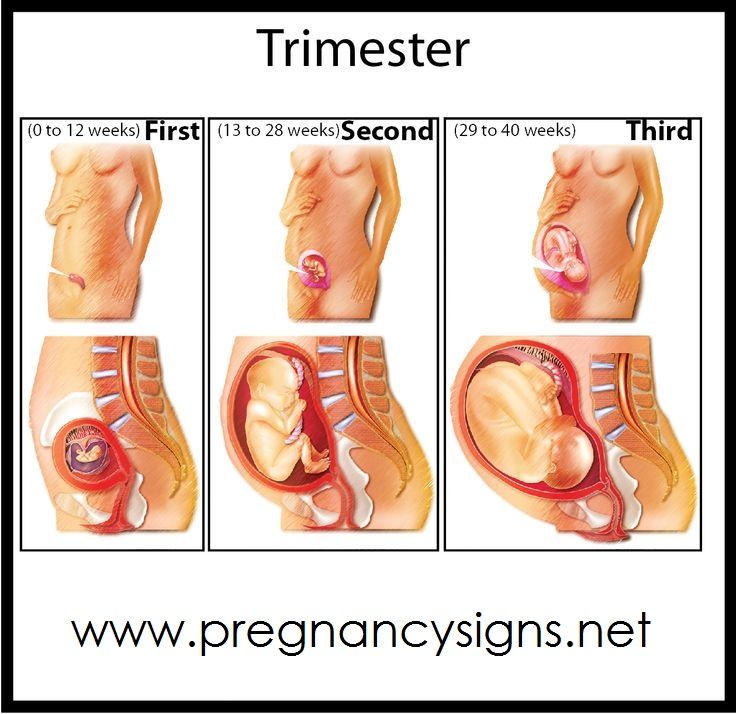
Weeks third trimester begins
28 Weeks Pregnant | Pregnancy
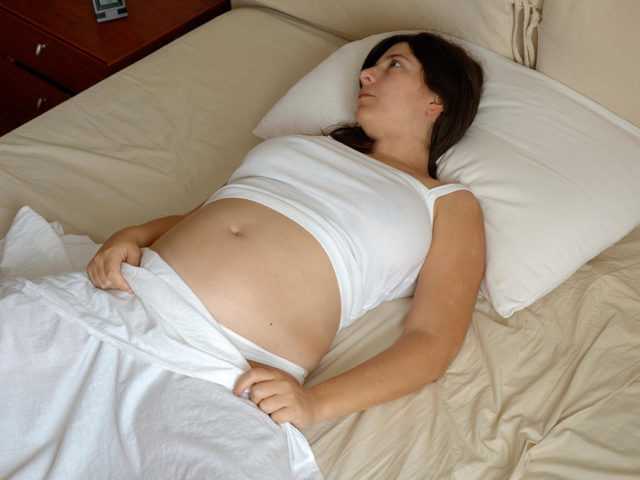
Welcome to the 3rd trimester! Pregnancy is divided into 3 stages, known as trimesters…. and you're now in the 3rd stage. Over the next few weeks, you will probably start to feel a bit more uncomfortable and tired.
What's happening in my body?
You may be getting a bit of heartburn and indigestion. That's down to your growing baby and hormones affecting your digestive system.
Your back will also be under strain, due to the extra weight you're carrying around. Your joints and ligaments will also be looser than usual.
Your ankles, feet and face could be puffing out a bit, particularly when it's hot. This is probably due to water retention, but get it checked out, just in case it's pre-eclampsia. This is a condition where you may feel perfectly well, but then your blood pressure can get dangerously high, very quickly.
Rest can help with a lot of your symptoms, so make sure you get lots of it. But if you are worried about anything at all, talk to your midwife or doctor, or call NHS 111.
3 ways to bust germs
Make sure you know about some of the harmful infections in pregnancy, so that you can do your best to avoid them.
Here are 3 ways you can protect your unborn baby…
-
Wash your hands regularly with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, particularly if you're in contact with children or nappies, as they could carry a virus called CMV (cytomegalovirus).
-
If you have a cat - wear gloves when emptying the cat litter tray, or ask someone else to deal with it. That's because cat poo can contain a bug that causes the dangerous toxoplasmosis infection. You should also wear gloves when gardening, in case you come into contact with animal poo.
-
If you have not had chickenpox let your doctor or midwife know if you come into contact with anyone who could be infectious. The disease can be spread up to 2 days before spots appear, until 5 days afterwards. It's safest for you when there are no new blisters or moist crusts on the spots.
If you're worried about coronavirus, have a look at the guidance from Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists on coronavirus and pregnancy.
Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds are common in pregnancy, due to hormonal changes, and can even strike when you're asleep. Here's what you can do:
- sit or stand up - don't lie down
- pinch your nose just above your nostrils for 10 to 15 minutes
- lean forward and breathe through your mouth
- put an icepack (or a bag of frozen peas wrapped in a tea towel) at the top of your nose
Read more tips for stopping nosebleeds.
3rd trimester pregnancy symptoms (at 28 weeks)
You may start getting new symptoms now, such as nosebleeds and indigestion.
Your signs of pregnancy could also include:
- sleeping problems (week 19 has information about feeling tired)
- stretch marks (read about stretch marks on week 17's page)
- swollen and bleeding gums (week 13 has information about gum health during pregnancy)
- pains on the side of your baby bump, caused by your expanding womb ("round ligament pains")
- piles (read about piles on week 22's page)
- headaches
- backache
- nosebleeds
- indigestion and heartburn (week 25 talks about digestive problems)
- bloating and constipation (read about bloating on week 16's page)
- leg cramps (week 20 explains how to deal with cramp)
- feeling hot
- dizziness
- swollen hands and feet
- urine infections
- vaginal infections (see week 15 for vaginal health)
- darkened skin on your face or brown patches – this is known as chloasma or the "mask of pregnancy"
- greasier, spotty skin
- thicker and shinier hair
You may also experience symptoms from earlier weeks, such as:
- mood swings (week 8's page has information on mood swings)
- morning sickness (read about dealing with morning sickness on week 6's page)
- weird pregnancy cravings (read about pregnancy cravings on week 5's page)
- a heightened sense of smell
- sore or leaky breasts (read about breast pain on week 14's page) - a white milky pregnancy discharge from your vagina and light spotting (seek medical advice for any bleeding)
Read Tommy's guide to common pregnancy symptoms.
What does my baby look like?
Your baby, or foetus, is around 37.6cm long from head to heel, and weighs about 1kg. That's approximately the size of a pineapple, and the weight of a big bag of brown sugar.
Your baby's heart rate is changing all the time. Around week 5 or 6, when it was first detectable, it was around 110 beats per minute (bpm). Then it soared to around 170 bpm in week 9 and 10. Now, it's slowed down to around 140 bpm and it will be around 130 bpm at birth.
That's still a lot faster than your heart rate, which will be around 80 to 85 beats per minute. This is partly because babies' hearts are so small that they can't pump much blood, but they can make up for this by going faster. It also helps to keep them warm.
Your baby's heart can be heard through a stethoscope. Someone else might be able to hear it by putting an ear to your pregnant belly – give it a go, but it's tricky finding the right spot.
Action stations
It's time to work out where your baby will sleep, and it's best to do this sooner, rather than later, before you start running out of energy.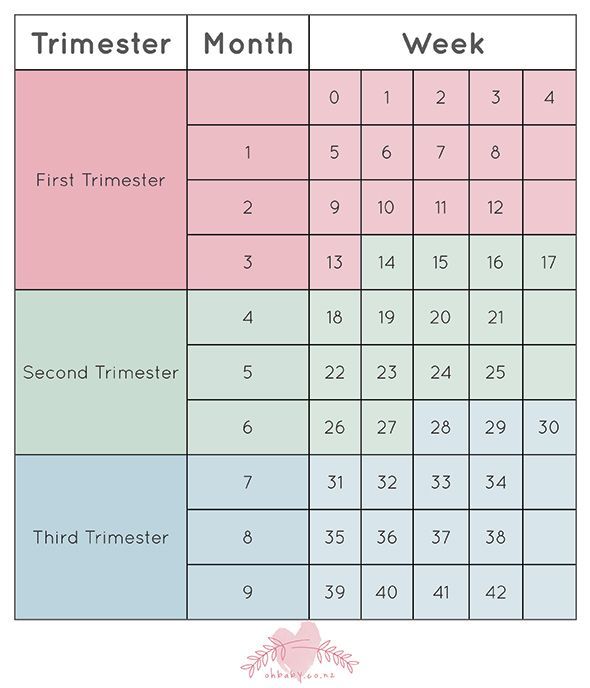 Your baby will spend a lot of time in a cot, so make sure it's safe. If you're buying a new cot, look for the British Standard mark BS EN 716-1. Read more about what you need for your baby.
Your baby will spend a lot of time in a cot, so make sure it's safe. If you're buying a new cot, look for the British Standard mark BS EN 716-1. Read more about what you need for your baby.
This week you could also...
You have maternity rights. You can ask for a risk assessment of your work place to ensure that you're working in a safe environment. You should not be lifting heavy things and you may need extra breaks and somewhere to sit. You can also attend antenatal appointments during paid work time.
It's a good time to tone up your pelvic floor muscles. Gentle exercises can help to prevent leakage when you laugh, sneeze or cough. Get the muscles going by pretending that you're having a wee and then stopping midflow. Visit Tommy’s for more ideas about pelvic floor exercises.
Ask your midwife or doctor about online antenatal classes – they start around now. The charity Tommy's has lots of useful information on antenatal classes and preparing you for birth.
Even if you've had children before, they're still worth going to as you can meet other parents-to-be. The NCT offers online antenatal classes with small groups of people that live locally to you.
The NCT offers online antenatal classes with small groups of people that live locally to you.
To keep bones and muscles healthy, we need vitamin D. From late March/early April to the end of September, most people make enough vitamin D from sunlight on their skin. However, between October and early March, you should consider taking a daily vitamin D supplement because we cannot make enough from sunlight.
Some people should take a vitamin D supplement all year round, find out if this applies to you on the NHS website. You just need 10 micrograms (it's the same for grown-ups and kids). Check if you're entitled to free vitamins.
It's recommended that you do 150 minutes of exercise a week while pregnant. You could start off with just 10 minutes of daily exercise - perhaps take a brisk walk outside. Check out Sport England's #StayInWorkOut online exercises (scroll to the pregnancy section). Listen to your body and do what feels right for you.
There's no need to eat for 2. Now you're in the 3rd trimester, you may need an extra 200 calories a day, but that's not much. It's about the same as 2 slices of wholemeal toast and margarine.
Now you're in the 3rd trimester, you may need an extra 200 calories a day, but that's not much. It's about the same as 2 slices of wholemeal toast and margarine.
Try and eat healthily with plenty of fresh fruit and veg, and avoid processed, fatty and salty foods. You may be able to get free milk, fruit and veg through the Healthy Start scheme.
How are you today? If you're feeling anxious or low, then talk to your midwife or doctor who can point you in the right direction to get all the support that you need. You could also discuss your worries with your partner, friends and family.
You may be worried about your relationship, or money, or having somewhere permanent to live. Don't keep it to yourself. It's important that you ask for help if you need it.
Getting pregnant again is probably the last thing on your mind. However now is a good time to start planning what type of contraception you would like to use after your baby is born. Getting pregnant again could happen sooner than you realise and too short a gap between babies is known to cause problems. Talk to your GP or midwife to help you decide.
Talk to your GP or midwife to help you decide.
You will be offered newborn screening tests for your baby soon after they are born. These screening tests are recommended by the NHS. This is because these tests can make sure that your baby is given appropriate treatment as quickly as possible. Your decisions about whether or not you want this tests will be respected, and health care professionals will support you. Ask your midwife or doctor for more information about newborn screening.
You and your family should follow the government and NHS guidance on coronavirus (COVID-19):
To find out about about COVID-19 and pregnancy, childbirth and breastfeeding, have a look at advice on the:
10 Things That Might Surprise You About Being Pregnant (for Parents)
Pregnancy info is everywhere. At your first prenatal visit, your doctor will likely give you armfuls of pamphlets that cover every test and trimester.
At your first prenatal visit, your doctor will likely give you armfuls of pamphlets that cover every test and trimester.
Despite all this information, here are 10 common surprises that pregnancy can bring.
1. The Nesting Instinct
Many pregnant women feel the nesting instinct, a powerful urge to prepare their home for the baby by cleaning and decorating.
As your due date draws closer, you may find yourself cleaning cupboards or washing walls — things you never would have imagined doing in your ninth month of pregnancy! This desire to prepare your home can be useful — you'll have fewer to-do items after the birth. But be careful not to overdo it.
2. Problems With Concentration
In the first trimester, tiredness and morning sickness can make many women feel worn out and mentally fuzzy. But even well-rested pregnant women may have trouble concentrating and periods of forgetfulness.
Thinking about the baby plays a role, as do hormonal changes. Everything — including work, bills, and doctor appointments — may seem less important than the baby and the coming birth.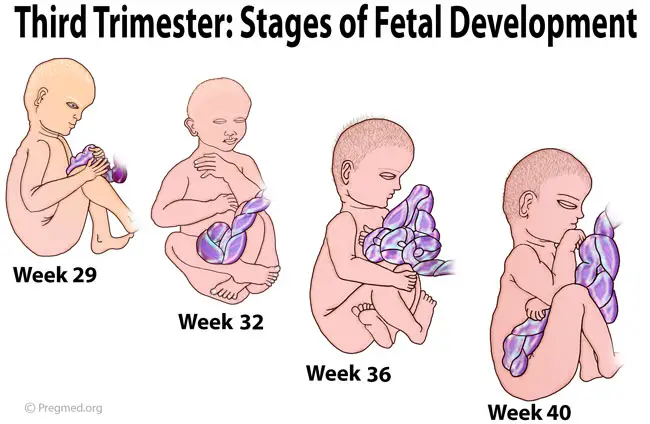 Making lists can help you remember dates and appointments.
Making lists can help you remember dates and appointments.
3. Mood Swings
Premenstrual syndrome and pregnancy are alike in many ways. Your breasts swell and become tender, your hormones go up and down, and you may feel moody. If you have PMS, you're likely to have more severe mood swings during pregnancy. They can make you go from being happy one minute to feeling like crying the next.
Mood swings are very common during pregnancy. They tend to happen more in the first trimester and toward the end of the third trimester.
Many pregnant women have depression during pregnancy. If you have symptoms such as sleep problems, changes in eating habits, and mood swings for longer than 2 weeks, talk to your health care provider.
4. Bra Size
An increase in breast size is one of the first signs of pregnancy. Breast growth in the first trimester is due to higher levels of the hormones
estrogenand progesterone. That growth in the first trimester might not be the end, either — your breasts can continue to grow throughout your pregnancy!
Your bra size also can be affected by your ribcage. When you're pregnant, your lung capacity increases so you can take in extra oxygen, which may lead to a bigger chest size. You may need to replace your bras several times during your pregnancy.
When you're pregnant, your lung capacity increases so you can take in extra oxygen, which may lead to a bigger chest size. You may need to replace your bras several times during your pregnancy.
5. Skin Changes
Do your friends say you have that pregnancy glow? It's one of many effects that can come from hormonal changes and your skin stretching.
Pregnant women have increased blood volume to provide extra blood flow to the uterus and other organs, especially the kidneys. The greater volume brings more blood to the vessels and increases oil gland secretion.
Some women develop brownish or yellowish patches called chloasma, or the "mask of pregnancy," on their faces. And some will notice a dark line on the midline of the lower abdomen, known as the linea nigra (or linea negra). They can also have hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) of the nipples, external genitalia, and anal region. That's because pregnancy hormones cause the body to make more pigment.
This increased pigment might not be even, so the darkened skin may appear as splotches of color.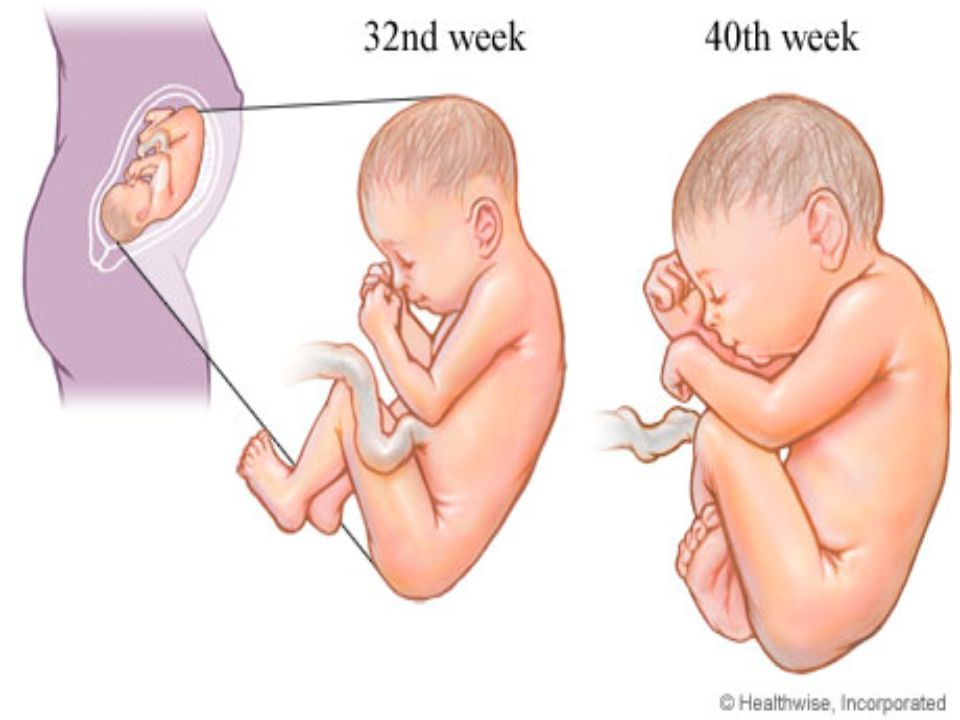 Chloasma can't be prevented, but wearing sunscreen and avoiding UV light can minimize its effects.
Chloasma can't be prevented, but wearing sunscreen and avoiding UV light can minimize its effects.
Acne is common during pregnancy because the skin's sebaceous glands make more oil. And moles or freckles that you had before pregnancy may get bigger and darker. Most of these skin changes should go away after you give birth.
Many pregnant women also get heat rash, caused by dampness and sweating. In general, pregnancy can be an itchy time for a woman. Skin stretching over the abdomen may cause itchiness and flaking. Your doctor can recommend creams to soothe dry or itchy skin.
page 4
6. Hair and Nails
Many women have changes in hair texture and growth during pregnancy. Hormones can make your hair grow faster and fall out less. But these hair changes usually aren't permanent. Many women lose some hair in the postpartum period or after they stop breastfeeding.
Some women find that they grow hair in unwanted places, such as on the face or belly or around the nipples. Changes in hair texture can make hair drier or oilier. Some women even find their hair changing color.
Changes in hair texture can make hair drier or oilier. Some women even find their hair changing color.
Nails, like hair, can change during pregnancy. Extra hormones can make them grow faster and become stronger. Some women, though, find that their nails split and break more easily during pregnancy. Like the changes in hair, nail changes aren't permanent. If your nails split and tear more easily when you're pregnant, keep them trimmed and avoid the chemicals in nail polish and nail polish remover.
7. Shoe Size
Even though you can't fit into any of your pre-pregnancy clothes, you still have your shoes, right? Maybe — but maybe not. Extra fluid in their pregnant bodies mean that many women have swollen feet and need to wear a larger shoe size. Wearing slip-on shoes in a larger size can be more comfortable, especially in the summer months.
8. Joint Mobility
During pregnancy, your body makes the hormone relaxin, which is believed to help prepare the pubic area and the cervix for the birth. Relaxin loosens the ligaments in your body, making you less stable and more at risk for injury. It's easy to overstretch or strain yourself, especially the joints in your pelvis, lower back, and knees. When exercising or lifting objects, go slowly and avoid sudden, jerking movements.
Relaxin loosens the ligaments in your body, making you less stable and more at risk for injury. It's easy to overstretch or strain yourself, especially the joints in your pelvis, lower back, and knees. When exercising or lifting objects, go slowly and avoid sudden, jerking movements.
9. Varicose Veins, Hemorrhoids, and Constipation
Varicose veins, usually found in the legs and genital area, happen when blood pools in veins enlarged by pregnancy hormones. Varicose veins often go away after pregnancy. To help prevent them:
- avoid standing or sitting for long periods
- wear loose-fitting clothing
- wear support hose
- raise your feet when you sit
Hemorrhoids — varicose veins in the rectum — are common during pregnancy as well. Your blood volume has increased and your uterus puts pressure on your pelvis. So the veins in your rectum may enlarge into grape-like clusters. Hemorrhoids can be very painful, and can bleed, itch, or sting, especially during or after a bowel movement (BM).
Constipation is another common pregnancy woe. It happens because pregnancy hormones slow the passing of food through the gastrointestinal tract. During the later stages of pregnancy, your uterus may push against your large intestine, making it hard for you to have a BM. And constipation can contribute to hemorrhoids because straining to go may enlarge the veins of the rectum.
The best way to deal with constipation and hemorrhoids is to prevent them. Eating a fiber-rich diet, drinking plenty of liquids daily, and exercising regularly can help keep BMs regular. Stool softeners (not laxatives) may also help. If you do have hemorrhoids, talk to your health care provider about a cream or ointment that can shrink them.
10. Things That Come Out of Your Body During Labor
So you've survived the mood swings and the hemorrhoids, and you think your surprises are over. But the day you give birth will probably hold the biggest surprises of all.
During pregnancy, fluid surrounds your baby in the amniotic sac. This sac breaks (or "ruptures") at the start of or during labor — a moment usually referred to as your water breaking. For most women in labor, contractions start before their water breaks. Sometimes the doctor has to rupture the amniotic sac (if the cervix is already dilated).
This sac breaks (or "ruptures") at the start of or during labor — a moment usually referred to as your water breaking. For most women in labor, contractions start before their water breaks. Sometimes the doctor has to rupture the amniotic sac (if the cervix is already dilated).
How much water can you expect? For a full-term baby, there are about 2 to 3 cups of amniotic fluid. Some women may feel an intense urge to pee that leads to a gush of fluid when their water breaks. Others may only feel a trickling down their leg because the baby's head acts like a stopper to prevent most of the fluid from leaking out.
Amniotic fluid is generally sweet-smelling and pale or colorless. It's replaced by your body every 3 hours, so don't be surprised if you continue to leak fluid, about a cup an hour, until delivery.
Other, unexpected things may come out of your body during labor. Some women have nausea and vomiting. Others have diarrhea before or during labor, and passing gas is also common.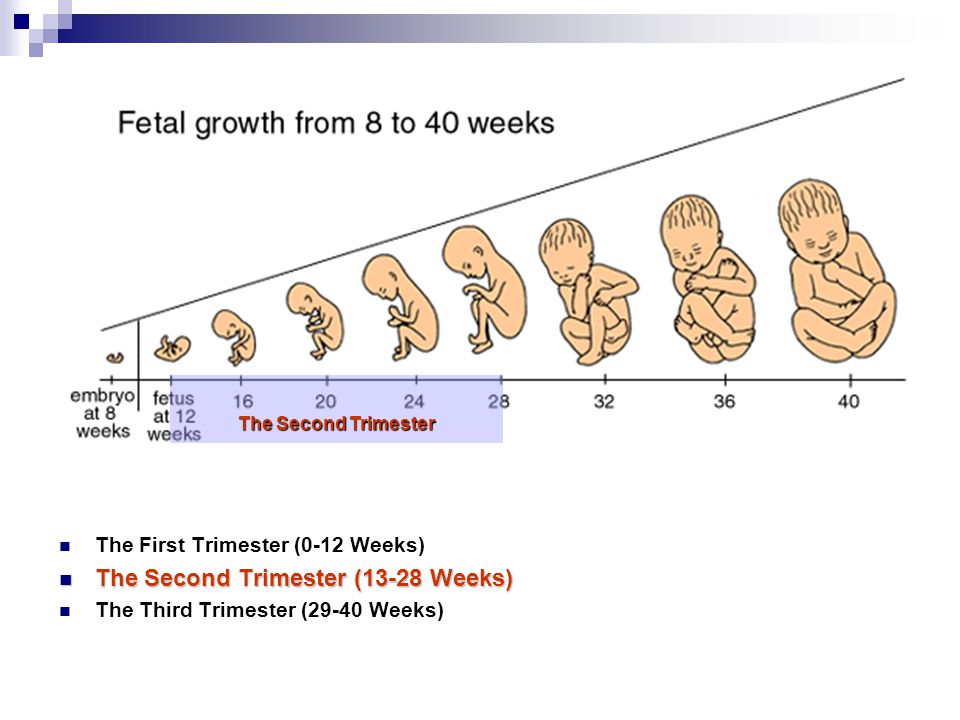 During the pushing phase of labor, you may lose control of your bladder or bowels.
During the pushing phase of labor, you may lose control of your bladder or bowels.
A birth plan can help communicate your wishes to your health care providers about how to handle these and other aspects of labor and delivery.
Lots of surprises are in store for you when you're pregnant — but none sweeter than the way you'll feel once your newborn is in your arms!
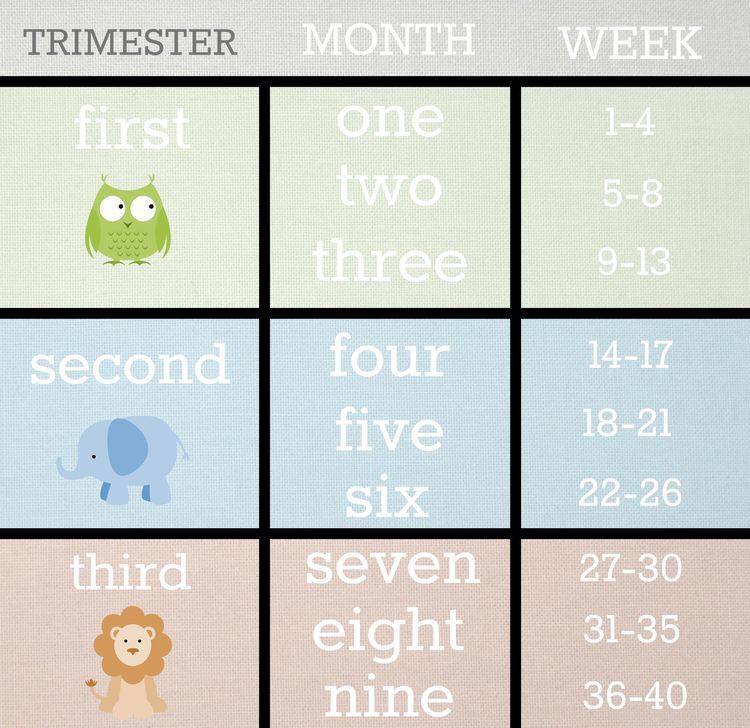
Third trimester of pregnancy (from 28 to 40 weeks)
At 30 weeks pregnant, you are ready to go on maternity leave. In the case of twins, prenatal leave is from 28 weeks. Active work, physical and mental overload during this period can provoke premature birth.
It's time to put on the bandage - it will help your baby stay in the right position and you in good shape after childbirth.
The child still needs a lot of nutrients, vitamins, mineral salts. Use your vacation to relax, but don't lie around all day. We hope that hiking in the fresh air has become a habit for you.
Do not forget to keep track of the ratio of drunk and excreted liquids. Accumulating in the body, the fluid disrupts the functioning of the kidneys, increases the load on the heart, which causes an increase in blood pressure. As a result, the child suffers: he lacks nutrients, oxygen.
Accumulating in the body, the fluid disrupts the functioning of the kidneys, increases the load on the heart, which causes an increase in blood pressure. As a result, the child suffers: he lacks nutrients, oxygen.
A sharp headache, flashing flies before the eyes, convulsions are signs of eclampsia, a severe complication of pregnancy that poses a threat to the life of the mother and child. Urgently call the ambulance.
At this time, the uterus becomes very sensitive to the pushes and movements of the child, its muscles periodically tighten. It's like she's doing gymnastics. If this rarely happens and you do not feel pain, then everything is in order and there is no cause for concern. But if the uterus tenses often, pain appears - call an ambulance. If spotting appears, amniotic fluid is pouring out, do not wait for contractions - immediately to the hospital!
Sex life from 32-33 weeks is not recommended.
At 32 weeks, another scheduled ultrasound examination is scheduled to assess the correct functioning of the placenta, if necessary, the study of fetal heart sounds.
The last month is the most difficult. The load on the body has increased to the maximum. You are already tired of the long wait. Approximately two weeks before delivery, a mucous plug will come off the cervix, which is a lump, sometimes slightly stained with blood.
Do not forget to make up for the lack of calcium in the body - until the last day of intrauterine existence, the child intensively stores minerals. Eat fully and properly - the fetus eagerly takes everything valuable for the formation of the body. He needs protein now. Be sure to take a prenatal multivitamin. Rest during the day. Lie on your side, slightly raise your legs.
Many women suffer from constipation at this time. Only a rational diet will help. Eliminate grapes, fresh cabbage, peas and other legumes, fresh milk, muffins, sweets. Useful: curdled milk, fermented baked milk, kefir. Steamed dried fruits normalize bowel function well. Don't take laxatives. In the last trimester of pregnancy, they can provoke uterine contractions and cause premature birth.
Sometimes, if the fetus is very large, the navel turns outward. Don't be scared and don't try to push it back. After giving birth, everything will return to normal.
By the last weeks of pregnancy, the mammary glands are greatly enlarged. The appearance of colostrum is another harbinger of close childbirth. The bra should be tight, with wide straps, always cotton.
Be prepared for contractions to start at any moment. Trim your fingernails and toenails short, and shave your pubic hair. Prepare things for the newborn and for yourself. Show your husband or relatives where they lie. An exchange card, passport, insurance policy, birth certificate should always be with you.
Think that you have to help your child come into the world. Everything will be ok!
3rd trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus
3rd trimester of pregnancy: what happens to the fetus - Private maternity hospital Ekaterininskaya Clinics3rd trimester: 27th week - birth
The baby is almost formed! In the last weeks of pregnancy, when he continues to gain weight and moves in an enclosed space, you may feel more comfortable.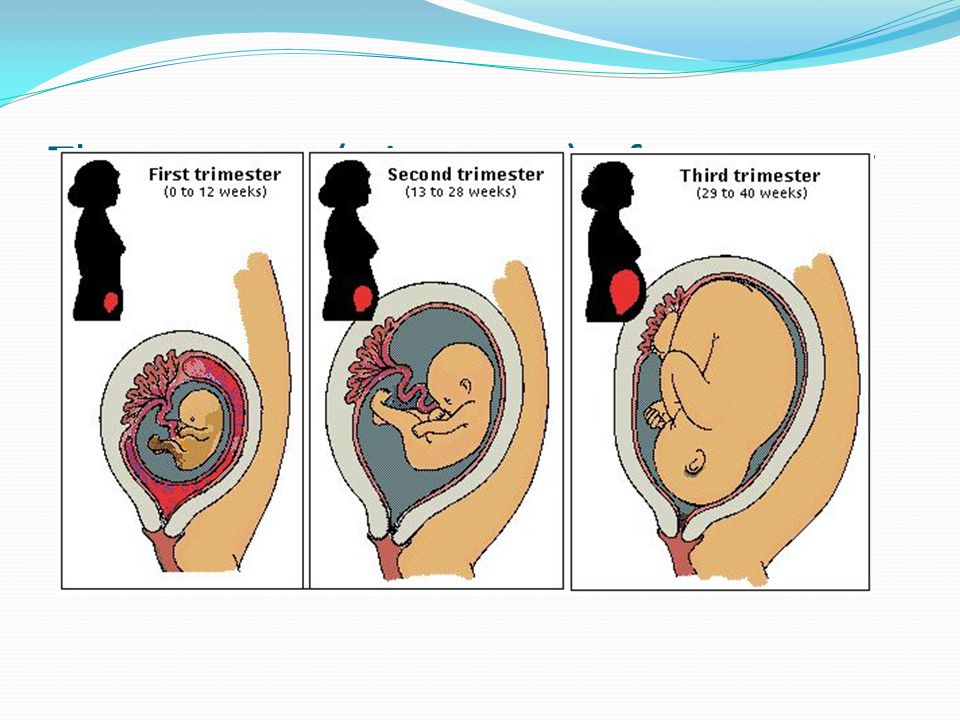 Try to get as much rest as possible. Symptoms of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy may include:
Try to get as much rest as possible. Symptoms of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy may include:
- Swelling of hands, feet and face. Excess fluid in the body can cause swelling of the hands, feet and swelling of the face. If possible, try to rest in a horizontal position more often, while raising your legs up, this will improve blood circulation and relieve leg fatigue.
- Discharge from the nipples. Colostrum may begin to come out of the nipples, a liquid that the baby will feed on until milk appears. To avoid stains on clothes, put special pads in your bra.
- Braxton Hicks contractions. Your baby is getting ready to be born and you may feel light "training" contractions. These contractions that come and go at regular intervals are called Braxton Hicks contractions. If the contractions are strong and prolonged, call your doctor. This could be the start of labor.
The main stages of the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
- During pregnancy, you will put on weight from 10 to 16 kg.
 Weight gain is mainly due to the weight of the baby, placenta and amniotic fluid and an increase in the amount of fat and fluid in the woman's body.
Weight gain is mainly due to the weight of the baby, placenta and amniotic fluid and an increase in the amount of fat and fluid in the woman's body. - 37 weeks is considered the full term of pregnancy.
Development of the child in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy
By the end of the 3rd trimester:
- The child takes a head down position in the pelvis, preparing for birth.
- The child's body systems are developed and ready to function independently.
- The soft, fluffy hairs that cover the body have disappeared.
- Baby's body length is about 46-56 cm from head to toes.
Mobile application of the clinic
You can make an appointment with a doctor, get tests
and much more...
Fill out the form to make an appointment or order a call back
I agree with personal data processing policy and user agreement I also give my consent to the processing of personal data.