What do low hcg levels mean
Low hCG levels in pregnancy: What does it mean?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is produced by cells in the placenta during pregnancy. Its job is to nurture and feed the embryo that is attached to the wall of the uterus.
Lower than normal levels of hCG may indicate a problem with the pregnancy including:
- miscarriage
- ectopic pregnancy
- fetal death
Levels of hCG can vary significantly between individuals and from one pregnancy to the next in the same person. But, typically, hCG levels follow a typical range throughout a healthy, uncomplicated pregnancy.
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG tend to decrease in the later stages of pregnancy.Levels of hCG typically increase in the first trimester of a healthy pregnancy.
Levels of hCG usually increase during the first trimester, peak by weeks 8 to 11, and then decline to a steady level in the later stages of the pregnancy.
This means that as the pregnancy develops, hCG becomes less useful as a way to monitor it. When hCG levels do not increase or decrease as they should, it may be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy.
Increasing levels of hCG usually mean that a pregnancy is healthy. However, low hCG levels are not always a sign that something is wrong.
Possible causes of low hCG levels are:
Blighted ovum
A blighted ovum occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, but the embryo fails to develop.
This can happen during early pregnancy, sometimes before a person even knows they are pregnant.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is also known as spontaneous abortion and happens when the embryo dies naturally before 20 weeks of gestation.
Levels of hCG may rise initially in these situations but fail to increase or decrease as they should afterward.
Miscalculated gestational age
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG may appear low if a doctor has miscalculated the baby’s due date.
This happens when the stage of pregnancy and the estimated date of birth are wrong.
Calculating these events is based on the dates of a woman’s last menstrual period, so miscalculations can occur if someone experiences irregular periods or is not sure when they had their last period.
Low levels of hCG can indicate whether a pregnancy is in a stage where low hCG levels are normal, such as in very early pregnancy, or in a pregnancy that is post-11 weeks.
Sometimes, in cases of miscalculated gestational age, the level of hCG may be lower than expected but not abnormal for the pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is an abnormal pregnancy where the embryo attaches outside of the uterus, usually inside the fallopian tube, the tube that carries the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Symptoms can include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy can be a very serious, and even life-threatening, condition. Levels of hCG remain low during an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a sign of a problem.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for situations where low hCG levels are a cause for concern.
However, treatment is available for the underlying conditions that cause low hCG levels, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy.
In case of a miscarriage
Treatment may involve removing any pregnancy tissue that has been left inside the uterus and might include medication or a surgical procedure.
In case of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor may also prescribe medications or surgery to remove the affected fallopian tube and the pregnancy itself.
Low hCG levels that result from a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy are usually accompanied by abdominal pain, with or without vaginal bleeding.
There is currently no way to prevent low hCG levels or its associated complications, such as a blighted ovum, a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a cause for concern. Levels of hCG can differ between individuals and between different pregnancies in the same person. Some people may naturally have lower levels of hCG than others.
Taking measurements of levels throughout the pregnancy can indicate if the pregnancy is developing as expected.
Even if a complication associated with low hCG levels occurs, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy, this does not mean that someone will be unable to get pregnant again or that their fertility is compromised. A successful pregnancy is still possible with low hCG levels.
Low hCG levels in pregnancy: What does it mean?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone that is produced by cells in the placenta during pregnancy. Its job is to nurture and feed the embryo that is attached to the wall of the uterus.
Lower than normal levels of hCG may indicate a problem with the pregnancy including:
- miscarriage
- ectopic pregnancy
- fetal death
Levels of hCG can vary significantly between individuals and from one pregnancy to the next in the same person. But, typically, hCG levels follow a typical range throughout a healthy, uncomplicated pregnancy.
Levels of hCG typically increase in the first trimester of a healthy pregnancy.
Levels of hCG usually increase during the first trimester, peak by weeks 8 to 11, and then decline to a steady level in the later stages of the pregnancy.
This means that as the pregnancy develops, hCG becomes less useful as a way to monitor it. When hCG levels do not increase or decrease as they should, it may be a sign of a problem with the pregnancy.
Increasing levels of hCG usually mean that a pregnancy is healthy. However, low hCG levels are not always a sign that something is wrong.
Possible causes of low hCG levels are:
Blighted ovum
A blighted ovum occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus, but the embryo fails to develop.
This can happen during early pregnancy, sometimes before a person even knows they are pregnant.
Miscarriage
Miscarriage is also known as spontaneous abortion and happens when the embryo dies naturally before 20 weeks of gestation.
Levels of hCG may rise initially in these situations but fail to increase or decrease as they should afterward.
Miscalculated gestational age
Share on PinterestLevels of hCG may appear low if a doctor has miscalculated the baby’s due date.
This happens when the stage of pregnancy and the estimated date of birth are wrong.
Calculating these events is based on the dates of a woman’s last menstrual period, so miscalculations can occur if someone experiences irregular periods or is not sure when they had their last period.
Low levels of hCG can indicate whether a pregnancy is in a stage where low hCG levels are normal, such as in very early pregnancy, or in a pregnancy that is post-11 weeks.
Sometimes, in cases of miscalculated gestational age, the level of hCG may be lower than expected but not abnormal for the pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy
This is an abnormal pregnancy where the embryo attaches outside of the uterus, usually inside the fallopian tube, the tube that carries the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
Symptoms can include abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. An ectopic pregnancy can be a very serious, and even life-threatening, condition. Levels of hCG remain low during an ectopic pregnancy.
Low levels of hCG are not always a sign of a problem.
Unfortunately, there is no cure for situations where low hCG levels are a cause for concern.
However, treatment is available for the underlying conditions that cause low hCG levels, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy.
In case of a miscarriage
Treatment may involve removing any pregnancy tissue that has been left inside the uterus and might include medication or a surgical procedure.
In case of an ectopic pregnancy, the doctor may also prescribe medications or surgery to remove the affected fallopian tube and the pregnancy itself.
Low hCG levels that result from a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy are usually accompanied by abdominal pain, with or without vaginal bleeding.
There is currently no way to prevent low hCG levels or its associated complications, such as a blighted ovum, a miscarriage, or an ectopic pregnancy.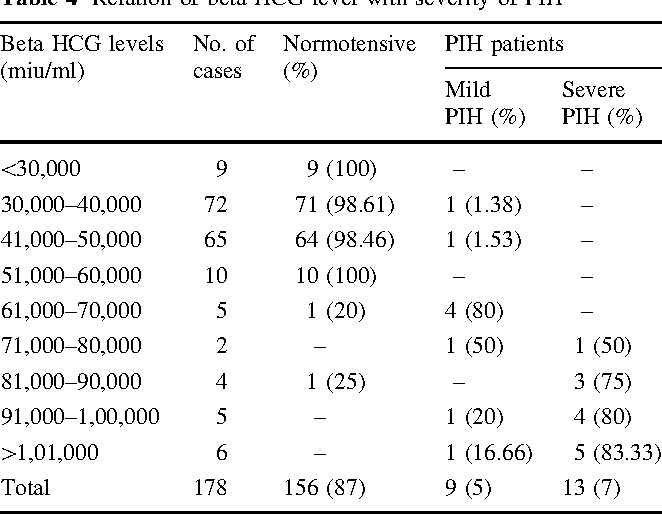
Low levels of hCG are not always a cause for concern. Levels of hCG can differ between individuals and between different pregnancies in the same person. Some people may naturally have lower levels of hCG than others.
Taking measurements of levels throughout the pregnancy can indicate if the pregnancy is developing as expected.
Even if a complication associated with low hCG levels occurs, such as a miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy, this does not mean that someone will be unable to get pregnant again or that their fertility is compromised. A successful pregnancy is still possible with low hCG levels.
What does low hCG mean. Pregnancy and low hCG
Pregnancy is a long-awaited period in the life of every woman. To determine the nature of the course of pregnancy, assess the degree of fetal development and early detection of pathological conditions, a woman is prescribed various research methods, one of which is an analysis of chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). In the early stages of pregnancy, it is overestimated or low hCG that may indicate developing complications.
In the early stages of pregnancy, it is overestimated or low hCG that may indicate developing complications.
HCG and its functions
HCG is often called the hormone of pregnancy, as it appears only after successful implantation of a fertilized egg and is produced by the chorion, or rather its trophoblast (predecessor of the placenta). The level of hCG is an important indicator of the course of pregnancy and fetal development.
Immediately after conception, the embryo is a small vesicle, the walls of which include actively multiplying cells. Some of them later form the embryo, and the other trophoblast, which develops into the chorion (the shell of the embryo) and then into the placenta.
Chorion, after successful implantation of the embryo into the endometrium, begins to synthesize hCG, which affects the body of the woman and the fetus. HCG during pregnancy is necessary to create favorable conditions for the development of the fetus, the formation of the placenta, and the activation of the corpus luteum, which is responsible for the synthesis of progesterone.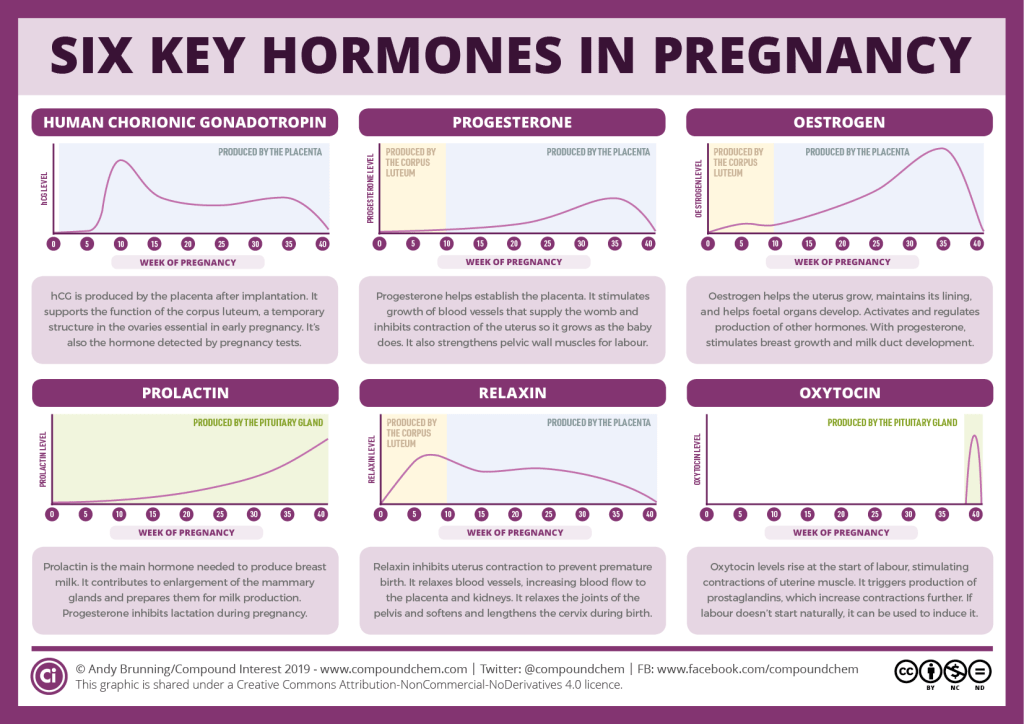 It is worth noting that it is progesterone that maintains the optimal state of the endometrium, provides a strong fixation of the embryo and its nutrition. Normally, in the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development and resolves, but hCG contributes to its preservation and stimulates its performance.
It is worth noting that it is progesterone that maintains the optimal state of the endometrium, provides a strong fixation of the embryo and its nutrition. Normally, in the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum undergoes reverse development and resolves, but hCG contributes to its preservation and stimulates its performance.
Therefore, high and low hCG are one of the signs of the development of pregnancy pathology, which makes it possible to identify it at an early stage and prevent the formation of negative consequences, in particular, fetal death.
HCG norms
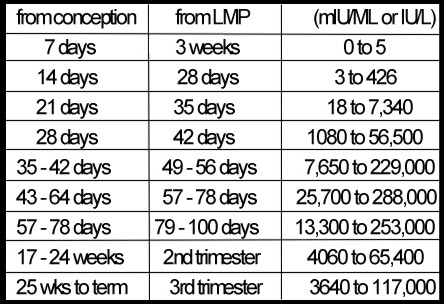
HCG is determined in the blood on the 6-8th day after successful implantation of the embryo. The norms of hCG are rather conditional and depend not only on the gestational age, but also on the number of fetuses, taking medications, hormone detection methods, laboratory equipment and other factors. Therefore, each laboratory presents its own tables to decipher the results. In addition, it is recommended to carry out an analysis for hCG in the same laboratory to obtain reliable and truthful data.
The first test for hCG is done to detect the fact of pregnancy. It can be done at home using rapid tests. Of course, hCG appears in the urine later than in the blood, but this simple diagnostic method is available to many women and is effective in 98% of cases. At the same time, with the help of an express test, low hCG can be suspected - the strip will be dim and mild. Hormone levels can also be determined by taking a blood test - this is the most accurate diagnostic method.
The second analysis is carried out at 10-12 weeks of gestation at the same time as the ultrasound. It is during this period that the highest level of hCG in the blood is determined. If poor results are obtained, the study is repeated, sometimes the analysis is prescribed right up to the very birth.
It is worth noting that not only the level of hCG is important, but also the degree of its increase. Indeed, in the first trimester, its concentration doubles every 2-3 days, reaching a maximum at 10-12 weeks.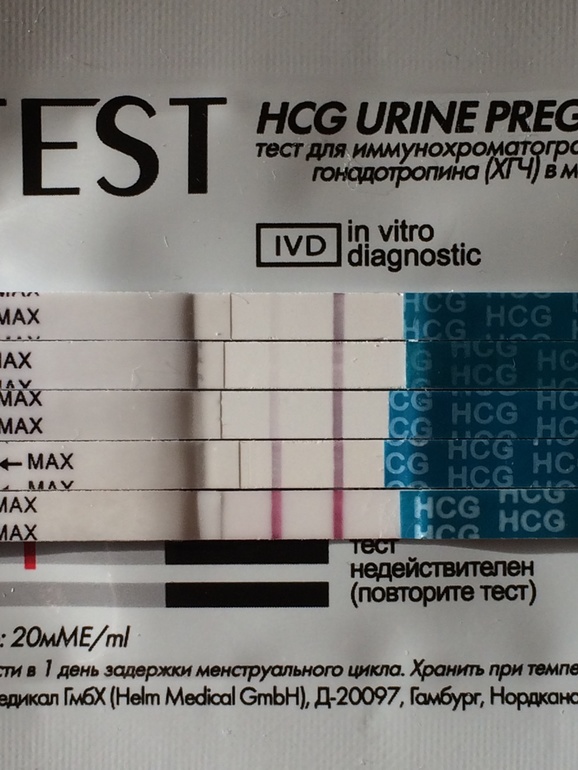 Therefore, to identify pathological conditions, tests are often prescribed at intervals of 2-3 days.
Therefore, to identify pathological conditions, tests are often prescribed at intervals of 2-3 days.
Low hCG
Low hCG is an indicator that is detected in various pathologies of pregnancy and the fetus. Although it is worth noting that false negative results obtained as a result of an incorrectly set gestational age or laboratory errors are not excluded.
Low hCG is caused by the inferiority of the chorion, a decrease in its functionality, hormonal disorders of the mother and fetus, placental abruption, improper attachment of the embryo and other reasons.
Low hCG is detected in the following conditions:
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Miscarriage;
- Fetal growth retardation;
- Threatened miscarriage;
- Fetal death;
- Chronic placental insufficiency;
- Postponement of pregnancy;
- Implantation problems after IVF (in vitro fertilization).
But the data of chorionic gonadotropin cannot serve as a reason for making a disappointing diagnosis; if negative results are obtained, additional examination methods should be undergone to clarify and identify the pathology.
Low hCG and missed pregnancy
A missed pregnancy is a cessation of the development and formation of the fetus, ending in his death. It is quite difficult to identify the pathology at an early stage, since the symptoms of the death of the embryo appear after a few weeks. But low hCG makes it possible to suspect a missed pregnancy and prevent the development of formidable complications. After receiving the analysis data, it is necessary to conduct repeated studies to determine the growth dynamics of hCG.
During normal pregnancy, an active increase in hCG levels is observed, but with a frozen one, it is not typical, often the hormone level may become less than the initial data. A slight increase in the concentration of hCG is not excluded, but the increase in the level is minimal and differs from the norm. Of course, it is impossible to accurately say the value of the hormone, indicating pathology, since each woman is individual.
Low hCG and ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a pathology in which the embryo is attached outside the uterine cavity: in the fallopian tubes, in the cervical or abdominal cavity. Low hCG during an ectopic pregnancy is detected after the first hormone test, including after an express test. The reduced level of hCG in this pathology is due to the defective functioning of the chorion. This is due to the fact that it can only adequately perform its work after attaching to the endometrium, in other parts there is insufficient nutrition and there are no normal conditions, so the chorion becomes weak and produces low hCG.
Low hCG during an ectopic pregnancy is detected after the first hormone test, including after an express test. The reduced level of hCG in this pathology is due to the defective functioning of the chorion. This is due to the fact that it can only adequately perform its work after attaching to the endometrium, in other parts there is insufficient nutrition and there are no normal conditions, so the chorion becomes weak and produces low hCG.
Hormone growth during ectopic pregnancy is also negative, although according to some reports, low hCG levels and its increase can be determined during normal pregnancy. Therefore, the basis for the diagnosis is the conduct of additional diagnostic methods, in particular ultrasound.
Low hCG, fetal growth retardation and placental insufficiency
Fetal growth retardation is a decrease in the weight and size of the child. Low hCG is a non-specific marker of pathology, so other examination methods are required. But it is worth noting that placental insufficiency precedes this condition, which causes fetal hypoxia, malnutrition and blood supply, and other negative reactions.
Since placental insufficiency reduces all functions of the protective membrane, the synthesis of hCG also decreases. Therefore, based on the data obtained, this pathology can be suspected. At the same time, in its initial stages, a decrease in not only hCG, but also progesterone and prolactin has a diagnostic value.
Low hCG during post-pregnancy is also associated with placental insufficiency, since immediately before childbirth, the functionality of the placenta begins to decrease, it ages, therefore, less hCG is produced.
Low hCG, threatened miscarriage and genetic abnormalities
Threatened miscarriage may be associated with placental insufficiency, unreliable implantation of the ovum, detachment of the chorion, incorrect attachment site and other conditions. Most of them lead to a decrease in the functionality of the chorion and placenta, which ends in a decrease in the synthesis of hCG.
hCG can act as a marker of genetic abnormalities. Often, such diseases cause a sharp increase in the level of hCG, but it may decrease, in particular with Edwards and Patau syndrome. In these cases, consultation with a geneticist is necessary.
Often, such diseases cause a sharp increase in the level of hCG, but it may decrease, in particular with Edwards and Patau syndrome. In these cases, consultation with a geneticist is necessary.
Low hCG and normal pregnancy
Sometimes low hCG can correspond to a normal pregnancy, so do not be afraid of the test results, but also do not leave everything without a doctor's control. Reduced hCG values can be caused by an incorrect gestational age, and a slight increase in concentration will appear due to the individual characteristics of the body. In some situations, low hCG is due to insufficient secretory function of the chorion. To correct this condition, chorionic gonadotropin is prescribed in the form of a drug.
Based on numerous studies, experts have found that the average increase in hCG in two days should be 66%. But at the same time, in 15% of cases, an increase in concentration by a lower value was observed during normal pregnancy. Scientists have proven that even with an increase in hCG by 53%, the full formation and bearing of the fetus is not excluded, and excess growth can also form under pathological conditions.
You can take tests for hCG and conduct other studies in the treatment of infertility at the clinic "IVF Center" in Smolensk.
What does low hCG indicate
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes significant changes that are necessary for the normal development of the unborn child. One of the most global changes is a change in the hormonal background, which affects not only the physical, but also the emotional state of a woman. Important for the development of the fetus is a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin. It supports the functioning of the corpus luteum and provides many other functions.
What is hCG
HCG or human chorionic gonadotropin - is produced in large quantities in the female body during pregnancy. It is also synthesized in non-pregnant women and men, but in very small amounts. In this case, its increase requires an urgent consultation of a specialist, since an increase in this hormone without pregnancy indicates the development of an oncological disease.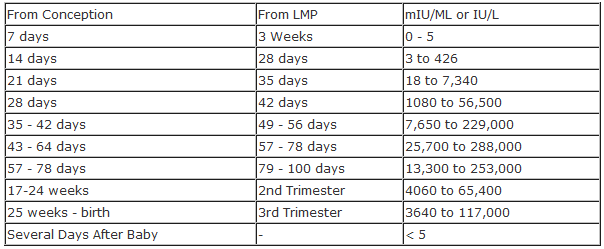 If you find an increased level of the hormone (in the absence of pregnancy or in men), you should contact your general practitioner, family doctor or oncologist to clarify the state of health.
If you find an increased level of the hormone (in the absence of pregnancy or in men), you should contact your general practitioner, family doctor or oncologist to clarify the state of health.
HCG is produced by the chorion (upper germinal membrane) of the fetus almost immediately after it is implanted in the uterus. The presence of hCG and its rapid increase indicates the normal development of pregnancy.
HCG is a gonadotropic hormone, similar to follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones, which are synthesized by the pituitary gland, but differ from them in amino acid sequence. It consists of two subunits - α and β. The α-subunit is identical to the α-subunits of follicle-stimulating, luteinizing and thyroid-stimulating hormones, and the β-subunit has a biological and immunoreactive uniqueness specifically for human chorionic gonadotropin. Therefore, the β-subunit is used as a biochemical marker in prenatal screenings. In addition, the "home" test for pregnancy in the form of a strip is based on determining the presence of the β-subunit.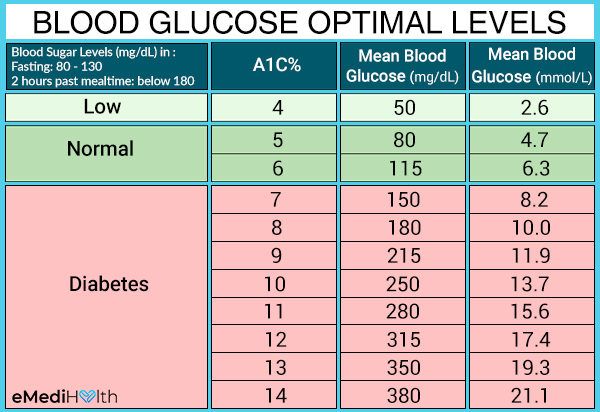
Functions of hCG
The main task of chorionic gonadotropin is to prolong the existence of the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone (a hormone necessary for the development of the fetus). At the same time, under the influence of hCG, the corpus luteum produces a very large amount of progesterone, which is impossible during the normal functioning of the body of a non-pregnant woman.
The corpus luteum forms at the site of a ruptured follicle after the release of an egg from it (ovulation). In a normal menstrual cycle, the corpus luteum exists for about 10-12 days, after which it dissolves. When pregnancy occurs, hCG does not allow it to disappear so that the production of progesterone does not stop. HCG will maintain the existence of the corpus luteum until the placenta of the fetus fully matures and begins to produce the required amount of progesterone on its own, i.e. by the end of the first trimester.
Thus, the level of the hormone begins to increase rapidly from the first days of pregnancy: starting from 0-25 mIU / ml and reaching approximately 200,000 mIU / ml by the twelfth week of pregnancy.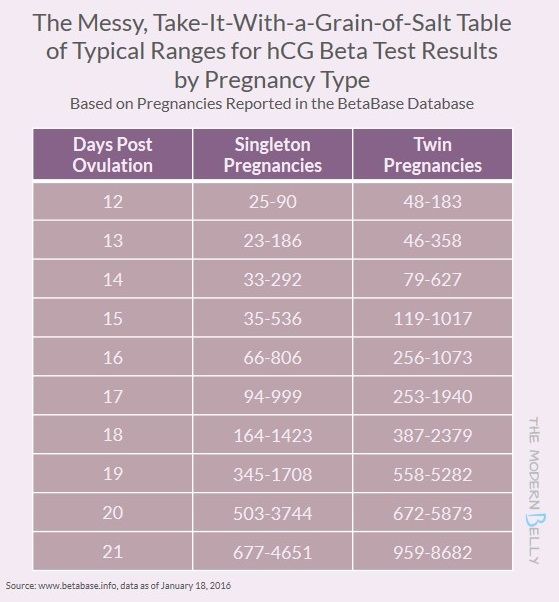 Further, the level of hCG will gradually decrease, while still continuing to remain quite high.
Further, the level of hCG will gradually decrease, while still continuing to remain quite high.
In addition, human chorionic gonadotropin has an effect on the secretion of hormones in the adrenal cortex. An increase in the synthesis of glucocorticoids in pregnant women plays an important role in the mechanisms of adaptation of the female body to a stressful state, which, in essence, is pregnancy. Also, glucocorticoids provide physiological immunosuppression, which is necessary to support the development of a semi-foreign organism, i.e. fetus.
Chorionic gonadotropin has a beneficial effect on the development of the placenta, improving its trophism, and helps to increase the number of chorionic villi. HCG is also used to stimulate ovulation during assisted reproductive technologies. An hCG injection is a mandatory component during IVF. HCG contributes to the normal completion of the maturation of the follicles and provokes the release of eggs to the outside.
IVF procedure in Kaliningrad is possible in the IVF Center clinic.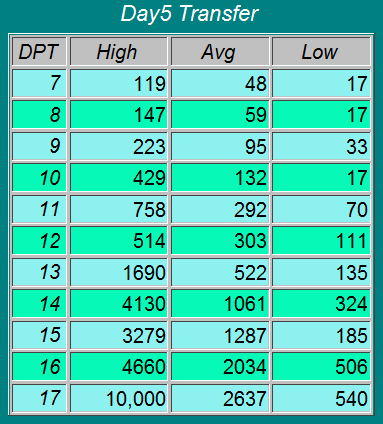 The clinic's specialists have extensive experience in various ART methods, including IVF.
The clinic's specialists have extensive experience in various ART methods, including IVF.
When to check the level of hCG
In order to check the presence of pregnancy, women, in most cases, firstly carry out a pregnancy test using a special strip. Such a test strip can be bought at any pharmacy or supermarket. A blood test for hCG levels is one of the first tests that a woman will take after IVF to confirm pregnancy. Usually the test is carried out after a few days of delay in menstruation. With a planned pregnancy or after IVF, it is not rational to conduct a test earlier than 2 weeks after ovulation or embryo transfer: you can get a false result.
Despite the fact that hCG begins to be synthesized in the body immediately after the implantation of the embryo in the uterus, its level in the urine will always be several times lower than in the blood. Therefore, the most informative is a blood test for the content of hCG in it. For examination, venous blood is used, which is taken on an empty stomach.
According to the level of chorionic hormone in the blood, you can determine the course of pregnancy if you monitor its performance in dynamics. The level should increase tens of thousands of times a week. With multiple pregnancies, the level will be even higher: hCG increases in proportion to the number of fetuses.
It should be noted that the same laboratory should be used to track the growth of hCG. This is due to the fact that laboratories may use different research methods: equipment and reagents may differ. The units of measurement may also differ.
The study of hCG in dynamics also allows you to notice a decrease in its level in time, which may indicate the appearance of pregnancy developmental disorders.
In addition to the course of pregnancy, hCG analysis is part of prenatal screenings, which are carried out in the first and second trimester, to identify the risk of genetic abnormalities (Down syndrome, Edwards, etc.). During screenings, the hCG β-subunit is examined, as well as indicators of other hormones, the results of preliminary ultrasound and the incoming questionnaire data, which indicate the history of the pregnant woman. If the screening results show a high risk of pathologies, the woman is referred for invasive examinations, which will more accurately show the condition of the fetus.
If the screening results show a high risk of pathologies, the woman is referred for invasive examinations, which will more accurately show the condition of the fetus.
Low hCG in ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a condition in which a fertilized egg is implanted elsewhere in the female reproductive system than in the uterine wall. In most cases, this site is the fallopian tubes. This condition is very dangerous for a woman's health: it can cause deformation of the reproductive organs, severe bleeding, and even death. An ectopic pregnancy is difficult to diagnose right away because its onset is very similar to a normal pregnancy. During an ectopic pregnancy, menstruation is delayed, the level of the hormone in the blood begins to rise, respectively, and the test strip will give a positive result.
In the early stages, an ectopic pregnancy can only be detected by ultrasound. A signal to check the localization of implantation will be low hCG. With an ectopic pregnancy, the hCG level will first rise as usual, and then it will begin to drop sharply.