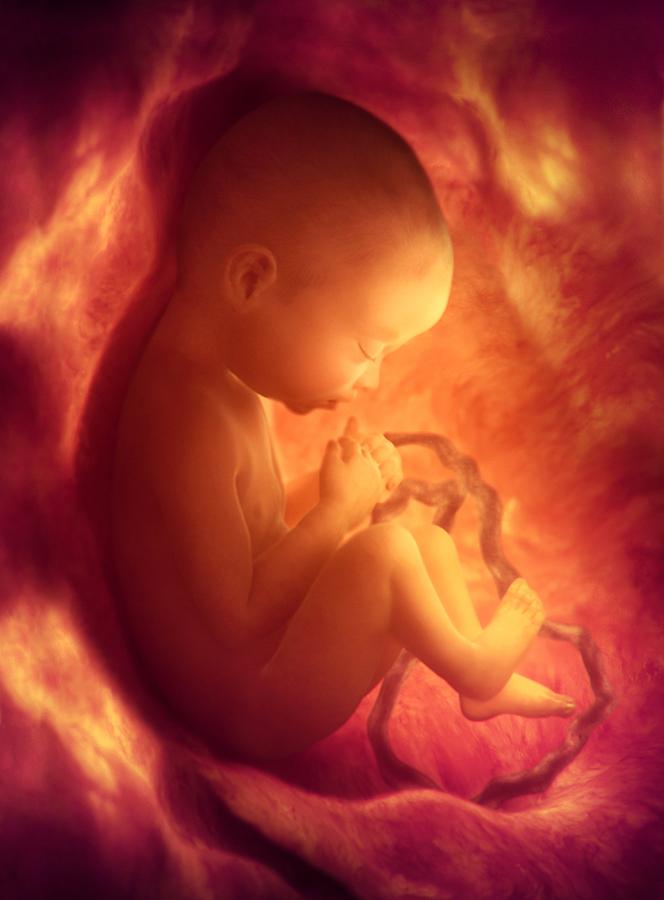
Fetus in pregnancy
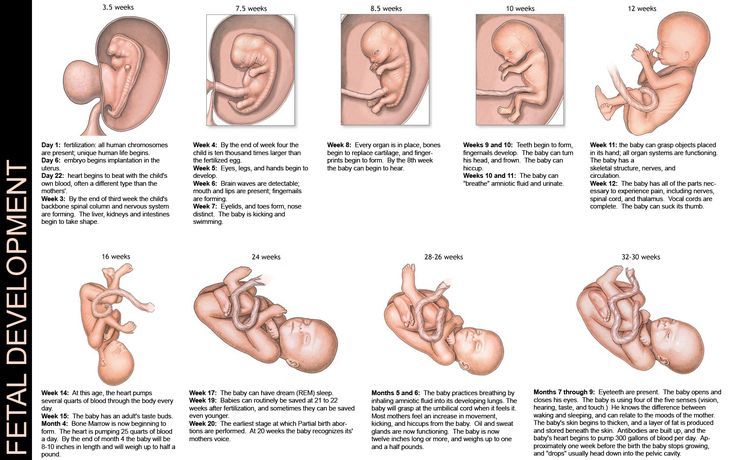
Fetal development: Month-By-Month Stages of Pregnancy
When does a pregnancy start?
The start of pregnancy is actually the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age, or menstrual age. It’s about two weeks ahead of when conception actually occurs. Though it may seem strange, the date of the first day of your last period will be an important date when determining your due date. Your healthcare provider will ask you about this date and will use it to figure out how far along you are in your pregnancy.
How does conception work?
Each month, your body goes through a reproductive cycle that can end in one of two ways. You will either have a menstrual period or become pregnant. This cycle is continuously happening during your reproductive years — from puberty in your teen years to menopause around age 50.
In a cycle that ends with pregnancy, there are several steps. First, a group of eggs (called oocytes) gets ready to leave the ovary for ovulation (release of the egg). The eggs develop in small, fluid-filled cysts called follicles. Think of these follicles as small containers for each immature egg. Out of this group of eggs, one will become mature and continue on through the cycle. This follicle then suppresses all the other follicles in the group. The other follicles stop growing at this point.
The mature follicle now opens and releases the egg from the ovary. This is ovulation. Ovulation generally happens about two weeks before your next menstrual period begins. It’s generally in the middle of your cycle.
After ovulation, the opened (ruptured) follicle develops into a structure called the corpus luteum. This secretes (releases) the hormones progesterone and estrogen. Progesterone helps prepare the endometrium (lining of the uterus). This lining is the place where a fertilized egg settles to develop. If you don’t become pregnant during a cycle, this lining is what is shed during your period.
On average, fertilization happens about two weeks after your last menstrual period.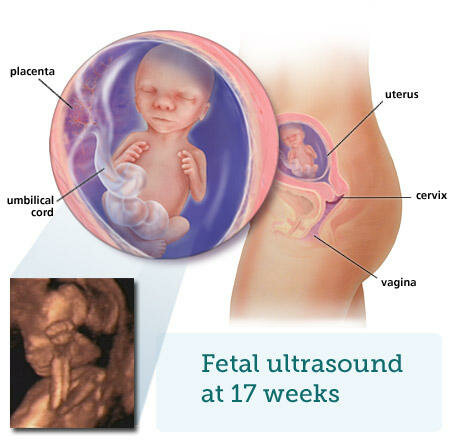 When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
When the sperm penetrates the egg, changes occur in the protein coating of the egg to prevent other sperm from entering.
At the moment of fertilization, your baby’s genetic make-up is complete, including its sex. The sex of your baby depends on what sperm fertilizes the egg at the moment of conception. Generally, women have a genetic combination of XX and men have XY. Women provide each egg with an X. Each sperm can be either an X or a Y. If the fertilized egg and sperm is a combination of an X and Y, it’s a boy. If there are two Xs, it’s a girl.
What happens right after conception?
Within 24 hours after fertilization, the egg begins rapidly dividing into many cells. It remains in the fallopian tube for about three days after conception. Then the fertilized egg (now called a blastocyte) continues to divide as it passes slowly through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once there, its next job is to attach to the endometrium. This is called implantation.
Before implantation though, the blastocyte breaks out of its protective covering.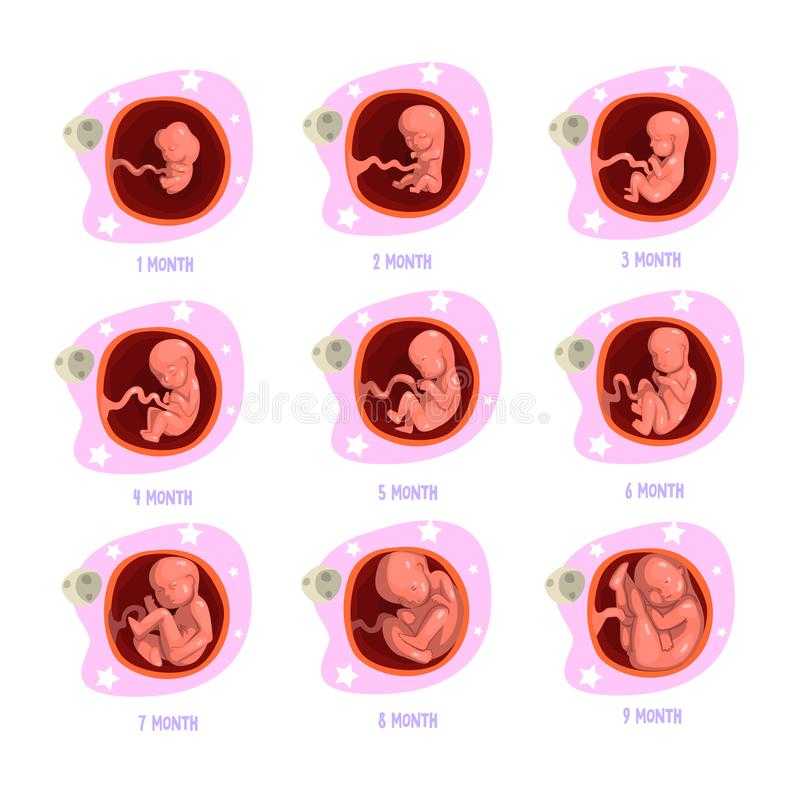 When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
When the blastocyte makes contact with the endometrium, the two exchange hormones to help the blastocyte attach. Some women notice spotting (slight bleeding) during the one or two days when implantation happens. This is normal and isn’t something you should worry about. At this point, the endometrium becomes thicker and the cervix (the opening between your uterus and birth canal) is sealed by a plug of mucus.
Within three weeks, the blastocyte cells ultimately form a little ball, or an embryo. By this time, the first nerve cells have formed.
Your developing fetus has already gone through a few name changes in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Generally, it's called an embryo from conception until the eighth week of development. After the eighth week, it's called a fetus until it’s born.
How early can I know I’m pregnant?
From the moment of conception, the hormone human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) will be present in your blood. This hormone is created by the cells that form the placenta (food source for the growing fetus). It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
It’s also the hormone detected in a pregnancy test. Even though this hormone is there from the beginning, it takes time for it to build within your body. It typically takes three to four weeks from the first day of your last period for the hCG to increase enough to be detected by pregnancy tests.
When should I reach out to my healthcare provider about a new pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers will have you wait to come in for an appointment until you have had a positive home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate once you have enough hCG circulating throughout your body. This can be a few weeks after conception. It’s best to call your healthcare provider once you have a positive pregnancy test to schedule your first appointment.
When you call, your healthcare provider may ask you if you are taking a prenatal vitamin. These supplements contain folic acid. It’s important that you get at least 400mcg of folic acid each day during a pregnancy to make sure the fetus's neural tube (beginning of the brain and spine) develops correctly. Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
Many healthcare providers suggest that you take prenatal vitamins with folic acid even when you aren’t pregnant. If you weren’t taking prenatal vitamins before your pregnancy, your provider may ask you to start as early as possible.
What’s the timeline for fetal development?
The fetus will change a lot throughout a typical pregnancy. This time is divided into three stages, called trimesters. Each trimester is a set of about three months. Your healthcare provider will probably talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. So, if you are three months pregnancy, you are about 12 weeks.
You will see distinct changes in the fetus, and yourself, during each trimester.
Traditionally, we think of a pregnancy as a nine-month process. However, this isn’t always the case. A full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, or 280 days. Depending on what months you are pregnant during (some are shorter and some longer) and what week you deliver, you could be pregnant for either nine months or 10 months. This is completely normal and healthy.
This is completely normal and healthy.
Once you get close to the end of your pregnancy, there are several category names you might hear regarding when you go into labor. These labels divide up the last few weeks of pregnancy. They’re also used to look out for certain complications in newborns. Babies that are born in the early term period or before may have a higher risk of breathing, hearing or learning issues than babies born a few weeks later in the full term time frame. When you’re looking at these labels, it’s important to know how they’re written. You may see the week first (38) and then you’ll see two numbers separated by a slash mark (6/7). This stands for how many days you currently are in the gestational week. So, if you see 38 6/7, it means that you are on day 6 of your 38th week.
The last few weeks of pregnancy are divided into the following groups:
- Early term: 37 0/7 weeks through 38 6/7 weeks.
- Full term: 39 0/7 weeks through 40 6/7 weeks.
- Late term: 41 0/7 weeks through 41 6/7 weeks.
- Post term: 42 0/7 weeks and on.
Talk to your healthcare provider about any questions you may have about gestational age and due date.
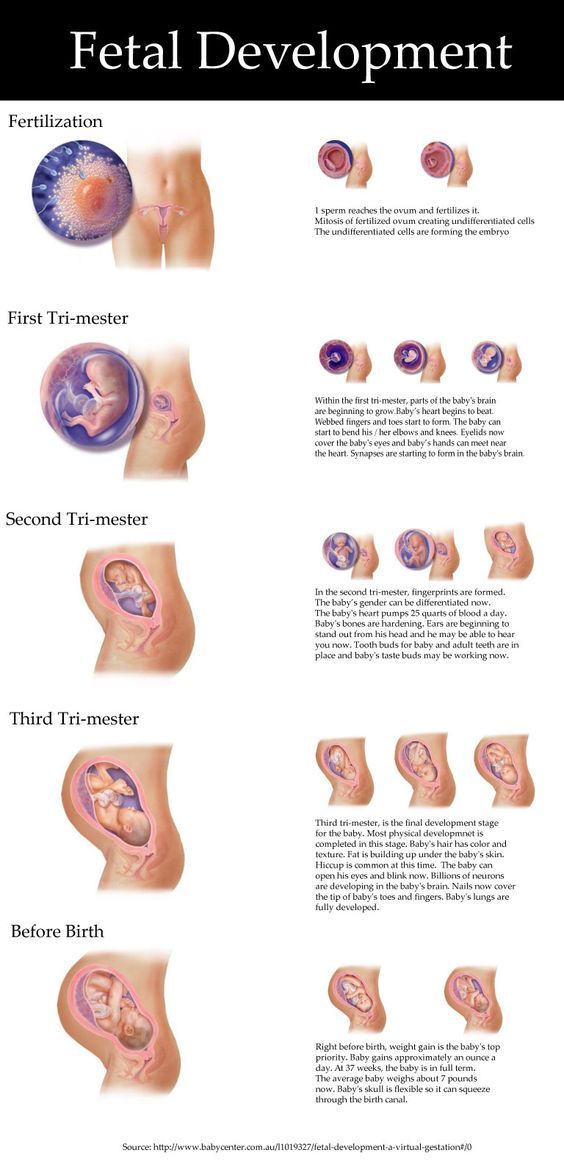
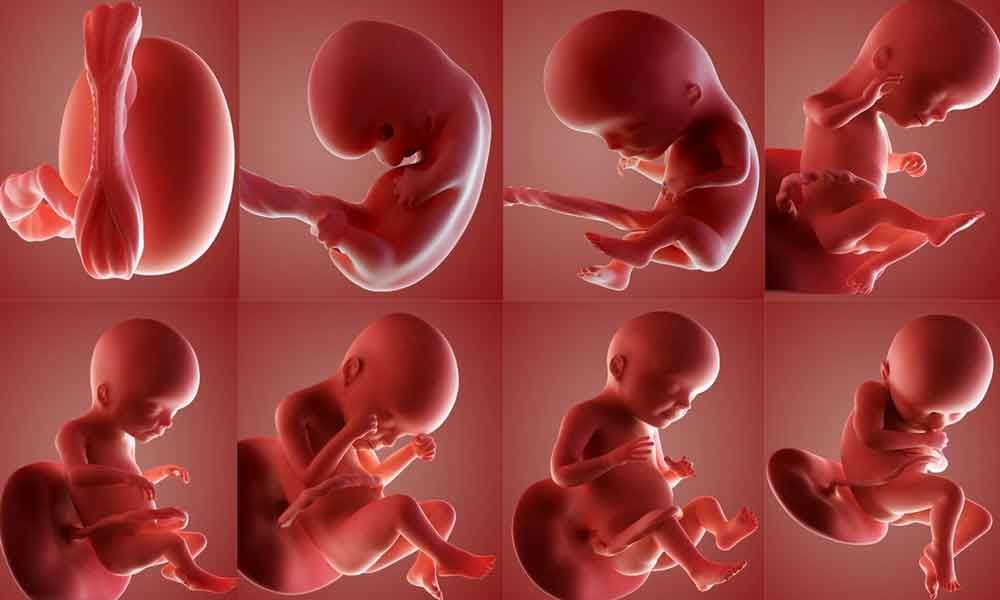
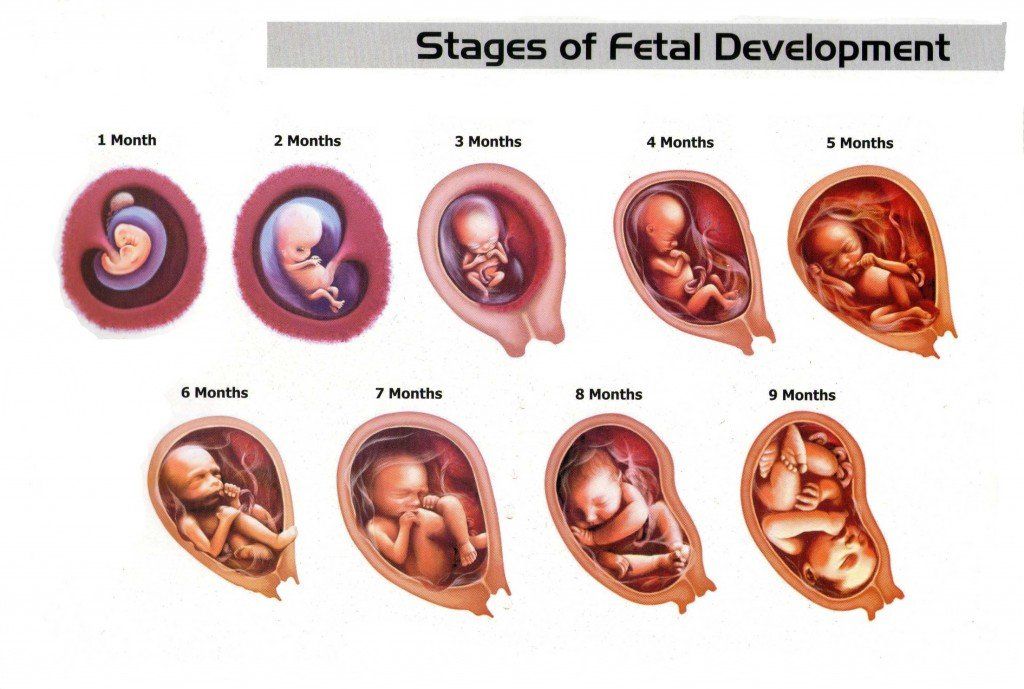
Stages of Growth Month-by-Month in Pregnancy
First trimester
The first trimester will span from conception to 12 weeks. This is generally the first three months of pregnancy. During this trimester, the fertilized egg will change from a small grouping of cells to a fetus that is starting to have a baby’s features.
Month 1 (weeks 1 through 4)
As the fertilized egg grows, a water-tight sac forms around it, gradually filling with fluid. This is called the amniotic sac, and it helps cushion the growing embryo.
During this time, the placenta also develops. The placenta is a round, flat organ that transfers nutrients from the mother to the fetus, and transfers wastes from the fetus. Think of the placenta as a food source for the fetus throughout your pregnancy.
In these first few weeks, a primitive face will take form with large dark circles for eyes. The mouth, lower jaw and throat are developing. Blood cells are taking shape, and circulation will begin. The tiny "heart" tube will beat 65 times a minute by the end of the fourth week.
By the end of the first month, the fetus is about 1/4 inch long – smaller than a grain of rice.
Month 2 (weeks 5 through 8)
Facial features continue to develop. Each ear begins as a little fold of skin at the side of the head. Tiny buds that eventually grow into arms and legs are forming. Fingers, toes and eyes are also forming.
The neural tube (brain, spinal cord and other neural tissue of the central nervous system) is well formed now. The digestive tract and sensory organs begin to develop too. Bone starts to replace cartilage.
The head is large in proportion to the rest of the body at this point. At about 6 weeks, a heartbeat can usually be detected.
After the 8th week, healthcare providers refer to it as a fetus instead of an embryo.
By the end of the second month, the fetus is about 1 inch long and weighs about 1/30 of an ounce.
Month 3 (weeks 9 through 12)
The arms, hands, fingers, feet and toes are fully formed. At this stage, the fetus is starting to explore a bit by doing things like opening and closing its fists and mouth. Fingernails and toenails are beginning to develop and the external ears are formed. The beginnings of teeth are forming under the gums. The reproductive organs also develop, but sex is still difficult to distinguish on ultrasound.
By the end of the third month, the fetus is fully formed. All the organs and limbs (extremities) are present and will continue to develop in order to become functional. The circulatory and urinary systems are also working and the liver produces bile.
At the end of the third month, the fetus is about 4 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce.
Since the most critical development has taken place, your chance of miscarriage drops considerably after three months.
Second trimester
This middle section of pregnancy is often thought of as the best part of the experience. By this time, any morning sickness is probably gone and the discomfort of early pregnancy has faded. The fetus will start to develop facial features during this month. You may also start to feel movement as the fetus flips and turns in the uterus. During this trimester, many people find out whether their baby will be designated male or female at birth. This is typically done during an anatomy scan (an ultrasound that checks physical development) around 20 weeks.
Month 4 (weeks 13 through 16)
The fetal heartbeat may now be audible through an instrument called a doppler. The fingers and toes are well-defined. Eyelids, eyebrows, eyelashes, nails and hair are formed. Teeth and bones become denser. The fetus can even suck his or her thumb, yawn, stretch and make faces.
The nervous system is starting to function. The reproductive organs and genitalia are now fully developed, and your doctor can see on ultrasound if the fetus will be designated male or female at birth.
By the end of the fourth month, the fetus is about 6 inches long and weighs about 4 ounces.
Month 5 (weeks 17 through 20)
At this stage, you may begin to feel the fetus moving around. The fetus is developing muscles and exercising them. This first movement is called quickening and can feel like a flutter.
Hair begins to grow on the head. The shoulders, back and temples are covered by a soft fine hair called lanugo. This hair protects the fetus and is usually shed at the end of your baby's first week of life.
The skin is covered with a whitish coating called vernix caseosa. This "cheesy" substance is thought to protect fetal skin from the long exposure to the amniotic fluid. This coating is shed just before birth.
By the end of the fifth month, the fetus is about 10 inches long and weighs from 1/2 to 1 pound.
Month 6 (weeks 21 through 24)
If you could look inside the uterus right now, you would see that the fetus's skin is reddish in color, wrinkled and veins are visible through translucent skin. The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The finger and toe prints are visible. In this stage, the eyelids begin to part and the eyes open.
The fetus responds to sounds by moving or increasing the pulse. You may notice jerking motions if the fetus hiccups.
If born prematurely, your baby may survive after the 23rd week with intensive care.
By the end of the sixth month, the fetus is about 12 inches long and weighs about 2 pounds.
Month 7 (weeks 25 through 28)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. At this point, hearing is fully developed. The fetus changes position frequently and responds to stimuli, including sound, pain and light. The amniotic fluid begins to diminish.
If born prematurely, your baby would be likely to survive after the seventh month.
At the end of the seventh month, the fetus is about 14 inches long and weighs from 2 to 4 pounds.
Third trimester
This is the final part of your pregnancy. You may be tempted to start the countdown till your due date and hope that it would come early, but each week of this final stage of development helps the fetus prepare for birth. Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Throughout the third trimester, the fetus gains weight quickly, adding body fat that will help after birth.
Remember, even though popular culture only mentions nine months of pregnancy, you may actually be pregnant for 10 months. The typical, full-term pregnancy is 40 weeks, which can take you into a tenth month. It’s also possible that you can go past your due date by a week or two (41 or 42 weeks). Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely as you approach your due date. If you pass your due date, and don’t go into spontaneous labor, your provider may induce you. This means that medications will be used to make you go into labor and have the baby. Make sure to talk to your healthcare provider during this trimester about your birth plan.
Month 8 (weeks 29 through 32)
The fetus continues to mature and develop reserves of body fat. You may notice more kicking. The brain developing rapidly at this time, and the fetus can see and hear. Most internal systems are well developed, but the lungs may still be immature.
The fetus is about 18 inches long and weighs as much as 5 pounds.
Month 9 (weeks 33 through 36)
During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and mature. The lungs are close to being fully developed at this point.
The fetus has coordinated reflexes and can blink, close the eyes, turn the head, grasp firmly, and respond to sounds, light and touch.
The fetus is about 17 to 19 inches long and weighs from 5 ½ pounds to 6 ½ pounds.
Month 10 (Weeks 37 through 40)
In this final month, you could go into labor at any time. You may notice that less movement because space is tight. At this point, The fetus's position may have changed to prepare for birth. Ideally, it's head down in your uterus. You may feel very uncomfortable in this final stretch of time as the fetus drops down into your pelvis and prepares for birth.
Your baby is ready to meet the world at this point. They are about 18 to 20 inches long and weigh about 7 pounds.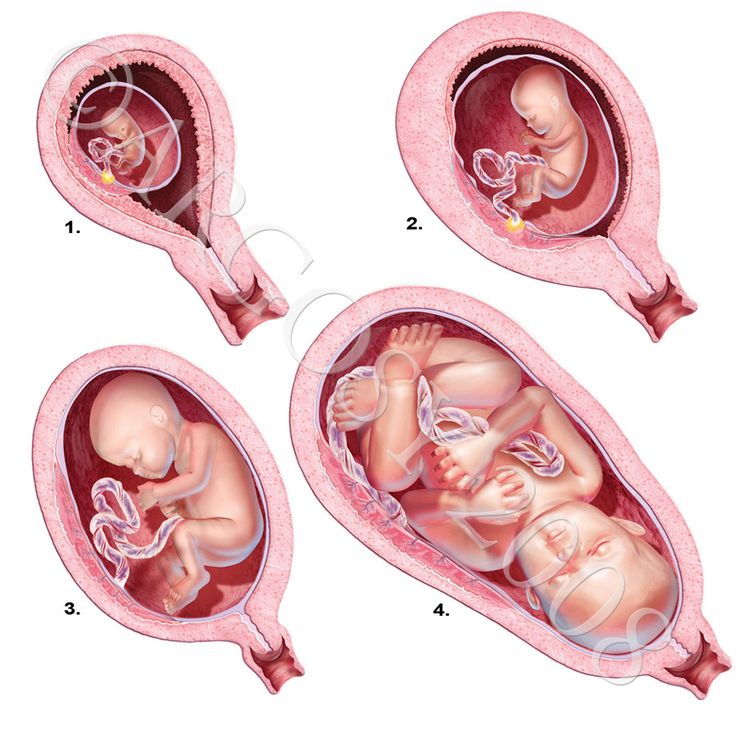
Fetal development by week: Your baby in the womb
- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby Names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
From conception to labor, your baby is constantly growing and developing. Your baby moves through different stages, starting as a blastocyst, then maturing into an embryo, and then a fetus. Around the 5 week mark, cells in your baby's future heart will begin to flicker. At 27 weeks they'll have regular sleep and wake cycles, and at 39 weeks your baby is physically developed. Use this timeline to learn how big your baby is, plus how they're developing throughout pregnancy.
Follow your baby's development week by week, from conception to labor, in these amazingly detailed, doctor-reviewed images.
2 weeks: Fertilization
At the start of this week, you ovulate. Your egg is fertilized 12 to 24 hours later if a sperm penetrates it. Over the next several days, the fertilized egg will start dividing into multiple cells as it travels down the fallopian tube, enters your uterus, and starts to burrow into the uterine lining.
Read about fertilization.
3 weeks: Implantation
Now nestled in the nutrient-rich lining of your uterus is a microscopic ball of hundreds of rapidly multiplying cells that will develop into your baby. This ball of cells, called a blastocyst, has begun to produce the pregnancy hormone hCG, which tells your ovaries to stop releasing eggs.
Read about implantation.
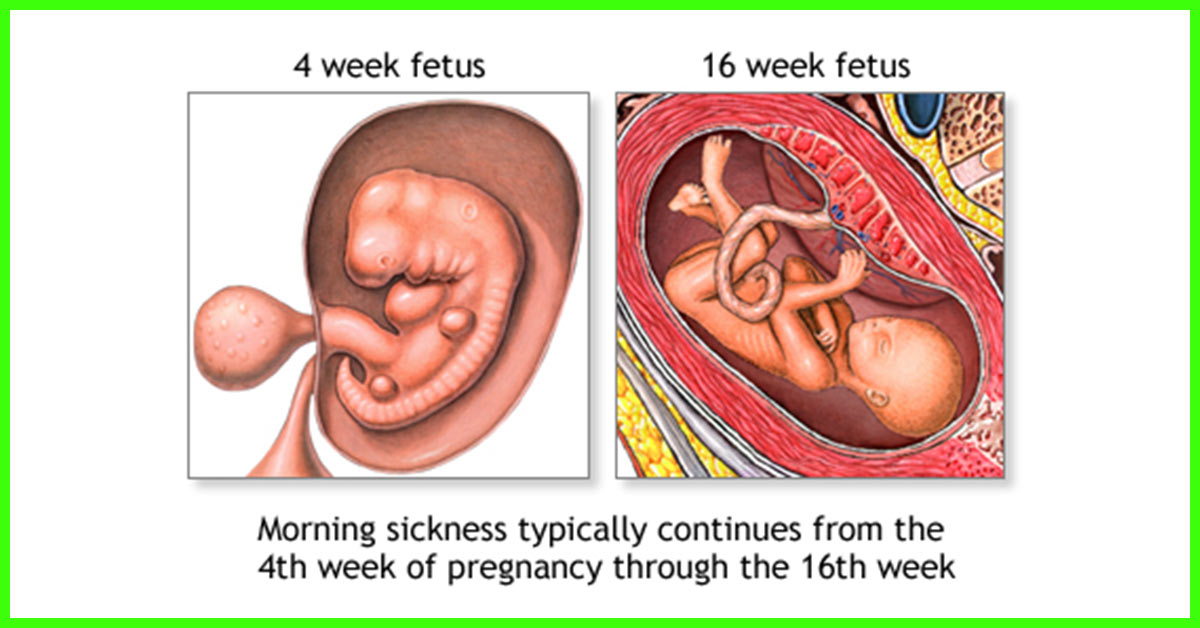
4 weeks
Your ball of cells is now officially an embryo. You're now about 4 weeks from the beginning of your last period. It's around this time – when your next period would normally be due – that you might be able to get a positive result on a home pregnancy test.
Your baby is the size of a poppy seed.
Read about your pregnancy at 4 weeks.
5 weeks
Your baby resembles a tadpole more than a human, but is growing fast. The circulatory system is beginning to form, and cells in the tiny "heart" will start to flicker this week.
Your baby is the size of a sesame seed.
Read about your pregnancy at 5 weeks.
6 weeks
Your baby's nose, mouth and ears are starting to take shape, and their intestines and brain are beginning to develop.
Your baby is the size of a lentil.
Read about your pregnancy at 6 weeks.
7 weeks
Your baby has doubled in size since last week, but still has a tail, which will soon disappear. Little hands and feet that look more like paddles are emerging from the developing arms and legs.
Your baby is the size of a blueberry.
Read about your pregnancy at 7 weeks.
8 weeks
Your baby has started moving around, though you won't feel your baby move yet. Nerve cells are branching out, forming primitive neural pathways. Breathing tubes now extend from their throat to their developing lungs.
Nerve cells are branching out, forming primitive neural pathways. Breathing tubes now extend from their throat to their developing lungs.
Your baby is the size of a kidney bean.
Read about your pregnancy at 8 weeks.
9 weeks
Your baby's basic anatomy is developing (they even have tiny earlobes now), but there's much more to come. Their embryonic tail has disappeared and they weigh just a fraction of an ounce but are about to start gaining weight fast.
Your baby is the size of a grape.
Read about your pregnancy at 9 weeks.
10 weeks
Your embryo has completed the most critical portion of development. Their skin is still translucent, but their tiny limbs can bend and fine details like nails are starting to form.
Your baby is the size of a kumquat
Read about your pregnancy at 10 weeks.
11 weeks
Your baby is almost fully formed. They're kicking, stretching, and even hiccupping as their diaphragm develops, although you can't feel any activity yet.
Your baby is the size of a fig.
Read about your pregnancy at 11 weeks.
12 weeks
This week your baby's reflexes kick in: Their fingers will soon begin to open and close, toes will curl, and their mouth will make sucking movements.
Your baby is the size of a lime.
Read about your pregnancy at 12 weeks.
13 weeks
This is the last week of your first trimester. Your baby's tiny fingers now have fingerprints, and their veins and organs are clearly visible through their skin. If you're having a girl, her ovaries contain more than 2 million eggs.
Your baby is the size of a pea pod.
Read about your pregnancy at 13 weeks.
Entering the second trimester: What lies ahead
In this illustration, you can see how big – and yet, how tiny still – your baby is as you begin your second trimester.
After the first trimester, a miscarriage is much less likely. And for many moms-to-be, early pregnancy symptoms like morning sickness and fatigue have faded away. If you're feeling more energetic now and haven't been exercising, it's a good time to start a regular pregnancy fitness routine.
If you're feeling more energetic now and haven't been exercising, it's a good time to start a regular pregnancy fitness routine.
Plus: See our ultimate pregnancy to-do list for the second trimester
14 weeks
Your baby's brain impulses have begun to fire and they're using their facial muscles. Their kidneys are working now, too. If you have an ultrasound, you may even see them sucking their thumb.
Your baby is the size of a lemon.
Read about your pregnancy at 14 weeks.
15 weeks
Your baby's eyelids are still fused shut, but they can sense light. If you shine a flashlight on your tummy, they'll move away from the beam. Ultrasounds done this week may reveal your baby's sex.
Your baby is the size of an apple.
Read about your pregnancy at 15 weeks.
16 weeks
The patterning on your baby's scalp has begun, though their hair isn't visible yet. Their legs are more developed, their head is more upright, and their ears are close to their final position.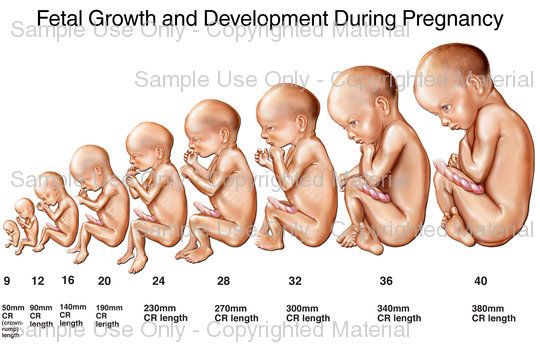
Your baby is the size of an avocado.
Read about your pregnancy at 16 weeks.
17 weeks
Your baby can move their joints, and their skeleton – formerly soft cartilage – is now hardening to bone. The umbilical cord is growing stronger and thicker.
Your baby is the size of a turnip.
Read about your pregnancy at 17 weeks.
18 weeks
Your baby is flexing their arms and legs, and you may be able to feel those movements. Internally, a protective coating of myelin is forming around their nerves.
Your baby is the size of a bell pepper.
Read about your pregnancy at 18 weeks.
19 weeks
Your baby's senses – smell, vision, touch, taste and hearing – are developing and they may be able to hear your voice. Talk, sing or read out loud to them, if you feel like it.
Your baby is the size of an heirloom tomato.
Read about your pregnancy at 19 weeks.
20 weeks
Your baby can swallow now and their digestive system is producing meconium, the dark, sticky goo that they'll pass in their first poop – either in their diaper or in the womb during delivery.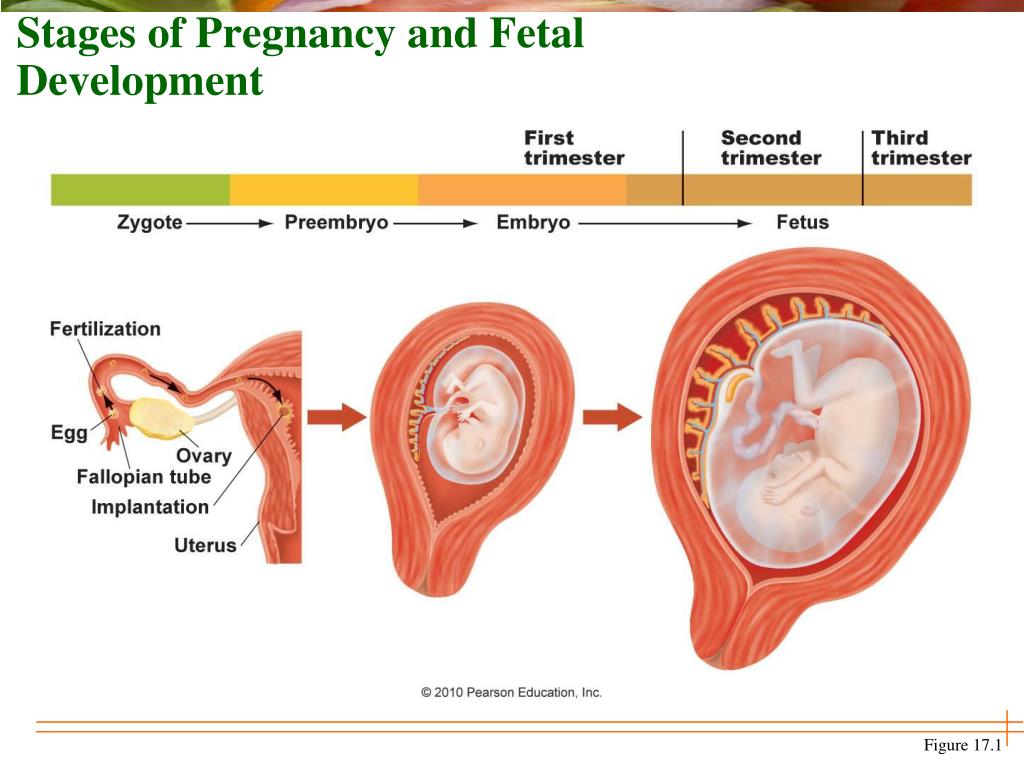
Your baby is the size of a banana.
Read about your pregnancy at 20 weeks.
21 weeks
Your baby's movements have gone from flutters to full-on kicks and jabs against the walls of your womb. You may start to notice patterns as you become more familiar with their activity.
Your baby is the size of a carrot.
Read about your pregnancy at 21 weeks.
22 weeks
Your baby now looks almost like a miniature newborn. Features such as lips and eyebrows are more distinct, but the pigment that will color their eyes isn't present yet.
Your baby is the size of a spaghetti squash.
Read about your pregnancy at 22 weeks.
23 weeks
Your baby's ears are getting better at picking up sounds. After birth, they may recognize some noises outside the womb that they're hearing inside now.
Your baby is the size of a large mango.
Read about your pregnancy at 23 weeks.
24 weeks
Your baby cuts a pretty long and lean figure, but chubbier times are coming. Their skin is still thin and translucent, but that will begin to change soon too.
Their skin is still thin and translucent, but that will begin to change soon too.
Your baby is the size of an ear of corn.
Read about your pregnancy at 24 weeks.
25 weeks
Your baby's wrinkled skin is starting to fill out with baby fat, making them look more like a newborn. Their hair is beginning to come in, and it has color and texture.
Your baby is now the same weight as an average rutabaga.
Read about your pregnancy at 25 weeks.
26 weeks
Your baby is now inhaling and exhaling amniotic fluid, which helps develop their lungs. These breathing movements are good practice for that first breath of air at birth.
Your baby is the size of a bunch of scallions.
Read about your pregnancy at 26 weeks.
27 weeks
This is the last week of your second trimester. Your baby now sleeps and wakes on a regular schedule, and their brain is very active. Their lungs aren't fully formed, but they could function outside the womb with medical help.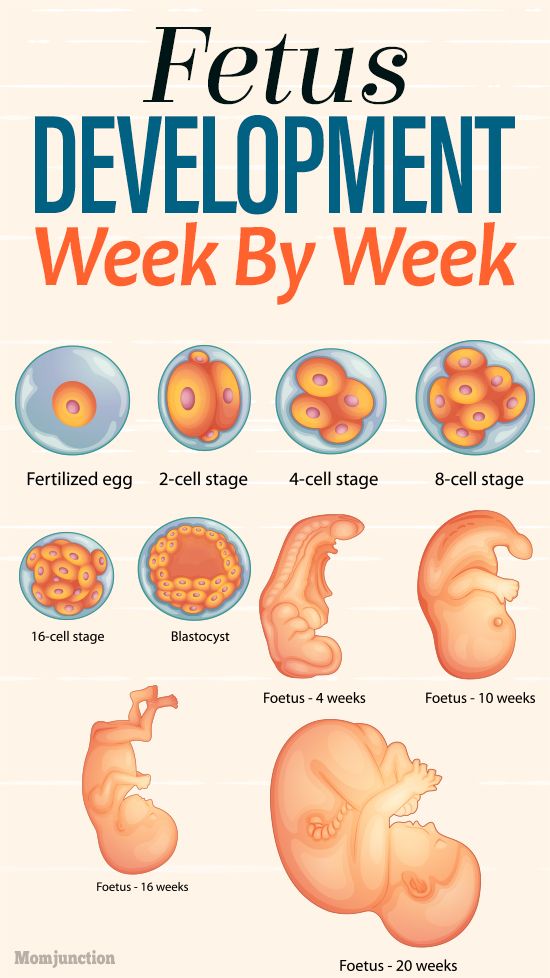
Your baby is the size of a head of cauliflower.
Read about your pregnancy at 27 weeks.
Entering the third trimester: What lies ahead
In this illustration, you'll notice that your growing baby takes up quite a bit of room these days. In the third trimester, you might be peeing more often or have leg cramps as they press on nerves in your hips and back.
Now's the time to do things like sign up for a childbirth class, choose a doctor for your baby, and create a baby registry, if you haven't done so already.
28 weeks
Your baby's eyesight is developing, which may enable them to sense light filtering in from the outside. They can blink, and their eyelashes have grown in.
Your baby is the size of a large eggplant.
Read about your pregnancy at 28 weeks.
29 weeks
Your baby's muscles and lungs are busy getting ready to function in the outside world, and their head is growing to make room for their developing brain.
Your baby is the size of a butternut squash.
Read about your pregnancy at 29 weeks.
30 weeks
Your baby is surrounded by a pint and a half of amniotic fluid, although there will be less of it as they grow and claim more space inside your uterus.
Your baby is the size of a large cabbage.
Read about your pregnancy at 30 weeks.
31 weeks
Your baby can now turn their head from side to side. A protective layer of fat is accumulating under their skin, filling out their arms and legs.
Your baby is the size of a coconut.
Read about your pregnancy at 31 weeks.
32 weeks
You're probably gaining about a pound a week now. Half of that goes straight to your baby, who will gain one-third to half their birth weight in the next seven weeks in preparation for life outside the womb.
Your baby is the size of a large jicama.
Read about your pregnancy at 32 weeks.
33 weeks
The bones in your baby's skull aren't fused yet. That allows them to shift as their head squeezes through the birth canal. They won't fully fuse until adulthood.
That allows them to shift as their head squeezes through the birth canal. They won't fully fuse until adulthood.
Your baby is the size of a pineapple.
Read about your pregnancy at 33 weeks.
34 weeks
Your baby's central nervous system is maturing, as are their lungs. Babies born between 34 and 37 weeks who have no other health problems usually do well in the long run.
Your baby is the size of a cantaloupe.
Read about your pregnancy at 34 weeks.
35 weeks
It's getting snug inside your womb – but you should still feel your baby moving as much as ever. Your baby's kidneys are fully developed, and their liver can process some waste products.
Your baby is the size of a honeydew melon.
Read about your pregnancy at 35 weeks.
36 weeks
Your baby is gaining about an ounce a day. They're also losing most of their lanugo hair that covered their body, along with the vernix caseosa, a waxy substance that was protecting their skin until now.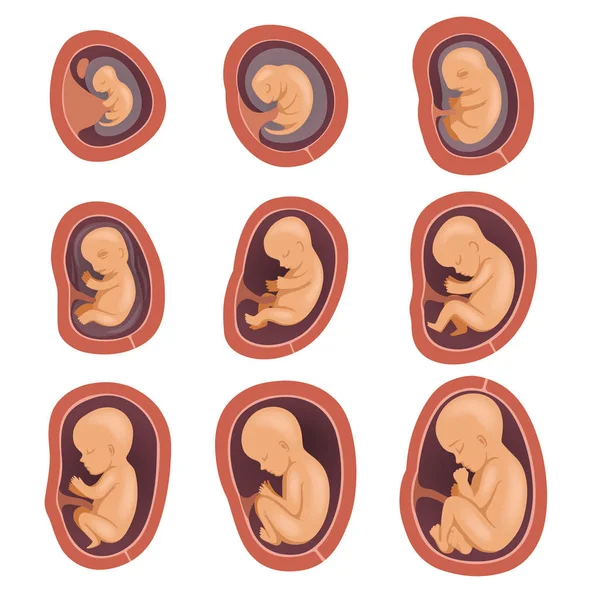
Your baby is the size of a head of romaine lettuce.
Read about your pregnancy at 36 weeks.
37 weeks
Your due date is very close, and though your baby looks like a newborn, they're not considered full-term until 39 weeks. Over the next two weeks, their lungs and brain will continue to mature.
Your baby is the size of a bunch of Swiss chard.
Read about your pregnancy at 37 weeks.
38 weeks
Are you curious about your baby's eye color? Their irises aren't fully pigmented at birth, so their eyes could change color up until they're about a year old.
Your baby is the size of a leek.
Read about your pregnancy at 38 weeks.
Turning full term
At 39 weeks, your baby will be considered full-term. In the illustration, you can see the mucus plug sealing your uterus and how squished your intestines are now.
39 weeks
Your baby's physical development is complete, but they're still busy putting on fat and growing bigger.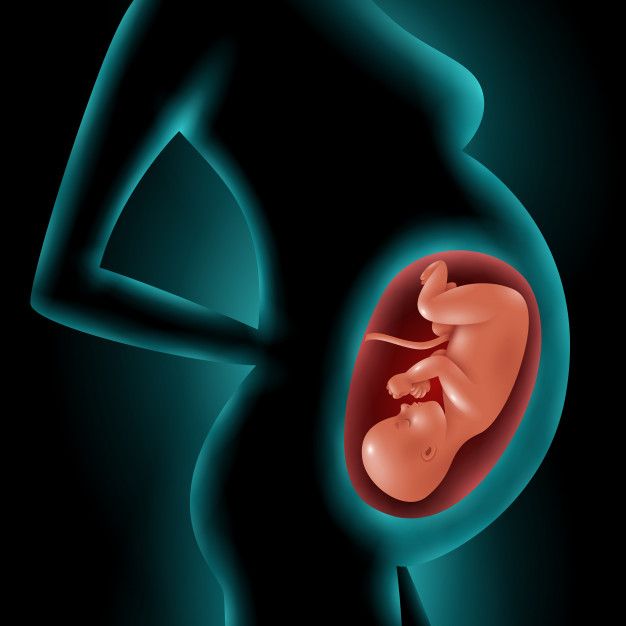
Your baby is the size of a mini watermelon.
Read about your pregnancy at 39 weeks.
40 weeks
If you're past your due date, you may not be as late as you think, especially if you calculated it solely based on the day of your last period. Sometimes women ovulate later than expected.
Your provider will continuously assess your pregnancy to make sure you can safely continue your pregnancy.
Your baby is the size of a small pumpkin.
Read about your pregnancy at 40 weeks.
41 weeks
Your baby is now considered late-term. Going more than two weeks past your due date can put you and your baby at risk for complications, so your provider will probably talk to you about inducing labor. They may perform a non-stress test (NST) to monitor your baby's fetal heart rate and your contractions to make sure your baby isn't in any distress.
Read about your pregnancy at 41 weeks.
Labor and delivery
Meeting your baby for the first time is so exciting – but exactly what will lead up to that moment is unpredictable, and it's natural to feel nervous. Here's some help as you prepare for the big day. Find out how you'll know you're in labor and what to expect from delivery:
Here's some help as you prepare for the big day. Find out how you'll know you're in labor and what to expect from delivery:
Learn the signs of labor and stages of labor
Read when to go to the hospital for labor
Take our free childbirth class
Was this article helpful?
Yes
No
Kate Marple
Kate Marple is a writer and editor who specializes in health, pregnancy, and parenting content. She's passionate about translating complicated medical information into helpful pregnancy and parenting advice that's easy to understand. She lives in San Francisco with her family.
Advertisement | page continues below
My pregnancy week by week
2
weeks
pregnant
3
weeks
pregnant
4
weeks
pregnant
5
weeks
pregnant
6
weeks
pregnant
7
weeks
pregnant
8
weeks
pregnant
9
weeks
pregnant
10
weeks
pregnant
11
weeks
pregnant
12
weeks
pregnant
13
weeks
pregnant
14
weeks
pregnant
15
weeks
pregnant
16
weeks
pregnant
17
weeks
pregnant
18
weeks
pregnant
19
weeks
pregnant
20
weeks
pregnant
21
weeks
pregnant
22
weeks
pregnant
23
weeks
pregnant
24
weeks
pregnant
25
weeks
pregnant
26
weeks
pregnant
27
weeks
pregnant
28
weeks
pregnant
29
weeks
pregnant
30
weeks
pregnant
31
weeks
pregnant
32
weeks
pregnant
33
weeks
pregnant
34
weeks
pregnant
35
weeks
pregnant
36
weeks
pregnant
37
weeks
pregnant
38
weeks
pregnant
39
weeks
pregnant
40
weeks
pregnant
41
weeks
pregnant
Advertisement
Child development by weeks | Regional Perinatal Center
Expectant mothers are always curious about how the fetus develops at a time when it is awaited with such impatience.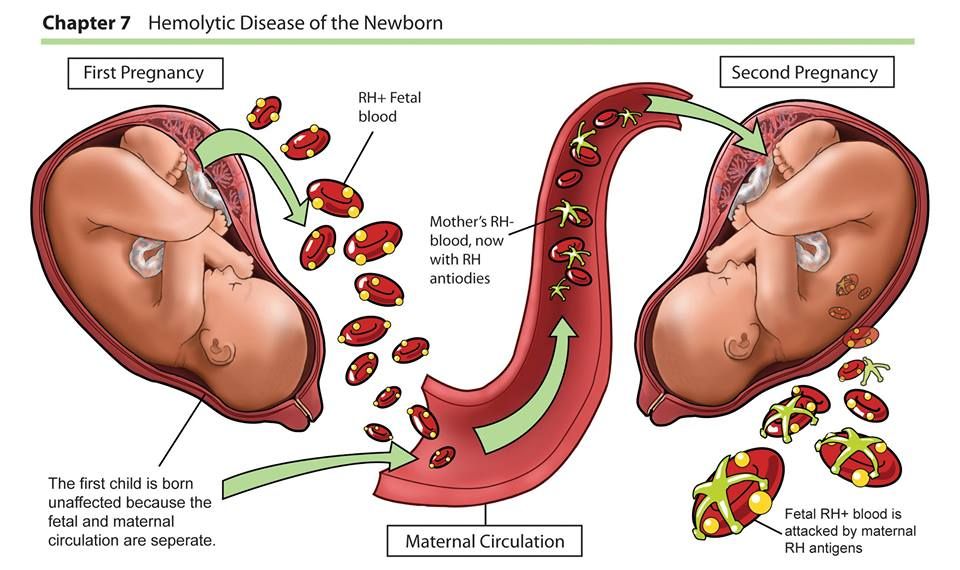 Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
Let's talk and look at the photos and pictures of how the fetus grows and develops week by week.
What does the puffer do for 9 whole months in mom's tummy? What does he feel, see and hear?
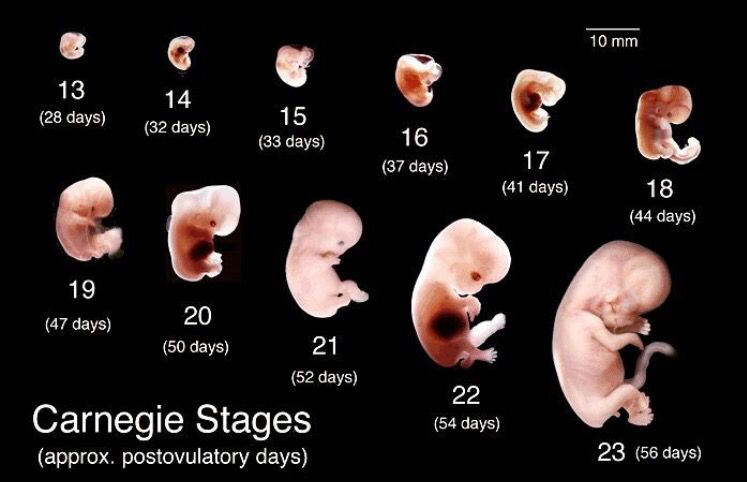
Let's start the story about the development of the fetus by weeks from the very beginning - from the moment of fertilization. A fetus up to 8 weeks old is called embryo , this occurs before the formation of all organ systems.
Embryo development: 1st week
The egg is fertilized and begins to actively split. The ovum travels to the uterus, getting rid of the membrane along the way.
On the 6th-8th days, implantation of eggs is carried out - implantation into the uterus. The egg settles on the surface of the uterine mucosa and, using the chorionic villi, attaches to the uterine mucosa.
Embryo development: 2-3 weeks
Picture of embryo development at 3 weeks.
The embryo is actively developing, starting to separate from the membranes. At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
At this stage, the beginnings of the muscular, skeletal and nervous systems are formed. Therefore, this period of pregnancy is considered important.
Embryo development: 4–7 weeks
Fetal development by week in pictures: week 4
Fetal development by week photo: week 4
Photo of an embryo before the 6th week of pregnancy.
The heart, head, arms, legs and tail are formed in the embryo :) . Gill slit is defined. The length of the embryo at the fifth week reaches 6 mm.
Fetal development by week photo: week 5
At the 7th week, the rudiments of the eyes, stomach and chest are determined, and fingers appear on the handles. The baby already has a sense organ - the vestibular apparatus. The length of the embryo is up to 12 mm.
Fetal development: 8th week
Fetal development by week photo: week 7-8
The face of the fetus can be identified, the mouth, nose, and auricles can be distinguished. The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
The head of the embryo is large and its length corresponds to the length of the body; the fetal body is formed. All significant, but not yet fully formed, elements of the baby's body already exist. The nervous system, muscles, skeleton continue to improve.
Fetal development in the photo already sensitive arms and legs: week 8
The fetus developed skin sensitivity in the mouth (preparation for the sucking reflex), and later in the face and palms.
At this stage of pregnancy, the genitals are already visible. Gill slits die. The fruit reaches 20 mm in length.
Fetal development: 9–10 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 9
Fingers and toes already with nails. The fetus begins to move in the pregnant woman's stomach, but the mother does not feel it yet. With a special stethoscope, you can hear the baby's heartbeat. Muscles continue to develop.
Weekly development of the fetus photo: week 10
The entire surface of the fetal body is sensitive and the baby develops tactile sensations with pleasure, touching his own body, the walls of the fetal bladder and the umbilical cord. It is very curious to observe this on ultrasound. By the way, the baby first moves away from the ultrasound sensor (of course, because it is cold and unusual!), And then puts his hands and heels trying to touch the sensor.
It's amazing when a mother puts her hand to her stomach, the baby tries to master the world and tries to touch with his pen "from the back".
The development of the fetus: 11–14 weeks
Development of the fetus in the photo of the legs: weeks 11
Hands, legs and eyelids are formed, and the genitals become distinguishable (you can find out the gender child). The fetus begins to swallow, and if something is not to its taste, for example, if something bitter got into the amniotic fluid (mother ate something), then the baby will begin to frown and stick out his tongue, making less swallowing movements.
Fruit skin appears translucent.
Development of the fetus: Week 12
Photo of the fetus 12 weeks per 3D ultrasound
buds are responsible for production for production urine. Blood forms inside the bones. And hairs begin to grow on the head. Moves more coordinated. The skin turns pink, the ears and other parts of the body, including the face, are already visible. Imagine, a child can already open his mouth and blink, as well as make grasping movements. The fetus begins to actively push in the mother's tummy. The sex of the fetus can be determined by ultrasound. Baby sucks his thumb, becomes more energetic. The auditory ossicles become stiff and now they are able to conduct sounds, the baby hears his mother - heartbeat, breathing, voice. The fetus intensively gains weight, fat deposits are formed. The weight of the fetus reaches 650 g, and the length is 300 mm. The lungs at this stage of fetal development are so developed that the baby can survive in the artificial conditions of the intensive care unit. Lungs continue to develop. Now the baby is already falling asleep and waking up. Downy hairs appear on the skin, the skin becomes wrinkled and covered with grease. The cartilage of the ears and nose is still soft. Lips and mouth become more sensitive. 9 out of 10 children born at this term survive. The lungs are now adapted to breathe normal air. Breathing is rhythmic and body temperature is controlled by the CNS. The baby can cry and responds to external sounds. Child opens eyes while awake and closes during sleep. The skin becomes thicker, smoother and pinkish. Starting from this period, the fetus will actively gain weight and grow rapidly. Almost all babies born prematurely at this time are viable. The weight of the fetus reaches 2500 g, and the length is 450 mm. The fetus reacts to a light source. The fetus is quite developed, prepared for birth and considered mature. The baby has mastered over 70 different reflex movements. Due to the subcutaneous fatty tissue, the baby's skin is pale pink. The head is covered with hairs up to 3 cm. The baby perfectly mastered the movements of his mother , knows when she is calm, excited, upset and reacts to this with her movements. During the intrauterine period, the fetus gets used to moving in space, which is why babies love it so much when they are carried in their arms or rolled in a stroller. For a baby, this is a completely natural state, so he will calm down and fall asleep when he is rocked. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers, the cartilages of the ears and nose are elastic. After the birth, the baby longs for touching his body, because at first he cannot feel himself - the arms and legs do not obey the child as confidently as it was in the amniotic fluid. Therefore, so that your baby does not feel lonely, it is advisable to carry him in your arms, press him to you while stroking his body. And one more thing, the baby remembers the rhythm and sound of your heart very well . Therefore, you can comfort the baby in this way - take him in your arms, put him on the left side and your miracle will calm down, stop crying and fall asleep. And for you, finally, the time of bliss will come :) . At 21 weeks, the baby is about 25 cm tall and the fetus weighs 300-400 g. At the 21st week, the muscles and skeleton of the fetus are actively developing. The child constantly moves, carefully bends and unbends the limbs, due to its small size it can do somersaults, turns, change the position of its body several times a day, lie transversely in the uterus, turn up or down with its head. At this stage, the baby hears well, not only distinguishes sharp sounds, but reacts to music, so the expectant mother can listen to classics or favorite songs, contribute to the development of the child. The development of the digestive system continues, taste buds are formed. The fetus is able to distinguish the taste of amniotic fluid. Pregnant woman at 21 weeks feels normal. A pregnant woman may put on weight as the baby grows, its muscle and fat mass increases. Expectant mothers eat with pleasure. Their appetite increases significantly, morning sickness and general malaise disappear. At this time, the baby's skeleton is formed, for the development of which calcium is needed. Pregnant women should monitor their health, take calcium supplements as prescribed by a doctor, since if it is lacking, problems with teeth are possible. Calcium is washed out of the tissues, the teeth begin to hurt and crumble. It is important not only to consume vitamins, but also to carefully balance the diet, add calcium-rich cottage cheese, sour cream and other dairy products to the daily menu. The body length of the fetus reaches 28-30 centimeters and its weight is approximately 500 g. The child more and more resembles a newborn, his head no longer looks so big, the length of the limbs increases. The kid no longer keeps his legs constantly bent, he periodically straightens them. Intensively increases the volume and mass of the child's brain. The baby is in constant motion, he can move his fingers and toes, move his head to the right and left. The child knows how to suck his thumb, he tilts his head forward and accurately puts his finger in his mouth. Such actions indicate an increase in sensitivity and development of the vestibular apparatus, improved coordination; the child already feels the position of his own body in space. The baby's brain at this time contains a complete set of neurons, the number of which does not change throughout a person's life. At 22 weeks, the uterus of a pregnant woman is located 2 cm above the navel. The abdomen is not yet very large, but the internal organs are already beginning to shrink due to the accelerated growth of the uterus. A woman may experience some discomfort, pain between the lower ribs. In order not to suffer from pain, you must constantly monitor your posture, choose a comfortable chair with a solid back for work. Special exercises, periodic changes in body position, turns and inclinations will help to solve the problem. It is necessary to avoid sedentary work, take short breaks and fully relax. The fundus of the uterus can press on the stomach, so a common problem at this time is a feeling of heaviness after eating and heartburn. The position of the stomach in pregnant women changes to a more horizontal one, the muscle relaxes, which closes the transition from the esophagus to the stomach, as a result of which the contents of the stomach fall back into the esophagus, irritate it, the woman feels a burning sensation and an unpleasant aftertaste. The 23rd week is an intensive formation of the respiratory system. The fetus begins to gradually make respiratory movements. If earlier the respiratory movements were periodic, now their duration can reach up to 40 minutes. In a minute, the child takes up to 50-60 breaths. The development of the respiratory system does not stop at this time, a kind of breathing exercises continue until childbirth, the baby improves skills and prepares to breathe air. When breathing in the womb, the baby swallows a small amount of amniotic fluid and then pushes it out. In this case, the epithelium is washed. When amniotic fluid is swallowed, part of it is absorbed by the blood vessels, and the original feces, that is, meconium, are formed from the remnants. If the baby is very active and swallows water very intensively, diaphragm irritation and contractions, also called "fetal hiccups", may occur. These rhythmic movements are not abnormal; such hiccups pass in a few minutes, does not pose a threat to the expectant mother and child. If the contractions do not stop within a few hours, you should go to the hospital, as a more serious problem, including hypoxia, can be the cause of hiccups. The 23rd week is an important stage in the intrauterine development of a person. It is at this time that the formation and improvement of the main components of the circulatory and immune systems, including the liver, lymph nodes, spleen and bone marrow, continue. During pregnancy, the fetal immune system goes through several stages of formation and cannot provide full protection against diseases. The baby is protected by maternal antibodies, while its own immune system learns to recognize potential threats, remember bacteria and viruses, and defend itself against their harmful effects. At 23 weeks' gestation, the uterus rises even higher and is located at a height of 4 cm from the woman's navel. The volume of the uterus increases significantly not only due to the growth of the child, but also due to an increase in the mass and volume of amniotic fluid and the placenta. At this time, the weight gain of a pregnant woman of 5-7 kg is optimal. Intensive growth of the uterus causes a shift in the center of gravity. A woman becomes awkward, may feel discomfort in the joints and pain in the spine while walking or sitting for a long time. At this time, the doctor may recommend that a pregnant woman wear special supportive underwear made from natural materials or a bandage. At 24 weeks of gestation, the baby continues to grow rapidly, he weighs already 600 g, and his height is approximately 33 cm. The fetus occupies the entire uterine cavity, so its movements become less impulsive, but more distinct; sharp movements are replaced by smaller ones. The baby can still radically change the position of his body, but prefers to sort out the umbilical cord, play with it, bend and unbend the arms and legs. This week the child's senses are being improved. He knows how to distinguish tastes, hears perfectly and orients himself in space, the baby's skin has a high sensitivity. The fetal brain continues to develop, connections with the senses are formed, so the child's behavior is characterized by a high degree of complexity. Studies have shown that the child reacts to external stimuli: if a bright light hits his mother's stomach, he turns his head away, closes his eyes or covers his face with his hands. A woman should be calm and peaceful, because her fear, excitement is transmitted to the child, he begins to move intensively or freezes abruptly. The baby may react to harsh sounds, noise, or other stimuli. The weight of the pregnant woman continues to increase, the increase this week is about 500 g. Rapid weight gain can cause edema. The growing uterus compresses large veins, which, in turn, significantly complicates the outflow of lymph; a woman's ankles and feet, hands swell, in the evening the problem worsens. A pregnant woman should fully rest, lie more, while raising her legs with a roller or placing an additional pillow in order to improve the outflow of venous blood and eliminate the risk of varicose veins. It is important to purchase comfortable shoes, abandon the "boats" on the stiletto heels and provide the feet with the necessary comfort. Wearing compression tights and stockings will help to significantly reduce the risk of developing varicose veins and the appearance of edema. When choosing the degree of compression and models, it is necessary to take into account the opinion of a phlebologist or gynecologist.
Development of the fetus for weeks: Week 14 9000 9000 Fetal development: 15-18 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 15 Fetal development: 19-23 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 19 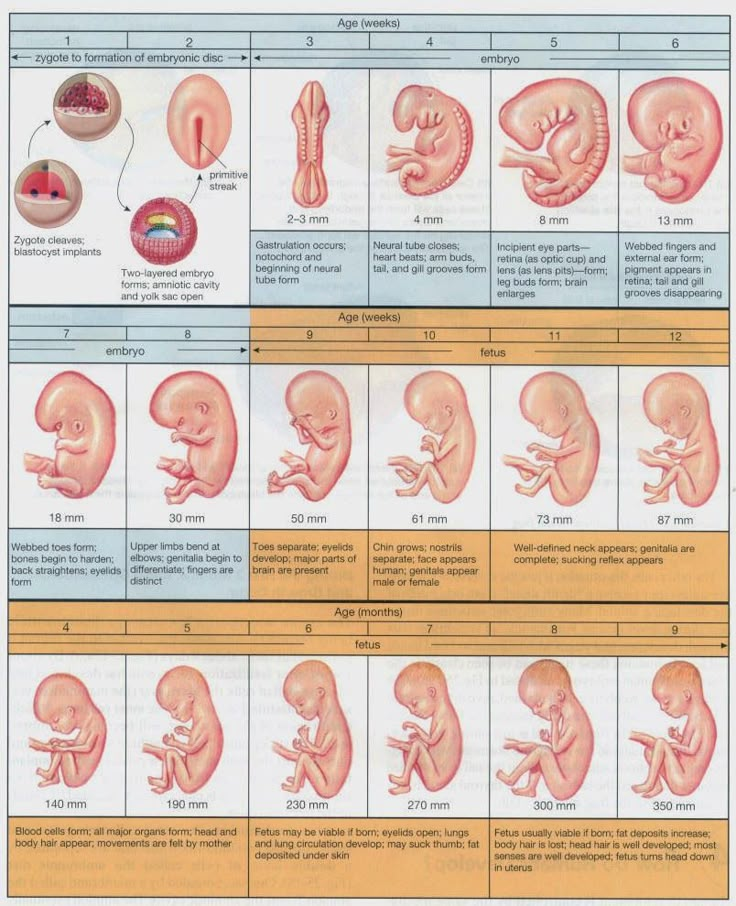 Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Pseudo-feces are formed in the intestines of the fetus - meconium , kidneys begin to work. During this period, the brain develops very actively.
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 20 Fetal development: 24-27 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 27 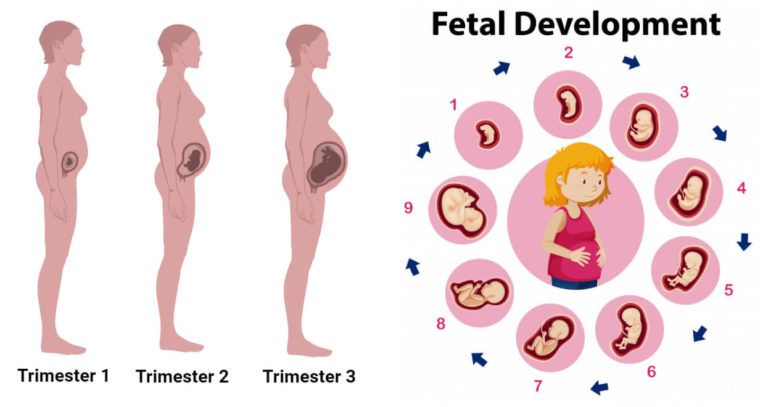 The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm.
The eyes develop, open slightly and can perceive light and squint from direct sunlight. In girls, the labia majora do not yet cover the small ones, and in boys, the testicles have not yet descended into the scrotum. Fetal weight reaches 900–1200 g, and the length is 350 mm. Fetal development: 28-32 weeks
Fetal development: 33-37 weeks
Fetal development by week photo: week 36 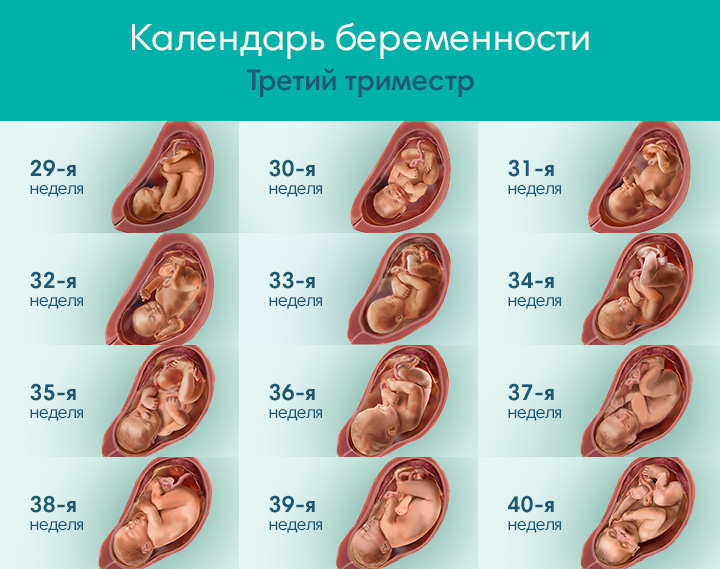 Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed.
Muscle tone increases and the baby can turn and raise his head. On which, the hairs become silky. The child develops a grasping reflex. The lungs are fully developed. Fetal development: 38-42 weeks
Fetal development by weeks photo: week 40 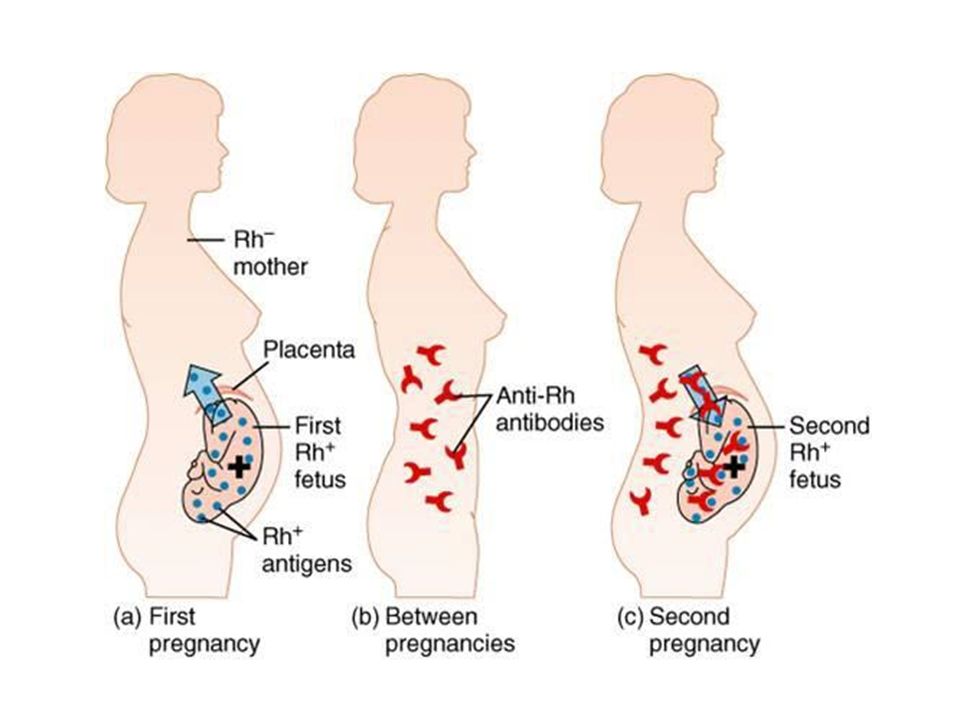 In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm.
In boys, the testicles have descended into the scrotum, and in girls, the large labia cover the small ones. The weight of the fetus reaches 3200-3600 g, and the length is 480-520 mm. 21-24 weeks of pregnancy
21st week of pregnancy
Development of the baby
 due to the lack of subcutaneous fat, the body is still very thin, and the head seems unnaturally large. At this time, the formation of eyelashes and eyebrows takes place, the baby learns to blink, and his skin gradually acquires a flesh color, thickens, constrictions appear on it.
due to the lack of subcutaneous fat, the body is still very thin, and the head seems unnaturally large. At this time, the formation of eyelashes and eyebrows takes place, the baby learns to blink, and his skin gradually acquires a flesh color, thickens, constrictions appear on it. Pregnant woman
 The expectant mother clearly feels the movements of the fetus; very often, the periods of sleep and activity of the child and the woman do not coincide, so pregnant women do not get enough sleep during this period, they wake up at night due to the intensive movements of the baby. Painful sensations at this time are quite rare, since the child does not have sufficient physical strength, and his movements do not differ in intensity.
The expectant mother clearly feels the movements of the fetus; very often, the periods of sleep and activity of the child and the woman do not coincide, so pregnant women do not get enough sleep during this period, they wake up at night due to the intensive movements of the baby. Painful sensations at this time are quite rare, since the child does not have sufficient physical strength, and his movements do not differ in intensity.  The consumption of fish, cereals and legumes, vegetables will help to fill the calcium deficiency.
The consumption of fish, cereals and legumes, vegetables will help to fill the calcium deficiency. 22nd week of pregnancy
Child development
 With age, only the re-formation of connections between cells and the improvement of the work of the human brain takes place.
With age, only the re-formation of connections between cells and the improvement of the work of the human brain takes place. Pregnant woman
 The reason for such changes is not only the pressure of the uterus on the stomach, but also a change in the hormonal background of a woman, an increase in the content of progesterone in the body. To get rid of heartburn, you need to chew food thoroughly, eat often, but in small portions. Do not eat before going to bed, as the food will not have time to be digested. If the symptoms worsen, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications and help the expectant mother balance her diet.
The reason for such changes is not only the pressure of the uterus on the stomach, but also a change in the hormonal background of a woman, an increase in the content of progesterone in the body. To get rid of heartburn, you need to chew food thoroughly, eat often, but in small portions. Do not eat before going to bed, as the food will not have time to be digested. If the symptoms worsen, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications and help the expectant mother balance her diet. 23rd week of pregnancy
Child development
 At this time, the thymus gland (or thymus) develops, which plays an important role in the functioning of the human endocrine system. It is in the thymus that lymphocytes mature. After a kind of "training" in the thymus, the cells enter the bloodstream and can resist infection, neutralize foreign cells in the body.
At this time, the thymus gland (or thymus) develops, which plays an important role in the functioning of the human endocrine system. It is in the thymus that lymphocytes mature. After a kind of "training" in the thymus, the cells enter the bloodstream and can resist infection, neutralize foreign cells in the body. Pregnant woman
 The expectant mother should carefully monitor the daily diet, do not overeat, since excessive weight gain can pose a threat not only to her health, but also to the baby.
The expectant mother should carefully monitor the daily diet, do not overeat, since excessive weight gain can pose a threat not only to her health, but also to the baby. 24th week of pregnancy
Child development
 The amount of muscle mass, namely the muscle fibers of the child, increases sharply. At this time, this indicator reaches its maximum. At later stages of pregnancy, the muscle mass of the fetus increases due to an increase in the volume of each muscle fiber.
The amount of muscle mass, namely the muscle fibers of the child, increases sharply. At this time, this indicator reaches its maximum. At later stages of pregnancy, the muscle mass of the fetus increases due to an increase in the volume of each muscle fiber. Pregnant woman
 The belly grows, the uterus not only increases in size, but also stretches. A woman may notice pain in the abdomen, but they do not differ in intensity and do not last long.
The belly grows, the uterus not only increases in size, but also stretches. A woman may notice pain in the abdomen, but they do not differ in intensity and do not last long.