Non invasive dna testing during pregnancy
What is noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and what disorders can it screen for?: MedlinePlus Genetics
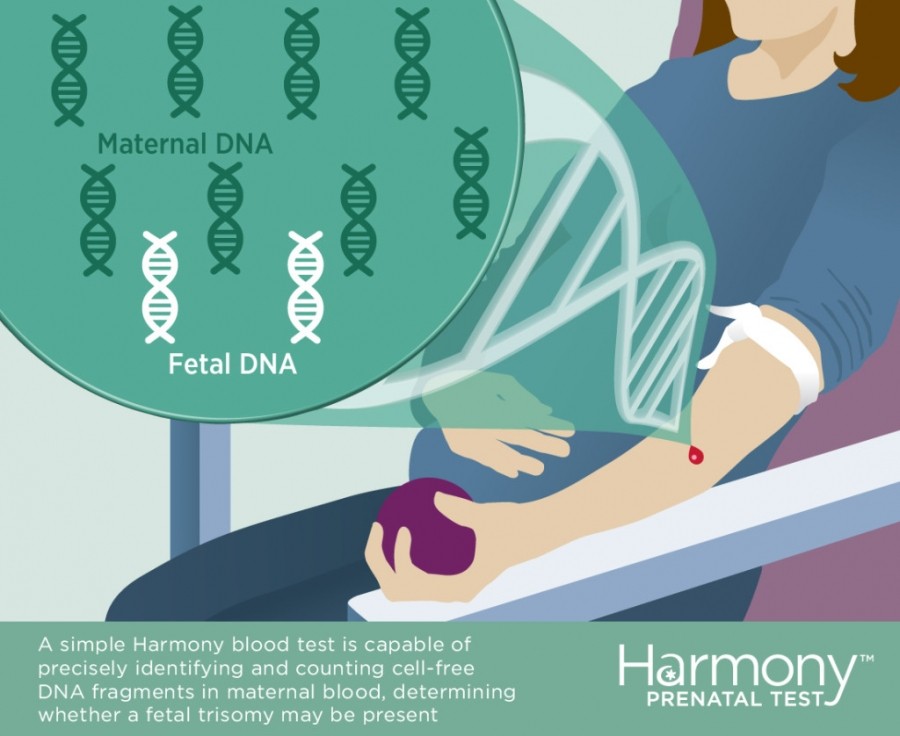
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT), sometimes called noninvasive prenatal screening (NIPS), is a method of determining the risk that the fetus will be born with certain genetic abnormalities. This testing analyzes small fragments of DNA that are circulating in a pregnant woman’s blood. Unlike most DNA, which is found inside a cell’s nucleus, these fragments are free-floating and not within cells, and so are called cell-free DNA (cfDNA). These small fragments usually contain fewer than 200 DNA building blocks (base pairs) and arise when cells die off and get broken down and their contents, including DNA, are released into the bloodstream.
During pregnancy, the mother’s bloodstream contains a mix of cfDNA that comes from her cells and cells from the placenta. The placenta is tissue in the uterus that links the fetus and the mother’s blood supply. These cells are shed into the mother’s bloodstream throughout pregnancy. The DNA in placental cells is usually identical to the DNA of the fetus. Analyzing cfDNA from the placenta provides an opportunity for early detection of certain genetic abnormalities without harming the fetus.
NIPT is most often used to look for chromosomal disorders that are caused by the presence of an extra or missing copy (aneuploidy) of a chromosome. NIPT primarily looks for Down syndrome (trisomy 21, caused by an extra chromosome 21), trisomy 18 (caused by an extra chromosome 18), trisomy 13 (caused by an extra chromosome 13), and extra or missing copies of the X chromosome and Y chromosome (the sex chromosomes). The accuracy of the test varies by disorder.
NIPT may include screening for additional chromosomal disorders that are caused by missing (deleted) or copied (duplicated) sections of a chromosome. NIPT is beginning to be used to test for genetic disorders that are caused by changes (variants) in single genes. As technology improves and the cost of genetic testing decreases, researchers expect that NIPT will become available for many more genetic conditions.
NIPT is considered noninvasive because it requires drawing blood only from the pregnant woman and does not pose any risk to the fetus. NIPT is a screening test, which means that it will not give a definitive answer about whether or not a fetus has a genetic condition. The test can only estimate whether the risk of having certain conditions is increased or decreased. In some cases, NIPT results indicate an increased risk for a genetic abnormality when the fetus is actually unaffected (false positive), or the results indicate a decreased risk for a genetic abnormality when the fetus is actually affected (false negative). Because NIPT analyzes both fetal and maternal cfDNA, the test may detect a genetic condition in the mother.
There must be enough fetal cfDNA in the mother’s bloodstream to be able to identify fetal chromosome abnormalities. The proportion of cfDNA in maternal blood that comes from the placenta is known as the fetal fraction. Generally, the fetal fraction must be above 4 percent, which typically occurs around the tenth week of pregnancy.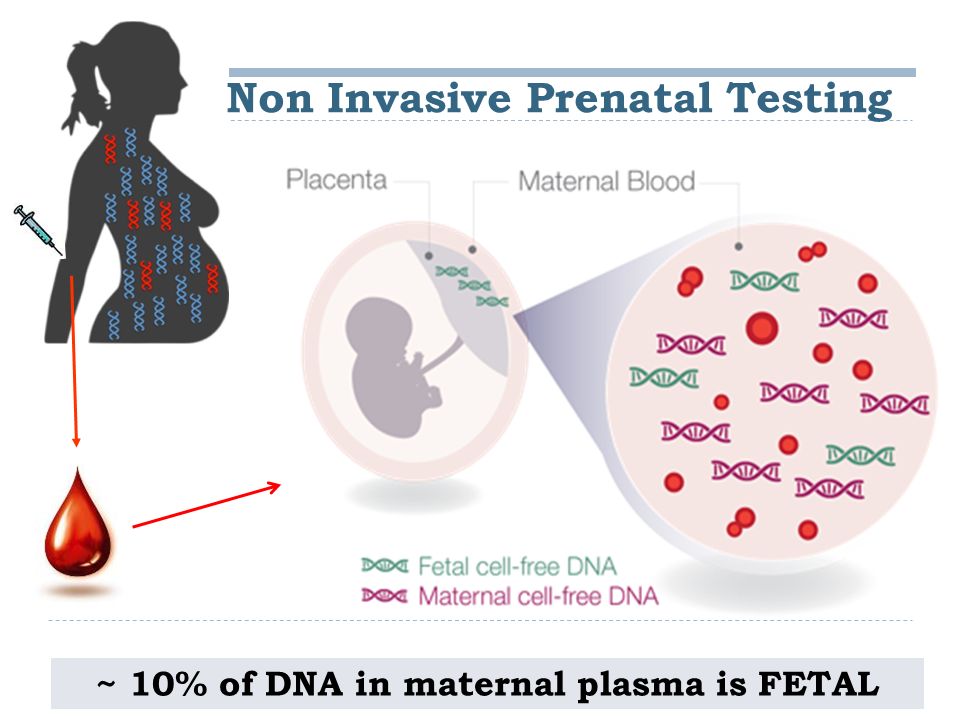 Low fetal fractions can lead to an inability to perform the test or a false negative result. Reasons for low fetal fractions include testing too early in the pregnancy, sampling errors, maternal obesity, and fetal abnormality.
Low fetal fractions can lead to an inability to perform the test or a false negative result. Reasons for low fetal fractions include testing too early in the pregnancy, sampling errors, maternal obesity, and fetal abnormality.
There are multiple NIPT methods to analyze fetal cfDNA. To determine chromosomal aneuploidy, the most common method is to count all cfDNA fragments (both fetal and maternal). If the percentage of cfDNA fragments from each chromosome is as expected, then the fetus has a decreased risk of having a chromosomal condition (negative test result). If the percentage of cfDNA fragments from a particular chromosome is more than expected, then the fetus has an increased likelihood of having a trisomy condition (positive test result). A positive screening result indicates that further testing (called diagnostic testing, because it is used to diagnose a disease) should be performed to confirm the result.
Committee Opinion No. 640: Cell-Free DNA Screening For Fetal Aneuploidy. Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;126(3):e31-7. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001051. PubMed: 26287791.
Obstet Gynecol. 2015 Sep;126(3):e31-7. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000001051. PubMed: 26287791.
Dondorp W, de Wert G, Bombard Y, Bianchi DW, Bergmann C, Borry P, Chitty LS, Fellmann F, Forzano F, Hall A, Henneman L, Howard HC, Lucassen A, Ormond K, Peterlin B, Radojkovic D, Rogowski W, Soller M, Tibben A, Tranebjærg L, van El CG, Cornel MC. Non-invasive prenatal testing for aneuploidy and beyond: challenges of responsible innovation in prenatal screening. Summary and recommendations. Eur J Hum Genet. 2015 Apr 1. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2015.56. [Epub ahead of print] PubMed: 25828867.
Goldwaser T, Klugman S. Cell-free DNA for the detection of fetal aneuploidy. Fertil Steril. 2018 Feb;109(2):195-200. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.12.019. PubMed: 29447662.
Gregg AR, Skotko BG, Benkendorf JL, Monaghan KG, Bajaj K, Best RG, Klugman S, Watson MS. Noninvasive prenatal screening for fetal aneuploidy, 2016 update: a position statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.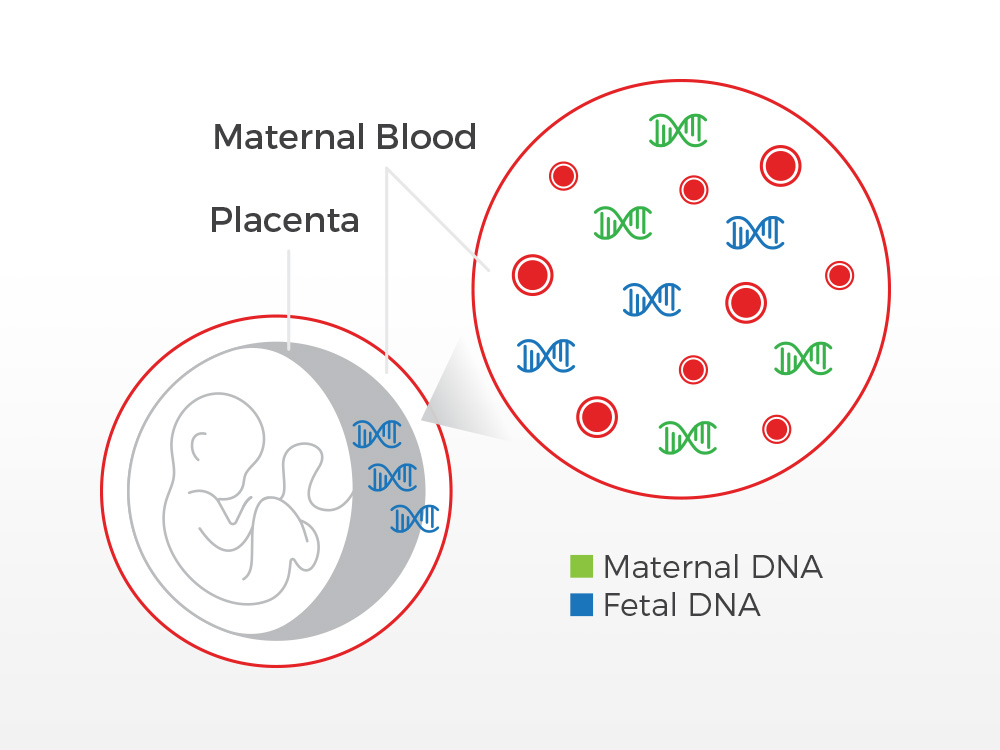 Genet Med. 2016 Oct;18(10):1056-65. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.97. Epub 2016 Jul 28. PubMed: 27467454.
Genet Med. 2016 Oct;18(10):1056-65. doi: 10.1038/gim.2016.97. Epub 2016 Jul 28. PubMed: 27467454.
Rose NC, Kaimal AJ, Dugoff L, Norton ME; American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics; Committee on Genetics; Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Screening for Fetal Chromosomal Abnormalities: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 226. Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Oct;136(4):e48-e69. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000004084. PubMed: 32804883.
Skrzypek H, Hui L. Noninvasive prenatal testing for fetal aneuploidy and single gene disorders. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2017 Jul;42:26-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Feb 28. PubMed: 28342726.
Non-Invasive Paternity Test | American Pregnancy Association
The most recent government statistics show that 40.3% of all births in the United States are to single mothers. Additionally, a married woman may be unsure about whether or not her husband is the biological father of her child. If you are a woman who falls into either of these categories, rest assured you’re not alone, a non-invasive prenatal paternity test, also known as a DNA test may be what you need.
If you are a woman who falls into either of these categories, rest assured you’re not alone, a non-invasive prenatal paternity test, also known as a DNA test may be what you need.
If you want or need paternity answers, they are readily available—even while you’re still pregnant—thanks to advancements in DNA science. Here is an overview of everything you need to know about (NIPP) or non-invasive prenatal paternity testing that you can take before birth.
Top 5 Reasons Why a Paternity Test While Pregnant Might Be The Right Choice
- Not knowing who the father of your child is can be stressful, and waiting till after the baby’s born to get a DNA test means months of worry.
- Knowing ahead of time can help you make decisions about your romantic and family relationships before the baby’s birth instead of afterward when life gets considerably more complicated.
- In anticipation of the birth of your little one, you may want the biological father involved in helping you through the pregnancy itself (attending childbirth classes, buying furniture and clothes, etc).

- If you know who the biological father is before the baby’s born, you can have some or all of your legal ducks in a row ahead of time, if necessary—for child support, custody, and more.
- You can be confident that the right person is with you in or waiting outside of the delivery room when the big moment arrives.
Science Behind Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Testing
The test can be performed as early as the 7th week of pregnancy, meaning you can choose to confirm who the father is nearly immediately after your pregnancy is confirmed. Unlike outdated methods for determining paternity like amniocentesis or a CVS (Chorionic Villus Sampling) test that can cause a miscarriage, a prenatal DNA is completely non-invasive and safe for both mother and fetus.
How Non-Invasive Testing Works
- DNA is collected from the mother with a simple blood draw, and DNA is collected from the possible father using a cheek swab
- Both samples are then sent to the lab for analysis
- The test analyzes free-floating fetal DNA from the mother’s plasma and compares it to the mother’s own DNA profile
- Once the fetus’s profile is determined, that profile is then compared to the possible father’s and paternity can be determined
- Results for the prenatal paternity test are generally returned in about one (1) week, once testing has begun.
 If the man tested is determined not to be the biological father, then the report shows a 0% probability of paternity. If the man tested is considered to be the biological father, the report shows a 99% or greater probability of paternity
If the man tested is determined not to be the biological father, then the report shows a 0% probability of paternity. If the man tested is considered to be the biological father, the report shows a 99% or greater probability of paternity
IMPORTANT: If you are carrying twins, doing a prenatal paternity test is not possible, since there is free-floating DNA from both fetuses in the mother’s bloodstream and current technology does not permit the lab to isolate each fetus’s profile separately.
Selecting a Lab For Non-Invasive Prenatal Paternity Tests
Like any other important diagnostic service, it’s important to remember that not all labs who do a paternity test before birth are created equal, so be sure to do some research and compare before making a choice!
What To Look For In a Lab:
- An accuracy guarantee: Make sure the lab stands behind its results
- Full accreditations along with an excellent reputation in the industry: Your prenatal paternity test results are too important to leave to chance—be sure the lab maintains extensive, current accreditations with important independent lab-oversight programs such as the AABB
- Tests that are consistently updated: With improvements in DNA technology, and updates to existing tests, ensure the
- Utilizes the latest and best technologies to give you the most accurate results
- Caring and professional support before, during, and after your test: Getting a DNA test isn’t hard, but it can be an emotional process.
 Having the support of a highly-trained and sympathetic customer care team who can answer all your questions knowledgeably and help you feel comfortable makes a big difference
Having the support of a highly-trained and sympathetic customer care team who can answer all your questions knowledgeably and help you feel comfortable makes a big difference - Beware of too-good-to-be-true pricing: This is one of the most important tests you may ever take, and you really do get what you pay for. So don’t let price be the only determining factor in making your decision
Is NIPP Testing Right for you?
Women have more accurate, accessible, and affordable options than ever when it comes to paternity testing. Which is right for you? The choice is yours.
DNA Diagnostics Center is a corporate sponsor of the American Pregnancy Association. DDC is the only testing facility that provides a non-invasive prenatal paternity test accredited by AABB. You may contact them at 1-800-798-0580.
Want to Know More?- Paternity Testing
- Single Parenting
- My Girlfriend is Pregnant
Paternity during pregnancy DNA test
Mandatory: alleged father, mother (pregnant).
At least 10 weeks' gestation, singleton pregnancy, any number (not necessarily the first)
Optional: Second Intended Father (required if he is a relative of the Intended Father.)
How does it work?
Establishing paternity during pregnancy. DNA analysis is based on the analysis of fetal DNA fragments that are present in the mother's blood as early as 6 weeks of pregnancy. These fragments are isolated and their full analysis is performed by sequencing SNP-markers. nine0005
No test
- No test for multiple pregnancies
- If the alleged fathers are related, samples of both alleged fathers are needed
- The test is not done for surrogacy.
Analyzes and prices:
Determining the sex of the fetus
from the 6th week of pregnancy
Standard test
9 900 rub
Expert test
13 600 rub
express test000515 000 rub
DNA tests NIPT on pathology in the fetus
Identification of pathologies in the fetus
from 10th week
NIPS T21
NIPT standard
500 500 500 500NIPT extended (31 Syndrome)
35 900 rub
NIPT VERACITY 3
23 600 rub
NIPT Veracy 8
26 900 RUB
NIPT VERACITY 12
27 900 rub
NIPT VERAGENE
9000 9000002 RUB 39,900
NIPT Prenetics
RUB 30,900
Panorama test Natera-USA b. p.
p.
28 900 rub.
37 900 rub
Establishment of paternity/motherhood
Buying scraping from the cheek
from 6 900 rub
DNA Test for paternity
9000 8 800 rubDNA Test for paternity Lite DNA paternity test for trial
19 900 rub
DNA Test Express Paternity
28 500 RUB
DNA DNA TRACTION
14 500 RUB
Paternity during pregnancy
53,0005,0005
Paternity during pregnancy
,С 9-0002 С 9-000 first week of pregnancy
Paternity during pregnancy
53,000 rubles
Motherhood during pregnancy
53,000 rubles
Prenatal diagnosis
Detection of hereditary diseases in the fetus
Rhesus factor of the fetus
8 900 rub
HMA PRENATAL
15 900 rub
SME PRENATAL
13,0005
Hereditary diseases
Screening for the carriage of hereditary diseases
Preparation for pregnancy Panel Panel "Basic"
9,500 rubles
Preparation for pregnancy panel "Expert"
33,000 rubles
Screening for SMA
12,400 rubles
Analysis of SMA carriage
13,500 rubles
Miscarriage and infertility
Genetic studies in case of miscarriage and infertility.
Study for the inexpressive of "Optima"
13 500 rub
Study for non -infinition "Fermatus"
80 000 RUB
Study during non -infinition "Optima extended"
17 000 RUB
Infertility "Ferty"
9000 75 75 75 75 75 75 000 rubInfertility FISH diagnostics
14 000 rub
exon levels
35 000 RUB
Chromosomal pathologies
Chromosomal microsomatic analysis
exon levels
35 000 RUB
1900
CARIOTIP
9000 9000 7Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genetic Genes
Hereditary diseases due to genetic causes
Epilepsy
35,000 rubles
Whole genome sequencing
98 000 rub
Sequencing of exoma
51 000 RUB
EXEMOME TRIO
138 000 RUB
PARECTION STRUMENTS A
9000 26 750 RUBPARECTIONAL DISECTIONS PROMESTIONS
9000 35 000 RUB DNA test for nationality0005DNA analysis for origin, race, nationality
"DNA genealogy" panel on the maternal side
13,900 rubles
"DNA genealogy" panel on the paternal side.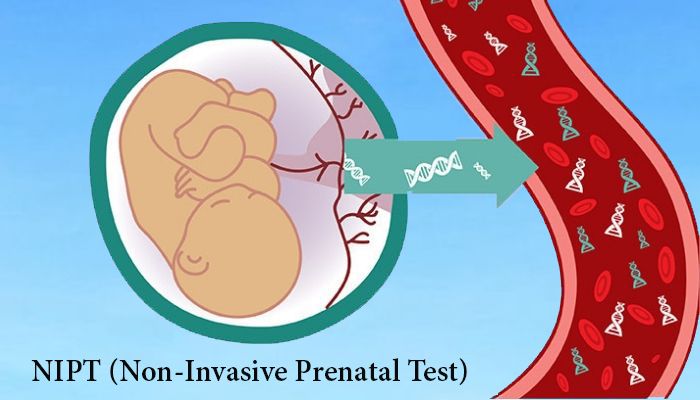
13 900 rub
DNA-Genealogy panel Nationality
12 900 RUB
DNA Genealogy Panel
31 000 RUB
DNA Genealogies
22 900 rub
DNN DNA Genealogy
RUB 22,900
Genetic passport/test
Tests that will tell you everything about you.
Genetic passport "All about me"
20 500 rub
Genetic test "Atlas"
19900 rub
Genetic passport "Standard"
29 600 rub
Genetic passport "Ultra"
9000,000 000 rub microbiome0005Microbiom of the nasopharynx
13 500 rub
Microbium of the genitourinary system
13 500 rub
Microbium according to the Osipov method
7
Health and genetics
Predisposition Genetics
MAX MAX
PanelRUB 33,000
Panel "Nutrigenetics: The best diet for weight loss"
RUB 11,500
Panel "Nutrigenetics: negative effects of coffee"
7 500 rub
Panel "Nutricigenics: the negative consequences of alcohol consumption and the risk of dependence"
11 500 rub
Panel "Nutrigenetics: Vitamins"
500 rub
Pan "Nutricigenics and Sport"
500 rub
Panel "Sport: for professionals"
RUB 19,900
Panel "Sport: choice of sport for beginners"
RUB 13,400
Panel "Women's health (complex)"
35 900 rub
Panel "Male Health (Complex)
35 900 RUB
Cosmetology and ANTI AGE"
11 900 RUB
Hereditary cancer
Non -invasive study for a predisposition to cancer
Panel "Hereditary colon cancer
27,500 rubles
Panel "Pharmacoses and hereditary cancer"
27,500 rubles
Panel "Hereditary breast cancer"
27,500 rubles
Panel "Female hereditary tumors"
27 500 rub
Panel "Hereditary tumor syndromes"
27 500 rub
Diagnostics and treatment of cancer
Any tumor is a genetic disease
Test oncoskan
9000 2 49 9000tests (40 genes)
45 000 rub
ONKONETICS test (20 genes)
37 000 rub
ONCOCARTA test
29 000 rub
Liquid biopsy 57 genes
4
Liquid biopsy 60 genes
RUB 61,000
MammaPrint test
RUB 208,000
Early pregnancy paternity testing
Allergens: mites, drugs, house dust
| House dust mite d1 Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus | | 500 |
| House dust mite d2 Dermatophagoides farinae | | 500 |
| House dust mixture hx2 (h3, d1, d2, i6) | | 500 |
| House dust h3 Hollister-Stier labs | | 500 |
| Amoxicillin c6 Amyxicilloyl | | 800 |
| Ampicillin c5 Ampicilloyl | | 800 |
| Articaine / Ultracaine c68 | | 800 |
| Lidocaine / Asilocaine c82 | | 800 |
Hepatitis
| Hepatitis B screening with confirmatory test | | 280 |
| Hepatitis C - screening with confirmatory test | | 440 |
Antibodies to protozoan parasites nine0427
Autoimmune antibodies
| Anti-gliadin IgG | | 790 |
| Anti-gliadin IgA | | 790 |
| Anti-Müllerian hormone | | 1230 |
| Antisperm antibodies | | nine70 |
| Antibodies to GAD (antibodies to glutamate decarboxylase) | | 1600 |
| B cell antibodies | | 1460 |
| Skin basement membrane antibodies | | 2300 nine0431 |
| Double-stranded DNA antibodies | | 630 |
| Insulin antibodies | | 760 |
| Total antibodies to cardiolipin (IgG, IgM, IgA) | | 1070 | nine0438
| Anti-mitochondrial antibodies | | 1460 |
| Anti-platelet IgG | | 1460 |
| Phospholipid antibodies IgG + IgM | | 820 |
| Anti-endomysium IgA + IgG | | 1 260 |
| Antinuclear antibodies | | 680 |
| Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (ACCP) | | 1460 |
| Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) p/col | | 810 |
| TSH receptor antibodies (AT-TSH) | | 1460 |
| CEC (determination of the level of circulating immune complexes) | | 870 |
Bacterial antibodies nine0427
Test kits
| Lipid spectrum | | nine0430 2490 |
| Blood biochemistry: standard | | 2290 |
| Blood biochemistry: advanced | | 3 990 |
| Women's Cancer Complex | | 3 690 |
| Oncological male complex | | 2790 |
| Oncopathology of the gastrointestinal tract | | 6 290 |
| Annual preventive examination | | 4 490 |
| Osteoporosis diagnostics | | 5 390 |
| Liver examination: standard | | 1790 |
| Liver examination: advanced | | 2 390 nine0431 |
| Hospitalization in a therapeutic hospital | | 3490 |
| Surgical hospitalization | | 4 990 |
| Hospitalization in the infectious diseases hospital | | nine0430 1 300 |
| Parasitic infections | | 3 190 |
| Healthy heart | | 1990 |
| Cardiorisk | | 5 190 |
| Revmoproby | | 3 590 |
| Joint diagnostics | | 2290 |
| Frequently ill children | | 2 390 |
| Kidney examination | nine04301 690 | |
| Pancreatic profile | | 3 390 |
| Diabetic profile | | 2990 |
| Female hormone profile | | 3 290 |
| Male hormone profile | | 3 690 |
| Anemia diagnostics | | 3 390 |
| Thyroid: screening | | nine0430 1 190 |
| Thyroid: expanded | | 1990 |
| Problem skin | | 4 790 |
| TORCH infections | | 3490 | nine0438
| Classic four (HIV, SYPHILIS, HEPATITIS B, HEPATITIS C) | | 1 300 |
| Before COVID-19 vaccination | | 1 250 |
| Pregnancy planning | | 8 590 |
| Parenthood planning | | 5 490 |
| Healthy baby | | 3 290 |
| Tests for kindergarten, school, camp | | 1 190 |
| Women's Health Standard | | 5 390 |
| Women's health: VIP | | 12 900 |
| Elegant age | | 3 990 |
| Men's Health Standard | | 5 990 |
| Men's health: VIP | | 12 900 |
| Male maturity | | 4 790 |
| Prostate examination | | 930 |
| Overweight | | 3 390 |
| Urogenital infections | | 5 990 |
| Diagnosis of diseases of the upper respiratory tract | | 4 990 |
Vitamins
| Vitamin A | | 2520 |
| 25-OH vitamin D | | 1550 |
| Vitamin B12 | | nine0430 700 |
| Folate (folic acid) | | 840 |
Bacteriology
| Dysbacteriosis | | 1 360 |
| Breast milk culture with ABP susceptibility testing | | 870 |
| Candida culture with ABP susceptibility testing | | 830 |
| Sputum culture with ABP susceptibility testing | | 920 |
| Urine culture with ABP susceptibility testing | nine0430870 | |
Mycoplasma (M. |