What week is first trimester over
Everything you need to know about the first trimester (weeks 1 to 12)
Tommy's PregnancyHub
You’re pregnant: congratulations! The first weeks of your pregnancy are a vital time as your body gets busy building a baby. How exciting!
First trimester: key stages
The first trimester begins on the first day of your last period and lasts until the end of week 12. This means that by the time you know for sure you're pregnant, you might already be five or six weeks pregnant!
A lot happens during these first three months. The fertilised egg rapidly divides into layers of cells and implants in the wall of your womb where it carries on growing. These layers of cells become an embryo, which is what the baby is called at this stage.
During this trimester, your baby grows faster than at any other time. By six weeks, a heartbeat can usually be heard and by the end of week 12, your baby's bones, muscles and all the organs of the body have formed. At this point, your baby looks like a tiny human being and is now called a fetus. He or she will even be practising swallowing!
Try our Healthy Pregnancy Tool to find out everything you need to know about your pregnancy
When am I due?
Find out your due date using our due date calculator!
When will I see a midwife?
Your first midwife appointment (also known as antenatal appointment) is the 'booking' appointment. This usually happens between week 8 and 10 of your pregnancy. Find out how to register with a midwife and when your appointments will be here.
Keeping your baby safe
There are some things that you can do during pregnancy that have an effect on your baby. Find out about them by clicking the link below.
Find the complete list of pregnancy dos and don'ts (and reasons why) here
Not sure whether you are pregnant?
Find out about the symptoms that mean you may be pregnant here.
Your physical and mental health in pregnancy
We also have lots of useful tips for coping with everyday pregnancy niggles. It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
Don't forget that your mental health is just as important as your physical health. It's normal to feel some anxiety and stress but it shouldn't be ongoing. If what you’re feeling isn’t normal for you, talk to your GP or midwife about it. They are there to help.
Exercise, such as yoga, has been shown to reduce anxiety and is a great way to stay active during your pregnancy, too.
Read more about mental wellbeing in pregnancy
Read more about diabetes and pregnancy
Read more about pregnancy with a high BMI
Read more about exercise and pregnancy
Read about the symptoms to look out for in pregnancy
Track your baby's development
Sign up to a free pregnancy email from our midwives to track your baby's development and give you reminders of all you need to know through the 9 months of pregnancy. Click here to sign up.
Review dates
Reviewed: 28 June 2018 | Next review: 28 June 2021
This content is currently being reviewed by our team.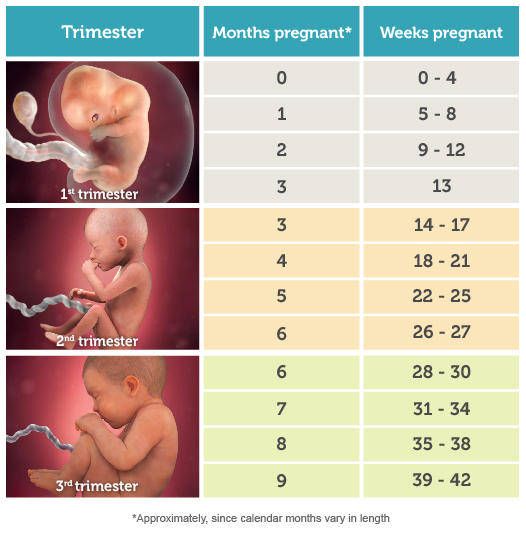 Updated information will be coming soon.
Updated information will be coming soon.
Back to top
Pregnancy - week by week
The unborn baby spends around 38 weeks in the womb, but the average length of pregnancy (gestation) is counted as 40 weeks. This is because pregnancy is counted from the first day of the woman’s last period, not the date of conception, which generally occurs two weeks later.
Pregnancy is divided into three trimesters:
- First trimester – conception to 12 weeks
- Second trimester – 12 to 24 weeks
- Third trimester – 24 to 40 weeks.
Conception
The moment of conception is when the woman’s ovum (egg) is fertilised by the man’s sperm. The gender and inherited characteristics are decided in that instant.
Week 1
This first week is actually your menstrual period. Because your expected birth date (EDD or EDB) is calculated from the first day of your last period, this week counts as part of your 40-week pregnancy, even though your baby hasn’t been conceived yet.
Because your expected birth date (EDD or EDB) is calculated from the first day of your last period, this week counts as part of your 40-week pregnancy, even though your baby hasn’t been conceived yet.
Week 2
Fertilisation of your egg by the sperm will take place near the end of this week.
Week 3
Thirty hours after conception, the cell splits into two. Three days later, the cell (zygote) has divided into 16 cells. After two more days, the zygote has migrated from the fallopian tube to the uterus (womb). Seven days after conception, the zygote burrows itself into the plump uterine lining (endometrium). The zygote is now known as a blastocyst.
Week 4
The developing baby is tinier than a grain of rice. The rapidly dividing cells are in the process of forming the various body systems, including the digestive system.
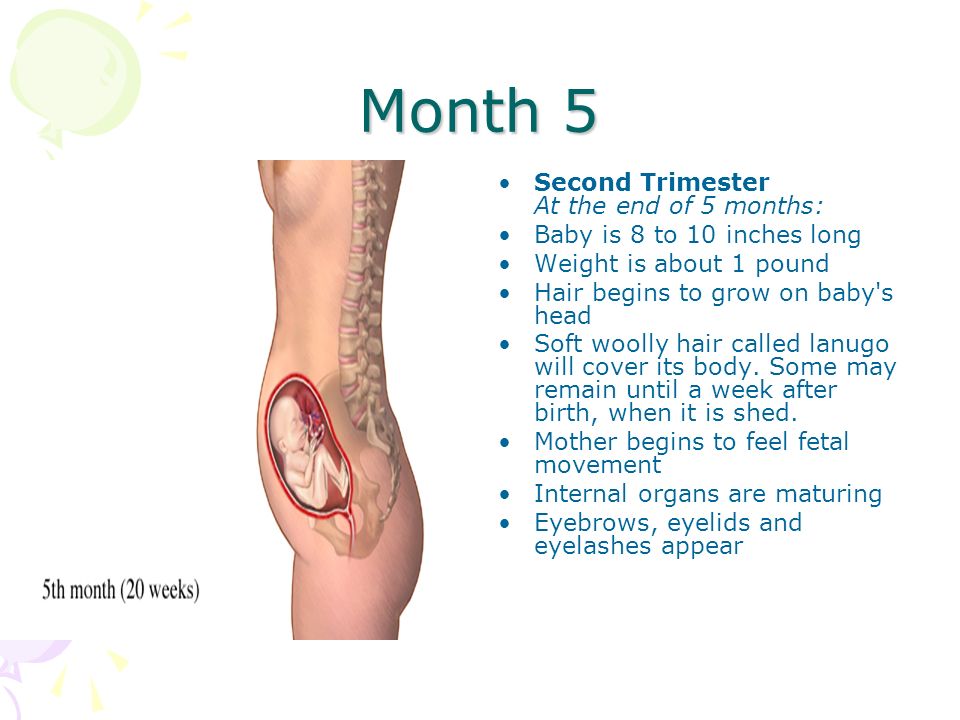
Week 5
The evolving neural tube will eventually become the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
Week 6
The baby is now known as an embryo. It is around 3 mm in length. By this stage, it is secreting special hormones that prevent the mother from having a menstrual period.
Week 7
The heart is beating. The embryo has developed its placenta and amniotic sac. The placenta is burrowing into the uterine wall to access oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s bloodstream.
Week 8
The embryo is now around 1.3 cm in length. The rapidly growing spinal cord looks like a tail. The head is disproportionately large.
Week 9
The eyes, mouth and tongue are forming. The tiny muscles allow the embryo to start moving about. Blood cells are being made by the embryo’s liver.
Week 10
The embryo is now known as a fetus and is about 2.5 cm in length. All of the bodily organs are formed. The hands and feet, which previously looked like nubs or paddles, are now evolving fingers and toes. The brain is active and has brain waves.
The hands and feet, which previously looked like nubs or paddles, are now evolving fingers and toes. The brain is active and has brain waves.
Week 11
Teeth are budding inside the gums. The tiny heart is developing further.
Week 12
The fingers and toes are recognisable, but still stuck together with webs of skin. The first trimester combined screening test (maternal blood test + ultrasound of baby) can be done around this time. This test checks for trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome) and trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
Week 13
The fetus can swim about quite vigorously. It is now more than 7 cm in length.
Week 14
The eyelids are fused over the fully developed eyes. The baby can now mutely cry, since it has vocal cords. It may even start sucking its thumb. The fingers and toes are growing nails.
Week 16
The fetus is around 14 cm in length. Eyelashes and eyebrows have appeared, and the tongue has tastebuds. The second trimester maternal serum screening will be offered at this time if the first trimester test was not done (see week 12).
Eyelashes and eyebrows have appeared, and the tongue has tastebuds. The second trimester maternal serum screening will be offered at this time if the first trimester test was not done (see week 12).
Week 18-20
An ultrasound will be offered. This fetal morphology scan is to check for structural abnormalities, position of placenta and multiple pregnancies. Interestingly, hiccoughs in the fetus can often be observed.
Week 20
The fetus is around 21 cm in length. The ears are fully functioning and can hear muffled sounds from the outside world. The fingertips have prints. The genitals can now be distinguished with an ultrasound scan.
Week 24
The fetus is around 33 cm in length. The fused eyelids now separate into upper and lower lids, enabling the baby to open and shut its eyes. The skin is covered in fine hair (lanugo) and protected by a layer of waxy secretion (vernix). The baby makes breathing movements with its lungs.
The baby makes breathing movements with its lungs.
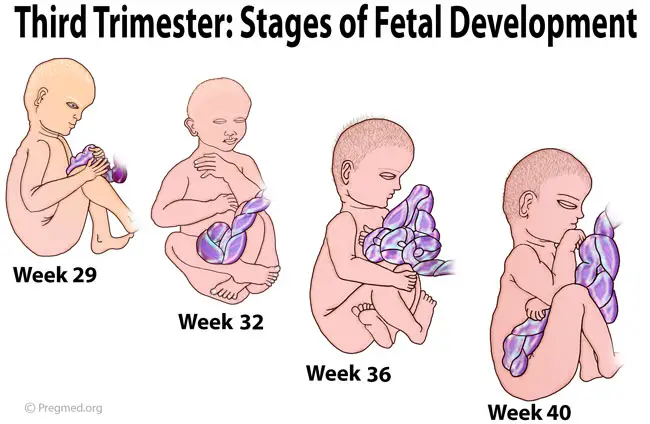
Week 28
Your baby now weighs about 1 kg (1,000 g) or 2 lb 2oz (two pounds, two ounces) and measures about 25 cm (10 inches) from crown to rump. The crown-to-toe length is around 37 cm. The growing body has caught up with the large head and the baby now seems more in proportion.
Week 32
The baby spends most of its time asleep. Its movements are strong and coordinated. It has probably assumed the ‘head down’ position by now, in preparation for birth.
Week 36
The baby is around 46 cm in length. It has probably nestled its head into its mother’s pelvis, ready for birth. If it is born now, its chances for survival are excellent. Development of the lungs is rapid over the next few weeks.
Week 40
The baby is around 51 cm in length and ready to be born. It is unknown exactly what causes the onset of labour. It is most likely a combination of physical, hormonal and emotional factors between the mother and baby.
It is most likely a combination of physical, hormonal and emotional factors between the mother and baby.
Where to get help
- Your doctor
- Obstetrician
- Midwife
Things to remember
- Pregnancy is counted as 40 weeks, starting from the first day of the mother’s last menstrual period. Your estimated date to birth is only to give you a guide. Babies come when they are ready and you need to be patient.
- The gender and inherited characteristics of the baby are decided at the moment of conception.
9-12 weeks of pregnancy
Ninth week for the baby
During the ninth week, the weight of the fetus changes from 1 gram to 10 grams, the length is 30-45 mm. The back of the fetus straightens and the embryonic tail disappears. The future child becomes completely similar to a small person. The head at this stage is pressed to the chest, the neck is bent, the arms are also brought to the chest.
The development of the brain, which is quite intensive, is one of the main processes of this period. The cerebellum begins to function, the hemispheres acquire a clear outline. Since the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, in the fetus they cease to be spontaneous and become clear and active, the fetus begins to feel the movement of its own body.
The cerebellum begins to function, the hemispheres acquire a clear outline. Since the cerebellum is responsible for the coordination of movements, in the fetus they cease to be spontaneous and become clear and active, the fetus begins to feel the movement of its own body.
The heart rate at this stage is 120-150 beats per minute, the heart has two ventricles and two atria. There is a circulatory system of vessels, blood begins to flow through them. While blood circulation in the upper part of the fetus is characterized by greater intensity than in the lower. Therefore, the arms are more developed in comparison with the legs. There is an elongation of the fingers, and the membranes between them slowly disappear. By the end of the ninth week, the formation of the eye ends, they are tightly covered with eyelids. There is a closing of the facial bones, on the head it is already possible to distinguish the nose and nostrils, auricles and lobes, and the upper lip. At this stage, the fetus becomes more and more like a human face.
Intensive development of internal organs leads to rounding of the tummy of the fetus. The digestive organs and the liver develop, which is important because it is responsible for hematopoiesis (the formation of new blood cells). Thus, "fetal" blood appears.
At this stage in the life of the fetus, such an important event occurs as the beginning of the synthesis of hormones, which include adrenaline. Intensive growth of the adrenal glands provides this process. Also, the beginning of the synthesis of hormones is associated with the complication of the structure of the adrenal glands. All this helps the fetus to comfortably adapt to a variety of changes and extreme conditions. It is the presence of adrenaline in the body that allows it to withstand various stresses. The fetus acquires the ability to endure stress, since adrenaline provides the regulation of a special mode of "survival".
Ninth week for the expectant mother
At this stage, the woman may still have drowsiness, fatigue, frequent mood changes and dizziness. Manifestations of toxicosis can reach their maximum. It is this period that is optimal in order to visit a gynecologist and register.
Manifestations of toxicosis can reach their maximum. It is this period that is optimal in order to visit a gynecologist and register.
The tenth week for the baby
This week is important and significant, it is from it that the fetal stage of development begins, and the unborn child is now officially called a fetus, not an embryo. All the internal organs have already been laid, which in the future will only have to grow and develop. Experts rightly consider the tenth week to be the final one in the first critical period: from that time on, the likelihood of developing defects that may arise due to chemical factors of various nature is no longer so high.
The fetus at this time is freely located in the uterine cavity, practically not touching its walls. The future baby has an intensive formation of the nervous system, the transmission of impulses by neuromuscular pathways is being established. This process leads to the emergence of intense movements. Such movements are reflex, they are active and are caused by contact with the walls of the uterus.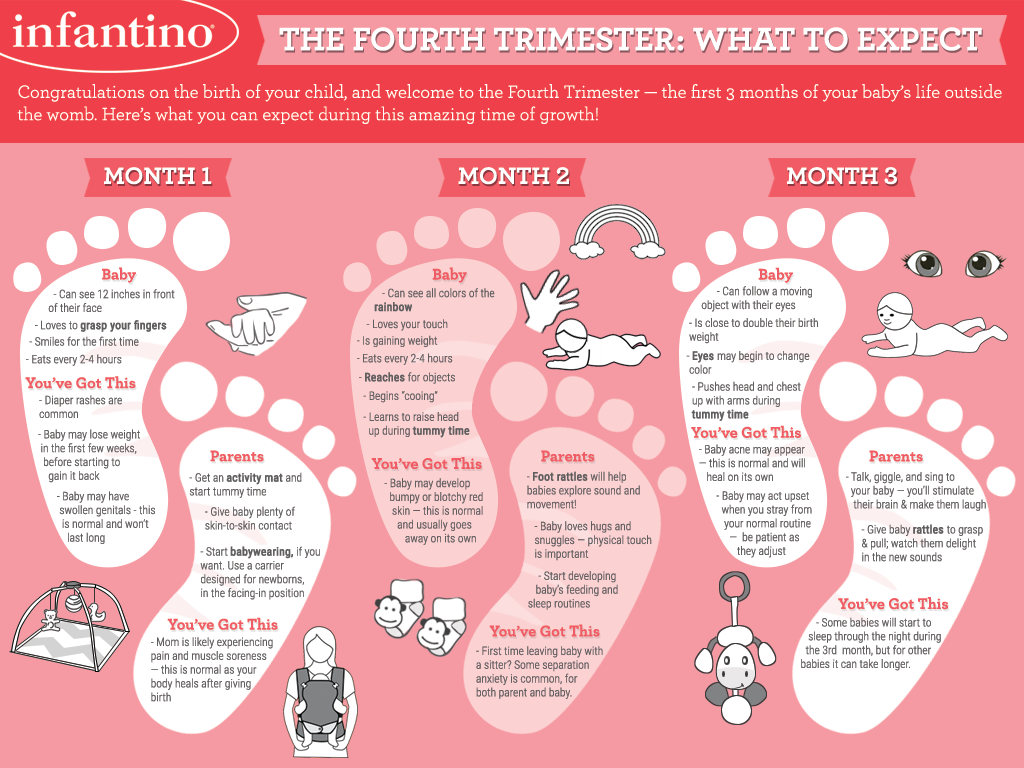 The fetus already makes fairly clear movements with its legs, head and handles. The woman is not yet able to feel the movements of the fetus, but they are clearly visible during an ultrasound examination.
The fetus already makes fairly clear movements with its legs, head and handles. The woman is not yet able to feel the movements of the fetus, but they are clearly visible during an ultrasound examination.
At this time, the diaphragm is finally formed - a flat muscle designed to separate the abdominal and chest cavities. There is a further development of internal organs.
The tenth week for the expectant mother
The woman feels increased anxiety, she retains emotional lability. All this is a consequence of ongoing hormonal changes. The only thing to be understood is that the balance will soon be restored, which means the return of a stable good mood.
The situation changes with the manifestations of toxicosis. Nausea begins to disturb less and less, and vomiting, as a rule, stops altogether. Nausea mostly in the morning. If toxicosis completely disappears, increased appetite may occur. At this time, it is important to monitor the diet and prevent a sharp increase in weight.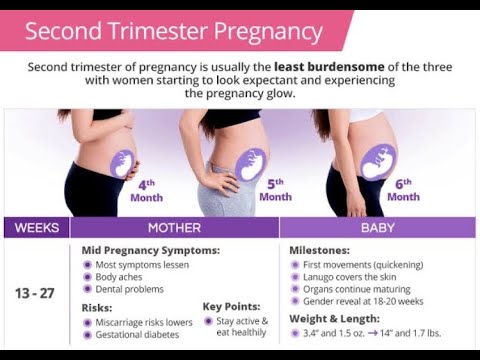 It is necessary to exclude overeating and the use of high-calorie foods. For a woman in position, this is harmful and can cause shortness of breath, swelling, deterioration of well-being. Excess weight is the reason for increasing the load on all body systems, which already spends a lot of energy on the development of the fetus.
It is necessary to exclude overeating and the use of high-calorie foods. For a woman in position, this is harmful and can cause shortness of breath, swelling, deterioration of well-being. Excess weight is the reason for increasing the load on all body systems, which already spends a lot of energy on the development of the fetus.
Women in the tenth week may notice a change in the abdomen. The reason may be overeating, as well as the redistribution of subcutaneous fat and muscle relaxation due to the influence of the pregnancy hormone - progesterone.
The uterus enlarges during this period, but not so much as to influence the shape of the abdomen, it reaches the size of a large apple or grapefruit. Accordingly, for others, pregnancy is still completely invisible.
Eleventh week for baby
The fetus in the eleventh week continues to grow rapidly. Outwardly, it looks like this: a fairly large head, small legs pressed to the tummy, a small torso and well-developed long arms.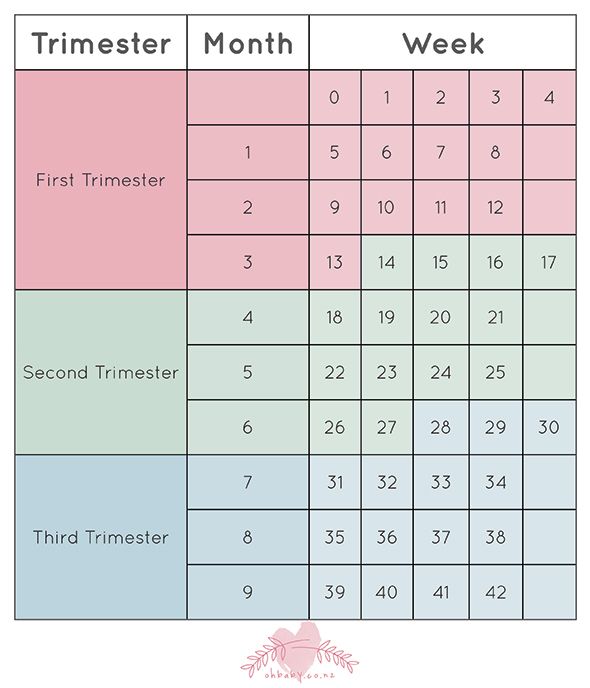 Such an uneven development is due to the fact that it was the upper part of the body that received the bulk of the nutrients and the proportion of oxygen throughout the entire previous period, in which such vital organs as the heart and brain are located.
Such an uneven development is due to the fact that it was the upper part of the body that received the bulk of the nutrients and the proportion of oxygen throughout the entire previous period, in which such vital organs as the heart and brain are located.
The fetus continues to form joints and bones, muscle growth. Not only large joints develop, but also small ones. In the jaws, the rudiments of teeth are formed, on the fingers - nails.
The movements of the unborn child become more and more purposeful. Loud noises and sudden movements begin to cause a response in him. Grasping and sucking reflexes develop - this can be seen in the movement of the fingers and lips. The formation of olfactory and taste buds begins. If amniotic fluid enters the nose or mouth, the fetus is able to taste it.
At this stage, the formation of the iris of the eyes also takes place, which after birth will determine their color. In newborns, in most cases, the eyes are blue or blue, brown are quite rare. The final color of the iris is formed by five months. It depends on the accumulated melanin pigment located in the iris. Genetic inheritance determines the amount of this pigment.
The final color of the iris is formed by five months. It depends on the accumulated melanin pigment located in the iris. Genetic inheritance determines the amount of this pigment.
Eleventh week for the expectant mother
At this time, in most cases, vomiting and nausea, as well as intolerance to certain odors, disappear. Thus, a woman gets the opportunity to form a complete diet and start eating varied, giving preference to various healthy foods. It is advisable to eat freshly prepared food. If you follow a certain diet, you can avoid any problems at this time, the main of which is a problem with digestion. The relaxing hormone progesterone causes the bowel muscles to become lazy, leading to bloating and constipation. If even strict adherence to the diet does not help to cope with problems, you need to contact a specialist who can prescribe safe medications.
As the fetus grows, blood volume also increases. As a result of such changes, a woman may experience increased sweating. Increased kidney function leads to more frequent urination. If there is no discomfort and pain with frequent urination, there is no reason to worry. Otherwise, you will also need to pay a visit to a specialist. Discomfort and pain can be symptoms of inflammation of the bladder, i.e. cystitis syndromes.
Increased kidney function leads to more frequent urination. If there is no discomfort and pain with frequent urination, there is no reason to worry. Otherwise, you will also need to pay a visit to a specialist. Discomfort and pain can be symptoms of inflammation of the bladder, i.e. cystitis syndromes.
At eleven weeks, the first prenatal screening is performed, which is aimed at identifying malformations. An ultrasound and biochemical study is performed. The first screening is not only aimed at identifying malformations. This examination allows you to find out the state of the chorion, the growth and degree of development of the fetus, the exact gestational age and other details.
Twelfth week for the baby
Twelfth week ends the first trimester of pregnancy. By the end of this period, the length of the fetus is 90 mm, and its weight is approximately 20 g. At this time, many significant events take place in the life of the fetus.
He has an intensive development of the brain, the formation of connections between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres.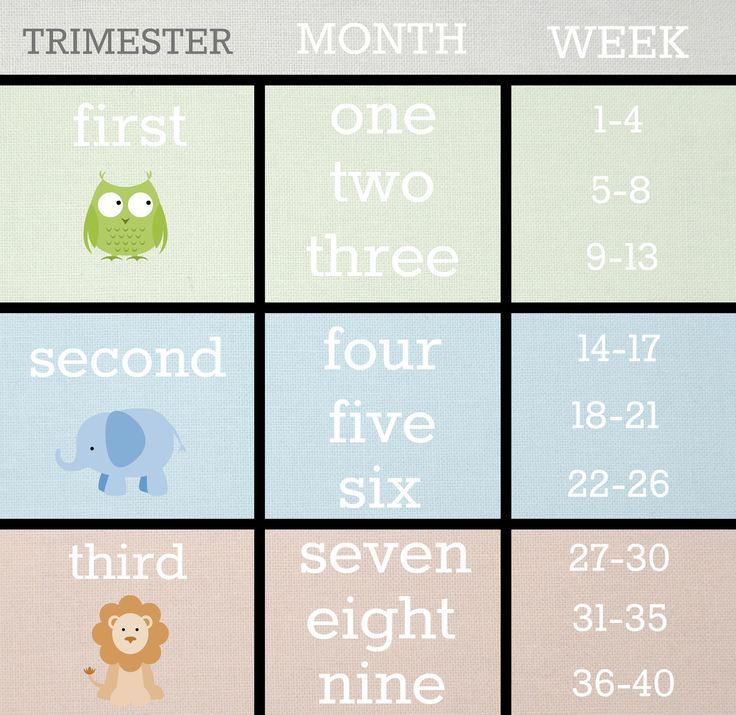 If we consider the structure of the brain, it resembles a smaller version of the brain of an adult. During all the first months, only erythrocytes were in the blood of the fetus, but at the twelfth week, leukocytes, which are the body's defenders and belong to the immune system, are added to them.
If we consider the structure of the brain, it resembles a smaller version of the brain of an adult. During all the first months, only erythrocytes were in the blood of the fetus, but at the twelfth week, leukocytes, which are the body's defenders and belong to the immune system, are added to them.
The digestive tract also develops. The liver, which at this stage is the most developed organ and occupies most of the abdominal cavity, begins to produce bile, and not only provide hematopoiesis, as it was before. It is from the twelfth week that the intestine actively grows and begins to fit into loops, which can later be seen in an adult. The first peristaltic movements occur, i.e., the contraction of the muscles of the intestine, which should in the future ensure the movement of food through it. The fetus, starting from this week, swallows amniotic fluid, and they pass through the intestines. This happens before birth. Peristaltic waves are a training of the intestinal muscles.
In addition, rhythmic muscle movements occur in the fetus, which are also training and imitate breathing. The glottis is tightly closed, so amniotic fluid is not able to penetrate to the respiratory organs.
The glottis is tightly closed, so amniotic fluid is not able to penetrate to the respiratory organs.
The kidneys begin to function in the fetus, urine in them is collected in small portions and exits through the urethra, entering the amniotic fluid.
At the twelfth week, the formation of the placenta is completed, which becomes able to function independently. The placenta is the most important organ for the fetus; through it, not only is the exchange of nutrients between the woman and the fetus. The placenta is an effective protector against internal and external toxins.
Twelfth week for the expectant mother
Twelve weeks is rightly considered the best in pregnancy. The woman's well-being returns to normal due to the transfer of control of the process from the corpus luteum, which produced progesterone, which is the culprit of many troubles, to the placenta. All manifestations of toxicosis disappear, women become relaxed and calm.
At this stage, the uterus has already enlarged enough and reached the edge of the pubis, but this is not able to affect the shape of the abdomen.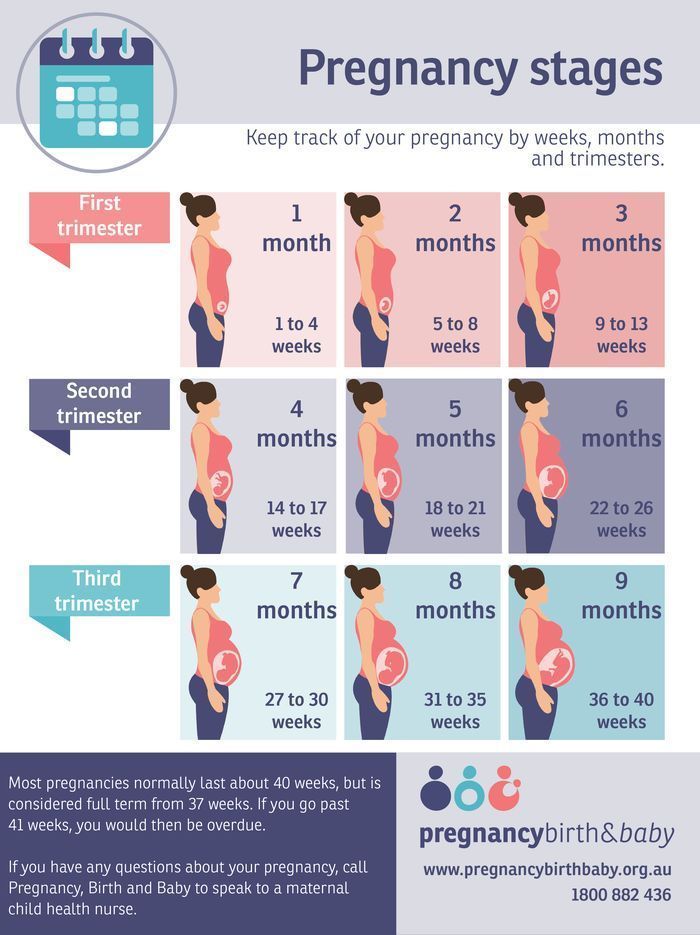
As a rule, the first trimester is not accompanied by weight gain. If toxicosis manifested itself to a large extent, even weight loss is possible. If a woman's appetite has not changed as a result of pregnancy, she should gain no more than 10% of her total weight during the entire pregnancy. Such an increase is usually 1-2 kg.
From the twelfth week, if the woman is doing well and there are no contraindications, it is recommended to start playing sports. At earlier periods, they are not dangerous, but most often experts recommend that women take care of themselves after the end of the first trimester.
Dance, yoga, swimming, fitness, and any other type of activity that has been designed specifically for pregnant women are perfect for the expectant mother. Before starting training, be sure to consult a doctor. If you choose the right load, classes will have a positive impact on the course of not only pregnancy, but also childbirth. Also, sports at this stage will contribute to a faster recovery after childbirth.
Pregnancy calendar
Asked the question "How to determine the gestational age?" We suggest you use our pregnancy calendar, which will easily and quickly determine the duration of pregnancy by week.
The most important information for a gynecologist is knowing the gestational age. All this is necessary in order to correctly prescribe the necessary tests and examinations for the quality management of pregnancy.
Knowing the gestational age, you can accurately calculate the date of delivery. With this information, the attending physician will inform you about the date of maternity leave. Therefore, correctly determining the gestational age is a very important procedure for all pregnant women.
Our interactive pregnancy calculator helps you determine your due date. Below is a step-by-step instruction on how to determine the gestational age.
Step 1. Determine the date of conception
It is important to know the date of conception if you want to determine the exact timing of pregnancy. It coincides with the date of the last ovulation. Enter your data in the pregnancy calendar and click on the "Calculate!" button. If you know the date of conception, you can skip this step.
Calculate the date of conception
Last period
Average cycle length
(from 22 to 45 days - default 28)
Average duration of the second phase
(from 9 to 16 days - default 14)
Estimated date of conception
Pregnancy video calendar
1 month of pregnancy 2 month pregnant 3 month pregnant 4 month pregnant 5th month of pregnancy 6 month pregnant 7 month pregnant 8 month pregnant 9 months pregnant
Pregnancy: week by week
Every week of pregnancy is special. It is important for every expectant mother not only to be observed during pregnancy by a doctor, but also to engage in self-education. And it doesn't matter, what week of pregnancy you are - our guide for expectant mothers describes the development of pregnancy by week . Each week of pregnancy includes useful tips and recommendations from the CIR doctors. You will have a clear idea of what happens from the 1st to the 40th week of pregnancy, how the child's developmental norms change (weight, height, formation of body parts, skeleton). This section describes pregnancy by week .
And it doesn't matter, what week of pregnancy you are - our guide for expectant mothers describes the development of pregnancy by week . Each week of pregnancy includes useful tips and recommendations from the CIR doctors. You will have a clear idea of what happens from the 1st to the 40th week of pregnancy, how the child's developmental norms change (weight, height, formation of body parts, skeleton). This section describes pregnancy by week .
So, about all the features fetal development and pregnancy by week , about what happens with your body in the first weeks of pregnancy and how you will change week by week, our pregnancy guide will help you find out. Just follow us.
-
1-4 weeks
Before conception, the growth and maturation of the egg begins in the ovary. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs: the egg leaves the ovary into the abdominal cavity, and then moves into the fallopian tube.
The egg and sperm combine: fertilization has occurred, the pregnancy begins to develop.
The size of the embryo at 4 weeks of gestation is 2-4 mm.
Read about the first weeks of pregnancy...
-
5-8 weeks
By the end of 7 weeks, the embryo is already about 1 centimeter long. It will grow by forming a million new cells every minute! By the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, your baby will grow to 1.5-2 cm. During an ultrasound scan with a coccyx-parietal size (CTE) of more than 4 mm, you can determine the heartbeat. Around this time, the nerve cells in your child's brain begin to form primitive neural pathways.
Read about 5-8 weeks of pregnancy...
-
9-12 weeks
At 9 weeks, the period when your unborn baby is called an "embryo" has ended. It is now a "fetus" as it looks like a miniature replica of a human. By 11-12 weeks, many internal organs are formed, the heart has four chambers. Hands, fingers, feet and toes, mouth, nose and nostrils, eyes and earlobes are already visible.
 The expectant mother has a feeling of fatigue, signs of toxicosis should change in the near future to a good and stable state of health.
The expectant mother has a feeling of fatigue, signs of toxicosis should change in the near future to a good and stable state of health. Read about 9-12 weeks of pregnancy...
-
13-16 weeks
From 14 weeks - the second trimester of pregnancy.
The first hair appears on the little man. By the 16th week, the nervous and muscular systems of the fetus are well developed enough for the first movements of the facial muscles to begin to appear. The eyes become sensitive to light stimuli. Baby grows up to 16 cm.
Read about 13-16 weeks of pregnancy...
-
17-20 weeks
Your child is growing and developing.
By the end of the 20th week, the skin is no longer as translucent as it used to be, because fat is now accumulating under the skin. Developed motor neurons of the brain enable the unborn child to make many movements, for example, even “put your thumb in your mouth”!
The body is getting bigger. The head no longer looks so bulky relative to the body.

Read about 17-20 weeks of pregnancy...
-
21-24 weeks
From 21 weeks, sensory receptors begin to form: taste buds (tongue), the brain is now able to process the sensation of touch.
By the end of 22 weeks, the baby will be about 25 cm long and weigh about 500 grams. The brain and nervous system continue to mature.
Read about 21-24 weeks of pregnancy...
-
25-28 weeks
End of the period of the most active growth. From weeks 20 to 30, a baby's weight doubles in 4 weeks. By the end of this month, the weight is from 1 to 1.5 kg.
Eyelids were not tightly closed until the 28th week. It is necessary for the development of the retina.
At this time, the child begins to hear, to distinguish between tastes. It often moves in response to touch and sound. The brain and nervous system are undergoing rapid growth and development.
Read about 25-28 weeks of pregnancy...
-
29-32 weeks
The third trimester of pregnancy has begun.

During this last trimester of pregnancy, your baby grows, accumulates fat, and his organs slowly mature. By 32 weeks pregnant, your baby will be about 40 centimeters long and weigh up to 2 kg.
At this time, the child may show high motor activity and even “hiccups” (so-called hiccup-like movements)! So the child practices breathing, trains the respiratory muscles.
Read about 29-32 weeks of pregnancy...
-
33-36 weeks
By the end of 36 weeks, the fetus will be about 48 cm tall and weigh about 2.4 - 2.8 kg. Over the next three weeks, the baby's weight will increase by about 200 grams per week. Facial features are rounded due to the layer of fat cells. The muscles of the cheeks and jaws are adapted for sucking. It can be seen on ultrasound how the baby sucks his finger or tries to put his fist in his mouth.
Read about 33-36 weeks of pregnancy...
-
37-40 weeks
The weight of the child by the 40th week of pregnancy is on average 3-4 kg.