6 week old baby fever
When Your Newborn Has a Fever
As adults, we have a tightly controlled thermostat to help regulate our body temperature. When we’re cold, we shiver to help raise our temperature, and when we’re too hot, we sweat to help cool ourselves down. These mechanisms, on the other hand, are not completely developed in newborns. What’s more, newborns lack the insulating fat layer that older babies and children develop.
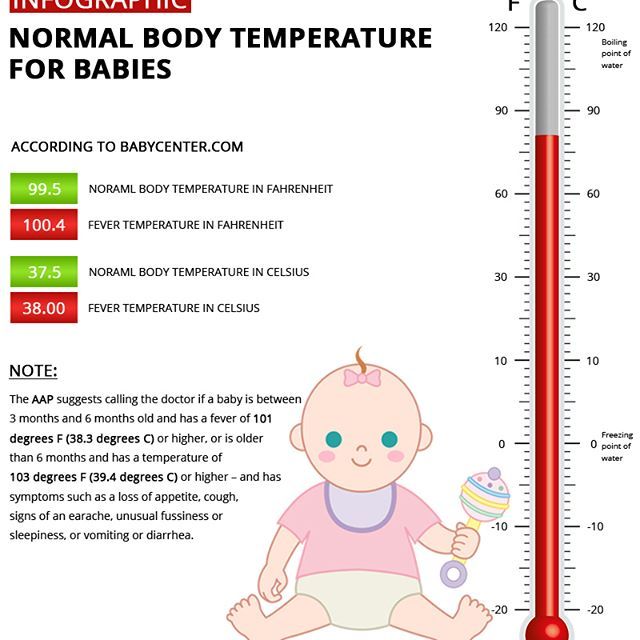
Because a newborn's temperature regulation system is immature, fever may or may not occur with infection or illness. However, fever in babies can be due to other causes that may be even more serious. Call your baby's doctor immediately if your baby younger than 2 months old has a rectal temperature of 100.4 degrees or higher. This requires an urgent evaluation by your doctor
In older infants and young children, a fever is any rectal temperature of 101 degrees or higher. Call the doctor if your 3-6 month old has a temperature of 101 or greater. With babies and children older than 6 months, you may need to call if the temperature is greater than 103, but more than likely, associated symptoms will prompt a call. A rectal temperature between 99 and 100 degrees is a low-grade fever, and usually does not need a doctor's care.
Fever in newborns may be due to:
-
InfectionFever is a normal response to infection in adults, but only about half of newborns with an infection have a fever. Some, especially premature babies, may have a lowered body temperature with infection or other signs such as a change in behavior, feeding, or color.
-
OverheatingWhile it’s important to keep your baby from becoming chilled, your baby can also become overheated with many layers of clothing and blankets. This can occur at home, near heaters, or near heat vents. It can also occur if your baby is over-bundled in a heated car. Never leave your baby alone in a closed car, even for a minute. The temperature can rise quickly and cause heat stroke and death.If your baby is overheated, he or she may have a hot, red, or flushed face, and may be restless.
 To prevent overheating, keep rooms at a normal temperature, about 72 to 75 degrees, and dress your baby the same way you feel comfortable at that temperature.
To prevent overheating, keep rooms at a normal temperature, about 72 to 75 degrees, and dress your baby the same way you feel comfortable at that temperature.
-
Low fluid intake or dehydrationSome babies may not take in enough fluids, which causes a rise in body temperature. This may happen around the second or third day after birth. If fluids are not replaced with increased feedings, dehydration (excessive loss of body water) can develop and cause serious complications. Intravenous (IV) fluids may be needed to treat dehydration.
In extremely rare cases, fever can signal a life-threatening disease called bacterial meningitis. If your infant has a fever greater than 101 degrees and is lethargic or you can't get him or her to wake up normally, you should take your infant to the emergency room immediately.
Taking Baby’s Temperature
For babies and toddlers up to 3 years old, taking the temperature rectally, by placing a thermometer in the baby’s anus, is best. This method is accurate and will give a quick reading of your baby's internal temperature.
This method is accurate and will give a quick reading of your baby's internal temperature.
Underarm temperature measurements may be used for babies ages 3 months and older. Other types of thermometers, such as ear thermometers, may not be accurate for newborns and require careful positioning to get a precise reading. Skin strips that are pressed on the skin to measure temperature are not recommended for babies. Touching your baby's skin can let you know if he or she is warm or cool, but you cannot measure body temperature simply by touch.
Oral and rectal thermometers have different shapes and one should not be substituted for the other. Do not use oral thermometers rectally as these can cause injury. Rectal thermometers have a security bulb designed specifically for safely taking rectal temperatures. To take your infant’s rectal temperature, follow these steps:
-
Place your baby across your lap or changing table, on his or her stomach, facing down. Place your hand nearest your baby's head on his or her lower back and separate your baby's buttocks with your thumb and forefinger.

-
Using your other hand, gently insert the lubricated bulb end of the thermometer one-half inch to one inch, or just past the anal sphincter muscle. Stop immediately if the thermometer meets resistance.
-
The thermometer should be pointed toward your baby’s navel.
-
Hold the thermometer with one hand on your baby's buttocks so the thermometer will move with your baby. Use the other hand to comfort your baby and prevent moving.
-
Never leave your baby unattended with a rectal thermometer inserted. Movement or a change in position can cause the thermometer to break.
-
Hold the thermometer for at least 1 minute or until an electronic thermometer beeps or signals.
-
Remove the thermometer.
-
Wipe the bulb.
-
Read the thermometer immediately and write down the temperature, date, and time of day.

-
Disinfect the thermometer with rubbing alcohol or an antiseptic solution.
If your baby's temperature is 100.4 degrees or higher, make sure he or she is not crying or dressed too warmly. Retake your baby's temperature again in about 30 minutes. If the temperature is still high, call your baby's doctor immediately.
How to Treat a Fever
If your baby’s temperature doesn’t warrant a call to the doctor, there are steps you can take at home to help lower the fever:
-
Bathe your baby in lukewarm water. Never use cold water or alcohol to bathe your baby because it may cause shivering and actually increase body temperature.
-
Dress your baby in light, comfortable clothing.
-
Make sure your baby is getting enough fluids to prevent dehydration.
-
NEVER give your baby aspirin to treat a fever.
 Aspirin has been linked to Reye's syndrome, a rare but potentially serious illness that affects the nervous system and can be debilitating or even fatal in children.
Aspirin has been linked to Reye's syndrome, a rare but potentially serious illness that affects the nervous system and can be debilitating or even fatal in children. -
Acetaminophen and ibuprofen are the two medications for children that help fight fever. Acetaminophen can be given to infants over 3 months without calling the doctor but children less than 6 months old should not be given ibuprofen. Read the instructions on the package or ask your doctor to be sure you give appropriate doses. Do not give more than the recommended dose of either medication. If your child is vomiting or dehydrated be sure to consult your pediatrician.
Fever (0-12 Months)
Is this your child's symptom?
- An abnormal high body temperature
- Fever is the only symptom. Your child has a true fever if:
- Rectal (bottom), Ear or Forehead temperature: 100.4° F (38.0° C) or higher
- Under the arm (armpit) temperature: 99° F (37.
 2° C) or higher
2° C) or higher - Caution: Ear temperatures are not accurate before 6 months of age
- Caution: Forehead temperatures must be digital. Forehead strips are not accurate.
Causes of Fever
- Overview. Almost all fevers are caused by a new infection. Viruses cause 10 times more infections than bacteria. The number of germs that cause an infection are in the hundreds. Only a few common ones will be listed.
- Viral Infections. Colds, flu and other viral infections are the most common cause. Fever may be the only symptom for the first 24 hours. The start of viral symptoms (runny nose, cough, loose stools) is often delayed. Roseola is the most extreme example. Fever may be the only symptom for 3 to 5 days. Then a rash appears.
- Bacterial Infections. A bladder infection is the most common cause of silent fever in girls.
- Vaccine Fever. Fever with most vaccines begins within 12 hours.
 It lasts 2 to 3 days. This is normal and harmless. It means the vaccine is working.
It lasts 2 to 3 days. This is normal and harmless. It means the vaccine is working. - Newborn Fever (Serious). Fever that occurs during the first 3 months of life can be serious. All of these babies need to be seen as soon as possible. The fever may be due to sepsis (a bloodstream infection). Bacterial infections in this age group can get worse quickly. They need rapid treatment.
- Meningitis (Very Serious). A bacterial infection of the membrane that covers the spinal cord and brain. The main symptoms are a stiff neck, headache and confusion. Younger children are lethargic or so irritable that they can't be consoled. If not treated early, can suffer brain damage.
- Overheated. The fever is usually low grade. Can occur during heat waves or from being overdressed. The temp becomes normal in a few hours after moving to a cooler place. Fever goes away quickly with rest and drinking extra fluids.
- Not Due to Teething.
 Research shows that "getting teeth" does not cause fevers.
Research shows that "getting teeth" does not cause fevers.
Fever and Crying
- Fever on its own shouldn't cause much crying.
- Frequent crying in a child with fever is caused by pain until proven otherwise.
- Hidden causes can be ear infections, kidney infections, sore throats and meningitis.
Normal Temperature Range
- Rectal. A reading of 98.6° F (37° C) is just the average rectal temp. A normal low can be 96.8° F (36° C) in the morning. It can change to a high of 100.3° F (37.9° C) late in the day. This is a normal range.
When to Call for Fever (0-12 Months)
Call 911 Now
- Not moving
- Can't wake up
- Severe trouble breathing (struggling for each breath; can barely speak or cry)
- Purple or blood-colored spots or dots on skin
- You think your child has a life-threatening emergency
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Trouble breathing, but not severe
- Great trouble swallowing fluids or spit
- Fever in baby less than 12 weeks old.
 Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen.
Caution: Do NOT give your baby any fever medicine before being seen. - Fever over 104° F (40° C)
- Shaking chills (shivering) lasting more than 30 minutes
- Nonstop crying or cries when touched or moved
- Won't move an arm or leg normally
- Dehydration suspected. No urine in over 8 hours, dark urine, very dry mouth and no tears.
- Weak immune system. Examples are sickle cell disease, HIV, cancer, organ transplant, taking oral steroids.
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Age 3-6 months old with fever
- Age 6-12 months old with fever that lasts more than 24 hours. There are no other symptoms (such as cough or diarrhea).
- Fever lasts more than 3 days
- Fever returns after gone for more than 24 hours
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Fever with no other symptoms and your child acts mildly ill
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
Care Advice for Fever
- What You Should Know About Fever:
- Having a fever means your child has a new infection.
- It's most likely caused by a virus.
- You may not know the cause of the fever until other symptoms develop. This may take 24 hours.
- For infants more than 3 months old, most fevers are good for sick children. They help the body fight infection.

- Use the ranges below to help put your child's level of fever into perspective:
- 100° - 102° F (37.8° - 39° C) Low grade fever: helpful, good range. Don't treat.
- 102° - 104° F (39 - 40° C) Average fever: helpful. Treat if causes discomfort.
- Over 104° F (40° C) High fever: causes discomfort, but harmless. Always treat.
- Over 106° F (41.1° C) Very high fever: important to bring it down. Rare to go this high.
- Over 108° F (42.3° C) Dangerous fever: fever itself can be harmful.
- Treatment for All Fevers - Extra Fluids:
- Fluids alone can lower the fever. Reason: being well hydrated helps the body give off heat through the skin.
- For shivering (or the chills), give your child a blanket. Make them comfortable.
- Offer your child extra water or other fluids by mouth. Cold fluids are better. Until 6 months old, only give extra formula or breastmilk.
- For all children, dress in 1 layer of light weight clothing, unless shivering.
 Reason: also helps heat loss from the skin.
Reason: also helps heat loss from the skin. - For shivering (or the chills), give your child a blanket. Make them comfortable.
- Caution: if a baby under 1 year has a fever, never overdress or bundle up. Reason: Babies can get over-heated more easily than older children.
- Fever Medicine:
- Caution: Do not give a baby under 3 months any fever medicine. Most of these babies will need to be seen.
- For fevers 100°-102° F (37.8° - 39°C), fever meds are not needed. Reason: fevers in this range help the body fight the infection. Fevers turn on the body's imune system. Fevers don't cause any discomfort. Fever meds are mainly needed for fevers higher than 102° F (39° C).
- Give an acetaminophen product (such as Tylenol).
- Another choice is an ibuprofen product (such as Advil) if over 6 months old.
- Goal of treatment: keep the fever at a helpful level. Most often, the fever meds lower the fever by 2° to 3° F (1 - 1.
 5° C). They do not bring it down to normal. It takes 1 or 2 hours to see the effect.
5° C). They do not bring it down to normal. It takes 1 or 2 hours to see the effect. - Do not use aspirin. Reason: Risk of Reye syndrome, a rare but serious brain disease.
- Do not use both acetaminophen and ibuprofen together. Reason: Not needed and a risk of giving too much.
- Pain: fever does not cause pain. If your child also has pain, it's from the infection. It may be a sore throat or muscle pain. Treat the pain, if it's more than mild.
- Return to Child Care:
- Your child can return to child care after the fever is gone. Your child should feel well enough to join in normal activities.
- What to Expect:
- Most fevers with viral illnesses range between 101° and 104° F (38.4° and 40° C).
- They may last for 2 or 3 days.
- They are not harmful.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- Any serious symptoms occur such as trouble breathing
- Fever goes above 104° F (40° C)
- Any fever occurs if less than 12 weeks old
- Fever without other symptoms lasts more than 24 hours
- Fever lasts more than 3 days (72 hours)
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.

Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 02/18/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023 Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
reasons, recommendations of doctors of the Central Medical Clinic CMD Perovo, st. Novogireevskaya
An increase in body temperature in a child is the most common reason for seeking emergency medical care. And of course, it is right when the child's parents, not self-medicating, seek medical help when their child has a fever.
However, it is useful for all parents to know some of the main causes of fever (fever) in a child and ways to normalize it.
Fever is divided into three main degrees of severity:
- A - fever from 37.0 to 37.9 degrees - mild or subfebrile fever, subfebrile condition;
- B - temperature increase from 38.
 0 to 39.0 degrees C - moderate fever;
0 to 39.0 degrees C - moderate fever; - B - from 39.0 to 41.0 - high fever;
- D - increase in body temperature above 41 degrees - excessive (life-threatening) fever.
Fever in an infant
The body temperature of a newborn child during the first 5 - 7 days of life fluctuates around 37.0, and in some children, an increase in body temperature during this period up to 38.0 - 39.0 is possible. This phenomenon is called transient hyperthermia of the newborn. In addition to hyperthermia, newborns are even more likely to have hypothermia, that is, a decrease in body temperature below normal. Due to the immaturity of the brain structures, not only newborn children, but also children of the younger age group up to 3-5 years old have a tendency to overheat quickly and to quickly hypothermia. Especially such a "volatility" of body temperature is typical, of course, for children in the first year of life. Therefore, if you, having measured the body temperature of a baby, found an increase in body temperature to 37. 0 - 37.4 degrees, do not rush to immediately call a pediatrician. It is enough to measure the body temperature, having previously unswaddled the child, or simply remove a warm blanket from him so that after 15-20 minutes the temperature returns to normal.
0 - 37.4 degrees, do not rush to immediately call a pediatrician. It is enough to measure the body temperature, having previously unswaddled the child, or simply remove a warm blanket from him so that after 15-20 minutes the temperature returns to normal.
Another common cause of an increase in body temperature in the first 1.5 - 2 years of a child's life is a reaction to teething. We wrote about this problem in a separate article on our website. In a nutshell, let me remind you that the reaction to teething in children is very individual. An increase in body temperature, most often, fits into the range from 37.1 to 37.6 degrees. Elevated temperature during teething usually lasts no more than 2-3 days, and in most children does not require the use of antipyretic drugs. However, in some cases, when teething, the child may have a fairly high fever of up to 38.0 and even up to 39.0 degrees. In this case, you can not do without the use of special anti-inflammatory gels for application to the gums and antipyretics in the form of suppositories (candles), such as Nurofen.
Prolonged, subfebrile fever in a child
If in infants the cause of sudden “temperature jumps”, most often, is the immaturity of the nervous system and the reaction to teething, then in older children, often prolonged subfebrile body temperature is kept against the background of psycho-emotional experiences, academic failure, conflict situations in the family. A separate problem is the active introduction of various electronic gadgets into the lives of modern children, sometimes from a very early age. So, for a child from 4 to 6 years old, who is already used to spending several hours a day at a computer or a game console, prolonged subfebrile condition can generally become commonplace, and parents, when they grab their heads from the thermometer readings, drag their child to neurologists , immunologists and infectious disease specialists, passing a bunch of tests, instead of just finding something more useful and healthy for the child.
Temperature in a newborn baby.
 How to bring down?
How to bring down? When the temperature rises in adults, the algorithm of actions is known. But here we have a newborn baby with a hot forehead - the worries of parents are absolutely understandable: you should be especially courteous with babies. Yes, and such little ones are unable to either say, or show, or make it clear what specifically worries.
In this article, we will figure out what is the normal temperature of a newborn baby and how to measure it correctly, where it comes from and what to do for new moms and dads in general - when to sound the alarm.
What is the normal body temperature of a newborn baby?
The rise in temperature is the main indicator of the functioning of the immune system. And he does not always report the course of an infectious disease! The fact is that the thermoregulation of the body of a newborn is imperfect. It simply reacts to the general temperature of the room in which it is located.
In a child of the first year of life, the body temperature can be 36, and 36.
8, and 37, and 37.5. And that's okay.
If the temperature in the room is above 25 degrees, the baby's body temperature can rise to 37. For the generally accepted 36.6 in the room where the small child is, it should not be higher than 22-23 degrees, and the baby should not be very warmly dressed.
What to do when a newborn has a temperature?
The very first thing is to undress the baby. Let it lie quietly for 15 minutes and measure the temperature again.
An increase in body temperature in a newborn baby up to 3 months is a reason to call a pediatrician ALWAYS.
From 3 months it is reasonable to assess the situation as a whole - look at the general condition of the baby. What can they be?
- If the temperature is about 37 degrees, the child is cheerful and active, eats well, without unnecessary whims, then it is worth keeping calm.
- If, even at a normal body temperature of 36.
 8-37, the child is apathetic, refuses to eat and is naughty a lot, or vice versa - he constantly sleeps - it is definitely worth calling a pediatrician. As well as when rising above 38-38.5, even without the slightest cold symptoms (runny nose, cough), or rash (by the way, we already wrote how to treat prickly heat). It is better to do this without delay - within the first two days!
8-37, the child is apathetic, refuses to eat and is naughty a lot, or vice versa - he constantly sleeps - it is definitely worth calling a pediatrician. As well as when rising above 38-38.5, even without the slightest cold symptoms (runny nose, cough), or rash (by the way, we already wrote how to treat prickly heat). It is better to do this without delay - within the first two days! - Pay attention to the trembling of the limbs in the baby (febrile convulsions), or rolling of the eyes at a temperature of 37.5-37.8! This is also a signal for an immediate call to the doctor.
- If the temperature of a newborn child rises, you take certain actions: for example, physical methods of cooling (undressing, airing the room) or giving antipyretics, but within 3-4 hours the temperature does not subside. Call the pediatrician!
- Maintaining an even temperature, for example, 37.5, but for more than 5 days is another reason to consult a doctor.

- Fever above 38-39 degrees. And she always has a reason. There are 2 types of fever: white and red type.
Consider the type of fever
- White type - hot forehead, but cold hands and feet with a marble tint. Plus there may be chills. This is the reaction of the nervous system and blood vessels to intoxication. In this situation, it is worth giving an antipyretic, and simply rubbing the arms and legs (massage) - to restore blood supply, relieve spasm from small vessels, due to which the limbs turn pale or turn blue.
- Red type - the child is all hot, wet from sweating. It is worth giving an antipyretic, wiping the baby with water, increasing heat transfer - offering more liquid.
!!! Children up to a year old cannot be rubbed with vinegar or alcohol solution, it is dangerous.
How to measure the temperature of a newborn baby?
The most famous thermometers are mercury and electronic.