Weight gain for newborns in the first month
Your Newborn's Growth (for Parents)
From your baby's first day, doctors will keep track of weight, length, and head size. Growth is a good indicator of general health. Babies who are growing well are generally healthy, while poor growth can be a sign of a problem.
How Big Are Newborns?
Newborns come in a range of healthy sizes. Most babies born between 37 and 40 weeks weigh somewhere between 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) and 8 pounds, 13 ounces (4,000 grams).
Newborns who are lighter or heavier than the average baby are usually fine. But they might get extra attention from the doctors and nurses after delivery to make sure there are no problems.
Different things can affect a baby's size at birth. The length of the pregnancy is important. Babies born around their due date or later tend to be larger than those born earlier.
Other factors include:
- Size of parents. Big and tall parents may have larger-than-average newborns; short and petite parents may have smaller-than-average newborns.
- Multiple births. If you have twins, triplets, or more, you can count on your babies being a bit small. Multiples have to share their growing space in the uterus, and they're often born early, which leads to small size at birth.
- Birth order. First babies are sometimes smaller than brothers or sisters born later.
- Gender. Girls tend to be smaller, boys larger, but the differences are slight at birth.
- Mom's health during pregnancy. Things that can lead to a lower birth weight include a mother with high blood pressure or heart problems; or one who used cigarettes, alcohol, or illegal drugs during the pregnancy. If the mother has diabetes or is obese, the baby may have a higher birth weight.
- Nutrition during pregnancy. Good nutrition is vital for a baby's growth — before and after birth. A poor diet during pregnancy can affect how much a newborn weighs and how the infant grows.
 Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average.
Gaining a lot of weight can make a baby more likely to be born bigger than average. - Baby's health. Medical problems, including some birth defects and some infections during the pregnancy, can affect a child's birth weight and later growth.
p
What About Preemies?
Premature babies generally are smaller and weigh less than other newborns. A preemie's weight will largely depend on how early he or she was born. The time an infant missed being in the womb was growing time, so the baby has to do that growing after birth.
Many pre-term babies are classified as having "low birth weight" or "very low birth weight." In medical terms:
- Low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces (2,500 grams) at birth. That's the case for about 1 in every 12 babies in the United States, so it's quite common.
- Very low birth weight means a baby weighs less than 3 pounds, 5 ounces (1,500 grams).

Most babies with low birth weight or very low birth weight were born prematurely.
Premature babies get special medical attention right away after they're born. A specialist called a neonatologist may help care for them. Many preemies spend time in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) while they get medical care.
Is Bigger Better?
A baby with chubby cheeks and dimpled thighs once was many people's picture of a healthy newborn. But a baby born much larger than average may have special medical problems that need attention.
Some very large babies — especially those born to mothers with diabetes, including gestational diabetes — may have problems for a few days keeping blood sugar levels up. They might need extra feedings or even IV (given into a vein)
glucoseto keep those levels from falling too low.
Will My Baby Lose Weight?
Yes, at first. Babies are born with some extra fluid, so it's normal for them to drop a few ounces when they lose that fluid in the first few days of life. A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
A healthy newborn is expected to lose 7% to 10% of the birth weight, but should regain that weight within the first 2 weeks or so after birth.
During their first month, most newborns gain weight at a rate of about 1 ounce (30 grams) per day. They generally grow in height about 1 to 1½ inches (2.54 to 3.81 centimeters) during the first month. Many newborns go through a period of rapid growth when they are 7 to 10 days old and again at 3 and 6 weeks.
p
Should I Be Concerned?
Newborns are so small, and it can be hard to know if your baby is gaining weight the way he or she should. You may worry that your baby has lost too much weight in the first few days or isn't taking enough breast milk or formula. If so, talk to your doctor, who may ask you about:
- How many feedings a day your baby gets. A breastfed baby may feed about 8 or more times in a 24-hour period; formula-fed babies usually eat less often, perhaps every 3 to 4 hours. A lactation (breastfeeding) counselor can make suggestions to increase comfort and improve technique, if a mom needs extra help.

- How much your baby eats at each feeding. A baby generally nurses for at least 10 minutes, should be heard to swallow after 3 or 4 sucks, and should seem satisfied when done. At this age, formula-fed babies may drink up to 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 milliliters) at a time.
- How often your baby pees. A breastfed baby may have only 1 or 2 wet diapers a day until the mother's milk comes in. Expect about 6 wet diapers by 3 to 5 days of age for all babies. After that, babies should have at least 6 to 8 wet diapers a day.
- How many bowel movements your baby has each day, and what they're like. Newborns may have only one poopy diaper a day at first. Poop is dark and tarry the first few days, then becomes soft or loose and greenish-yellow by about 3 to 4 days. Newborns usually have several poopy diapers a day if breastfed and fewer if formula-fed.
What Else Should I Know?
Being small or large at birth doesn't mean a baby will be small or large later in childhood or as an adult. Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
Plenty of tall teens began life as small babies, and the biggest baby in the family can grow up to be a petite adult.
By the time they're adults, kids tend to resemble their parents in size. Genetics, as well as good nutrition and your attention, will play a large part in how your baby grows in the years to come.
Whether your baby starts out large, small, or average, in the next few months you can expect your little one to keep growing fast.
Reviewed by: Madhu Desiraju, MD
Date reviewed: October 2018
Average baby weight at birth and newborn weight gain
The average baby weight at birth is just over 7 pounds. Newborns usually have weight loss of about 5 to 10 percent in the first days, but they're back to their newborn weight by the time they're about 2 weeks old. By the end of the first month, babies typically weigh a pound or two above their newborn weight. And most babies will double their birth weight by about 4 months.
What's the average weight for a newborn?
The average baby weight at birth in the United States is just over 7 pounds (7. 18 pounds or 3,255.71 grams, to be very exact).
18 pounds or 3,255.71 grams, to be very exact).
Here's the breakdown of birthweights among babies born in the United States in 2020:
- 499 grams or less (less than 1 pound 2 ounces): 0.13 percent
- 500 to 999 grams (1 pound 2 ounces to 2 pounds): 0.49 percent
- 1,000 to 1,499 grams (2 pounds 3 ounces to 3 pounds 5 ounces): 0.71 percent
- 1,500 to 1,999 grams (3 pounds 5 ounces to 4 pounds 7 ounces): 1.61 percent
- 2,000 to 2,499 grams (4 pounds 7 ounces to 5 pounds 8 ounces): 5.29 percent
- 2,500 to 2,999 grams (5 pound 8 ounces to 6 pounds 10 ounces): 19.14 percent
- 3,000 to 3,499 grams (6 pounds 10 ounces to 7 pounds 11 ounces): 38.91 percent
- 3,500 to 3,999 grams (7 pounds 11 ounces to 8 pounds 13 ounces): 26.16 percent
- 4,000 to 4,499 grams (8 pounds 13 ounces to 9 pounds 15 ounces) 6.50 percent
- 4,500 to 4,999 grams (9 pounds 15 ounces to 11 pounds): 0.87 percent
- 5,000 grams or more (11 pounds or more): 0.
 10 percent
10 percent
Low birth weight is considered less than 2,500 grams (5 pounds, 8 ounces). In 2020, 8.24 percent of babies were born low birth weight, and 1.34 percent were born very low birth weight (less than 1,500 grams, or 3 pounds 4 ounces).
A high birth weight means that a baby weighs 4,000 grams (8 pounds 13 ounces) or more. About 7.5 percent of babies are born with a high birth weight.
A newborn's weight depends on a number of factors, including the parents' size and ethnicity, Mom's health and age, and how much Mom gained during pregnancy. Other factors include the baby's health and gestational age (premature babies are often smaller), whether the baby is a boy or girl, a first baby or later baby, or a singleton or multiple. Being small or large at birth doesn't mean your baby will be small or large later in life.
Why does newborn weight gain matter?
Tracking your newborn's growth in height and weight over time gives your baby's doctor a good sense of your baby's general health.
When a baby doesn't gain weight at a healthy rate, they may be diagnosed with a condition called failure to gain weight (or failure to thrive). This usually happens if they aren't eating well or aren't absorbing or using nutrients properly. It could be due to a feeding problem, a gastrointestinal issue, or some other medical condition.
Healthcare providers will keep a close eye on your baby's weight gain because good nutrition is crucial for your baby's mental and physical development.
Advertisement | page continues below
While you're still in the hospital, a doctor or nurse will weigh your baby at birth and every 24 hours after birth. Your baby will be weighed again when you come in for your first doctor visits (usually in the first week after you leave the hospital, when your baby is 3 to 5 days old) and at all your baby's well-child visits during the first year. These measurements are recorded on your baby's growth chart.
If your baby is having any health problems, including unexpected weight loss or jaundice, you may have to see the doctor more often in the first few weeks.
What's normal weight loss for a newborn in the first days after birth?
Most healthy, full-term babies lose between 5 and 10 percent of their birth weight in the first days after birth. This can be worrisome if you're not expecting it, but it's perfectly normal.
This early weight loss happens because babies are born with extra fluid that gets eliminated after birth. This weight loss isn't a concern unless a baby loses more than 10 percent of their birth weight.
Your baby needs little food now (their tummy is tiny!), so it might take your little one a couple of weeks to gain the weight back, but within 5 days they'll probably be heading upward on the scale. If your baby loses a lot of weight or is ill or a preemie, it can take longer, perhaps 3 weeks or so.
How much weight will a newborn gain in the first weeks after birth?
Babies usually start to gain weight again 5 to 7 days after birth, and most should be back to (or above) their birth weight by the time they're about 2 weeks old.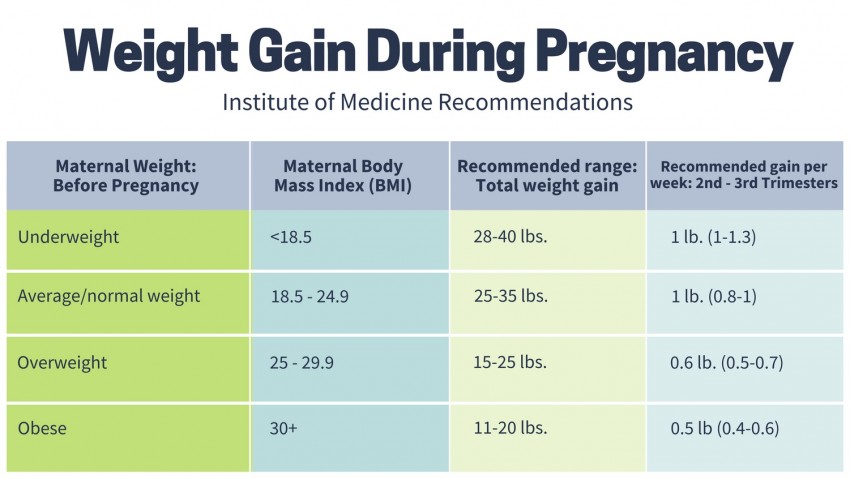
In the first month, newborns typically gain about an ounce (30 grams) daily, or a total of 5 to 7 ounces a week. By the end of the first month, most babies will weigh between 1 and 2 pounds above their birth weight. They also grow about 1 to 1.5 inches (2.54 to 3.81 centimeters) in height during this month.
Many factors go into a baby's weight gain in those first weeks of life, including how fast your breast milk comes in (if you're breastfeeding) and how much your baby wants to eat. For example, you may notice your baby wants to eat more often or for longer when they're between 7 and 10 days old, when they're having a growth spurt. (When a baby wants to eat again soon after a full feeding, it's called cluster feeding.)
Look for more growth spurts around 2 to 3 weeks, and at 6 weeks, 3 months, and 6 months. (Although not all babies follow this timeline, and a growth spurt can happen at any time!)
After the first month, a baby typically gains about 3 to 5 ounces a week until 12 months. While breastfed infants may gain more quickly in the first few months, formula-fed babies gain more rapidly after that. Over the course of the first year, healthy breastfed babies tend to gain more slowly than formula-fed infants. By their second year, their weights are typically similar.
While breastfed infants may gain more quickly in the first few months, formula-fed babies gain more rapidly after that. Over the course of the first year, healthy breastfed babies tend to gain more slowly than formula-fed infants. By their second year, their weights are typically similar.
How can I tell if my newborn is gaining enough weight?
You may not have a scale suitable for weighing your baby at home. Luckily, counting your baby's dirty diapers is another good way to tell that your baby is doing fine:
- Wet diapers: In the first five days, your newborn may wet only a few diapers each day. After that, expect about 6 to 8 wet diapers a day.
- Poopy diapers: In the first few days, some babies may poop just once daily. After that, expect your baby to poop at least twice a day. (A breastfed baby will have more poopy diapers, say five or more. A formula-fed baby may only have a few.)
It's helpful to track newborn diaper changes in a journal, on BabyCenter's printable baby care log, or with an app on your phone.
In addition, your baby's healthcare provider will be tracking your baby's weight (along with their height and head circumference) at each visit.
Find out more ways to tell if your baby is getting enough breast milk or formula.
What if my baby loses too much weight after birth or isn't gaining enough?
It's a good idea to check in with your baby's healthcare provider if you notice that your baby isn't feeding well or wetting or soiling enough diapers.
Talk with their provider about specific measures you can take, including:
- Regular weighing. You may want to bring your baby to the doctor's office for frequent weighing until they're on track.
- If you're breastfeeding, have your baby empty one breast before offering them the other. This way, they'll get the hindmilk (which is highest in fat) at the end.
- If you're breastfeeding, nurse your baby every two hours during the day. If you're bottle feeding, offer the bottle every three hours.
 In either case, don't go for more than four hours at night between feedings.
In either case, don't go for more than four hours at night between feedings. - If you're breastfeeding, work with a lactation consultant to make sure your baby's latch is good and to address any breastfeeding problems. (Sometimes a simple change in position or technique is all that's needed.)
- Avoid giving your baby a pacifier until after they've eaten.
Ask your baby's provider when they'd like you to get in touch between visits. (They may say to call if your baby wets fewer than four diapers in a day, for example, or if your baby starts refusing to eat). Always call with concerns, including any signs of dehydration such as darker, stronger urine or a dry, parched mouth and lips.
Take your baby to the emergency department if they show any signs of serious dehydration, including sunken eyes and sunken fontanels (the soft spots on your baby's head), excessive sleepiness, or extreme fussiness.
When do babies double their birth weight?
Babies typically double their birth weight by about 4 months old.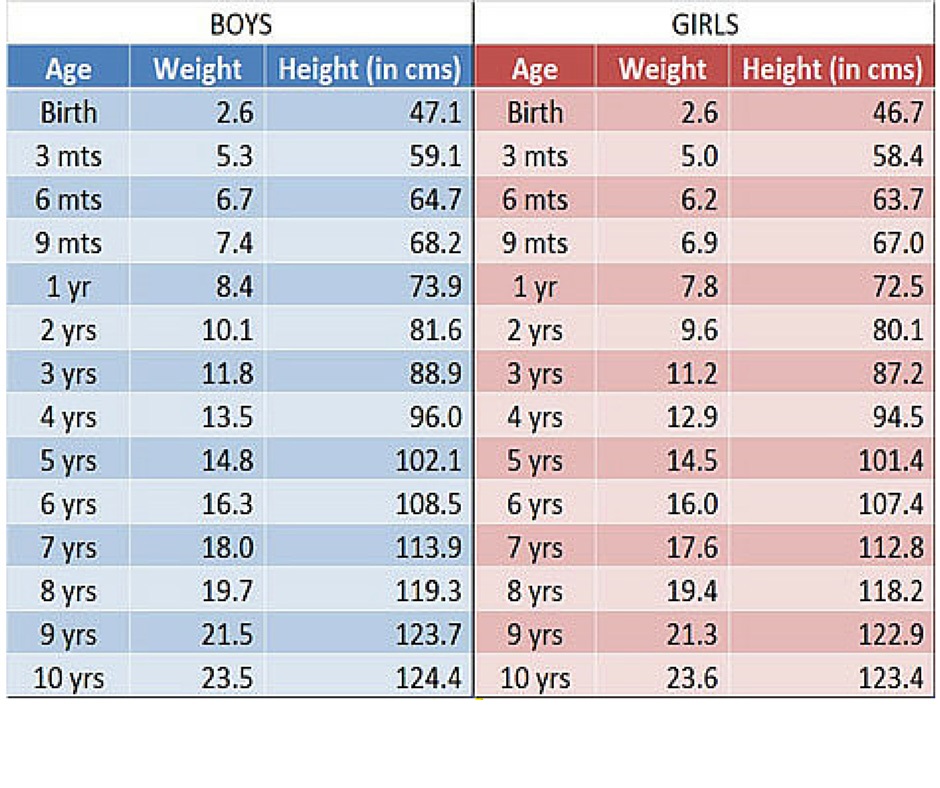 By their first birthday, your baby will probably triple their birth weight!
By their first birthday, your baby will probably triple their birth weight!
Along the way, your baby may stop gaining for a short period, or even lose a bit of weight. But over time, the trend of your baby's growth on a curve should be steady. Between visits, let your healthcare provider know if you're concerned that your baby isn't gaining enough.
Curious about how your baby compares with other babies their age? Read more about the average weight and growth for babies, toddlers, and kids.
Learn more:
- Measuring your baby's head circumference, length, and weight
- Baby weight and height percentile calculator
- Child height predictor
Rates of weight gain in newborns by months - a checklist from an expert.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Perinatal center MMCC Kommunarka — childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Everything about the new Perinatal Center in Kommunarka: conditions of stay, features, photos, address, phone.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Perinatal center GKB №67 named after. L.A. Vorokhobov — childbirth under the MHI policy
Perinatal Center City Clinical Hospital No. 67 named after. L.A. Vorokhobova - reviews, doctors, registration for childbirth free of charge under compulsory medical insurance.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Center for family planning and reproduction - childbirth free of charge under compulsory medical insurance
TsPSiR on Sevastopolskaya - about the center, reviews, doctors, an appointment for childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals Bauman - childbirth under the MHI policy
Perinatal Center of the City Clinical Hospital No. 29 named after N.E. Bauman on Hospital Square, 2. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
O.M. Filatova - childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Maternity Hospital City Clinical Hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatov on Vykhino, st. Veshnyakovskaya, d.
15 named after. O.M. Filatov on Vykhino, st. Veshnyakovskaya, d.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Perinatal center GKB im. S.S. Yudina - childbirth under the MHI policy
Maternity hospital No. 7 GKB im. S.S. Yudina on Kolomensky passage, 4, building 2. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the MHI policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity ward №2 A.K. Yeramishantseva (Maternity Hospital No. 40) - childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Maternity ward №2 GKB im. A.K. Eramishantseva (Maternity Hospital No. 40) on Taimyrskaya, 6. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity ward No. 1 A.K. Yeramishantseva - childbirth under the policy of OMS
Maternity Ward No. 1 of the City Clinical Hospital named after. A.K. Yeramishantsev. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital №3 GKB №67 named after. L.A. Vorokhobova (previously RD No. 3 TsPSiR Branch No. 4) - childbirth under the MHI policy
Maternity hospital No. 3 GKB No. 67 named after. L.A. Vorokhobov on Nezhinskaya, 3 (formerly RD No. 3 TsPSiR Branch No. 4). Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital No. 52 - childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Maternity hospital No. 26 at the city clinical hospital No. 52 on Sosnovaya, 11. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Perinatal center GKB im. M.P. Konchalovsky - childbirth under the policy of compulsory medical insurance
Perinatal Center of the City Clinical Hospital named after. M.P. Konchalovsky in Zelenograd. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital №2 GKB im. F. I. Inozemtseva (formerly maternity hospital No. 20 of the D. D. Pletnev City Clinical Hospital) - childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Maternity hospital No. 2 GKB im. F.I. Inozemtseva (formerly Maternity Hospital No. 20 of the Pletnev City Clinical Hospital) on Verkhnaya Pervomaiskaya, 57. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the CHI policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
F.I. Inozemtseva — childbirth under the compulsory medical insurance policy
Maternity hospital No. 36 GKB im. F.I. Inozemtseva on Fortunatovskaya, 1, bldg. 2. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the CHI policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital №4 GKB im. V.V. Vinogradova - childbirth under the MHI policy
Maternity hospital No. 4 GKB im. V.V. Vinogradova on the street. Novatorov, d. 3. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.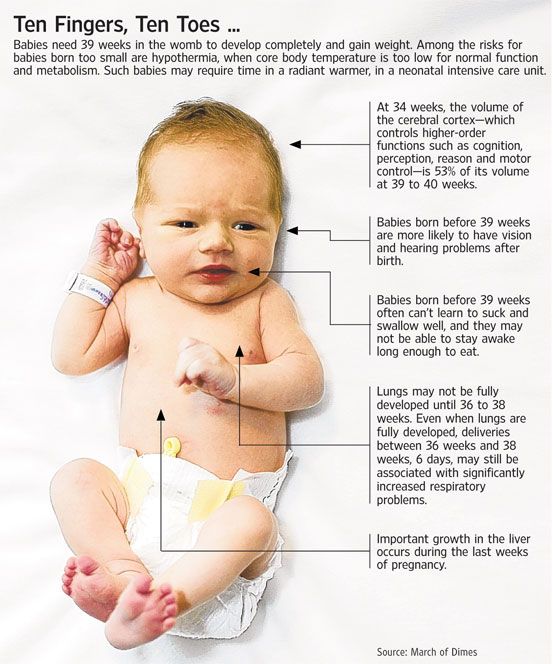
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital GKB im. V.V. Veresaeva - childbirth under the policy of compulsory medical insurance
Maternity hospital No. 17 GKB im. V.V. Veresaeva on the 800th anniversary of Moscow, house 22. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital №27 V.V. Veresaeva - childbirth under the policy of compulsory medical insurance
Maternity hospital No. 27 (formerly the City Clinical Hospital named after S.I. Spasokukotsky) - about the hospital, reviews, doctors, registration for childbirth free of charge under the policy of compulsory medical insurance.
Catalog of maternity hospitals
Maternity hospital №8 City clinical hospital №15 named after. O.M. Filatov (formerly Maternity Hospital No. 8 GKB named after V.P. Demikhov)
Maternity hospital No. 8 City clinical hospital No. 15 named after. O.M. Filatov on Samarkand Boulevard, 3. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the MHI policy.
O.M. Filatov on Samarkand Boulevard, 3. Registration for childbirth is free of charge under the MHI policy.
Height and weight gain for children of the first year of life. Tables
Dear parents, your baby is growing and you are worried about whether he is gaining enough weight and height. For control, there are centile tables for assessing the physical development of children, weight and height indicators. At the same time, you must remember that each baby is individual, he cannot grow according to the textbook. These weight and height recommendations are based on an average number of children and 10% deviation is normal. In addition, the centile corridor from 25% to 75% is an average physical indicator. That is why they say: Physical development is mesosomatic, macrosomatic, microsomatic.
It is important that the weight and height indicators are in the same centile corridor, but no more than two adjacent ones. Then we can talk about harmonious development.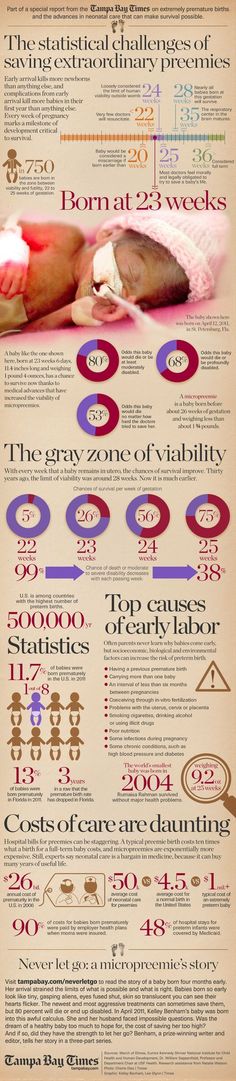 If the gap is more than two centile corridors, the development is disharmonious. Then we can think either about an unbalanced diet or about a pathology associated with obesity (paratrophy), or protein-energy deficiency (hypotrophy). In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions.
If the gap is more than two centile corridors, the development is disharmonious. Then we can think either about an unbalanced diet or about a pathology associated with obesity (paratrophy), or protein-energy deficiency (hypotrophy). In addition, one should not forget about the constitutional characteristics of the child, about genetic predisposition. Therefore, in no case should you compare your child with a neighbor's. To talk about the health of a child, we evaluate his condition according to many criteria. This is neuropsychic development, laboratory examination data, anamnesis, heredity. How many times in my practice have I met children who gained 400-450 g in weight every month, by the year they barely gained 7.8-8 kg. But at the same time, children already at 10 months began to walk, pronounce syllables, and follow complex instructions.
We'll talk about weight and height gain for term babies. In preterm infants, rates of weight gain and height differ according to the degree of prematurity.
In addition, children can be born with intrauterine malnutrition.
The tables for girls and boys are different in terms of numerical indicators, but at 1 year of age, these differences are quite minimal.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of girls from 0 to 12 months.
| Body length (height), cm. Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg. Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 45. | 47.5 | 49.8 | 50.7 | 52.0 | 53.1 | 53.9 | 0 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.1 |
| 48.5 | 50.3 | 52.1 | 53.5 | 55.0 | 56.1 | 57.3 | 1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 5.1 |
| 51.2 | 53.3 | 55.2 | 56.8 | 58. | 59.3 | 60.6 | 2 | 3.8 | 4.2 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 |
| 54.0 | 56.2 | 57.6 | 59.3 | 67.7 | 61.8 | 63.6 | 3 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.7 |
| 56.7 | 58.4 | 60.0 | 61.2 | 62.8 | 64.0 | 65.7 | 4 | 5. | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.0 | 7.5 |
| 59.1 | 60.8 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 65.1 | 66.0 | 68.0 | 5 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.1 |
| 60.8 | 62.5 | 64.1 | 65.5 | 67.1 | 68.8 | 70.0 | 6 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7. | 8.3 | 8.7 |
| 62.7 | 64.1 | 65.9 | 67.5 | 69.2 | 70.4 | 71.9 | 7 | 6.4 | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.3 |
| 64.5 | 66.0 | 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.5 | 72.5 | 73.7 | 8 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 9.7 |
| 66.0 | 67. | 69.1 | 70.2 | 72.0 | 74.1 | 75.5 | 9 | 7.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.1 |
| 67.5 | 69.0 | 70.3 | 71.9 | 73.2 | 75.3 | 76.8 | 10 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.1 | 10.5 |
| 68.9 | 70.1 | 71.5 | 73.0 | 74.7 | 76. | 78.1 | eleven | 7.7 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.5 | 10.9 |
| 70.1 | 71.4 | 72.8 | 74.1 | 75.8 | 78.0 | 79.6 | 12 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.2 | 10.8 | 11.3 |
At the same time, up to the age of three months, the child adds 20-30 grams per day daily, respectively, from 140 to 200 per week. If we talk about the average weight gain by months, then it is only 600 g per month, since the child after birth has physiological weight loss (with urine, feces, transition from intrauterine feeding to breastfeeding during the adaptation period), approximately 10% of the weight, which is 200-300 grams.
More often, by 3-4 days, the child restores its original weight, and then there is an increase. But I had a case in practice when the child began to gain weight from the 20th day of life, while the girl was active, reflexes were alive, her appetite was good, she could withstand the night interval, stool 4-5 times a day, urination was sufficient, developed according to age. Therefore, do not worry. Our indicator is the well-being of the child. If the baby is active, eats with appetite, sleep is calm, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed, be calm, your baby is healthy and not hungry. You see from the table the range of weight per year is from 8 to 13 kg. This is the norm. There is no reason to run to the endocrinologist, genetics, to examine the child.
Or the opposite situation: in the first months of life, a child gains 1-1.5 kg while breastfeeding. If the baby does not have colic, he does not spit up, there are no gastrointestinal manifestations, he is active, the skin is clean, physiological functions are not disturbed - this is also the norm. Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them.
Remember, as often happens, premature babies quickly gain weight and catch up with their peers by the year. And large babies gain weight more slowly. In my entire thirty-year practice, only two children weighed 14-15 kg by the year, although their parents were large and tall. By the age of three, they weighed almost the same, added only in height, the rest of their peers caught up with them.
| Month | Weight gain in grams |
| 1 | 600.0 |
| 2 | 800.0 |
| 3 | 800.0 |
| 4 | 750.0 |
| 5 | 700.0 |
| 6 | 650.0 |
| 7 | 600.0 |
| 8 | 550. |
| 9 | 500.0 |
| 10 | 450.0 |
| eleven | 400.0 |
| 12 | 350.0 |
It is believed that by 4-4.5 months the child should double the weight, and triple by the end of the year.
It happens that the increase in height and weight goes in leaps, seasonality, unevenness, and sometimes asymmetry of growth are noted. Pediatricians are concerned about the circumference of the head and chest, by 2-3 months they should be equal. Further, the breast grows faster. This is important so as not to miss the pathology.
The younger the child, the faster his growth. In the first 3 months of life, body length increases by 3 cm monthly, in the second quarter by 2.5-2 cm monthly. In the third - 1.5-2 cm, in the fourth - 1 cm monthly. The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
The total increase in height in the first year of life is about 25 cm.
Centile tables for assessing the physical development of boys from 0 to 12 months.
| Body length (height), cm. Centiles in % | Age in months | Body weight, kg Centiles in % | ||||||||||||
| 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | 3 | 10 | 25 | 50 | 75 | 90 | 97 | |
| 46.5 | 48.0 | 49.8 | 51.3 | 52.3 | 53.5 | 55. | 0 | 2.7 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 3.7 | 3.9 | 4.4 |
| 49.5 | 51.2 | 52.7 | 54.5 | 55.6 | 56.5 | 57.3 | 1 | 3.3 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 5.1 | 5.4 |
| 53.6 | 53.8 | 55.3 | 57.3 | 58.2 | 59.4 | 60.9 | 2 | 3.9 | 4.2 | 4. | 5.1 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 |
| 55.3 | 56.5 | 58.1 | 60.0 | 60.9 | 62.0 | 63.8 | 3 | 4.5 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.8 | 6.4 | 7.0 | 7.3 |
| 57.5 | 58.7 | 60.6 | 62.0 | 63.1 | 64.5 | 66.3 | 4 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 8. |
| 59.9 | 61.1 | 62.3 | 64.3 | 65.6 | 67.0 | 68.9 | 5 | 5.6 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 8.8 |
| 61.7 | 63.0 | 64.8 | 66.1 | 67.7 | 69.0 | 71.2 | 6 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 9.0 | 9.4 |
| 63.8 | 65.1 | 66. | 68.0 | 69.8 | 71.1 | 73.5 | 7 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 9.9 |
| 65.5 | 66.8 | 68.1 | 70.0 | 71.3 | 73.1 | 75.3 | 8 | 7.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.6 | 9.4 | 10.0 | 10.5 |
| 67.3 | 68.2 | 69.8 | 71.3 | 73.2 | 75.1 | 75. | 9 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.1 | 9.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 |
| 68.8 | 69.1 | 71.2 | 73.0 | 75.1 | 76.9 | 78.8 | 10 | 7.9 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 10.9 | 11.4 |
| 70.1 | 71.3 | 72.6 | 74.3 | 76.2 | 78.0 | 80.3 | eleven | 8.2 | 8.6 | 9. | ||||
 8
8  0
0 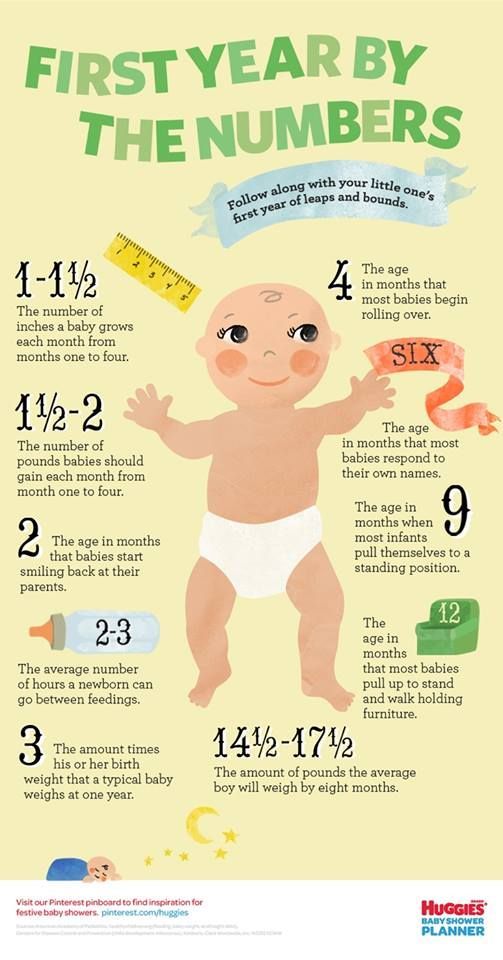 0
0  8
8  5
5 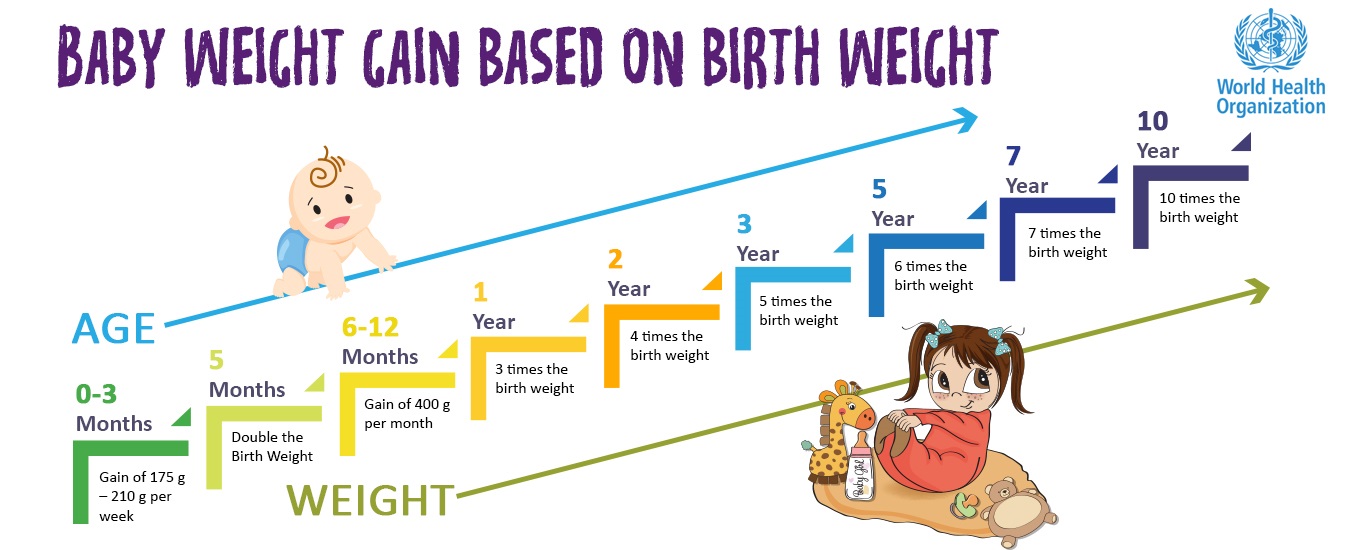 5
5 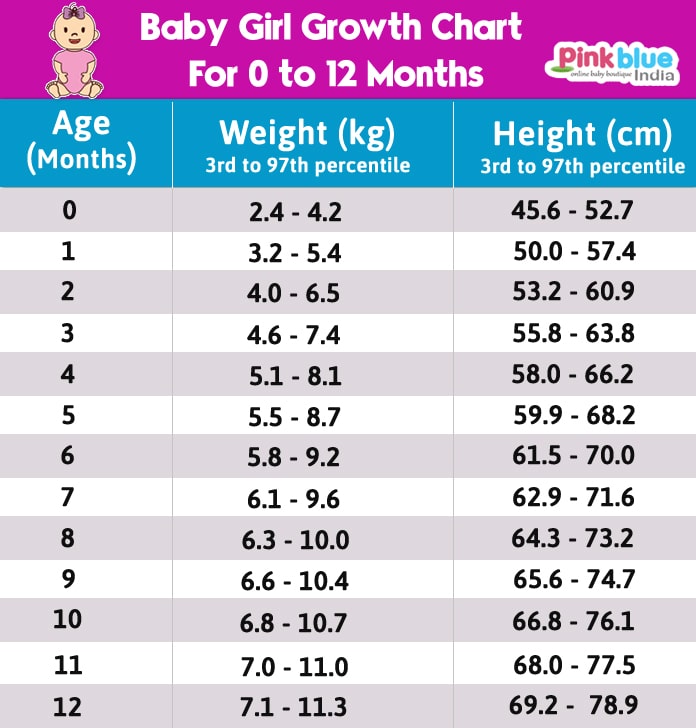 0
0  0
0  6
6  1
1  3
3