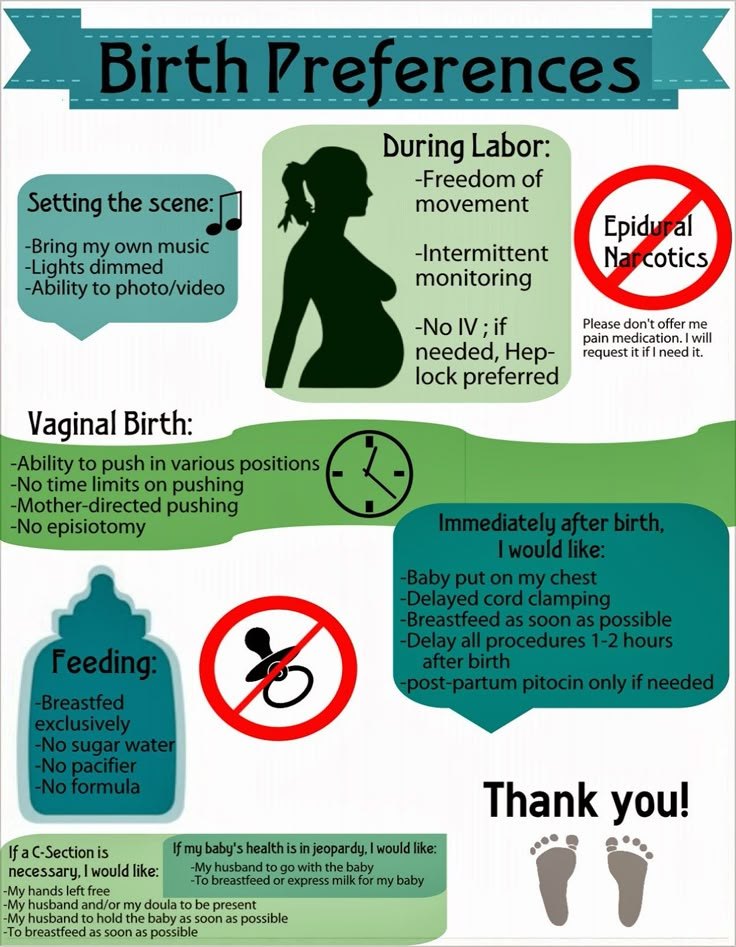
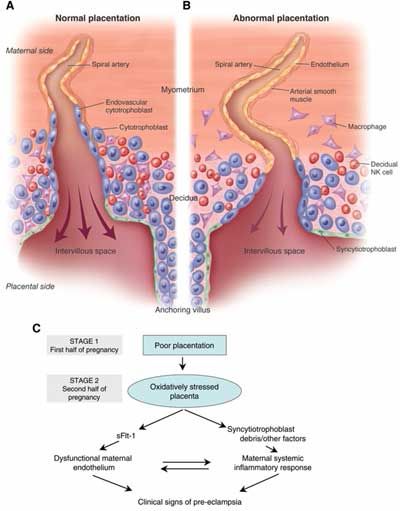
Why is 37 weeks full term
What is considered full-term pregnancy?
Pregnancy can be an exciting and often stressful time in life. In preparing for this huge life change, one thing you can get familiar with in advance is how your doctor might refer to your developing pregnancy and your gestational stage. One phrase you might hear? "Full-term" pregnancy.
In this article, we'll explain this newer terminology and why experts recently expanded the term nomenclature with new definitions. If you’re in a rush to get to the main takeaways, here they are up front:
- A full-term pregnancy is a pregnancy carried for about 39 to 40 completed weeks since your last menstrual period (LMP). This time frame allows for full development of the fetus and increases the chances of healthy outcomes.
- Experts used to only differentiate "preterm" from "term" pregnancies (before 37 weeks and after 37 weeks). New research showed that babies born at 39 weeks of gestation fare better than babies born at 37 weeks, so they redefined what “term” meant and classified "full-term" as the ideal time period for birth.
- Doctors use "full-term" as a guideline for when a pregnancy is far along enough to safely induce delivery for elective reasons (meaning not for medical reasons). Think of it more as a medical framework rather than something you need to pay close attention to.
- Unless you're inducing delivery or scheduling a cesarean section (C-section), there's no way to completely control when birth happens. The most important thing to do is to maintain healthy habits during your pregnancy.
“The vast majority of babies born after 37 weeks will do just fine and not need to go to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU),” says Dr. Jenn Conti, MD, MS, MSc, OB-GYN and Modern Fertility medical advisor. “What this newer information has done is encourage the medical community to not electively induce labor before 39 weeks."
What is considered “full-term” pregnancy?
A pregnancy is "full-term" if a fetus grows inside the uterus for 39 to 40 completed weeks after your last menstrual period (LMP). That 39-40 weeks provides enough time for the fetus to fully develop (see a stage-by-stage breakdown here) and have the lowest chance of needing additional support to breathe, control its temperature, and control its blood sugar outside of the uterus. But this hasn't always been doctors' definition of term pregnancy.
That 39-40 weeks provides enough time for the fetus to fully develop (see a stage-by-stage breakdown here) and have the lowest chance of needing additional support to breathe, control its temperature, and control its blood sugar outside of the uterus. But this hasn't always been doctors' definition of term pregnancy.
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), doctors were initially taught that 37-42 weeks marked a term pregnancy. Until very recently, there was only the distinction of “preterm” and “term” pregnancies. The issue with this binary definition was that there was a wider discrepancy between neonatal outcomes within those final five weeks of pregnancy — and it was difficult to predict one-size-fits-all outcomes for infants.
Fast forward to 2012 when a group of OB-GYN experts further characterized exactly what happens in the last weeks of pregnancy. More research pointed to the idea that babies born before 39 weeks were more likely to have adverse outcomes (particularly in terms of lung development) when compared to babies born at 37 weeks. So, ACOG adjusted their guidelines, creating the idea of "full-term" pregnancy at 39 weeks.
So, ACOG adjusted their guidelines, creating the idea of "full-term" pregnancy at 39 weeks.
Why does dating terminology matter in pregnancy?
While every week and trimester in pregnancy is important for development, delivery doesn't have to happen when you're exactly 40 weeks pregnant in order for a baby to be healthy. The language around "full-term" is more for your healthcare provider than it is for you.
"Babies come on their own all the time before 39 weeks," explains Dr. Conti. "We use the definition of 'full-term' as a guideline for when to allow elective inductions of labor only." In other words, how "term" your pregnancy is (early term/preterm, full-term, postterm) helps your healthcare provider determine when they may or may not recommend induction of labor for non-medical reasons.
Is there anything you can do to influence when you deliver?
Unless you're inducing delivery (either electively after 39 weeks or at any gestational age for a medical indication) or scheduling a cesarean section (C-section), there's no way to know with certainty when your delivery will happen — and there's no way to completely control it (research shows that genetics may even play a role).
What is under your control is working toward a healthy lifestyle during pregnancy:
- Take a prenatal vitamin with folate: Starting a prenatal vitamin with folate at least one month before conception through pregnancy supports healthy fetal neural tube (brain and spine) development.* Even though your prenatal might have a lot of the nutrients your body needs, it's also important to eat balanced, nutritious meals during pregnancy.
- Know what foods to stay away from: Unpasteurized cheese, uncooked meats, and unwashed produce can all have the bacteria Listeria — and pregnant people are 10 times more likely to develop an infection from it (which can be passed on to the fetus).
- Get in regular exercise: Exercise during pregnancy is recommended. Try for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise a day (think of a brisk walk).

- Abstain from alcohol, cigarettes, and moderate your caffeine intake: Medical guidelines are clear that alcohol and cigarettes are a no-go during pregnancy. But caffeine is okay in moderation — just cap it at 200 mg a day.
“It’s also super important to talk to your healthcare provider about your mental health,” says Dr. Conti. “Pregnancy and the postpartum are times when hormones, changing family and financial dynamics, and other life stressors can all influence how you’re feeling mentally — and having a strong support system is vital. One of my absolute favorite resources for patients is Postpartum Support International.”
Does delivering before or after you're full-term mean your due date was "incorrect"?
No. Your estimated due date is the day your pregnancy turns 40 weeks. This date, which is calculated based on the first day of your last menstrual period (LMP), an early ultrasound, the date of IUI insemination, or of an IVF embryo transfer, helps your doctor check for developmental milestones — and identify if any issues arise.
But your due date is an estimate of when you should deliver: Only 5% of babies are delivered on their actual due date. What's more important than exact delivery age is whether or not fetal development is far enough along for an infant to be born without increased risk of health problems — that's where close attention to the gestational age and subdivisions of a "term" pregnancy factor in. If a delivery comes before or after you're full-term, that doesn't mean the due date was "incorrect" — it means you didn't deliver at 39 to 40 completed weeks.
A pregnancy is "full-term" if delivery happens between 39 and 40 completed weeks, when there's a decrease in the likelihood of adverse outcomes and health risks. But because delivery timing isn't fully within our control, the most important things to do are take steps to support a healthy pregnancy and make sure to attend all of your prenatal appointments so your healthcare provider can monitor you.
Always remember that your healthcare provider is there to answer any questions you have throughout your pregnancy. And if you're looking to connect with and get support from other pregnant people, our free online community has a dedicated channel you can request to join today.
And if you're looking to connect with and get support from other pregnant people, our free online community has a dedicated channel you can request to join today.
This article was medically reviewed by Dr. Jennifer Conti, MD, MS, MSc.
Definition of Term Pregnancy | ACOG
Number 579 (Reaffirmed 2022)
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists Committee on Obstetric Practice Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine
This document reflects emerging clinical and scientific advances as of the date issued and is subject to change. The information should not be construed as dictating an exclusive course of treatment or procedure to be followed.
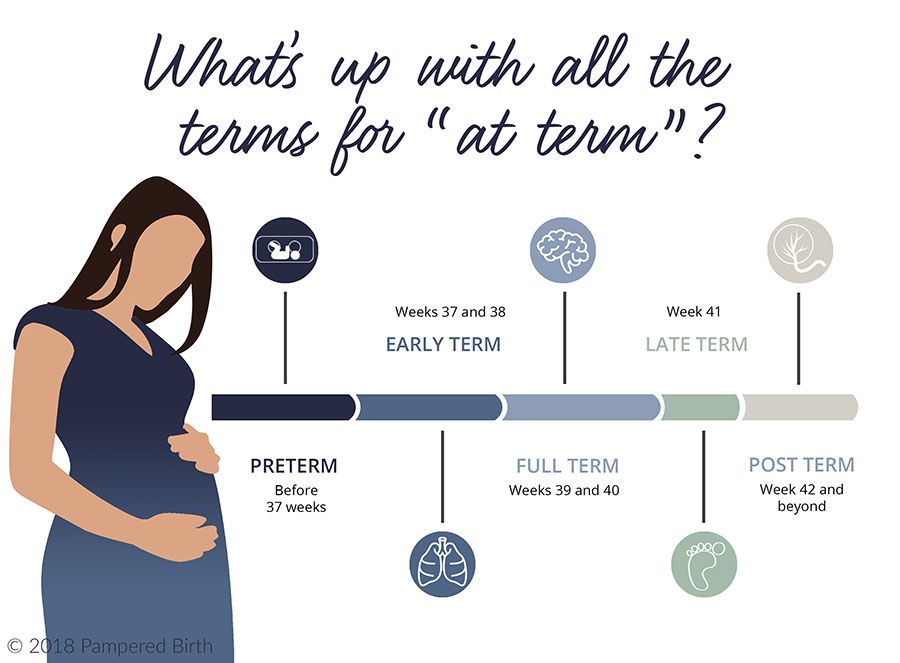
ABSTRACT: In the past, the period from 3 weeks before until 2 weeks after the estimated date of delivery was considered “term,” with the expectation that neonatal outcomes from deliveries in this interval were uniform and good. Increasingly, however, research has shown that neonatal outcomes, especially respiratory morbidity, vary depending on the timing of delivery within this 5-week gestational age range. To address this lack of uniformity, a work group was convened in late 2012, which recommended that the label “term” be replaced with the designations early term (37 0/7 weeks of gestation through 38 6/7 weeks of gestation), full term (39 0/7 weeks of gestation through 40 6/7 weeks of gestation), late term (41 0/7 weeks of gestation through 41 6/7 weeks of gestation), and postterm (42 0/7 weeks of gestation and beyond) to more accurately describe deliveries occurring at or beyond 37 0/7 weeks of gestation. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine endorse and encourage the uniform use of the work group’s recommended new gestational age designations by all clinicians, researchers, and public health officials to facilitate data reporting, delivery of quality health care, and clinical research.
Increasingly, however, research has shown that neonatal outcomes, especially respiratory morbidity, vary depending on the timing of delivery within this 5-week gestational age range. To address this lack of uniformity, a work group was convened in late 2012, which recommended that the label “term” be replaced with the designations early term (37 0/7 weeks of gestation through 38 6/7 weeks of gestation), full term (39 0/7 weeks of gestation through 40 6/7 weeks of gestation), late term (41 0/7 weeks of gestation through 41 6/7 weeks of gestation), and postterm (42 0/7 weeks of gestation and beyond) to more accurately describe deliveries occurring at or beyond 37 0/7 weeks of gestation. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine endorse and encourage the uniform use of the work group’s recommended new gestational age designations by all clinicians, researchers, and public health officials to facilitate data reporting, delivery of quality health care, and clinical research.
Gestation in singleton pregnancies lasts an average of 40 weeks (280 days) from the first day of the last menstrual period to the estimated date of delivery. In the past, the period from 3 weeks before until 2 weeks after the estimated date of delivery was considered “term” 1, with the expectation that neonatal outcomes from deliveries in this interval were uniform and good. Increasingly, however, research has identified that neonatal outcomes, especially respiratory morbidity, vary depending on the timing of delivery even within this 5-week gestational age range. The frequency of adverse neonatal outcomes is lowest among uncomplicated pregnancies delivered between 39 0/7 weeks of gestation and 40 6/7 weeks of gestation 2, 3. For this reason, quality improvement projects have focused, for example, on eliminating nonmedically indicated deliveries at less than 39 0/7 weeks of gestation 4.
In order to facilitate data reporting, delivery of quality health care, and clinical research, it is important that all clinicians, researchers, and public health officials use both uniform labels when describing deliveries in this period and a uniform approach to determining gestational age. To address the lack of uniformity in neonatal outcomes between 37 0/7 weeks of gestation and 42 0/7 weeks of gestation, a work group was convened in late 2012 to determine whether term pregnancy should be redefined 5. The work group included representatives from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (the College), the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), and other professional societies and stakeholder organizations. The work group recommended that the label “term” be replaced by the designations early term, full term, late term, and postterm to more accurately describe deliveries occurring at or beyond 37 0/7 weeks of gestation Box 1. The group recommended that the use of the label “term” to describe all deliveries between 37 0/7 weeks of gestation and 41 6/7 weeks of gestation should be discouraged. Details of the evidence and rationale that are the foundation of these recommendations can be found in published summaries of this conference 5.
To address the lack of uniformity in neonatal outcomes between 37 0/7 weeks of gestation and 42 0/7 weeks of gestation, a work group was convened in late 2012 to determine whether term pregnancy should be redefined 5. The work group included representatives from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (the College), the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), and other professional societies and stakeholder organizations. The work group recommended that the label “term” be replaced by the designations early term, full term, late term, and postterm to more accurately describe deliveries occurring at or beyond 37 0/7 weeks of gestation Box 1. The group recommended that the use of the label “term” to describe all deliveries between 37 0/7 weeks of gestation and 41 6/7 weeks of gestation should be discouraged. Details of the evidence and rationale that are the foundation of these recommendations can be found in published summaries of this conference 5.
The College and SMFM endorse and encourage the uniform use of the work group’s recommended new gestational age designations by all clinicians, researchers, and public health officials to facilitate data reporting, delivery of quality health care, and clinical research.
Early term: 37 0/7 weeks through 38 6/7 weeks
Full term: 39 0/7 weeks through 40 6/7 weeks
Late term: 41 0/7 weeks through 41 6/7 weeks
Postterm: 42 0/7 weeks and beyond
Uniform definitions of term are predicated on a uniform method of determining gestational age. The work group provided a method for determination of gestational age 5 that, like other similar methods 6, focused on a hierarchy of clinical and ultrasonographic criteria. Individual methods may differ in the details of when and how ultrasonographic biometry should be used to change estimated date of delivery based on last menstrual period; however, it is not the purpose of this document to establish the priority of one method over another. The College and SMFM are working with other expert groups to establish evidence-based consensus on criteria for determining gestational age.
The College and SMFM are working with other expert groups to establish evidence-based consensus on criteria for determining gestational age.
Copyright November 2013 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, 409 12th Street, SW, PO Box 96920, Washington, DC 20090-6920. All rights reserved.
ISSN 1074-861X
Definition of term pregnancy. Committee Opinion No. 579. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2013;122:1139–40.
37-40 weeks of pregnancy
37th week of pregnancy for a baby
At 37 weeks of gestation, the baby is approximately 48 cm tall and weighs 2,600 g. facial features, pronounced cartilage tissue. The accumulation of subcutaneous fat at this stage of pregnancy makes the outline of the body softer and more rounded. The skin of the child is gradually smoothed out, it is no longer as pink as in the previous weeks of intrauterine development, the integument gradually brightens. The body of the baby is still abundantly covered with grease, but the amount of fluff is noticeably reduced, fluff hair remains only on the shoulders and back, in some babies they disappear almost completely.
Fat accumulation continues this week. It reaches a maximum of 15% of the total body weight of the child. It is difficult to overestimate the importance of adipose tissue for newborns, it is it that protects the child from overheating or hypothermia, since the baby's thermoregulation system after childbirth is still not sufficiently formed and continues to develop in the first months of a small person's life.
At this time, not only the volume of subcutaneous fat increases, but muscles and skeleton also develop intensively. The child constantly moves arms and legs. These unique workouts help increase muscle mass. Also, the baby makes rhythmic respiratory movements that strengthen the intercostal muscles and the diaphragm, and prepare the respiratory organs for childbirth.
Pregnant woman at 37 weeks
As the due date approaches, pregnant women begin to notice the appearance of their precursors, that is, certain signs, changes that occur under the influence of hormones. The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
The body of a woman is preparing to give birth to a child, progesterone gives way to the dominant role of the birth hormone estrogen, the state of health of a pregnant woman changes.
From the 37th week, expectant mothers can observe the following changes:
- slight weight loss;
- abdominal shrinkage;
- the appearance of training or "false" contractions and the increase in their intensity;
- discharge of mucus from the cervix.
The nature of the stool changes, it becomes looser, aching pains in the lower back of varying intensity may appear, the fundus of the uterus descends. A woman notes some signs on her own, others are observed by a gynecologist during a routine examination.
Harbingers do not appear in all women. Some expectant mothers notice only some of the above symptoms, while others observe signs of an impending birth not two or three weeks before their date, but just a few hours. Both the appearance of precursors at the 37th week and their absence are a variant of the norm and depend on the individual characteristics of the woman's body.
This week the woman's body is intensified preparation for the birth of a child. If the fetus is located correctly, head down, it gradually descends, goes to the lower part of the uterus, presses to the body and bends the limbs, intuitively taking the most comfortable position for passing the birth canal. The consequence of the movement of the fetus is the omission of the bottom of the uterus. The abdomen drops, the pressure on the diaphragm significantly decreases, the pregnant woman can breathe easily, the shortness of breath that haunted her in previous weeks disappears. The pressure on the stomach also decreases, heartburn disappears, a feeling of heaviness after eating and other unpleasant sensations. Moving the baby can put pressure on the bowels and bladder. A pregnant woman at this time often experiences the urge to urinate, may suffer from frequent loose stools. The reason for frequent bowel movements is not only the mechanical effect of the uterus on it, but also an increase in the content of estrogens in the body, hormones that contribute to the excretion of fluid. At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
At the 37th week, the expectant mother can empty her intestines up to 3-4 times a day and at the same time observe a significant liquefaction of feces.
38th week of pregnancy: the development of the future baby
At the 38th week, the fetus is fully formed, so childbirth at this time is no longer dangerous for both the mother and the baby. The weight of the fetus is about 3 kg, but this indicator can vary significantly for different babies, the weight depends on the individual characteristics of the mother and child, the structural features of the body and other factors. The body length of a newborn is approximately 50 cm.
All organs and systems at 38 weeks of age are characterized by physiological and morphological maturity, they are fully ready for work. At this time, the child prepares for childbirth, makes respiratory movements and prepares the intercostal muscles for breathing. The tissues of the lungs are bathed in amniotic fluid, which helps maintain the right level of surfactant that coats the baby's lungs from the inside. All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
All elements of the respiratory system are ready for use. With the first breath after birth, the alveoli begin to transfer oxygen from the air to the blood, gas exchange occurs, the respiratory and circulatory systems begin to work intensively.
Pregnant woman
The body of a pregnant woman continues to actively prepare for the birth of a baby, the estrogen content rapidly increases, and the progesterone level decreases significantly. A change in the hormonal background contributes to the softening of the tissues of the birth canal and cervix. Throughout pregnancy, the lumen of the cervical canal is closed by a plug of thick mucus, which protects the baby from infection, and the uterine cavity protects against the penetration of microorganisms dangerous to health. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the consistency of the mucus changes, it becomes more liquid and begins to gradually flow out. In some women, mucus leaves gradually, while in other women in labor at the same time. The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
The discharge resembles colorless egg white in its consistency and appearance. Sometimes the mucus is colored pinkish, brown or yellow. The discharge of the cork is painless, a woman may experience a slight feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen. More abundant vaginal discharge than during the entire pregnancy can signal the passage of the cork.
A woman should carefully monitor the color and volume of discharge, since too much colorless discharge may indicate not only the cork has come off, but also be one of the symptoms of amniotic fluid leakage. Indicator pads and amnio tests or test strips will help determine the cause of the discharge. Pads are sold in many pharmacies and can be easily used at home. If amniotic fluid leakage is confirmed, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After the mucus plug has passed, you should stop visiting the pool and swimming in open water, as the risk of infection of the child increases significantly. It is also necessary to exclude sexual contact.
39th week of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus?
At 39 weeks, the baby weighs 3100-3500 g and is 50-52 cm tall. Height and weight are very relative and can vary significantly. The baby is rapidly preparing for the most important test of his life - birth, which requires endurance and considerable effort. During this period of pregnancy, the size and weight of the child's adrenal glands, that is, the glands of the endocrine system, which are responsible for the reaction of the human body to stress factors, increase. It is the hormones adrenaline and norepinephrine produced by the adrenal glands that help the child quickly adapt to new temperature conditions, tactile, sound and light impulses.
All the senses of the baby are developed at 39 weeks. Within a few moments after birth, the baby can focus his eyes, he reacts to bright light and moving objects, many scientists claim that newborns distinguish colors, see the faces of parents and doctors. The hearing of the baby in the last weeks of intrauterine life is also fully developed; after birth, he reacts to loud sounds and noise. A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
A newborn baby is able to determine the main shades of taste, recognize sour, bitter, sweet and salty.
In the womb, the baby is in an aquatic environment that minimizes contact. Immediately after birth, the baby experiences many tactile sensations, unlike intrauterine life, he feels the touch of his mother's hands and diapers, towels, dressings and other materials. Babies especially like the touch of skin to skin, so in a modern maternity hospital, newborns must be laid out on their mother's stomach even before cutting the umbilical cord. The child adapts to the new environment more easily, feels protected. Laying out a child has not only a psychological aspect, since it contributes to the colonization of microorganisms from the mother's skin to the skin and mucous membranes of the baby, and increases its immunity.
Pregnant woman
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the expectant mother strives to prepare her apartment or house as much as possible for the arrival of a new family member. Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, but nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
Scientists call this sign of impending birth the nesting syndrome. Many women observe signs of the syndrome from the thirtieth week of pregnancy, but nesting reaches its maximum point at the 39-40th week. Pregnant women tend to do general cleaning and repairs, re-paste the wallpaper and purchase a lot of new things that, in their opinion, are simply necessary in the house. After giving birth, many purchases are puzzling. The reason for this behavior is an increase in the level of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. These hormones are produced by the adrenal glands, they are necessary not only for the woman, but also for the baby to prepare for the upcoming birth.
40th week of pregnancy: how does the baby develop?
40 weeks - term pregnancy. The weight of a child who was born at such a period ranges from 2,600 g to 4,400 g, and his body length is 48-53 cm. These indicators are very arbitrary, since miniature babies weighing 2,600 g and real heroes are born at 40 weeks, whose body weight approaches 5,000 g. The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
The length of the newborns can also vary from 45 to 55 cm.
Most women give birth exactly at 40 weeks. At this time, the baby is completely ready for birth, it meets all the parameters of a full-term baby. Before childbirth, the child closely presses the arms and legs to the body, bends the head as much as possible and presses against the exit from the uterus. This position allows you to make it possible to pass the birth canal with the narrowest part of the skull. In the course of labor, with each contraction, the child gradually moves down, he does not move in a straight line, but makes helical-translational movements, as if screwing into the mother's birth canal. During the progress of the newborn, the complete descent of his head, the cervix fully opens. This is followed by attempts, that is, contractions of the uterus, which advance the child through the birth canal. Gradually, the head of the baby is shown, and after it - his torso. Childbirth is a complex mechanism that is aimed not only at the safe passage of the birth canal by the child, protecting him from accidental injuries due to increased pressure, but also at preventing ruptures of the woman's soft tissues.
Pregnant woman
The long wait for meeting her unborn child is coming to an end, and the 40th week of pregnancy is the last for most women. Every day, the anxiety of the expectant mother increases, a long wait affects the mood and well-being. Women strive to have a baby as soon as possible so that pregnancy and painful contractions are a thing of the past. Every pregnant woman dreams of meeting a baby, wants to hug him to her chest and stroke the delicate head.
Many women, especially primiparas, are afraid that labor will begin unnoticed, but such cases are extremely rare. A woman feels the onset of childbirth, feels regular contractions, which are repeated at regular intervals and gradually increase, the time interval between them is reduced.
Labor may be preceded by prenatal rupture of amniotic fluid, which occurs in a certain percentage of women in labor. After the waters break, contractions may be quite weak or completely absent. Regardless of the intensity of contractions, the outpouring of water is one of the signs of the onset of labor and requires immediate contact with specialists, hospitalization of a woman in a maternity hospital or hospital, since when the water breaks, the integrity of the bladder is violated and the risk of penetration of microorganisms dangerous to the health of the child increases into the uterine cavity. It is important that after the water breaks, the baby is born in a maximum of 10-12 hours.
It is important that after the water breaks, the baby is born in a maximum of 10-12 hours.
A pregnant woman should properly tune in to childbirth, concentrate on the desired result and believe in her own strength, fulfill the task assigned to her by nature. The right psychological attitude and theoretical knowledge will help a woman become a mother, successfully go through all the stages of childbirth and press the long-awaited child to her heart.
37th week of pregnancy - what happens to the baby, development and weight of the baby, belly at the thirty-seventh week of pregnancy
WHAT'S HAPPENING
At the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the baby's body produces hormones important for life. One of them - cortisone - is necessary for the full maturation of the lungs. Iron accumulates actively in the liver. Without this trace element, the proper functioning of the body is impossible. In the last trimester of pregnancy, the liver of the fetus contains five times more iron than that of adults. This supply is enough for the baby for the first six months of life.
This supply is enough for the baby for the first six months of life.
At the 37th week of pregnancy, the main systems of the body continue to improve. The neurons of the brain begin to become covered with myelin sheath, which helps the nerves transmit signals. This process will continue throughout the first year of a child's life.
The ear and nasal cartilages harden, but the bones of the skull, due to the fontanelles, will remain flexible so that it is easier for the baby to overcome the obstacles of the birth canal. The fontanel is an area where there is no bone tissue. A newborn baby has as many as six of them, but most close immediately after birth. As the cranial bones grow, the fontanelles will gradually disappear.
YOUR FEELING
By the 37th week of pregnancy, the belly stops growing, but the baby continues to gain weight, which is why it becomes more and more crowded. There is practically nowhere to move, so there is less movement than before. But still they should be about 10 during the day.
But still they should be about 10 during the day.
For many women, the belly begins to sink, which is one of the signs that labor is approaching. If this does not happen by 37 weeks, do not be upset: sometimes the stomach drops only at the very end of pregnancy. But if this still happened, this does not mean that the birth will begin right now - most likely, you need to wait a week or two. Now there will be no problems with breathing, however, due to the strong pressure of the fetus on the bladder, you will have to go to the toilet even more often.
The huge size of the uterus can still cause discomfort in the spine. Try to get more rest by shifting the main responsibilities around the house to the future dad and other family members.
At 36 - 37 weeks of pregnancy, Braxton-Hicks training bouts intensify and become longer. At the same time, you have a clear feeling of tension and relaxation of the muscles of the uterus, but there should not be any pain. Soreness in the lower abdomen and the regular nature of contractions indicate the onset of labor. In this case, you must urgently consult a doctor who will refer you to the hospital.
Soreness in the lower abdomen and the regular nature of contractions indicate the onset of labor. In this case, you must urgently consult a doctor who will refer you to the hospital.
At the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the amount of vaginal discharge may increase. There is nothing to worry about - the time has come for the mucous plug to come out: its particles are lumps of mucus with red streaks that can be found in light secretions. Sometimes the cork comes out all at once. In this case, you will see a lump of mucus with a volume of about two tablespoons.
RISK FACTORS
One of the risk factors at 36 to 37 weeks of gestation is group B streptococcus. This is a bacterium that can settle in the vagina or around the rectum. Group B streptococcus occurs in about 35% of healthy adults. But if its colonies are present in a pregnant woman, a child may become infected during childbirth. And infected newborns need serious antibiotic treatment and careful monitoring in the hospital, because group B streptococcus can cause dangerous complications in babies, such as meningitis, pneumonia, and blood poisoning. If the test for the presence of this bacterium is positive, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics before and during childbirth. This measure will prevent the transmission of infection to the baby.
If the test for the presence of this bacterium is positive, your doctor will likely prescribe antibiotics before and during childbirth. This measure will prevent the transmission of infection to the baby.
Childbirth at the 37th week of pregnancy no longer poses a serious danger. In the presence of cramping pains in the abdomen and lower back, early departure of amniotic fluid, you should call an ambulance. Sometimes a woman even needs a premature birth - for example, if she is diagnosed with:
- Fetal hypoxia;
- Infectious disease;
- placental abruption;
- Entwining the baby with the umbilical cord.
In these cases, the method of delivery is chosen by the attending physician.
MEDICAL SUPERVISION
At the appointment, the gynecologist will examine you on the armchair for the readiness of the cervix for childbirth, because starting from the 36th - 37th week of pregnancy, the baby may ask to be born at any moment. During a vaginal examination, the doctor pays attention to the location, density and length of the cervix.
During a vaginal examination, the doctor pays attention to the location, density and length of the cervix.
While the baby lives in the mother's tummy, the lower segment of the uterus has thick walls, which begin to stretch during childbirth, becoming softer and thinner. This is called "smoothing". Before the onset of childbirth, it is equal to zero, with active labor, the walls of the cervix are smoothed out by 50%, and just before the birth of the baby - by 100%.
Also at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the doctor checks the degree of disclosure (stretching) of the cervix. This indicator is determined in centimeters. With full disclosure, the width of the pharynx reaches 10 cm. If during the examination it is found that the cervix is not ready for childbirth, the doctor prescribes medication or non-drug means to increase its maturity.
When examined at 37 weeks of pregnancy, the gynecologist takes a smear. The results of the tests will make it possible to judge the presence or absence of infection in the birth canal. If necessary, treatment is prescribed, because at the time of birth, the child should be protected as much as possible from possible infection. Also during this visit, the doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat, measure your weight and blood pressure, assess the width of the pelvis and the presentation of the fetus.
If necessary, treatment is prescribed, because at the time of birth, the child should be protected as much as possible from possible infection. Also during this visit, the doctor will listen to the baby's heartbeat, measure your weight and blood pressure, assess the width of the pelvis and the presentation of the fetus.
Ultrasound at this time is usually not done. It may be needed only if any abnormalities were detected during pregnancy.
RECOMMENDATIONS
Starting from the 37th week of pregnancy, the baby can be born at any time. Check if everything is prepared for the hospital. At the last moment, you will not be up to it. When packing bags, don't forget to put sanitary pads (not tampons!) and two or three bras in them.
If insomnia bothers you, be more active during the day. At 36 - 37 weeks of pregnancy, you can do simple housework, walk in the fresh air, attend courses for expectant mothers and do gymnastics for pregnant women. And before you go to bed, air the bedroom well.
Keep track of your nutrition. At 37 weeks of pregnancy, you should consume as many dairy products as possible. Let your daily menu include: kefir, cottage cheese, natural yogurt, curdled milk, sour cream and cheese. In addition, you really need foods rich in iron and vitamin C.
At 37 weeks pregnant, many couples refuse to have intimate relationships. With good physical condition and the absence of medical contraindications, sex is not prohibited at this stage.
Pregnancy and childbirthNinth month of pregnancy: changes in the female body and fetal development by week
Newborn careDowry for a newborn
What do you need to have at home for discharge, what stroller and crib to choose, and what equipment to buy?
Pregnancy and childbirthWhat to take with you to the hospital
Pregnancy and childbirthPsychology of pregnancy and motherhood
Positive attitude and overcoming fears during pregnancy, psychological hygiene and well-being of a woman.