A lot of cramping early pregnancy
Pregnancy Cramps: What They Mean and When to Worry
When you’re pregnant, your body undergoes many changes as it makes room for your little one (or two or more!). While some of these changes may be no big whoop, others, particularly things like cramping, can have you quickly searching Google for their causes.
While some mild pregnancy cramps are a normal symptom of your ever-expanding body, other cramps could indicate a serious problem. Pregnancy cramps can give many women anxiety, so it’s important to know the common reasons for their occurrence and what you should do about them.
We asked Srijaya Soujanya Nalla, MD, an OBGYN at Banner Health Clinic in Loveland, CO, to help explain the normal causes for cramping, abnormal causes and treatment recommendations for both.
[However, if you’re experiencing severe cramping with or without bleeding, stop reading this article and call your doctor immediately.]
What’s considered normal cramping during pregnancy?
“Early on in your pregnancy, it’s natural to feel some mild cramping in your lower abdomen at infrequent times as your body prepares for your growing baby,” Dr. Nalla said.
As your belly grows, so does your uterus. This may cause you to feel some slight pulling, tugging or stretching similar to menstrual cramps.
“Later in your pregnancy, you may experience some mild lower abdominal discomfort due to the tightening of your uterus. These are normal as long as they occur in irregular intervals and subside on their own,” Dr. Nalla said. “A common cause later in pregnancy is due to round ligament pain, a muscle that supports the uterus. As it stretches, it can cause some mild aches and pains.”
Other causes for mild cramping include:
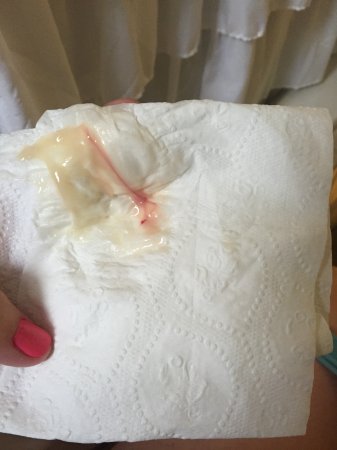
- Implantation bleeding
- Gas, bloating and constipation
- Sex
- Exercise
- Braxton Hicks contractions
What should I do for mild cramping while pregnant?
Time your cramps to see how regular they are and how often you feel them. “As long as they don’t fall into the abnormal category, there are some things that you can do to make them better,” Dr.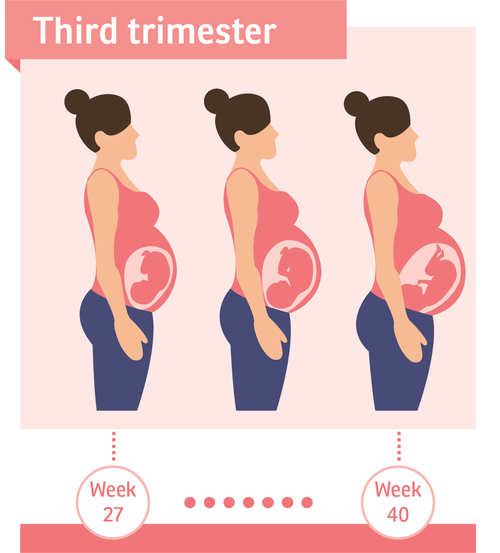 Nalla said. Some of these activities include:
Nalla said. Some of these activities include:
- Rest: Try to sit, lie down or change positions.
- Soak in the tub: Take a warm soak in the tub or a warm shower.
- Take some acetaminophen: Products like Tylenol are commonly used by pregnant women for pain and fever but talk to your health care provider first.
- Practice deep breathing: Use relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga or controlled breathing.
- Stay hydrated: Pregnant women need 50 percent more water. Keep a bottle of water on hand wherever you go.
When should I be concerned about cramping during pregnancy?
While cramping can be common, there are some serious causes of abdominal pain you shouldn’t ignore.
“Any cramping that is severe in intensity, occurs at regular intervals and progressively gets worse with time is abnormal,” Dr. Nalla said. “In addition, any amount of cramping associated with vaginal bleeding, increased/watery discharge, or pelvic pressure is not normal either. ”
”
Some causes for abnormal cramping may be due to:
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Miscarriage
- Preeclampsia
- Bladder infection or urinary tract infection
What should I do if I’m concerned about the cramping?
It’s normal to experience some mild cramping during pregnancy, but always speak with your health care provider if you are ever concerned or are experiencing the above warning symptoms.
“In some cases, an ultrasound can be done to help determine the cause for severe cramping,” Dr. Nalla said. “Sometimes severe cramping can be the first sign of an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage. Other times, it could be non-pregnancy related issues like a bladder infection or constipation which are quite common in pregnancy.”
When it comes to your health and the health of your baby, it’s better to err on the side of caution and talk to your health care provider.
You can find a Banner Health specialist near you by visiting bannerhealth. com or for general pregnancy-related questions, you can call the Banner Health Nurse Now at 844-259-9494 for free, 24/7 medical advice.
com or for general pregnancy-related questions, you can call the Banner Health Nurse Now at 844-259-9494 for free, 24/7 medical advice.
Related Pregnancy Articles:
- Is a Headache During Pregnancy Something to Worry About?
- If You’re Expecting and Your Hands and Feet Itch, It Could Be Cholestasis
- Expect the Unexpected: How Your Body Changes During Pregnancy
- Prenatal Screenings and Tests: What to Expect Every Trimester
- Driving While Pregnant: Common Questions Answered
Women's Health Pregnancy
Join the Conversation
Bad Cramps During Early Pregnancy: First-Trimester Lower Abdomen Pains
What do early pregnancy cramps feel like?
If you’ve been pregnant before, you’re probably very familiar with this cramping pain. Cramping during early pregnancy feels a lot like normal period cramps. The pain is usually located in the lower abdomen and typically only lasts for a few minutes.
Are cramps normal during early pregnancy?
Stomach cramps during early pregnancy are relatively common. If you get a few stomach cramps during the first trimester of pregnancy, it’s probably not a cause for alarm. These cramps are typically part of the normal physical changes in the body that occur in preparation for the baby.
Very early in your pregnancy, you may get cramps as well as light bleeding when the embryo is implanted into the wall of the uterus. This process can sometimes lead to implantation cramps and bleeding. As the pregnancy progresses, you may also feel cramping as your uterus changes and stretches to accommodate the baby.
In the following sections, we will talk about the causes of pregnancy cramps and when to call your health care provider.
Causes of cramping in early pregnancy
It is common to experience mild pain or cramps in your abdomen during pregnancy. In most cases, abdominal pain in early pregnancy is caused by normal bodily changes such as:
- Implantation — When a fertilized egg forms a blastocyst and implants into the lining of the uterine wall, it can cause a bit of cramping in your lower abdomen.
 This is known as implantation cramping and is often one of the first signs of pregnancy.
This is known as implantation cramping and is often one of the first signs of pregnancy. - Uterine growth — During the first two trimesters, there is rapid uterine growth to accommodate the growing fetus. This can also lead to early pregnancy cramping. As the ligaments and muscles that support the uterus also grow, you might experience sharp pain when you stand, change position, or sneeze/cough.
- Orgasm — If you have sex while pregnant, you may experience cramps after an orgasm. The pain may feel similar to a period cramp and usually goes away quickly. This doesn’t mean that you have to stop having sex if you’re pregnant, though. That being said, if the pain is severe and accompanied by bleeding, consult with your health care provider immediately.
In rare cases, early pregnancy cramps may be caused by the following pregnancy problems:
- Early miscarriage — In some cases, cramping may mean a miscarriage.
 But this is not always the case. When cramping is severe, prolonged, and/or occurs along with bleeding or vaginal discharge, make sure to seek immediate medical attention. An early pregnancy miscarriage is most likely to occur in the first trimester.
But this is not always the case. When cramping is severe, prolonged, and/or occurs along with bleeding or vaginal discharge, make sure to seek immediate medical attention. An early pregnancy miscarriage is most likely to occur in the first trimester. - Ectopic pregnancy — An ectopic pregnancy is when the fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus. For instance, it may attach to the uterine tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix. An ectopic pregnancy may result in severe abdominal cramps that may be accompanied by bleeding. If you experience severe cramping, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Signs of first-trimester cramps
Stomach pain in early pregnancy can be worrying, especially if it’s your first pregnancy and you’re not familiar with the physical sensations. While cramping during early pregnancy is usually normal, it’s still good to pay attention to your pregnancy pains.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
If something feels out of the ordinary, contact your health care provider as soon as possible. Understanding the signs and symptoms of early pregnancy (or first-trimester) cramps, can help you figure out what is normal and when to call your health care provider.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of early pregnancy (or first-trimester) cramps, can help you figure out what is normal and when to call your health care provider.
Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms during early pregnancy:
- Normal cramping pain — Normal pregnancy cramps are very similar to period cramps, which are usually not very severe. In early pregnancy, you may experience short cramps in your lower abdomen.
- Light bleeding — Light spotting during early pregnancy might be linked to implantation bleeding.
If you’re not sure if you’re pregnant and experience cramping along with nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, and spotting, make sure to take a pregnancy test. These can be early symptoms of pregnancy.
How to treat stomach cramps during the first trimester
Needless to say, painful cramps during early pregnancy can be inconvenient and uncomfortable. You might be experiencing physical and emotional changes, and adding cramps to your discomfort might feel overwhelming. Treating pregnancy cramps can help you feel more comfortable and as stress free as possible.
Treating pregnancy cramps can help you feel more comfortable and as stress free as possible.
If you’re experiencing cramps, here are a few tips for alleviating them quickly:
- Drink water. You are more likely to experience cramps if you are dehydrated. Make sure that you drink at least eight cups of water each day.
- Change positions. When you experience cramps, try shifting positions while lying or sitting down. Don’t put pressure on the source of the pain.
- Stretch and exercise. Try doing mild pregnancy exercises or stretch your body to soothe cramped muscles. In addition to relieving active cramps, this can also help prevent future ones.
- Gentle massage. A massage can stimulate blood circulation in your muscles, relieving uncomfortable cramps. Getting a gentle lower back massage might help relieve aches.
- Sleep. Try to get a good night’s sleep during early pregnancy as this makes you feel rested.
 Try to get enough sleep every night.
Try to get enough sleep every night.
When to see a health care provider about your early pregnancy cramps
Although early pregnancy cramps are usually normal and not life threatening, it’s also important to see your health care provider if the cramps become severe. Your health care provider can rule out any conditions such as miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or infectious diseases that may affect you or your baby. Here are a few signs and symptoms to watch out for. Make sure to see your health care provider if you experience any of these:
- Bleeding — If your cramps are accompanied by any amount of blood, consult your health care provider as soon as possible.
- Severe pain — If you experience severe cramps that don’t go away and are getting worse, head to the hospital immediately.
Why pulls the stomach in the early stages of pregnancy?
Why does the stomach pull in the early stages of pregnancy? This question often worries expectant mothers, and at times leads to panic. When is discomfort pathology, and when is it normal?
When is discomfort pathology, and when is it normal?
Pregnancy is a special time for a mother and her baby. After all, the connection between them is inextricable, and every negative influence or stress affects both of them.
Possible causes of pain
Every woman dreams of having an easy pregnancy and no cause for alarm. However, a very common complaint among pregnant women is pain in the lower abdomen of a pulling or aching nature.
Complaints are so common that it is necessary to clearly understand when pulling sensations during pregnancy are pathological and require immediate medical attention, and when they are completely physiological and require only general recommendations.
Of course, pain in the lower abdomen can appear at any stage of pregnancy, however, most often women notice their appearance in the early stages of pregnancy.
Painful sensations in the abdomen during pregnancy are very diverse both in subjective sensations and in their localization, in intensity of occurrence. Pain can appear both at rest and after any physical activity. Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in one place, or radiate to other areas.
Pain can appear both at rest and after any physical activity. Unpleasant sensations can manifest themselves in one place, or radiate to other areas.
Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen are rarely avoided during pregnancy. These sensations can occur not only in pathology. During pregnancy, the uterus increases in size, there is a tension in its ligaments and muscles. In addition, there is a displacement of the pelvic organs. All this leads to the appearance of pulling or aching sensations in the abdomen. All these phenomena are manifestations of physiological changes that occur to a woman during pregnancy.
Of course, this state of fear does not cause and does not require any intervention on the part of the doctor. However, pulling pains in the lower abdomen are not always a physiological process. It happens that this indicates that the pregnancy proceeds with pathology and requires medical adjustment.
That is why, if there are pulling or aching pains in the lower abdomen, it is necessary to contact an obstetrician-gynecologist in order to accurately determine the cause of the pain.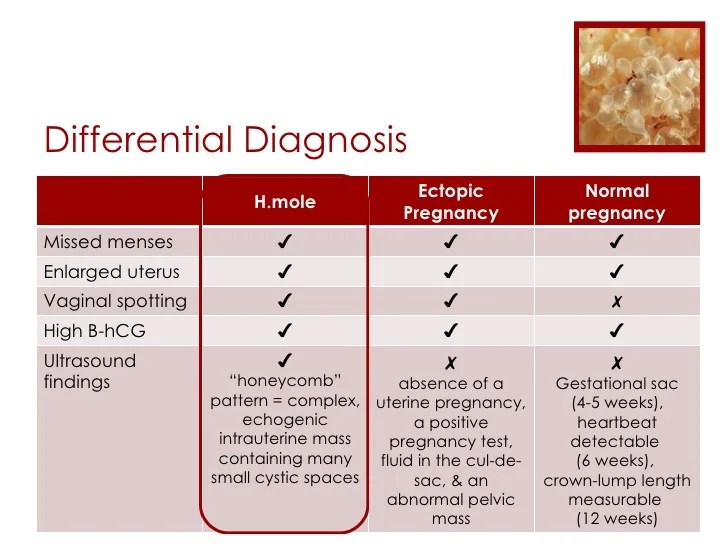
Never self-medicate. Remember that you are responsible not only for yourself, but also for the little man that you carry under your heart.
Abdominal pain during pregnancy may be:
- obstetric;
- "non-obstetric".
Pain associated with pregnancy may be developmental:
- physiological changes during pregnancy;
- threatened miscarriage;
- miscarriages;
- ectopic pregnancy.
Pain not associated with pregnancy may occur with:
- inflammatory processes;
- pathologies of the digestive system;
- surgical diseases;
- diseases of other organs or systems.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy as a variant of the norm
Not all pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy is a manifestation of pathology. Sometimes they can occur during the normal course of pregnancy.
As a physiological process, pain in the lower abdomen can occur in the following situations:
- sign of pregnancy;
- displacement of the pelvic organs by the growing uterus;
- stretching of the ligaments and muscles associated with the growth of the uterus.

Abdominal pain is a sign of pregnancy
Finding out that you are pregnant is now not a big deal, because there are pregnancy tests. In addition, a delay in menstruation can serve as evidence of pregnancy.
All this is good when menstruation is regular and delayed by at least 14 days. In this case, the pregnancy test may be positive. However, do not forget that not all tests are highly accurate, so it can show two cherished strips much later than we would like.
Therefore, it is necessary to pay close attention to the sensations of your body, because it signals the onset of pregnancy long before the manifestation of a delay in menstruation.
If you assume that pregnancy is possible, then listen carefully to your body: it can send you a signal in the form of pulling pains in the lower abdomen. At the same time, the pains will differ in their intensity: one woman will say that the pains are unbearable, the other will not notice them at all. Each woman is individual.
Each woman is individual.
If each menstruation is preceded by unpleasant pain in the lower abdomen or lower back, you may not understand that once again they are associated with the onset of pregnancy.
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy may be associated with the implantation process. To do this, you need to remember the process of fertilization of the egg by the sperm. After their fusion in the fallopian tubes, the fertilized egg enters the uterus under the influence of the movement of cilia in the fallopian tubes. The uterine endometrium is a loose mass where a fertilized egg is implanted.
The process of implantation is the insertion of a fertilized egg into the endometrium of the uterus. At this time, there is a violation of the integrity of the endometrium, which may be accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. In addition, sometimes slight dark bloody discharge may appear from the genital tract, which can be perceived as the beginning of another menstruation.
Threatened miscarriage
A fairly common cause of pain in the lower abdomen is a threatened miscarriage. This condition is individual and does not depend on physical exertion or complete rest, but on the condition of the woman and her unborn child.
Among the reasons that may cause a miscarriage may be:
- severe physical exertion;
- sexual contact;
- malnutrition of the ovum;
- genetic disorders and other causes.
Of course, this is not evidence that a miscarriage will not occur with complete rest. Miscarriage can occur due to genetic abnormalities, and due to stress. No woman is immune from the threat of pregnancy loss.
That is why attention and sensitivity to the state of your body is so necessary, which will in every possible way send signals that the pregnancy is not going the way you want.
Threatened miscarriage is accompanied by:
- aching or pulling pains in the lower abdomen;
- aching or drawing pains in the small of the back or sacrum.

- bloody discharge from the genital tract.
If you have pain in the lower abdomen, you need to see a doctor, as a threatened miscarriage, if medical assistance is not provided, can turn into an abortion that has begun, the treatment of which is much more difficult, if not completely useless.
An ambulance should be called if:
- pain in the lower abdomen gets worse;
- pains begin to radiate to other areas;
- painful sensations do not go away for a long time;
- bloody discharge from the genital tract appeared.
Increased pain
If the pulling pains in the lower abdomen are weak, do not increase and do not radiate to other areas, then you can come to the antenatal clinic in the daytime on your own. This will not threaten serious complications of your condition.
If the pain becomes more intense, does not go away at rest, you should not self-medicate, take drugs without a doctor's prescription.
Do not put anything on the stomach. Both hot and cold application can contribute to the onset of a miscarriage. In addition, with the threat of termination of pregnancy, this manipulation will not remove the pain.
Localized pain
When a threatened miscarriage occurs, pain of a pulling or aching nature disturbs the pregnant woman in the lower abdomen.
If the pains have a clear localization in a certain place, most often on the right or left, then a mandatory consultation with a specialist is necessary, since an ectopic pregnancy or surgical pathology, such as appendicitis, may develop.
Bloody discharge from the genital tract
If bloody discharge from the genital tract has joined the pulling pain in the lower abdomen, urgent medical attention is needed. This phenomenon may indicate a miscarriage that has begun.
The discharge may be scanty, spotting or copious, dark or bright. In any case, you can not do without consulting an obstetrician-gynecologist.
There are situations when there is no pain, but there is bloody discharge from the genital tract. This case also requires specialist advice.
Any bloody discharge from the genital tract may indicate a miscarriage. Only timely treatment can contribute to the preservation and prolongation of pregnancy.
In some cases, the appearance of bloody discharge from the genital tract may be a manifestation of a miscarriage, which requires immediate medical attention.
Illegal pregnancy
The fertilized egg does not always develop correctly. In some cases, there is a cessation of its division and death. Most often, missed pregnancy occurs due to any mutations. At the same time, the woman does not suspect that the pregnancy has stopped.
However, the dead fetal egg begins to be rejected on its own. At the same time, there are pulling pains in the lower abdomen, which are soon joined by bloody discharge from the genital tract.
When a miscarriage is diagnosed, curettage of the uterine cavity may be indicated. Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Conservative management is also possible, but this can only be determined by a specialist after consultation.
Ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy most often occurs as a tubal pregnancy, when the fertilized egg does not reach the uterus, and the implantation process occurs in the fallopian tube. At the same time, the development of the fetal egg can continue for a long time without any manifestations, up to 12 weeks of pregnancy. However, most often such a pregnancy is interrupted at 6 to 8 weeks.
The fertilized egg develops and grows, which causes pain in the right or left side of the lower abdomen. The pains are unilateral, are obsessive, tend to increase.
In addition to pain in the lower abdomen, bloody discharge from the genital tract appears, and the pain begins to radiate to the leg from the side of the pain. There may be unpleasant sensations of pressure on the rectum. Medical surgery is the only way to save a woman's life. Preservation of pregnancy is impossible.
"Non-obstetric" causes of pain in the lower abdomen
Inflammatory processes
Among the "non-obstetric" causes of pain in the lower abdomen, the most common are inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs. If earlier it was believed that there could be no inflammation in pregnant women, now it has been proven that a decrease in the immunity of a pregnant woman awakens all pathological processes in her body.
Pain in inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs differ in their intensity. At the same time, they occur in the lower abdomen and most often have a pulling or aching character.
Pathology of the digestive system
Very often, pulling pains in the lower abdomen can occur in a pregnant woman due to problems with the digestive tract. During pregnancy, there is a decrease in intestinal contractility. In addition, there are significant changes in the hormonal background of a woman. Therefore, very often pregnancy is accompanied by constipation and bloating. To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
To normalize digestion, a change in diet is recommended and mild laxatives can be taken.
Surgical pathology
Of the surgical pathologies that may be accompanied by pulling pains in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, acute appendicitis is the most common.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is obligatory to differentiate obstetric and gynecological diseases from appendicitis, since it has similar symptoms. There are pains in the lower abdomen, which most often occur in the navel or stomach, and then descend to the right iliac region. Nausea, vomiting, fever joins. The only treatment is surgery. In this case, the pregnancy is preserved.
Diseases of other organs or systems
In addition to obstetric and surgical causes, which can cause pulling pains in the lower abdomen in early pregnancy, other body systems may also be involved in the pathological process. The most common lesion is the urinary tract.
Cystitis
Due to the anatomical features of a woman, cystitis can occur at any time and in any condition, so pregnant women are just as susceptible to it as non-pregnant women.
The bladder, located in the lower third of the abdomen, may give false symptoms of threatened miscarriage.
Cystitis, in addition to pulling or aching pains in the lower abdomen, is accompanied by pain during urination, pain at the end of the act of urination. In addition, with cystitis, the urine may be stained with blood, and it is difficult to distinguish this from bloody discharge during a miscarriage.
In any case, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist, pass a general urine test, and then consult a urologist and treat the infection. Any infection can adversely affect the condition of the fetus, so timely treatment is the key to the normal development of your child.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
For more details, consult a qualified specialist at the Semeynaya clinic.
To clarify the prices for a gynecologist's appointment or other questions, follow the link below:
Treatment of abdominal pain - OSTEOMED clinic network Pain in the abdomen during pregnancy can be of different localization and in most cases they do not conceal anything threatening.
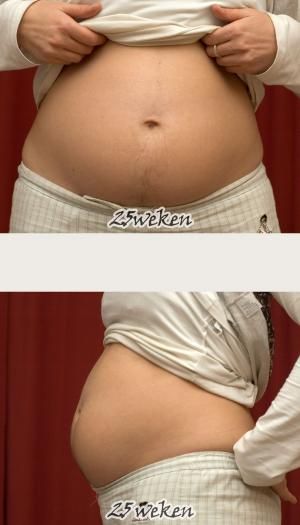 Basically, this is a normal reaction of the body to the increasing weight and growth of the uterus. The most hectic period of pregnancy is the first trimester, because ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and the like can take place here. Anxiety contributes to a lot of hormonal failure in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly reorganize in a new way, which will allow them to endure, give birth to a healthy child without problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, in each of these stages there is a certain hormonal jump, in which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable.
Basically, this is a normal reaction of the body to the increasing weight and growth of the uterus. The most hectic period of pregnancy is the first trimester, because ectopic pregnancy, spontaneous abortion and the like can take place here. Anxiety contributes to a lot of hormonal failure in the body. After all, during this period they need to quickly reorganize in a new way, which will allow them to endure, give birth to a healthy child without problems, and even set up proper lactation. Moreover, in each of these stages there is a certain hormonal jump, in which the emotional state of the pregnant woman is often changeable. Quite often, pain in the lower abdomen is felt during early pregnancy. If they do not bring much discomfort, there is no spotting, as well as other symptoms of a possible pathology or disease, then treatment is not required. At the beginning of pregnancy, such pains can be associated with hormonal changes, in the middle - with the rapid growth of the uterus, and at the end - with the preparation of the uterus for childbirth.
First trimester abdominal pain
If the stomach hurts during early pregnancy, then this does not always indicate some kind of pathology. With mild, rarely occurring and quickly passing pains, you should not worry. But for greater certainty, as soon as the test showed two strips, it is worth contacting a gynecologist as soon as possible. This will not only relieve the hassle, but also morally set you up for the upcoming event. With frequent aching, intense and cramping pains, it is urgent to find time and be sure to see a doctor. After all, this may indicate an ectopic pregnancy, which will require urgent surgical intervention. In addition, spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) can also be the cause. However, often, but not always, abdominal pain is accompanied by lower back pain and bleeding. If all indicators of pregnancy are normal, but the stomach still aches, this is explained very simply. The body is rebuilt, the tissues supporting the uterus become softer, looser, while the uterus itself grows and shifts, which contributes to tingling and sipping pains in the lower abdomen.
Pain in the lower abdomen
Pain in the lower abdomen during pregnancy, and especially in the later stages, are often due to internal pressure, that is, the growing uterus presses on the internal organs, thus disrupting their full-fledged work. The intestine reacts very sensitively to the hormones of "pregnancy" with a decrease in motility, a violation of peristalsis, which is a common cause of constipation, bloating and colic. To avoid this, you need to move more often, eat foods rich in fiber (fruits, vegetables, whole grain bread) and, of course, drink more fluids. Also, pain concentrated in the lower abdomen can be caused by a sprain due to the rapid growth of the uterus, or it can be triggered by premature detachment of the placenta. In the latter case, urgent medical attention is needed, because irreparable harm can be done to the mother and child. In this case, rapid delivery and immediate stopping of bleeding are indicated. In addition, during pregnancy, new or exacerbated chronic diseases can develop, which can also give signals in the lower abdomen. These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain. If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen.
These are cholecystitis, intestinal dysbacteriosis and others. In some cases, emergency surgery is indicated, and therefore it is worth paying attention to the slightest changes in the nature of the pain. If there is even the slightest doubt, you should urgently consult a doctor, otherwise it may be too late. In addition, problems with the genitourinary system are quite possible, which can also provoke pain in the lower abdomen.
Uterine tone
Uterine tone is painless or slightly painful uterine contractions. If a pregnant woman feels a spasm in the lower abdomen, the stomach becomes like a stone (this is especially noticeable in the second half of pregnancy) - this is a tone. The tone is diagnosed by a gynecologist during an external examination. The fact that the tone was recorded on the ultrasound, contrary to popular belief, is not an indication for treatment and hospitalization. The uterus is a muscular organ, and it is quite normal that it contracts periodically. The key word here is periodically, and, of course, painlessly and for a short time. With uterine tone, doctors recommend taking a horizontal position, lying on your side, you can take an antispasmodic pill and use a Papaverine suppository.
The key word here is periodically, and, of course, painlessly and for a short time. With uterine tone, doctors recommend taking a horizontal position, lying on your side, you can take an antispasmodic pill and use a Papaverine suppository.
Preliminaries
As a rule, there are minor pains in the lower abdomen during late pregnancy - these are preparatory contractions. Thus, the uterus prepares for the upcoming birth. In some women, the uterus begins to “prepare” like this at 32 weeks, in others for 1-2 weeks, and someone either does not notice these weak contractions, or considers this the norm, and therefore does not pay attention. It is very important to learn to distinguish between preliminary contractions and true ones, those that begin already in childbirth. Preliminary contractions last for several seconds, and they are not regular, unlike true ones, and do not intensify. It has been observed that nulliparous women are more likely to experience pre-contractions than multiparous women. This kind of pain is removed very easily by non-drug methods - you can just take a deep breath, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps.
This kind of pain is removed very easily by non-drug methods - you can just take a deep breath, lie down and relax. In many cases, taking a warm (not hot!) bath helps.
Gynecological pathologies
Those 4 reasons that we described above are variants of the norm. However, it is urgent to consult a doctor if these conditions are accompanied by bloody or brown vaginal discharge, clear or greenish vaginal discharge (they may turn out to be amniotic fluid), if the pain lasts for several minutes, is not relieved by antispasmodics and only increases when weakness appears, dizziness, flies before the eyes, etc. In a word, if the condition worsens. Such symptoms may indicate a threat or a spontaneous miscarriage, a frozen or ectopic pregnancy (when an early pregnancy, pain in the lower abdomen), premature or term birth, etc.
Other reasons
However, not always abdominal pain in expectant mothers occurs precisely because of gynecological problems and is a consequence of pregnancy. Here are some other possible reasons.
Here are some other possible reasons.
1. Cystitis and other diseases of the female excretory system. The ureter is located next to the internal genital organs, because this pain is often confused with "gynecological". Usually the pain occurs in such cases suddenly, has a "stabbing" character. Pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by frequent and painful urination. The urologist treats the genitourinary system. You should not start the disease, because it is caused by an infection that is unsafe for the child. Folk remedies, like bearberry, do not help well, but the doctor can prescribe effective medications that are approved for use by pregnant women.
2. Problems with the intestines: diarrhea, constipation, bloating. It should be noted that the last 2 are frequent occurrences in expectant mothers. Constipation is caused by a decrease in physical activity, displacement of internal organs due to the growth of the uterus, malnutrition, and insufficient fluid intake. Bloating is caused by the consumption of appropriate foods, as well as soda. Sometimes it is enough to go to the toilet for the pain in the abdomen to go away if it's constipation.
Bloating is caused by the consumption of appropriate foods, as well as soda. Sometimes it is enough to go to the toilet for the pain in the abdomen to go away if it's constipation.
3. Poisoning or rotovirus infection. Their symptoms are very similar. Usually it all starts with cramping pains in the lower abdomen, sometimes the pain goes to the navel. Then comes diarrhea and/or vomiting.
4. Appendicitis. If you have pregnancy, pulling pains in the lower abdomen do not always indicate tone or minor ailments, this may be a symptom of appendicitis, especially if the pain is right-sided, accompanied by fever. The correct diagnosis can be made by the surgeon. If the pain does not go away within an hour or two, but only increases, you should not attribute everything to an intestinal disorder and drink drugs like "smecta", this is very dangerous. If surgery is not carried out in time, it can lead to peritonitis.
And this is not all the reasons. Pregnant women, not for the first time, can quite easily distinguish the pain caused by uterine spasm from other types of pain. But in any case, it does not hurt to see a doctor.
But in any case, it does not hurt to see a doctor.
Upper abdominal pain
Pain at the top of the abdomen during pregnancy mainly occurs in the later stages. Their cause is the same uterus, which is constantly growing, slowly begins to reach the upper organs of the peritoneum. This primarily affects the liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, disturbances in which lead to symptoms such as belching, bitterness in the mouth. In addition, very often in the last trimester of pregnancy, the stomach throws gastric juice up the esophagus, causing considerable discomfort. To avoid these unpleasant moments, you need to eat a balanced diet, which should be eaten in small portions. It is desirable, of course, to exclude fried, spicy, too salty and too sweet.
Stitches
Stinging abdominal pain during pregnancy occurs for many reasons. This may be stagnation of feces in the intestines, which also provokes flatulence and constipation. By the way, the latter, in the future, can become one of the causes of hemorrhoids. It is also necessary to pay attention to the intensity of pain. If it is weak, rarely occurring, then you should not dwell on it. But if the pain is severe, especially sharp, you need to consult a doctor. Acute pain may be due to the development of appendicitis, inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), pancreas. Often, during the filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of pains of a pulling nature in this area, which turn into stitches, and become more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted.
By the way, the latter, in the future, can become one of the causes of hemorrhoids. It is also necessary to pay attention to the intensity of pain. If it is weak, rarely occurring, then you should not dwell on it. But if the pain is severe, especially sharp, you need to consult a doctor. Acute pain may be due to the development of appendicitis, inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), pancreas. Often, during the filling of the bladder, expectant mothers complain of pains of a pulling nature in this area, which turn into stitches, and become more painful when urinating, which indicates cystitis. In addition, stabbing pains may indicate the presence of infectious diseases, which are most often sexually transmitted.
Left abdominal pain
Abdominal pain on the left during pregnancy can be caused by various diseases of the internal organs. They can signal various lesions of the stomach and pancreas, the splenic flexure of the colon and, in fact, the spleen itself, as well as the left kidney. In addition, pain localized in the left side of the abdomen is possible when a hiatal hernia occurs.
In addition, pain localized in the left side of the abdomen is possible when a hiatal hernia occurs.
Abdominal pain on the right
Abdominal pain on the right during pregnancy most often occurs with diseases of the gallbladder, liver, duodenum, and right kidney. If the pain is accompanied by other symptoms, you should consult a doctor. For example, the symptoms of inflammation of the gallbladder include not only pain in the right side of the abdomen, but also nausea and vomiting (which are often confused with toxicosis). As a rule, following a salt-free diet with the complete exclusion of fatty, fried and spicy foods helps to cope with this problem. Possible formation of sand or kidney stones. Basically, during pregnancy, they try not to affect this organ, because it is of great importance when carrying a child. But if the doctor sees some kind of pathology or the hopelessness of the current situation, which can affect the further course of pregnancy, then measures will be taken to eliminate the cause of pain, with the maximum benefit for the fetus and woman.
Abdominal pain when walking
Often, the stomach hurts when walking in a pregnant woman, causing some discomfort. Basically, this problem concerns the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, that is, those periods when the uterus begins to actively grow, thereby causing a change in the center of balance. This is one of the reasons for the so-called duck walk. Many pregnant women are ashamed of this and try hard to walk the same way as they used to walk, which causes pain. The second reason is the softening of the joints located between the pelvic bones. Thus, the body prepares for the passage of the baby through the birth canal. To reduce or even get rid of pain, you should pay attention to the position of your body when walking. The correct position of the torso during pregnancy is to take the shoulders back, shifting the center of gravity from the toe to the heel, and the use of a special bandage for pregnant women will also bring invaluable help, which will not only reduce the load from the abdomen, but also remove tension from the spine.
Severe pain
The stomach hurts a lot during pregnancy during the course of some, at least not very good changes. Normally, there should be no severe pain. But if they have already arisen, then you should not endure them, it is imperative to consult with the district gynecologist. Severe pain can be the result of ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption, miscarriage, premature birth, as well as diseases associated with inflammation and chronic diseases of the internal organs. In principle, in any of these cases, it is necessary to call an ambulance as soon as possible, because untimely assistance can lead to disastrous consequences. The most important thing in this matter is not to miss the precious time that can give life to a small miracle, and maybe more than one.
Abdominal pain can be of different localization, intensity and etiology. If you have any doubts about this, you should immediately consult a doctor. If other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, and the like, join pain in the abdomen, you should urgently, without delay, call an ambulance.