What to do for swollen hands
Swollen arms and hands (oedema)
Swelling in the arms or hands (oedema) often goes away on its own. See a GP if it does not get better in a few days.
Common causes of swollen arms and hands
Swelling in the arms and hands is often caused by a build-up of fluid in these areas.
It's usually caused by:
- staying in the same position for too long
- eating too much salty food
- being pregnant
- taking certain medicines – such as some blood pressure medicines, contraceptive pills, antidepressants and steroids
It can also be caused by:
- an injury – such as a strain or sprain
- sudden changes in temperature – such as very hot weather
- an insect bite or sting
- a skin allergy such as angioedema
- problems with your kidneys, liver or heart
- a blood clot
- an infection
- some conditions such as lymphoedema or psoriatic arthritis
Information:
Find out more about swollen ankles, feet and fingers in pregnancy
Check if you have oedema
Symptoms of oedema include:
Swollen or puffy arms or hands.Credit:
DR P. MARAZZI / SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/477302/view
Shiny, stretched skin.Credit:
SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY https://www.sciencephoto.com/media/648284/view
How to ease swelling yourself
Swelling in your arms or hands should go away on its own, but there are some things you can try to help.
Do
-
lie down and use pillows to raise the swollen area when you can
-
move your whole arm and shoulder
-
try raising your hand above your head while you open and close your fist
-
massage your arm or hand towards your body using firm but not painful pressure – for example, start at your fingertips and massage towards your palm
-
get some gentle exercise, like walking, to improve your blood flow
-
drink plenty of water
-
wash, dry and moisturise your arms or hands to avoid infections
-
put your hands in a bath of warm water and then cold water to help move the fluid away from the area
Non-urgent advice: See a GP if your arm or hand is swollen and:
- your arm or hand is swollen and it has not improved after treating it at home for a few days
- the swelling gets worse
Urgent advice: Ask for an urgent GP appointment or get help from NHS 111 if:
- you have swelling in only 1 arm or hand and there's no obvious cause, such as an injury
- the swelling is severe, painful or starts very suddenly
- the swollen area is red or feels hot to the touch
- your arm or hand is swollen and your temperature is very high, or you feel hot and shivery
- you have diabetes and your arm or hand is swollen
You can call 111 or get help from 111 online.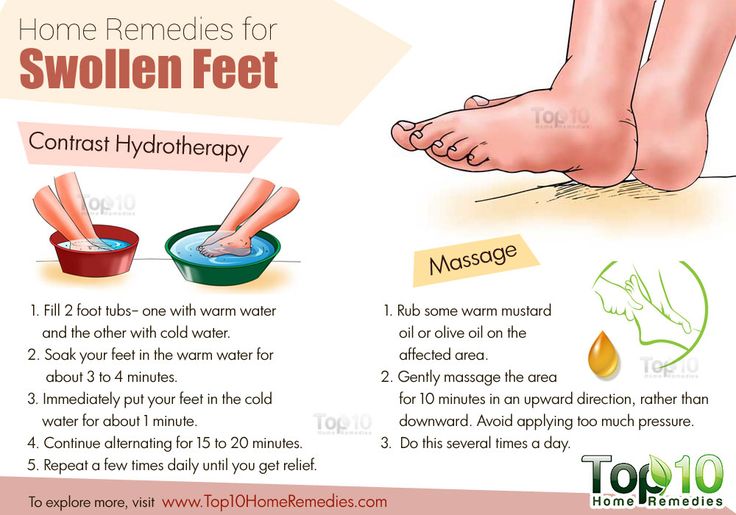
Immediate action required: Call 999 if:
- you feel short of breath or are struggling to breathe
- your chest feels tight, heavy or painful
You could have a blood clot in your lungs, which needs immediate treatment in hospital.
Treatment for swelling
Treatment for swelling or oedema that does not go away on its own will depend on the cause.
Possible treatments include:
- changing your medicine if this is the cause of the swelling
- treating any condition that is causing the swelling
- diuretics (water pills) to help reduce the swelling
- wearing special gloves or sleeves to stop any swelling from coming back (compression aids)
Treatment may also include lifestyle changes, such as losing weight or going on a low-salt diet.
Page last reviewed: 02 March 2022
Next review due: 02 March 2025
Swollen Fingers: Causes and Treatment
Swollen fingers and general swelling in the hands and arms is common with many injuries and medical conditions. It is important to identify the cause so that appropriate treatment can be started, and complications can be avoided.
Causes
Swelling can occur because of an injury to the hand or arm or a medical condition. Traumatic injuries, such as a crushing injury or broken bones, result in a lot of fluid rushing to the injured area. This is part of the body’s natural healing response. The body creates inflammation and delivers extra blood and fluid to the injury so that there are more cells and healing factors available for repair. Too much inflammation, however, can be painful and harmful.
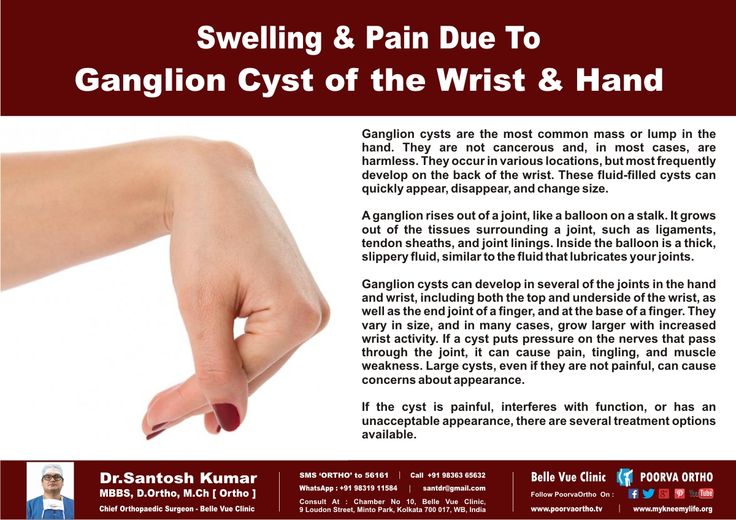
Medical conditions can cause swollen fingers and general swelling as well. Arthritis commonly results in swelling of the hands, often in the morning upon waking up.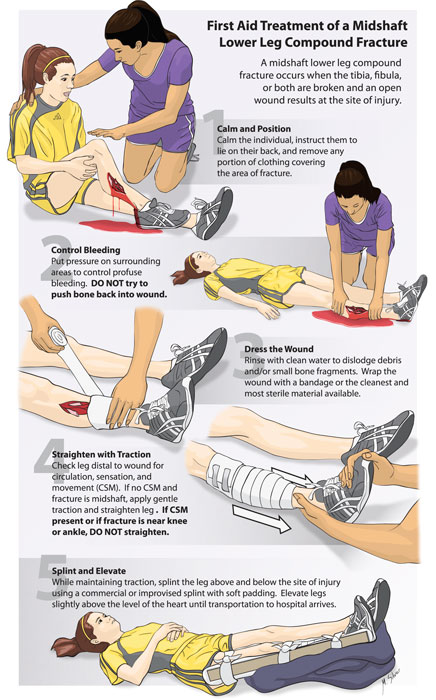 Infections can also result in swelling, and these should be treated right away. More localized swelling from ganglion cysts or tumors should be looked at in your hand surgeon’s office.
Infections can also result in swelling, and these should be treated right away. More localized swelling from ganglion cysts or tumors should be looked at in your hand surgeon’s office.
Signs and Symptoms
Because of the pressure build-up, swelling can cause pain and discomfort. With swollen fingers, it can also temporarily reduce your flexibility and mobility which, if left for a long period of time, can result in significant stiffness. In certain cases, swelling can become so severe that it can reduce blood flow or injure nerves and muscles in the forearm and hand. This is especially true with very bad fractures and infections.
Treatment
Swollen fingers and general swelling occurs mostly because of the buildup of fluid in spaces within the hand and wrist. This fluid typically collects in areas that cannot be “pumped” out by the blood vessels. Because of this, keeping the hand and arm down results in gravity keeping the fluid in its place and even allowing for more fluid to enter into the hand. Therefore, keeping the hand and arm elevated, ideally above the level of your heart, will help gravity take the fluid out of the hand and arm. Think of it like water flowing downhill; keeping the hand down makes the water go into the hand and keeping the hand up makes the water go back into the body. Keeping the hand elevated, potentially for extended periods of time, is critical. This is especially true after an injury or surgery, as it takes much longer for the swelling to come out of the hand than it does to get into it.
Therefore, keeping the hand and arm elevated, ideally above the level of your heart, will help gravity take the fluid out of the hand and arm. Think of it like water flowing downhill; keeping the hand down makes the water go into the hand and keeping the hand up makes the water go back into the body. Keeping the hand elevated, potentially for extended periods of time, is critical. This is especially true after an injury or surgery, as it takes much longer for the swelling to come out of the hand than it does to get into it.
Other things you can do to help swelling include:
- Applying ice to the affected area or over the bandage, which can also help reduce pain
- Splinting/immobilizing, which can help stop more swelling from coming into the hand or arm
- Taking anti-inflammatory medications (e.g. NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen), which can reduce swelling, especially when swelling is caused by arthritis
- Moving the fingers, wrist, and arm regularly, if allowed with your condition, which can help pump the fluid back to the body.
 This is especially important for people with fractures of the wrist; anything that is not splinted or casted should move regularly (as approved by your hand surgeon).
This is especially important for people with fractures of the wrist; anything that is not splinted or casted should move regularly (as approved by your hand surgeon). - Wearing compressive wraps such as ACE™ wraps or isotoner gloves, which can be very helpful in massaging fluid back to the body. Do not apply too tightly.
If you’re experience swelling that was caused by an infection, address it immediately by calling your hand surgeon or going to the emergency room for an evaluation. You may need antibiotics or even surgery to remove the infection. If you develop numbness or tingling with any kind of swelling, especially after a traumatic injury, please go to an emergency room immediately.
© 2019American Society for Surgery of the Hand
This content is written, edited and updated by hand surgeon members of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand.Find a hand surgeon near you.
Related Topics
Edema Treatment for the Arm and Hand
Related Articles
SM-Clinic cardiologist spoke about the causes of hand swelling in adults
Edema of the hands occurs quite often, and can be a manifestation of physiological changes or one of the symptoms of pathology.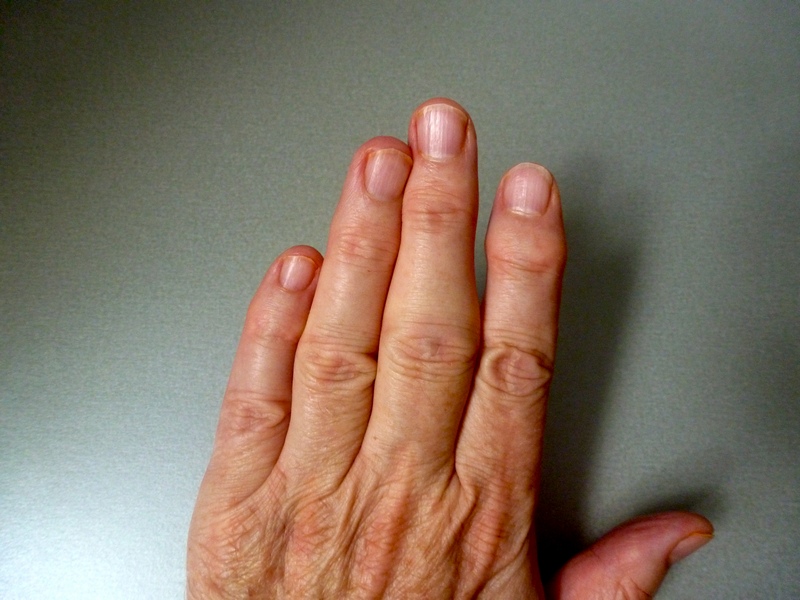 When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
When should edema alert and where to address the problem?
ALENA PARETSKAYA
Pathophysiologist, immunologist, member
St. Petersburg Society of Pathophysiologists
ANDREY GRACHEV
Leading cardiologist of the holding
SM-Clinic, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
Swelling of the hand is a cause for concern if it occurs frequently or almost daily, is accompanied by additional symptoms, is aggravated or is not eliminated by simple methods.
What you need to know about arm swelling
- Why your arm swells
- How to remove swelling
- Questions and answers
Why the hand swells in adults
Swelling of the arm or both at once may be physiological or be a sign of pathology. It may be localized or spread to surrounding tissues. With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
Swelling in the right or left arm occurs when the blood or lymphatic vessels are compressed by items of clothing during sleep. Swelling of the fingers and hands, which is especially noticeable if you remove rings or watches, occurs after alcohol or excess salty foods, fluids at night.
Right hand
A small local edema, if the mobility of the limb is preserved, is possible with bruises. In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
Edema is possible with fractures of bones, dislocations of joints. Then there is pain, limb deformity, complete impossibility of movement.
Edema may appear with frostbite of the fingers, burns, infectious processes in the area of the hand, forearm or shoulder.
Left hand
Swelling of the finger of the left hand (as well as the right one) is possible with panaritium - suppuration in the phalanx. If it is a deeper lesion, the edema passes to the hand. Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Joint damage in other forms of arthritis also leads to tissue swelling. With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
Edema is typical for joint damage - thrombosis. In addition to edema, a feeling of fullness, pain, thickening of tissues, discoloration of the skin, crawling, and a change in sensitivity are typical.
Morning
Lymphatic edema is possible after operations to remove the mammary gland, if the axillary lymph nodes were excised. Puffiness may increase or appear in the morning with malformations of the lymphatic capillaries, with post-burn scars, thrombophlebitis, lymphadenitis. Without treatment, swelling can become permanent.
Hand edema also occurs against the background of heart failure. In the morning they are minimal, intensify in the evening. In contrast, renal swelling of the hands is most pronounced in the morning and decreases or disappears during the day.
Pregnancy
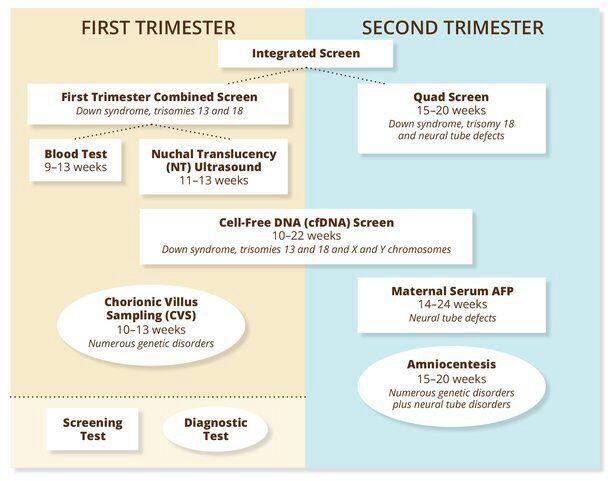
Puffiness in the fingers or hands is due to hormonal changes, especially as the pregnancy progresses. In the first trimester, a slight swelling of the fingers is typical, which is almost not noticeable. By the third trimester, swelling can be pronounced, making it difficult to wear rings, watches, bracelets. Puffiness gradually disappears in the first days after childbirth.
However, in pregnant women, pathological edema associated with hypertension, overweight and the development of preeclampsia is also possible. Then the appearance of protein in the urine, a pronounced weight gain per week, severe swelling of the arms and legs, face, and body are typical.
How to relieve hand swelling in adults
At home or for first aid, you need to give your hand an elevated position.
If this is an injury, the hand should be immobilized with a bandage or splint, a cold compress should be applied to the affected area, and an anesthetic should be taken.
If these are diseases of the joints, it is necessary to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs locally and orally. If the swelling develops quickly, with severe pain and dysfunction of the hand, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors have two options for treating edema - conservative and surgical. It depends on the cause, the severity of the condition, and possible complications. In case of injuries, emergency care, bandages, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia are indicated.
In vascular edema, antispasmodic, angioprotective and phlebotonic drugs are used.
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage or manual therapy are also prescribed.
If the injury is serious or severe lesions of blood vessels, bones, joints are detected, the edema is not eliminated, surgical interventions are used.
Popular questions and answers
Edema can be a short-term phenomenon and does not threaten anything. But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem.
But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. Andrey Grachev, a cardiologist, helped us figure out the problem.
Why is hand swelling dangerous?
Swelling is often a sign of a serious infection, cancer, heart or kidney problems. And if the swelling is persistent, then the disease has worsened or is rapidly progressing. Edema can be complicated by tissue malnutrition, skin inflammation, stretch marks, and discoloration.
When should I see a doctor for swollen hands?
In any situation when you notice swelling of the hands - in the morning, in the evening or during the day, you need a doctor's consultation and at least a minimal set of tests and examinations. Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it.
Is it possible to remove swelling of the hands with folk remedies?
There are a number of diuretic decoctions and infusions, but it is extremely dangerous to use them on your own, not knowing what the causes of edema are. This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
This can lead to a worsening of the situation, an electrolyte imbalance, a sharp decrease in pressure, dehydration and malaise.
In addition, various traditional medicines can cause allergies, worsen the condition, negatively affect the effects of the drugs taken and have a number of contraindications for taking. Folk remedies are not equal to the concept of "safe".
What if only one arm is swollen?
If one arm is swollen, see a surgeon or physician, depending on the suspected cause. At the time of the examination, it is worth disturbing the sore arm less, giving it an elevated position so that the liquid flows more easily, do not sleep on this side, do not press the arm to the body. Also, do not massage the swollen hand, carry out any activities without the permission of the doctor.
Published on the portal kp.ru
why hands swell and how to quickly relieve swelling at home
Hand edema is a cause for concern if it occurs frequently or almost daily, is accompanied by additional symptoms, worsens or is not eliminated by simple methods.
Why the hand swells in adults
Swelling of the hand or both at once can be physiological or be a sign of pathology. It may be localized or spread to surrounding tissues. With swelling, the limb increases in volume, discomfort, soreness, and inconvenience when performing precise finger movements may be felt. It is difficult to remove the rings from the fingers or the watch from the wrist.
Swelling on the right or left arm occurs when the blood or lymphatic vessels are compressed by items of clothing during sleep. Swelling of the fingers and hands, which is especially noticeable if you remove rings or watches, occurs after alcohol or excess salty foods, fluids at night.
Right arm
Slight local edema, if the mobility of the limb is preserved, is possible with bruises. In the area of edema, there may be soreness, redness, bruises or abrasions may appear. If it is a hematoma, the edema will be more pronounced, a seal is determined under the skin, in the center of which fluctuation (fluid movement) is felt. Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
Swelling is typical for sprains in the area of the carpal, elbow or shoulder joint, with torn ligaments or their rupture. Severe pain is characteristic, which increases with movement, if the ligaments are torn, it is almost impossible to move the hand.
Edema is possible with fractures of bones, dislocations of joints. Then there is pain, limb deformity, complete impossibility of movement.
Edema may appear with frostbite of the fingers, burns, infectious processes in the area of the hand, forearm or shoulder.
Left hand
Swelling of the finger of the left hand (as well as the right one) is possible with panaritium - suppuration in the phalanx. If it is a deeper lesion, the edema passes to the hand. Carbuncles or boils on any part of the arm can also lead to swelling. In this case, cyanosis or a purple area with suppuration is visible in the center of the inflamed focus. Edema is possible with suppuration of wounds, erysipelas, purulent arthritis and osteomyelitis.
Joint damage in other forms of arthritis also leads to tissue swelling. With rheumatoid arthritis, the joints of both hands are symmetrically affected, with gout, the fingers swell, with psoriasis, the joints of the fingers and hand.
Edema is typical for joint damage - thrombosis. In addition to edema, a feeling of fullness, pain, thickening of tissues, discoloration of the skin, crawling, and a change in sensitivity are typical.
Morning
Lymphedema is possible after breast removal surgery if axillary lymph nodes have been excised. Puffiness may increase or appear in the morning with malformations of the lymphatic capillaries, with post-burn scars, thrombophlebitis, lymphadenitis. Without treatment, swelling can become permanent.
Hand edema also occurs against the background of heart failure. In the morning they are minimal, intensify in the evening. In contrast, renal swelling of the hands is most pronounced in the morning and decreases or disappears during the day.
Pregnancy
Swelling in the fingers or hands is due to hormonal changes, especially as the pregnancy progresses. In the first trimester, a slight swelling of the fingers is typical, which is almost not noticeable. By the third trimester, swelling can be pronounced, making it difficult to wear rings, watches, bracelets. Puffiness gradually disappears in the first days after childbirth.
However, in pregnant women, pathological edema associated with hypertension, overweight and the development of preeclampsia is also possible. Then the appearance of protein in the urine, a pronounced weight gain per week, severe swelling of the arms and legs, face, and body are typical.
How to relieve swelling of the hands in adults
At home or for first aid, you need to give an elevated position to the hand.
If this is an injury, the hand should be immobilized with a bandage or splint, a cold compress should be applied to the affected area, and an anesthetic should be taken.
If these are diseases of the joints, it is necessary to use painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs locally and orally. If the swelling develops quickly, with severe pain and dysfunction of the hand, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Doctors have two options for treating edema - conservative and surgical. It depends on the cause, the severity of the condition, and possible complications.
Andrei Grachev Doctor of Medical Sciences, cardiologist, academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences
In case of injuries, emergency care, bandages, anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia are indicated. With vascular edema, antispasmodic, angioprotective and phlebotonic drugs are used.
Physiotherapy, gymnastics, massage or manual therapy are also prescribed.
If the injury is serious or severe lesions of blood vessels, bones, joints are detected, the edema is not eliminated, surgical interventions are used.
Popular Questions and Answers
Swelling may be short term and not life-threatening. But sometimes they are symptoms of dangerous conditions. cardiologist Andrey Grachev helped us figure out the problem.
Why is hand swelling dangerous?
Swelling is often a sign of a serious infection, cancer, heart or kidney problems. And if the swelling is persistent, then the disease has worsened or is rapidly progressing. Edema can be complicated by tissue malnutrition, skin inflammation, stretch marks, and discoloration.
When should I see a doctor for swollen hands?
In any situation when you notice swelling of the hands - in the morning, in the evening or during the day, you need a doctor's consultation and at least a minimal set of tests and examinations. Edema itself is a symptom of problems in the body, and you need to find out what caused it.
Is it possible to remove swelling of the hands with folk remedies?
There are a number of diuretic decoctions and infusions, but it is extremely dangerous to use them on your own, not knowing what the causes of edema are.