When do lower back pains start in pregnancy
Back Pain During Pregnancy | Cedars-Sinai
Overview
Back pain in pregnancy is very common, affecting an estimated 50 percent to 80 percent of pregnant women.
It can range from mild pain associated with specific activities to acute pain that becomes chronic.
About 10 percent of the time the pain becomes so severe that it can interfere with the ability to work or carry out normal activities during pregnancy.
Studies show that lower back pain usually occurs between the fifth and seventh months of being pregnant, although in some cases it begins as early as eight to 12 weeks.
Women with pre-existing lower back problems are at higher risk for back pain, and their back pain can occur earlier in their pregnancy.
Symptoms
Lumbar pain during pregnancy is generally located at and above the waist in the center of the back, and it may be concurrent with pain that radiates into the woman's leg or foot.
Posterior pelvic pain (in the back of the pelvis) is four times more prevalent than lumbar pain in pregnancy. It is a deep pain felt below the waistline, on one or both sides or across the tailbone.
Causes and Risk Factors
Increase of hormones — Hormones released during pregnancy allow pelvic-area ligaments to soften and joints to loosen in preparation for the birthing process. This change may affect the support your back normally experiences.
Center of gravity — Your center of gravity will gradually move forward as your uterus and baby grow, which causes your posture to change.
Additional weight — Your developing pregnancy and baby create additional weight that your back must support.
Posture or position — Poor posture, excessive standing and bending over can trigger or escalate back pain.
Stress — Stress usually accumulates in weak areas of the body. Because of the changes in your pelvic area, you may experience an increase in back pain during stressful periods of your pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of back pain during pregnancy is based on a review of the patient’s medical history, a physical examination and possibly an MRI, to rule out a herniated disk. No X-ray or CT scan will be performed because these procedures use radiation.
Treatment
Watch your posture when you are sitting. Lounging in a chair all day puts more strain on your spine than anything else. At home and at work, make sure the chairs you use most provide good support, preferably with a straight back, arms and a firm cushion. Use a footrest to elevate your feet slightly, and don't cross your legs. That can cause your pelvis to tilt forward, exacerbating those strained back muscles.
Take breaks. Walk or stand and stretch at least once an hour. Sitting too long can make your back hurt even more. Try not to stand too long either. If you work on your feet, try to place one foot on a low stool to take some pressure off your lower back.
Avoid lifting heavy loads.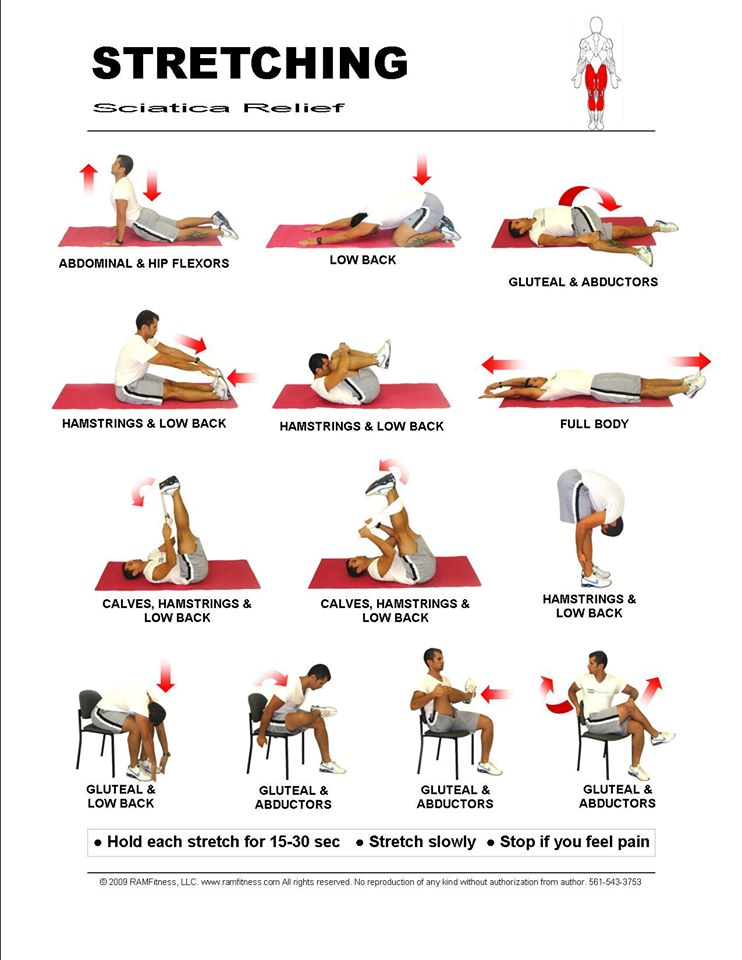 If you must, do it slowly. Stabilize yourself by assuming a wide stance; bend at the knees, not at the waist; and lift with your arms and legs, not your back.
If you must, do it slowly. Stabilize yourself by assuming a wide stance; bend at the knees, not at the waist; and lift with your arms and legs, not your back.
Watch your weight.
Wear the right shoes. Extremely high heels are out, as are completely flat ones. Experts recommend a 2-inch heel to keep your body in proper alignment.
No reaching. Use a low, stable step stool to get items from high places and you’ll avoid additional strain.
Think happy thoughts. A calm mind leads to a looser back. You can also try some prenatal yoga, which will relax both your mind and your back.
Physiotherapy, yoga, exercise (walking, biking and swimming) are all considered safe for most pregnant women and can be performed for 20 to 45 minutes, three to five days a week. Pregnant women should take care to exercise at a mild to moderate level, but not to the point of exhaustion.
Strengthen your stomach. Do pelvic tilts to strengthen your abs, which in turn support your back. Or sit on an exercise ball and rock back and forth.
Or sit on an exercise ball and rock back and forth.
Go hot and cold. Soothe sore muscles by applying cold compresses, then warm compresses in 15-minute intervals.
Take a warm bath. Or turn the showerhead to pulsating to massage your back.
Get a massage. Wait until after the first trimester to get one. Go to a masseuse who knows you’re pregnant and is trained in the art of prenatal massage.
Always Talk to Your OB
Sometimes back pain is a red flag that something serious is going on. Among the most worrisome causes of pregnancy back pain is preterm labor. Women should watch for pain that is new and cyclical — which could be a sign of uterine contractions — along with vaginal bleeding or any change in vaginal discharge that could indicate a placental issue or an early rupture of your waters.
If you experience numbness, tingling or a sharp, shooting pain in your buttocks, legs or feet, call your doctor to make sure there are no serious conditions. Even though the cause of numbness is usually not a more worrisome condition, such as preterm labor, it could signify compression of the sciatic nerve or other nerves that connect your spine to the lower body and pelvic area.
Even though the cause of numbness is usually not a more worrisome condition, such as preterm labor, it could signify compression of the sciatic nerve or other nerves that connect your spine to the lower body and pelvic area.
Pregnant women should always consult with their healthcare professional before taking any prescription or over-the-counter medicine. Women taking pain medicines who are considering becoming pregnant should also consult with their healthcare professionals to discuss the risks and benefits of pain medicine. Healthcare professionals should continue to follow the recommendations on the drug labels when prescribing pain medicines to pregnant patients.
© 2000-2022 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Back pain in pregnancy - NHS
It is very common to get backache or back pain during pregnancy, especially in the early stages.
During pregnancy, the ligaments in your body naturally become softer and stretch to prepare you for labour. This can put a strain on the joints of your lower back and pelvis, which can cause back pain.
Avoiding and easing back pain in pregnancy
Try these tips:
- bend your knees and keep your back straight when you lift or pick something up from the floor
- avoid lifting heavy objects
- move your feet when you turn to avoid twisting your spine
- wear flat shoes to evenly distribute your weight
- try to balance the weight between 2 bags when carrying shopping
- keep your back straight and well supported when sitting – look for maternity support pillows
- get enough rest, particularly later in pregnancy
- have a massage or a warm bath
- use a mattress that supports you properly – you can put a piece of hardboard under a soft mattress to make it firmer, if necessary
- go to a group or individual back care class
You can take paracetamol to ease back pain while you are pregnant, unless your GP or midwife says not to. Always follow the instructions on the packet.
Always follow the instructions on the packet.
When to get help for back pain in pregnancy
If your backache is very painful, talk to your GP or midwife. They may be able to refer you to an obstetric physiotherapist at your hospital, who can give you advice and may suggest some helpful exercises.
Non-urgent advice: Contact your GP or midwife urgently if:
You have back pain and you:
- are in your second or third trimester – this could be a sign of early labour
- also have a fever, bleeding from your vagina or pain when you pee
- have pain in one or more of your sides (under your ribs)
Immediate action required: Call 999 or go to A&E if:
You have back pain and:
- you lose feeling in one or both of your legs, your bum, or your genitals
Exercises to ease back pain in pregnancy
This gentle exercise helps to strengthen stomach (abdominal) muscles, which can ease back pain in pregnancy:
Credit:
Agencja FREE / Alamy Stock Photo https://www. alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-doing-exercises-32344372.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=FC98903A-AC65-4C38-BF96-00BB1F4352CB&p=29056&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dBTHBG4%26qt_raw%3dBTHBG4%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d387440%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-doing-exercises-32344372.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=FC98903A-AC65-4C38-BF96-00BB1F4352CB&p=29056&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dBTHBG4%26qt_raw%3dBTHBG4%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d387440%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
1) Start on all fours with knees under hips, hands under shoulders, fingers facing forwards and stomach muscles lifted to keep your back straight.
Credit:
Agencja FREE / Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-doing-exercises-32344367.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=DA3DDA5D-3D86-471C-9DFB-66A032C21750&p=29056&n=440&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3Dbar%26st%3D0%26sortby%3D3%26qt%3D%2520Pregnant%2520woman%2520doing%2520exercises%26qt_raw%3D%2520Pregnant%2520woman%2520doing%2520exercises%26qn%3D%26lic%3D3%26edrf%3D0%26mr%3D0%26pr%3D0%26aoa%3D1%26creative%3D%26videos%3D%26nu%3D%26ccc%3D%26bespoke%3D4%26apalib%3D%26ag%3D0%26hc%3D0%26et%3D0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3D0%26loc%3D0%26ot%3D0%26imgt%3D0%26dtfr%3D%26dtto%3D%26size%3D0xFF%26blackwhite%3D%26cutout%3D%26archive%3D1%26name%3D%26groupid%3D%26pseudoid%3D%26userid%3D%26id%3D%26a%3D%26xstx%3D0%26cbstore%3D0%26resultview%3DsortbyRelevant%26lightbox%3D%26gname%3D%26gtype%3D%26apalic%3D%26tbar%3D1%26pc%3D%26simid%3D%26cap%3D1%26customgeoip%3DGB%26vd%3D0%26cid%3D%26pe%3D%26so%3D%26lb%3D%26pl%3D0%26plno%3D%26fi%3D0%26langcode%3Den%26upl%3D0%26cufr%3D%26cuto%3D%26howler%3D%26cvrem%3D0%26cvtype%3D0%26cvloc%3D0%26cl%3D0%26upfr%3D%26upto%3D%26primcat%3D%26seccat%3D%26cvcategory%3D*%26restriction%3D%26random%3D%26ispremium%3D1%26flip%3D0%26contributorqt%3D%26plgalleryno%3D%26plpublic%3D0%26viewaspublic%3D0%26isplcurate%3D0%26imageurl%3D%26saveQry%3D%26editorial%3D%26t%3D0%26edoptin%3D%26apaid%3D%7B18B189B6-6A83-41BD-8442-2448A6B7E281%7D%26custspecid%3D14369B5F-24B7-4344-B743-D5DE569A1F46
2) Pull in your stomach muscles and raise your back up towards the ceiling, letting your head and bum relax downwards gently – do not let your elbows lock and only move your back as far as you comfortably can.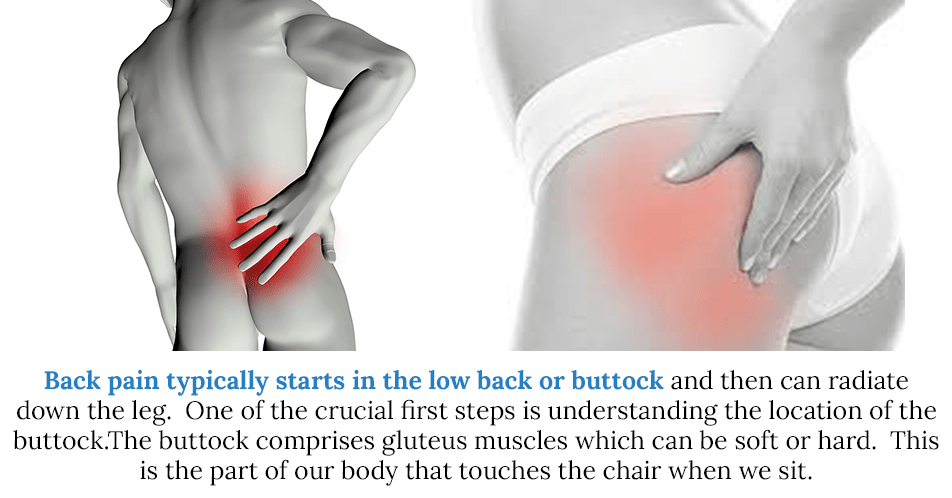
Credit:
Agencja FREE / Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-pregnant-woman-doing-exercises-32344372.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=FC98903A-AC65-4C38-BF96-00BB1F4352CB&p=29056&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dBTHBG4%26qt_raw%3dBTHBG4%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d387440%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
3) Hold for a few seconds then slowly return to the box position – take care not to hollow your back, it should always return to a straight, neutral position.
4) Do this slowly and rhythmically 10 times, making your muscles work hard and moving your back carefully.
Doing prenatal yoga or aquanatal classes (gentle exercise classes in water) with a qualified instructor can also help build your muscles to better support your back. Ask at your local leisure centre.
Page last reviewed: 15 March 2021
Next review due: 15 March 2024
Lower back pain during pregnancy: what to do?
Often during pregnancy, the expectant mother experiences pain in the lumbar spine. This is primarily due to a growing tummy and an increasing load on the spine, but there are other reasons for which low back pain can occur.
Let's talk about this in more detail.
During pregnancy, low back pain can be both physiological and pathological.
First of all, these can be normal processes of adaptation of the musculoskeletal system to the upcoming childbirth, but there may also be exacerbations of chronic diseases of the mother, such as pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), osteochondrosis, scoliosis, etc. And here (ATTENTION!) only a doctor will help to deal with the causes of pain, and not girlfriends "who had exactly the same thing."
And here (ATTENTION!) only a doctor will help to deal with the causes of pain, and not girlfriends "who had exactly the same thing."
Physiologically, during pregnancy, the entire ligamentous apparatus is prepared for childbirth. In the ovaries and placenta, the hormone RELAXIN is produced, under the influence of which the connective tissue becomes more extensible and loose. This is necessary so that during childbirth the pelvic bones become more mobile, and make it possible for the child to be born through a dense pelvic ring. These changes can cause back pain.
Usually, such pains appear from 20 weeks of pregnancy (5 months) and decrease or disappear only after childbirth. To cope with them partly helps DIET, rich in calcium. Be sure to include dairy products, nuts, fish, meat, greens in your diet.
In addition, there are some practical tips recommended for all pregnant women.
So, AVOID:
- sudden movements;
- long standing;
- wrong postures when sitting;
- excessive exercise;
- uncomfortable shoes with high and/or unstable heels.

In diseases of the spine (osteochondrosis, scoliosis, herniated discs) can also help SPECIAL GYMNASTICS, aimed at strengthening the muscles of the back, abdomen, thighs and buttocks. Recommended aerobics, aqua aerobics, swimming. A CORRECTLY SELECTED BANDAGE and non-drug treatments such as MASSAGE will also help, since the drugs that usually treat these diseases are contraindicated during pregnancy.
NEUROLOGIST'S CONSULTATION IS NECESSARY FOR PAIN ASSOCIATED WITH SPINE DISEASES.
If the pain in the lower back is aching (pulling), accompanied by fever, edema, frequent urination, headache, discoloration of urine, increased blood pressure, then it is necessary to conduct an examination of the urinary system - the bladder and kidneys. With renal colic, the pain is sharp, cramping, urine may be mixed with blood. To establish an accurate diagnosis, ADDITIONAL STUDIES are carried out: ultrasound, laboratory blood and urine tests. Antibiotic therapy is prescribed for the treatment of inflammatory processes in the kidneys, taking into account the sensitivity of the microorganism to the antibiotic.
Treatment must be carried out in a hospital under the supervision of a doctor, because. these diseases affect the condition of the fetus, the course of pregnancy and the health of the woman.
In addition to all of the above, pain in the lumbar spine can be one of the signs of threatened miscarriage. More often, such pain is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen. In such a situation, it is necessary to urgently CONTACT THE OB/GYNECOLOGIST to examine and decide on the tactics of further actions, which should be aimed at removing the tone of the smooth muscles of the uterus.
If you notice such signs before 37 weeks of pregnancy and at the same time there is discharge from the genital tract, if pain is felt in the lower abdomen, and the intervals between these pains are reduced, then you need to urgently seek medical help, this may indicate a threat of termination of pregnancy .
At a later date, pain in the sacrum may be the first sign of labor that has begun.
Be healthy, take care of yourself and your future baby!
About the author
- Sytova Valentina Ivanovna
- Obstetrician-gynecologist of the first category
- All publications of the author and it all becomes relaxed. Poor posture and poor muscle tone can also affect spinal mechanics.
The lumbar curve of the spine begins to slowly increase as the pelvis begins to move back. This posture begins to affect the weakened muscles and leads to the accumulation of fatigue in the muscles of the lower back. A woman may experience moderately painful muscle spasms at first, which may be the first sign of the possibility of persistent low back pain as the pregnancy progresses. The growing uterus shifts the center of gravity and weakens the abdominal muscles, changes posture and puts excessive stress on the back. If the uterus affects the nerves, then this can lead to pain. In addition, being overweight during pregnancy puts more stress on the muscles and joints, and therefore, by the end of the day, a pregnant woman may feel discomfort.
Experts describe the two most common patterns of low back pain during pregnancy: low back pain that occurs in the area of the lumbar vertebrae in the lower back, and posterior pelvic pain, which is felt in the back of the pelvis. Some women have symptoms of both types of low back pain.
Lower back pain is similar to the pain that a woman experienced before pregnancy. Pain is felt in the lower back and around the spine, approximately at waist level. Women may also experience pain that radiates to the legs. Prolonged sitting or standing can aggravate the pain and, as a rule, the pain tends to increase towards the end of the day. Many more women experience back pelvic pain, which is felt less than lower back pain. The pain may be deep inside the buttocks, on one or both buttocks, or in the back of the thighs. Pain can be triggered by activities such as walking, climbing stairs, getting in and out of the bathroom on a low cabinet, turning in bed, or twisting and lifting heavy objects.

Positions that involve leaning forward, such as sitting, in a chair, and working at a desk while leaning forward, can exacerbate posterior pelvic pain. Women with posterior pelvic pain are also more likely to experience pain over the pubic bone.
When low back pain radiates to the buttocks and thighs, sciatica is often suspected - although sciatica is not very common in pregnant women. True sciatica, which can be caused by a herniated disc or the presence of a disc protrusion in the lumbar spine, occurs in only 1 percent of pregnant women.
If there is compression and inflammation of the sciatic nerve (disc herniation), then the pain in the legs is more severe than with normal low back pain. Pain can be felt not only in the thigh, but also below the knee or even radiate to the foot. It is also possible the presence of sensory disturbances, such as numbness or tingling sensations.
In severe sciatica, there may be numbness in the groin area, as well as in the genital area.
 You may also have trouble urinating or defecation. If a pregnant woman has suspicions of sciatica, then she must definitely contact her doctor. If symptoms such as impaired sensation in the legs and weakness in one or both legs or loss of sensation in the groin and impaired urination or defecation appear, then you need to see a doctor urgently! Such symptoms may be evidence of the development of the "cauda equina" syndrome in the presence of a herniated disc in a pregnant woman, and in such cases an emergency operation is necessary.
You may also have trouble urinating or defecation. If a pregnant woman has suspicions of sciatica, then she must definitely contact her doctor. If symptoms such as impaired sensation in the legs and weakness in one or both legs or loss of sensation in the groin and impaired urination or defecation appear, then you need to see a doctor urgently! Such symptoms may be evidence of the development of the "cauda equina" syndrome in the presence of a herniated disc in a pregnant woman, and in such cases an emergency operation is necessary. Risk factors for low back pain
It is not surprising that, most likely, low back pain in pregnant women is most likely if there were already pains before pregnancy or there were degenerative changes in the lumbar spine (protrusions, herniated discs). Also at higher risk are pregnant women who led an inactive lifestyle before pregnancy, as a result of which their back muscles are weak, as well as the abdominal muscles. Pregnancy with multiple fetuses (twins) significantly increases the risk of lower back pain.
 Obesity may also be a risk factor for developing low back pain during pregnancy.
Obesity may also be a risk factor for developing low back pain during pregnancy. Diagnosis of low back pain.
Examinations such as CT (MSCT) are rarely used to diagnose the causes of low back pain in pregnant women due to possible teratogenic effects on the fetus. MRI is also not recommended, especially in the first trimester of pregnancy. But, if there are clinical indications, then MRI can be performed. Therefore, as a rule, the diagnosis of low back pain in pregnant women is mainly based on physical examination data, symptoms and medical history (for example, the presence of a disc herniation before pregnancy).
Treatment
The use of any medication during pregnancy is a big risk, since all medication will also enter the body of the fetus. Therefore, the usual prescription of painkillers, muscle relaxants, or steroids (NSAIDs) for back pain is contraindicated in pregnant women. In addition, the use of acupuncture physiotherapy is also not recommended.
 It is possible to use light massage and very gentle manual therapy techniques.
It is possible to use light massage and very gentle manual therapy techniques. At the forefront of the treatment of back pain in pregnant women comes exercise therapy (gymnastics) and certain recommendations for the implementation of daily activities. Gymnastics can be specialized, such as prenatal yoga. Good effect gives swimming and walking.
Swimming is an excellent choice of exercise for pregnant women because it strengthens the abdominal and lower back muscles, and being in the water relieves stress on joints and ligaments.
Need to maintain proper biomechanics during pregnancy:
- Stand up straight. This becomes more and more difficult to do as the shape of the body changes, but one must try to keep the back straight and the shoulders back. Pregnant women tend to drop their shoulders and arch their back as their belly grows, which puts more stress on the spine.
- If it is necessary to sit during the day, then one should sit straight.
 Leg support (bedside table) can help prevent lower back pain, and you can also put a special pillow under the lower back. Take frequent breaks from sitting. You need to get up and walk for several minutes, at least once an hour.
Leg support (bedside table) can help prevent lower back pain, and you can also put a special pillow under the lower back. Take frequent breaks from sitting. You need to get up and walk for several minutes, at least once an hour. - It is equally important not to stand too long. If you need to stand all day, then it is advisable to rest while lying on your side during a break, supporting your upper leg and stomach with pillows.
- Avoid movements that increase pain. If there is posterior pelvic pain, then one should try to limit activities such as climbing stairs. It is also advisable to avoid any activity that requires extreme movement of the hips or spine.
- It is important to wear comfortable shoes and avoid high heels. As the abdomen grows, the center of gravity shifts and when wearing shoes with heels, the risk of falls increases.
- Always bend your knees and pick things up from your haunches to minimize stress on your back. Spinal twisting should be avoided and activities such as vacuuming or mopping should be avoided.