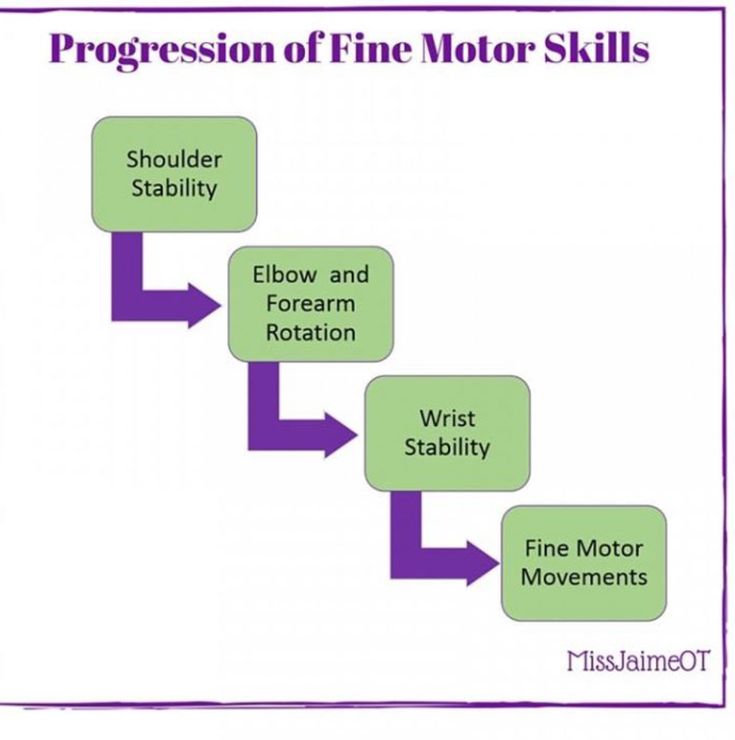
What does a uti feel like during pregnancy
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy - symptoms, causes
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) in pregnancy - symptoms, causes | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
What is a urinary tract infection?
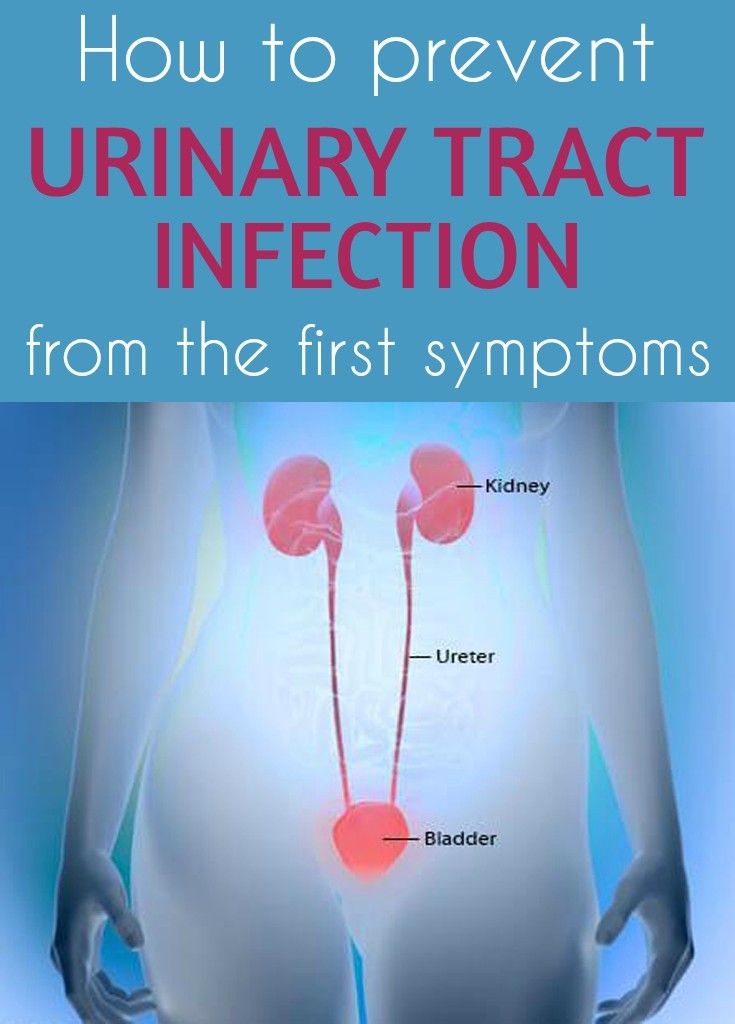
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary system. UTIs are the most common bacterial infection that women develop during pregnancy. They can occur in different parts of the urinary tract, including the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis) or kidneys (pyelonephritis). Sometimes when a UTI develops and bacteria are detected in the urinary tract, you may not have any symptoms of an infection. This is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria.
While anyone can get a UTI, they are much more common in women than men and they are also more likely to occur in the very young and the elderly.
What are the symptoms of UTIs during pregnancy?
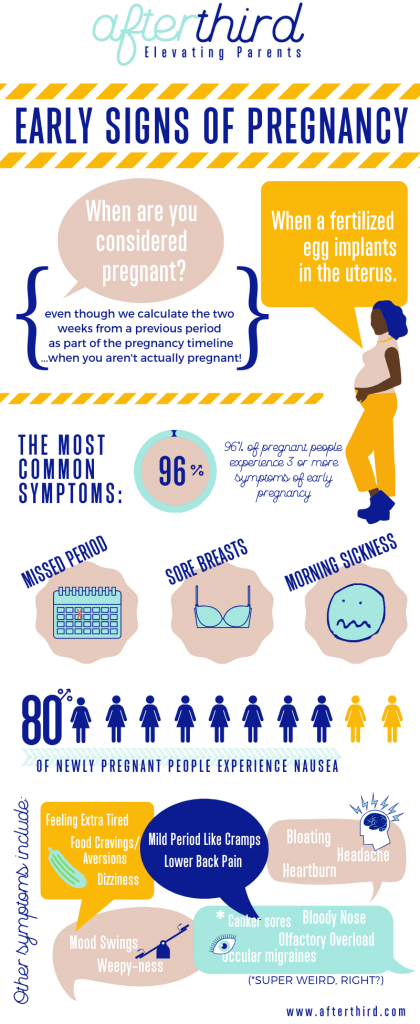
Common symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy are similar to those that you might experience at any other time, and include:
- a burning sensation when you pass urine
- feeling the urge to urinate more often than usual
- urinating before you reach the toilet (‘leaking’ or incontinence)
- feeling like your bladder is full, even after you have urinated
- urine that looks cloudy, bloody or is very smelly
- pain above the pubic bone
- fever
Sometimes the first sign of an infection is a faint prickly sensation when you pass urine. If the infection is more advanced and has moved up to the kidneys, you may also experience fever with a particularly high temperature, back pain and vomiting.
What are the common causes of UTIs?
Your urinary tract is normally free of bacteria. If bacteria enter the tract and multiply, they can cause a UTI. There are several factors that increase the risk of developing an infection:
- Infection with common bacteria in your gut, usually from faeces (poo) can contaminate your urinary tract
- Being sexually active increases the risk of bacteria moving around the genital area and entering the urinary tract
- If you have weak pelvic floor muscles your bladder might not empty completely, which can lead to an infection
- Women with diabetes are at increased risk of developing a UTI since the sugar in their urine may cause bacteria to multiply
Are UTIs a risk during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, many changes occur in your body that increase your risk of developing a UTI, including changes to the make-up of your urine and immune system. As your baby grows, there is also an increase in the pressure on your bladder, which can reduce the flow of your urine and lead to an infection.
As your baby grows, there is also an increase in the pressure on your bladder, which can reduce the flow of your urine and lead to an infection.
UTIs can affect women whether they are pregnant or not. However, pregnant women are more likely to develop repeated or more severe infections. Up to 1 in 10 pregnant women will have a UTI but not have any symptoms at all.
Is there a risk to my baby?
Having a UTI during pregnancy can increase your risk of developing high blood pressure, and your baby may be born early and smaller than usual. For this reason, even if you don’t have any symptoms, it is important to treat a UTI as soon as possible.
How are UTIs diagnosed?
UTIs are diagnosed by taking a urine sample which is checked in a laboratory for bacteria. Your doctor may also perform a physical examination if they think you have an infection.
All pregnant women are offered a urine test, usually at their first antenatal visit or soon after. You may need to repeat the urine test if you have a history of UTIs; have symptoms of a UTI; have a contaminated sample or if your doctor thinks you are at high risk of developing a UTI. If you have frequent UTIs, you may also need additional tests such as an ultrasound of your kidneys.
If you have frequent UTIs, you may also need additional tests such as an ultrasound of your kidneys.
How are UTIs treated during pregnancy?
When you have a UTI, it is important to drink plenty of water to flush out the urinary tract. UTIs are treated with antibiotics that are safe in pregnancy. Your doctor will select the right antibiotic, based on your infection and the type of bacteria found in your urine sample.
Can I prevent UTIs?
You can lower your risk of developing a UTI during pregnancy by:
- drinking plenty of fluids, especially water
- quickly treating any vaginal infection that may occur, including thrush or a sexually transmitted infection
- avoiding becoming constipated
Some women have also found the following tips helpful:
- urinate immediately after sex
- don’t delay going to the toilet — go as soon as you feel the need
- wipe from the front to the back after going to the toilet
- wear cotton underwear
When should I see my doctor?
See your midwife or doctor if you have any symptoms of a UTI. It’s important not to delay treatment since infections develop quickly, and can affect both you and your baby.
It’s important not to delay treatment since infections develop quickly, and can affect both you and your baby.
More information
UTIs are very common during pregnancy, and are best treated early. If you notice the symptoms of an infection, seek medical advice from your doctor, midwife or pharmacist.
For more information on UTIs, visit the Kidney Health Australia page on UTIs.
Sources:
Government of South Australia (Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnancy), Jean Hailes (Urinary Tract Infections), Kidney Health Australia (Factsheet: Urinary Tract Infections), Government of Western Australia North Metropolitan Health Service (Urinary Tract Infection in Pregnant Women)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2021
Back To Top
Related pages
- Incontinence during pregnancy
- Frequent urination during pregnancy
Need more information?
Urinary tract infection (UTI) - MyDr.
 com.au
com.au Urinary tract infection occurs when part of the urinary tract becomes infected. UTIs are usually caused by bacteria and generally clear up with a course of antibiotics.
Read more on myDr website
Urinary tract infection (UTI) | SA Health
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection of the urinary system. Infection may occur in the kidneys, bladder or urethra.
Read more on SA Health website
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) explained - NPS MedicineWise
Learn about the causes & treatments for urinary tract infections (UTIs).
Read more on NPS MedicineWise website
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Jean Hailes
A comprehensive guide to urinary tract infections. Everything you should know about UTIs including causes, symptoms, management and treatment.
Everything you should know about UTIs including causes, symptoms, management and treatment.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Incontinence & Bladder Weakness | Jean Hailes
What makes a normal bladder. Types of incontinence. Causes and symptoms. Diagnosis and treatment. Prevention and management.
Read more on Jean Hailes for Women's Health website
Pyelonephritis
Infection of the kidneys.
Read more on Queensland Health website
Check-ups, tests and scans available during your pregnancy
Antenatal care includes several check-ups, tests and scans, some of which are offered to women as a normal part of antenatal care in Australia. Learn more here.
Learn more here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Thrush | SA Health
Thrush or Candidiasis is a common vaginal infection, caused by an overgrowth of yeasts and is not considered to be a sexually transmitted infection
Read more on SA Health website
Pregnancy at week 9
Your baby is now the size of a peanut. You won't be showing just yet, but you may have put on a little weight.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Your first antenatal visit
Find out what will happen and what you can learn during your first antenatal care visit with your GP or midwife.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Sign in
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
UTIs During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Treatment, Common Questions
Urinary tract infections (UTIs), also known as bladder infections, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, according to research published in the American Journal of Medicine. Roughly 31 percent of pregnant women will have either a symptomatic or an asymptomatic (without symptoms) UTI during pregnancy, research suggests. UTIs occur when bacteria enters into the usually sterile urinary tract and multiplies, causing painful urination and other symptoms. Certain factors during pregnancy make this occurrence more likely to happen. Here’s what you need to know to keep you and your baby healthy.
UTIs occur when bacteria enters into the usually sterile urinary tract and multiplies, causing painful urination and other symptoms. Certain factors during pregnancy make this occurrence more likely to happen. Here’s what you need to know to keep you and your baby healthy.
RELATED: 8 Home Remedies for Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) Symptoms
Why Are UTIs Common in Pregnant Women?When you’re pregnant, the anatomy of your urinary tract actually changes. For instance, your kidneys become larger and your growing uterus can compress your ureters and bladder. Because of this compression, fully emptying your bladder during pregnancy becomes more difficult. In addition, your progesterone and estrogen levels increase during pregnancy, which can weaken your bladder and ureters. Pregnancy also alters the makeup of your urine, reducing the acidity and increasing the amount of protein, hormones, and sugar in your urine. That excess sugar, for one, can encourage bacterial growth.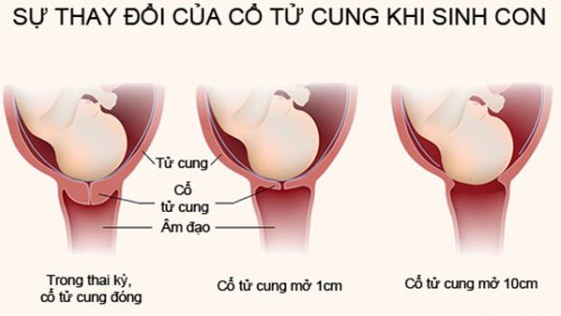 All of the above contribute to a heightened chance of developing a UTI in pregnancy. And that is why it’s recommended that all pregnant women receive a urinalysis and urine culture at 12 to 16 weeks or during the first prenatal visit.
All of the above contribute to a heightened chance of developing a UTI in pregnancy. And that is why it’s recommended that all pregnant women receive a urinalysis and urine culture at 12 to 16 weeks or during the first prenatal visit.
RELATED: 7 Things an Anesthesiologist Wants You to Know About Pain
UTIs by Pregnancy TrimesterYour risk of UTI goes up beginning at week 6 of your pregnancy; the chances you’ll have a UTI vary by trimester.
First TrimesterAbout 41 percent of UTIs are diagnosed during the first trimester. Because getting a UTI during the first trimester is so common, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that your healthcare provider obtain a urinalysis and urine culture at your first prenatal visit. That recommendation holds whether you present with UTI symptoms or not.
Second TrimesterAccording to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI during their second trimester compared with the first trimester.
Compared with the second trimester, the number of women who experience a UTI during the third trimester is almost halved. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to research published in the Archives of Medical Science. Thus, it’s recommended to do a repeat urine culture during the third trimester, too.
Common UTI Symptoms in Pregnant Women“While mildly painful urination during pregnancy can often mean a yeast infection, not a UTI, it’s always best to see your healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms,” says Heather Bartos, MD, an ob-gyn in Cross Roads, Texas. After all, research suggests that about 18 percent of UTIs that occur during pregnancy are symptomatic UTIs, meaning the telltale UTI signs and symptoms are present:
- Strong and frequent urge to use the bathroom
- Burning while urinating
- Regularly passing only small amounts of urine
- Cloudy, red, pink or cola-colored urine
- Foul-smelling urine
- Pelvic pain, usually in the center of the pelvis
In pregnancy, women are also more susceptible to asymptomatic UTIs, meaning you have significant bacteria in your urine but your urinary tract is free of signs and symptoms. Experiencing no symptoms, however, does not mean that asymptomatic UTIs are benign. “An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
Experiencing no symptoms, however, does not mean that asymptomatic UTIs are benign. “An asymptomatic UTI can lead to a symptomatic UTI or even a kidney infection,” says Dr. Bartos. In fact, research shows that if asymptomatic UTIs are left untreated, 30 percent of pregnant women will go on to develop a symptomatic UTI, and half of those women will eventually be diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Up to 23 percent will have a kidney infection recurrence during the same pregnancy. It’s important to note that classic UTI signs, like frequent and painful urination, may or may not occur with a kidney infection. Here, some signs to look out for:
- High-grade fever
- Chills and rigors (sudden feeling of cold with shivering)
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lower back pain
- Flank pain (often right side)
- Possible reduced urine output
“UTIs can rapidly progress to a kidney infection in pregnancy, which can be much more dangerous than a kidney infection in nonpregnant women,” says Bartos. “Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
“Severe infections can lead to respiratory problems and sepsis, which can then lead to preterm labor or even the need to urgently deliver the baby.” Beyond a kidney infection, simply having a UTI during pregnancy appears to possibly be a contributing factor to low birth weight. Women who have a UTI in pregnancy also have a 1.31-fold higher risk of developing preeclampsia, a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure, according to a meta-analysis published in September 2018 in the journal Medicine. It’s thought that a UTI may alter a pregnant woman’s inflammatory response, which can spur preeclampsia.
RELATED: National Period Day Is October 19
Can Having a UTI While Pregnant Hurt the Baby?Possibly. “A UTI itself doesn’t hurt the baby directly,” says Bartos. “It’s the failure to treat a UTI that can cause things like preterm birth or, rarely, infection of the amniotic sac. ” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
” For example, research published in American Family Physician shows that treating pregnant women who have asymptomatic UTIs decreases the incidence of preterm birth and low-birth-weight infants. That’s why screening and prompt treatment are important.
Urinary tract infections are not associated with preterm labor, according to research published in the Journal of the Chinese Medical Association. However, if a urinary tract infection is left untreated, it can progress to a kidney infection. And a kidney infection (pyelonephritis) during pregnancy can modestly increase your chances of early contractions and delivery. Research published in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology notes that women diagnosed with acute pyelonephritis in pregnancy have a 10.3 percent chance of preterm delivery compared with the 7.9 percent chance among women without a kidney infection during pregnancy.
RELATED: Common Types of Vaginal Infections
Do UTIs Differ by Trimester?At week 6, UTI risk starts to go up, with two-fifths of UTIs occurring during the first trimester. Because of the likelihood of getting a UTI during the first trimester, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommends that pregnant women have a urinalysis and urine culture at their first prenatal visit — whether they have UTI symptoms or not. In the second trimester, about half as many pregnant women are diagnosed with a UTI as in the first trimester, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and that number is almost halved again for the third trimester. However, 80 to 90 percent of acute kidney infections in pregnancy (many caused by the progression of an untreated UTI) occur in the second and third trimesters, according to data published in the Archives of Medical Science, so pregnant women should have a repeat urine culture during the third trimester.
RELATED: March Is Endometriosis Awareness Month
What Are Pregnancy-Safe UTI Treatment Options?How do you treat a UTI when pregnant? It’s similar to how you treat a UTI when not pregnant — with a few key differences. A short-course of antibiotics is the standard treatment for asymptomatic and symptomatic urinary tract infections that occur during pregnancy. There are, however, two important contrasts in treating UTIs in pregnant women versus nonpregnant women. First, asymptomatic UTIs diagnosed during the first trimester are treated with antibiotics, whereas nonpregnant women’s infections are often not treated in this manner. (Outside of pregnancy, asymptomatic bacteriuria is usually not treated with antibiotics.) Also, the preferred antibiotic drugs used to treat UTI in pregnancy often differ than what would be used while not pregnant. For instance, the following antibiotics have not been associated with any birth defects, thus are likely safe to use at any point during pregnancy:
- Penicillins Amoxicillin, ampicillin, and augmentin are in this group.
- Erythromycin Some of the brand names include Ery-Tab, Akne-Mycin, E.E.S. Eryc, and Pediamycin.
- Cephalosporins Keflex (cephalexin) is a cephalosporin.
UTI history and resistance patterns must be considered before prescribing any of these drugs.
Because certain antibiotics pose a potential risk for birth defects (anencephaly, heart defects, and cleft palate) when taken during the first trimester, they are only considered a first-line treatment for UTIs occurring during the second and third trimesters, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Prescribing the antibiotics listed below during the first trimester is considered appropriate only when no other suitable alternative treatments are available:
- Nitrofurantoin Macrobid, Furadantin, and Macrodantin are in this category.
- Sulfonamides Bactrim (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) is part of this class.

Be sure to double-check what your healthcare provider is prescribing, since despite the warnings, nitrofurantoin remains the most frequently prescribed antibiotic during the first trimester.
Treatment for Urinary Tract Infections: Antibiotics, Medication, and Home Remedies
By Holly PevznerDiagnosing UTI: Tests and Screenings, Early Diagnosis, and Your Doctors
By Holly PevznerSigns and Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections
Symptoms of a UTI may include a constant urge to urinate, frequent urination, or discomfort while urinating.
By Holly Pevzner
How to Prevent Urinary Tract Infections, or UTIs
Urinary tract infections, or UTIs, are the most common type of bacterial infection diagnosed today, with more than half of all women experiencing at least. ..
..
By Holly Pevzner
What Is a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
By Holly PevznerCauses and Risk Factors of UTIs
Urinary tract infections occur when harmful bacteria enter the urethra—the tube that carries urine out of the body. Risk factors for UTIs may differ between...
By Lindsey Konkel
Increased tone of the uterus during pregnancy
Nicotine constricts the blood vessels of the expectant mother, as well as the vessels of the placenta and umbilical cord, through which the fetus is nourished. Of course, smoking by itself is unlikely to lead to hypertonicity, but in combination with other factors, it may well
If the work is associated with constant stress, it has harmful effects or it is physically difficult, give it up as soon as possible. If this is not possible, use your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
If this is not possible, use your rights, which are enshrined in the labor legislation of the Russian Federation
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions: it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after a long time)
what is hypertonicity
, - muscle, and according to the laws of physiology, muscle tissue is reduced under the influence of any factor. Slightly the uterus contracts in women every month during menstruation, much stronger during labor pains. The uterus can also contract during pregnancy, doctors call this condition hypertonicity. What it looks like: suddenly, at some point, a woman feels that her stomach is tense, becomes hard, as if “hardening”. This state lasts for a long time - half an hour, an hour, half a day or even all day. Additionally, discomfort (or pain) in the lower back or sacrum may also appear. It is clear that such tension in the abdomen worries the mother, because since the uterus is contracting, then perhaps there is a threat of termination of pregnancy. But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses. nine0003
But here it all depends on how much and how often the stomach tenses. nine0003
Braxton-Hicks contractions
It turns out that the stomach can tense up not only when there is a threat of miscarriage. Starting from the end of the second trimester, the expectant mother can feel the so-called training contractions (Brexton-Hicks contractions) - the stomach also tenses with them for a while, as if “hardening”, - in general, the sensations are the same as with hypertonicity. But the main difference between such contractions and hypertonicity is that they last for a very short time (a few seconds - a couple of minutes) and pass by themselves, as well as if you change the position of the body or take a shower. Braxton-Hicks contractions occur up to about ten times a day, and by the end of pregnancy they appear even more often. These contractions are completely normal during pregnancy, and they do not indicate any threat of interruption. It’s just that with their help, the uterus, as it were, prepares (trains) for childbirth. nine0003
nine0003
where does hypertonicity come from
Hypertonicity can appear in any trimester of pregnancy. In the early stages, it occurs more often due to the fact that there is not enough progesterone, a hormone that is needed for the normal course of pregnancy. Another cause of hypertonicity is some changes in the uterine wall, for example, fibroids (a knot of uterine muscle tissue), endometriosis (growth of the uterine mucosa into the thickness of the wall), and inflammatory diseases. In these situations, the wall of the uterus is not able to stretch as it should. At later dates, hypertonicity can develop, on the contrary, with overstretching of the uterus (with polyhydramnios, large fetuses, multiple pregnancies). Very often, hypertonicity is provoked by some kind of physical activity too strong for a woman, for example, if, in a fit of “nesting”, the mother suddenly began to move and rearrange something in the apartment herself, or she simply moved for a very long time without resting. Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain. nine0003
Someone hypertonicity occurs after psychological overstrain. nine0003
how to recognize hypertonicity
Hypertonicity must be distinguished from Braxton-Hicks contractions - as mentioned earlier, it lasts much longer than these training contractions and usually does not go away on its own (or goes away only after some long time). But if the mother cannot understand whether she has hypertension or not, you should consult a doctor. If there is still an increased tone of the uterus, the doctor, simply by placing his hand on his stomach, will feel a seal, tension, up to the feeling of a stone at hand. In addition, you can always do an ultrasound, on which, with hypertonicity, areas of local thickening of the muscular layer of the uterus are visible, and also look at the cervix, by the state of which you can also judge whether there is a threat of abortion or not. nine0003
what to do in case of hypertonicity
If it appears, the first thing you need to do is:
1. Calm down and lie down if possible. Do not panic, extra stress will not bring any benefits, especially since without consulting a doctor it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how pronounced it is. Or maybe it's a false alarm? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
Calm down and lie down if possible. Do not panic, extra stress will not bring any benefits, especially since without consulting a doctor it is still not clear whether there is hypertonicity and how pronounced it is. Or maybe it's a false alarm? In addition, you can use relaxation techniques (breathing, auto-training, etc.).
2. Call your doctor. Of course, the doctor will not make a diagnosis in absentia, but since he knows the history of the expectant mother, her real or possible problems, he will be able to give the right direction for further action. nine0003
3. If it is not possible to contact your doctor, you can contact any clinic or antenatal clinic where pregnant women are treated. If medical institutions are already closed (late evening, at night), you can call an ambulance - she will take you to the nearest hospital or maternity hospital (you can also get there by taxi).
4. Hypertonicity is well eliminated by special medicines that relax the uterus (tocolytics), and if the doctor has prescribed them, then you should not be afraid to take them: they help quickly enough and do not harm the child. nine0003
nine0003
how to prevent hypertonicity
There are simple rules that can prevent hypertonicity or reduce the risk of its occurrence:
1. Quit smoking, watch your weight, do not eat surrogate foods. No matter how trite it may sound, but it is a healthy lifestyle that is the basis of our well-being.
2. Distribute your forces correctly. Laundry, cooking can wait if the expectant mother suddenly feels that she needs a rest. If any activities require physical or psychological stress, cancel them for a while. Do not attend events or places where you may feel uncomfortable, reduce communication with people that are unpleasant for you. nine0003
3. Follow your doctor's recommendations: if he recommends any examination or treatment, do not neglect them.
Listen to your body, follow the doctor's advice, tune in to the positive - this is the key to a successful pregnancy. And then no hypertonicity is terrible for you!
Changes in the cervix during pregnancy
Pregnancy is always pleasant, but sometimes not planned. And not all women have time to prepare for it, to be fully examined before its onset. And the detection of diseases of the cervix already during pregnancy can be an unpleasant discovery. nine0003
And not all women have time to prepare for it, to be fully examined before its onset. And the detection of diseases of the cervix already during pregnancy can be an unpleasant discovery. nine0003
The cervix is the lower segment of the uterus in the form of a cylinder or cone. In the center is the cervical canal, one end of which opens into the uterine cavity, and the other into the vagina. On average, the length of the cervix is 3–4 cm, the diameter is about 2.5 cm, and the cervical canal is closed. The cervix has two parts: lower and upper. The lower part is called the vaginal, because it protrudes into the vaginal cavity, and the upper part is supravaginal, because it is located above the vagina. The cervix is connected to the vagina through the vaginal fornices. There is an anterior arch - short, posterior - deeper and two lateral ones. Inside the cervix passes the cervical canal, which opens into the uterine cavity with an internal pharynx, and is clogged with mucus from the side of the vagina. Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm. nine0003
Mucus is normally impervious to infections and microbes, or to spermatozoa. But in the middle of the menstrual cycle, the mucus thins and becomes permeable to sperm. nine0003
Outside, the surface of the cervix has a pinkish tint, it is smooth and shiny, durable, and from the inside it is bright pink, velvety and loose.
The cervix during pregnancy is an important organ, both in anatomical and functional terms. It must be remembered that it promotes the process of fertilization, prevents infection from entering the uterine cavity and appendages, helps to "endure" the baby and participates in childbirth. That is why regular monitoring of the condition of the cervix during pregnancy is simply necessary. nine0003
During pregnancy, a number of physiological changes occur in this organ. For example, a short time after fertilization, its color changes: it becomes cyanotic. The reason for this is the extensive vascular network and its blood supply. Due to the action of estriol and progesterone, the tissue of the cervix becomes soft. During pregnancy, the cervical glands expand and become more branched.
During pregnancy, the cervical glands expand and become more branched.
Screening examination of the cervix during pregnancy includes: cytological examination, smears for flora and detection of infections. Cytological examination is often the first key step in the examination of the cervix, since it allows to detect very early pathological changes that occur at the cellular level, including in the absence of visible changes in the cervical epithelium. The examination is carried out to identify the pathology of the cervix and the selection of pregnant women who need a more in-depth examination and appropriate treatment in the postpartum period. When conducting a screening examination, in addition to a doctor's examination, a colposcopy may be recommended. As you know, the cervix is covered with two types of epithelium: squamous stratified from the side of the vagina and single-layer cylindrical from the side of the cervical canal. Epithelial cells are constantly desquamated and end up in the lumen of the cervical canal and in the vagina. Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones. nine0003
Their structural characteristics make it possible, when examined under a microscope, to distinguish healthy cells from atypical ones, including cancerous ones. nine0003
During pregnancy, in addition to physiological changes in the cervix, some borderline and pathological processes may occur.
Under the influence of hormonal changes that occur in a woman's body during the menstrual cycle, cyclic changes also occur in the cells of the epithelium of the cervical canal. During the period of ovulation, the secretion of mucus by the glands of the cervical canal increases, and its qualitative characteristics change. With injuries or inflammatory lesions, sometimes the glands of the cervix can become clogged, a secret accumulates in them and cysts form - Naboth follicles or Naboth gland cysts that have been asymptomatic for many years. Small cysts do not require any treatment. And pregnancy, as a rule, is not affected. Only large cysts that strongly deform the cervix and continue to grow may require opening and evacuation of the contents.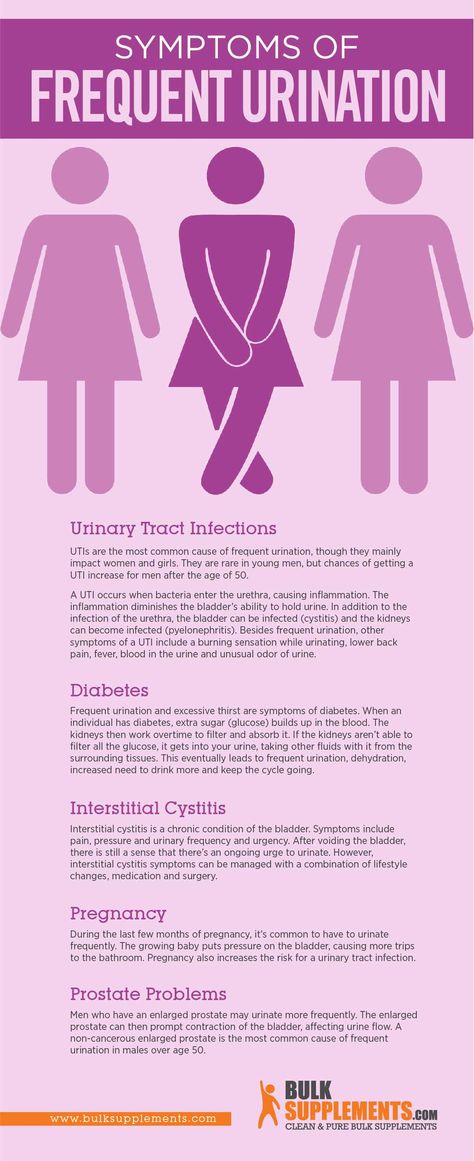 However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
However, this is very rare and usually requires monitoring during pregnancy.
Quite often, in pregnant women, during a mirror examination of the vaginal part, polyps cervix. The occurrence of polyps is most often associated with a chronic inflammatory process. As a result, a focal proliferation of the mucosa is formed, sometimes with the involvement of muscle tissue and the formation of a pedicle. They are mostly asymptomatic. Sometimes they are a source of blood discharge from the genital tract, more often of contact origin (after sexual intercourse or defecation). The size of the polyp is different - from millet grain rarely to the size of a walnut, their shape also varies. Polyps are single and multiple, their stalk is located either at the edge of the external pharynx, or goes deep into the cervical canal. Sometimes during pregnancy there is an increase in the size of the polyp, in some cases quite fast. Rarely, polyps first appear during pregnancy. The presence of a polyp is always a potential threat of miscarriage, primarily because it creates favorable conditions for ascending infection.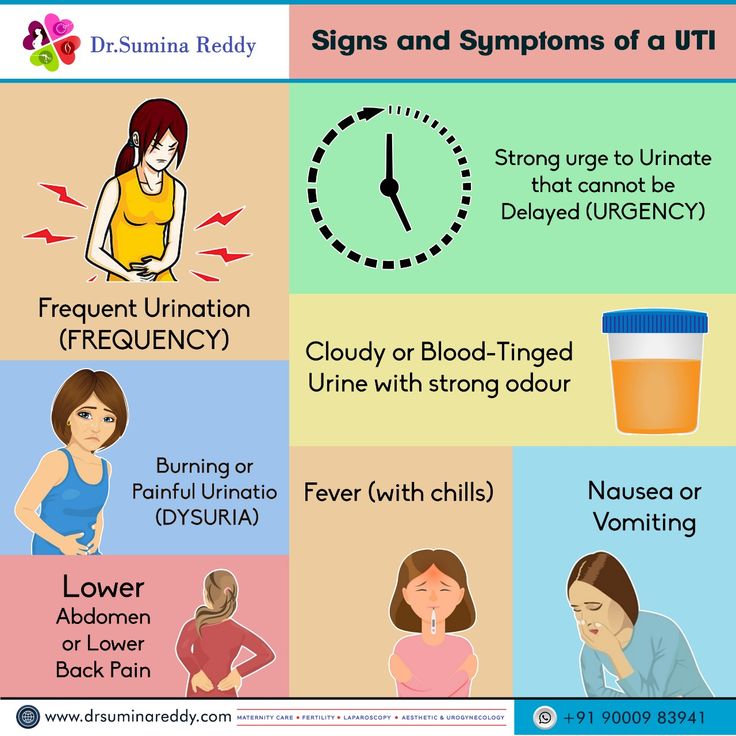 Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth. nine0003
Therefore, as a rule, more frequent monitoring of the cervix follows. The tendency to trauma, bleeding, the presence of signs of tissue necrosis and decay, as well as questionable secretions require special attention and control. Treatment of cervical polyps is only surgical and during pregnancy, in most cases, treatment is postponed until the postpartum period, since even large polyps do not interfere with childbirth. nine0003
The most common pathology of the cervix in women is erosion . Erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane. True erosion is not very common. The most common pseudo-erosion (ectopia) is a pathological lesion of the cervical mucosa, in which the usual flat stratified epithelium of the outer part of the cervix is replaced by cylindrical cells from the cervical canal. Often this happens as a result of mechanical action: with frequent and rough sexual intercourse, desquamation of the stratified squamous epithelium occurs. Erosion is a multifactorial disease. The reasons may be: nine0003
The reasons may be: nine0003
- genital infections, vaginal dysbacteriosis and inflammatory diseases of the female genital area;
- is an early onset of sexual activity and frequent change of sexual partners. The mucous membrane of the female genital organs finally matures by the age of 20-23. If an infection interferes with this delicate process, erosion is practically unavoidable;
- is a cervical injury. The main cause of such injuries is, of course, childbirth and abortion;
- hormonal disorders; nine0094
- , cervical pathology may also occur with a decrease in the protective functions of immunity.
The presence of erosion does not affect pregnancy in any way, as well as pregnancy on erosion. Treatment during pregnancy consists in the use of general and local anti-inflammatory drugs for inflammatory diseases of the vagina and cervix. And in most cases, just dynamic observation is enough. Surgical treatment is not carried out throughout the entire pregnancy, since the excess of risks and benefits is significant, and after treatment during childbirth, there may be problems with opening the cervix. nine0003
nine0003
Almost all women with various diseases of the cervix safely bear and happily give birth to beautiful babies!
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select the clinic
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the prices for programs in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the cost of services by phone / with the managers of the clinic
nine0002 Clinical Hospital IDKMother and Child Clinic Enthusiastov SamaraAll areasSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Molecular genetics laboratoryGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomOther gynecological operationsTelemedicine for adultsTherapeutic examinationsAdult ultrasound examinations
01.
Specialist consultations (adults)
02.