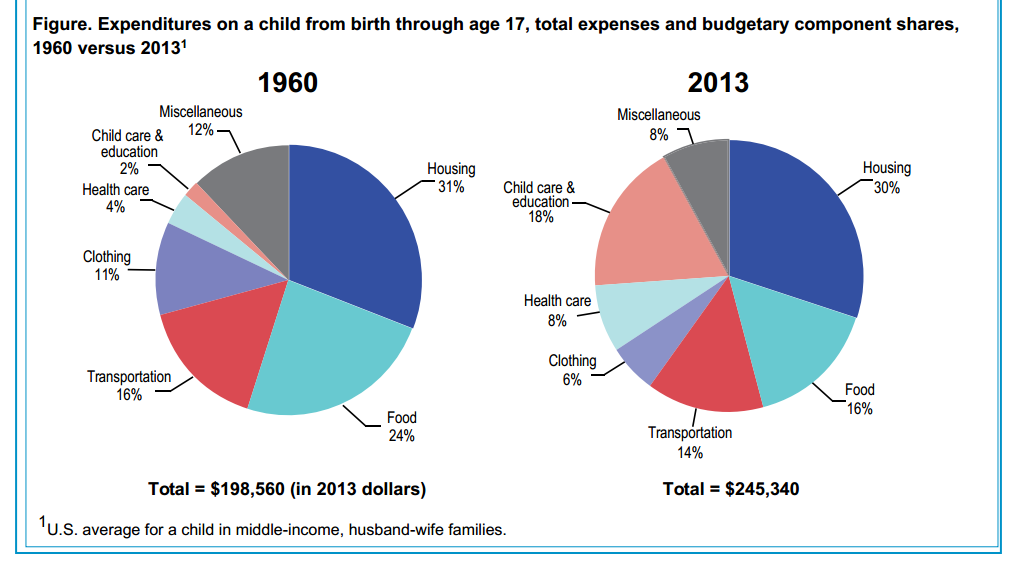
Are nosebleeds normal
Nosebleed causes & treatments | NHS inform
Most nosebleeds can be stopped without the need for medical attention, but occasionally further treatment may be required.
What to do
To stop a nosebleed:
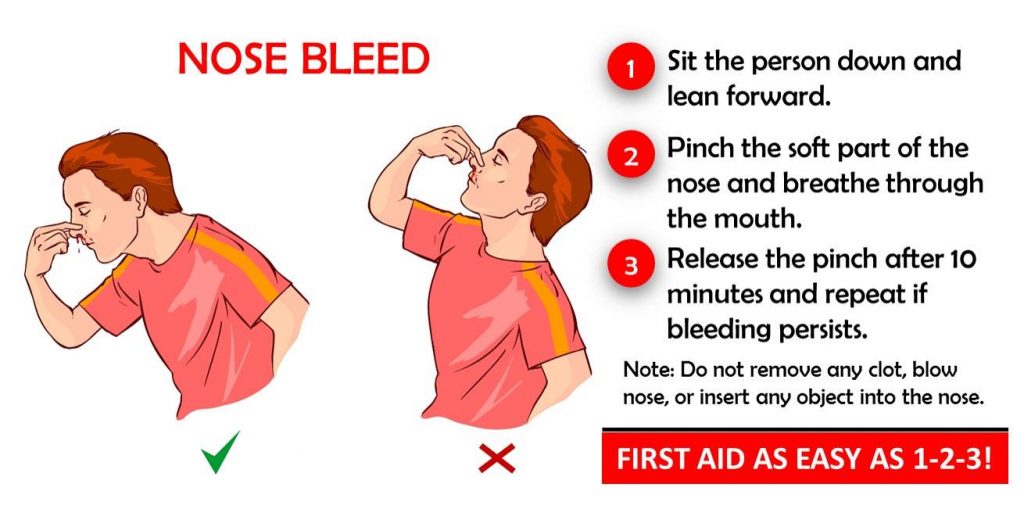
- sit down and firmly pinch the soft part of your nose, just above your nostrils, for at least 10-15 minutes
- lean forward and breathe through your mouth – this will drain blood into your nose instead of down the back of your throat
- place an ice pack or bag of frozen vegetables covered by a towel on the bridge of your nose
- stay upright, rather than lying down as this reduces the blood pressure in the blood vessels of your nose and will discourage further bleeding
If the bleeding eventually stops, you won't usually need to seek medical advice. However, you should still follow the recovery advice outlined below.
When to seek medical advice
Contact your GP or call the NHS 111 service if:
- you're taking a blood-thinning medicine (anticoagulant) such as warfarin or have a clotting disorder such as haemophilia and the bleeding doesn't stop
- you have symptoms of anaemia such as heart palpitations, shortness of breath and a pale complexion
- a child under two years of age has a nosebleed (this is rare and there's a chance it's caused by something serious)
- you have nosebleeds that come and go regularly
Ask someone to drive you to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department or call 999 for an ambulance if:
- the bleeding continues for longer than 20 minutes
- the bleeding is heavy and you've lost a lot of blood
- you're having difficulty breathing
- you swallow a large amount of blood that makes you vomit
- the nosebleed developed after a serious injury, such as a car crash
Find your nearest A&E department
Medical treatment
If you see your GP or go to hospital with a nosebleed, you will be assessed to determine how serious your condition is and what's likely to have caused it. This may involve looking inside your nose, measuring your pulse and blood pressure, carrying out blood tests and asking about any other symptoms you have.
The main treatments that your GP or hospital doctor may use to stop your nose bleeding are described below.
Antibiotic ointment
Your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic ointment. This should be applied by squeezing a pea-sized amount onto the front of the nasal septum (wall between the nostrils).
This can reduce the inflammation and crusting in the nose and reduce the severity and frequency of nosebleeds.
Antibiotic ointment is particularly effective in children.
Cautery
If your doctor is able to identify exactly where the bleeding is coming from, they may carry out a minor procedure to seal the bleeding blood vessel by cauterising (burning) it.
This is normally done using a stick of a chemical called silver nitrate. A local anaesthetic will be sprayed into your nose to numb it and the silver nitrate stick will be held against the bleeding point for up to 10 seconds.
Nasal packing
If cautery is ineffective or your doctor is unable to identify a specific bleeding point, they may recommend packing your nose with gauze or special nasal sponges to stop the flow of blood by applying pressure to the source of the bleeding.
Packing will usually be carried out after local anaesthetic has been sprayed into your nose. The gauze or sponges often need to be left in place for 24-48 hours before being removed by a health professional. You'll usually need to be admitted to hospital to be monitored during this time.
Further treatment
If the treatments above don't help, you may be referred to a hospital specialist such as an ear, nose and throat (ENT) doctor for further treatment.
Additional treatments that may be used in hospital include:
- electrocautery – an electric current running through a wire is used to cauterise the blood vessel where the bleeding is coming from
- blood transfusions – a procedure to replace the blood you've lost
- tranexamic acid – medication that can reduce bleeding by helping your blood to clot
- packing under anaesthetic – your nose is carefully packed with gauze while you are unconscious from general anaesthetic
- ligation – an operation using small instruments to tie off bleeding blood vessels in the back of your nose
Recovery
Once your nose has stopped bleeding, you should follow the advice below to reduce the risk of your nose bleeding again and to stop you picking up an infection:
- avoid blowing or picking your nose, heavy lifting, strenuous exercise, lying flat, and drinking alcohol or hot drinks for 24 hours
- don't remove any crusts that form inside your nose – these may be unpleasant, but they're a useful part of the healing process
- if you need to sneeze, try to sneeze with your mouth open to reduce the pressure in your nose
- avoid people with coughs and colds
If you see a GP or a hospital doctor about your nosebleed, they may give you a prescription for an antiseptic nasal cream once the bleeding stops. This should be applied to the inside of your nostrils several times a day for up to two weeks to help prevent further bleeding.
This should be applied to the inside of your nostrils several times a day for up to two weeks to help prevent further bleeding.
If your nose does start to bleed again, follow the first aid advice above and seek medical advice if the bleeding doesn't stop.
Nosebleeds (for Teens) - Nemours KidsHealth
Nosebleeds are usually harmless and easily controlled, but they can look scary. Try not to worry — most nosebleeds are easy to stop.
How Can I Stop a Nosebleed?Try these simple tips to stop a nosebleed:
- Get some tissues or a damp cloth to catch the blood.
- Sit up or stand.
- Tilt your head forward and pinch your nostrils together just below the bony center part of your nose. Applying pressure helps stop the blood flow and the nosebleed will usually stop with 10 minutes of steady pressure. Don't stop applying pressure to keep checking if the bleeding has stopped.
If you get a nosebleed, don't blow your nose. This can cause more bleeding. Also, don't tilt your head back. This common practice will cause blood to run into your throat. This can make you cough or choke, and if you swallow a lot of blood, you might vomit.
This can cause more bleeding. Also, don't tilt your head back. This common practice will cause blood to run into your throat. This can make you cough or choke, and if you swallow a lot of blood, you might vomit.
If you've tried the steps above twice and the bleeding continues after the second attempt, you'll need to see your school nurse or a doctor.
After you've stopped the initial nosebleed, don't lift heavy objects or do other activities that cause you to strain, and try not to blow your nose for 24 hours.
Now that your nosebleed is over, let's take a look at what a nosebleed is and what can cause it.
Different Kinds of Nosebleeds
The most common kind of nosebleed is an anterior nosebleed, which comes from the front of the nose. Capillaries, or very small blood vessels, that are inside the nose may break and bleed, causing this type of nosebleed.
Another kind of nosebleed is a posterior nosebleed, which comes from the deepest part of the nose.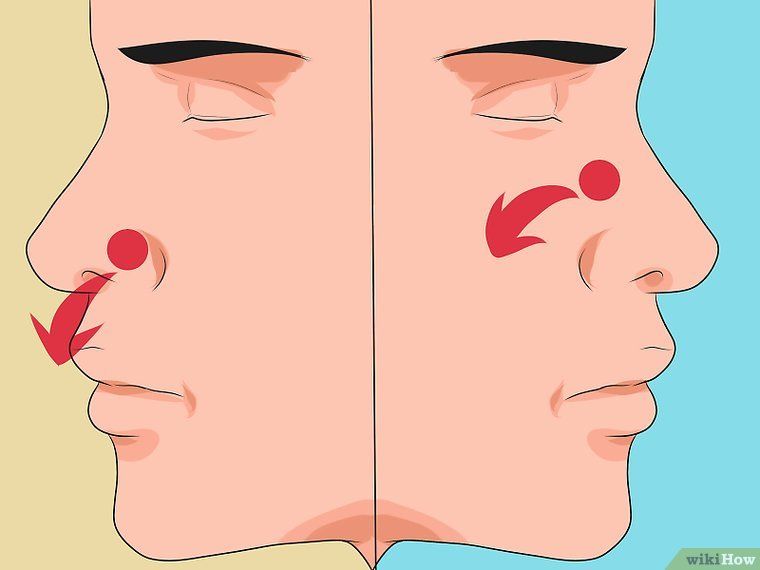 Blood from a posterior nosebleed flows down the back of the throat even if the person is sitting or standing. Teens rarely have posterior nosebleeds. They're more common in older people, people who have high blood pressure, and people who have had nose or face injuries.
Blood from a posterior nosebleed flows down the back of the throat even if the person is sitting or standing. Teens rarely have posterior nosebleeds. They're more common in older people, people who have high blood pressure, and people who have had nose or face injuries.
What Causes Nosebleeds?
The most common cause of anterior nosebleeds is dry air. A dry climate or heated indoor air irritates and dries out nasal membranes, causing crusts that may itch and then bleed when scratched or picked. Colds may also irritate the lining of the nose. Bleeding may happen after repeated nose-blowing. When you combine a cold with dry winter air, you have the perfect formula for nosebleeds.
Allergies can also cause problems, and a doctor may prescribe medicine such as antihistamines or decongestants to control an itchy, runny, or stuffy nose. The medicine can also dry out the nasal membranes and contribute to nosebleeds.
An injury to the nose may cause bleeding and isn't usually cause for alarm. If you ever have a facial injury, use the tips outlined earlier to stop the nosebleed. If you can't stop the bleeding after 10 minutes or you are concerned about other facial injuries, see a medical professional right away.
If you ever have a facial injury, use the tips outlined earlier to stop the nosebleed. If you can't stop the bleeding after 10 minutes or you are concerned about other facial injuries, see a medical professional right away.
Nosebleeds are rarely cause for alarm, but frequent nosebleeds might indicate a more serious problem. If you get nosebleeds more than once a week, you should see your doctor. Most cases of frequent nosebleeds are easily treated. Sometimes tiny blood vessels inside the nose become irritated and don't heal. This happens more frequently in teens who have ongoing allergies or frequent colds. A doctor may have a solution if you have this problem.
If your doctor rules out a sinus infection, allergies, or irritated blood vessels, he or she may order other tests to see why you're getting frequent nosebleeds. Rarely, a bleeding disorder or abnormally formed blood vessels could be a possibility.
Cocaine (or other drugs that are snorted through the nose) can also cause nosebleeds.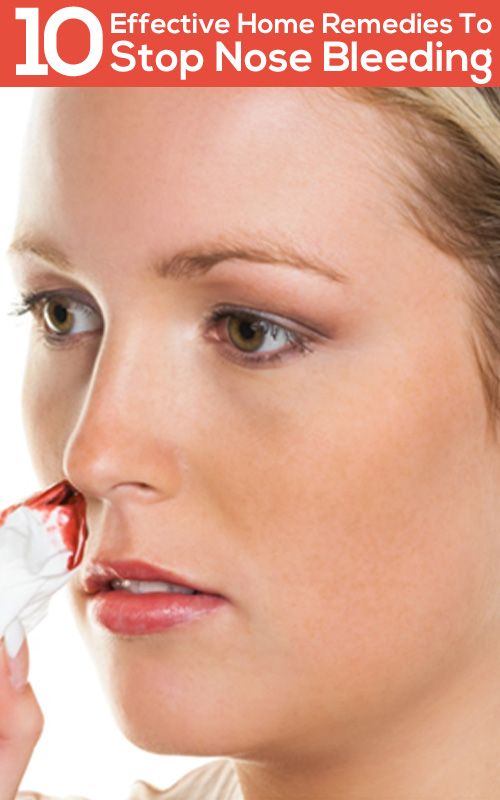 If you suspect a friend is using cocaine, try talking about it and get help from a trusted adult.
If you suspect a friend is using cocaine, try talking about it and get help from a trusted adult.
Can I Prevent Nosebleeds?
- When you blow your nose (especially when you have a cold), do so gently into a soft tissue. Don't blow forcefully or pick your nose.
- Your doctor may recommend a cool-mist humidifier to moisten your indoor air.
- Keep the inside of your nose moist with saline (saltwater) nasal spray or gel, or dab petroleum jelly or antibiotic ointment gently around the opening of the nostrils.
- Wear protective athletic equipment when playing sports that could cause injury to the nose.
An occasional nosebleed may make you worry, but there's no need to panic — now you know what to do!
Reviewed by: Michelle P. Tellado, MD
Date reviewed: September 2019
Why does the nose bleed? — GAUZ OZP City Clinical Hospital No. 8
- Post author: Press Secretary
- The entry was published: 07/24/2019
- Post category: Prevention
. As a rule, this is not dangerous and is quite understandable. But this is not always the case, since nosebleeds can be caused by quite serious reasons that you do not know about. Now we will consider what needs to be done if blood flows from the nose and in which cases it is worth contacting a specialist.
As a rule, this is not dangerous and is quite understandable. But this is not always the case, since nosebleeds can be caused by quite serious reasons that you do not know about. Now we will consider what needs to be done if blood flows from the nose and in which cases it is worth contacting a specialist.
Causes of bleeding
- High blood pressure. The nose contains a large number of nerve endings and thin blood vessels that can rupture due to high blood pressure.
- Mechanical damage. Due to the fragility of the capillaries in the nose, blood can flow as a result of even a slight injury, for example, with a handkerchief in case of a cold. Also, during a cold, blood vessels swell and may burst.
- Dry air. Now this is one of the most urgent reasons, because in winter, in the cold or in a room where the air is dry, the nasal mucosa dries up, which can also bleed from the nose.

In addition to problems in the nasal cavity, there are a number of reasons related to disorders of the whole body, which can cause bleeding. For example, with certain diseases of the cardiovascular system, hypertension, atherosclerotic lesions of the cerebral vessels, problems with blood circulation in the cervical spine, blood circulation is disturbed, resulting in increased pressure in the nasal capillaries. Thus, nosebleeds can signal serious health problems.
Also, experts note that nosebleeds for no apparent reason can be a symptom of blood clotting problems as a result of a vitamin deficiency or an overdose of drugs.
Among other things, the cause of bleeding can be increased body temperature as a result of overheating in the sun, fever during the development of an infectious disease, and also in pregnant women as a result of a hormonal surge.
What to do if your nose bleeds?
- Sit upright with your head tilted slightly forward.
 Remember that it is forbidden to tilt your head back - blood should not drain into the throat area.
Remember that it is forbidden to tilt your head back - blood should not drain into the throat area. - Hold the soft area of the bridge of your nose for 10-15 minutes, breathe through your mouth.
- Put something cool on your nose.
- If bleeding continues after 15 minutes, call an ambulance.
Remember that frequent bleeding is a good reason to see a doctor.
Source: http://www.takzdorovo.ru
Tags: blood pressure, health, examination, prevention
Nosebleed: what to do?
Is your city Moscow?
- Pharmacies
- Catalog
- Discounts and promotions
- Loyalty program
- Jobs
- Help
- Rent
- Contacts
- COVID-19
September 1, 2021
Nosebleed, or epistaxis, is an unexpected and even frightening phenomenon.
Is it worth being alert when such an unpleasant symptom appears, what factors provoke it and how can one help in such a situation? Let's figure it out further.
Why does the nose bleed?
Bleeding from the nose is classified into "anterior" and "posterior". In the first case, the cause is damage to small blood vessels, this type is usually easy to stop. The second case is considered more dangerous, bleeding occurs due to injury to large vessels located deeper in the nose, so it cannot be dealt with at home. If the blood is "in full swing" - this is a reason for an urgent call for an ambulance.
Causes of nosebleeds include:
- nose injuries;
- thinning of the mucous membrane;
- inflammatory processes in the nasal cavity;
- vascular fragility, diseases of the heart and blood;
- sudden increase in blood pressure;
- uncontrolled intake of certain drugs (anticoagulants, NSAIDs, vasoconstrictor drops for the common cold).

What should I do if my nose bleeds?
At the moment when the bleeding begins, it is important to try not to be nervous, because the excitement makes our heart beat faster, which leads to more blood loss.
The bleeding stop algorithm is as follows:
- Sit straight, tilt your head forward.
- You should be comfortable: loosen the belt and collar, if necessary, open the window.
- Apply a cold, wet towel or ice to your nose, and place a warm heating pad on your feet. This will help constrict the vessels in your nose and dilate them in your legs, which will reduce bleeding.
- Clamp the bleeding vessel: squeeze the wings of the nose with your fingers for 3-5 minutes, the blood should stop. Also for this purpose, you can enter a gauze swab previously moistened with hydrogen peroxide into the nostril.
If you have completed all of the above steps and the blood continues to flow, call an ambulance immediately, because even a small loss of blood can lead to fainting.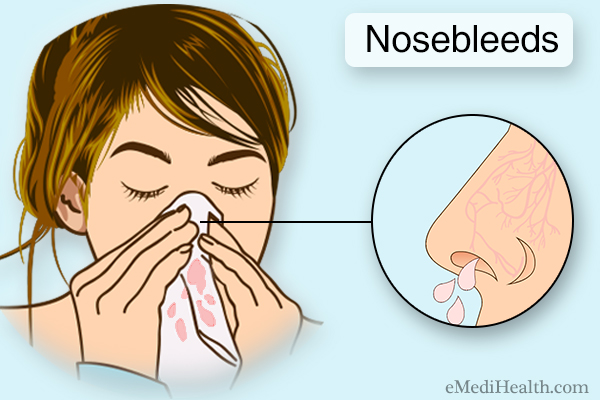
What to remember about nosebleeds?
- Do not lie down or let your feet be higher than your head - this will increase bleeding;
- Do not tilt your head: a large amount of blood in the stomach can cause vomiting, and blood can flow into the windpipe and make breathing difficult.
- After the bleeding has stopped, refrain from eating and caffeinated drinks to avoid high blood pressure and new bleeding.
Prevention of nosebleeds
Remember, frequent nosebleeds are a reason to see a doctor. The specialist will identify the cause of the problem and prescribe treatment, which may include the use of hemostatic agents, as well as drugs that improve blood circulation.
To prevent rebleeding, your specialist may recommend:
- Taking medications and vitamins to strengthen blood vessels.
- Proper diet. Adding foods rich in vitamin K and C to the menu. Vitamin K is responsible for blood clotting, they are rich in parsley, spinach, basil, bananas, avocados, broccoli, bran, etc.