Types of rashes that itch
22 Common Skin Rashes, Pictures, Causes & Treatment
A rash is any area of irritated or swollen skin on your body. Rashes are often itchy and painful and can appear differently on different skin tones. While they are often described as red, on darker skin tones they may be purple, gray, or white.
There are many different causes of rashes. Here’s a list of 22 potential causes with pictures.
Warning: graphic images ahead.
Fleabites
Share on PinterestFlea bites of the lower leg causing red bumps and scabbing. Angela Hampton Picture Library / Alamy Stock Photo
- usually located in clusters on the lower legs and feet
- itchy, small red bumps on lighter skin tones, and more plum-like in color on darker skin tones
- symptoms begin immediately after being bitten
Read the full article on fleabites.
Fifth disease
Share on PinterestFifth disease is a viral illness caused by parvovirus, which can cause a ‘slapped cheek’ rash. Kardelen Yang?n Via Wikipedia
- symptoms include headache, fatigue, low fever, sore throat, runny nose, diarrhea, and nausea
- children are more likely than adults to experience a rash
- round, bright red rash on the cheeks, but it may be less noticeable on darker skin tones
- usually after the face rash, a lacy-patterned rash may appear on the arms, legs, and upper body and might be more visible after a hot shower or bath
Read the full article on fifth disease.
Rosacea
Share on PinterestWeinkle, A. P., Doktor, V., & Emer, J. (2015). Update on the management of rosacea. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 8, 159177. https://doi.org/10.2147/CCID.S58940
- chronic (long-term) skin disease that goes through cycles of fading and relapse
- relapses may be triggered by spicy foods, alcoholic beverages, sunlight, stress, and the intestinal bacteria Helicobacter pylori
- the four subtypes of rosacea encompass a wide variety of symptoms
- common symptoms include facial flushing, raised red bumps, facial redness, skin dryness, and skin sensitivity
- on darker skin tones, brown or yellowish-brown bumps may appear, and the rash can have a dusky coloration
Read the full article on rosacea.
Impetigo
Share on PinterestThis image also depicts impetigo on dark skin. Photography courtesy of Grook Da Oger/Wikimedia
- most common in children 2 to 5 years old, but can happen at any age
- often located in the area around the mouth, chin, and nose
- irritating rash and fluid-filled blisters that pop easily and form a honey-colored crust
- can also appear brown, purple, or gray on darker skin tones
Read the full article on impetigo.
Ringworm
Share on PinterestRingworm on the face of a child. BSIP SA / Alamy Stock Photo
- itchy, circular scaly patches with raised borders
- on lighter skin tones, the patches can appear pink or red
- on darker skin tones, the patches can appear gray or brown
- skin in the middle of the ring appears clearer, and the edges of the ring may spread outward
Read the full article on ringworm.
Contact dermatitis
Share on PinterestContact dermatitis of the arm. vvoe/Shutterstock
vvoe/Shutterstock
- appears hours to days after contact with an allergen
- has visible borders and typically appears where your skin touched the irritating substance
- on lighter skin tones, it can appear red
- on darker skin tones, it may be less noticeable
- may have blisters that weep, ooze, or become crusty
- typically itchy, scaly, or raw
Read the full article on contact dermatitis.
Allergic eczema
Share on PinterestDmitriy SIMAKOV/Getty Images
- may resemble a burn
- often found on hands and forearms
- skin is itchy, scaly, or raw
- may have blisters that weep, ooze, or become crusty
- on lighter skin tones, it can appear red
- on darker skin tones, it can cause darker brown, purple, or gray patches
Read the full article on allergic eczema.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease
Share on PinterestHand-foot-and-mouth disease MidgleyDJ at en.wikipedia, CC BY-SA 3. 0, via Wikimedia Commons
0, via Wikimedia Commons
- usually affects children under age 5
- painful, red blisters in the mouth and on the tongue and gums
- flat or raised red spots located on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- on darker skin tones, it can be skin-colored or grayish-brown
- spots may also appear on the buttocks or genital area
Read the full article on hand, foot, and mouth disease.
Diaper rash
Share on Pinterest
- located on areas that have contact with a diaper
- skin looks red, wet, and slightly lighter or darker than typical skin color
- may be warm to the touch
Read the full article on diaper rash.
Eczema
Share on PinterestBenislav/Shuttertstock
- dry, rough, flaky, inflamed, and irritated skin
- affected areas may be red and itchy
- hair loss may occur in the area with the rash
- on darker skin tones, it can appear as darker brown or gray patches
Read the full article on eczema.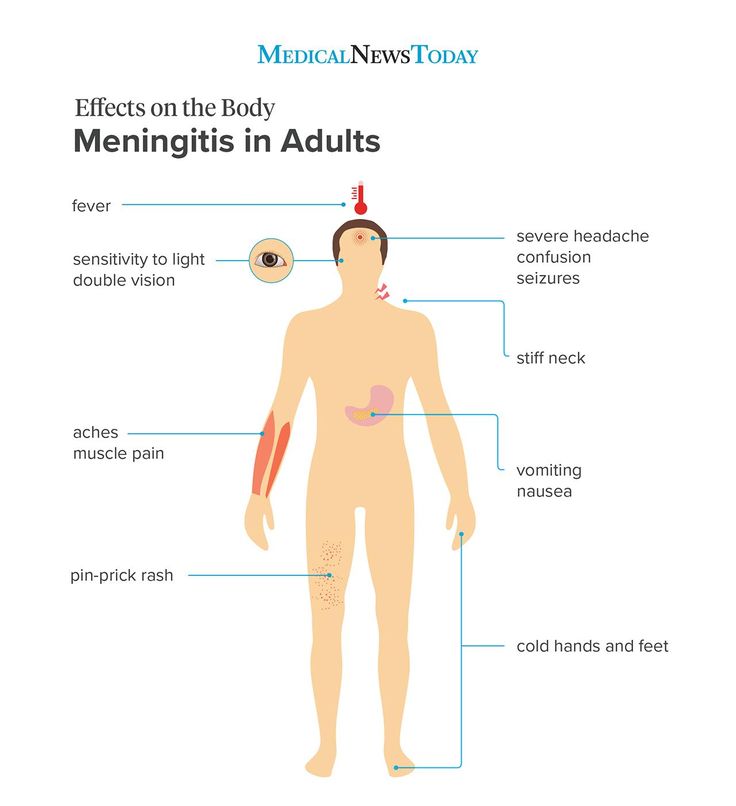
Psoriasis
Share on PinterestPsoriasis is an inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, scaly plaques on the skin. It is immune system mediated, and genetics likely also play a role. Vitek2808/Shutterstock
- scaly, silvery, sharply defined skin patches
- on darker skin tones, it may look darker than the surrounding skin or it might appear purple
- commonly located on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back
- may be itchy or asymptomatic
Read the full article on psoriasis.
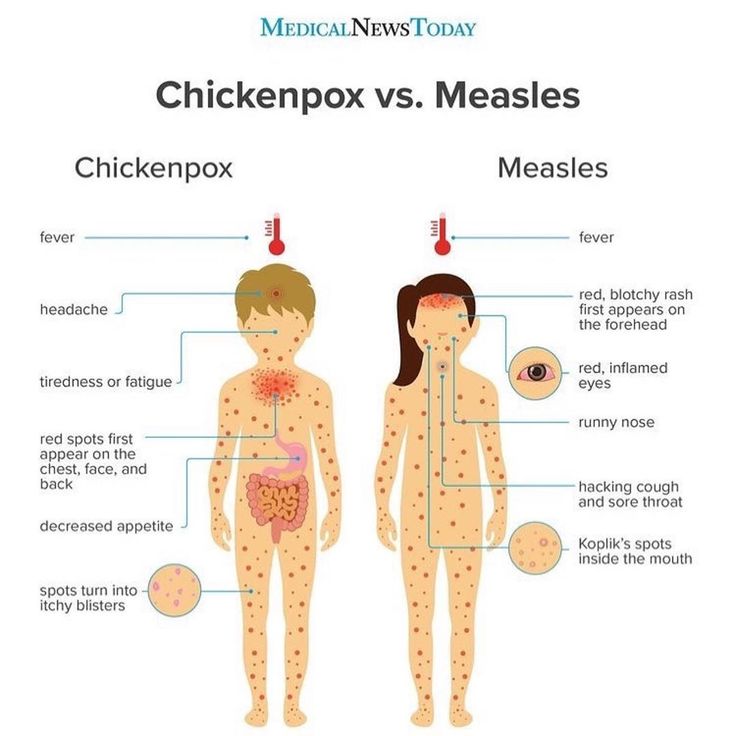
Chickenpox
Share on PinterestChild with chickenpox Grook da oger, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- clusters of itchy, red, fluid-filled blisters in various stages of healing all over the body
- on darker skin tones, it can be red, the same as the natural skin tone, or a little darker; scabs can appear gray
- rash is accompanied by fever, body aches, sore throat, and loss of appetite
- remains contagious until all blisters have crusted over
Read the full article on chickenpox.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
Share on Pinterestbutterfly rash.SLE systemic lupus erythematosus
- an autoimmune disease that displays a wide variety of symptoms and affects many body systems and organs
- a wide array of skin and mucous membrane symptoms that range from rashes to ulcers
- classic butterfly-shaped face rash that crosses from cheek to cheek over the nose
- can appear bright red on lighter skin tones
- on darker skin tones, it may appear red, brown, or darker than the original skin color
- rashes may appear or get worse with sun exposure
Read the full article on systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Share on Pinterestchatuphot/Shutterstock
- painful rash that may burn, tingle, or itch, even if there are no blisters present
- clusters of fluid-filled blisters that break easily and weep fluid
- rash emerges in a band-like pattern that appears most commonly on the torso, but may occur on other parts of the body, including the face
- may be accompanied by low fever, chills, headache, or fatigue
Read the full article on shingles.
Cellulitis
Share on PinterestCellulitis of the lower legs. TisforThan/Shutterstock
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- caused by bacteria or fungi entering through a crack or cut in the skin
- tends to be red or pink
- it may appear less obvious on darker skin tones and can also look brown, gray, or purple
- painful, swollen skin with or without oozing that spreads quickly
- hot and tender to the touch
- might be a sign of serious infection requiring medical attention
Read the full article on cellulitis.
Drug allergy
Share on Pinterest
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- mild to severe itchy, red rash may occur days to weeks after taking a drug
- severe drug allergies can be life threatening, and symptoms include rash, blisters, hives, racing heart, swelling, itching, and difficulty breathing
- other symptoms include fever, stomach upset, and tiny purple or red dots on the skin
Read the full article on drug allergies.
Scabies
Share on PinterestScabies is an itchy skin infestation with mites. Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
- symptoms may take 2 to 5 weeks to appear
- extremely itchy rash with small bumps that may be scaly
- raised, white, or flesh-toned lines
Read the full article on scabies.
Measles
Share on PinterestMeasles on the torso of a child phichet chaiyabin/Shutterstock
- symptoms include fever, sore throat, red watery eyes, loss of appetite, cough, and runny nose
- depending on skin tone, the rash may be red, skin-colored, or darker than the natural skin color
- the rash spreads from the face down the body 3 to 5 days after first symptoms appear
- tiny white spots with bluish-white centers on a red background can appear inside the mouth
Read the full article on measles.
Tick bite
Share on PinterestAitor Diago/Getty Images
- painless and causes only minor signs and symptoms, such as a change in skin color, swelling, or a sore on the skin
- rash, burning sensation, or blisters
- difficulty breathing, which requires immediate medical attention
- the tick often remains attached to the skin for a long time
- bites rarely appear in groups
- may look like a target, circular, expanding — 70 to 80 percent of people with Lyme disease will have this rash
Read the full article on tick bites.
Seborrheic eczema
Share on PinterestZay Nyi Nyi/Shutterstock
- yellow or white scaly patches that flake off
- affected areas may be red — though they may appear faint on darker skin tones —, itchy, greasy, yellowish or white patches
- hair loss may occur in the rash area
Read the full article on seborrheic eczema.
Scarlet fever
Share on PinterestChild with scarlet fever rash and rosy cheeks badobadop, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
- occurs at the same time as or right after a strep throat infection
- rash is made up of tiny bumps that make it feel like “sandpaper”
- bright red tongue
- people with lighter skin tones can have a bright red rash all over the body (but not on the palms of your hands and soles of your feet)
- on people with darker skin tones, it may be more difficult to see the rash, but their skin will have a sandpaper-like texture
Read the full article on scarlet fever.
Kawasaki disease
Share on Pinterest
This condition is considered a medical emergency. Urgent care is required.
- usually affects children under age 5
- red cracked lips, swollen tongue (strawberry tongue), high fever, swollen red palms and soles of the feet, swollen lymph nodes, bloodshot eyes
- can be harder to recognize on darker skin tones
- may cause severe heart problems
Read the full article on Kawasaki disease.
Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is one of the most common causes of rashes. This type of rash occurs when the skin comes into direct contact with a foreign substance that causes an adverse reaction, leading to a rash. The resulting rash may be itchy, red, or inflamed.
Possible causes of contact dermatitis include:
- beauty products
- soaps
- laundry detergent
- dyes in clothing
- chemicals in rubber, elastic, or latex
- poisonous plants, such as poison oak, poison ivy, or poison sumac
Medications
Taking medications may also cause rashes. They can form as a result of:
They can form as a result of:
- an allergic reaction to the medication
- a side effect of the medication
- photosensitivity from the medication
Other causes
Other possible causes of rashes include the following:
- A rash can sometimes develop in the area of a bug bite, such as a fleabite. Tick bites are of particular concern because they can transmit disease.
- Atopic dermatitis, the most common form of eczema, is a rash that may be more common in people with asthma or allergies. The rash is often reddish, though it can be skin-colored or darker on people with darker skin tones. It can be itchy with a scaly texture.
- Psoriasis is a common skin condition that can cause a scaly, itchy, red, or purplish rash to form along the scalp, elbows, and joints.
- Seborrheic eczema is a type of eczema that most often affects the scalp and causes redness, scaly patches, and dandruff. It can also occur on the ears, brows, or nose. When babies have it, it’s known as cradle cap.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune disease that can trigger a rash on the cheeks and nose. This rash is known as a “butterfly,” or malar, rash.
- Rosacea is a chronic skin condition of unknown cause. There are several types of rosacea, but all are characterized by redness and rash on the face.
- Ringworm is a fungal infection that causes a distinctive ring-shaped rash. The same fungus that causes ringworm on the body and the scalp also causes jock itch and athlete’s foot.
- Diaper rash is a common skin irritation in infants and toddlers. It can be associated with prolonged exposure to a wet diaper.
- Scabies is an infestation by tiny mites that live on and burrow into your skin. It causes a bumpy, itchy rash.
- Cellulitis is a bacterial infection of the skin. It usually appears as a red, swollen area that is painful and tender to the touch. If left untreated, the infection causing the cellulitis can spread and become life threatening.
Causes of rashes in children
Children are particularly prone to rashes that develop as a result of illnesses:
- Chickenpox is caused by a virus, and the rash is characterized by small itchy bumps and blisters that form all over the body.
- Measles is a viral respiratory infection that causes a widespread rash consisting of itchy, red bumps.
- Scarlet fever is an infection due to group A Streptococcus bacteria that produces a toxin, causing a bright red or skin-tone-colored, sandpaper-like rash.
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral infection that can cause red lesions on the mouth and a rash on the hands and feet.
- Fifth disease is a viral infection that causes a red, flat rash on the torso, arms, and legs.
- Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious illness that triggers a rash and fever in the early stages and can lead to heart complications.
- Impetigo is a contagious bacterial infection that causes an itchy, crusty rash and yellow, fluid-filled sores on the affected area, such as the face, neck, or hands.
You can treat most contact rashes, but it depends on the cause. Follow these guidelines to help ease discomfort and speed up the healing process:
- Use mild, gentle cleansers instead of scented bar soaps.
- Use warm water instead of hot water for washing your skin and hair.
- Pat the rash dry instead of rubbing it.
- Let the rash breathe. If it’s possible, avoid covering it with clothing.
- Stop using new cosmetics or lotions that may have triggered the rash.
- Apply unscented moisturizing lotion to areas affected by eczema.
- Avoid scratching the rash because doing so can make it worse and could lead to infection.
- Apply an over-the-counter (OTC) hydrocortisone cream to the affected area if the rash is very itchy and causing discomfort. Calamine lotion can also help relieve rashes from chickenpox, poison ivy, or poison oak.
- Take an oatmeal bath. This can soothe the itchiness associated with rashes from eczema or psoriasis. Here’s how to make an oatmeal bath.
- Wash your hair and scalp regularly with dandruff shampoo if you have dandruff along with a rash. Medicated dandruff shampoo is commonly available at drugstores, but your doctor can prescribe stronger types if you need them.
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications
Talk with a healthcare professional, who may recommend OTC medication like ibuprofen or acetaminophen to treat mild pain associated with the rash.
Avoid taking these medications for an extended period because they can have side effects. Ask a healthcare professional how long it’s safe for you to take them. You may not be able to take them if you have liver or kidney disease or a history of stomach ulcers.
Call a healthcare professional if the rash doesn’t go away with home remedies. You should also contact them if you’re experiencing other symptoms in addition to your rash and you suspect you have an illness.
If you don’t already have a physician, you can use the Healthline FindCare tool to find a professional near you.
Go to the hospital immediately if you experience a rash along with any of the following symptoms:
- increasing pain or discoloration in the rash area
- tightness or itchiness in the throat
- difficulty breathing
- swelling of the face or limbs
- fever of 100.
 4°F (38°C) or higher
4°F (38°C) or higher - confusion
- dizziness
- severe head or neck pain
- repeated vomiting or diarrhea
Contact a healthcare professional if you have a rash as well as other systemic symptoms, including:
- joint pain
- a sore throat
- red streaks or tender areas near the rash
- a recent tick bite or animal bite
Your healthcare professional will perform a physical exam and inspect your rash. Expect to answer questions about your:
- rash
- medical history
- diet
- recent use of products or medications
- hygiene
Your healthcare professional may also:
- take your temperature
- order tests, such as an allergy test or complete blood count
- perform a skin biopsy, which involves taking a small sample of skin tissue for analysis
- refer you to a specialist, such as a dermatologist, for further evaluation
Your healthcare professional may also prescribe medication or medicated lotion to relieve your rash. Most people can treat their rashes effectively with medical treatments and home care.
Most people can treat their rashes effectively with medical treatments and home care.
Follow these tips if you have a rash:
- Use home remedies to soothe mild contact rashes.
- Identify potential triggers for the rash and avoid them as much as possible.
- Call a healthcare professional if the rash doesn’t go away with home treatments. You should also contact them if you’re experiencing other symptoms in addition to your rash and you suspect you have an illness.
- Carefully follow any treatments your doctor prescribes. Speak with a healthcare professional if your rash persists or gets worse despite treatment.
Healthline and our partners may receive a portion of revenues if you make a purchase using a link above.
Read the article in Spanish.
Contact Dermatitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Here’s our process.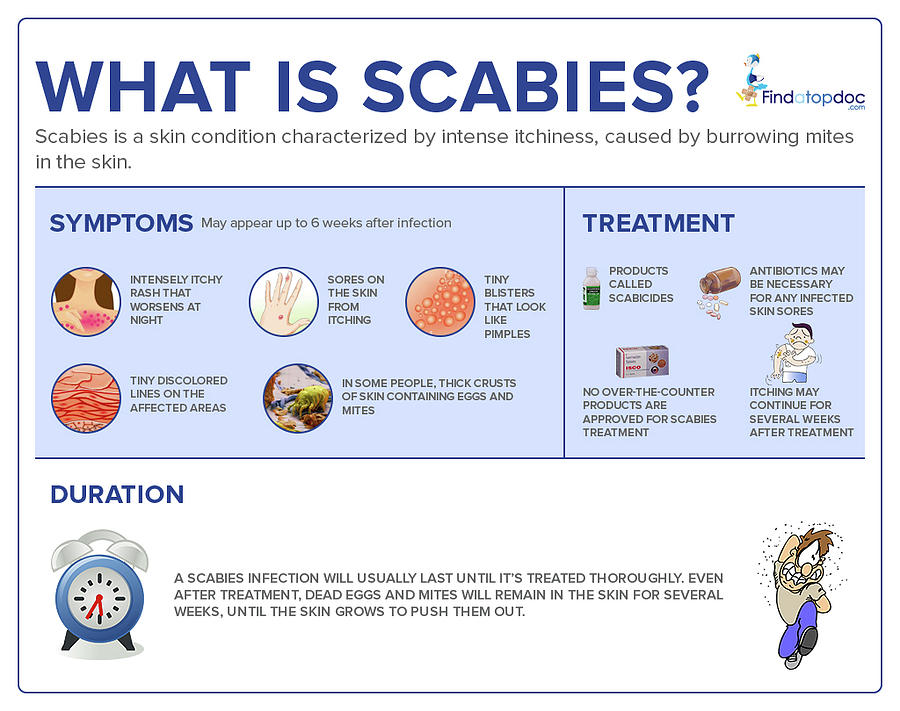
Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind.
Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we:
- Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
- Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence?
- Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process.Overview
Have you ever used a new type of skin care product or detergent, only to have your skin become red and irritated? If so, you may have experienced contact dermatitis. This condition occurs when chemicals you come into contact with cause a reaction.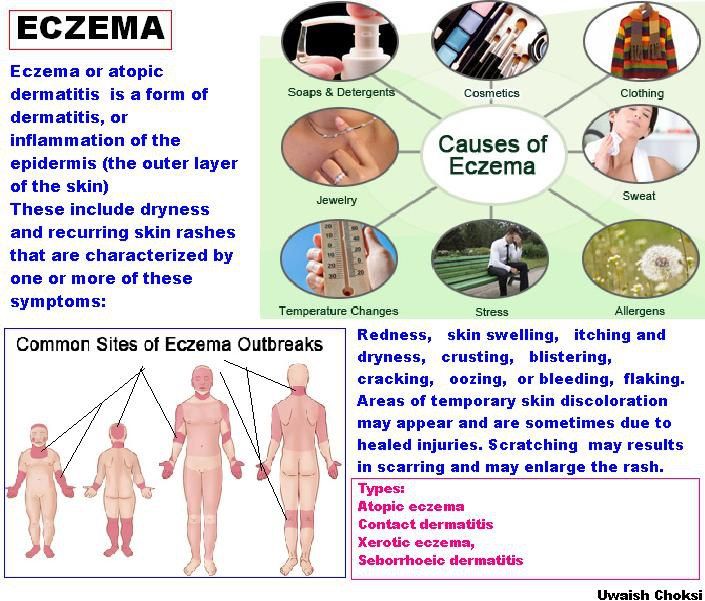
Most contact dermatitis reactions aren’t severe, but they can be unpleasant until the itching goes away.
Contact dermatitis symptoms depend on the cause and how sensitive you are to the substance.
Allergic contact dermatitisSymptoms associated with allergic contact dermatitis include:
- dry, scaly, flaky skin
- hives
- oozing blisters
- skin redness
- skin that appears darkened or leathery
- skin that burns
- extreme itching
- sun sensitivity
- swelling, especially in the eyes, face, or groin areas
Irritant contact dermatitis may cause slightly different symptoms, such as:
- blistering
- cracking skin due to extreme dryness
- swelling
- skin that feels stiff or tight
- ulcerations
- open sores that form crusts
There are three types of contact dermatitis:
- allergic contact dermatitis
- irritant contact dermatitis
- photocontact dermatitis
Photocontact dermatitis is less common. It’s a reaction that can occur when the active ingredients in a skin product are exposed to the sun and result in irritation.
It’s a reaction that can occur when the active ingredients in a skin product are exposed to the sun and result in irritation.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when the skin develops an allergic reaction after being exposed to a foreign substance. This causes the body to release inflammatory chemicals that can make the skin feel itchy and irritated.
Common causes of allergic contact dermatitis include contact with:
- jewelry made from nickel or gold
- latex gloves
- perfumes or chemicals in cosmetics and skin care products
- poison oak or poison ivy
Irritant contact dermatitis is the most common type of contact dermatitis. It happens when the skin comes in contact with a toxic material.
Toxic substances that can cause irritant contact dermatitis include:
- battery acid
- bleach
- drain cleaners
- kerosene
- detergents
- pepper spray
Irritant contact dermatitis can also occur when the skin comes in contact with less irritating materials — like soap or even water — too often.
People whose hands are frequently exposed to water, such as hairdressers, bartenders, and healthcare workers, often experience irritant contact dermatitis of the hands, for example.
Most cases of contact dermatitis go away on their own once the substance is no longer in contact with the skin. Here are some tips you can try at home:
- Avoid scratching your irritated skin. Scratching can make the irritation worse or even cause a skin infection that requires antibiotics.
- Clean your skin with mild soap and lukewarm water to remove any irritants.
- Stop using any products you think might be causing the problem.
- Apply bland petroleum jelly like Vaseline to soothe the area.
- Try using anti-itch treatments such as calamine lotion or hydrocortisone cream (Cortisone-10).
- If needed, take an antihistamine drug such as diphenhydramine to cut down on itching and to reduce your allergic response.
You can purchase these items at most drugstores or online.
Most times, contact dermatitis isn’t cause for concern. However, you should seek medical attention if your rash is close to your eyes or mouth, covers a large area of your body, or doesn’t improve with home treatment.
Your doctor can prescribe a more potent steroid cream if home treatments don’t soothe your skin.
Contact your doctor if your symptoms are severe or don’t improve with time. Your doctor will take a thorough medical history and examine your skin. Questions they may ask you include:
- When did you first notice your symptoms?
- What makes your symptoms better or worse?
- Did you go hiking just before the rash started?
- What products do you use on your skin every day?
- What chemicals do you come in contact with on a daily basis?
- What do you do for a living?
Your doctor may refer you to an allergy specialist or dermatologist to pinpoint the cause of your contact dermatitis. This specialist can perform allergy testing called a patch test. It involves exposing a small patch of your skin to an allergen.
It involves exposing a small patch of your skin to an allergen.
If your skin reacts, the allergy specialist can determine the likely cause of your contact dermatitis.
Avoiding initial exposure to irritants can help prevent contact dermatitis. Try these tips:
- Purchase products labeled “hypoallergenic” or “unscented.”
- Refrain from wearing latex gloves if you have a latex allergy. Opt for vinyl gloves instead.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and pants when hiking in the wilderness.
- If you notice irritation from a new product, stop using it immediately.
If you know you have sensitive skin, do a spot test with any new products. You can apply the new product to one place on your forearm. Cover the area, and don’t expose it to water or soap. Check for any reaction at 48 and 96 hours after application. If there’s any redness or irritation, don’t use the product.
Common skin rashes: how to distinguish them?
There are many different types of rashes. And despite the similarity between different types of rashes, they can be caused by different reasons and, accordingly, require different types of treatment. If some types of rashes do not bother a person, then others can signal serious health problems. In this context, it is important to be able to distinguish between different types of skin rashes in order to know when to see a doctor. nine0003
And despite the similarity between different types of rashes, they can be caused by different reasons and, accordingly, require different types of treatment. If some types of rashes do not bother a person, then others can signal serious health problems. In this context, it is important to be able to distinguish between different types of skin rashes in order to know when to see a doctor. nine0003
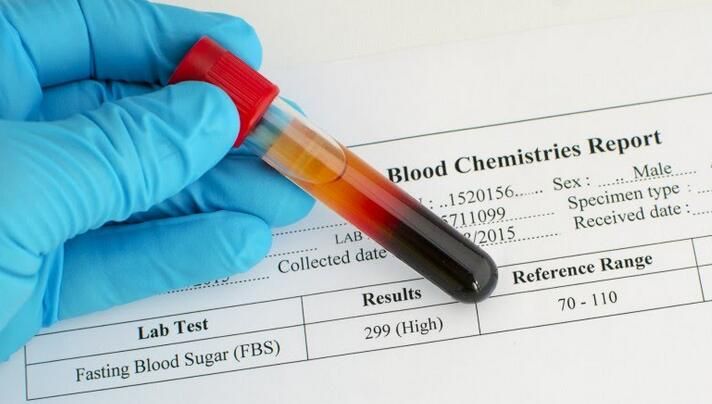
Acne. The most common type of skin rash is acne. Most people experience acne at some point in their lives. About 80% of people aged 11-30 suffer from acne. It usually develops during adolescence and affects areas of the skin on the face, back, and chest. However, some people also have acne in adulthood - about 1 in 20 women and 1 in 100 men.
Atopic dermatitis. Another common cause of skin rashes is atopic dermatitis, or eczema. It usually develops at an early age and is characterized by the appearance of dry, scaly patches on the scalp, forehead, and face during the first year of life. These scaly patches can also "bubble" and release fluid. Another unpleasant manifestation of atopic dermatitis is debilitating itching. If the symptoms of atopic dermatitis appear later in childhood, the rash may occur in the elbows or knees. Eczema also sometimes appears on the neck, wrists, ankles, between the buttocks and legs. A family history of psoriasis, asthma, or hay fever may affect the risk of developing atopic dermatitis. About 50% of people with severe forms of atopic dermatitis also have bronchial asthma, and about 66% have hay fever. The studies also revealed a link between atopic dermatitis and life in polluted areas of cities. nine0003
These scaly patches can also "bubble" and release fluid. Another unpleasant manifestation of atopic dermatitis is debilitating itching. If the symptoms of atopic dermatitis appear later in childhood, the rash may occur in the elbows or knees. Eczema also sometimes appears on the neck, wrists, ankles, between the buttocks and legs. A family history of psoriasis, asthma, or hay fever may affect the risk of developing atopic dermatitis. About 50% of people with severe forms of atopic dermatitis also have bronchial asthma, and about 66% have hay fever. The studies also revealed a link between atopic dermatitis and life in polluted areas of cities. nine0003
Urticaria. About 20% of individuals are affected at some point in their lives with hives, also known as urticarial rash. At the same time, watery, itchy bumps appear on the skin, which resemble insect bites. Urticaria can occur on any part of the body and "move" over the skin. As a rule, urticaria appears for a short period, but in chronic cases it can last more than 6 weeks.
Urticaria may be caused by exposure to certain foods such as peanuts, eggs, nuts, shellfish, and medications such as antibiotics, acetylsalicylic acid and ibuprofen. Other possible causes of hives include insect bites, blood transfusions, bacterial and viral infections, exposure to latex, animal dander, pollen, and plant venom. nine0003
Infectious diseases of the skin. A bacterial infection of the dermis - the deep layer of the skin - can lead to the development of cellulitis, a pathology characterized by swelling, redness and a rash on the skin, as well as systemic reactions - fever, chills, nausea. If a bacterial infection affects the hair follicles and does not penetrate the skin, the condition is called folliculitis. With this disease, acne occurs around individual hair follicles.
nine0002 Psoriasis. This pathology usually develops in patients aged 15–35 years, but can also occur in children and the elderly. This is an immune disease that is manifested by the appearance of red scaly spots on the skin. About 10-15% of patients with psoriasis have their first symptoms before the age of 10 years.
About 10-15% of patients with psoriasis have their first symptoms before the age of 10 years. Keloid scars and actinic keratosis can also be confused with skin rashes. The latter is characterized by the appearance of areas of rough scaly skin on the back, arms, forearms and face due to prolonged exposure to the sun and skin aging. nine0003
Keloid scars may result from tissue scarring from cuts, burns, piercings, tattoos, etc.
Based on www.medicalnewstoday.com
Types of rashes on the face: causes and how to deal with
Types of rashes on the face: causes and how to deal with Human skin is an organ that is exposed to external factors every day. With increased sensitivity and disruption of the sebaceous glands, rashes appear. Not only young girls and boys are concerned about the solution to this problem, acne has “matured” significantly over the past 10 years. Eruptions on the face systematically occur in people of both sexes of all ages. Why acne and acne appear, is it possible to get rid of them once and for all, read on. Let's talk about common rashes, present their classification according to severity. nine0003
Let's talk about common rashes, present their classification according to severity. nine0003
First, let's look at the causes of rashes on the face. They occur on the skin of any type, each needs special care and individual selection of cosmetic products. The main cause of acne is an increase in the level of male hormones in the blood. Unfavorable conditions further enhance the inflammatory process. Among them:
- abrupt change in ambient temperature;
- frequent touching with dirty hands;
- fast food and fatty foods, other. nine0033
Normal skin also develops rashes on the face: small or large painful pimples. This is due to improper care and hormonal changes. Internal processes in the body play a key role, well-being and appearance depend on them. With a hormonal surge, colossal problems can arise: from weight gain to changes in skin type. Rashes often appear, they are also the result of taking complex medications. The described problem has many causes, in each case an individual approach is needed to find the most correct solution. nine0003
nine0003
- comedo. Another name is a sebaceous plug, which clogs the pore and can cause serious inflammation. This is the beginning of the problem. Comedones are white and black, open and closed. With adequate care and high-quality cleansing, they pass quickly; if an infection gets in, they turn into papules;
- pustules. Red neoplasm with purulent contents. After maturation, a white dot appears in the focus of inflammation;
- papule. Ripe pimple, which is accompanied by painful sensations. When pressed, it becomes pale, causes discomfort on palpation. Papules vary in color from red to bluish; nine0033
- lightning pimple. It occurs in large numbers in people who have been suffering from acne for a long time. Lightning neoplasms are considered the most severe, when they appear, it is necessary to urgently seek medical help. This acne affects locally, provokes a change in the formula of leukocytes in the blood, is manifested by strong and painful sensations in the muscles and bones;
- nodular cystic pimple.
 Another severe form of acne that develops from a pustule. Occurs in large numbers, causes discomfort and is located deep in the dermis. These rashes are interconnected by fistulous ducts. nine0033
Another severe form of acne that develops from a pustule. Occurs in large numbers, causes discomfort and is located deep in the dermis. These rashes are interconnected by fistulous ducts. nine0033
As you can see, painful acne in most cases should be treated by a specialist. The complexity of the clinical picture is judged by the severity of acne. There are only four of them:
1. Eruptions occur on one of the areas of the face. Often they are comedones, and not neoplasms of more serious forms.
2. Mostly white pimples, papules and pustules appear in several areas, sometimes also on the body. This degree differs from the previous one in the scale of localization. nine0003
3. There is a pronounced inflammatory process, a significant number of rashes and redness. Experts note hyperemia, there is post-acne.
4. Pimples of large size, spherical shape affect several layers of the skin, have a red-bluish color. Alternate with atrophic scars.
Skin genetics are taken into account in the analysis of problems. The greater the thickness of the cover, the higher the likelihood of developing seborrhea. Fighting acne at home is only in the initial stages, severe forms are the specialty of dermatologists. nine0003
The greater the thickness of the cover, the higher the likelihood of developing seborrhea. Fighting acne at home is only in the initial stages, severe forms are the specialty of dermatologists. nine0003
Acne is caused by a hormonal imbalance. If improperly selected care is added to it, ideal conditions are formed for the reproduction of bacteria. The microorganism that causes acne is called propion bacteria.
It is better to consult a beautician or dermatologist for advice. It is worth reviewing the diet, eliminating sweets, fatty and spicy foods, coffee. Food must be healthy and fresh, otherwise the problem will get worse. Daily cosmetic care is of great importance. nine0003
The algorithm for correct actions is as follows:
1. Mandatory make-up removal at the end of the day.
2. Cleansing with lotion or foam for problematic skin.
3. Toning (very important for the normalization of the sebaceous glands and other processes that occur at the cellular level).
4. Moisturizing. When the seasons change, care is reviewed, nutrition is added in winter, if necessary. In summer, use products with a light formula. About allergic rashes Now about situations when small pimples appear on the face. These rashes can really be masked with tonal means, but you should not do this so as not to provoke the appearance of purulent neoplasms. nine0003
Allergic reactions often present with itching that is difficult to get rid of. The problem arises for the following reasons: violation of barrier functions or genetically predetermined reactivity of the skin. In the latter case, anything can provoke the manifestation of an allergy on the face. For example, aggressive weather conditions, food, stressful situations.
Allergic rashes on the face are treated as follows:
- use hypoallergenic cosmetics; nine0033
- exclude citrus fruits, berries, chocolate, coffee, nuts, honey, canned food from the diet;
- avoid cosmetic procedures.
If you follow the recommendations, after 7-10 days the face will be clean.
Eruptions on the face are not only acne. It is impossible not to say about herpetic formations and visible redness on the cheeks. The latter refers to rosacea, when the vascular network is clearly visible. It is almost impossible to hide it, you need to contact a dermatologist. Herpes appears in the presence of a corresponding pathogen in the body and a decrease in immunity. The virus cannot be destroyed, it is in a dormant state for a long time and wakes up after stress, colds, and other diseases. You can get rid of herpetic eruptions on the face in a few days, for this it is enough to buy a targeted ointment in a pharmacy. To avoid relapses, avoid hypothermia and strengthen the immune system (active lifestyle, proper nutrition). nine0003
During the treatment of acne on the face, special preparations are prescribed. These are antiseptic and antibacterial compounds for external use. Experts also strongly recommend sticking to a diet and doing a general detox. Gentle nutrition and the use of sorbents help to eliminate harmful substances, normalize hormonal levels and improve skin condition. In parallel with ointments and gels, vitamin complexes are often used. Separately, make up facial care. For each stage, an individual selection of cosmetics is carried out. Many who have experienced breakouts think that oily and combination skin does not need moisturizing, so they do not apply the appropriate creams. In fact, this care stage is unacceptable to exclude. If you use only cleansing compounds, the face will become dry, peeling and itching will appear. Systematic disinfection without moisture adversely affects both pathogenic and natural protective flora. nine0003
Experts also strongly recommend sticking to a diet and doing a general detox. Gentle nutrition and the use of sorbents help to eliminate harmful substances, normalize hormonal levels and improve skin condition. In parallel with ointments and gels, vitamin complexes are often used. Separately, make up facial care. For each stage, an individual selection of cosmetics is carried out. Many who have experienced breakouts think that oily and combination skin does not need moisturizing, so they do not apply the appropriate creams. In fact, this care stage is unacceptable to exclude. If you use only cleansing compounds, the face will become dry, peeling and itching will appear. Systematic disinfection without moisture adversely affects both pathogenic and natural protective flora. nine0003
Try Christina's Comodex products . This is an integrated approach to problem solving.
Important: Test on a small area of the body before using a new product. Taking antibacterial and hormonal drugs is relevant for severe forms of acne.