36 weeks cervix soft
Telltale Signs Predict When Baby Will Arrive (or Not) | Methodist Health System
The final month of pregnancy is filled with excitement and anticipation. So many preparations have been made for the big arrival: Showers have been given, nurseries painted, cribs assembled and diapers purchased.
Then you wait.
You wait for some type of sign. Is that a contraction? Did I feel a trickle? I swear I lost my mucous plug! All signs that baby might be on the way.
Signs From an Exam
Each week during an office visit with their Methodist OB/GYN, many soon-to-be moms look to us for a sign things are getting close. One frequent request is to have a cervical exam…. that somehow a number means the time is near.
The truth of the matter is a number really doesn’t predict the arrival of a baby.
When a cervical exam is preformed your provider is looking for more than dilation of the cervix. Many things need to happen before it’s “all systems go.”
Signs From Baby’s Position
One of the first subtle signals a pregnancy is nearing its end is when the baby settles into the pelvis, also known as engagement. The head “drops” into the pelvis by a couple centimeters. This can happen from a few days or even just a few hours before the onset of labor.
Signs From Your Cervix
Next the cervix softens, going from a consistency similar to the tip of your nose to soft and squishy like your lips.
As the uterus practices contracting, the cervix moves from behind the baby’s head to forward on top of its head, closer to the opening of the vagina. This is referred to as the position of the cervix.
The cervix has to thin out or “efface.” I think of it like a mini-donut that starts out about two inches thick and slowly thins out. A cervix that is 50 percent effaced is about 1 inch thick, while 100 percent effaced means it is paper thin.
Signs of Dilation
Usually the last thing to happen is cervical dilation. As dilation slowly starts, you might lose a collection of mucous sitting at the inside of the cervix, up by the baby. This usually does not have much clinical significance. The "mucous plug" can actually reaccumulate!
The "mucous plug" can actually reaccumulate!
What happens with dilation? Visualize the mini-donut again. The cervical opening starts out like a dimple and gradually opens. One centimeter is the size of your fingertip, two centimeters the width of a penny and four centimeters is the size of a Ritz cracker. Ten centimeters, the width of a bagel, is how much the cervix needs to dilate to pass over the baby’s head.
Most of these things occur prior to the onset of labor. Some women are about two or three centimeters dilated when they start to go into labor, however you may not be dilated at all or sit around for weeks at four centimeters.
The number doesn’t indicate when labor is going to start, but it gives us a little reassurance things are moving forward. For some, it gives some false reassurance things will happen at any time. Others worry it never will.
There’s No Real Answer (Sorry)
So many women focus on all these signs to give an indicator when the time is near. But the truth is, no one knows when labor will begin. When it comes to anticipating delivery, it’s best to just leave the work up to Mother Nature, and time will tell when your new bundle of joy will arrive. He or she will be worth the (much anticipated) wait.
But the truth is, no one knows when labor will begin. When it comes to anticipating delivery, it’s best to just leave the work up to Mother Nature, and time will tell when your new bundle of joy will arrive. He or she will be worth the (much anticipated) wait.
Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and More
Soft Cervix: Causes, Symptoms, Treatments, and More- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Erica Hersh on May 13, 2019
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Erica Hersh on May 13, 2019
Your cervix is the lower end of your uterus, sitting at the top of your vagina. It can be closed or open, high or low, and soft or firm, depending on factors such as:
- where you are in your menstrual cycle
- if you’re pregnant
- natural positioning or feel
In most people, the cervix is usually closed and firm but it opens to let blood out during menstruation.
During childbirth, the cervix opens to allow the passage of the baby. For this to happen, your cervix naturally gets softer during pregnancy.
A soft cervix is what it sounds like — it feels soft to the touch. When firm, your cervix will feel like an unripe piece of fruit. When it gets soft, it feels more like ripe fruit. You might also hear that a firm cervix feels like the tip of your nose and a soft cervix feels like your lips.
In early pregnancy, your cervix will become soft and high in your vagina. This is one of the first things that happens after fertilization.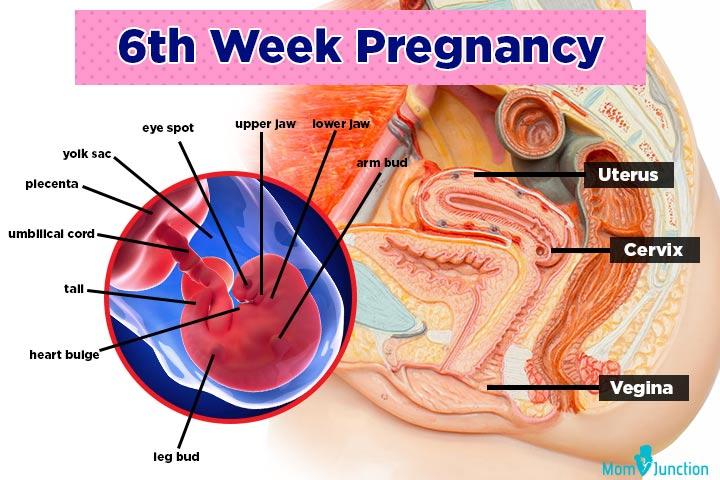 Your cervix will then harden but stay high.
Your cervix will then harden but stay high.
As your pregnancy progresses, the cervix will again get softer, which helps allow for childbirth. As the cervix softens, it also thins out (effaces) and opens (dilates).
This is a normal part of pregnancy. However, if your cervix opens or gets too soft too early, it can lead to preterm labor. This condition is called cervical insufficiency or incompetent cervix.
The cause of cervical insufficiency is usually unknown. However, having previous cervical trauma and certain conditions, such as connective tissue disorders, can put you at a higher risk.
You may not have any symptoms of cervical insufficiency early on, so it’s important to get regular prenatal care. This will help your doctor find and treat this condition early if you do have it.
Symptoms
If you do get symptoms, they may include:
- spotting, or light bleeding
- back pain
- pelvic pressure
- cramps
Treatment
Treatment is available for a cervix that opens and softens too early. This includes:
This includes:
- bed rest
- progesterone shots
- frequent monitoring with ultrasounds
- cervical cerclage, which is when your doctor puts in a stitch to hold your cervix closed until you get closer to full term
Treatment will depend on how far along you are in your pregnancy and other health factors.
Your gynecologist may have told you that you have a soft cervix. Or you may have felt it if you use certain fertility methods, such as the cervical mucous method. Either way, your cervix may just be naturally soft.
This isn’t a cause for concern if you’re not pregnant. It may become an issue if you get pregnant, but doesn’t necessarily cause problems for everyone with a naturally soft cervix.
Your cervix also gets softer at different points in your menstrual cycle. During ovulation, the cervix gets higher and often gets softer. It creates more mucus, and opens so that sperm can meet and fertilize an egg. Note that most hormonal birth control methods stop you from ovulating.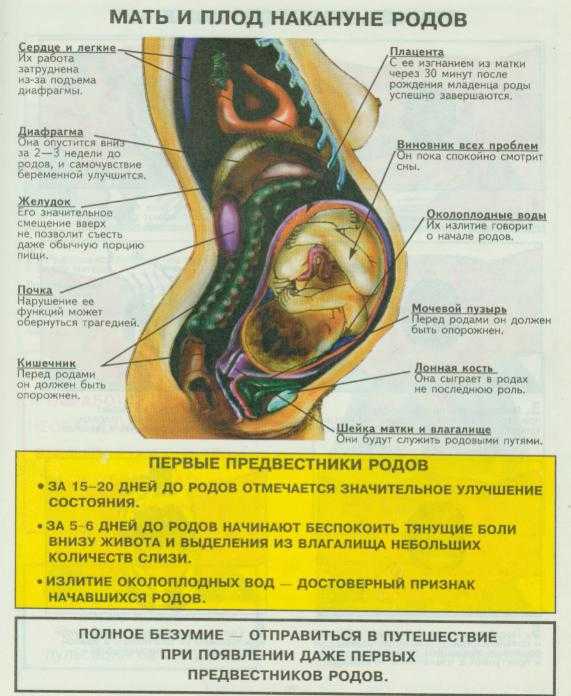
After ovulation, your cervix will drop and harden. It may be low but stay soft as you get closer to menstruating. If fertilization didn’t happen during ovulation, your cervix will open to allow menstruation to happen, but will stay low and hard.
A soft cervix could raise your risk of preterm labor. If you’re pregnant, your doctor can provide treatment that will help your cervix stay firm and closed, and decrease your risk of preterm labor.
If you’re not currently pregnant but have a history of cervical insufficiency during pregnancy, your cervix may just feel softer than it did before. This isn’t a problem when you’re not pregnant, but tell your doctor about your history if you do get pregnant again.
In most cases, a doctor is the one who will discover that you have a soft cervix. They can recommend medical treatment, if necessary.
However, if you check your cervix regularly and start noticing that it’s softer than it usually is at a particular time of the month, or you have other cervical changes, you should see your doctor. While a soft cervix alone is usually nothing to worry about, it’s usually a good idea to get changes in your body checked out.
While a soft cervix alone is usually nothing to worry about, it’s usually a good idea to get changes in your body checked out.
A soft cervix is usually nothing to worry about. In fact, your cervix naturally gets softer during ovulation. It also gets softer as a pregnancy progresses.
However, if you’re pregnant, a soft cervix when you’re not close to full term can raise your risk of preterm labor. If you know you have a soft cervix and are pregnant, talk to your doctor about treatment options.
Last medically reviewed on May 13, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Birth control pill.
 (2017).
(2017).
hhs.gov/opa/pregnancy-prevention/birth-control-methods/birth-control-pills/index.html - Cervix. (n.d.).
cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-terms/def/cervix - Hernandez-Andrade E, et al. (2018). A soft cervix, categorized by shear-wave elastography, in women with short or with normal cervical length at 18–24 weeks is associated with a higher prevalence of spontaneous preterm delivery. DOI:
10.1515/jpm-2018-0062 - House M, et al. (2009). Relationships between mechanical properties and extracellular matrix constituents of the cervical stroma during pregnancy. DOI:
10.1053/j.semperi.2009.06.002 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Incompetent cervix.
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/incompetent-cervix/symptoms-causes/syc-20373836 - Stages in the menstrual cycle. (2014).
ourbodiesourselves.org/book-excerpts/health-article/stages-in-the-menstrual-cycle/ - Timmons B, et al.
 (2010). Cervical remodeling during pregnancy and parturition.
(2010). Cervical remodeling during pregnancy and parturition.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2880223/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
May 13, 2019
Written By
Erica Hersh
Edited By
John Bassham
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Sullivan, PhD, MSN, RN, CNE, COI
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI — By Erica Hersh on May 13, 2019
related stories
Why Is My Cervix Closed If I’m Not Pregnant?
How Does the Cervix Change in Early Pregnancy?
How Does a Posterior Cervix Affect Pregnancy?
Cervix Before Period: How to Identify Changes Throughout Your Menstrual Cycle
Diagnosing and Treating a Short Cervix During Pregnancy
Read this next
Why Is My Cervix Closed If I’m Not Pregnant?
Medically reviewed by Karen Gill, M.
 D.
D.A closed cervix is normal during pregnancy, but it can also happen if you aren't pregnant. Learn what can cause a closed cervix when you aren't…
READ MORE
How Does the Cervix Change in Early Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Your cervix changes throughout your menstrual cycle and in pregnancy. If you know what to look for, you may be able to use these subtle changes to…
READ MORE
How Does a Posterior Cervix Affect Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
It's normal to have a posterior cervix for most of your pregnancy. But what if that's still the case as your due date approaches? Here's what to know.
READ MORE
Cervix Before Period: How to Identify Changes Throughout Your Menstrual Cycle
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.
 D., MSN
D., MSNYour cervix changes position many times throughout your period and overall menstrual cycle. Each change in position is tied to a particular phase in…
READ MORE
Diagnosing and Treating a Short Cervix During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
A short cervix is something you may not know you have. We'll tell you the importance of getting a diagnosis if you're pregnant.
READ MORE
Your Guide to Birth Control Pills: Types, Effectiveness, and Safety
Medically reviewed by Carolyn Kay, M.D.
Birth control pills are an option for people who are sexually active and can become pregnant. Find out if birth control pills are the right…
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Retroverted Uterus
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COIA retroverted uterus is a uterus that curves in a backwards position at the cervix instead of a forward position. Many women are either born with a…
READ MORE
Orgasm During Pregnancy: Why It’s Fine (and How It’s Different)
If you're wondering if a pregnant orgasm feels different, here's why.
READ MORE
Joy Is Our Birthright: Striving for Black Maternal Health Equity
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Black Maternal Health Week was created to reduce disparities Black women and birthing people face today. Here are 5 solutions that can help.
READ MORE
Anemia in Pregnancy: What It Is and How to Prevent It
Anemia is common during pregnancy. Here’s how to prevent and treat anemia in pregnancy with healthy foods, supplements, and more.

READ MORE
Soft cervix during pregnancy: what does it mean?
During pregnancy, a woman's organs undergo significant changes. During this period, doctors carefully monitor the condition of the expectant mother. Gynecological examination occurs two to three times during the entire pregnancy, provided there are no pathologies. The cervix is not disturbed once again, since it is responsible for the safety of the fetus.
The cervix in everyday life
The average menstrual cycle for a woman is 28 days. The normal state of the cervix is dense and closed. Color: light pink. During the period of ovulation, which falls on the 13th-15th day of the cycle, it softens, and the cervical canal expands. The level of the female hormone estradiol rises significantly before the rupture of the follicle, the body prepares for fertilization. All these changes occur for a better passage of sperm to the uterus, where the egg may already be.
Cervical opening for 1 finger. Opening of the cervix...
The process of childbirth is interesting for every expectant mother. Most multiparous women already imagine, with...
It must be remembered that a soft cervix in a healthy woman in the middle of the menstrual cycle is normal!
After ovulation, the cervix remains softened for several days, regardless of whether fertilization has occurred or not. After that, the cervical canal narrows, and the organ itself becomes dense.
Causes of abnormalities
There are a number of reasons why the structure of the cervix can be disturbed.
These could be:
- The first weeks of pregnancy.
- Period after childbirth and before them.
- Severe previous labor with multiple ruptures.
- Congenital abnormalities.
- Decreased muscle tone of the cervix (isthmic-cervical insufficiency). Both mechanical damage and hormonal disorders contribute to the occurrence.

- Inflammation of the female organs. Often this is the cause of female infertility.
- Previous abortions.
- Hormonal failures.
- Taking medication.
The first weeks after fertilization
After the attachment of the fetal egg in the uterine cavity, a complex process of restructuring the circulatory system begins, which is necessary for feeding the fetus. The ovaries, under the influence of the corpus luteum, begin to produce more and more progesterone, which is responsible for the texture of the cervix. There is a closure of the cervical canal and its filling with mucous contents. This provides protection of the fetal membranes from various bacteria. The cervical region itself becomes dense after a few weeks. This keeps the growing fetus in the uterus.
Cervical dilatation by 2 fingers: when to give birth? Symptoms...
Pregnancy becomes an exciting stage in the life of every girl. If multiparous...
But it happens that a soft cervix during pregnancy in the first trimester is a reason for taking medications. Your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy. Usually drugs containing progesterone are prescribed.
Your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy. Usually drugs containing progesterone are prescribed.
Pregnancy and "No-shpa"
"No-shpa" can also be prescribed by a doctor. During pregnancy in the early stages, there may be a threat of miscarriage due to the tone of the uterus. Drotaverine, which is the active ingredient of "No-shpy", relaxes smooth muscles, relieves spasms. For the fetus, it does not pose any danger. The drug is excreted from the body completely in a day.
In case of headache, toothache during early pregnancy, "No-shpa" can act as an analgesic. For problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you can also use this drug, but only after consulting a doctor.
In the second trimester, the use of "No-shpa" is inappropriate due to the effect of the drug on the cervix.
Softening of the cervix in the second trimester
During pregnancy, periodic stretching of the lower abdomen is not abnormal if it is not periodic. In this case, a doctor's examination may be necessary, since this is the only way to determine the soft cervix. It is possible to self-diagnose her condition, but this is a very risky procedure.
It is possible to self-diagnose her condition, but this is a very risky procedure.
A soft cervix during pregnancy at a period of 20-30 weeks threatens with premature birth or miscarriage, therefore, depending on the degree of softening and the reasons, the doctor prescribes:
- bed rest;
- hospitalization;
- pessary insertion;
- suturing;
- appropriate medical treatment.
Placement of a pessary and sutures
The scariest thing on this list for a woman is the pessary and sutures. And this is natural, since any intervention carries a percentage of risk. But this is what allows you to save the pregnancy and carry the child to the due date.
The insertion of a pessary or Meyer ring is painless and takes about 30 minutes. This is not a surgical intervention, so the feeling of fear should not arise.
The obstetric pessary resembles a soft rubber ring made of surgical silicone or plastic. Its purpose is to unload the uterus, which is under a lot of pressure. The doctor inserts it into the vagina and puts it on the soft cervix. In everyday life, this device does not interfere with the woman in any way and is not felt inside.
The doctor inserts it into the vagina and puts it on the soft cervix. In everyday life, this device does not interfere with the woman in any way and is not felt inside.
The Meyer ring is worn almost until childbirth. Remove the pessary in the hospital for a period of 38-39 weeks.
Stitching is performed only under anesthesia, so the woman does not experience any pain. The optimal period is 23-25 weeks. Before suturing, a thorough examination of the internal genital organs is carried out. Only experienced doctors are allowed to this procedure, so the expectant mother does not need to worry. The risk of complications in this case is minimal, but the chances of a happy ending of pregnancy are quite high.
Stress has a great influence on the cervix. That is why a pregnant woman needs to be protected from negativity, surrounded by her care. The expectant mother needs to be outdoors more often, devote sufficient time to physical activity. Reading, as well as watching positive films and programs, will help improve your mood.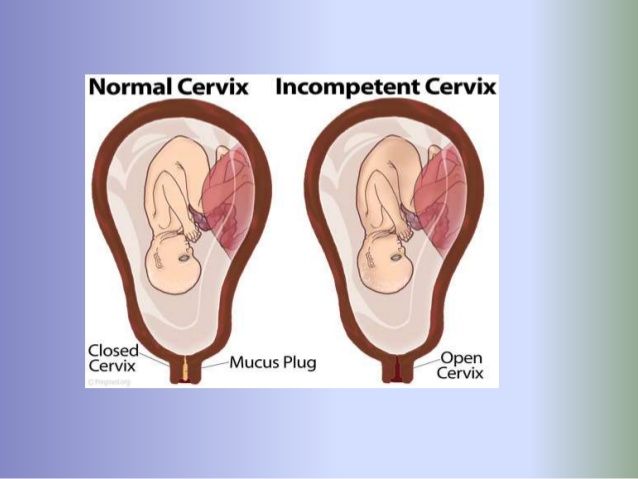
Bed rest has long been controversial. It has already been proven that walking does not affect the smoothing and softness of the cervix. And constant lying is fraught with other unpleasant consequences in the form of excess weight, weakening of muscle tone. If you trust your doctor, it is better to discuss this issue with him and listen to his opinion and your own feelings.
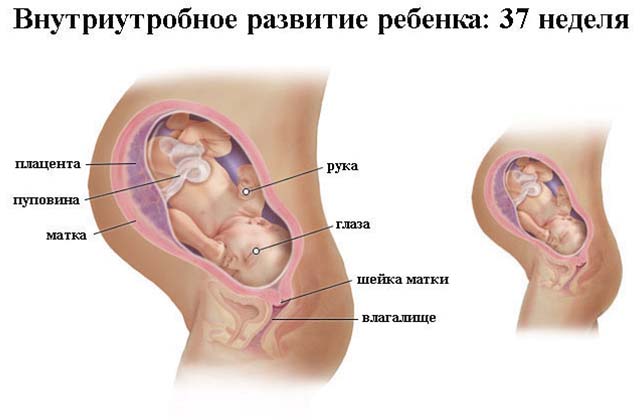
The cervix in the third trimester
From about 35-36 weeks of pregnancy, the body begins to prepare for childbirth. The cervix begins to smooth and soften. Her condition is determined upon examination. During the entire pregnancy, the length of the cervix is 3.5-4.5 cm, and after 37 weeks it shortens to 2.5 cm. The doctor can diagnose a soft cervix at 39 weeks of pregnancy. Also, upon examination, it can be seen that the internal pharynx is ajar by 1-2 cm. Therefore, childbirth will begin soon.
Cervical Preparation Procedures
If the doctor does not determine that the cervix is high and soft at 38-40 weeks, this indicates that the cervix is not ready for childbirth. In this case, means are used to accelerate the smoothing of the neck.
In this case, means are used to accelerate the smoothing of the neck.
For better softening, "No-shpa" can be prescribed. It has proven itself well, as a decrease in internal gaps has been noted with its use. Helps soften the cervix and male sperm, because it contains prostaglandin, which affects the maturation of the cervix. Also, in the process of having sex, when a woman reaches orgasm, the muscles of the uterus contract. This contributes to the launch of generic processes.
A doctor may prescribe special gels or vaginal suppositories containing the synthetic hormone prostaglandin. Cheap and effective kelp sticks are also used. They contain substances that provoke the opening of the internal pharynx, smoothing and softening the cervix.
Folk remedies
To make the cervix soft, you can resort to folk remedies, but only after consulting a doctor:
- Drink decoctions and infusions of wild rose, hawthorn, raspberry leaves and sage.
- Nipple massage.
 They must be gently and gently massaged for 10 minutes 3 times a day. It naturally produces the hormone oxytocin. It promotes contraction of the uterus.
They must be gently and gently massaged for 10 minutes 3 times a day. It naturally produces the hormone oxytocin. It promotes contraction of the uterus. - Evening primrose oil capsules. It is rich in fatty acids that stimulate the production of prostaglandins. The scheme of application is prescribed by a doctor.
- Eating fatty fish: mackerel, herring, sprat, silver carp and others.
If during pregnancy the question arises why the cervix is soft, and what it means, then at the beginning or middle of pregnancy this indicates deviations and the threat of interruption. And in the later stages - this is a natural phenomenon that prepares the body for childbirth.
What is the length of the cervix indicates the likelihood of preterm birth - clinic "Dobrobut"
Publication date: 2020-06-30
Cervicometry during pregnancy - what it is
Cervicometry is a transvaginal ultrasound technique that measures the length of the cervix.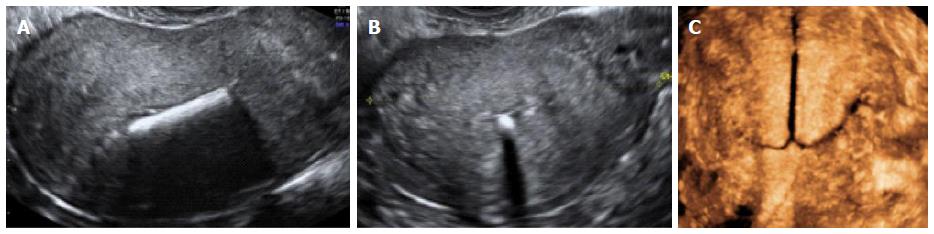 When the cervix is too short, there is an increased risk of preterm labor. How cervicometry is done and in what cases the study is indicated will be discussed below.
When the cervix is too short, there is an increased risk of preterm labor. How cervicometry is done and in what cases the study is indicated will be discussed below.
Norms of the length of the cervix by week of pregnancy
Cervicometry during pregnancy - what is it? This is the most reliable way to measure the length of the closed part of the cervix. The transvaginal ultrasound technique is superior in accuracy to the transabdominal method for determining the length of the cervix. Cervicometry is performed for all pregnant women, but for women who have had a history of preterm birth, the results of the study are especially important. These patients are shown cervicometry every 15 days in the interval from 14 to 24 weeks of pregnancy. For other pregnant women, a single examination at 20-24 weeks is recommended. The procedure is absolutely safe for the mother and fetus and is practically no different from a standard ultrasound examination.
Norms of the length of the cervix by week of pregnancy:
- 16-20 weeks: 40-45 mm;
- 25-28 weeks: 35-40 mm;
- 32-36 weeks: 30-35 mm.

If the cervix is 30 mm or more, the likelihood of preterm birth does not exceed the general population. What length of the cervix indicates a high risk of preterm birth? If a shortened cervix (less than 15 mm) is detected, urgent hospitalization and a set of measures to prevent preterm birth (cervical cerclage, progesterone administration) are indicated. If, according to the results of cervicometry, the length of the cervix is less than 25 mm, then the patient is given a conclusion “ECHO-signs of CCI” with a recommendation to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Cervicometry: Preparation and Technique
Empty your bladder before examining. Cervicometry is performed in the lithotomy position (the woman lies on her back with bent knees). The doctor gently inserts the ultrasound probe into the vagina towards the anterior fornix. In this case, a sagittal view of the organ is obtained. The mucosa of the endocervix serves as a reference point for determining the position of the internal os.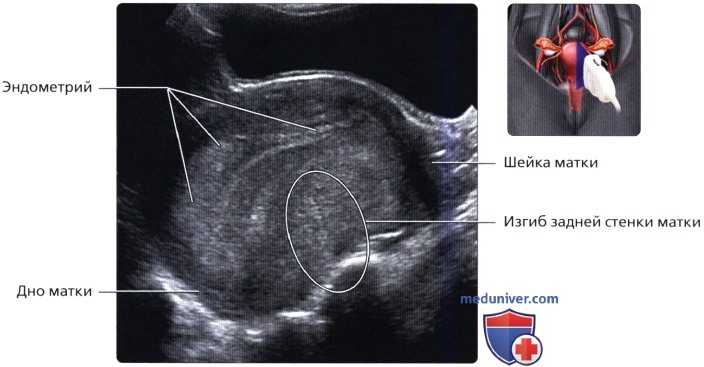 The doctor measures the closed part of the cervix, starting from the external os and up to the V-shaped notch of the internal os. This concludes the study and the patient is given a conclusion.
The doctor measures the closed part of the cervix, starting from the external os and up to the V-shaped notch of the internal os. This concludes the study and the patient is given a conclusion.
Transvaginal cervicometry detects a number of important clinical conditions that range from preterm labor to polyhydramnios (polyhydramnios). Detection of a short cervix by transvaginal ultrasound at 18–24 weeks of gestation is the most important predictor of spontaneous preterm birth. If the length of the cervix at 14–24 weeks of gestation is less than 15 mm, then with a probability of 50%, preterm birth may occur at a gestational age of up to 33 weeks. In women with a previous unfavorable anamnesis, a pattern can be traced: the shorter the cervix, the more likely recurrent preterm birth, and with a length of less than 10 mm, the probability increases to 90%. That is why it is so important during pregnancy to be observed by a gynecologist and timely conduct transvaginal cervicometry.
The price of ultrasound cervicometry can be found on our website https://www.dobrobut.com
Related services:
Gynecological Check-up
Colposcopy
Do you want to get an online explanation from the doctor of the Dobrobut MS?
Download our Google Play and App Store app
Our doctors
See all doctors 748
Our certificates
Certificate no. QIZ 804 468 C1
Certificate no. QIZ 804 469 C1
Certificate No. QIZ 804 470 C1
Certificate no. QIZ 804 471 C1
View all certificates
Request a call back
Enter your phone number
Other articles
Visceral therapy (visceral massage): indications and contraindications for
What is visceral therapy and what are the benefits.