What causes the skin to darken
Skin Pigmentation Disorders | Hyperpigmentation
Also called: Hyperpigmentation, Hypopigmentation
On this page
Basics
- Summary
- Start Here
- Diagnosis and Tests
- Treatments and Therapies
Learn More
- Living With
- Specifics
- Genetics
See, Play and Learn
- Images
Research
- Clinical Trials
- Journal Articles
Resources
- Find an Expert
For You
- Children
- Teenagers
- Patient Handouts
Pigmentation means coloring. Skin pigmentation disorders affect the color of your skin. Your skin gets its color from a pigment called melanin. Special cells in the skin make melanin. When these cells become damaged or unhealthy, it affects melanin production. Some pigmentation disorders affect just patches of skin. Others affect your entire body.
If your body makes too much melanin, your skin gets darker. Pregnancy, Addison's disease, and sun exposure all can make your skin darker. If your body makes too little melanin, your skin gets lighter. Vitiligo is a condition that causes patches of light skin. Albinism is a genetic condition affecting a person's skin. A person with albinism may have no color, lighter than normal skin color, or patchy missing skin color. Infections, blisters and burns can also cause lighter skin.
- Skin Pigment (Merck & Co.
 , Inc.) Also in Spanish
, Inc.) Also in Spanish
- Wood's Lamp Examination (VisualDX)
- Chemical Peels (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery)
- Dermabrasion (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery)
- Laser Resurfacing (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery)
- Melasma: Diagnosis and Treatment (American Academy of Dermatology)
- Melasma: Tips for Managing (American Academy of Dermatology)
- Acanthosis Nigricans (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research) Also in Spanish
- Age Spots (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery)
- Albinism (Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research)
- Hyperpigmentation (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Incontinentia Pigmenti (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke)
- Lentigines (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Melasma (American Academy of Dermatology)
- Pityriasis Alba (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Progressive Pigmentary Purpura (American Osteopathic College of Dermatology)
- Acanthosis Nigricans (VisualDX)
- Lentigo Simplex (VisualDX)
- Melasma (VisualDX)
- Oral Melanotic Macule (VisualDX)
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (VisualDX)
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation (VisualDX)
- ClinicalTrials.
 gov: Hyperpigmentation (National Institutes of Health)
gov: Hyperpigmentation (National Institutes of Health) - ClinicalTrials.gov: Hypopigmentation (National Institutes of Health)
- ClinicalTrials.
 gov: Pigmentation Disorders (National Institutes of Health)
gov: Pigmentation Disorders (National Institutes of Health)
- Article: Linear Pigmented Purpuric Dermatoses.
- Article: Shining Light on Autophagy in Skin Pigmentation and Pigmentary Disorders.
- Article: Paediatric Poliosis as the Presenting Feature of Scalp Vitiligo: A Retrospective.
 ..
.. - Skin Pigmentation Disorders -- see more articles
- Find a Dermatologic Surgeon (American Society for Dermatologic Surgery)
- Find a Dermatologist (American Academy of Dermatology)
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases Also in Spanish
- Café au Lait Macule (VisualDX)
- Pityriasis Alba (VisualDX)
- What Are Freckles? (Nemours Foundation)
- Acanthosis Nigricans (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
- Albinism (Nemours Foundation) Also in Spanish
What Causes Skin to Darken?
We include products we think are useful for our readers.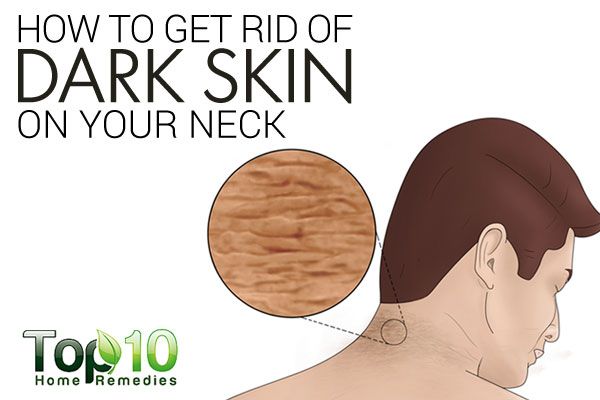 If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.
What’s hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation isn’t necessarily a condition but a term that describes skin that appears darker. It can:
- occur in small patches
- cover large areas
- affect the entire body
While increased pigmentation usually isn’t harmful, it can be a symptom of another medical condition. Learn about types of hyperpigmentation, causes, and how to treat it.
There are several types of hyperpigmentation, the common ones being melasma, sunspots, and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
- Melasma. Melasma is believed to be caused by hormonal changes and may develop during pregnancy. Areas of hyperpigmentation can appear on any area of the body, but they appear most commonly on the stomach and face.
- Sunspots. Also called liver spots or solar lentigines, sunspots are common. They’re related to excess sun exposure over time.
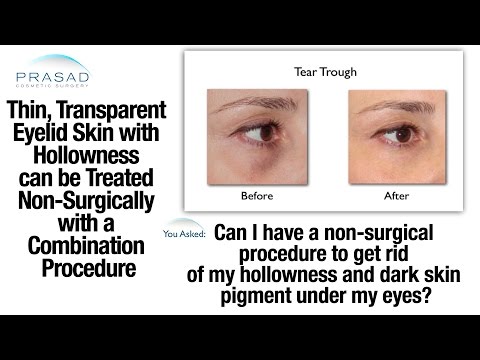 Generally, they appear as spots on areas exposed to the sun, like the hands and face.
Generally, they appear as spots on areas exposed to the sun, like the hands and face. - Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. This is a result of injury or inflammation to the skin. A common cause of this type is acne.
Darkened areas on the skin are the main symptoms of hyperpigmentation. Patches can vary in size and develop anywhere on the body.
The biggest risk factors for general hyperpigmentation are sun exposure and inflammation, as both situations can increase melanin production. The greater your exposure to the sun, the greater your risk of increased skin pigmentation.
Depending on the type of disorder, other risk factors for hyperpigmented patches may include:
- oral contraceptive use or pregnancy, as seen with melasma
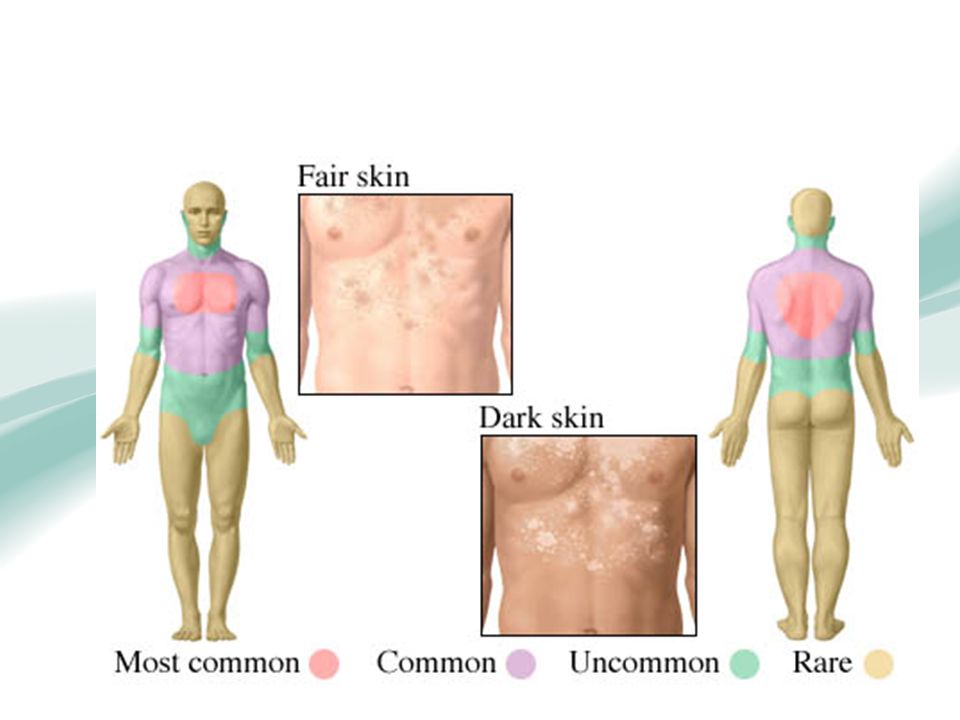
- darker skin type, which is more prone to pigmentation changes
- drugs that increase your sensitivity to the sunlight
- trauma to the skin, such as a wound or superficial burn injury
A common cause of hyperpigmentation is an excess production of melanin. Melanin is a pigment that gives skin its color. It’s produced by skin cells called melanocytes. Several different conditions or factors can alter the production of melanin in your body.
Melanin is a pigment that gives skin its color. It’s produced by skin cells called melanocytes. Several different conditions or factors can alter the production of melanin in your body.
Certain medications can cause hyperpigmentation. Also, some chemotherapy drugs can cause hyperpigmentation as a side effect.
Pregnancy changes hormone levels and can affect melanin production in some women.
A rare endocrine disease called Addison’s disease can produce hyperpigmentation that’s most obvious in areas of sun exposure, such as the face, neck, and hands, and areas exposure to friction, such as elbows and knees.
The hyperpigmentation is a direct result of an increased level of a hormone in your body that results in increased melanin synthesis.
Excessive sun exposure can also cause an increase in melanin.
A dermatologist can diagnose the cause of your hyperpigmentation. They will request your medical history and give you a physical exam to determine the cause. In some cases, a skin biopsy can narrow down the cause.
In some cases, a skin biopsy can narrow down the cause.
Topical prescription medication can treat some cases of hyperpigmentation. This medication usually contains hydroquinone, which lightens the skin.
However, prolonged use of topical hydroquinone (without any breaks in use) can cause darkening of the skin, known as ochronosis. So it’s best to use topical hydroquinone only under the care of a dermatologist so that they can properly guide you on how to use the medication without any adverse effects.
Using topical retinoids also assists with lightening dark spots of the skin.
Both of these medications can take a few months to lighten darkened areas.
Home care also includes using sunscreen. Sunscreen is the single most important factor in improving most causes of hyperpigmentation. Look for:
- a physical blocking sunscreen, preferably with zinc oxide as the main active ingredient
- at least an SPF 30 to 50
- broad spectrum coverage
Use a sunscreen daily. Reapply it every 2 hours if you’re out in the sun — more frequently if you’re sweating or swimming.
Reapply it every 2 hours if you’re out in the sun — more frequently if you’re sweating or swimming.
There are also skin disorders with which visible light may play a role in perpetuating the hyperpigmentation, such as in melasma.
In that case, look for a mineral sunscreen that also has iron oxide in it, which can block some visible light. Use daily. Wear sun-protective clothing that’s SPF-infused.
Shop for SPF-infused clothing online.
Your doctor may also suggest laser treatment or chemical peels to reduce hyperpigmentation, depending on the cause of your hyperpigmentation.
It’s not always possible to prevent hyperpigmentation. However, you can protect yourself by:
- using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30
- wearing hats or clothing that block sunlight
- avoiding the sun during the time of the day when it’s strongest, which is typically 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Avoiding certain medications may also help prevent hyperpigmentation.
Hyperpigmentation isn’t generally harmful and usually isn’t a sign of a serious medical condition.
In some cases, dark areas will fade on their own with good sun protection. In other cases, more aggressive treatment is needed. There’s no guarantee that the dark spots will fade completely, even with treatment.
6 dangerous diseases that can be found out by the condition of the skin
- In the city N
- Articles
Did you know that the condition of the skin can determine whether a person is healthy? Moreover, certain changes in the skin can serve as a signal of a specific disease. Today we will tell you about six skin problems that occur with dangerous ailments.
- Browning
- Vitiligo
- Sweating
- Edema
- Spots and bubbles
- Suspicious moles
Darkening
Darkening of the skin may indicate the development of Addison's disease - chronic insufficiency of the adrenal cortex. And I must say that this symptom may appear several months earlier than others. Therefore, if you immediately notice darkening, you can immediately consult a doctor and spend much less time, effort and money on treatment. Usually the skin darkens all over the body, this is most clearly seen on the bends of the elbows, knees and fingers. And one more thing: the scars that appeared during the period of the disease, as a rule, are brighter than other areas of the skin. Addison's disease can end very badly, up to death, so if darkening is detected, contact an endocrinologist immediately.
And I must say that this symptom may appear several months earlier than others. Therefore, if you immediately notice darkening, you can immediately consult a doctor and spend much less time, effort and money on treatment. Usually the skin darkens all over the body, this is most clearly seen on the bends of the elbows, knees and fingers. And one more thing: the scars that appeared during the period of the disease, as a rule, are brighter than other areas of the skin. Addison's disease can end very badly, up to death, so if darkening is detected, contact an endocrinologist immediately.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo - light spots on the skin - can also be a sign of Addison's disease. These spots occur due to autoimmune destruction of skin cells that produce melanin, which gives the skin a dark hue. In this case, darkening of the skin of vitiligo can appear simultaneously. Well, you already know what to do with them.
Sweating
Excessive sweating may be caused by disorders of the thyroid gland, such as diffuse toxic goiter. With such a disease, the sweat glands begin to work much more intensively than usual, and you can sweat even while sitting on a chair in a ventilated room. Both separate areas of the skin and the whole body can be covered with sweat, and the sweat itself can have a very unpleasant odor. In addition, with the development of diffuse toxic goiter, a person may experience darkening of the skin of the eyelids, thinning of the skin and itching. When such symptoms appear, you need to contact an endocrinologist or dermatologist.
With such a disease, the sweat glands begin to work much more intensively than usual, and you can sweat even while sitting on a chair in a ventilated room. Both separate areas of the skin and the whole body can be covered with sweat, and the sweat itself can have a very unpleasant odor. In addition, with the development of diffuse toxic goiter, a person may experience darkening of the skin of the eyelids, thinning of the skin and itching. When such symptoms appear, you need to contact an endocrinologist or dermatologist.
Edema
The constant appearance of edema on the skin may indicate another thyroid disease - hypothyroidism. It occurs when the thyroid gland stops producing enough hormones and is accompanied by symptoms such as paleness and swelling, especially on the face and eyelids. Also, often with hypothyroidism, the skin begins to peel off, hair falls out, and sweating becomes less intense. If any of these symptoms appear, you should make an appointment with an endocrinologist.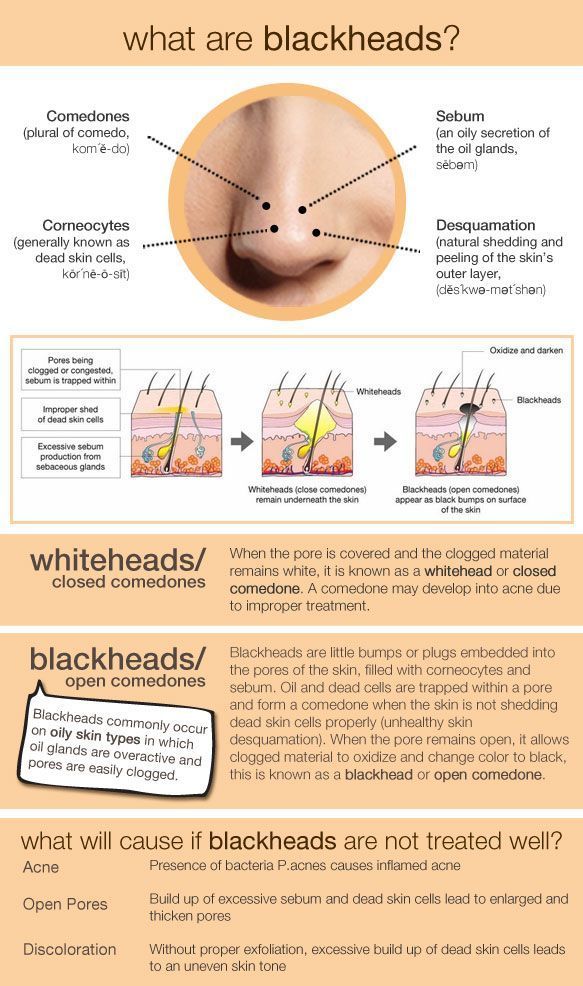
Spots and blisters
Red spots, blisters and blisters on the skin may be due to allergies. It is impossible to ignore such manifestations, otherwise allergic reactions can become more severe. And do not rush to refuse to go to the doctor, hoping that you have never been allergic - an allergy can appear on anything and at any age. So be sure to visit a therapist, an allergist or a dermatologist.
Suspicious moles
The most dangerous change on the skin is a suspicious mole. It can appear literally out of nowhere, change color, increase in size, itch, peel or bleed, be dark or transparent. If you notice this in yourself, urgently go to a good dermatologist or oncologist, because this is what melanoma looks like - the most dangerous oncological disease that quickly penetrates into all layers of the skin and metastasizes throughout the body. Therefore, you need to act as quickly as possible.
Previously, V Goroda N news agency told about three odors that can be a sign of serious illness.
According to mhealth.ru, rg.ru.
Read also Clinics accepting CHI in Nizhny Novgorod (list for 2023)Any use of materials is allowed only if there is an active link to vgoroden.ru
Add In city N inDrunken vandals brutally beat a married couple in the entrance of a house in the Soviet district 13 districts of the Nizhny Novgorod region most affected by the new freezing rain Nizhny Novgorod won the vote for the title of "Youth Capital of Russia"
How to identify dangerous diseases by skin condition?
Some skin problems that may appear to be just cosmetic problems can indicate serious illness!
Men Today
Tags:
Question answer
Health
Skin diseases
Skin care
Getty Images
How can you tell if you're healthy just by looking at your skin, the largest human organ, the first to face all negative environmental influences and reflect many changes in the body?
Contents of the article
Do not self-medicate! In our articles, we collect the latest scientific data and the opinions of authoritative health experts.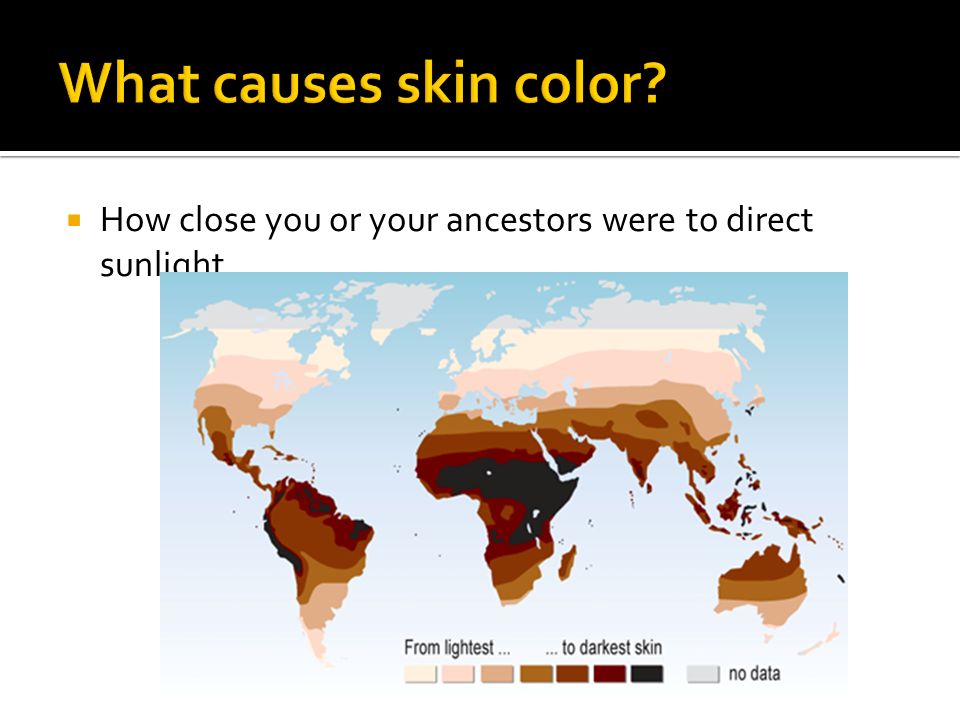 But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
But remember: only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe treatment.
The skin suddenly began to darken
Possible cause: Addison's disease (chronic adrenal insufficiency)
We are not talking about a spa tan, but about hyperpigmentation - darkening of the skin and mucous membranes. It is important to know that this symptom appears months, and sometimes even years, before other symptoms that signal adrenal insufficiency - Addison's disease. This means that by noticing changes in advance, you can provide the body with the necessary assistance in time.
In this disease, the skin darkens over the entire area, but the changes are most clearly visible in the places of folds and stretches - look at your elbows/knees/fingers, a healthy person should not have skin color changes in these places. And one more important sign that will help during self-diagnosis: scars formed after the onset of the disease are usually colored brighter than other areas of the skin (old scars do not darken). Palmar folds, nail plates, oral mucosa, anal mucosa may also darken.
Palmar folds, nail plates, oral mucosa, anal mucosa may also darken.
Non-pigmented areas appear on the skin
Possible cause: and again Addison's disease (chronic adrenal insufficiency)
Similar light bald spots among dark areas of the skin are called vitiligo. They arise due to the autoimmune destruction of melanocyte skin cells that produce the melanin pigment - it gives the skin a swarthy tint. A similar symptom of Addison's disease can occur along with the general darkening of the skin, which we have already described in the previous paragraph.
Skin is thin and sweats all the time
Possible cause: diffuse toxic goiter (thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone)
You are in a well-ventilated area and are not physically active that you sweat? It is possible that the body needs help. For example, with a disease such as diffuse toxic goiter, the sweat glands begin to work too actively, as a result, you constantly notice that your skin is moist. It is curious, but it is not uncommon for cases when only half of the body sweats with this disease. Sweat may have a fetid odor.
For example, with a disease such as diffuse toxic goiter, the sweat glands begin to work too actively, as a result, you constantly notice that your skin is moist. It is curious, but it is not uncommon for cases when only half of the body sweats with this disease. Sweat may have a fetid odor.
However, increased sweating is far from being the only symptom of diffuse toxic goiter. In patients, there is also a general thinning of the skin, periodically accompanied by itching. In some areas of the skin, problems with pigmentation may also appear - the skin on them can become either too dark or too light. Another characteristic symptom of diffuse toxic goiter is darkening of the skin of the eyelids.
The skin began to swell frequently
Possible cause: hypothyroidism (the thyroid gland produces not enough hormones)
When the body feels a lack of thyroid hormones, it sends us danger signals, including through the skin: mucous edema forms, the skin becomes pale, swollen. Changes are especially clearly visible, as a rule, on the face and eyelids. Of course, we are not talking about one-time changes that appear if you drink too much water at night (or drink too much of something stronger), but about the systematic manifestation of a symptom.
Changes are especially clearly visible, as a rule, on the face and eyelids. Of course, we are not talking about one-time changes that appear if you drink too much water at night (or drink too much of something stronger), but about the systematic manifestation of a symptom.
In case of hypothyroidism, other changes occur in the patient's skin - it becomes dry and begins to peel off. In addition, the ducts of the sweat glands atrophy, the body has difficulty with sweating. With a lack of thyroid hormones, hair loss is also possible.
Eruptions of a different nature appeared on the skin: spots, blisters, blisters
Possible cause: allergy
Most likely, these are manifestations of a toxic-allergic reaction of the body to various drugs, food, household chemicals. If you do not respond in time, then all these problems can result in severe complications with a different clinical picture and end in death (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome).