Why is my infant constipated
Symptoms, Treatment and When to Call a Doctor
Nationwide Children’s Hospital
Constipation (con-sta-PA-shun) in infants can worry parents. Most of the time, your baby is not really constipated. They may not have developed a routine for pooping yet. Some babies do not develop a bowel movement (BM) pattern for a while.
An infant’s BM pattern can change if their diet changes, like switching from breastmilk to formula, starting solid foods, or drinking less formula than usual. If your baby’s stool (poop) is not soft or easily passed, then they may be constipated.
In rare cases, constipation may be caused by a lack of nerves going to the intestines or by a problem with the way the intestine formed at birth. Your baby can be tested for these conditions if your health care provider feels it is needed.
Signs of Constipation
- less stools than their usual pattern
- straining more than normal to have a bowel movement
- a change in how the stool looks from soft and mushy to:
- small, hard pebbles, or like a large, round golf ball
- loose and watery
- abdomen (belly) bloated or swollen with gas
- painful cramps
Treatment
- If your baby is not eating baby food yet, you may give 1 to 2 ounces of 100% fruit juice (pear, prune, cherry, or apple) once a day.
Stop the juice if their stools become too loose.
- If they are old enough to eat baby foods, feed them pureed pears, peaches, or prunes instead of giving them juice.
- If your baby eats cereal, it may help to give oatmeal, wheat, or barley cereal. Rice cereal can cause constipation in some children.
- Sometimes giving your baby a warm bath to relax them or exercising their legs, like riding a bicycle, will help stimulate the bowels to move (Picture 1).
- If it has been a few days since your baby has pooped and the juice or pureed food has not worked, then you can try a glycerin suppository. Place your baby on their back. Gently push the suppository into their anus (bottom). Suppositories are meant for occasional use.
- Contact your baby’s health care provider before giving them laxatives, baby mineral oil, or enemas to treat constipation.
Medical Therapy
Your child’s health care provider may order the following treatments:
- Give your child medication.

- Check your child’s temperature using a digital, rectal thermometer. Put a small amount of petroleum jelly (Vaseline®) on its tip before inserting into the rectum. Taking a rectal temperature may stimulate the baby to pass stool.
When to Call the Health Care Provider
Call the health care provider if any of the following occurs:
- Your baby is irritable and seems to be having stomach pain. Infants will pull their legs up to their stomach and cry when they are in pain.
- Your baby has constipation and develops vomiting, and their belly looks like it is bloated or filled with gas.
- You see blood in their stool.
- Their constipation does not get better with treatment.
If you have any questions or concerns, call your baby’s health care provider.
Constipation: Infant (PDF), Spanish (PDF), Somali (PDF), Arabic (PDF), Nepali (PDF)
HH-I-14 ©Copyright 1984, Revised 2022, Nationwide Children’s Hospital
You Might Also Be Interested In
Blog
The Pee Palette: What Do All of Those Colors Mean?
Blog
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy: How It Can Help
Podcast
PediaCast 503 Your Childs Stomach Part 1
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments
Constipation in babies - causes, signs and treatments | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
What is constipation?
Constipation is when your baby’s poo is hard and dry, making it difficult for them to poo. Sometimes, doing a hard poo can be painful. It’s common for babies to have constipation when they are changing from formula or breast milk to solid foods.
Sometimes, doing a hard poo can be painful. It’s common for babies to have constipation when they are changing from formula or breast milk to solid foods.
What is normal?
All babies are unique, and this includes how often they poo. There is a very wide range of ‘normal’. Some babies poo after every feed. Others will only poo once every few days. When it comes to how often they poo, once in 7 days, or 7 times in one day are both fine, so long as your baby is happy and well. But while the number of poos is not critical, if your baby seems to have pain when trying to poo or has a very hard, dry poo, you can speak with their doctor or child health nurse for advice.
Why is my baby constipated?
One of the main causes of constipation in babies is a change in diet. A change in diet may include:
- changing from being formula-fed
- changing from being breastfed
- exposure to new foods and flavours
- not drinking enough liquids (breastmilk, formula or water)
It is more common for bottle (infant formula) fed babies to have constipation than breast-fed babies.
If your baby has started eating solid food, a lack of fibre in their diet may also potentially cause of constipation. Some babies simply have a natural tendency towards constipation, even when they have a good diet and drink enough fluids. This doesn’t mean they are unhealthy or unwell.
In extreme cases, rare illnesses can cause constipation such as:
- problems with nerve endings in the bowel
- problems relating to the spinal cord
- thyroid deficiency
- other metabolic disorders
Baby poo guide
Learn more about your baby's poo.
All babies are checked for these conditions, so this is usually not something you need to be concerned about. But if you are worried about your baby or are notice that pooing is painful for them, seek medical advice.
How to recognise the signs of constipation
The main signs of constipation are hard, dry poos. The following are other signs of constipation:
- Your baby may show signs of straining when trying to pass a poo.

- Your baby may be unsettled, may seem fussy or irritated.
- Your baby may be eating less or feeding less well than usual.
- A tear or crack might appear in the skin around the anus, which may at times bleed.
In some cases, if your child is constipated, they may look bloated or their stomach may appear larger than usual. It can be possible to feel their poo (hard, solid lumps) while pressing softly on their stomach.
How to treat constipation at home
Try these tips to help babies who have difficulty passing poos:
- If your baby has infant formula, always measure the water first before adding the formula powder — this helps ensure that the ratio of water-to-formula is correct.
- If your baby is old enough to drink water, offer extra drinks (boiled and cooled first).
- Gently rub their stomach to help stimulate the bowel — your baby might also feel better with gentle massage to help manage the pain of constipation.
- A warm bath can help calm and settle your baby and relieve discomfort.

If your baby is older than 6 months, add some extra fruit and vegetables to their diet to boost their fibre intake.
If your child is older than 9 months, adding stewed prunes or apricots to their meal may help. They can have up to 3 tablespoons, 3 times a week. Cereal that has bran may also help mild constipation. Older babies can try prune juice diluted with water (half prune juice and half water). Start slowly, with 10 millilitres. Increase as needed until they can do a soft poo.
Does my child need to see a doctor?
Constipation is common. Often it will pass without intervention, or with the help of the strategies listed above. If you are worried that your baby has constipation, is uncomfortable or is in pain, their doctor can assess them and recommend baby-safe strategies. There are medical treatments for constipation that your doctor may consider, based on your baby’s circumstances.
If your baby was previously treated for constipation but still struggles to poo, it is important to go back to your doctor for a review. There are several treatments they can try.
There are several treatments they can try.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
The Royal Children’s Hospital Melbourne (Kids Health Information 2020 - Constipation), Queensland Health (Constipation in children), Perth Children’s Hospital (Constipation in children)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: September 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Your child's health
- Poos and wees
- Baby poo guide
Need more information?
Constipation in babies and children | Raising Children Network
Children with constipation have hard poo that’s difficult to push out.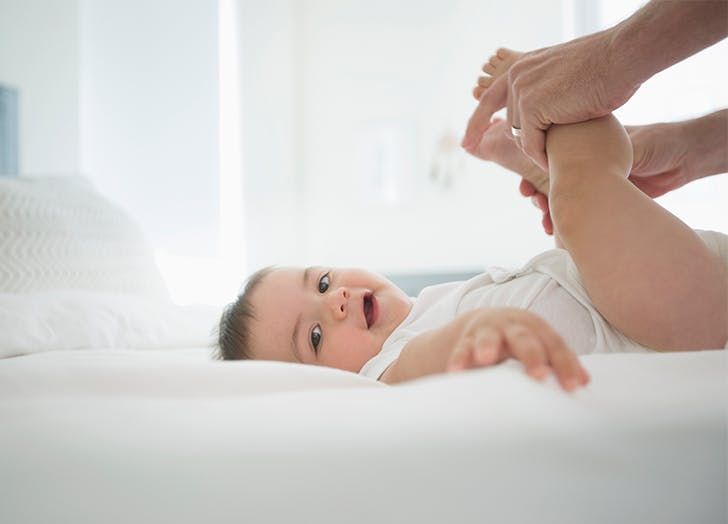 A high-fibre diet and regular toileting usually helps. Some children need laxatives.
A high-fibre diet and regular toileting usually helps. Some children need laxatives.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Colic in infants - MyDr.com.au
Colic is a pattern of unexplained, excessive crying in an otherwise healthy and well-fed baby and happens to 1 in 5 Australian babies.
Read more on myDr website
All about baby poo
Babies poo! Some poo after every feed, while others can go for days without a dirty nappy. But what you do find in the nappy can say something your baby's health - learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Constipation and children - Better Health Channel
A healthy diet, plenty of fluids, exercise and regular toilet habits can help relieve constipation in children
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Common myths about babies
Find out about some of the common myths you may hear or read about young babies.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
When can babies drink water?
You may wonder when it is safe to start giving your baby water. Whether you are breastfeeding or formula-feeding, learn how and when to get started.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Poos and wees
Babies have very delicate skin and need changing soon after they wet themselves or passed a stool (poo) to prevent nappy rash and stop them from smelling.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breast feeding your baby - MyDr.com.au
Breast milk has long been known as the ideal food for babies and infants. Major health organisations recommend that women breast feed their babies exclusively until they are 6 months old, and continue breast feeding, along with solids, until they are 12 months old or more. Breast milk has many benefits.
Breast milk has many benefits.
Read more on myDr website
What's in the nappy? - video
It may not sound like fun, but checking your baby's poos and wees will help monitor their health and wellbeing.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Breastfeeding... Is it for me? | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Before your baby is born, you should decide whether you wish to breastfeed your baby or not
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Constipation in a child - causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of constipation
Constipation in a child - the absence of stool for a day or more, as well as a change in the nature of the feces when they become hard and dry with a normal frequency of defecation.
Children often experience constipation due to malnutrition, stress, problems with the digestive system. To accurately determine the cause of a malfunction in the intestines, the child needs to be examined.
To accurately determine the cause of a malfunction in the intestines, the child needs to be examined.
Causes of constipation in a child
The specific cause is determined by the doctor on the basis of the collected history, clinical symptoms and examination data. There are several factors that can cause constipation in a child.
Non-compliance with nutrition rules
Most often, young parents face such a problem for the first time immediately after the introduction of the first complementary foods to a child at 6 months of age. Cereals and solid foods begin to dominate the baby's diet, while the usual breast milk fades into the background. All this affects both intestinal motility and the consistency of stool. They become hard and take the form of small balls (the so-called "sheep feces"). Because of this, every act of defecation in the baby is difficult and painful, so he often cries during a bowel movement.
The cause of constipation in children 3-4 years old is a lack of fiber in the diet. But it is she who stimulates intestinal motility. The child consumes few vegetables and fruits, which are the main sources of fiber, since cottage cheese, cereals, and meat begin to predominate in his menu.
But it is she who stimulates intestinal motility. The child consumes few vegetables and fruits, which are the main sources of fiber, since cottage cheese, cereals, and meat begin to predominate in his menu.
In this case, it is enough to change the baby's diet by adding more vegetables, fruits, "soft" foods and liquid foods to the diet, as well as adjust the drinking regimen.
Psychological state of the child
"Psychological constipation" occurs in children who are taught to use the potty. Parents need to be patient, because if the baby feels irritation, each act of defecation will become a source of stress for him.
Preschoolers and younger children may have difficulty going to the toilet when they first start kindergarten or school. Then they begin to restrain natural needs, which is fraught with constipation. In this case, calm conversations with the child can help.
Dysbacteriosis
Reproduction of pathogenic microflora and suppression of vital activity of beneficial bacteria also cause constipation. Due to indigestion, bowel movements begin to occur with a delay. The feces become greenish-gray and acquire an unpleasant odor. In this case, the child complains of rumbling and pain in the abdomen.
Due to indigestion, bowel movements begin to occur with a delay. The feces become greenish-gray and acquire an unpleasant odor. In this case, the child complains of rumbling and pain in the abdomen.
Infectious process
Quite often, constipation develops after an infectious disease that occurs with a high temperature. Because of the fever, fluid from the body is lost during increased sweating and during evaporation with rapid breathing. Therefore, due to lack of fluid, stools acquire a dense texture and move poorly through the intestines.
Pathologies of the rectum and chronic diseases of the digestive system
Constipation can be a symptom of many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Inflammation of the mucosa or ulcerative defects on it disrupt the normal process of digestion. This is reflected in the frequency of trips to the toilet.
As for the pathologies of the rectum, they are all characterized by painful defecation. Therefore, the child tries his best to restrain himself so as not to experience discomfort during a bowel movement.
Helminthiases
Worm infestations can be diagnosed at any age. However, in young children, they often provoke constipation. Infection occurs with errors in personal hygiene. As a result, digestion is disturbed, beriberi and anemia develop, and due to the deterioration in the movement of feces through the intestines, problems with defecation appear.
Other causes
Constipation in a child can also be caused by irritation of the skin around the anus or an allergic reaction in this area. In this case, the act of defecation provokes pain and discomfort, so the child deliberately avoids it.
Constipation can also be one of the symptoms of pathologies such as hypothyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, anemia, food allergies. Sometimes the cause of constipation in a child may be a hereditary predisposition or a side effect of taking certain medications. In any case, only a doctor can determine the cause of the problem.
Symptoms of a pathological condition
Constipation is accompanied by a number of unpleasant local and general symptoms. Among the local manifestations, parents usually note in a child:
Among the local manifestations, parents usually note in a child:
- decreased frequency of bowel movements;
- incomplete bowel movement;
- dense consistency of feces;
- baby complains of pain during bowel movements.
With constipation, especially prolonged, the general condition of the child may suffer. In many cases, this is due to intoxication of the body. In particular, parents notice:
- weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite and headache;
- appearance of pimples on the skin;
- bloating due to accumulation of gases.
At the same time, one should not forget about the clinical symptoms of the underlying disease (if any), against which constipation appeared.
In order to recognize the problem of constipation in a child and consult a doctor in time to select a treatment, parents need to know the norms for the frequency and nature of the stool in children of different ages.
| Age | Stool frequency | Character of feces |
| Up to 3 months breastfeeding | On average, 1 to 6 times a day. | Viscous, semi-fluid. The color varies from yellow to yellowish green. It may be homogeneous or contain inclusions in the form of light lumps. |
| Up to 3 months, artificial feeding | 1 to 4 times a day | Pasty consistency. Yellowish or light brown. |
| From 6 months to 1 year | 1 to 3 times a day | Soft, may not be decorated. Color - from dark yellow to brown. |
| 1 to 3 years | 1-2 times a day | Decorated, brown. |
| 3 years and older | On average, 1 time per day. Permissible frequency - 3 times a week. | Decorated, brown or dark brown. |
Classification and stages of development of constipation
A unified classification of this pathological condition has not been developed. However, in clinical practice, depending on the origin, there are:
- primary constipation - occurs as a result of anomalies in the development of the digestive system;
- secondary constipation - is a symptom of another disease;
- idiopathic constipation - the exact etiology of the pathological condition has not been established.
According to the nature and duration of the course, constipation can be:
- acute, when problems with bowel movement occur suddenly;
- chronic, in which the child suffers from a defecation disorder for more than 3 months.

There are also constipation:
- functional when there is no organic lesion of the digestive tract;
- hypertensive - the intestines with feces are in a strong tone;
- hypotonic - the tone of the intestine is weakened and in this state is not able to maintain normal motility.
There are also 3 stages of compensation for the pathological condition:
- Stage 1, fully compensated - bowel movement occurs 1 time in 2-3 days;
- Stage 2, subcompensation - the act of defecation in a child happens 1 time in 5-7 days;
- Stage 3, decompensation - stool occurs once a week or less.
Mechanism of constipation
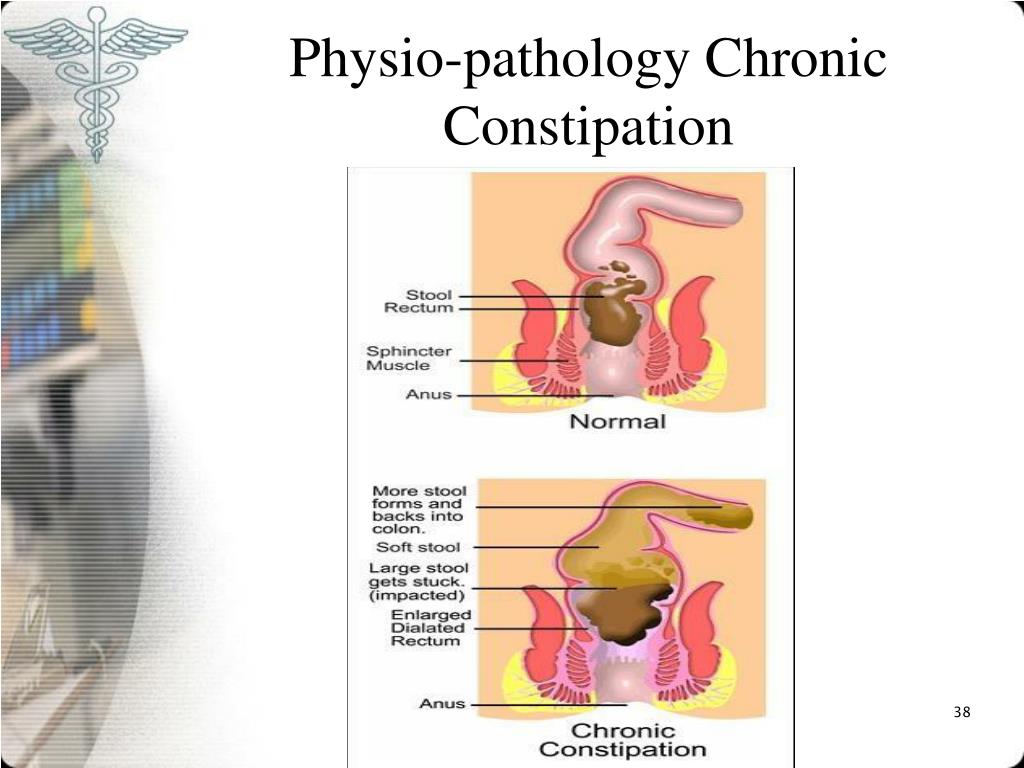
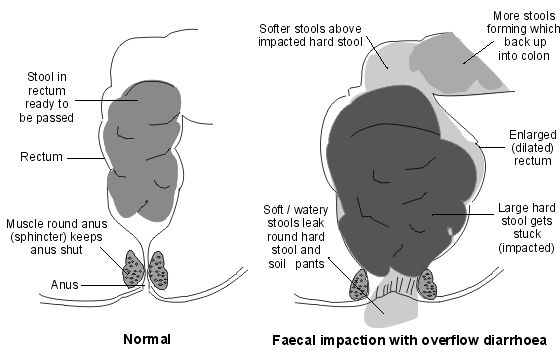
In constipation, stool stays in the intestines for a long time, which makes it even drier and denser, as additional fluid is absorbed. Bowel movements are difficult and painful. Often there is injury to the mucosa. During the act of defecation, the child experiences very unpleasant sensations, so he tries to restrain himself.
The more often this happens, the faster the intestines adapt to this condition. First, there is a slowdown in impulses signaling the need for an act of defecation. Further, fecal masses begin to stagnate. All this provokes the development of general intoxication of the body, contributes to the appearance of dysbacteriosis, indigestion and further aggravates the child's condition.
Fossilized feces gradually stretch the capsule of the rectum. The anal sphincter weakens. Liquid calculi begin to flow around the formed lump, and stone smearing begins.
When should I see a doctor?
The child needs medical attention if:
- the child complains of severe abdominal pain;
- no stool for more than 3 days;
- when emptying the intestines, the rectal mucosa falls out, or hemorrhoids appear;
- there are traces of fresh blood or mucus in the stools;
- stool changes its characteristics - becomes dry, hard, fetid;
- the general condition of the child suffers - the body temperature rises, flatulence, nausea, and vomiting appear.

Diagnostic methods
First, at the appointment, the doctor collects an anamnesis of the disease, asking the parents in detail, and also evaluates the diet and drinking regimen of the baby based on the data. Next, the doctor conducts a general examination of the child, paying attention to the skin turgor and its color, palpates the abdomen. If necessary, conducts a digital examination of the rectum, assessing the condition and filling of its ampoule, sphincter tone and the integrity of the mucosa.
After the examination, the doctor recommends to the parents a full examination of the child, which usually includes:
Only on the basis of the results of the examination, the doctor can determine the cause of constipation and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Constipation treatments
Treatment of constipation should only be complex. It is prescribed necessarily taking into account the causes and concomitant pathologies. The treatment regimen includes drugs, herbal medicine, physiotherapy (electrophoresis), reflexology, exercise therapy.
But first of all it is necessary to change the way of life. If a child is diagnosed with functional constipation, he is advised to move more, since any physical activity stimulates the motor function of the intestine.
The second aspect is diet. The child's diet should contain a sufficient amount of foods rich in fiber, which stimulates digestion and peristalsis. In parallel, it is necessary to adjust the baby's drinking regimen.
As a drug treatment for constipation, parents can use:
- probiotics and prebiotics with lactulose;
- laxatives and cholagogues;
- antispasmodics.

Only the attending physician can prescribe a specific drug and adjust the dosage according to age.
Diet for constipation
Correction of diet for constipation is the main component of the success of treatment. Nutrition should be age-appropriate and meet its needs for essential substances.
If the baby is breastfed, continue breastfeeding. If necessary, it is worth adjusting the mother's diet: reduce consumption or completely eliminate foods that increase gas formation from the diet. With artificial feeding, it is recommended to choose a mixture containing special additives.
For the first feeding, it is better to choose puree from vegetables that stimulate intestinal motility: zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower. All babies, regardless of the type of feeding, after the start of complementary foods, need a sufficient amount of boiled water.
If an older child has constipation, it is essential to include enough fresh fruits and vegetables, natural sources of fibre, in the diet. There are some exceptions to this rule: for example, pears, persimmons, and blueberries are astringent and can aggravate constipation.
There are some exceptions to this rule: for example, pears, persimmons, and blueberries are astringent and can aggravate constipation.
A significant amount of fiber is also found in oatmeal and buckwheat, wholemeal bread, and bran. Specially prepared bran can be purchased at a pharmacy. To treat constipation in a child, bran is poured with warm water, settled for 20 minutes and added to main dishes. The dose is selected individually, starting with 1 teaspoon. With constipation, bran should be given 2-3 times a day, and after solving the problem, the frequency of intake is reduced to 1 time per day. When taking bran, it is necessary to provide the child with plenty of fluids, otherwise bran can play the role of a sorbent and further increase constipation.
The child's food should be mainly crumbly, contain meat (poultry, fish) in pieces. Breakfast should be plentiful in order to reflexively stimulate the act of defecation in the morning.
To eliminate constipation, you should avoid eating pureed foods, strong tea, coffee, jelly, rice and semolina porridge. It is also necessary to minimize the presence of sweets and muffins in the diet. It is better to replace fresh milk with fermented milk products.
It is also necessary to minimize the presence of sweets and muffins in the diet. It is better to replace fresh milk with fermented milk products.
The best drink for children suffering from chronic constipation is plain boiled water. You can give diluted vegetable and fruit juices with pulp. Without following the condition of abundant drinking, any adjustments to the child's diet may be ineffective.
Daily routine
The habit of following a daily routine helps to establish the correct functioning of the vegetative part of the nervous system and develop the habit of emptying the intestines at a certain time.
In the morning, immediately after waking up, give your child half a glass of water (for children under 3 years old - a third of a glass). Then the child can do morning hygiene procedures, exercises. Usually these actions take no more than 20 minutes, after which the baby has breakfast.
Ideally, a defecation should occur after a meal. By agreement with the attending physician, it can be called in auxiliary ways, for example, with the help of a candle or microclysters. In case of success, the child should definitely be praised, and if he did not succeed, do not scold.
In case of success, the child should definitely be praised, and if he did not succeed, do not scold.
All children need walks and active play. Movement stimulates peristalsis, which ensures effective prevention of constipation in a child - this rule is also relevant for babies at 1-2 years old, and preschoolers 5-6 years old, and older children.
Possible complications of constipation
Long-term constipation may cause distension of the colon. If the feces stand in one place for a long time, this can lead to impaired blood circulation in the intestinal walls and the formation of hemorrhoids. With excessive straining, the rectum sometimes falls out.
Constipation can lead to general intoxication, dysbacteriosis, provoke colitis, paraproctitis and other chronic bowel diseases.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for the pathological condition is favorable, but the sooner attention is paid to the problem, the better for the child.
Prevention of constipation consists in the gradual introduction of complementary foods, rational nutrition, adherence to the drinking regimen, periodic examinations for helminths and timely treatment of pathologies of the digestive tract.
How to calculate the correct amount of fluid for a child
- Babies under 1 year of age should drink at least 100 ml of water per day.
- After one year, if the child weighs 10–20 kg, add another 50 ml per kilogram to the original 100 ml.
- Children over 20 kg should add 20 ml per kilogram to 600 ml.
- For babies 3-5 years old and older, the calculation of the daily volume of liquid is easier - just take 30 ml of water per kilogram of body weight.
Questions most frequently asked by parents
What is forbidden to do with constipation in a child?
Small children, who have just started to potty training by their parents, should not be shouted at and forced to sit on it. In addition, with constipation at any age, you should not give foods that slow down intestinal motility (semolina and rice porridge, persimmon, pear, jelly).
What can be done before the doctor arrives?
Parents can give a laxative suppository and a microclyster. Laxatives, even if there is an instruction, are recommended to be given only after consulting a doctor.
Laxatives, even if there is an instruction, are recommended to be given only after consulting a doctor.
How to make an enema for a baby?
It is necessary to take a rubber bulb of small volume, draw water at room temperature (temperature not higher than 22–26 ° C), grease the tip with Vaseline. Babies up to a year old are placed on their backs, older children on their left side. With one hand, the buttocks are parted, with the other, the tip of the rubber bulb is carefully inserted to a depth of 3–5 cm.
Then the bulb is slowly squeezed and the entire portion of water is squeezed out. Then the pear is taken out, the buttocks of the child are squeezed for 2–3 minutes, after which they are put on a potty or sent to the toilet.
What can be given to a child for constipation?
Kefir, beetroot juice, chamomile decoction, dates, walnuts and dried apricots have a laxative effect.
What should be the baby's diet so that he does not suffer from constipation?
Each person's body is individual. The assimilation of products occurs in different ways. Therefore, no one will give a definite answer, except for a doctor who has been observing a child since birth. Only he will help to create the optimal menu for him, taking into account all the features of his digestive system.
symptoms, causes, diagnosis, how to help a child with constipation
How to solve the problem and help the baby?
Constipation is one of the most common problems in children. According to statistics, in Russia constipation occurs in every fourth child 1 . And this problem significantly complicates the calm and cheerful life of both the child and and parents, because constipation often causes pain, the child the mood deteriorates, the parents are on their nerves - in general, there is little good.
In order not to miss the problem of constipation in the baby, we armed ourselves
scientific knowledge and talk about how to identify constipation,
why does it occur and what to give a child with constipation?
Causes of constipation in children
There are quite a few of them and almost all of them depend on age child. That is, constipation in infants and schoolchildren cause different reasons. Let's consider them in more detail.
Stress and change routine
These reasons are typical, as a rule, for babies. under the age of one year. In this tender age, coordination muscle contractions of the intestinal wall can be violated 5 , which leads to difficulties with defecation. In addition, constipation in infants may occur after switching to artificial mixtures 1 . In breast milk contains many beneficial intestinal flora substances - dietary fiber, a large amount of fat, proteins in the optimal ratio. All of them contribute normal bowel movements 6 .
under the age of one year. In this tender age, coordination muscle contractions of the intestinal wall can be violated 5 , which leads to difficulties with defecation. In addition, constipation in infants may occur after switching to artificial mixtures 1 . In breast milk contains many beneficial intestinal flora substances - dietary fiber, a large amount of fat, proteins in the optimal ratio. All of them contribute normal bowel movements 6 .
Stress and change routine
Common causes of constipation are new conditions that break the child's usual daily routine and environment. So, for example, a violation of defecation often appears during potty training, with the start of attending kindergarten or schooling 1 .
Irritable syndrome intestines
This disorder is noted in an older age group - in children from 4 to 18 years old. In this disease, the child periodically abdominal pain occurs, which may be accompanied by symptoms indigestion and constipation 1.7 .
In this disease, the child periodically abdominal pain occurs, which may be accompanied by symptoms indigestion and constipation 1.7 .
How to understand that a child has constipation?
It seems that the answer to this question very simple - child rarely walks "big". However, this is not quite correct figure. Case that the frequency of stool in healthy children can be very different 1 .
However, if a child's routine of going to the toilet has changed, you should be alert and analyze what is happening. Yes, yes, literally turn into a patient detective and examine the contents of a pot or toilet. This may not be the most pleasant occupation, but the result of research can greatly facilitate both your life and the child's.
So, first of all, you need to evaluate the shape of the stool. This will help to determine with some accuracy whether there is constipation or not 1 . We will not determine the shape “by eye”, but with the help of the Bristol scale of fecal shapes, developed by doctors. According to this scale, there are seven types of stool. We are only interested in two of them.
Criteria for constipation according to the Bristol Stool Form Scale
3 :Hard and dry, nut-like lumps (called "sheep" stool)
Sausage-shaped stool with a lumpy texture.
In addition to determining the shape of the stool, you should pay attention to other signs of constipation. For example, a child may begin to push too hard, take uncharacteristic positions, try to poop, and in general, spend much more time on the potty or toilet than usual. 1
If there is no stool for several days, constipation is considered acute. If the constipation problem persists for 3 months or more, this is regarded by specialists as a “chronic condition” 2.4 .
Treatment of constipation in a child
So what should you do if your child is constipated?
First of all, you need to make certain changes in the daily routine. All of them are quite simple and effective. Remember.
Remember.
Maintain regular toileting
Natural urge to defecate usually appears after eating. Therefore, a small child stands in the morning some time after taking put food on a pot or invite him to go to the toilet. You can develop a kind of reflex in a child - for example, "had breakfast - pooped" 1 .
Comfort
To form a positive perception of going to the toilet in a child, it is also important to provide comfortable conditions for him: for example, to choose a suitable potty so that the child can take a comfortable position 10 . In addition, it is necessary that during defecation, the baby has some kind of support where you can rest your feet, for example, a low bench that can be placed in the toilet, since an increase in intra-abdominal pressure when straining is important to resolve constipation 1 .
In addition, it is necessary that during defecation, the baby has some kind of support where you can rest your feet, for example, a low bench that can be placed in the toilet, since an increase in intra-abdominal pressure when straining is important to resolve constipation 1 .
Adjust nutrition
This is a very important step in the treatment of constipation. From the menu you need to remove fats, sweets (yes, we understand how difficult it is with this item) and marinades.
And replace all this splendor with cereals, vegetables and fruits. Especially good for constipation are plum, peach and apple purees and juices 1 .
Important to understand
Lifestyle changes may not help immediately. Therefore, there are modern remedies for constipation in children, which can contribute to a faster resolution of this problem. One of these is Guttalax®, a topical laxative that can stimulate the activity of the large intestine, which can lead to softening of the stool and normal defecation 8 . However, it is important to remember that prescription medications in children drugs should only take place after consultation with a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the cause of constipation and help deal with them.
One of these is Guttalax®, a topical laxative that can stimulate the activity of the large intestine, which can lead to softening of the stool and normal defecation 8 . However, it is important to remember that prescription medications in children drugs should only take place after consultation with a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the cause of constipation and help deal with them.
Unlike other laxatives, which can sometimes focus the child's attention on a problem, for example, they do not have an acceptable taste for everyone 11 , or are administered rectally, which can increase the child's fear and discomfort regarding defecation 12 , Guttalax® you can let your baby quietly and naturally normalize the bowel rhythm 8.
 Permissible frequency - up to 1 time per week.
Permissible frequency - up to 1 time per week.