Ultrasound of baby without brain
Facts about Anencephaly | CDC
Anencephaly (pronounced an-en-sef-uh-lee) is a serious birth defect in which a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull.
Click here to view a larger image
What is anencephaly?
Anencephaly is a serious birth defect in which a baby is born without parts of the brain and skull. It is a type of neural tube defect (NTD). As the neural tube forms and closes, it helps form the baby’s brain and skull (upper part of the neural tube), spinal cord, and back bones (lower part of the neural tube).
Anencephaly happens if the upper part of the neural tube does not close all the way. This often results in a baby being born without the front part of the brain (forebrain) and the thinking and coordinating part of the brain (cerebrum). The remaining parts of the brain are often not covered by bone or skin.
How Many Babies are Born with Anencephaly?
Researchers estimate that about 1 in every 4,600 babies is born with anencephaly in the United States. 1
Causes and Prevention
The causes of anencephaly among most infants are unknown. Some babies have anencephaly because of a change in their genes or chromosomes. Anencephaly might also be caused by a combination of genes and other factors, such as the things the mother comes in contact with in the environment or what the mother eats or drinks, or certain medicines she uses during pregnancy.
Getting enough folic acid before and during early pregnancy can help prevent neural tube defects, such as anencephaly. If you are pregnant or could get pregnant, take 400 micrograms (mcg) of folic acid every day. If you have already had a pregnancy affected by an NTD, you can speak with your doctor about taking a higher dose of folic acid before pregnancy and during early pregnancy.
- Since the United States began fortifying grains with folic acid, there has been a 28% decline in pregnancies affected by neural tube defects (spina bifida and anencephaly).1
- In order to get the recommended 400 micrograms of folic acid every day, a woman of reproductive age can take a supplement containing folic acid or to eat foods fortified with folic acid, or both, depending on her dietary habits.
CDC is dedicated to better understanding the causes of birth defects. Understanding the factors that are more common among babies with a birth defect will help us learn more about the causes. CDC funds the Centers for Birth Defects Research and Prevention, which collaborate on large studies such as the National Birth Defects Prevention Study (NBDPS; births 1997-2011), to understand the causes of and risks for birth defects, including anencephaly.
If you are pregnant or thinking about becoming pregnant, talk with your doctor about ways to increase your chances of having a healthy baby.
Diagnosis
Anencephaly can be diagnosed during pregnancy or after the baby is born.
During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, there are screening tests (prenatal tests) to check for birth defects and other conditions. Anencephaly would result in an abnormal result on a blood or serum screening test or it might be seen during an ultrasound (which creates pictures of the body). For more information about screening and confirmatory tests during pregnancy, visit CDC’s birth defects diagnosis web page.
For more information about screening and confirmatory tests during pregnancy, visit CDC’s birth defects diagnosis web page.
After the Baby is Born
In some cases, anencephaly might not be diagnosed until after the baby is born. Anencephaly is immediately seen at birth.
Treatments
There is no known cure or standard treatment for anencephaly. Almost all babies born with anencephaly will die shortly after birth.
References
- Mai CT, Isenburg JL, Canfield MA, Meyer RE, Correa A, Alverson CJ, Lupo PJ, Riehle‐Colarusso T, Cho SJ, Aggarwal D, Kirby RS. National population‐based estimates for major birth defects, 2010–2014. Birth Defects Research. 2019; 111(18): 1420-1435.
The images are in the public domain and thus free of any copyright restrictions. As a matter of courtesy we request that the content provider (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities) be credited and notified in any public or private usage of this image.
Anencephaly - Fetal Health Foundation
Anencephaly is a condition in which major portions of the brain, skull, and scalp are absent. It is the most severe and single most common prenatally detected spinal cord (neural tube) defect (Goldstein and Filly, 1988). Although the upper portions of the brain (the cerebral hemispheres) can develop in this condition, any exposed brain tissue is eventually destroyed. As a result, the brain will appear as a bloody (hemorrhagic) mass of tissue fibers. The cerebral cortex, the portion of the brain responsible for “higher order” functions in humans (such as movement, thought, speech, etc), will not be present, let alone functional. The brainstem and cerebellum may be spared. The brainstem controls many of the functions that happen automatically such as maintenance of heart rate, breathing, body temperature control, etc. The cerebellum is primarily responsible for balance and our innate sense of the space that our body occupies. Despite the severe brain abnormalities, the facial bones and base of the skull are nearly normally formed. The front portion of the skull (frontal bone), however, is always absent and the brain tissue is always abnormal. Less commonly, there is a mild form in which a small portion of skull is missing (meroacrania). The most severe form is when the brain is completely absent (holoacrania).
Despite the severe brain abnormalities, the facial bones and base of the skull are nearly normally formed. The front portion of the skull (frontal bone), however, is always absent and the brain tissue is always abnormal. Less commonly, there is a mild form in which a small portion of skull is missing (meroacrania). The most severe form is when the brain is completely absent (holoacrania).
Anencephaly accounts for approximately one-half of all cases of spinal cord (neural tube) defects (Chescheir et al., 2003). The incidence of anencephaly in livebirths and stillbirths has been estimated as 0.3 per 1000 by the Centers for Disease Control (Medical Task Force on Anencephaly, 1990). Female fetuses are 3-4 times more commonly affected than males (Naidich et al., 1992). There is also an increased incidence of anencephaly in Hispanic women (Feuchtbaum et al., 1999). Some of the other risk factors include maternal diabetes prior to conception and maternal obesity (Mitchell, 2005).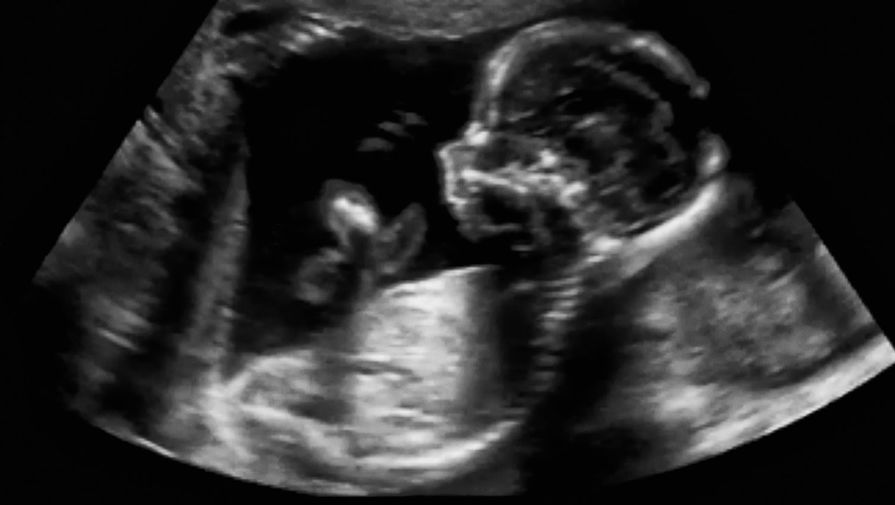 The most important environmental influence is diet. There is a well-documented protective effect of maternal folic acid supplementation starting at least 1 month prior to conception.
The most important environmental influence is diet. There is a well-documented protective effect of maternal folic acid supplementation starting at least 1 month prior to conception.
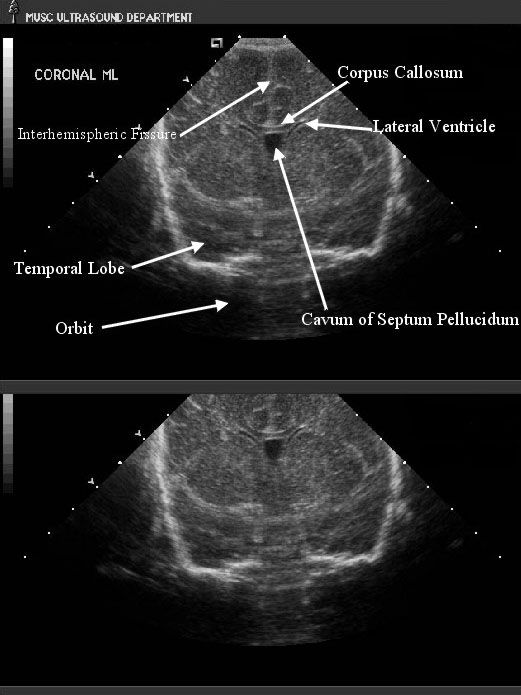
In first trimester fetuses with anencephaly, the upper portion of the brain (the cerebral hemispheres) will be in direct contact with the amniotic fluid because the skull is absent. By ultrasound, the appearance will resemble “Mickey Mouse ears.” Additionally, a measurement from the top of head to the rump (crown rump length or CRL) is significantly reduced in affected fetuses in the first trimester. In the second trimester, the upper brain portions, above the level of the eyes, will not be visible by ultrasound because they are no longer present. The ultrasound diagnosis of this condition is very accurate, particularly if the sonographer is able to directly view the fetal face. If the condition is isolated, meaning not part of a greater syndrome along with other abnormalities, these fetuses will grow at approximately the same rate as fetuses without the condition. Often, the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is significantly increased (polyhydramnios). Some fetuses with anencephaly will have other major abnormalities.
Often, the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the fetus is significantly increased (polyhydramnios). Some fetuses with anencephaly will have other major abnormalities.
The major consideration as far as other potential diagnoses is to distinguish anencephaly from the presence of tissue fibers extending from the gestational sac (amniotic bands) that effectively amputate portions of the fetus. It is important to note that the skull defect associated with anencephaly always affects both sides (symmetric). With amniotic bands, there should be evidence of other defects, such as limb (arms/legs) or digital (fingers/toes) amputations, abdominal wall defects, or spinal defects. Amniotic bands are often associated with there being little or no amniotic fluid around the fetus (oligohydramnios). In contrast, anencephaly is often associated with excess fluid (polyhydramnios).
Of those fetuses with anencephaly, a small portion will die while still in the uterus (intrauterine fetal demise or stillbirth). Approximately 25% will have excessive amniotic fluid around the fetus (polyhydramnios). Polyhydramnios may cause extra stretching of the uterus resulting in preterm contractions. Sometimes, these patients require cesarean section because the fetus is breech. These infants will die in the immediate newborn period.
Approximately 25% will have excessive amniotic fluid around the fetus (polyhydramnios). Polyhydramnios may cause extra stretching of the uterus resulting in preterm contractions. Sometimes, these patients require cesarean section because the fetus is breech. These infants will die in the immediate newborn period.
If prenatal screening is performed to detect spinal cord (neural tube) defects, the maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein level (MSAFP) will be significantly elevated in 90% of fetuses with anencephaly (Medical Task Force on Anencephaly, 1990). A detailed ultrasound examination is indicated for all patients with significantly elevated MSAFP levels. If there are no other abnormalities and the anencephaly is considered isolated, then a test to determine if there is a chromosomal abnormality may be recommended (amniocentesis). The chromosomes represent the instructions for how a fetus should form. It is quite likely that the chromosomes will be normal. Most fetuses with anencephaly deliver around 37 weeks of gestation (Melnick and Myrianthopoulos,1987). Because pregnancy with a fetus with anencephaly carries an increased medical risk for the mother, prospective parents may be offered the opportunity to terminate, especially if the diagnosis is made prior to 24 weeks of gestation. Cesarean delivery is indicated only for maternal health considerations or, perhaps, if the fetus is breech.
Most fetuses with anencephaly deliver around 37 weeks of gestation (Melnick and Myrianthopoulos,1987). Because pregnancy with a fetus with anencephaly carries an increased medical risk for the mother, prospective parents may be offered the opportunity to terminate, especially if the diagnosis is made prior to 24 weeks of gestation. Cesarean delivery is indicated only for maternal health considerations or, perhaps, if the fetus is breech.
There is no fetal intervention recommended for anencephaly.
The diagnosis of anencephaly can be confirmed on physical examination when the following criteria are met: a large portion of the skull is absent, the scalp is absent over the skull defect, and a hemorrhagic, fibrotic mass of tissue is exposed to the environment. The newborn will seem unconscious because the upper brain portions (cerebral hemispheres) are absent or not functioning. The parts that control the breathing, heartbeat and body temperature will be functional. The newborn has reflex responses to pain. Most newborns will die within the first few hours or days of life, though about 10% may live up to one week.
Most newborns will die within the first few hours or days of life, though about 10% may live up to one week.
Surgical treatment is not applicable in anencephaly.
The major issue in long-term outcome is the potential use of anencephalic fetuses or infants as organ donors. Difficulties exist, however, because of the traditional means of determining brain death for organ donors. For babies with anencephaly, the diagnosis of brain death depends on documentation of disappearance of previously existing brainstem functions (i.e., breathing or spontaneous movements), Most major organs from anencephalic infants are smaller than average for body size and have often not formed appropriately. Therefore, these organs might not be able to be donated.
A family history of spina bifida and/or anencephaly is one of the strongest risk factors for recurrence. Most cases of anencephaly have a recurrence risk of between 2% and 5% following a single case (Medical Task Force on Anencephaly, 1990).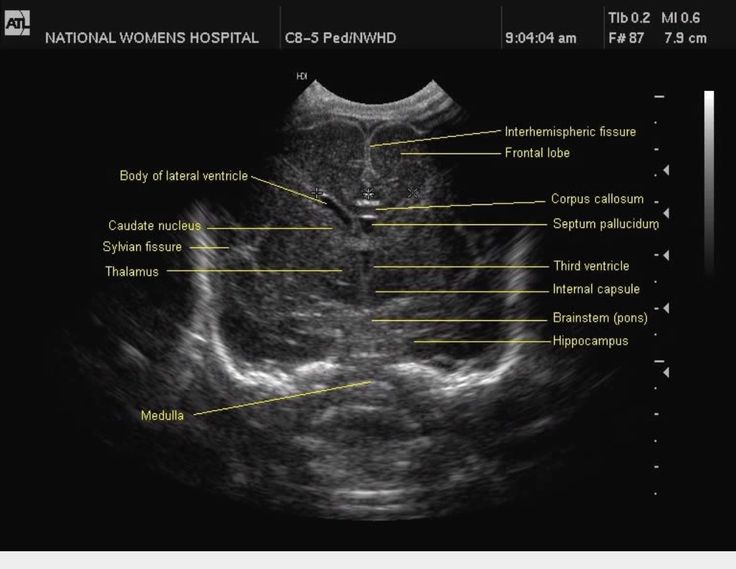 Some cases of anencephaly are associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomies 13 and 18, and triploidy. For women who have previously had a fetus or infant affected with anencephaly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends increasing the intake of folic acid to 4000 mcg (4mg) per day beginning at least 1 month prior to conception (Committee on Genetics,1999).
Some cases of anencephaly are associated with chromosomal abnormalities such as trisomies 13 and 18, and triploidy. For women who have previously had a fetus or infant affected with anencephaly, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends increasing the intake of folic acid to 4000 mcg (4mg) per day beginning at least 1 month prior to conception (Committee on Genetics,1999).
A Difficult Diagnosis
The Fetal Health Foundation was founded by parents seeking hope for a fetal diagnosis. We try to provide accurate medical information, support, and hope. In the case of a diagnosis like this, we also want to offer resources that can help parents make the most of their time with their child.
Further reading and resources:
Read the story of our board member, Aran, meeting her daughter, Brianna Marie.
Read about memorial photography work of Now I Lay Me Down To Sleep. We are grateful for these volunteers.
Wondering how you can help someone during a difficult pregnancy? We share our thoughts.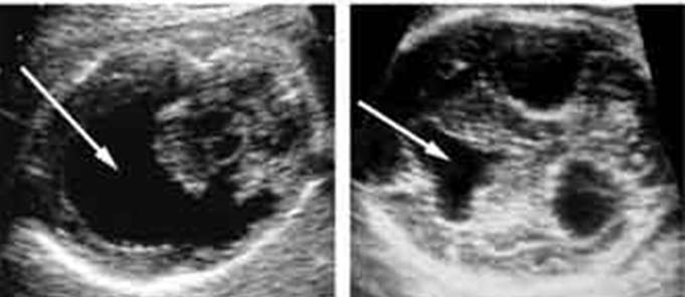
References
Chescheir N. ACOG Committee on Practice Bulletins-Obstetrics. ACOG practice bulletin. Neutral tube defects. Number 44, July 2003. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003;83:123-133.
Committee on Genetics, American Academy of Pediatrics. Folic acid for the prevention of neural tube defects. Pediatrics. 1999;104:325-327.
Feuchtbaum LB, Currier RJ, Riggle S, Roberson M, Lorey FW, Cunningham GC. Neural tube defect prevalence (1990–1994): eliciting patterns by type of defect and maternal race/ethnicity. Genet Test. 1999;3:265-272.
Goldstein RB, Filly RA. Prenatal diagnosis of anencephaly: spectrum of sonographic appearances and distinction from the amniotic band syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1988;151:547-550.
Medical Task Force on Anencephaly. The infant with anencephaly. N Engl J Med. 1990;332:669-674.
Melnick M, Myrianthopoulos NC. Studies in neural tube defects. II. Pathologic findings in a prospectively collected series of anencephalics. Am J Med Genet. 1987;26:797-810.
1987;26:797-810.
Mitchell LE. Epidemiology of neural tube defects. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2005;135C:88-94.
Naidich TP, Altman NR, Braffman BH, McLone DG, Zimmerman RA. Cephaloceles and related malformations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1992;13:655-690.
Neurosonography - what is it and why is it performed? At what age can a child have the procedure and is it safe
Unfortunately, childbirth does not always go perfectly. Approximately 80% of cases there are some problems. They can relate to both weak labor activity, and the entanglement of the baby with the umbilical cord, prolonged labor, painful attempts, etc. The difficulties that have arisen are usually eliminated without harm to the newborn and his mother. If for some reason the problems have not been eliminated and there is a possibility that the child will be injured or have congenital brain anomalies, neurosonography (NSG) is performed. nine0003
What is neurosonography?
Neurosonography of the brain is a diagnostic procedure that has been carried out relatively recently. It allows you to study the brain of a newborn using ultrasound. An NSG is carried out both in the direction of a neonatologist and for the purpose of a preventive examination. Previously, such diagnostics were carried out only in the most dangerous cases. Today neurosonography of the brain in children is prescribed almost everywhere. The technique has replaced MRI. nine0003
It allows you to study the brain of a newborn using ultrasound. An NSG is carried out both in the direction of a neonatologist and for the purpose of a preventive examination. Previously, such diagnostics were carried out only in the most dangerous cases. Today neurosonography of the brain in children is prescribed almost everywhere. The technique has replaced MRI. nine0003
Important! Magnetic resonance imaging is quite dangerous for a weakened body of babies and can provoke a number of serious complications.
Unlike MRI, neurosonography of the brain of newborns is as safe as possible. It can be carried out in the very first minutes of a baby's life. Modern diagnostics has made it possible to significantly reduce the mortality rate of newborns due to the rapid detection of brain pathologies in them.
Indications for examination
Neurosonography of newborns is performed to determine the conditions:
- Brain
- Spinal Cord
- Vessels
- Skull bones
- Scalp
- Spine
Ultrasound can detect:
- Cysts
- Bone injuries and soft tissue defects
- Tumors
Also, during the diagnosis, symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, the state of the nerves are determined, various pathologies are detected.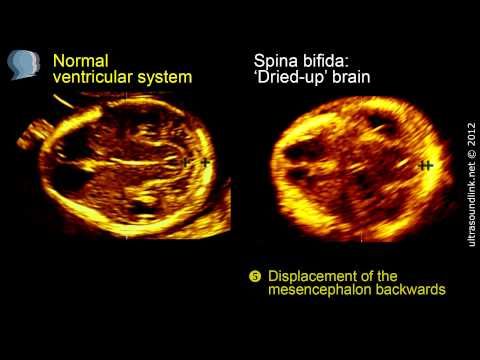 As a rule, the passage of NSG is recommended for preventive purposes.
As a rule, the passage of NSG is recommended for preventive purposes.
Neurosonography for a child can be prescribed for:
- Complicated labor activity
- Birth defects
- Genetic diseases
- Postterm pregnancy
- After caesarean section
- Birthing forceps
- Use of drugs that stimulate contractions
- Prematurity
- Intrauterine infection
- Infant skull injury
- Neonatal resuscitation
The study is conducted not only for babies in the first days of life. Neurosonography is often prescribed per month, per year. In some cases, even adult patients are diagnosed. The research method used is no longer called “neurosonography”, but “ultrasound of the brain”. The modern research method is used for injuries and during surgical interventions or after their completion. nine0003
Is the examination safe?
Neurosonography of the brain is a study that is absolutely safe. Ultrasound diagnosis is painless. In this case, the child does not need special preparation or recovery after the procedure. There are no proven facts that ultrasound examinations adversely affect the health of children in the long term. Due to this, neurosonography is performed for all babies (even those who are in intensive care cuveuses). nine0003
Ultrasound diagnosis is painless. In this case, the child does not need special preparation or recovery after the procedure. There are no proven facts that ultrasound examinations adversely affect the health of children in the long term. Due to this, neurosonography is performed for all babies (even those who are in intensive care cuveuses). nine0003
Types of neurosonography
There are several options for neurosonography. The method of execution depends on how diagnostic manipulations are carried out.
There are the following types of neurosonography:
- Through the fontanel. This procedure can only be performed on infants. It can be done until the fontanel is overgrown
- Transcranial. This procedure can be performed on children, adolescents and even adults. The examination is carried out through the bones of the skull. Usually the sensor is installed in the temple area
- Transcranial-transfontanellar. Such a study is characterized by increased accuracy and reduces the risk of diagnostic errors.
 It should be understood that this type of examination is usually the longest
It should be understood that this type of examination is usually the longest - Examination through bone defects: holes, cracks, etc. (including those performed during surgical interventions)
The choice in favor of this or that type of research is made by the doctor. This choice depends on the age of the patient, his individual characteristics, methods of diagnosis and its goals. nine0003
Procedure details
The main feature of the procedure is that it can only be performed through the cracks of the skull. This is due to the fact that ultrasonic waves do not pass through the strengthened bones. This makes it easier to perform newborn examinations.
Neurosonography is an effective technique that has no contraindications.
Its advantages also include:
- Non-invasive - no need to damage the skin and tissues
- Fast conduction (typically 15-20 minutes)
- Accuracy of the results obtained
- Minimal risk of errors during examination
- Wide range of indications
Neurosonography allows you to confirm or refute the alleged diagnosis, correct the treatment, reveal hidden pathologies that cannot be detected by other examinations.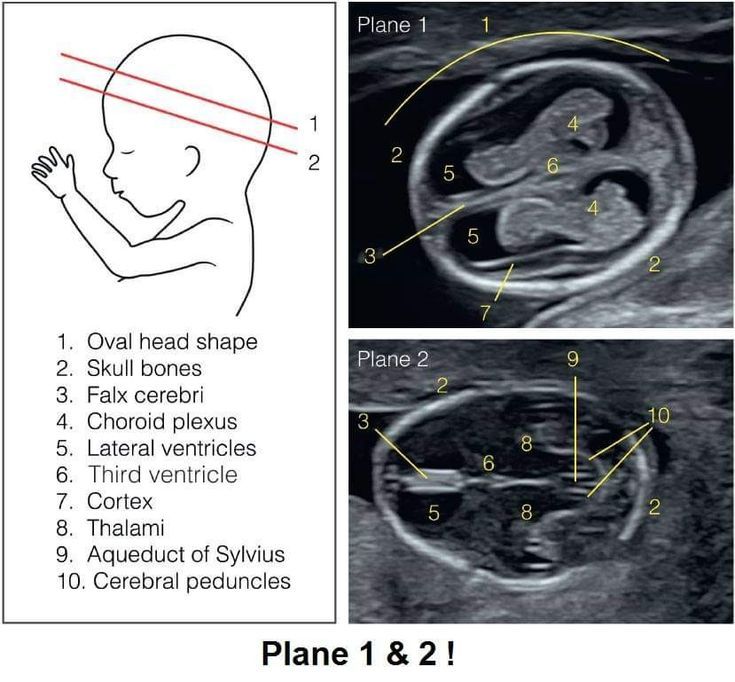 At the same time, the technique is simple to implement and accessible to many. nine0003
At the same time, the technique is simple to implement and accessible to many. nine0003
How is it carried out?
The examination is carried out using a standard ultrasound machine.
To carry out the examination, it is necessary to remove a hat or other headgear, hairpins, bows, etc. from the head. It is most convenient to hold the child in your arms. So the baby will calm down and will not make unnecessary movements during the procedure. The doctor will apply a special gel to the area of study (it is absolutely safe and does not cause allergic reactions), which improves the conductivity of ultrasound. After that, the specialist will perform a direct diagnosis. He will drive the sensor along the head, but these movements will not cause discomfort in the baby. On the monitor, the specialist will see a dynamic image of all internal structures. nine0003
Upon completion of the examination, you will receive a conclusion about the state of the brain and tissues. For interpretation of the results obtained, you should contact the doctor who is observing your child or gave a referral for neurosonography.
For interpretation of the results obtained, you should contact the doctor who is observing your child or gave a referral for neurosonography.
Do I need to prepare for a diagnosis?
The procedure does not require additional preparation.
Mom or another person who came to the examination with the baby should:
- Pre-feed the baby. So the baby will be as calm as possible
- Stay close to the little patient all the time, if necessary, entertain him with his favorite toys. If the child is relaxed, the study will be as accurate and reliable as possible
- Try to avoid sudden movements of the crumbs
No additional recommendations are issued. You do not need to somehow feed the child in a special way or limit his fluid intake. The study is no different from a traditional ultrasound. nine0003
Explanation of study indicators
A specialist should decipher the results of the study. This is due to the fact that when evaluating all indicators, the doctor focuses on the weight of the child and his other individual characteristics, already identified pathologies and past diseases.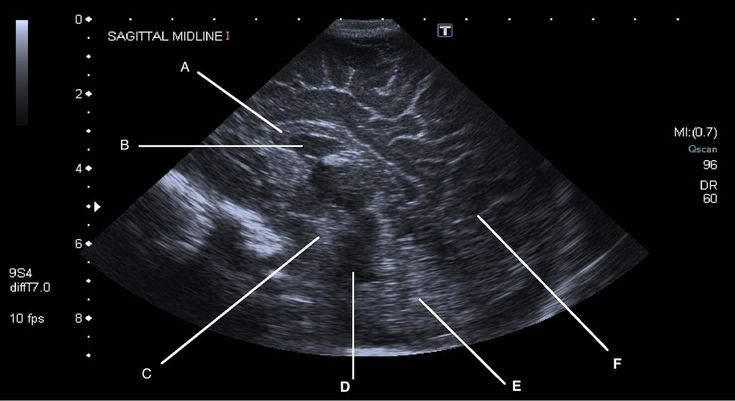 It should also be noted that in newborns, in almost 70% of cases, some abnormalities in the development of the brain are found. They are not critical and do not speak of dangerous pathological conditions. During the first year of life, all indicators usually return to normal. This has no negative consequences for the health of the crumbs. As a rule, small deviations become the reason for regular monitoring of the baby's condition. The doctor will inform you about the need (if it is detected) for constant monitoring. nine0003
It should also be noted that in newborns, in almost 70% of cases, some abnormalities in the development of the brain are found. They are not critical and do not speak of dangerous pathological conditions. During the first year of life, all indicators usually return to normal. This has no negative consequences for the health of the crumbs. As a rule, small deviations become the reason for regular monitoring of the baby's condition. The doctor will inform you about the need (if it is detected) for constant monitoring. nine0003
When deciphering the indicators of the study, attention is paid to such important parameters as:
- Structure of the cerebellum
- Structure of the cerebral hemispheres
- Presence/absence of neoplasms
- Pathological conditions
- Features of intracranial fluid
Standards and deviations of indicators
In the study protocol, the doctor indicates:
- The shape of the brain tissue (symmetrical or asymmetric).
 In the absence of deviations from the norm, the brain tissues have an absolutely symmetrical structure
In the absence of deviations from the norm, the brain tissues have an absolutely symmetrical structure - Visualization of the sulci and convolutions of the brain
- Absence/presence of inclusions in the ventricles of the brain. Normally, these departments are homogeneous and exactly the same
- The shape of the cerebellum. Normally, it is symmetrical and trapezoid
- Absence/presence of fluid between the two hemispheres. Normally, no fluid is detected, and the vascular plexuses have a homogeneous structure
Important! The doctor will definitely tell you about deviations from the norm. He will also explain all the results of the survey. Do not try to decrypt yourself. To a non-specialist, all the figures and various descriptions are completely incomprehensible. In addition, there are differences in performance, depending on the age of the small patient. nine0003
Where is the diagnosis carried out?
Neurosonography is a diagnostic that is carried out today in all major perinatal centers. It is carried out free of charge immediately after the birth of the baby (if indicated). For preventive purposes, the study is carried out only on a paid basis. The price of neurosonography of the brain of newborns and other patients depends on a number of factors. You can always check it in advance.
It is carried out free of charge immediately after the birth of the baby (if indicated). For preventive purposes, the study is carried out only on a paid basis. The price of neurosonography of the brain of newborns and other patients depends on a number of factors. You can always check it in advance.
Important! Paid diagnostics should be carried out only in well-known medical institutions with modern equipment. It is very important to clarify in advance who is conducting the research. The doctor must have all the necessary professional knowledge and skills. nine0003
Benefits of diagnostics at MEDSI
- Highly qualified doctors. The study is carried out by a specialist with the necessary knowledge and skills, in accordance with the established medical protocol
- No queues. You do not have to disturb and worry the baby
- New generation ultrasound systems. Expert-class equipment is used for the study. It meets WHO requirements for accuracy and safety
- High speed and quality.
 The study is carried out as quickly as possible. This eliminates the risks of discomfort in the baby
The study is carried out as quickly as possible. This eliminates the risks of discomfort in the baby - Instant issuance of a conclusion. You don't have to wait for additional processing
- Comfortable conditions. Neurosonography in Moscow in our clinics is carried out in modern rooms. They are comfortable both for the little patient and for his parents or other accompanying persons
To sign up for the study, just call +7 (495) 7-800-500. The specialist will announce the exact cost of the diagnosis and tell you how it is carried out in our clinic.
reasons for brainlessness in the fetus
Anencephaly is an intrauterine anomaly of development, which is characterized by underdevelopment of the cerebral hemispheres, the absence of part of the head and cranial bones (acrania). As a result, the child develops severe malformations: the absence of a brain often leads to the death of the fetus before birth.
Anencephaly in a child: causes of the defect
Anencephaly develops in the fetus during the laying of neurostructures. The exact causes that lead to the abnormal structure of the brain have not been established to this day. Therefore, doctors agree that the disease is caused by multifactorial causes. The main teratogenic factors that lead to the fact that a child is born without a brain include:
The exact causes that lead to the abnormal structure of the brain have not been established to this day. Therefore, doctors agree that the disease is caused by multifactorial causes. The main teratogenic factors that lead to the fact that a child is born without a brain include:
- Toxic effects in early pregnancy. Anomalies and malformations of the central nervous system, in particular, the development of cerebral anencephaly, are caused by heavy metal salts, chemical emissions into the environment, as well as the use of drugs that are prescribed to patients to relieve the symptoms of diabetes mellitus. Alcohol, narcotic substances, and tobacco tar have a pronounced negative effect on the development of the embryo. nine0018
- Infectious diseases. At the stage of embryological development, infection with cytomegalovirus, toxoplasmosis, rubella is extremely dangerous. It is believed that anencephaly in the fetus is formed if the infection occurred before the 28th day of its intrauterine development.
- Radiation. Ionizing radiation often acts as a cause of anencephaly in a child. Isotopes damage the fetal genome. The situation is aggravated by the fact that when exposed to radiation, additional toxic reactions are provoked in the body, which will certainly affect the embryo. nine0018
Anencephaly in a child can also be caused by hereditary factors. For example, if the parents have genetic mutations. The risk of brain defects in a newborn increases with related marriages, incest, and beriberi in the mother. The risk group for the birth of a child without a brain includes women who have a history of extragenital pathologies: hypothyroidism, heart failure, diabetes mellitus. Severe gestation can affect brain development. nine0003
The first place - about 25% of all cases among the malformations of the central nervous system in the fetus belongs to anencephaly. The disease is more diagnosed in female embryos. If a woman has a baby born without a brain, then the risk of recurrence of anencephaly in the next baby is 5%.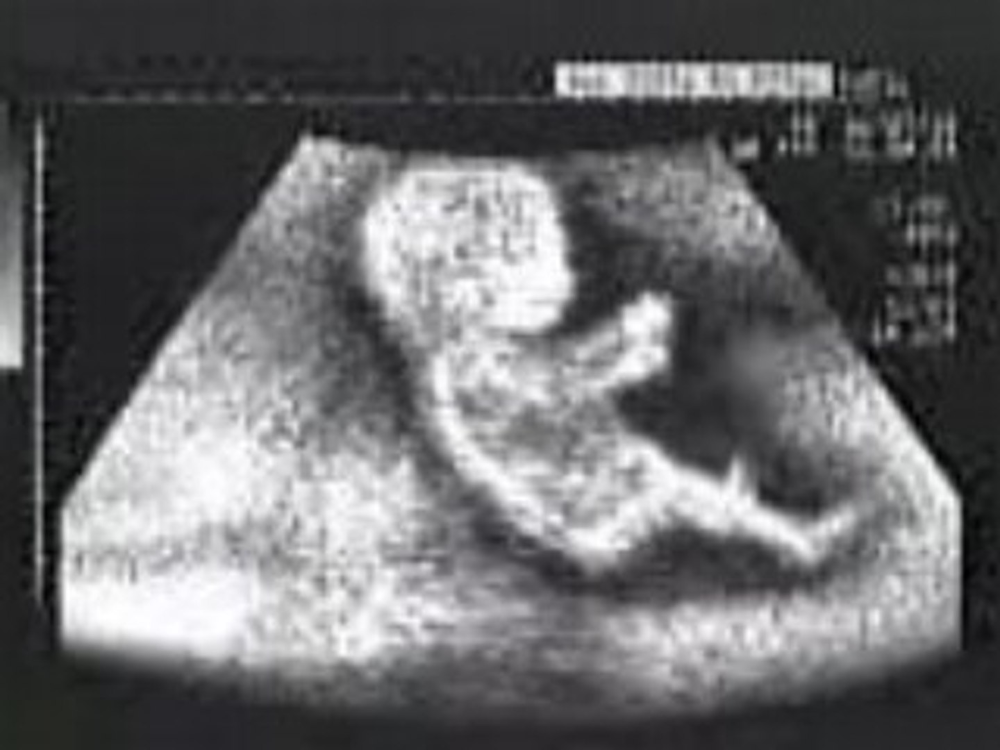
Symptoms of cerebral anencephaly
If a baby is born without a brain, then the following symptoms indicate its disease:
nine0016After birth, children are unconscious. They are completely deaf and blind. If you act on them with external stimuli, then the receptors do not respond to signals. In most cases, such newborns are diagnosed with additional defects: cleft palate, anomalies in the development of the adrenal glands, spinal hernia. nine0003
Anencephaly diagnostics
Children born without a brain are doomed to die. In 100% of cases, such patients are fatal, since the defects in this diagnosis are not compatible with life. You can detect an anomaly in the development of the brain as part of the passage of pregnancy screening.
Important! Anencephaly is an absolute indication for termination of pregnancy. Abortion is recommended for all women, regardless of their gestational age. Therefore, it is so important to undergo ultrasound examinations in the early stages of pregnancy - the detection of abnormal fetal development with further interruption reduces the risks to the health and life of a woman in the event of natural fetal death. nine0003
To confirm the diagnosis of anencephaly, several medical methods are used:
- prenatal screening. As part of the ultrasound, the doctor can see the irregular shape of the brain, the absence of full-fledged musculoskeletal structures of the skull. Visualization also reveals the absence of cerebral hemispheres.
- Fetal MRI. If the ultrasound picture worries the doctor, then he recommends an additional examination to determine the degree of brain development and possible anencephaly. Magnetic resonance imaging is performed for women from 14-15 weeks of pregnancy.
 Using a tomograph, you can clarify the anatomical features of the brain, the structure of the skull and other parts of the body. nine0018
Using a tomograph, you can clarify the anatomical features of the brain, the structure of the skull and other parts of the body. nine0018 - Amniocentesis. This invasive technique is used to detect chromosomal and gene mutations. During the study, amniotic fluid is taken through the puncture of the uterus, after which their biochemical parameters are determined.
- Biochemical screening. In the first trimester, a marker of anencephaly and other mutations is changes in blood biochemistry, in particular, an increase in the level of hCG or alpha-fetoprotein, as well as a decrease in the concentration of protein-A. nine0018
Book an online consultation if your doctor suspects anencephaly based on the results of instrumental diagnostics. Our neurologists compare the data in order to differentiate the diagnosis from other syndromic diseases, they will talk about the risks of giving birth to anencephalos, their state of health and other nuances. You can get advice around the clock.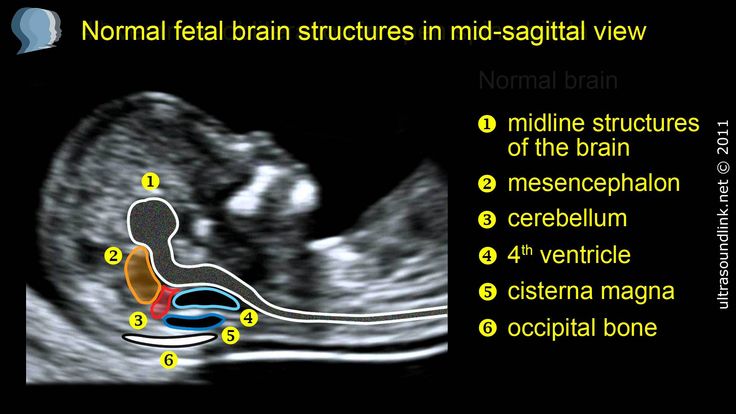
If a woman makes the final decision to have an abortion, then an additional examination of the pregnant woman is necessary. In addition to a gynecological examination, you should take a KLA, as well as blood for HIV, hepatitis, syphilis. In the future, when planning a pregnancy, a consultation with a geneticist will be required, who will assess the risks of having a baby with an abnormal development of the brain. nine0003
Treatment of anencephaly
Despite the fact that people cannot live without a brain, many parents refuse to terminate a pregnancy. Therefore, the question becomes objective, what kind of medical care is provided to live-born children. Neonatologists do everything to make the short-term life of a newborn less painful and painful.
Palliative care for anencephaly includes:
- Respiratory support - in children with malformations, normal tissue oxygenation is impossible, so they are shown mechanical ventilation.
 Without a ventilator, the baby will die immediately after birth. nine0018
Without a ventilator, the baby will die immediately after birth. nine0018 - Nutritional help. To maintain the viability of the body, patients are prescribed parenteral nutrition, which includes glucose and an amino acid mixture.
Indispensable at this stage is the psychological support of parents who may not be able to cope with this test on their own. The psychotherapist allows a woman to get rid of suicidal thoughts, depression, apathy and guilt.
nine0239 Example.
Tatyana and Sergey found out about the pregnancy, at the first screening a defect in the development of the cerebral hemispheres was discovered. To clarify the diagnosis, they were referred for a consultation with a geneticist with further amniocentesis. After analysis of amniotic fluid, the malformation was confirmed. At the prenatal consultation, a decision was made to terminate the pregnancy medically.
FAQ
How long do children with anacephaly live? nine0003
+
The prognosis for anencephaly is unfavorable.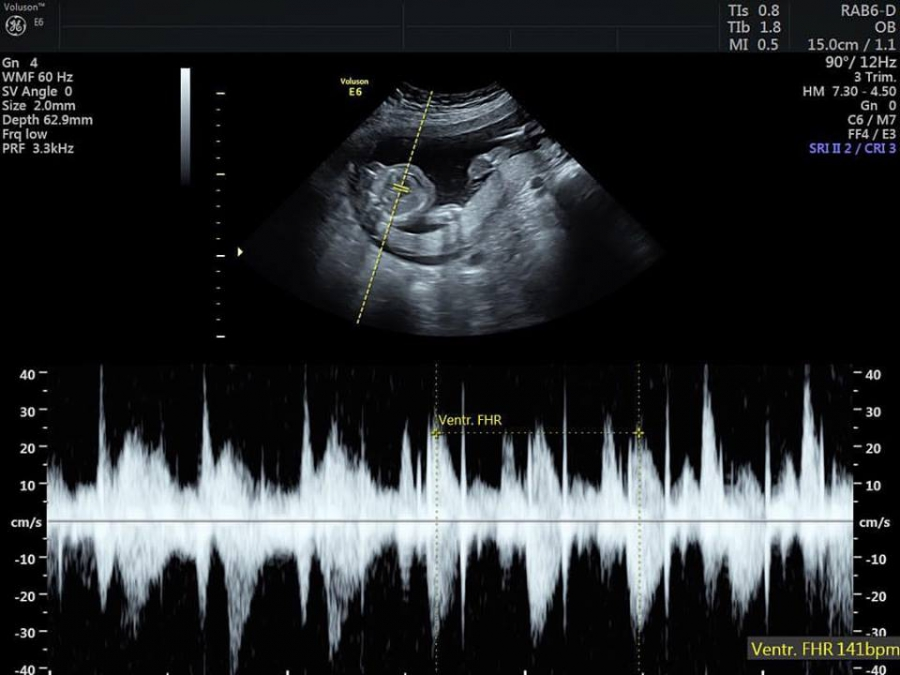 Prenatal fetal death occurs in 7% of cases. Approximately 20% of children die during childbirth. 50% of live-born children die in the first day of life. Only 23% of anaecephals live more than 1 day. Only 3 medical cases have been recorded in history, when a newborn, in the absence of a brain, could live for more than 2 years.
Prenatal fetal death occurs in 7% of cases. Approximately 20% of children die during childbirth. 50% of live-born children die in the first day of life. Only 23% of anaecephals live more than 1 day. Only 3 medical cases have been recorded in history, when a newborn, in the absence of a brain, could live for more than 2 years.
Is anencephaly dangerous for the health of the mother?
+
The disease itself does not directly affect the well-being or health of a woman. The danger to the mother arises only if a miscarriage occurs. As a result of the decomposition of the fetus, mummification, the body is poisoned by decay products, which causes symptoms of intoxication.
How are children born with anencephaly?
+
During childbirth, certain difficulties may arise. For example, a woman may not be in labor because the child's adrenal and pituitary glands do not produce the hormones that cause contractions. Therefore, in most cases, births are caused by doctors. At the same time, it is important that the amniotic sac is not damaged - due to the lack of a full-fledged head, there is no proper pressure on the tissues, so the cervix does not expand. If there is an opportunity to save water, then the duration of the birth process is comparable to the duration of ordinary childbirth. nine0003
Therefore, in most cases, births are caused by doctors. At the same time, it is important that the amniotic sac is not damaged - due to the lack of a full-fledged head, there is no proper pressure on the tissues, so the cervix does not expand. If there is an opportunity to save water, then the duration of the birth process is comparable to the duration of ordinary childbirth. nine0003
Are there measures to prevent CNS malformations?
+
According to recent studies, it is possible to reduce the risk of defects if a woman takes 0.4 mg of folic acid daily in the process of preparing for pregnancy and during the first trimester of gestation. Potential cases of anencephaly were prevented in 50-70% of cases. And, of course, during pregnancy, exposure to teratogenic factors should be avoided. nine0003
Expert opinion
Anencephaly is a malformation of the brain that inevitably leads to the death of a newborn. However, do not despair - the possibility of having a second baby with no brain, although it exists, is unlikely.