW) and height of a fetus, and the formulas aren't always the same. The measurements that are used in equations to estimate weight usually include biparietal (head) diameter (BPD), head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC) and femur (thigh bone) length (FL).
Height is a straightforward measurement, but the method of measuring it changes after the first trimester. For the first 13 weeks, the height measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's bottom. After the first 13 weeks, the measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's heel – explaining why, on the chart below, your baby appears to grow 3 inches from week 13 to week 14!
For the first 13 weeks, the height measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's bottom. After the first 13 weeks, the measurement is taken from the top of the head to the baby's heel – explaining why, on the chart below, your baby appears to grow 3 inches from week 13 to week 14!
Hadlock, the main source we use in our fetal growth chart, provides one of the most commonly used – and most accurate – equations for estimating fetal height and weight. The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG) and the Society for Maternal and Fetal Medicine (SMFM) use Hadlock's figures to diagnose and manage fetal growth conditions, such as intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR).
The numbers on our chart should coincide with the numbers your healthcare provider will be checking against when they measure your baby using ultrasound. (Providers don't measure height after 13 weeks, however, so don't expect to get those numbers at your ultrasound appointments.)
Note that the data used by Hadlock was gathered from middle-class Caucasian women with no history of maternal diseases known to affect fetal growth and no evidence of congenital anomalies. Your provider may make adjustments based on your individual circumstances.
Your provider may make adjustments based on your individual circumstances.
Fetal growth chart
Wondering how big your baby is during each week of pregnancy? The numbers in our chart below can give you a sense of your baby's size. Keep in mind that your baby may be much smaller or larger than these averages. That's okay – after all, healthy babies can weigh less than 5 pounds or more than 9 pounds at birth.
Boy's measurements are different than girl's measurements, even this early. For the numbers on our chart, we've taken an average of boys and girls. And remember, the height measurements up to 13 weeks are head-to-bottom estimates, while the height measurements starting at week 14 are head-to-toe estimates.
| Gestational age | Length (US) | Weight (US) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (head to bottom) | (head to bottom) | |||
| 8 weeks | 0. 62 inches 62 inches | 0.71 ounces | 1.57 cm | 20 grams |
| 9 weeks | 0.91 inches | 0.95 ounces | 2.30 cm | 27 grams |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 inch | 1.23 ounces | 3.1 cm | 35 grams |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 inch | 1.59 ounces | 4.1 cm | 45 grams |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 inches | 2.05 ounces | 5.4 cm | 58 grams |
| 13 weeks | 2.64 inches | 2.58 ounces | 6.7 cm | 73 grams |
| (head to toe) | (head to toe) | |||
| 14 weeks | 5.79 inches | (head to toe)3.28 ounces | 14.7cm | 93 grams |
| 15 weeks | 6.57 inches | 4.13 ounces | 16.7 cm | 117 grams |
| 16 weeks | 7.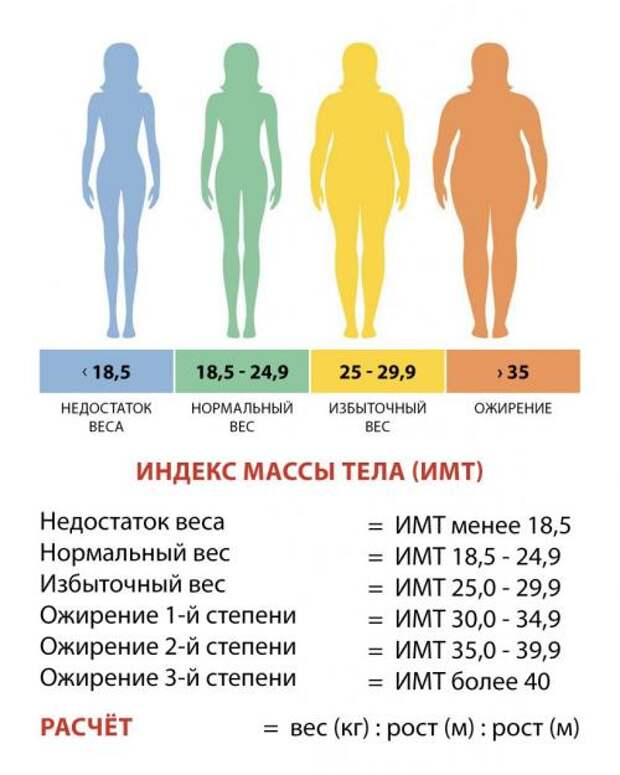 32 inches 32 inches | 5.15 ounces | 18.6 cm | 146 grams |
| 17 weeks | 8.03 inches | 6.38 ounces | 20.4 cm | 181 grams |
| 18 weeks | 8.74 inches | 7.87 ounces | 22.2 cm | 223 grams |
| 19 weeks | 9.45 inches | 9.63 ounces | 24.0 cm | 273 grams |
| 20 weeks | 10.12 inches | 11.68 ounces | 25.7 cm | 331 grams |
| 21 weeks | 10.79 inches | 14.07 ounces | 27.4 cm | 399 grams |
| 22 weeks | 11.42 inches | 1.05 pounds | 29.0 cm | 478 grams |
| 23 weeks | 12.05 inches | 1.25 pounds | 30.6 cm | 568 grams |
| 24 weeks | 12.68 inches | 1.48 pounds | 32.2 cm | 670 grams |
| 25 weeks | 13. 27 inches 27 inches | 1.73 pounds | 33.7 cm | 785 grams |
| 26 weeks | 13.82 inches | 2.01 pounds | 35.1 cm | 913 grams |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 inches | 2.33 pounds | 36.6 cm | 1055 grams |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 inches | 2.67 pounds | 37.6 cm | 1210 grams |
| 29 weeks | 15.47 inches | 3.04 pounds | 39.3 cm | 1379 grams |
| 30 weeks | 15.95 inches | 3.44 pounds | 40.5 cm | 1559 grams |
| 31 weeks | 16.46 inches | 3.86 pounds | 41.8 cm | 1751 grams |
| 32 weeks | 16.93 inches | 4.30 pounds | 43.0 cm | 1953 grams |
| 33 weeks | 17.36 inches | 4.77 pounds | 44.1 cm | 2162 grams |
| 34 weeks | 17. 84 inches 84 inches | 5.24 pounds | 45.3 cm | 2377 grams |
| 35 weeks | 18.23 inches | 5.72 pounds | 46.3 cm | 2595 grams |
| 36 weeks | 18.62 inches | 6.20 pounds | 47.3 cm | 2813 grams |
| 37 weeks | 19.02 inches | 6.68 pounds | 48.3 cm | 3028 grams |
| 38 weeks | 19.41 inches | 7.13 pounds | 49.3 cm | 3236 grams |
| 39 weeks | 19.72 inches | 7.57 pounds | 50.1 cm | 3435 grams |
| 40 weeks | 20.08 inches | 7.98 pounds | 51.0 cm | 3619 grams |
| 41 weeks | 20.39 inches | 8.35 pounds | 51.8 cm | 3787 grams |
Thanks to Dr. Mark Curran, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, for his help preparing this chart.
Advertisement | page continues below
Fetal weight by week: How it changes
Your baby steadily gains weight over the course of your pregnancy, but it's not always at the same rate. If you're having one baby (not twins or multiples), your baby's rate of growth accelerates until 35 weeks, then decelerates.
Here are some highlights, based on estimations:
- Up until 16 weeks, a fetus grows an average of about 19 grams per week, gradually increasing from 7 grams per week at 8 weeks to 15 grams per week at 12 weeks and 29 grams per week at 16 weeks.
- By 20 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 59 grams per week (just over 2 ounces).
- By 30 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 175 grams each week (more than 6 ounces).
- At 35 weeks, a fetus is gaining about 215 grams each week, or about 7.5 ounces. At this point their growth rate peaks.
- After 35 weeks, growth slows to about 188 grams per week, or 6.6 ounces. (Twins slow earlier, at around 28 weeks, and then average about 170 grams each week.
 )
) - In the last few weeks of pregnancy, the growth rate continues to gradually slow to about 168 grams (a little less than 6 ounces) per week by week 40.
Using a tape measure stretched over your belly, your provider will use a fundal height measurement to check your baby's size at your prenatal visits. Beginning at about 24 weeks, the measurement in centimeters should roughly match the gestational age of your baby. If you're 26 weeks pregnant, for example, your fundal height should be about 26 cm, give or take a centimeter in each direction.
If your provider is concerned that your baby is too small, they'll monitor your baby's size with ultrasound, which is more accurate. Using ultrasound, your practitioner can take various measurements (head circumference and diameter, abdomen circumference, femur length) and use them to estimate your baby's size. They may also use a Doppler ultrasound to look at the blood flow to your placenta.
If your baby's estimated weight is less than the 10th percentile for their gestational age, they may be diagnosed with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), also called fetal growth restriction (FGR). IUGR can happen at any time during pregnancy. Some babies with IUGR just turn out to be small for their age, but sometimes there's a problem that's preventing the baby from growing properly.
IUGR can happen at any time during pregnancy. Some babies with IUGR just turn out to be small for their age, but sometimes there's a problem that's preventing the baby from growing properly.
At birth, a baby with IUGR is called "small for gestational age." While most SGA babies who are otherwise healthy grow just fine, some (especially those born prematurely) are at higher risk of problems such as c-section, jaundice, low blood sugar, and even long-term developmental and health problems.
Your baby's size by week
Here are some highlights of your baby's growth during pregnancy:
At 20 weeks, about the midpoint in your pregnancy, your baby is transmitting taste signals to their brain. And you may feel them hiccupping. Your baby's weight at 20 weeks is about 11.68 ounces, and they're about the length of a (10.12-inch) banana.
At 32 weeks, your baby's lungs are developing fast, and your baby's storing minerals like iron for their first 6 months of life. Your baby's weight at 32 weeks is 4. 30 pounds, and their length is 16.93 inches, about the size of a jicama.
30 pounds, and their length is 16.93 inches, about the size of a jicama.
At 33 weeks, things are getting snug in there! Your baby's skin is becoming less wrinkled as they fill in – your baby's weight at 33 weeks is about 4.77 pounds. At 17.36 inches, your baby is now about the size of a pineapple.
At 37 weeks, your baby's brain and lungs are still maturing, and they're still moving a lot, despite the close quarters. Your baby's weight at 37 weeks is about 6.68 pounds, and they're about the length of a bunch of Swiss chard, 19.02 inches.
Once your baby is born, they'll be weighed and measured, and your provider will continue to monitor their growth. While the average newborn weight is a little over 7 pounds, most newborns lose about 5 to 10 percent of their weight in the first days. No worries – they gain it back by the time they're about 2 weeks old, and by 4 months they usually double their birth weight.
Learn more:
- To-do lists for the first, second, and third trimesters
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- Pregnancy Weight Gain Calculator
- How to understand pregnancy weeks, months, and trimesters
Last weeks of pregnancy - 37,38,39,40 weeks of pregnancy: what happens, the development of pregnancy and fetus
Week by week
37 - 40 weeks of pregnancy
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
37th week
BABY
At this time, the growth of the fetus is about 48-49 cm, and the weight reaches 2600-2800 gr. Outwardly, the baby is practically no different from a newborn baby. Facial features are distinct, the cartilages of the nose and auricles are compacted, become elastic. The outlines of the body are significantly rounded due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. The skin of the fetus is smoothed, gradually losing its intense pink color, becoming more light due to subcutaneous fat and thickening of the upper layer of the skin. The amount of cheese-like lubricant covering the baby's body at this time is very large. Vellus hair (lanugo), on the contrary, slowly disappears from the surface of the body, remains in a small amount on the shoulders and back of the back.
Outwardly, the baby is practically no different from a newborn baby. Facial features are distinct, the cartilages of the nose and auricles are compacted, become elastic. The outlines of the body are significantly rounded due to the accumulation of subcutaneous fat. The skin of the fetus is smoothed, gradually losing its intense pink color, becoming more light due to subcutaneous fat and thickening of the upper layer of the skin. The amount of cheese-like lubricant covering the baby's body at this time is very large. Vellus hair (lanugo), on the contrary, slowly disappears from the surface of the body, remains in a small amount on the shoulders and back of the back.
The accumulation of subcutaneous fat by this time is maximum. The mass of subcutaneous fat is about 15% of the total body weight of the fetus. The accumulation of fat is an important step in preparing for extrauterine life, since it is a sufficient layer of fat that will protect the baby from hypothermia or overheating after birth. This is due to the peculiarity of the thermoregulation system, which does not have time to "ripen" by the time of birth and continues to improve in the first months of a child's life.
This is due to the peculiarity of the thermoregulation system, which does not have time to "ripen" by the time of birth and continues to improve in the first months of a child's life.
The increase in fetal weight is not only due to subcutaneous fat, but also due to the ongoing intensive development of muscles and bone growth. Constant movements of the arms and legs lead to an increase in the muscle mass of the limbs. Frequent rhythmic breathing movements strengthen the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
Expectant MOTHER
Pregnant women begin to show signs of the forthcoming birth - precursors at terms close to full-term. This is a series of changes that occur under the influence of hormones, which indicates the direct preparation of the body of a pregnant woman for childbirth. Harbingers arise as a result of a change in hormonal dominance - the “pregnancy hormone” progesterone passes the reins of power to the birth hormone, estrogen.
Harbingers of childbirth include the following changes - a slight decrease in body weight and a decrease in the volume of the abdomen, omission of the uterine fundus, an increase in training contractions, pulling pains in the lower back, a change in the nature of the stool (relaxation), cervical mucus discharge.
Harbingers are not obligatory manifestations. Both the presence of all warning signs and the complete absence of them are variants of the norm. The appearance of precursors - both one and several do not make it possible to predict the exact onset of labor. Pronounced hormonal changes, and hence the intensity of the precursors, can begin both two weeks before the birth, and two hours.
At this time, preparation for the upcoming birth is very intensive. When located head down, the fetus moves down. The fetus is pressed with its head against the lower segment of the uterus, bending the arms and legs as much as possible.
In this way, the baby assumes the most comfortable (so-called "ovoid") position for passing through the birth canal. As a result of the movement of the baby to the entrance to the small pelvis, the bottom of the uterus descends. Pregnant women feel this as a change in the shape of the abdomen, some of its omission. This significantly "unloads" the diaphragm - a flat muscle that separates the organs of the abdominal cavity from the organs of the chest cavity. The pressure on the lungs is significantly reduced, this is felt by pregnant women with easier breathing. The mechanical effect on the stomach decreases, which leads to the disappearance of heartburn, a feeling of heaviness after eating. However, "moving" the uterus will exacerbate the effects on the bladder and rectum. Frequent urination is caused by irritation of the receptors (nerve endings) of the bladder by the lower segment of the uterus. Increased frequency, as well as a change in physiological functions (a tendency to diarrhea) is associated not only with mechanical irritation of the rectum, but also with the influence of estrogens. A high content of estrogen removes fluid from the body of a pregnant woman on the eve of childbirth, which is manifested by increased stools (up to 3-4 times a day) and liquefaction of feces.
The pressure on the lungs is significantly reduced, this is felt by pregnant women with easier breathing. The mechanical effect on the stomach decreases, which leads to the disappearance of heartburn, a feeling of heaviness after eating. However, "moving" the uterus will exacerbate the effects on the bladder and rectum. Frequent urination is caused by irritation of the receptors (nerve endings) of the bladder by the lower segment of the uterus. Increased frequency, as well as a change in physiological functions (a tendency to diarrhea) is associated not only with mechanical irritation of the rectum, but also with the influence of estrogens. A high content of estrogen removes fluid from the body of a pregnant woman on the eve of childbirth, which is manifested by increased stools (up to 3-4 times a day) and liquefaction of feces.
38th week
BABY
By the end of the 38th week, the fetus reaches a weight of 2900-3000 g, and the body length is 49-50 cm. largely depends on the individual body structure and constitution of each child.
largely depends on the individual body structure and constitution of each child.
38 weeks is extremely important as this is the stage when the fetus is fully formed. At this time, all organs of the fetus acquire functional and morphological maturity. All further changes are aimed at preparing the fetus for childbirth.
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the fetus makes intensive respiratory movements, which actively prepares the respiratory muscles (diaphragm and intercostal muscles). These same movements contribute to the washing of the lung tissue with amniotic fluid, which provides the necessary consistency of the surfactant, a substance that covers the lungs from the inside. At this time, the respiratory organs have a fully formed air conduction system (trachea, bronchi, lungs) and a mature gas exchange system - the smallest bubbles-alveoli are ready with the first breath to begin the process of transferring oxygen and carbon dioxide between air and blood.
Expectant MAMA
Starting from the 38th week, the body of a pregnant woman is intensively preparing for the upcoming birth - the amount of progesterone decreases, and estrogen increases. This has a direct effect on the tissues of the birth canal - the hormones of childbirth make the cervix elastic, softened. Cervical mucus throughout pregnancy has a thick consistency, densely filling the lumen of the cervical canal - the cervix. This kind of cork prevents the penetration of microbes from the vagina into the uterine cavity, protects the fetus from infection. At the end of pregnancy, the cervical canal opens slightly, the mucous mass is separated from the walls of the cervix and is released outside. This process refers to the harbingers of childbirth and is called the discharge of the mucous plug. Cervical mucus can stand out at once or move away gradually, over hours or days. The cork has the appearance of a mucous clot without color, similar to egg white or being colored pink, yellowish or brown. The discharge of mucus may be accompanied by some discomfort in the lower abdomen, or pass completely unnoticed. Most often, the discharge of the mucous plug is felt by pregnant women as more abundant vaginal discharge.
This has a direct effect on the tissues of the birth canal - the hormones of childbirth make the cervix elastic, softened. Cervical mucus throughout pregnancy has a thick consistency, densely filling the lumen of the cervical canal - the cervix. This kind of cork prevents the penetration of microbes from the vagina into the uterine cavity, protects the fetus from infection. At the end of pregnancy, the cervical canal opens slightly, the mucous mass is separated from the walls of the cervix and is released outside. This process refers to the harbingers of childbirth and is called the discharge of the mucous plug. Cervical mucus can stand out at once or move away gradually, over hours or days. The cork has the appearance of a mucous clot without color, similar to egg white or being colored pink, yellowish or brown. The discharge of mucus may be accompanied by some discomfort in the lower abdomen, or pass completely unnoticed. Most often, the discharge of the mucous plug is felt by pregnant women as more abundant vaginal discharge.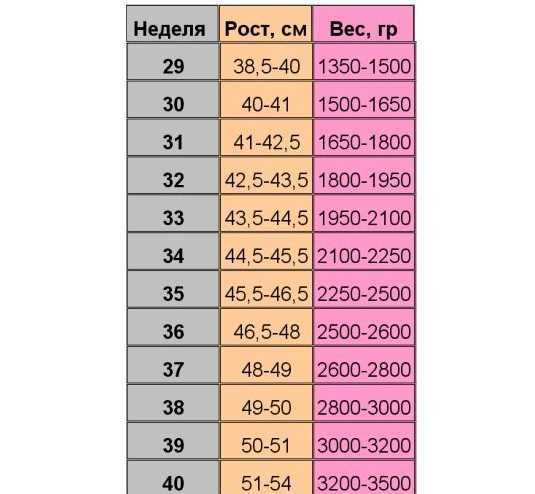
In the event that the abundance of transparent discharge increases, i.e. every minute they become more and more, then you should consult a doctor to exclude the situation of leakage of amniotic fluid. In rare cases, sensations similar to the discharge of a cork - intense transparent discharge from the vagina may accompany prenatal outflow of water. The use of special test strips (amniotests) or indicator pads will clarify the situation. Indicator pads are sold in pharmacies and can be used at home. When using amniotests, it is advisable to seek the help of a doctor. After the discharge of the mucous plug, it is not recommended to take baths, you should exclude visiting pools, swimming in reservoirs, as well as sexual intercourse. Since the possibility of ascending infection increases dramatically, i.e. microbes from the vagina gain access to the uterus, and hence to the fetus.
39th week
BABY
The weight of the baby is 3100-3500 g, height - 50-52 cm. The upcoming birth is a rather complicated process for the fetus, requiring endurance and stress resistance. At week 39, the mass of the adrenal glands increases significantly. These are endocrine glands that regulate metabolism and the body's response to stress. In the first seconds after birth, the baby experiences a lot of new temperature, sound, light, tactile impulses. The hormones of "urgent adaptation" produced by the adrenal glands - adrenaline and norepinephrine - allow the baby to adapt to new conditions.
The upcoming birth is a rather complicated process for the fetus, requiring endurance and stress resistance. At week 39, the mass of the adrenal glands increases significantly. These are endocrine glands that regulate metabolism and the body's response to stress. In the first seconds after birth, the baby experiences a lot of new temperature, sound, light, tactile impulses. The hormones of "urgent adaptation" produced by the adrenal glands - adrenaline and norepinephrine - allow the baby to adapt to new conditions.
Baby's sense organs are well developed by the term. Vision functions at a high level, and by the time of birth, the child already knows how to focus his eyes, react to bright light, distinguish colors, fix moving objects. The baby's hearing is also well developed, which allows him to respond to loud sounds. Taste sensitivity is quite differentiated - the baby clearly distinguishes between sweet, bitter, sour, salty.
Tactile sensitivity (feeling of touch) of the baby in the first minutes after birth experience a lot of new stimuli. In the intrauterine period of development, the fetus was in the aquatic environment and the skin did not experience significant contacts. Immediately after birth, the baby feels the touch of hands, diaper fabric, possibly tools or dressings (cotton wool, gauze swabs, etc.). Of the whole range of sensations, the most comfortable for him is “skin to skin” - which is why laying a newborn on his mother’s stomach even before crossing the umbilical cord is an important stage in the early postpartum period and helps the baby to more easily survive the abundance of new sensations. The contact of the baby's skin with the mother's body allows microorganisms to colonize from the surface of the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the child. The composition of the maternal microflora is the most "correct" primary microflora for the child.
In the intrauterine period of development, the fetus was in the aquatic environment and the skin did not experience significant contacts. Immediately after birth, the baby feels the touch of hands, diaper fabric, possibly tools or dressings (cotton wool, gauze swabs, etc.). Of the whole range of sensations, the most comfortable for him is “skin to skin” - which is why laying a newborn on his mother’s stomach even before crossing the umbilical cord is an important stage in the early postpartum period and helps the baby to more easily survive the abundance of new sensations. The contact of the baby's skin with the mother's body allows microorganisms to colonize from the surface of the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the child. The composition of the maternal microflora is the most "correct" primary microflora for the child.
Expectant MOTHER
One of the brightest precursors can be considered "nesting syndrome" - this is a psychological sign of the upcoming birth. Some manifestations of this syndrome can be observed from the thirtieth week, but reach their apotheosis for a period of 39-40 weeks, usually a few days before delivery.
Some manifestations of this syndrome can be observed from the thirtieth week, but reach their apotheosis for a period of 39-40 weeks, usually a few days before delivery.
Many pregnant women on the eve of childbirth feel an increased need for active actions, which manifests itself in the desire to do a general cleaning, to purchase a lot of necessary (or not quite necessary) things - clothes and household items. "Nesting syndrome" is an exclusively instinctive phenomenon, manifested against the background of an increase in the level of hormones (adrenaline and norepinephrine). These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands of the mother and are necessary for the child to form his readiness for the upcoming birth. The "excess" of hormones affects the behavior of the expectant mother.
40th week
BABY
The body length of a full-term fetus is on average from 48 cm to 53 cm, weight from 3600-4500. The range of indicators of height and weight of a full-term infant is very variable. Mass values can range from 2600g to 4500g, and even these limits are not strict. The body length of newborns ranges from 45-55 cm.
Mass values can range from 2600g to 4500g, and even these limits are not strict. The body length of newborns ranges from 45-55 cm.
Most births occur exactly at 40 weeks of gestation. It is at this time that the fetus fully corresponds to all the parameters of a mature, full-term newborn. The baby is pressed against the exit from the uterine cavity, the arms and legs are closely pressed against the side surfaces of the body, the head is bent as much as possible. This physiological position helps the fetus to pass the smallest size of the head through the narrowest part of the pelvis. With the onset of labor, each contraction pushes the baby down. As the contractions increase, the fetus moves along the birth canal, making rotational-translational movements (screw-like, as if screwing in). By the time the fetal head is completely lowered, the cervix of the uterus opens to the state of the uterine os. Continued uterine contractions (pulls) move the baby down until the birth of the head occurs, followed by the baby's torso. The whole mechanism of childbirth is aimed at protecting the child from possible injury from excessive pressure and preventing ruptures of the mother's soft tissues.
The whole mechanism of childbirth is aimed at protecting the child from possible injury from excessive pressure and preventing ruptures of the mother's soft tissues.
Expectant MOM
The 40th week of pregnancy for most expectant mothers is the last in the period of expectation of a child. The long wait increases the anxiety of expectant mothers as the birth approaches. The excitement is mixed with the desire for an early delivery, so that the “terrible” childbirth is in the past. The desire to see your child as soon as possible, to hold him close to you increases the intolerance of expectation. Many pregnant women are worried about the possibility of an imperceptible onset of childbirth. Such cases are extremely rare, in most cases the onset of labor is clearly felt by pregnant women. The main sign of childbirth is regular contractions, repeated at regular intervals. The duration of contractions will gradually increase, and the interval between them will decrease. Labor can also begin with the passage of amniotic fluid (antenatal rupture). In this case, contractions may be weak or absent altogether. However, the rupture of amniotic fluid is considered the beginning of labor and requires hospitalization in the maternity hospital. When the water leaves, the integrity of the bladder is broken, which makes it possible for microbes to enter the uterine cavity. The risk of infection dictates the need for delivery after the water breaks within the next few hours - the permissible anhydrous interval is no more than 10-12 hours.
Labor can also begin with the passage of amniotic fluid (antenatal rupture). In this case, contractions may be weak or absent altogether. However, the rupture of amniotic fluid is considered the beginning of labor and requires hospitalization in the maternity hospital. When the water leaves, the integrity of the bladder is broken, which makes it possible for microbes to enter the uterine cavity. The risk of infection dictates the need for delivery after the water breaks within the next few hours - the permissible anhydrous interval is no more than 10-12 hours.
The right attitude for childbirth, self-confidence, theoretical knowledge and psychological readiness will become unconditional assistants in the work that a pregnant woman has to do.
37 weeks of pregnancy - what happens to the baby, the development and weight of the child, the belly at the thirty-seventh week of pregnancy
WHAT'S HAPPENING
At the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the baby's body produces hormones important for life. One of them - cortisone - is necessary for the full maturation of the lungs. Iron accumulates actively in the liver. Without this trace element, the proper functioning of the body is impossible. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the liver of the fetus contains five times more iron than that of adults. This supply is enough for the baby for the first six months of life.
One of them - cortisone - is necessary for the full maturation of the lungs. Iron accumulates actively in the liver. Without this trace element, the proper functioning of the body is impossible. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the liver of the fetus contains five times more iron than that of adults. This supply is enough for the baby for the first six months of life.
At the 37th week of pregnancy, the main systems of the body continue to improve. The neurons of the brain begin to become covered with myelin sheath, which helps the nerves transmit signals. This process will continue throughout the first year of a child's life.
The ear and nasal cartilages harden, but the bones of the skull, due to the fontanelles, will remain flexible so that it is easier for the baby to overcome the obstacles of the birth canal. The fontanel is an area where there is no bone tissue. A newborn baby has as many as six of them, but most close immediately after birth. As the cranial bones grow, the fontanelles will gradually disappear.
YOUR WELL FEELING
By the 37th week of pregnancy, the belly stops growing, but the baby continues to gain weight, which is why it becomes more and more crowded. There is practically nowhere to move, so there is less movement than before. But still they should be about 10 during the day.
For many women, the belly begins to sink, which is one of the signs that labor is approaching. If this does not happen by 37 weeks, do not be upset: sometimes the stomach drops only at the very end of pregnancy. But if this still happened, this does not mean that the birth will begin right now - most likely, you need to wait a week or two. Now there will be no problems with breathing, however, due to the strong pressure of the fetus on the bladder, you will have to go to the toilet even more often.
The huge size of the uterus can still cause discomfort in the spine. Try to get more rest by shifting the main responsibilities around the house to the future dad and other family members.
At 36 - 37 weeks of pregnancy, Braxton-Hicks training bouts intensify and become longer. At the same time, you have a clear feeling of tension and relaxation of the muscles of the uterus, but there should not be any pain. Soreness in the lower abdomen and the regular nature of contractions indicate the onset of labor. In this case, you must urgently consult a doctor who will refer you to the hospital.
At the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the amount of vaginal discharge may increase. There is nothing to worry about - the time has come for the mucous plug to come out: its particles are lumps of mucus with red streaks that can be found in light secretions. Sometimes the cork comes out all at once. In this case, you will see a lump of mucus with a volume of about two tablespoons.
RISK FACTORS
One of the risk factors at 36 to 37 weeks of gestation is group B streptococcus. This is a bacterium that can settle in the vagina or around the rectum. Group B streptococcus occurs in about 35% of healthy adults. But if its colonies are present in a pregnant woman, a child may become infected during childbirth. And infected newborns need serious antibiotic treatment and careful monitoring in the hospital, because group B streptococcus can cause dangerous complications in babies, such as meningitis, pneumonia, and blood poisoning. If the test for the presence of this bacterium is positive, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics before and during childbirth. This measure will prevent the transmission of infection to the baby.
Group B streptococcus occurs in about 35% of healthy adults. But if its colonies are present in a pregnant woman, a child may become infected during childbirth. And infected newborns need serious antibiotic treatment and careful monitoring in the hospital, because group B streptococcus can cause dangerous complications in babies, such as meningitis, pneumonia, and blood poisoning. If the test for the presence of this bacterium is positive, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics before and during childbirth. This measure will prevent the transmission of infection to the baby.
Childbirth at the 37th week of pregnancy no longer poses a serious danger. In the presence of cramping pains in the abdomen and lower back, early departure of amniotic fluid, you should call an ambulance. Sometimes a woman even needs a premature birth - for example, if she is diagnosed with:
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Infectious disease;
- placental abruption;
- Entwining the baby with the umbilical cord.
In these cases, the method of delivery is chosen by the attending physician.
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the appointment, the gynecologist will examine you on the armchair for the readiness of the cervix for childbirth, because starting from the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the baby may ask to be born at any moment. During a vaginal examination, the doctor pays attention to the location, density and length of the cervix.
While the baby lives in the mother's tummy, the lower segment of the uterus has thick walls, which begin to stretch during childbirth, becoming softer and thinner. This is called "smoothing". Before the onset of childbirth, it is equal to zero, with active labor, the walls of the cervix are smoothed out by 50%, and just before the birth of the baby - by 100%.
Also at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the doctor checks the degree of disclosure (stretching) of the cervix. This indicator is determined in centimeters. With full disclosure, the width of the pharynx reaches 10 cm. If during the examination it is found that the cervix is not ready for childbirth, the doctor prescribes medication or non-drug means to increase its maturity.
If during the examination it is found that the cervix is not ready for childbirth, the doctor prescribes medication or non-drug means to increase its maturity.
When examined at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the gynecologist takes a smear. The results of the tests will make it possible to judge the presence or absence of infection in the birth canal. If necessary, treatment is prescribed, because at the time of birth, the child should be protected as much as possible from possible infection. Also during this visit, the doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat, measure your weight and blood pressure, assess the width of the pelvis and the presentation of the fetus.
Ultrasound at this time is usually not done. It may be needed only if any abnormalities were detected during pregnancy.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Starting from the 37th week of pregnancy, the baby can be born at any time. Check if everything is prepared for the hospital. At the last moment, you will not be up to it. When packing bags, don't forget to put sanitary pads (not tampons!) and two or three bras in them.
When packing bags, don't forget to put sanitary pads (not tampons!) and two or three bras in them.
If insomnia bothers you, be more active during the day. At 36 - 37 weeks of pregnancy, you can do simple housework, walk in the fresh air, attend courses for expectant mothers and do gymnastics for pregnant women. And before you go to bed, air the bedroom well.
Keep track of your nutrition. At 37 weeks of pregnancy, you should consume as many dairy products as possible. Let your daily menu include: kefir, cottage cheese, natural yogurt, curdled milk, sour cream and cheese. In addition, you really need foods rich in iron and vitamin C.
At 37 weeks pregnant, many couples refuse to have intimate relationships. With good physical condition and the absence of medical contraindications, sex is not prohibited at this stage.
Pregnancy and childbirthNinth month of pregnancy: changes in the female body and fetal development by week
Newborn careDowry for a newborn
What do you need to have at home for discharge, what stroller and crib to choose, and what equipment to buy?
Pregnancy and childbirthWhat to take with you to the maternity hospital
Pregnancy and childbirthPsychology of pregnancy and motherhood
Positive attitude and overcoming fears during pregnancy, psychological hygiene and well-being of a woman.