What cheese can i eat pregnant
Foods to avoid in pregnancy
Most foods and drinks are safe to have during pregnancy. But there are some things you should be careful with or avoid.
Cheese, milk and other dairyWhat you can eat
- pasteurised or unpasteurised hard cheeses, such as cheddar, Gruyere and parmesan
- pasteurised semi-hard cheeses, such as Edam and Stilton
- pasteurised soft cheeses, such as cottage cheese, mozzarella, feta, cream cheese, paneer, ricotta, halloumi, goats' cheese without a white coating on the outside (rind) and processed cheese spreads
- soft or blue cheese (pasteurised or unpasteurised) that has been cooked until steaming hot
- pasteurised milk, yoghurt, cream and ice cream
What to avoid
- any other foods made from unpasteurised milk, such as soft ripened goats' cheese
- pasteurised or unpasteurised mould-ripened soft cheeses with a white coating on the outside, such as Brie, Camembert and chèvre (unless cooked until steaming hot)
- pasteurised or unpasteurised soft blue cheeses, such as Danish blue, Gorgonzola and Roquefort (unless cooked until steaming hot)
- unpasteurised cows' milk, goats' milk, sheep's milk or cream
Why
There's a small chance that unpasteurised or soft ripened dairy products may contain Listeria bacteria. This can cause an infection called listeriosis.
Listeriosis can lead to miscarriage or stillbirth, or make your newborn baby very unwell.
Soft cheeses with a white coating on the outside have more moisture. This can make it easier for bacteria to grow.
Cooking cheese until it's steaming hot kills bacteria, reducing the risk of listeriosis.
Meat and poultryWhat you can eat
- meats such as chicken, pork and beef, as long as they're well-cooked with no trace of pink or blood; be especially careful with poultry, pork, sausages and burgers
- cold, pre-packed meats such as ham and corned beef
What to be careful with
- cold cured meats, such as salami, pepperoni, chorizo and prosciutto (unless cooked thoroughly)
What to avoid
- raw or undercooked meat
- liver and liver products
- all types of pâté, including vegetarian pâté
- game meats such as goose, partridge or pheasant
Why
There's a small risk of getting toxoplasmosis if you eat raw and undercooked meat, which can cause miscarriage.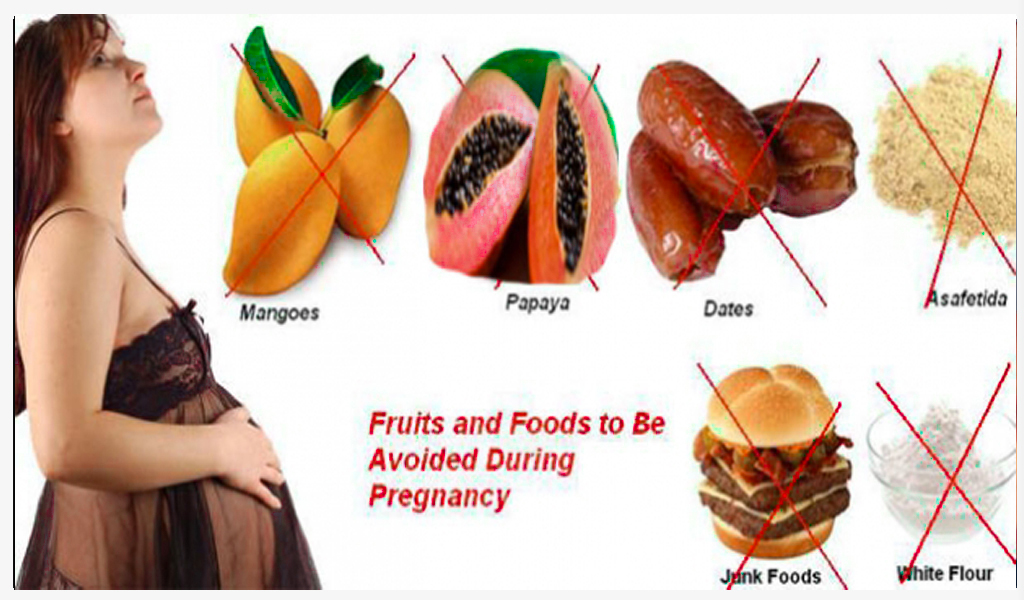
Cured meats are not cooked, so they may have parasites in them that cause toxoplasmosis.
Liver and liver products have lots of vitamin A in them. This can be harmful to an unborn baby.
Game meats may contain lead shot.
EggsWhat you can eat
- raw, partially cooked and fully cooked British Lion hen eggs (they have a lion stamp on them) and hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- foods made with raw hen egg, such as mousse and mayonnaise, if made with British Lion eggs or hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- well cooked eggs (white and yolk) from any hen eggs that are not British Lion eggs or produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- well cooked eggs (white and yolk) of all other eggs, including duck, goose or quail
What to avoid
- raw or partially cooked hen eggs that are not British Lion or produced under the Laid in Britain scheme
- raw or partially cooked duck, goose or quail eggs
Why
British Lion hen eggs and hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme are less likely to have salmonella in them.
Salmonella is unlikely to harm your unborn baby, but you could get food poisoning.
You should cook all eggs thoroughly, unless they are British Lion hen eggs or hen eggs produced under the Laid in Britain scheme.
FishWhat you can eat
- cooked fish and seafood
- sushi, as long as the fish has been cooked thoroughly
- cooked shellfish, such as mussels, lobster, crab, prawns, scallops and clams
- cold pre-cooked prawns
What to be careful with
- smoked fish, such as smoked salmon and trout
Smoked fish and listeria
Due to a listeria outbreak linked to smoked fish, people at higher risk of serious infection (including people who are pregnant) should only eat smoked fish products that have been thoroughly cooked.
When cooking smoked fish products at home, make sure they are steaming hot all the way through.
Find out more about the listeria outbreak in smoked fish from the Food Standards Agency
What to limit
- you should eat no more than 2 portions of oily fish a week, such as salmon, trout, mackerel or herring
- you should eat no more than 2 tuna steaks (about 140g cooked or 170g raw) or 4 medium-size cans of tuna (about 140g when drained) per week
Information:
Tuna does not count as an oily fish
You can have 2 tuna steaks, or 4 medium-size cans of fish, as well as 2 portions of oily fish.
What to avoid
- swordfish
- marlin
- shark
- raw shellfish
Why
You should limit tuna because it has more mercury in it than other fish. If you eat too much mercury, it can be harmful to your unborn baby.
If you eat too much mercury, it can be harmful to your unborn baby.
You should limit oily fish because they can have pollutants such as dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in them. If you eat too much of these, they can be harmful to your unborn baby.
You should avoid raw shellfish because they can have harmful bacteria, viruses or toxins in them. These can make you unwell and give you food poisoning.
Other foods and drinksCaffeine
You can have caffeine, but no more than 200mg per day.
There is:
- 100mg in a mug of instant coffee
- 140mg in a mug of filter coffee
- 75mg in a mug of tea (green tea can have the same amount of caffeine as regular tea)
- 40mg in a can of cola
- 80mg in a 250ml can of energy drink
- less than 25mg in a 50g bar of plain dark chocolate
- less than 10mg in a 50g bar of plain milk chocolate
Alcohol
Drinking alcohol in pregnancy can lead to long-term harm to your baby.
If you're pregnant or planning to get pregnant, the safest approach is to not drink alcohol at all.
This keeps risks to your baby to a minimum.
Herbal teas
You should drink no more than 4 cups of herbal tea a day.
Liquorice
Liquorice is safe to eat. But you should avoid liquorice root.
Fruits, vegetables and salads
Be careful with fruits, vegetables and salads as they can have soil on them, which can make you unwell.
Make sure to thoroughly wash all fruits, vegetables and salad ingredients.
Peanuts
You do not need to avoid eating peanuts when you're pregnant.
Only avoid eating peanuts if you're advised to by a healthcare professional or if you have a nut allergy.
Vitamins
Do not take high-dose multivitamin supplements, or any supplements with vitamin A in them.
Urgent advice: Call 111 if:
- you feel unwell after eating one of the foods to avoid
- you have signs of listeriosis or toxoplasmosis infection
Try not to worry if you've eaten one of the foods to avoid.
Get Start4Life pregnancy and baby emails
Sign up for Start4Life's weekly emails for expert advice, videos and tips on pregnancy, birth and beyond.
Page last reviewed: 16 April 2020
Next review due: 16 April 2023
Foods to avoid when pregnant
Foods to avoid when pregnant | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
There are some foods you should not eat when you're pregnant because they might make you ill or harm your baby. Make sure you know the important facts about which foods you should avoid or take extra care with when you're pregnant. The best foods to eat are freshly cooked or freshly prepared food.
Make sure you know the important facts about which foods you should avoid or take extra care with when you're pregnant. The best foods to eat are freshly cooked or freshly prepared food.
Some types of cheese
Don't eat mould-ripened soft cheese, such as brie, camembert and chevre (a type of goat's cheese) and others with a similar rind. You should also avoid soft blue-veined cheeses such as Danish blue or gorgonzola. These are made with mould and they can contain listeria, a type of bacteria that can harm your unborn baby.
Although infection with listeria (listeriosis) is rare, it is important to take special precautions in pregnancy because even a mild form of the illness in a pregnant woman can lead to miscarriage, stillbirth or severe illness in a newborn baby.
You can eat hard cheeses such as cheddar, parmesan and stilton, even if they're made with unpasteurised milk. Hard cheeses don't contain as much water as soft cheeses so bacteria are less likely to grow in them. Many other types of cheese are okay to eat, but make sure they're made from pasteurised milk. They include cottage cheese, mozzarella, cream cheese, paneer, haloumi, goat's cheese and processed cheeses such as cheese spreads.
Many other types of cheese are okay to eat, but make sure they're made from pasteurised milk. They include cottage cheese, mozzarella, cream cheese, paneer, haloumi, goat's cheese and processed cheeses such as cheese spreads.
Pâté
Avoid all types of pâté, including vegetable pâtés, as they can contain listeria.
Raw or partially cooked eggs
Make sure that eggs are thoroughly cooked until the whites and yolks are solid. This prevents the risk of salmonella food poisoning. Don’t eat foods that contain raw and undercooked eggs, such as homemade mayonnaise. If you wish to have dishes that contain raw or partially cooked eggs, consider using pasteurised liquid egg. Don’t use cracked or dirty eggs.
Raw or undercooked meat
Cook all meat and poultry thoroughly so it is steaming hot and there is no trace of pink or blood. Take particular care with poultry, pork, sausages and minced meat, including burgers.
Don't eat rare meat. Toxoplasmosis is an infection caused by a parasite that can be found in meat, soil, cat faeces and untreated water. If you are pregnant the infection can damage your baby, but it's important to remember that toxoplasmosis in pregnancy is very rare.
If you are pregnant the infection can damage your baby, but it's important to remember that toxoplasmosis in pregnancy is very rare.
If you feel you may have been at risk, discuss it with your doctor, midwife or obstetrician. If you are infected while you're pregnant, treatment for toxoplasmosis is available.
Wash all surfaces and utensils thoroughly after preparing raw meat. It's also important to remember to wash and dry your hands after touching or handling raw meat. This will help to avoid the spread of harmful bugs such as salmonella, campylobacter and E. coli that can cause food poisoning.
Liver products
Don't eat liver or liver products such as liver pâté or liver sausage, as they may contain a lot of vitamin A. Too much vitamin A can harm your baby.
Supplements containing vitamin A
Don't take high-dose multivitamin supplements, fish liver oil supplements or any supplements containing vitamin A.
Some types of fish
Fish contains protein and essential omega-3 fatty acids, so it is recommended in pregnancy.
However, some types of fish have higher levels of mercury, which can affect the baby’s developing nervous system. It’s important to limit your intake of fish with higher levels of mercury. Shark (flake), broadbill, marlin and swordfish should be eaten no more than once a fortnight and don’t eat any other fish during that fortnight. Orange roughy and catfish should be eaten no more than once a week, and no other fish should be eaten during that week.
For more information about mercury in fish, visit Food Standards Australia.
Raw shellfish
Eat cooked rather than raw shellfish as it can contain harmful bacteria and viruses that can cause food poisoning and have a higher risk of listeria contamination.
Pre-packaged salads
Pre-prepared or pre-packaged fruit or vegetable salads, including those from buffets and salad bars have a higher risk of listeria contamination.
Certain fruit and vegetables
Don’t eat rockmelon, due to a risk of listeria, or bean sprouts, due to salmonella.
Sushi
Don’t eat chilled seafood such as raw oysters, sashimi and sushi, smoked ready-to-eat seafood and cooked ready-to-eat prawns, which have a higher risk of listeria contamination.
The safest way to enjoy sushi is to choose the fully cooked or vegetarian varieties, such as those that include:
- cooked seafood, for example fully cooked eel (unagi) or shrimp (ebi)
- vegetables, for example cucumber (kappa) maki
- avocado — for example California roll
- fully cooked egg
Cold cured meats
Cold cured meats include salami, parma ham, chorizo and pepperoni. In Australia, pregnant women are advised to avoid eating cold cured meats or smoked fish as there is a small risk of these foods harbouring listeria, or the toxoplasma parasite that causes toxoplasmosis. These include:
- cold meats from delicatessen counters and sandwich bars, and packaged, sliced ready-to-eat meats
- cold cooked ready-to-eat chicken (whole, portions, or diced)
Unpasteurised milk
If you have milk, drink only pasteurised or UHT (ultra-heat treated) milk (also called long-life milk). If only raw (unpasteurised) milk is available, boil it first. Don’t drink unpasteurised goat’s or sheep’s milk or eat food that is made out of them, such as soft goat’s cheese.
If only raw (unpasteurised) milk is available, boil it first. Don’t drink unpasteurised goat’s or sheep’s milk or eat food that is made out of them, such as soft goat’s cheese.
Don't eat soft-serve ice-creams while you're pregnant as they have a higher risk of listeria contamination.
Alcohol
There is no safe level of alcohol that you can have during your pregnancy. Whether you are planning a pregnancy, already pregnant or breastfeeding, not drinking is the safest option as alcohol can harm your unborn baby.
Caffeine
High levels of caffeine can increase the risk of miscarriage, low birth weight and experiencing a difficult birth. Caffeine is naturally found in lots of foods, such as coffee, tea and chocolate, and is added to some soft drinks and energy drinks. Some cold and flu remedies also contain caffeine. Talk to your midwife, doctor or pharmacist before taking these remedies.
You don’t need to cut out caffeine completely, but don’t have more than 200mg a day. The approximate amounts of caffeine found in food and drinks are:
The approximate amounts of caffeine found in food and drinks are:
- 1 cup of instant coffee: 60mg
- 1 shot of espresso coffee: 100mg
- 1 cup of plunger coffee: 80mg
- 1 cup of tea: 30mg
- 375ml can of cola: 49mg
- 250ml can of energy drink: 80mg
- 100g bar of milk chocolate: 20mg
Don’t worry if you occasionally have more than 200mg, the risks are quite small. To cut down on caffeine, try decaffeinated tea and coffee, fruit juice or mineral water instead of regular tea, coffee and cola.
Energy drinks
Energy drinks are not recommended during pregnancy as they may contain high levels of caffeine, and other ingredients not recommended for pregnant women.
Foods with soil on them
Wash fruit, vegetables and salads to remove all traces of soil and visible dirt. Learn more about safe food preparation.
Peanuts and allergies
If you would like to eat peanuts or food containing peanuts (such as peanut butter) during pregnancy, you can choose to do so as part of a healthy balanced diet, unless you are allergic to them or your health professional advises you not to. Exclusion of any particular foods (including foods considered to be highly allergenic) from the maternal diet during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended, as this has not been shown to prevent allergies in your baby.
Exclusion of any particular foods (including foods considered to be highly allergenic) from the maternal diet during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended, as this has not been shown to prevent allergies in your baby.
Check out our handy guide to food and drink during pregnancy (infographic) that you can print off to stick on the fridge or keep in your bag.
Sources:
Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (Infant feeding and allergy prevention), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (Caffeine), Food Standards Australia New Zealand (Mercury in fish), Eat For Health (Healthy eating during your pregnancy), NSW Food Authority (Foods to eat or avoid when pregnant), The Royal Women's Hospital Melbourne (Food safety during pregnancy), Department of Primary Industries (Food safety during pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: August 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Healthy diet during pregnancy
- Guide to food and drink during pregnancy
- Food preparation and safety
- Food cravings during pregnancy
- Alcohol and pregnancy
- Vitamins and supplements during pregnancy
Need more information?
Pregnancy diet: Foods to avoid
Everyone knows that when you're pregnant, you're eating for two. Less obvious, however, is knowing the particular foods pregnant women shouldn't eat in order to avoid infectious, food-borne diseases, as these can cause miscarriage, low birth weight or a higher risk of Mum getting sick.
Read more on Parenthub website
Guide to food and drink during pregnancy
This infographic is a handy guide to find out what is safe to eat during your pregnancy and the foods and drinks you should avoid.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Things to avoid during pregnancy
From hair dye to house paints, there are a few products or lifestyle habits pregnant women and their partners should be cautious of during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Food cravings during pregnancy
Food cravings are sudden urges to eat a particular type of food. They are a real phenomenon and affect many females during pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Appetite changes and food aversions during pregnancy
It’s common to experience food cravings or a food aversion during pregnancy. Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Find out how to ensure you continue to eat healthily if this affects you.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Healthy diet during pregnancy
A healthy diet is an important part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but especially vital if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Your body needs extra nutrients during pregnancy and breastfeeding. You should also limit or avoid some foods and drinks. Here we look at the do's and don't's of eating while pregnant and breastfeeding, and when you should seek the services of an Accredited Practising Dietitian (APD).
Read more on Dietitians Australia website
Pregnancy and your diet | NT.
 GOV.AU
GOV.AU Foods you should avoid, listeriosis information, mercury in fish, weight gain in pregnancy.
Read more on NT Health website
Pregnancy and Healthy Eating
It’s especially important to eat healthy food during pregnancy and while breast feeding.
Read more on Healthy Eating Active Living NSW website
Toxic household products to avoid during pregnancy
If you're pregnant but exposed to a small amount of chemicals, it's unlikely to harm you or your baby. But it’s still best to avoid contact with toxic products.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
Need further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Is it possible to eat cheese during pregnancy?
Cheese is a tasty and healthy product, beloved by many. That is why the statement of some doctors that any cheese is strictly forbidden to women during pregnancy can seriously spoil the mood. However, you should not despair - if you dig deeper, it turns out that everything is not so categorical. Below we will understand what are the benefits and harms of cheeses for pregnant women.
Which cheeses should be avoided during pregnancy
Despite all its usefulness and the abundance of microelements and vitamins in its composition, some types of cheese can sometimes cause irreparable harm to a woman and her unborn baby. These are unpasteurized cheeses, which may contain Listeria monocyotogenes, the bacterium that causes listeriosis. Acute infectious disease is severe and is accompanied by chills, high fever, muscle pain, nausea and vomiting. Such a severe clinical picture can lead to a miscarriage or the development of severe pathologies in the fetus - given this, it is necessary to be extremely selective in choosing cheeses during childbearing.
These are unpasteurized cheeses, which may contain Listeria monocyotogenes, the bacterium that causes listeriosis. Acute infectious disease is severe and is accompanied by chills, high fever, muscle pain, nausea and vomiting. Such a severe clinical picture can lead to a miscarriage or the development of severe pathologies in the fetus - given this, it is necessary to be extremely selective in choosing cheeses during childbearing.
The infectious bacterium lives in unpasteurized cheeses made from sheep's and goat's milk that have not undergone heat treatment. We are talking about soft types of cheese and varieties with mold: dor blue, brie, camembert, cambonzola, etc. Also at risk are cheeses with blue mold: Roquefort, Gorgonzola, Savoy cheese. Such products contain a lot of liquid and little acid, which is the most favorable environment for the development of Listeria monocyotogenes.
Why mold is harmful when carrying a child
In addition to the risk of getting sick with listeriosis, eating delicious marbled cheeses, you run the risk of experiencing all the delights of the impact on the body of "noble" mold. So, valuable blue mold, which gives cheeses such a refined taste, endows the product with a number of side qualities. Being a pure antibiotic, mold kills the beneficial microflora that inhabits the body, which can cause intestinal dysbacteriosis and disrupt the digestive tract.
So, valuable blue mold, which gives cheeses such a refined taste, endows the product with a number of side qualities. Being a pure antibiotic, mold kills the beneficial microflora that inhabits the body, which can cause intestinal dysbacteriosis and disrupt the digestive tract.
An imbalance of water and lactic acid in moldy foods can lead to the growth of fungus in the body, which is also highly undesirable for a pregnant woman who is already in a vulnerable state. Given the foregoing, doctors strongly recommend abandoning "live" cheeses for the period of bearing a child.
Which cheeses are safe for pregnant women? Under the influence of high temperature and careful processing, pathogenic bacteria die, making the cheese not only tasty, but also safe. Such cheeses include: gouda, maasdam, parmesan, cheddar, Poshekhonsky, etc. - all of them will not harm a pregnant woman, since the environment favorable for the life of bacteria is destroyed during high temperature processing.
 Eating hard cheeses, you will get the whole range of nutrients, saturate the body with calcium and, in addition, diversify your diet with a delicious product.
Eating hard cheeses, you will get the whole range of nutrients, saturate the body with calcium and, in addition, diversify your diet with a delicious product. There is also good news for lovers of soft cheeses: there are varieties that pregnant women can safely include in their diet. These include delicious varieties such as feta, philadelphia, mascarpone, cottage cheese, goat cheese without rind (pasteurized), processed cheeses, etc. The technology for the production of such cheeses involves heat treatment, during which bacteria die. With soft cheeses, you can create various dishes, including delicious and healthy desserts - what could be better for a pregnant woman!
When to start eating moldy soft cheeses
Once your baby is born and the breastfeeding period is over, you can enjoy the full range of cheeses, including the gourmet blue mold varieties. Soft cheeses from Zhukovka are rightfully considered one of the best. Accurate adherence to production technology, verified to the gram of the recipe - all this allows you to make truly gourmet cheeses. By the way, the manufacturer's assortment also includes pasteurized soft varieties, for example, classic feta cheese, which is safe for women in an interesting position.
By the way, the manufacturer's assortment also includes pasteurized soft varieties, for example, classic feta cheese, which is safe for women in an interesting position.
Which types of cheese can and cannot be eaten during pregnancy
Many women are interested in what types of cheese can and cannot be eaten during pregnancy. There are different points of view and considerations, but we will still give facts that you should definitely take into account in order to maintain your health and the health of your baby.
Contents
- Introduction
- Raw milk
- Pasteurized milk
- Cheeses you CAN eat during pregnancy
- Unpasteurized soft cheese
Introduction
During pregnancy, cheese is a good source of protein and essential calcium for the development of the baby's muscles, bones, hair and nails. It also strengthens the bone structure of the expectant mother and prepares her for breastfeeding.
It also strengthens the bone structure of the expectant mother and prepares her for breastfeeding.
However, due to the weakened immune system during pregnancy, women should be careful when choosing cheese. You should choose the appropriate types of cheese for her and the child, as not all are allowed. We ask that you take this very seriously, as infection with Listeria bacteria and other microbes can cause miscarriage.
The main factors that allow the consumption of cheese during pregnancy are the technique of making the cheese and the temperature of the milk used. Raw cheeses are made from milk without heat treatment. Basically, in many varieties of cheese, milk is pasteurized.
Raw milk
Such milk is used to make raw cheese at a temperature not exceeding 40 °C, or it is subjected to a non-heat treatment with an equivalent effect, in particular in terms of reducing the concentration of microorganisms.
Pasteurized milk
Milk heated to at least 72°C for 15 seconds. This method ensures the destruction of Listeria bacteria and other microbes.
This method ensures the destruction of Listeria bacteria and other microbes.
Cheeses that CAN be eaten during pregnancy
Pressed hard cheeses
A priori all hard cheeses are safe to eat during pregnancy. Cheeses made from unpasteurized milk that have been pressed and matured for more than six months are also allowed, as in this case they are not moist enough for the development of Listeria. These bacteria may be present, but the numbers are so low that they are not considered dangerous.
The permitted cheese category includes:
Cheddar, Edam, Provolone, Manchego
The production technology of these four types of hard cheeses and exposure to high temperatures make them suitable for consumption during pregnancy. Among the useful properties, we note the high presence of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, iron, vitamins B6 and B12, and vitamin D. This set is ideal for strengthening the child's immunity, the formation of his bones and cells.
Smoked hard cheese
Smoked cheeses are recognizable by their yellow or slightly brown appearance. Smoked Gouda, Cheddar and Gruyère are some of the varieties of smoked cheese that can be eaten with confidence during pregnancy. Their nutritional properties are 20% protein, 50% carbohydrates and 30% fat.
Pasteurized milk soft cheeses
The list is quite long. The most important thing about these fresh cheeses is that pasteurized milk is used in the preparation.
Mozzarella Cheese
Made from buffalo milk, this soft Italian cheese contains high nutritional value, as well as thiamin, riboflavin, biotin and vitamin B6. It also contains fat, lactose, calcium and protein. It can be safely consumed during pregnancy, either in a salad with tomato and basil or melted on pizza. MOST IMPORTANTLY, be sure to choose a pasteurized dairy product.
Fresh cheese with herbs
Fresh cheese pasta, natural, garlic or herbal, is a rich source of protein, calcium and phosphorus, necessary for the structure of the child's bones. It is also rich in vitamins A, D and B vitamins. This type of cheese can be consumed without risk by pregnant women.
It is also rich in vitamins A, D and B vitamins. This type of cheese can be consumed without risk by pregnant women.
Feta cheese is another recommendation for pregnant women. This is a salty sheep cheese that you can eat without fear for your health and your baby. The calorie content of the product is 264 kcal per 100 grams. It also contains fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K. This cheese can be used, for example, in a Greek salad or crumbled into a salad with cucumber, tomatoes, and olives.
Goat cheese (some varieties)
Skinless goat cheese made from pasteurized milk can be consumed during pregnancy without risk to the baby. This type of cheese provides a large contribution of calcium and protein and is also a source of vitamins A, D, K. It contains riboflavin, niacin, thiamine, potassium, iron, phosphorus and at the same time contains much less calories, fat and cholesterol, unlike cheeses from cow's milk. Other varieties of goat cheese, such as unpasteurized soft cheese and unbleached rind cheese, do not guarantee good fetal health.
Ricotta, Mascarpone
These soft and creamy Italian cheeses are safe during pregnancy. Nutritional properties in 100 g of cheese: protein 48%, fat 43%, carbohydrates 8%. The high levels of calcium in this type of cheese can be obtained as desserts such as icing, cheesecake, tiramisu, or as an ingredient in risotto and pasta.
Cheeses NOT to Eat During Pregnancy
In this list, we will list the types of cheeses made from raw milk that, although they contain valuable nutritional properties for the healthy development of the fetus, they have not been heat treated to kill Listeria bacteria . Based on this, the use of these cheeses for pregnant women is completely contraindicated.
Other blue cheeses with mold, which fall into this category of risk during pregnancy:
- Azul de Overn
- Fourme d'Ambert
- Gorgonzole
- Rocher
Non -focused SPECTIONAL SPIRE 9,00022 from goat's and sheep's milk such as Çabichu cheese and Valençay cheese are dangerous when consumed during pregnancy.

However, pregnant women can enjoy soft, moldy and raw cheeses, provided they are cooked at home at 74°C or more to destroy all traces of Listeria.
But it is important to emphasize that the cheese should be used exactly the one for which the milk has been heated to a temperature of 74 ° C and above, and not just heated or in a melted state.
How does Listeria get into these cheeses?
Many animals can carry Listeria bacteria without being sick. Based on this, farmers cannot be sure that the fresh milk they produce is safe to consume.
Listeria ("Listeria" - Latin) is a very small bacterium that exists and multiplies without problems at low temperatures, so storing cheese in the refrigerator will not stop the growth of bacteria, but vice versa. Cheese contaminated with Listeria may appear completely normal and retain its characteristic odor without any change, so it is impossible to independently determine the presence of a dangerous bacterium. These bacteria do not necessarily infect all people who consume cheese containing them. But it has been proven to be very harmful for pregnant women due to the weakening of the immune system.
But it has been proven to be very harmful for pregnant women due to the weakening of the immune system.
Risk of eating certain cheeses during pregnancy
Pregnant women are at a higher risk of contracting foodborne illness than the general population. Consumption of any food or type of cheese during pregnancy carries three risks of infection: Toxoplasmosis, Salmonella and Listeriosis. All of these diseases can be detrimental to the fetus, even if the mother is immune to these bacteria.
To avoid this risk, a pregnant woman should pay attention to the cheeses she eats. Even if you know you shouldn't eat them, they can still be a temptation in your fridge. To avoid the complication of Listeria infection during pregnancy, you should pay close attention to the signs that may be present: mild fever, flu-like symptoms, and sometimes gastrointestinal symptoms. Usually, these symptoms appear a few weeks after infection, and we note once again that although this is not a dangerous disease for the mother, it has devastating consequences for the fetus.
Listeriosis Complications
Listeriosis caused by certain types of raw cheese can actually cause miscarriage in the first trimester of pregnancy. It can also lead to preterm labor in late pregnancy.
The child can also be infected with bacteria that can cause:
- Paralysis
- Seizures
- Blindness
- Developmental disorders
- Brain disorders
- Heart problems
- Kidney disease
- Blood infections
- Brain infections
I ate cheese, which is contraindicated for pregnant women. What should I do?
A pregnant woman who has consumed raw milk cheese should be aware of some symptoms that may appear after about two months, such as fever or headache.
If you experience fever or headaches during this period, you should consult a doctor, who should be told the name of the cheese consumed. Your OB/GYN or GP will ask for a blood test to check for or rule out the presence of Listeria bacteria.