34 week baby weight average
Baby size by week | BabyCenter
- Pregnancy
- Your Body
By Karen Miles
|
|
July 6, 2021
Find out how big your baby is during each week of their development with our fetal growth chart. From early in pregnancy, babies grow at different rates, so these numbers are merely averages. Your baby's actual size by week (in length and weight) may vary substantially.
Photo credit: Thinkstock
How big is my baby?
Wondering how big your baby is during each week of pregnancy? The numbers in our chart below can give you a sense of your baby's size. Keep in mind that your baby may be much smaller or larger than these averages. That's okay – after all, healthy babies can weigh less than 5 pounds or more than 9 pounds at birth.
Boy's measurements are different than girl's measurements, even this early. For the numbers on our chart, we've taken an average of boys and girls.
Another thing to note: Until 14 weeks, a baby's length measurement is given from head to bottom. After 14 weeks, the measurement given is from head to toe.
If you're curious, see our pregnancy timing article to learn how the weeks of pregnancy are counted. And if you don't know your due date, use our due date calculator to find out.
Fetal growth chart
| Gestational age | Length (US) | Weight (US) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
| (head to bottom) | (head to bottom) | |||
| 10 weeks | 1.22 inch | 1.23 ounces | 3.1 cm | 35 grams |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 inch | 1.59 ounces | 4.1 cm | 45 grams |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 inches | 2. 05 ounces 05 ounces | 5.4 cm | 58 grams |
| 13 weeks | 2.64 inches | 2.58 ounces | 6.7 cm | 73 grams |
| (head to toe) | (head to toe) | |||
| 14 weeks | 5.79 inches | 3.28 ounces | 14.7cm | 93 grams |
| 15 weeks | 6.57 inches | 4.13 ounces | 16.7 cm | 117 grams |
| 16 weeks | 7.32 inches | 5.15 ounces | 18.6 cm | 146 grams |
| 17 weeks | 8.03 inches | 6.38 ounces | 20.4 cm | 181 grams |
| 18 weeks | 8.74 inches | 7.87 ounces | 22.2 cm | 223 grams |
| 19 weeks | 9.45 inches | 9.63 ounces | 24.0 cm | 273 grams |
| 20 weeks | 10. 12 inches 12 inches | 11.68 ounces | 25.7 cm | 331 grams |
| 21 weeks | 10.79 inches | 14.07 ounces | 27.4 cm | 399 grams |
| 22 weeks | 11.42 inches | 1.05 pounds | 29.0 cm | 478 grams |
| 23 weeks | 12.05 inches | 1.25 pounds | 30.6 cm | 568 grams |
| 24 weeks | 12.68 inches | 1.48 pounds | 32.2 cm | 670 grams |
| 25 weeks | 13.27 inches | 1.73 pounds | 33.7 cm | 785 grams |
| 26 weeks | 13.82 inches | 2.01 pounds | 35.1 cm | 913 grams |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 inches | 2.33 pounds | 36.6 cm | 1055 grams |
| 28 weeks | 14.80 inches | 2. 67 pounds 67 pounds | 37.6 cm | 1210 grams |
| 29 weeks | 15.47 inches | 3.04 pounds | 39.3 cm | 1379 grams |
| 30 weeks | 15.95 inches | 3.44 pounds | 40.5 cm | 1559 grams |
| 31 weeks | 16.46 inches | 3.86 pounds | 41.8 cm | 1751 grams |
| 32 weeks | 16.93 inches | 4.31 pounds | 43.0 cm | 1702 grams |
| 33 weeks | 17.36 inches | 4.77 pounds | 44.1 cm | 1953 grams |
| 34 weeks | 17.84 inches | 5.24 pounds | 45.3 cm | 2377 grams |
| 35 weeks | 18.23 inches | 5.72 pounds | 46.3 cm | 2595 grams |
| 36 weeks | 18.62 inches | 6.20 pounds | 47. 3 cm 3 cm | 2813 grams |
| 37 weeks | 19.02 inches | 6.68 pounds | 48.3 cm | 3028 grams |
| 38 weeks | 19.41 inches | 7.13 pounds | 49.3 cm | 3236 grams |
| 39 weeks | 19.72 inches | 7.57 pounds | 50.1 cm | 3435 grams |
| 40 weeks | 20.08 inches | 7.98 pounds | 51.0 cm | 3619 grams |
| 41 weeks | 20.39 inches | 8.35 pounds | 51.8 cm | 3787 grams |
Thanks to Dr. Mark Curran, maternal-fetal medicine specialist, for his help in preparation of this table.
Where to go next:
- See the ultimate pregnancy to-do list for the first, second, and third trimesters
- Use our Baby Names Finder
- Video: Watch how your body changes to make room for your growing baby
Sources
BabyCenter's editorial team is committed to providing the most helpful and trustworthy pregnancy and parenting information in the world. When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
When creating and updating content, we rely on credible sources: respected health organizations, professional groups of doctors and other experts, and published studies in peer-reviewed journals. We believe you should always know the source of the information you're seeing. Learn more about our editorial and medical review policies.
Curran MA. 2019. Estimation of fetal weight and age. Perinatology.com. https://perinatology.com/calculators/Estimation%20of%20Fetal%20Weight%20and%20Age.htm [Accessed June 2021]
Deter RS et al. 2018. Individualized growth assessment: Conceptual framework and practical implementation for the evaluation of fetal and neonatal growth. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 208 (2 Suppl): S656-S678. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5882201/ [Accessed June 2021]
Fenton TR. 2003. A new growth chart for preterm babies: Babson and Benda's chart updated with recent data and a new format. BMC Pediatrics. https://www. ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC324406/pdf/1471-2431-3-13.pdf [Accessed June 2021]
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC324406/pdf/1471-2431-3-13.pdf [Accessed June 2021]
Gardosi J et al. 2018. Customized growth charts: rationale, validation and clinical benefits. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 218(2): S609-S618. https://www.ajog.org/article/S0002-9378(17)32486-9/fulltext [Accessed June 2021]
Hadlock FP et al. 1984. Estimating fetal age: Computer-assisted analysis of multiple fetal growth parameters. Radiology 152 (2) https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiology.152.2.6739822 [Accessed June 2021]
Hadlock FP et al. 1992. Fetal crown rump length: Reevaluation of relation to menstrual age (5-18 weeks) with high resolution real-time. US Radiology 182(2):501-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1732970/ [Accessed June 2021]
Hadlock FP, et al. 1991. In utero analysis of fetal growth: a sonographic weight standard. Radiology 181(1):129-33. https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiology.181.1.1887021 [Accessed June 2021]
Kiserud T et al. 2017. The World Health Organization fetal growth charts: A multinational longitudinal study of ultrasound biometric measurements and estimated fetal weight. PLoS Medicine 14(1): e1002220. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5261648/ [Accessed June 2021]
2017. The World Health Organization fetal growth charts: A multinational longitudinal study of ultrasound biometric measurements and estimated fetal weight. PLoS Medicine 14(1): e1002220. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5261648/ [Accessed June 2021]
Martins JG et al. 2020. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine Consult Series #52: Diagnosis and management of fetal growth restriction: (Replaces Clinical Guideline Number 3, April 2012). Practice Guideline. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 223(4): B2-B17. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32407785/ [Accessed June 2021]
Nicolaides KH. Et al. 2018. Fetal medicine foundation fetal and neonatal population weight charts. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 52(1). https://obgyn.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/uog.19073 [Accessed June 2021]
Show more
advertisement | page continues below
advertisement
Featured video
All pregnancy, parenting, and birth videos >
Get the BabyCenter app
The #1 app for tracking pregnancy and baby growth.
Download now
Fetal Chart from Baby My Baby
Free info for you and your baby! Text BABY to 511411
Search
Search for:
(crown to rump measurements)
| Gestational Age | Length (inches) | Weight (oz/lb) | Length (cm) | Mass (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 weeks | 0.63 | 0.04 oz | 1.6 | 1 |
| 9 weeks | .9 | 0.07 oz | 2.3 | 2 |
| 10 weeks | 1.22 | 0.14 oz | 3.1 | 4 |
| 11 weeks | 1.61 | 0.25 oz | 4.1 | 7 |
| 12 weeks | 2.13 | 0.49 oz | 5.4 | 14 |
| 13 weeks | 2.19 | 0.81 oz | 7.4 | 23 |
| 14 weeks | 3.42 | 1.52 oz | 8.7 | 43 |
| 15 weeks | 3.98 | 2.47 oz | 10.1 | 70 |
| 16 weeks | 4.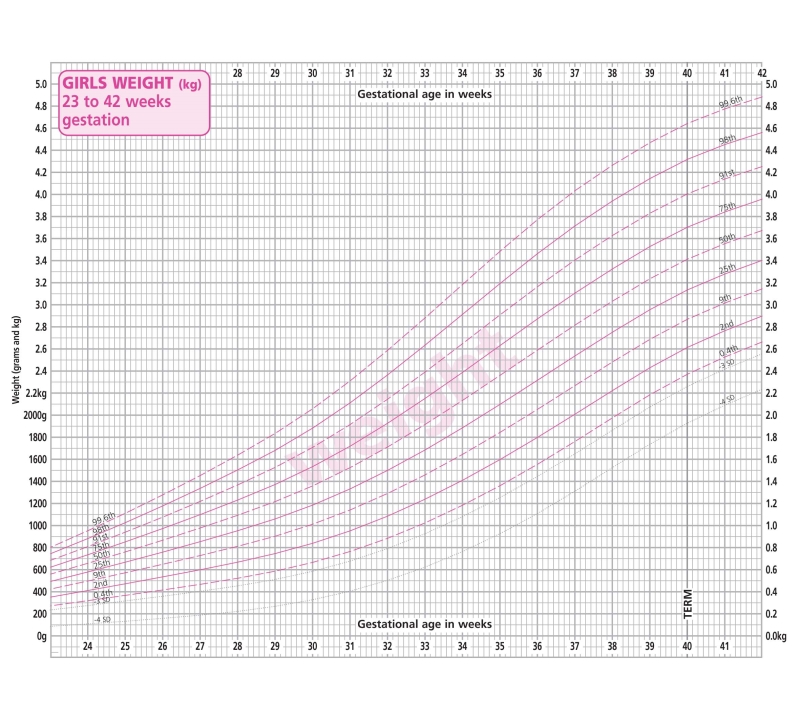 57 57 | 3.53 oz | 11.6 | 100 |
| 17 weeks | 5.12 | 4.94 oz | 13 | 140 |
| 18 weeks | 5.59 | 6.70 oz | 14.2 | 190 |
| 19 weeks | 6.02 | 8.47 oz | 15.3 | 240 |
| 20 weeks | 6.46 | 10.58 oz | 16.4 | 300 |
| 21 weeks | 10.51 | 12.70 oz | 26.7 | 360 |
| 22 weeks | 10.94 | 15.17 oz | 27.8 | 430 |
| 23 weeks | 11.38 | 1.10 lb | 28.9 | 501 |
| 24 weeks | 11.81 | 1.32 lb | 30 | 600 |
| 25 weeks | 13.62 | 1.46 lb | 34.6 | 660 |
| 26 weeks | 14.02 | 1.68 lb | 35.6 | 760 |
| 27 weeks | 14.41 | 1.93 lb | 36.6 | 875 |
| 28 weeks | 14.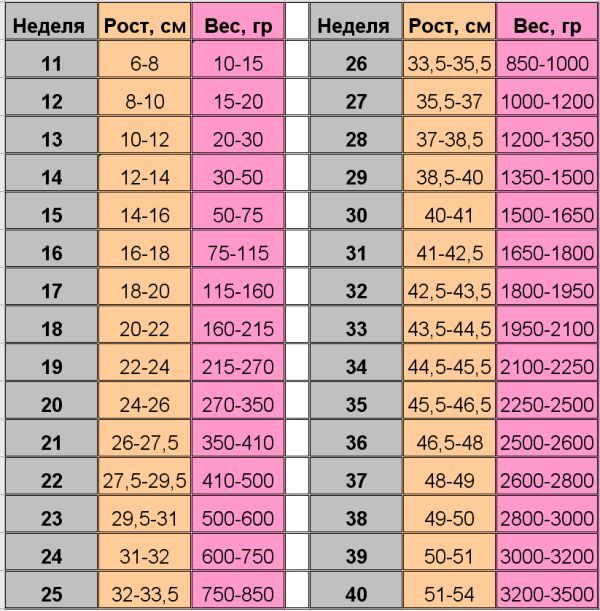 80 80 | 2.22 lb | 37.6 | 1005 |
| 29 weeks | 15.2 | 2.54 lb | 38.6 | 1153 |
| 30 weeks | 15.71 | 2.91 lb | 39.9 | 1319 |
| 31 weeks | 16.18 | 3.31 lb | 41.1 | 1502 |
| 32 weeks | 16.19 | 3.75 lb | 42.4 | 1702 |
| 33 weeks | 17.20 | 4.23 lb | 43.7 | 1918 |
| 34 weeks | 17.72 | 4.73 lb | 45 | 2146 |
| 35 weeks | 18.19 | 5.25 lb | 46.2 | 2383 |
| 36 weeks | 18.66 | 5.78 lb | 47.4 | 2622 |
| 37 weeks | 19.13 | 6.30 lb | 48.6 | 2859 |
| 38 weeks | 19.61 | 6.80 lb | 49.8 | 3083 |
| 39 weeks | 19.96 | 7.25 lb | 50.7 | 3288 |
| 40 weeks | 20. 16 16 | 7.63 lb | 51.2 | 3462 |
| 41 weeks | 20.35 | 7.93 lb | 51.7 | 3597 |
| 42 weeks | 20.28 | 8.12 lb | 51.5 | 3685 |
| 43 weeks | 20.20 | 8.19 lb | 51.3 | 3717 |
English
34th week of pregnancy what happens to the fetus
At the 34th week of pregnancy, the eighth month is coming to an end, which means there is less and less time left before delivery. Mom is actively preparing for the appearance of a new man in the family - she buys tiny rompers and undershirts, diapers, a cradle and other necessary things. Most parents already know the gender of the baby and have even decided on the choice of a name.
How does the child grow?
Almost all the systems of the fetus have been formed, and it is already ready for life outside the mother's body. For the 34th week of pregnancy, the following processes in the development of the child are characteristic:
- The breathing system is ready for the first breath.
- The baby's body weight is 2 - 2.5 kg, and the height reaches 45 cm. If the fetus weighs more, the woman is prescribed a special diet to control weight.
- Approaching the final stage of the formation of the nervous system.
- Lanugo - primary fluff growth and lubrication - disappears, replaced by subcutaneous fat.
- The adrenal glands work, the function of which is directly related to the woman's lactation. During this period, the concentration of the hormone responsible for breastfeeding in a baby is 10 times higher than in an adult.
- The baby often sucks his thumb, developing a sucking reflex for his own nutrition after birth.
- The digestive system is also constantly training - the baby swallows amniotic fluid.
- The kidneys excrete urine, the liver takes care of its functions of hematopoiesis and purification.
- The endocrine system actively produces hormones.
- The skin is smoothed and acquires a natural tone.

- As shown by CTG, the fetal heart rate is 110-160 beats per minute.
The bone and muscle system is also strengthened, taking away all calcium reserves from the mother's body. Therefore, a woman should consume more foods containing this element and vitamin complexes.
Important! At the 34th week of pregnancy, the activity of the baby may decrease slightly. But this has nothing to do with its development. It's just that a growing organism has little room for free movement. But if there are no tremors for a long time, this is a good reason to see a doctor.
What happens in the mother's body?
The less time left before childbirth, the more worried the woman. This is normal, but if all examinations have been completed and the results are satisfactory for a given period, there is no reason to worry.
Mom's tummy is already so big that it's hard for her to get up and sit down, move around because of the displaced center of gravity. It rises 15 cm above the navel and 35 cm above the pubic bone.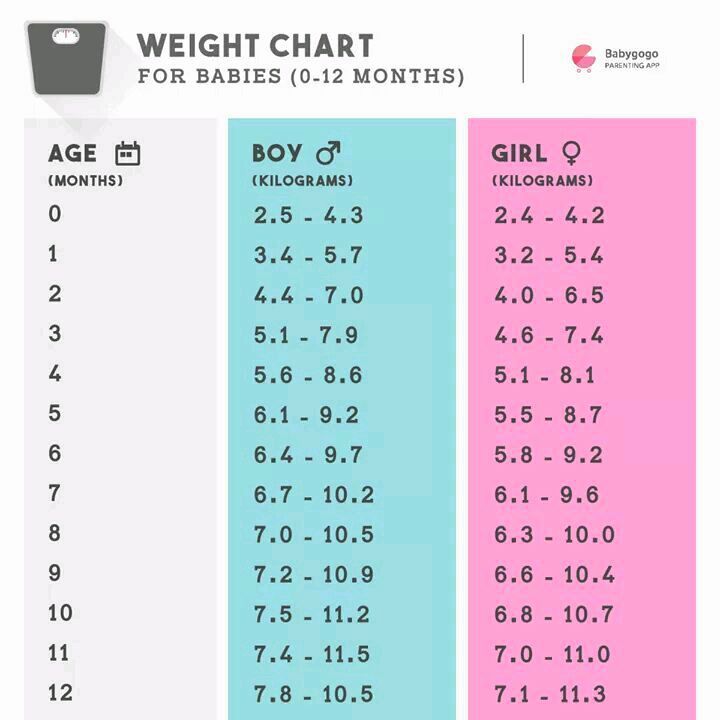 The breast increases in volume, and colostrum can already stand out from the nipples, although not necessarily.
The breast increases in volume, and colostrum can already stand out from the nipples, although not necessarily.
The body of a woman is intensively preparing for childbirth, soreness in the sacrum, pelvis, lower back is a normal phenomenon. But the nature of the pain must be monitored so as not to miss the harbinger of preterm labor.
Important! From the 34th week of pregnancy, a doctor's examination should take place every 10 days. So the woman can feel calmer - the condition of her and the child is under the reliable control of the doctor.
Swelling and fatigue of the legs may even increase. There is nothing dangerous in this, because the body weight of both mother and baby is growing. During the day, you need to give your feet a rest by placing them on a raised platform. Insomnia is also often a nuisance. This is usually due to the fact that the sleep patterns of a woman and a baby do not match. Often the child wants to play just when the mother goes to bed. If he often hiccups, you should also not worry - this is how the fetus prepares for the ability to breathe and eat on its own.
If he often hiccups, you should also not worry - this is how the fetus prepares for the ability to breathe and eat on its own.
At this stage of pregnancy, the baby feels everything, already shows his character, and he can be understood. He can express in the form of jolts dissatisfaction with food he did not like or loud sounds. He also feels the mood of his mother well. Therefore, a woman should get away from stress, keep calm. The good mood of the mother is reflected in the behavior of the child.
34 weeks of pregnancy - fetal development, mother's feelings. What happens to mom at 34 weeks pregnant?
At the end of this week, the placenta will reach the second degree of maturity. The permeability of the placental barrier, which gradually increased with increasing gestational age, will begin to decline. But remember that nicotine, alcohol, certain drugs, viruses, and infectious agents still cross the placenta easily.
If the pregnancy was uneventful, your baby is almost ready to be born. If he is born this week, he will most likely be able to breathe on his own and require little or no medical attention. Children born between the 34th and 37th weeks of gestation, of course, differ from full-term newborns, but very quickly catch up with them in development. The baby's kidneys and lungs have reached functional maturity. The nervous system develops, the child is getting better control of his body. Studies show that this week the fetal respiratory rate depends on the maternal blood glucose level.
If he is born this week, he will most likely be able to breathe on his own and require little or no medical attention. Children born between the 34th and 37th weeks of gestation, of course, differ from full-term newborns, but very quickly catch up with them in development. The baby's kidneys and lungs have reached functional maturity. The nervous system develops, the child is getting better control of his body. Studies show that this week the fetal respiratory rate depends on the maternal blood glucose level.
Most babies are head down by 34 weeks. If this has not already happened, the doctor may suggest an external obstetric rotation of the baby. During this procedure, the OB/GYN doctor pushes the baby from the outside through the wall of the uterus, helping him roll over on his head. The procedure is carried out for a period of 36-37 weeks in a hospital under the control of ultrasound and CTG.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.