When do baby teeth develop
Anatomy and Development of the Mouth and Teeth
Anatomy and Development of the Mouth and Teeth | Johns Hopkins MedicineTeeth start developing in the fetus. Good nutrition from the mother during pregnancy is important in the development of the teeth. The mother's diet should have adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, vitamin C, and vitamin D. Certain medicines, such as tetracycline, should not be taken by the mother while she is pregnant. These can cause discoloration to the developing teeth of the embryo. There are 4 main stages of development of the tooth:
-
The first stage begins in the fetus at about 6 weeks of age. This is when the basic substance of the tooth forms.
-
Next, the hard tissue that surrounds the teeth is formed, around 3 to 4 months of gestation.
-
After the child is born, the next stage occurs when the tooth actually protrudes through the gum.
-
Finally, there is the loss of the primary "baby" teeth.
Parts of the tooth
Each tooth has 4 main parts, including the following:
-
Enamel. The outer layer of the tooth and the hardest material in the body.
-
Dentin. The inner layer and the main part of the tooth, and the largest dental tissue.
-
Pulp. Soft tissue on the inside of the tooth that contains the nerve, blood supply, and the ability to produce dentin.
-
Root. The part of the tooth that secures it into the jaw.
When will my child's teeth come in?
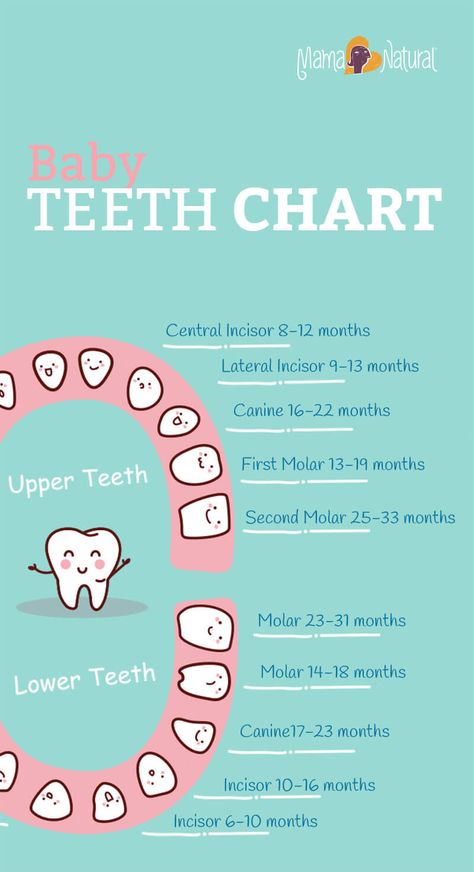
While every child is different, the primary teeth begin to come in between the ages of 6 and 12 months. Most of the primary teeth (baby teeth) will have erupted by 33 months. Girls tend to have their teeth come in before boys.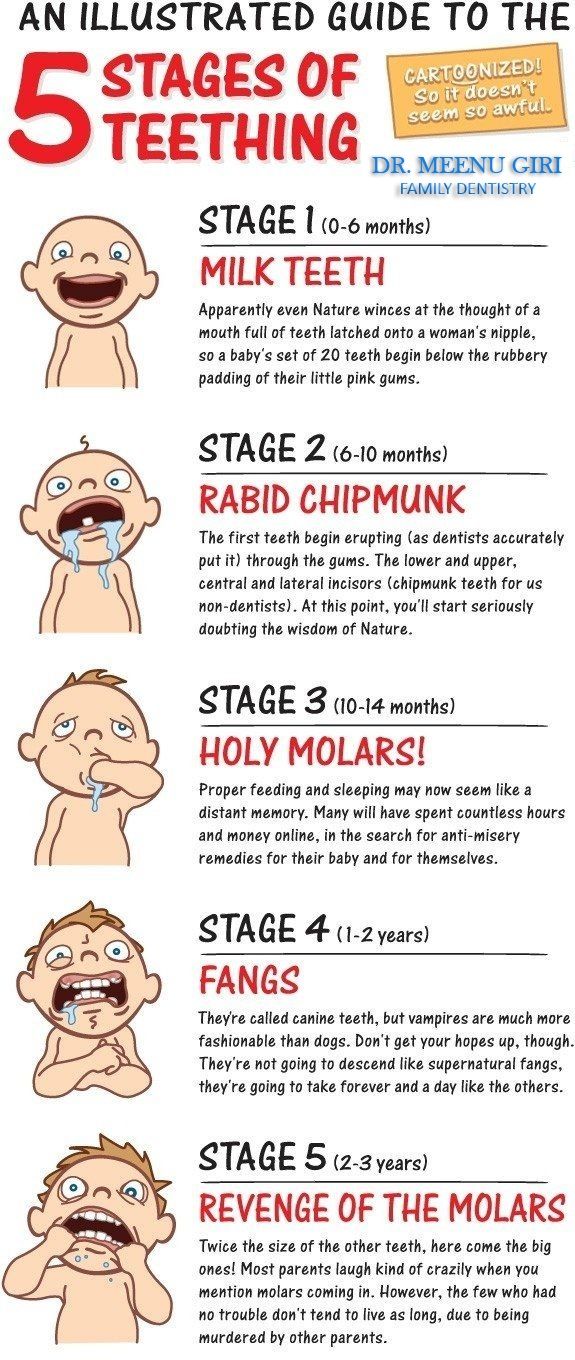 The following are general guidelines for the eruption of the baby teeth:
The following are general guidelines for the eruption of the baby teeth:
-
The first tooth to erupt is usually a middle, front tooth on the lower jaw, known as the central incisor. This is followed by the second central incisor on the lower jaw.
-
Next, the four upper incisors usually come in.
-
The above is followed by the first 4 molars, and the remaining bottom 2 lateral incisors. Lateral incisors are beside (lateral to) the central incisors. Next, the 4 first molars come in.
-
Then the cuspids, or the pointed teeth, appear.
-
Usually, after the child reaches 2 years old, the 4 second molars (the last of the baby teeth) appear.
The teeth on the upper jaw usually erupt 1 to 2 months after the same tooth on the lower jaw. There are a total of 20 primary teeth. Usually, about 1 tooth erupts per month once the teeth have started coming in. There is normally a space between all the baby teeth. This leaves room for the larger permanent teeth to erupt.
There is normally a space between all the baby teeth. This leaves room for the larger permanent teeth to erupt.
The eruption sequence can vary quite a bit from child to child. So, don't become overly concerned if your child's teeth do not follow the pattern above. However, if teeth fail to come in a year after the expected time, check with your child's dentist to make sure they are developing properly. Below is a chart showing average ages of eruption and shedding:
When will my child's permanent teeth come in?
Your child will begin losing his or her primary teeth (baby teeth) around the age of 6. The first teeth to be lost are usually the central incisors. This is then followed by the eruption of the first permanent molars. The last baby tooth is usually lost around the age of 12, and is the cuspid or second molar. There will be a total of 32 permanent, or adult, teeth.
Related
-
Anatomy and Development of the Mouth and Teeth
Care of the Mouth and Teeth
-
Anatomy and Development of the Mouth and Teeth
Tongue-Tie (Ankyloglossia)
Related Topics
How your baby's teeth develop
How your baby's teeth develop | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
Babies are usually born with 20 baby teeth (also known as primary teeth).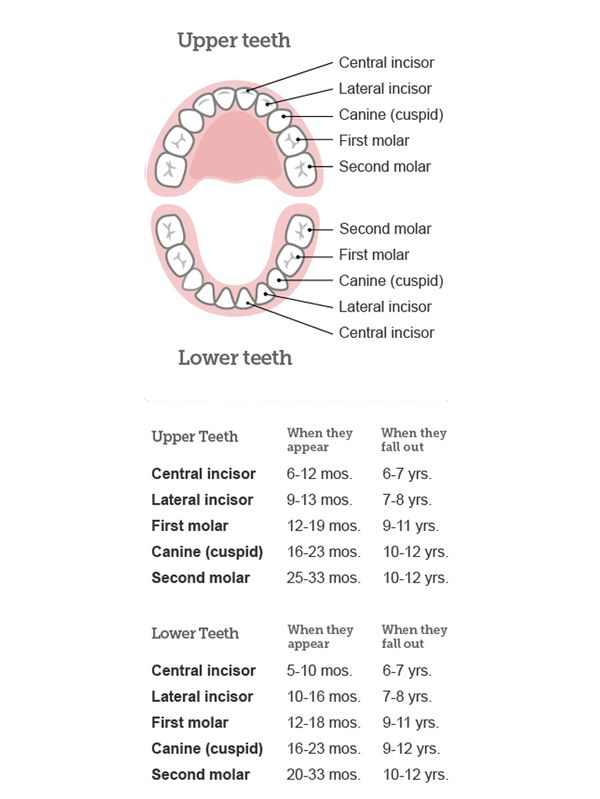 They start to come through the gums at about 6 months and all the teeth have usually appeared by the time the baby is 2 to 3 years old. This process is called teething. The teeth will fall out at various times during childhood.
They start to come through the gums at about 6 months and all the teeth have usually appeared by the time the baby is 2 to 3 years old. This process is called teething. The teeth will fall out at various times during childhood.
About baby teeth
Babies are born with the following teeth:
- 4 second molars
- 4 first molars
- 4 canine teeth
- 4 lateral incisors
- 4 central incisors
There is one set on each side of the upper jaw, and one on each side of the lower jaw.
The teeth in the centre of the bottom jaw often come through first, sometime between 4 months and 10 months.
Each child is different so don’t worry if your baby’s teeth appear earlier or later. Talk to your dentist if you are worried.
Your child’s jaw will continue to grow and permanent teeth will start to replace the baby teeth when the child is around age 6.
The outer covering of baby teeth is made of thinner enamel than the enamel of permanent teeth and this makes the baby teeth look whiter. It also means they are more likely to get tooth decay.
Baby teeth also have shorter and different shaped roots from permanent teeth, making it easier for the roots to dissolve later and to allow space for permanent teeth to grow underneath them.
Babies can be quite uncomfortable when they are teething. Try chilled (not frozen) teething rings, wash cloths or dummies to ease the pain.
Baby teeth are important
Baby teeth help your child to chew food easily and to pronounce words properly. They are also needed to hold a place in the jaw for the permanent teeth to come through later.
It is important to keep baby teeth clean. This will protect against infection, cavities and pain. Decayed baby teeth can damage the permanent teeth underneath.
How to care for baby teeth
Baby teeth can start to decay as soon as they appear in the mouth. Frequent exposure to sugary liquids can destroy the teeth.
Frequent exposure to sugary liquids can destroy the teeth.
You should wipe your baby’s gums with a wet facecloth or a clean gauze pad after each feed. You can brush your baby’s first tooth as soon as it appears with a soft toothbrush and a little water.
Older children should be supervised while they are cleaning their teeth. Children over 18 months can use a pea-sized amount of children’s low-fluoride toothpaste and if possible should be taught not to swallow it. They should rinse with water after brushing.
To reduce the risk of tooth decay:
- Never allow your baby to fall asleep with a bottle containing milk, formula, fruit juice or sweetened liquid.
- Don’t dip a dummy in sugar or honey.
- Clean the dummy before you give it to your baby.
- Visit your dentist by about 12 months.
If you are worried about your baby’s tooth development, call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to talk to a maternal child health nurse.
Sources:
Australian Dental Association (Teething chart, When the teeth come marching in), Australian Dental Association (Babies), WebMD (Your Teeth From Birth to Adulthood), Sydney Children's Hospital Network (Teeth - Caring for your child's teeth), Tresillian (Teething)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.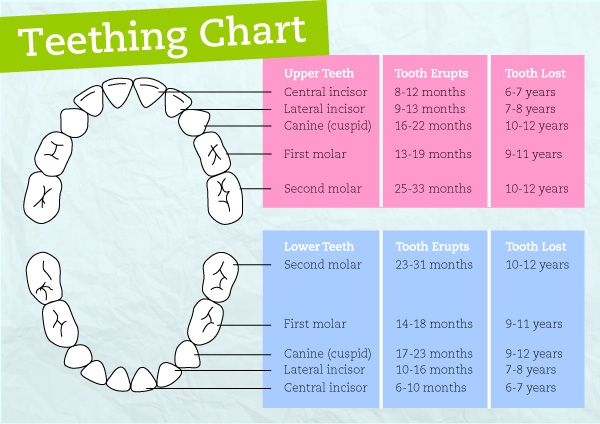
Last reviewed: September 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Dental care for children
- Dental care for infants and toddlers
Need more information?
Teething
Teething can start between 4 and 10 months and usually makes babies fussy and cranky. Find out how to ease your baby’s teething discomfort and care for new and emerging teeth.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Are amber beads safe for babies?
Amber beads are designed to help babies while teething, but do they actually work and are they safe?
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Teething Top Tips & Videos | Tresillian
The times when teeth appear vary from baby to baby but generally most babies get their first tooth on the lower jaw from around 6-10 months of age. Find out how to help your baby with teething.
Find out how to help your baby with teething.
Read more on Tresillian website
Teething Signs & Symptoms | Tresillian
Babies will experience discomfort during the teething phase of their early development. Discover teething remedies which help reduce the pain and settle your baby.
Read more on Tresillian website
Teeth development in children - Better Health Channel
Teething symptoms are common in children and can be managed without medications.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Tooth arrival chart
Babies are usually born with 20 baby teeth. Use this chart to see when you can expect their teeth to come through.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your baby's growth and development - 7 months old
Your 7-month-old baby is growing fast and may even be sitting up on their own and eating solid foods. Learn more here about how your baby is developing when they reach 7 months.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Teeth - Tooth development | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Before birth Your baby's first teeth (primary teeth) begin to form in the 16th week of pregnancy
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Teeth grinding
Find out the causes of teeth grinding (bruxism), the effects of teeth grinding and what to do if your toddler grinds their teeth in their sleep.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Teeth - Caring for your child's teeth | Sydney Children's Hospitals Network
Tooth decay The main cause of tooth decay is an acid attack on the surfaces of the teeth
Read more on Sydney Children's Hospitals Network website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.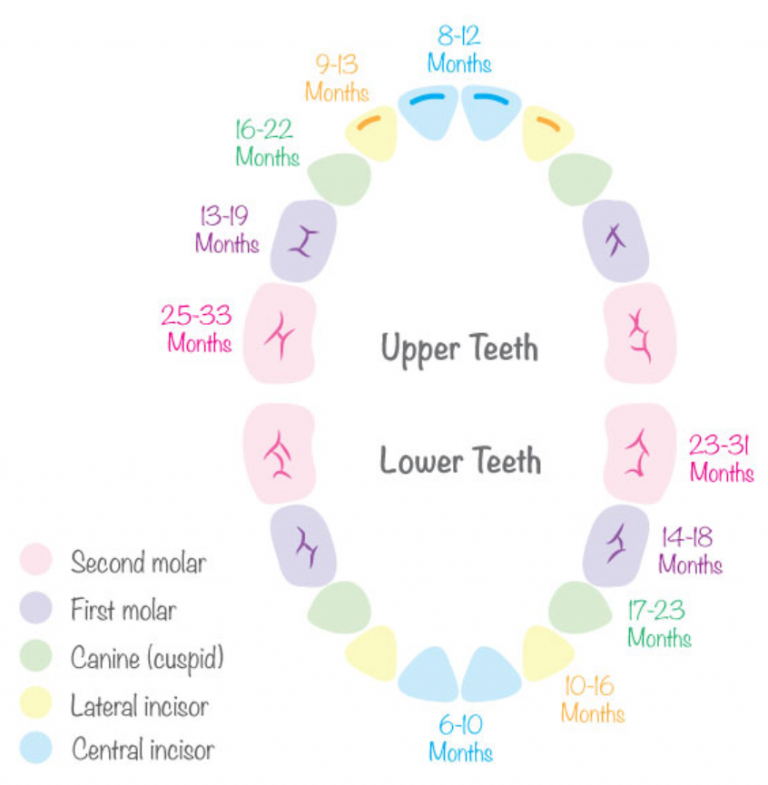
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
When do baby's first teeth erupt?
All babies teething according to their own individual program: for some, this process begins earlier, for others later. As practice shows, the first tooth in most children appears at the age of 6 to 8.5 months, and by the year every healthy child has at least one milk tooth in his mouth.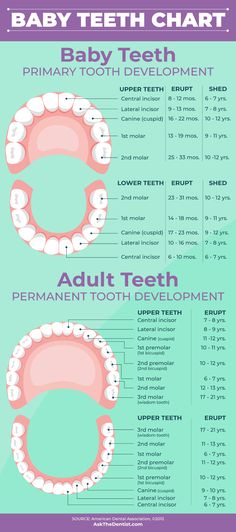
At the age of three or four months, teeth preparing for eruption begin to actively declare themselves: the baby becomes capricious, cries, tries to bite everything that gets into his hands.
The first to appear are usually the two lower, centrally located teeth (lower central incisors or "ones"). Then - the central upper incisors, after which, by about ten months, the upper "twos", or lateral upper incisors, erupt. By eleven to twelve months, the lateral incisors can also be seen on the lower jaw. Thus, ideally, a one-year-old child is the proud owner of eight milk teeth.
By about sixteen months, many babies already have first molars on the bottom and top. Fangs ("threes") appear at the top and bottom later, in the eighteenth - twenty-second month of a child's life. The second upper and lower molars erupt at the age of 24-33 months. But again, it should be remembered that this process is individual and the order of teething may also be different.
Teeth often grow in pairs: two, and sometimes four at the same time. In girls, for the most part, teeth erupt earlier than in boys. By the age of 2.5-3 years, a complete set of twenty fully erupted teeth can be found in a baby.
In girls, for the most part, teeth erupt earlier than in boys. By the age of 2.5-3 years, a complete set of twenty fully erupted teeth can be found in a baby.
Alertness must be shown if a child who is almost a year old does not have a single tooth. In principle, some children may have a congenital feature in the form of late teething, but you should not draw any conclusions on your own, you should definitely consult with a qualified specialist who, if necessary, will prescribe additional examinations.
Causes of late teething in children:
- hereditary predisposition, which is a variant of the norm and can be traced in other blood relatives;
- decreased thyroid function;
- rickets;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- violations of enzymatic (fermentation) metabolism;
- pituitary insufficiency;
- lack of calcium in the child's body;
- genetically determined diseases.
For the baby himself, the process of teething can proceed in different ways. Some children practically do not experience discomfort, others suffer from pain, their sleep is disturbed, their appetite worsens, their temperature rises (up to 38-39 ° C), salivation increases, nasal congestion, wet cough (due to profuse salivation), constipation or, conversely, , increased stool.
Some children practically do not experience discomfort, others suffer from pain, their sleep is disturbed, their appetite worsens, their temperature rises (up to 38-39 ° C), salivation increases, nasal congestion, wet cough (due to profuse salivation), constipation or, conversely, , increased stool.
Experts recommend starting caring for the child's oral cavity even before the first teeth erupt: in the morning and evening, before going to bed, the child's gums should be gently wiped with a swab previously moistened with warm water. After the first teeth appear, you need to clean them with a special fingertip brush, which can also be used to massage the gum tissue. The front teeth should be cleaned with vertical movements, the side teeth with circular movements.
The network of Healthy Smile dental clinics employs experienced pediatric dentists, to whom you can book your baby for a free consultation.
Healthy Smile clinics provide discounts for regular customers, family discounts, various payment methods are possible, and the list of promotional offers to reduce the cost of certain types of services, including for children, is regularly updated.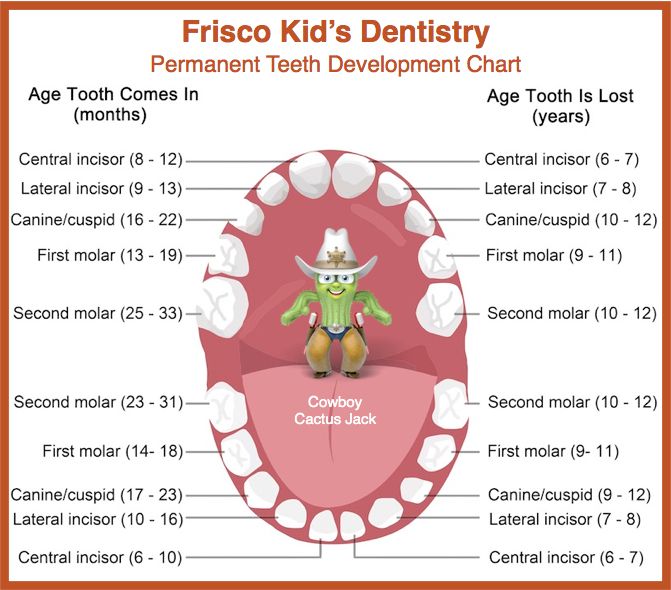
Desired date and time
Telephone
What is your name?
By clicking on the "Make an appointment" button, you consent to the processing of your personal data.
First teeth - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Bogorad Maria Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist, Ophthalmologist for children
Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo, Clinical Hospital Lapino-1
When to expect
The milk teeth of the future baby are laid at the 7th–8th week of intrauterine development, and the permanent teeth at the end of the 4th month of pregnancy. In total, 20 milk teeth are laid in a child, while permanent ones - 32. To provide the crumbs with a Hollywood smile, the expectant mother needs to eat right throughout all nine months of pregnancy. There are no calcium preparations that would be 100% absorbed, so it is very important to draw “natural” calcium from food, especially cottage cheese. And, of course, the most pregnant woman needs to cure all her teeth - now there are very sparing technologies for this.
And, of course, the most pregnant woman needs to cure all her teeth - now there are very sparing technologies for this.
The eruption of the first milk teeth in most cases begins at the 3-8th month of a baby's life and ends closer to three years. But it also happens that children are born already with one or two teeth, or teeth can erupt in the first weeks of life. Often the timing of teething depends on genetic characteristics, but much more - on other factors. They affect the teeth and diseases of the crumbs (for example, with rickets, frequent SARS and dyspepsia, teeth erupt later). It is worth paying attention to the nature of nutrition, the quality of drinking water, even the climate! In northern residents, teeth erupt on average a little later than in southerners. Sometimes teething is delayed, and the first tooth appears closer to the year. Usually there is nothing wrong with this. It is believed that not so much the timing as the order of teething speaks about the health of the child. If it is broken, pay attention to this fact and show the baby to a pediatric dentist.
If it is broken, pay attention to this fact and show the baby to a pediatric dentist.
The process has begun
Profuse salivation indicates that the teething process has begun. In addition, the baby begins to pull into his mouth everything that only comes to his hand. This means that the gums itch, causing him discomfort. Trying to relieve itching, the baby instinctively acts correctly - micro-massage of the gums improves microcirculation in them, teeth erupt easier and faster. During this period, provide the child with teethers: hypoallergenic silicone toys filled with water. The teether should not be cooled in the freezer - only in the refrigerator: otherwise the crumb will get hurt on a hard surface. If the gums are very swollen, and the baby is crying in pain, use special dental gels that have a mild local anesthetic effect.
For most children, the process of teething goes fairly smoothly. There may be short periods of anxiety, violations of the regime of the day and nutrition.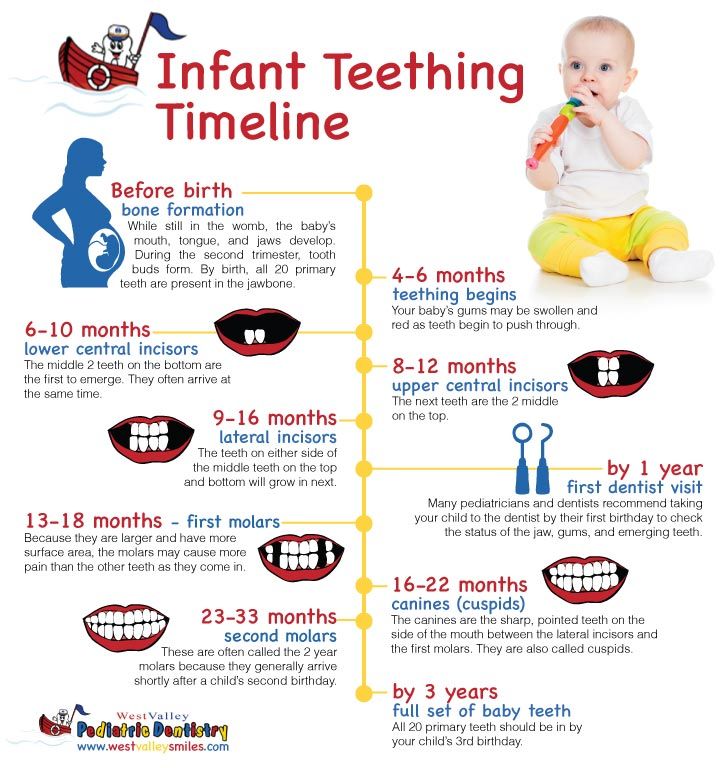 Sometimes even teething is accompanied by diarrhea, runny nose, cough and fever. And during the period of the appearance of teeth, the baby is vulnerable to all kinds of infections. The immunity of the crumbs decreases these days, and it is easier to “pick up” the virus, so it’s not worth writing off the worsening of the condition only on the teeth. If a child has a fever when a tooth is cut, it is necessary to look for another inflammatory focus in the body.
Sometimes even teething is accompanied by diarrhea, runny nose, cough and fever. And during the period of the appearance of teeth, the baby is vulnerable to all kinds of infections. The immunity of the crumbs decreases these days, and it is easier to “pick up” the virus, so it’s not worth writing off the worsening of the condition only on the teeth. If a child has a fever when a tooth is cut, it is necessary to look for another inflammatory focus in the body.
At 6 months the baby usually boasts central lower incisors. This is an excuse to start brushing your teeth. Why so early? Milk teeth are small and sharp, have an uneven wavy edge, are close to each other and, as a rule, have a yellowish tint. These teeth have a low degree of mineralization. Their enamel and dentin are very thin. All this contributes to the rapid emergence and spread of caries. In order to prevent it, you need to brush your teeth regularly: for this, you can use various massage brushes that not only teach the child to hygiene, but also facilitate the process of teething.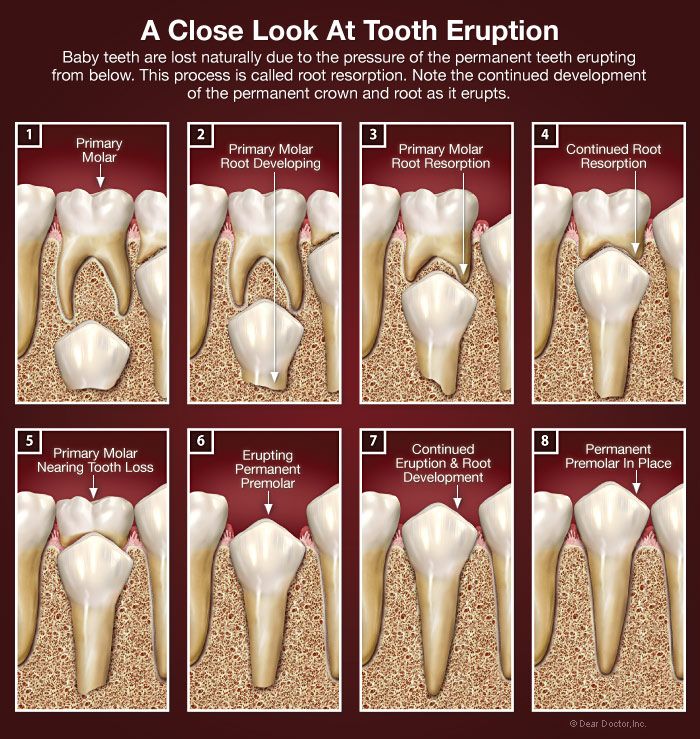 Teeth are immediately taught to clean correctly - from the gums to the edge, slightly "sweeping", semicircular movements, and in no case horizontal. If possible, brush your teeth after every meal (and at least twice a day). Is there no such possibility? Give the baby a drink - the water will wash away the remnants of food.
Teeth are immediately taught to clean correctly - from the gums to the edge, slightly "sweeping", semicircular movements, and in no case horizontal. If possible, brush your teeth after every meal (and at least twice a day). Is there no such possibility? Give the baby a drink - the water will wash away the remnants of food.
At 8 months the upper central incisors usually erupt. In 9 months the upper lateral incisors appear. At 11 months and the lower lateral incisors are already in place in many children! By , the baby has eight normal teeth . But there may not be a single one - delayed teething occurs in 25% of cases with normal psychomotor development of the child. In extremely rare cases, the absence of teeth is associated with adentia - the absence of their rudiments. You can check this with a pediatric dentist using the radiovisiography method. By 13–15 months , first the upper first molars appear, and then the lower ones.
From the age of one, the baby's teeth can be brushed with children's toothpaste and a special children's brush.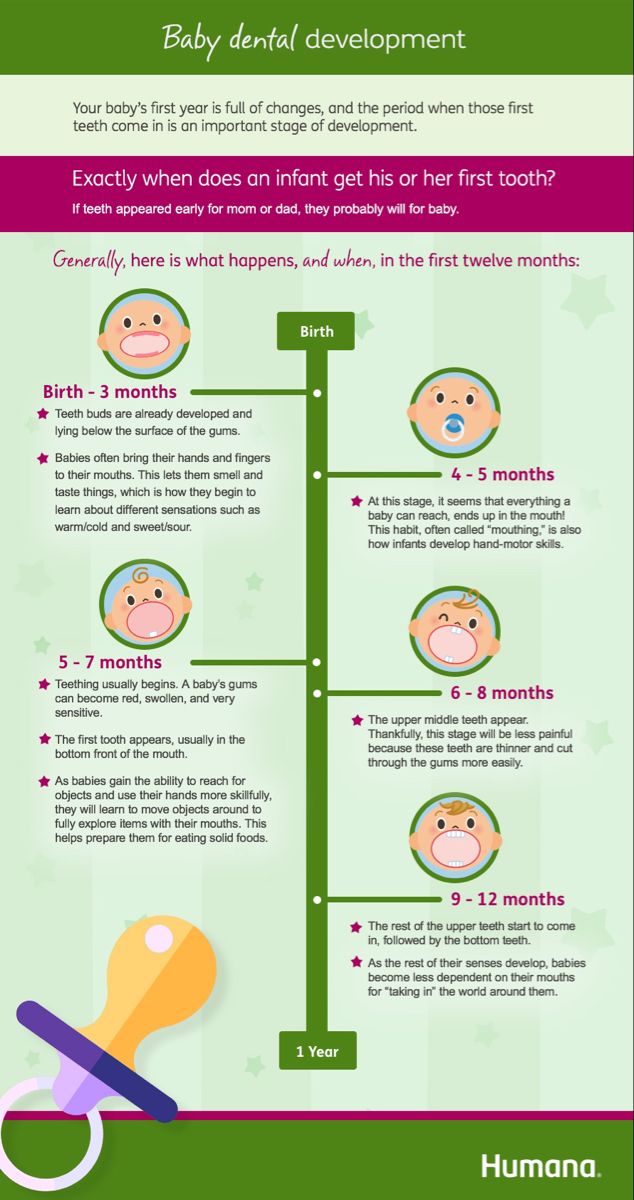 The service life of the brush is no more than 2 months, even if it looks like new. Many babies swallow delicious pasta. You should not be afraid of this if it is childish and its quantity is no more than a pea. Of course, up to 2–2.5 years, brushing your teeth should be done with the help of, and then under the vigilant control of your mother.
The service life of the brush is no more than 2 months, even if it looks like new. Many babies swallow delicious pasta. You should not be afraid of this if it is childish and its quantity is no more than a pea. Of course, up to 2–2.5 years, brushing your teeth should be done with the help of, and then under the vigilant control of your mother.
B 18 months fangs erupt. Usually these teeth cause more problems than others, their eruption is more painful, and this process is often accompanied by malaise. At 20 months the second molars erupt. And sometimes already at this age, the mother may notice the first problems. Doctors reassure: carious milk teeth are not a reason to worry that permanent ones will also be bad. As practice shows, there are no regularities here. Of course, if parents do not neglect the prevention of diseases and dental hygiene. At 2.5 years old, a normal baby has a full set of milk teeth. There are 20 of them - 10 on each jaw .
Milk teeth do not last long - soon they will fall out and permanent ones will appear in their place. Usually the change of teeth begins at about 5-6 years and lasts until 20, when the wisdom teeth erupt.
Usually the change of teeth begins at about 5-6 years and lasts until 20, when the wisdom teeth erupt.
From the age of 6 months, it is obligatory to come for preventive examinations twice a year. When this becomes a habit, the baby will not be afraid of doctors, and by the age of 7–8 (when a visit to the clinic can no longer be avoided) he will sit in the dental chair quite calmly
In order for the baby's teeth to grow strong and healthy, you need to start taking care of them almost before conception. And it is also better to get to know the dentist early
Terms of eruption and loss of milk teeth
| Upper teeth | |||
| Tooth name | Eruption period | Eruption procedure | Drop time |
| Central cutter | 8 months - 1 year | 2 | 6-7 years old |
| Side cutter | 9 months - 1 year 2 months | 3 | 7-8 years old |
| Fang | 1 year 3 months - 1 year 10 months | 7 | 10-12 years old |
| First molar | 1 year - 1 year 6 months | 5 | 9-11 years old |
| Second molar | 2 years - 2 years 8 months | 10 | 10-12 years old |
| Lower teeth | |||
| Central cutter | 6 months -10 months | 1 | 6–7 years old |
| Side cutter | 10 months -1 year 4 months | 4 | 7-8 years old |
| Fang | 1 year 4 months - 2 years | 8 | 9-12 years old |
| First molar | 1 year 2 months - 1 year 7 months | 6 | 9-11 years old |
| Second molar | 1 year 10 months - 2 years 8 months | 9 | 10-12 years old |
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Bogorad Maria Vladimirovna
Clinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child" Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo
Pediatric Ophthalmology for ChildrenOphthalmology
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary.