30Th week of pregnancy weight gain
Third trimester weight gain: What to expect
Women experience many significant physical and emotional changes during pregnancy. Third trimester weight gain is an important part of later pregnancy and is not usually a cause for concern.
Many women will experience rapid weight gain during their third trimester. This is because the fetus typically gains the most weight in this time, according to the Office on Women’s Health (OWH).
In this article, learn what to expect during the third trimester, when to see a doctor, and some tips on how to gain weight safely during pregnancy.
The amount of weight a woman gains during pregnancy depends on several factors, including:
- their pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI)
- the number of gestations
- physical activity levels
- nutritional habits
The amount of weight a woman might expect to gain during her pregnancy depends on her pre-pregnancy BMI.
The following table contains pregnancy weight gain recommendations, in pounds (Ib), based on BMI from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC):
| BMI before pregnancy | Weight gain recommendations for women pregnant with one fetus | Weight gain recommendations for women pregnant with twins |
| 28–40 lb | 50–62 lb | |
| 18. | 25–35 lb | 37–54 lb |
| 25–29.9 | 15–25 lb | 31–50 lb |
| ≥30 | 11–20 lb | 25–42 lb |
Women who are pregnant should seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of the following symptoms:
- persistent nausea
- multiple episodes of vomiting every day
- sudden swelling of the face and hands after the 20th week of pregnancy, as this may indicate preeclampsia
- chronic fatigue
- shortness of breath
- extreme thirst or hunger
- vaginal spotting or bleeding
- cramping in the abdomen or pelvic region
- increased vaginal discharge
If a woman has concerns about third trimester weight gain, it is important that they speak with a doctor.
A fetus usually gains the most weight during the third trimester. They will gain an average of 5 lb and grow around 4–6 inches during the third trimester, according to the OWH.
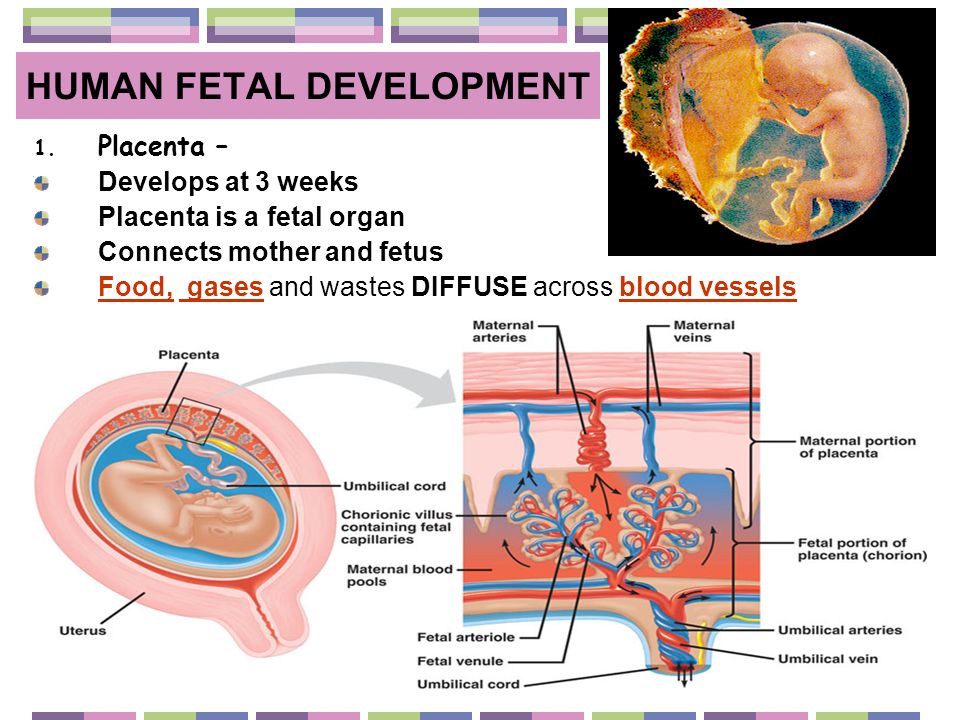
In addition to the weight from the growing fetus, the body also gains weight from:
- the placenta
- amniotic fluid
- breast tissue
- increased blood supply
- a larger uterus
- fat stores for delivery and breastfeeding
Other changes in the third trimester
The following changes and conditions can also occur during the third trimester of pregnancy:
- shortness of breath
- heartburn
- swelling of the feet, ankles, fingers, and face
- hemorrhoids
- swollen or tender breasts
- Braxton–Hicks contractions, which are “false alarms” that are less intense than labor contractions but help the body prepare for it
Women can expect to gain weight during pregnancy. However, in the United States, roughly 50% of all women exceed the recommended ranges for pregnancy weight gain, according to one 2017 study.
However, in the United States, roughly 50% of all women exceed the recommended ranges for pregnancy weight gain, according to one 2017 study.
Excessive weight gain during pregnancy can contribute to adverse health effects such as:
- gestational diabetes
- high blood pressure
- long term weight gain
- premature birth
- obesity
- a higher risk of medical conditions such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease
Pregnant women can gain weight safely using these following tips:
Work with a healthcare provider
At the start of a pregnancy, a woman’s healthcare provider will determine their weight gain requirements by measuring their BMI.
Healthcare providers will continue to monitor a woman’s weight gain throughout the pregnancy.
Eat a varied diet
Eating a balanced diet will provide vital nutrients, such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, that help sustain both the woman and the fetus.
Women can maximize their nutritional intake by consuming a variety of healthful foods and drinks, including:
- fruits and vegetables
- whole grains
- low fat or fat free dairy products
- proteins, such as poultry, beef, and fish
The Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion recommend that women who are pregnant eat 8–12 ounces of seafood each week.
However, certain fish and seafood may contain mercury, which can negatively impact the woman’s health and the fetus’s development.
Safe fish and seafood options include:
- cod
- salmon
- canned tuna
- herring
- oysters
- shrimp
- trout
- tilapia
- catfish
Seafood and fish to avoid during pregnancy due to their mercury content include:
- bigeye tuna
- king mackerel
- marlin
- orange roughy
- shark
- swordfish
- tilefish
Choosing seafood from sustainable sources can help ensure that it is of good nutritional quality.
Eat several small meals per day
Finishing large meals may present a challenge for pregnant women. Some, for example, may have trouble eating or keeping food down if they have symptoms such as appetite changes, nausea, and vomiting.
Also, toward the end of a pregnancy, the growing fetus and enlarged uterus can crowd the abdomen, leaving less space for the stomach to expand.
In these cases, women may wish to try eating several small meals throughout the day, which means that the body has less to digest in one sitting. This may help minimize uncomfortable digestive issues such as nausea and heartburn.
Track calories
Tracking calories can help a person meet their daily caloric needs without overeating.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, women with a BMI in the “normal” range before pregnancy should aim to consume an extra 340 calories per day during their second trimester and an extra 450 calories per day during their third trimester.
Exercise regularly
Exercising regularly can help reduce the risk of complications, such as preeclampsia, preterm birth, and obesity.
Getting regular exercise during pregnancy also offers numerous other benefits, including:
- reduced back pain
- reduced constipation
- improved cardiovascular health
- improved postpartum weight loss
Learn about the best types of exercise during pregnancy here.
In general, women should try to get 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week. This can include:
- walking
- cycling on a stationary bike
- swimming
- yoga
In this article, learn more general tips for gaining weight safely.
During the third trimester of pregnancy, women can expect to gain around 0.5 to 1 lb per week. Some ways to gain weight safely during pregnancy include eating a healthful and diverse diet and getting regular exercise.
Women can work with their healthcare team to track their weight gain throughout their pregnancy.
Weight Gain During Pregnancy: How Much Is Normal?
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
In this Article
- Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
- How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
- What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
- When to Call Your Doctor
Eating a healthy, balanced diet will help your baby get the nutrients they need and grow at a healthy rate. But how many extra calories do you really need?
But how many extra calories do you really need?
Though you do need some extra calories, it's not necessary to ''eat for two.'' The average pregnant woman needs only about 300 healthycalories more a day than they did before they were pregnant. This will help them gain the right amount of weight during pregnancy.
Ask your health care provider how much weight you should gain. A woman who was average weight before getting pregnant should gain 25 to 35 pounds after becoming pregnant. Underweight women should gain 28 to 40 pounds. And overweight women may need to gain only 15 to 25 pounds during pregnancy.
In general, you should gain about 2 to 4 pounds during the first 3 months you're pregnant and 1 pound a week during the rest of your pregnancy. If you are expecting twins you should gain 35 to 45 pounds during your pregnancy. This would be an average of 1 ½ pounds per week after the usual weight gain in the first 3 months.
It's especially important to gain the right amount of weight when you're expecting twins because your weight affects the babies' weight. And because twins are often born before the due date, a higher birth weight is important for their health. When carrying twins, you may need between 3,000 and 3,500 calories a day.
And because twins are often born before the due date, a higher birth weight is important for their health. When carrying twins, you may need between 3,000 and 3,500 calories a day.
Where Does the Extra Weight Go During Pregnancy?
- Baby: 8 pounds
- Placenta: 2-3 pounds
- Amniotic fluid: 2-3 pounds
- Breast tissue: 2-3 pounds
- Blood supply: 4 pounds
- Stored fat for delivery and breastfeeding: 5-9 pounds
- Larger uterus: 2-5 pounds
- Total: 25-35 pounds
Is It Safe to Lose Weight When Pregnant?
If a woman is very overweight when they get pregnant, their doctor may want them to lose weight. They should only lose weight under their doctor's care. But in most cases, women should not try to lose weight or diet during pregnancy.
How to Gain the Right Amount of Weight During Pregnancy
If your health care provider wants you to gain weight while you're pregnant, try these tips:
- Eat five to six small meals every day.

- Keep quick, easy snacks on hand, such as nuts, raisins, cheese and crackers, dried fruit, and ice cream or yogurt.
- Spread peanut butter on toast, crackers, apples, bananas, or celery. One tablespoon of creamy peanut butter gives you about 100 calories and 7 grams of protein.
- Add nonfat powdered milk to mashed potatoes, scrambled eggs, and hot cereal.
- Add extras to your meal, such as butter or margarine, cream cheese, gravy, sour cream, and cheese.
What if You Gain Too Much Weight During Pregnancy?
If you have gained more weight than your doctor recommended, talk to your doctor about it. In most cases, you'll want to wait until after delivery to lose weight.
Here are some tips to slow your weight gain:
- When eating fast food, choose lower-fat items such as broiled chicken breast sandwich with tomato and lettuce (no sauce or mayonnaise), side salad with low-fat dressing, plain bagels, or a plain baked potato. Avoid foods such as French fries, mozzarella sticks, or breaded chicken patties.

- Avoid whole milk products. You need at least four servings of milk products every day. However, using skim, 1%, or 2% milk will greatly reduce the amount of calories and fat you eat. Also, choose low-fat or fat-free cheese or yogurt.
- Limit sweet or sugary drinks. Sweetened drinks such as soft drinks, fruit punch, fruit drinks, iced tea, lemonade, or powdered drink mixes have lots of empty calories. Choose water, club soda, or mineral water to skip extra calories.
- Don't add salt to foods when cooking. Salt causes you to retain water.
- Limit sweets and high-calorie snacks. Cookies, candies, donuts, cakes, syrup, honey, and potato chips have a lot of calories and little nutrition. Try not to eat these foods every day. Instead, try fresh fruit, low-fat yogurt, angel food cake with strawberries, or pretzels as lower-calorie snack and dessert choices.
- Use fats in moderation. Fats include cooking oils, margarine, butter, gravy, sauces, mayonnaise, regular salad dressings, sauces, lard, sour cream, and cream cheese.
 Try lower-fat alternatives.
Try lower-fat alternatives. - Cook food the healthy way. Frying foods in oil or butter will add calories and fat. Baking, broiling, grilling, and boiling are healthier preparation methods.
- Exercise. Moderate exercise can help burn excess calories. Walking or swimming is usually safe for pregnant women. Ask your health care provider what exercise would be right for you before getting started.
When to Call Your Doctor
Talk to your doctor if you:
- Want to know a good target weight gain for you
- Think you are gaining too much weight
- Are losing weight during the second or third trimester
- Have an eating disorder that is keeping you from eating a healthy amount of food
- Need help setting a good menu plan to gain a healthy amount of weight
- Gain weight rapidly. This could be a sign of preeclampsia, pregnancy-related high blood pressure, a serious health issue
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Weight during pregnancy.
 What increase is considered optimal?
What increase is considered optimal? Why is excessive weight gain during pregnancy particularly harmful? What should be the calorie content of the diet? How to build your diet so that you can eat varied (and tasty), but at the same time not gain too much? Let's figure it out.
What makes up weight gain during pregnancy?
An increase in the subcutaneous fat layer during pregnancy is a normal and natural process.
While the baby is growing inside you, he needs energy and external protection. But during pregnancy, weight increases not only and not so much due to the adipose tissue of the mother: there is more fluid in the body, the uterus grows, the fetus and placenta develop, and the breasts increase in preparation for the feeding process.
Interestingly, weight loss during the period of toxicosis can later provoke its increase: the body will try to regain what was lost.
Expectant mothers especially actively gain weight in the second trimester and the beginning of the third, but closer to childbirth, a pregnant woman can even lose 1-2 kilograms. nine0004
nine0004
As long as the weight increases more or less evenly and does not go beyond the upper limit of the norm, there is nothing to worry about. But if your weight is rapidly going up, you should be wary.
How to correctly calculate the weight, and what increase is considered optimal?
In Russian obstetric practice, it is generally accepted that the total gain should not exceed 12 kg. for the entire pregnancy. Of these 12 kg. 5-6 accounts for the fetus, placenta, amniotic fluid, another 1.5-2 - for an increase in the uterus and mammary glands, and only 3-3.5 - for the fat mass of a woman. nine0004
But this is a general indicator, a kind of "average temperature in the hospital." The optimal increase is calculated individually and depends on the initial weight of the pregnant woman, her age, the number of fetuses and the size of the child (children), physical activity.
WHO recommends that optimal weight gain be calculated based on Body Mass Index (BMI).
It is determined by the formula: body weight (kg) / height squared (m).
| BMI | Recommended weight gain |
|---|---|
| 19.8-26 (normal body weight) | 12.5-15 kg |
| 26.1-29 (overweight) | 11.5 - 14 kg |
| over 29 (obese) | 7-9 kg |
How to calculate the optimal weight gain?
To do this, use the following chart:
- Calculate your BMI: divide your initial weight in kg. for height in meters squared. nine0072
For example, your "pre-pregnancy" weight was 60 kg with a height of 170 cm.
BMI = 60: (170 x 170) = 20.76.
- A BMI of less than 18.5 indicates underweight. Indicators from 18.5 to 25 are within the norm, from 25 to 30 are above the norm, and a figure greater than 30 indicates obesity.

- Now that you know your BMI, find the optimal weekly increase in the table and compare it with yours.
| Week of pregnancy | nine0033 Underweight before pregnancy (BMI less than 18.5)Normal pre-pregnancy weight (BMI 18.5 to 24.9) | Overweight before pregnancy (BMI over 30) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 0-0.9 kg | 0-0.7 kg | 0-0.5 kg |
| 6 | 0-1.4 kg | 0-1 kg | 0-0.6 kg |
| 8 | 0-1.6 kg | 0-1.2 kg | 0-0.7 kg |
| 10 | 0-1.8 kg | 0-1.3 kg | 0-0.8 kg |
| 12 | 0-2 kg | 0-1.5 kg | 0-1 kg |
| 14 | 0.5-2.7 kg | 0.5-2 kg | 0.5-1.2 kg |
| 16 | up to 3.6 kg | up to 3 kg | up to 1.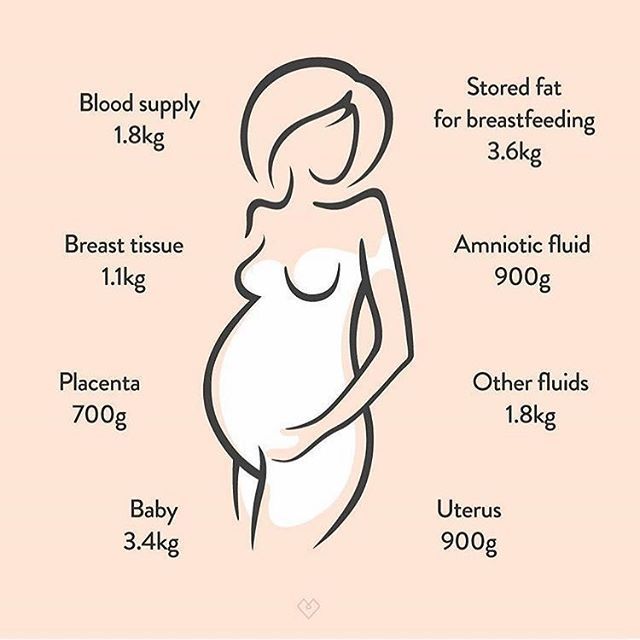 4 kg 4 kg |
| 18 | up to 4.6 kg | up to 4 kg | up to 2.3 kg | nine0039
| 20 | up to 6 kg | up to 5.9 kg | up to 2.9 kg |
| 22 | up to 7.2 kg | up to 7 kg | up to 3.4 kg |
| 24 | up to 8.6 kg | up to 8.5 kg | up to 3.9 kg |
| 26 | up to 10 kg | up to 10 kg | up to 5 kg |
| 28 | up to 13 kg | up to 11 kg | up to 5.4 kg |
| 30 | up to 14 kg | up to 12 kg | up to 5.9 kg |
| 32 | up to 15 kg | up to 13 kg | up to 6.4 kg |
| 34 | up to 16 kg | up to 14 kg | up to 7.3 kg |
| 36 | up to 17 kg | up to 15 kg | up to 7.9 kg |
| 38 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 8. 6 kg 6 kg |
| 40 | up to 18 kg | up to 16 kg | up to 9.1 kg |
Recently, doctors are increasingly talking about an individual approach and urge not to panic if the increase is slightly beyond the normal range. When assessing the state of health of a pregnant woman, the doctor focuses not only on weight, but also takes into account the results of tests and examinations and other important indicators.
Why is excessive weight gain dangerous?
Gaining extra pounds can lead to gestational diabetes, hypertension, preeclampsia, or cause a caesarean section.
In addition, excessive weight gain during pregnancy may increase the risk of obesity and associated cardiovascular disease.
What can I do to keep my weight within normal limits during pregnancy?
First of all, consult a nutritionist. If there is no such doctor in the antenatal clinic, it makes sense to contact a specialist on a commercial basis. He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself. nine0003 To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
He will develop an individual diet, which will contain all the useful elements, and will offer to keep a food diary. It will also tell you how to eat right and weigh yourself. nine0003 To prevent excessive weight gain during pregnancy, it is enough to follow simple rules of a healthy diet:
- Eat often and in small portions;
- Always keep a “healthy snack” on hand: fresh apple wedges, unsweetened crackers, dried fruit, or sugar-free yogurt;
- Refuse soda, chips, sausages and sausages;
- Minimize sweets;
- Avoid fast food;
- Limit the use of condiments, especially salt, which retains water in the body; nine0072
- Choose steamed dishes;
- Eat more fiber-rich foods such as whole grain bread, bran, vegetables;
The diet of a pregnant woman should be varied. Include grains, vegetables, fruits, dairy products, meat and fish, legumes, or nuts.
It must be remembered that expectant mothers should never starve and adhere to extreme diets.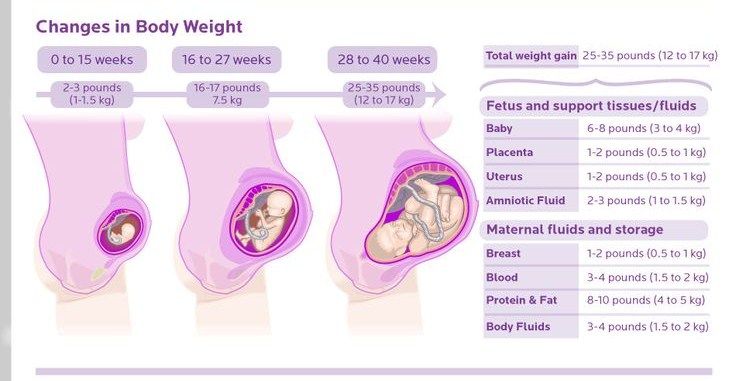
How many calories per day do you need during pregnancy? nine0006
It is difficult to calculate the energy value per day on your own, and then strictly adhere to a certain number of calories, and it is not necessary, unless it is recommended by a nutritionist or endocrinologist. On average, you can aim for 2000-2500 calories per day, but it is important to understand that the need for calories depends on many factors: age, initial weight, health status and level of physical activity.
When should I be on the alert?
Strictly speaking, it is better for a pregnant woman not to worry and entrust her condition to a doctor who will control the development of pregnancy, analyzes and monitor weight. It is important to take tests to determine the level of fasting blood glucose once a trimester. The appearance of glucosuria, an increase in fasting blood glucose (more than 5.5 mmol / l) or an hour after a meal (more than 7.7 mmol / l) indicate the possible development of "diabetes in pregnancy", in connection with which the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment . In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
In addition, a sharp increase in body weight can cause preeclampsia. nine0004
These and other diseases can be dangerous, which is why you need to carefully monitor the body weight during the gestation period, but remember that pregnancy is not the time for strict diets.
When using any materials from the site nutriclub.ru, a link to the site is required.
© Nutriclub, 2020
You will also be interested
- Nutriclub - healthy nutrition and child development nine0072
- Pregnancy
- Mom's health and well-being
- weight during pregnancy. What increase is considered optimal? - Nutriclub
29-32 weeks of pregnancy
29th week
Baby
At the 29th week of pregnancy, the baby continues to accumulate fat under the skin, folds and wrinkles are smoothed out, and as a result, the skin becomes smoother. The body is still completely covered with vellus hair, the amount of which is sharply reduced at this stage. But on the head, hair growth is activated. They become denser, darker and grow back quickly. In the womb, the baby often blinks, moves less actively, the movements become less intense and frequent, but smoother. There is less and less space left in the uterus, so the child is most often in the same position, spreading his limbs, exposing his head and pelvic end. His height by this week is 36-37 cm, and his weight is 1,200-1,300 g. At this time, the child takes a head presentation, since his head is heavier than his buttocks. But it is not uncommon for cases when in the body of water at 29week the baby is still in the breech presentation. The expectant mother should not worry about this, because there are still a few weeks for the child to take the correct position. Otherwise, breech presentation will be one of the good reasons for choosing a method of delivery.
The body is still completely covered with vellus hair, the amount of which is sharply reduced at this stage. But on the head, hair growth is activated. They become denser, darker and grow back quickly. In the womb, the baby often blinks, moves less actively, the movements become less intense and frequent, but smoother. There is less and less space left in the uterus, so the child is most often in the same position, spreading his limbs, exposing his head and pelvic end. His height by this week is 36-37 cm, and his weight is 1,200-1,300 g. At this time, the child takes a head presentation, since his head is heavier than his buttocks. But it is not uncommon for cases when in the body of water at 29week the baby is still in the breech presentation. The expectant mother should not worry about this, because there are still a few weeks for the child to take the correct position. Otherwise, breech presentation will be one of the good reasons for choosing a method of delivery.
Expectant mother
Women at 29 weeks of pregnancy still experience discomfort as the uterus continues to grow rapidly. This is especially felt by the organs that are located next to it - the bladder, stomach, and also the lower part of the large intestine. As the uterus grows, they move and occupy a rather uncomfortable position, which can affect their work in the future. That is why at this time women often complain of a feeling of heaviness after eating, suffer from heartburn. Heartburn occurs as a consequence of throwing stomach contents into the esophagus and is manifested by an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, as well as a burning sensation inside. During pregnancy, the muscles that separate the esophagus from the stomach become highly hormonal and relax. This creates such a situation. The rebuilt position of the stomach only worsens the situation. It is impossible to completely get rid of this condition. Of course, after childbirth, this problem will be solved by itself, but in order to somehow help herself, a woman should eat often, but in small portions. It is important that you chew your food thoroughly.
This is especially felt by the organs that are located next to it - the bladder, stomach, and also the lower part of the large intestine. As the uterus grows, they move and occupy a rather uncomfortable position, which can affect their work in the future. That is why at this time women often complain of a feeling of heaviness after eating, suffer from heartburn. Heartburn occurs as a consequence of throwing stomach contents into the esophagus and is manifested by an unpleasant aftertaste in the mouth, as well as a burning sensation inside. During pregnancy, the muscles that separate the esophagus from the stomach become highly hormonal and relax. This creates such a situation. The rebuilt position of the stomach only worsens the situation. It is impossible to completely get rid of this condition. Of course, after childbirth, this problem will be solved by itself, but in order to somehow help herself, a woman should eat often, but in small portions. It is important that you chew your food thoroughly. These simple rules will help reduce the risk of heartburn after eating. nine0004
These simple rules will help reduce the risk of heartburn after eating. nine0004
In addition, at the 29th week, expectant mothers notice frequent urination, which in most cases will accompany them until the very birth. Frequent urges are due to rapidly progressive pressure on the bladder. False urges are also not uncommon during this period. These are situations when the bladder is not yet full, but the brain has already sent a signal to urinate. In such cases, urination does not occur at all or passes in a minimal amount. During pregnancy, frequent and completely painless urination is not a sign of any disease. However, if symptoms such as pain, the appearance of cloudy urine join this process, you should immediately inform your doctor about this, who will be able to establish the cause of these changes and exclude or confirm pyelonephritis. nine0004
30th week
Baby
The 30th week is characterized by an intensive growth of the baby's muscle mass. He actively trains the muscles of the limbs, makes frequent movements, because during childbirth all muscle groups of the arms, legs, chest, and back must be prepared. In the second stage of labor or during the immediate birth of a child, there is an active contraction of the uterus, the muscles of the abdominal wall. The child moves independently. In this he is helped by a high tone of the muscles of the body, which greatly facilitates the movement through the birth canal, and also allows you to make translational movements. Also this week, the preparation of the internal organs of the fetus for extrauterine life continues. The baby's chest is actively training, expanding and contracting. Such movements are very similar to breathing. The lungs are washed with amniotic fluid, intensive production of surfactant continues. This substance ensures normal pulmonary respiration. You can also note the development of the alveoli. These vesicles in the lung tissue are necessary for gas exchange, because it is very important for the survival of the fetus to be ready for spontaneous breathing at the time of birth. It is worth noting that childbirth at the thirtieth week, which is due to any reasons, gives a high chance of independent breathing of the newborn, because the lung tissue is already mature and quite ready to perform its functions.
In the second stage of labor or during the immediate birth of a child, there is an active contraction of the uterus, the muscles of the abdominal wall. The child moves independently. In this he is helped by a high tone of the muscles of the body, which greatly facilitates the movement through the birth canal, and also allows you to make translational movements. Also this week, the preparation of the internal organs of the fetus for extrauterine life continues. The baby's chest is actively training, expanding and contracting. Such movements are very similar to breathing. The lungs are washed with amniotic fluid, intensive production of surfactant continues. This substance ensures normal pulmonary respiration. You can also note the development of the alveoli. These vesicles in the lung tissue are necessary for gas exchange, because it is very important for the survival of the fetus to be ready for spontaneous breathing at the time of birth. It is worth noting that childbirth at the thirtieth week, which is due to any reasons, gives a high chance of independent breathing of the newborn, because the lung tissue is already mature and quite ready to perform its functions. nine0004
nine0004
The fetus actively swallows the amniotic fluid, thereby contracting the digestive tract and stimulating the liver and pancreas. The liver in the body of any person performs an important function, cleansing the blood, and already at this stage of pregnancy is ready for full functioning. The formation of liver lobules by the thirtieth week is almost complete.
Amniotic fluid constantly flows and stimulates the kidneys to function intensively: the production of urine from the liquid part of the water. The daily rate of urine at this time in a child can reach 0.5 liters. nine0004
Active work is also observed in the pancreas, which produces hormones and enzymes from the amniotic fluid. One of the most important is insulin. Potentially, the pancreas is ready for full-fledged work already at this time and will be able to supply the body of the newborn with everything necessary.
Thus, at the thirtieth week, the internal organs of the fetus will be able to provide its vital functions in case of childbirth. Although their development actively continues until the very birth.
Although their development actively continues until the very birth.
The height of the baby is 37-38 cm, and the body weight is about 1300-1400 g.
Expectant mother
Expectant mother may experience active breast swelling in the thirtieth week, as well as the release of colostrum. This secret of the mammary gland - "primary milk" - is quite thick, has a white or yellowish tint. The release of colostrum can occur at different times, everything is very individual, but most often this happens after the 30th week of pregnancy. If you find such discharge in yourself, then this means that your body is actively preparing for the upcoming lactation. In the first few days after the birth of a child, colostrum from the woman's body will be released very actively until the appearance of breast milk. nine0004
During pregnancy, the fetus itself stimulates the production of colostrum. His adrenal glands produce a special hormone that, when interacting with placental hormones, activates the production of prolactin. Prolactin is a maternal pituitary hormone that is responsible for milk production after childbirth.
Prolactin is a maternal pituitary hormone that is responsible for milk production after childbirth.
At the 30th week of pregnancy, a woman receives a certificate of temporary incapacity for work, and also goes through the procedure for issuing maternity leave, which lasts only 140 days. nine0004
31st week
Baby
At 31 weeks of intrauterine life, the fetus weighs 1500-1600 g and has a height of 39-40 cm. This period is characterized by continued development of the nervous system. The brain grows at a high rate, the convolutions deepen, and the surface area of the cortex increases. The brain, as well as its departments, thanks to nerve connections, function as one. In the baby, periods of sleep and activity are already clearly changing. Sleep, as before, takes up most of the time. It is worth noting that the child closes his eyes during sleep, and opens them during the period of activity. The eyelids are so well developed that the fetus can already blink, open and close its eyes, squint and even squint at this stage. If bright light hits the stomach, it makes the baby close his eyes, which indicates a good level of development of his nervous system. nine0004
If bright light hits the stomach, it makes the baby close his eyes, which indicates a good level of development of his nervous system. nine0004
Expectant mother
By this time, the weight of the expectant mother increases by 7-8 kg. For a woman in position, it is important to monitor the rate of weight gain, because too much weight gain may indicate poor kidney function. So, per week, the weight should increase by no more than 300-400 g. In addition, it is important to monitor the presence of edema on the limbs and notify the doctor if they are found. Fluid retention is a sign of a pregnancy complication. Preeclampsia, which is also called late toxicosis, is characterized not only by swelling, but also by an increase in blood pressure, as well as the appearance of protein in the urine. nine0004
At the initial stages, preeclampsia can be completely asymptomatic, so a pregnant woman may not notice changes at all, feel great. That is why it is important to constantly visit a doctor who can already determine the presence of late toxicosis by analysis. Preeclampsia is one of the main causes of complications in both the mother and her child. It can provoke fetal growth retardation, hypoxia, adversely affect the functioning of the kidneys, the vascular system and the heart, as well as the woman's liver. nine0004
Preeclampsia is one of the main causes of complications in both the mother and her child. It can provoke fetal growth retardation, hypoxia, adversely affect the functioning of the kidneys, the vascular system and the heart, as well as the woman's liver. nine0004
Preeclampsia is mildly manifested in the form of edema. It can be corrected by normalizing the water-salt metabolism. The doctor may prescribe special diets for the pregnant woman, as well as drugs that will help cope with this condition.
Moderate or severe preeclampsia (nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia) requires urgent hospitalization. In a hospital setting, intensive care is provided. Nephropathy in a future mother manifests itself not only in the form of edema, but also in the form of high blood pressure, as well as the appearance of a protein in the urine, which is detected during tests. nine0004
Active progression of preeclampsia can cause a severe degree of nephropathy, which smoothly flows into preeclampsia. This condition is manifested not only by edema, high blood pressure, protein in the urine, but also by circulatory disorders in the brain. Women note frequent dizziness, pain, as well as nausea, vomiting, and changes in reflexes.
This condition is manifested not only by edema, high blood pressure, protein in the urine, but also by circulatory disorders in the brain. Women note frequent dizziness, pain, as well as nausea, vomiting, and changes in reflexes.
Preeclampsia at the most severe stage (eclampsia) is characterized by the manifestation of convulsive seizures, which can cause coma. That is why it is important for a pregnant woman to detect signs of preeclampsia in the early stages in order to avoid an increase in symptoms, which in the future can lead to irreversible consequences. nine0004
32nd week
Baby
This week of pregnancy is an important stage in the development of fetal immunity, in the blood of which there is a sharp increase in its own immunoglobulins. These substances protect the child from infection. At the time of delivery, the level of immunoglobulins will increase greatly under the influence of the mother's immunoglobulins entering the child's body. The last weeks of pregnancy are characterized by excellent permeability of the placental barrier, so protective cells from the mother's body easily pass into the baby's blood. nine0004
nine0004
In this week of pregnancy, the baby weighs about 1,700-1,800 g, and its body length is 41-42 cm. . The even distribution of fat under the skin allows the baby to change the color of the skin from bright red to pink.
The accumulation of subcutaneous fat is very important for thermogenesis. This process is necessary to constantly maintain body temperature at the same level. In an adult, these processes are controlled by special thermoregulation centers in the brain. At the time of birth, the child is not yet able to fully provide thermoregulation, so the presence of subcutaneous fat is so important for him to maintain the required body temperature. nine0004
Expectant mother
The third trimester of pregnancy can be manifested by pain in the back, pubis, as well as knee and hip joints. There may also be a feeling of fullness of the pelvic bones, pain. Such phenomena are present in many pregnant women, since the center of gravity changes, the spine shifts (due to the growth of the abdomen).