How you get pregnant
How Does Pregnancy Happen? | Pregnancy Symptoms & Signs
In This Section
- How Pregnancy Happens
- What are some tips for getting pregnant?
How Does Pregnancy Happen | Planned Parenthood Video
How Does Pregnancy Happen | Planned Parenthood VideoHow does pregnancy happen?
In order for pregnancy to happen, sperm needs to meet up with an egg. Pregnancy officially starts when a fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus. It takes up to 2-3 weeks after sex for pregnancy to happen.
How do people get pregnant?
Pregnancy is actually a pretty complicated process that has several steps. It all starts with sperm cells and an egg.
Sperm are microscopic cells that are made in testicles. Sperm mixes with other fluids to make semen (cum), which comes out of the penis during ejaculation. Millions and millions of sperm come out every time you ejaculate — but it only takes 1 sperm cell to meet with an egg for pregnancy to happen.
Eggs live in ovaries, and the hormones that control your menstrual cycle cause a few eggs to mature every month. When your egg is mature, it means it’s ready to be fertilized by a sperm cell. These hormones also make the lining of your uterus thick and spongy, which gets your body ready for pregnancy.
About halfway through your menstrual cycle, one mature egg leaves the ovary — called ovulation — and travels through the fallopian tube towards your uterus.
The egg hangs out for about 12-24 hours, slowly moving through the fallopian tube, to see if any sperm are around.
If semen gets in your vagina, sperm cells can swim up through the cervix. The sperm and uterus work together to move the sperm towards the fallopian tubes. If an egg is moving through your fallopian tubes at the same time, the sperm and egg can join together. The sperm has up to six days to join with an egg before it dies.
The sperm and uterus work together to move the sperm towards the fallopian tubes. If an egg is moving through your fallopian tubes at the same time, the sperm and egg can join together. The sperm has up to six days to join with an egg before it dies.
When a sperm cell joins with an egg, it’s called fertilization. Fertilization doesn’t happen right away. Since sperm can hang out in your uterus and fallopian tube for up to 6 days after sex, there’s up to 6 days between sex and fertilization.
If a sperm cell does join up with your egg, the fertilized egg moves down the fallopian tube toward the uterus. It begins to divide into more and more cells, forming a ball as it grows. The ball of cells (called a blastocyst) gets to the uterus about 3–4 days after fertilization.
The ball of cells floats in the uterus for another 2–3 days. If the ball of cells attaches to the lining of your uterus, it’s called implantation — when pregnancy officially begins.
Implantation usually starts about 6 days after fertilization, and takes about 3-4 days to complete. The embryo develops from cells on the inside of the ball. The placenta develops from the cells on the outside of the ball.
The embryo develops from cells on the inside of the ball. The placenta develops from the cells on the outside of the ball.
When a fertilized egg implants in the uterus, it releases pregnancy hormones that prevent the lining of your uterus from shedding — that’s why people don’t get periods when they’re pregnant. If your egg doesn’t meet up with sperm, or a fertilized egg doesn’t implant in your uterus, the thick lining of your uterus isn’t needed and it leaves your body during your period. Up to half of all fertilized eggs naturally don’t implant in the uterus — they pass out of your body during your period.
What are early pregnancy symptoms?
Many people notice symptoms early in their pregnancy, but others may not have any symptoms at all.
Common signs and symptoms of pregnancy can include:
-
Missed period
-
Swollen or tender breasts
-
Nausea and/or vomiting
-
Feeling tired
-
Bloating
-
Constipation
-
Peeing more often than usual
Some early pregnancy symptoms can sometimes feel like other common conditions (like PMS). So the only way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take a pregnancy test. You can either take a home pregnancy test (the kind you buy at the drug or grocery store), or get a pregnancy test at your doctor’s office or local Planned Parenthood Health Center.
So the only way to know for sure if you’re pregnant is to take a pregnancy test. You can either take a home pregnancy test (the kind you buy at the drug or grocery store), or get a pregnancy test at your doctor’s office or local Planned Parenthood Health Center.
How do people get pregnant with twins?
There are 2 ways that twins can happen. Identical twins are made when 1 already-fertilized egg splits into 2 separate embryos. Because identical twins come from the same sperm and egg, they have the same genetic material (DNA) and look exactly alike.
Non-identical twins (also called “fraternal” twins), are made when two separate eggs are fertilized by two separate sperm, and both fertilized eggs implant in the uterus. This can happen if your ovaries release more than one egg, or during certain kinds of fertility treatments. Non-identical twins have completely different genetic material (DNA), and usually don’t look alike. They’re the most common type of twin.
What is gestational age?
The term “gestational age” basically means how far along into a pregnancy you are. Gestational age is counted by starting with the first day of your last menstrual period (called LMP).
Gestational age is counted by starting with the first day of your last menstrual period (called LMP).
Gestational age can be kind of confusing, since it measures pregnancy from your last period — about 3-4 weeks BEFORE you’re actually pregnant. Common knowledge about pregnancy says it lasts 9 months, and it’s true that you’re usually pregnant for about 9 months. But the way pregnancy is measured makes it a little longer. A typical full-term pregnancy ranges from 38-42 weeks LMP — around 10 months.
Many people can’t remember the exact date of their last menstrual period — that’s totally okay. Your nurse or doctor can find out the gestational age using an ultrasound.
More questions from patients:
Can you get pregnant from precum?
Your chances of getting pregnant from precum are pretty low. But it is possible.
Precum (also known as pre-ejaculate) is a small amount of fluid that comes out of the penis when you’re aroused, but before ejaculation happens. It doesn’t usually have any sperm in it. But some people’s precum does have a small amount of sperm in it sometimes. This means sperm can get into the vagina and possibly fertilize an egg.
It doesn’t usually have any sperm in it. But some people’s precum does have a small amount of sperm in it sometimes. This means sperm can get into the vagina and possibly fertilize an egg.
There’s no way to know who has sperm in their precum and who doesn’t, so that’s one reason why the withdrawal method (pulling out) isn’t the best at preventing pregnancy.
If you don’t want to get pregnant, put on a condom before your genitals touch your partner’s. Even better, use both condoms and another kind of birth control together.
What are the stages of pregnancy?
Pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks. The stages of pregnancy are divided into 3 trimesters. Each trimester is a little longer than 13 weeks.
You’ll go through many changes during each trimester. Some people feel lots of discomfort. Others don’t feel much at all.
During the first trimester, you’ll probably have lots of body changes, including:
-
Tiredness
-
Tender, swollen breasts
-
Morning sickness
-
Cravings or distaste for certain foods
-
Mood swings
-
Constipation
-
Needing to pee more often
-
Headache
-
Heartburn
-
Weight gain or loss
Most of these symptoms go away when you get to the second trimester. This is when your belly gets bigger and you’ll feel the fetus move. You may also notice:
This is when your belly gets bigger and you’ll feel the fetus move. You may also notice:
-
Body aches
-
Stretch marks
-
Darkening of your areolas
-
A line on your skin running from your belly button to pubic bone
-
Patches of darker skin
-
Numb or tingling hands
-
Itching on your abdomen, palms, and feet
-
Swelling of your ankles, fingers, or face
In the third trimester, some of the same symptoms may continue. You may also experience:
-
Shortness of breath
-
Needing to pee even more often
-
Hemorrhoids
-
Your breasts leaking a watery pre-milk called colostrum
-
Your belly button sticking out
-
Trouble sleeping
-
The baby "dropping" or moving lower in your abdomen
-
Contractions
If you aren’t sure if your symptoms are normal, call your doctor or midwife or visit your local Planned Parenthood health center.
- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
Back to top
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
How to get pregnant | Tommy's
For the best chance of getting pregnant, you need to get your eggs and your partner's sperm together as often as possible.
More than 8 out of 10 couples where the woman is aged under 40 will get pregnant within one year if they have regular unprotected sex. More than 9 out of 10 couples will get pregnant within two years.
Regular, unprotected sex means having sex every 2 to 3 days without using contraception.
You don't need to time having sex only around ovulation, though it is helpful to know when you are ovulating. Having vaginal sex every 2 to 3 days will give you the best chance of getting pregnant. Sperm can live for 2 to 3 days and this means there will always be fresh sperm in your system when you ovulate (release an egg).
Remember it’s important for you and your partner to try and keep sex enjoyable by concentrating on each other and your relationship, rather than worrying about conceiving. This will help you limit stress.
Are you ready to conceive? Use our tool to find out.
How does pregnancy start?
Your cycle starts on the first day of your period and continues up to the first day of your next period.
This is what happens during the cycle and the start of a pregnancy.
- Eggs mature in your ovaries once a month.
- The lining of your womb starts to get thicker to prepare for fertilised eggs.
- Once the egg is mature it is released from one of the ovaries – this is called ovulation.
- During ovulation your cervical mucus (this is the substance in your cervix, between the vagina and the womb) becomes thinner and clearer to help any sperm to swim to the egg.
- If you have sex, millions of sperm will swim up the cervix into the uterus and the fallopian tubes to meet a mature egg.
- If sperm is present at the point of ovulation, or during the next 24 hours, the egg may be fertilised (only one sperm has to join with the egg for this to happen).
- If the egg is fertilised, it starts to move towards the womb and divide into more cells.
- Once it reaches the womb the fertilised egg has to attach the lining of the womb, this is called implantation and is the start of pregnancy.
 Many fertilised eggs don’t implant and are passed out of the body.
Many fertilised eggs don’t implant and are passed out of the body. - If the egg has not been fertilised, the egg is re-absorbed by the body, the hormone levels drop, and the womb lining is shed – the beginning of your next period.
Now that you know all about how to get pregnant, use our tool to find out if you are ready to conceive.
Best time to have sex to get pregnant
To boost your chances of conceiving, aim to have regular sex (every 2 to 3 days) throughout your cycle so you know that there should hopefully be good-quality sperm waiting when the egg is released. An active sex life is all most people need to conceive.
If you know when you ovulate each month you can give yourself the best chance of getting pregnant by having sex in the days leading up to ovulation. Continue having sex during ovulation. After this your fertile time will be over for that cycle.
Use our ovulation calculator to find out more about ovulation.
Best position to have sex in to get pregnant
The position that you have sex in does not make a difference to conception so long as the man ejaculates sperm into the vagina. Once this happens the sperm can swim up through the cervix and into the womb and fallopian tubes to meet an egg if it is there.
Once this happens the sperm can swim up through the cervix and into the womb and fallopian tubes to meet an egg if it is there.
Many people also say that if the woman raises her legs upwards after sex it helps the sperm get to the womb. There is no evidence to say that this is true. The route from the vagina to the womb is not a straight line, so you do not need to worry about all the sperm coming back out when you stand up.
When does ovulation happen?
Ovulation usually happens about 10 to 16 days before the start of your next period, so it helps to know your cycle length before you start trying to get pregnant.
You may have not known when you ovulate within your cycle, and if you have been using a hormone contraceptive such as the Pill, you won’t have had a natural menstrual cycle for a while, because the Pill prevents ovulation (egg release) from happening.
As a first step, mark on your diary the dates that you bleed during a period. You can then count how many days from the first day of your period to your next period to work out the length of your cycle.
Use our ovulation calculator to find out more about ovulation.
The following signs can also help you know when you ovulate:
Cervical mucus changes
The cervix secretes mucus throughout the menstrual cycle, starting off sticky white and gradually becoming thinner and clearer.
Before and during ovulation the mucus increases and becomes much thinner, slippery and stretchy. Women often compare it to raw egg white.
This thinner mucus is designed to help the sperm swim easily through it.
The last day you notice the wetter secretions is sometimes known as ‘peak day’ and for most women this occurs very close to the time of ovulation.
Temperature
You can also find out about your menstrual cycle by keeping a note of your temperature each morning when you wake up. Your temperature rises by about 0.2°C when ovulation has taken place.
As it only shows you when you have ovulated, and doesn’t tell you when your fertile time starts, this is not very useful for most women.
Using ovulation predictor kits (OPK)
Ovulation predictor kits are available from chemists and are fairly simple to use. They work by detecting a hormone in your urine that increases when ovulation is about to take place.
The simplest urine kit tests for luteinising hormone (LH), which increases 24-36 hours before ovulation. This will help to identify the best two days for conception, although a woman can be fertile for a day or so before and after this time.
It is best to become familiar with your usual menstrual cycle to help figure out when you should start testing. If you have an irregular cycle then an ovulation predictor kit can help you identify the time of ovulation but expect to use more of the test strips.
Find out how long it takes to get pregnant.
How to determine pregnancy without a test
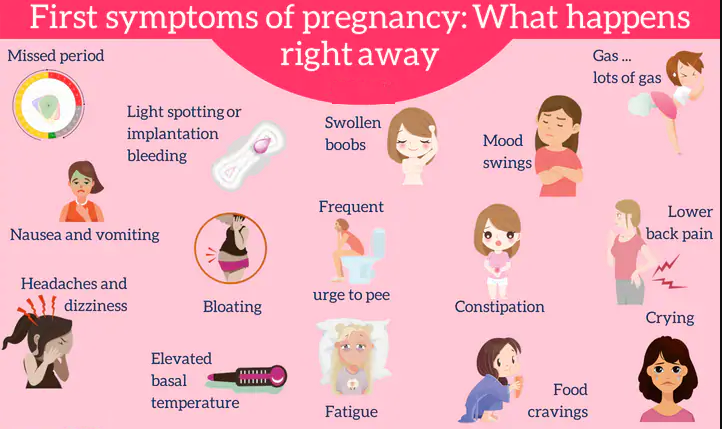
How to determine pregnancy without a test and what signs indirectly indicate that your beloved baby will be born soon? Of course, only a blood test can give a 100% guarantee, but the presence of certain signs may indicate its possible onset.
Classic signs of pregnancy
The most common early signs and symptoms may include
- Delayed menses. nine0011 Problems with the regularity of the menstrual cycle may be associated with hormonal imbalance in the body. But if the delay arose for the first time, and before that the cycle was as accurate as a clock, then it is likely that you are pregnant.
- Early toxicosis with severe nausea and vomiting - the most common sign of an interesting situation, but not every woman has.
- Pain in both breasts or enlargement. Nipples can become very sensitive and change color. Sometimes in the early stages, colostrum is released from them with slight pressure. nine0012
- Pain in the pelvic region, similar to menstruation. But this sign can also indicate such a serious pathology as an ectopic pregnancy.
- Increased amount of discharge from the genitals. This can usually be observed during ovulation.
 Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease. nine0012
Normal discharge is clear and odorless. When a whitish tint or a curdled structure appears, thrush can also be assumed, which is a common problem for expectant mothers. But in this case, you can not do without treatment. During the period of bearing a child, it is necessary to protect your body as much as possible from any, even such a safe disease. nine0012 - Increased or vice versa reduced libido. Every woman experiences jumps in sexual desire in one direction or the other due to hormonal changes occurring in the body. Therefore, men should treat this with understanding, knowing that they have not become less loved, but these are just signs of pregnancy.
- Frequent urination, despite the fact that you do not drink more often and there are no inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system. A similar phenomenon is associated with a slight relaxation of the sphincter of the bladder due to hormonal processes. And with the growth of the uterus and, accordingly, with the increase in pressure on the bladder, going to the toilet will become even more frequent.
 nine0012
nine0012
Additional symptoms of pregnancy
There are less obvious signs that may occur during the first trimester. These include:
- Strange Desires . For example, at night I sharply wanted chocolate, and during the day - salted fish. Such desires may not be mere whims. If you want sour, then perhaps there is not enough vitamin C in the body. You want to gnaw on the wall with calcium deficiency, and sniff gasoline - with a lack of iron, anemia. nine0012
- Constant irritability, tearfulness. The flow of hormones in a woman's body in the early stages can make her unusually emotional. So-called mood swings can be a clear sign of pregnancy.
- Bloating . Hormonal changes can cause feelings of fullness in the abdomen, as at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Bloody discharge pale pink. This symptom is called implantation bleeding. This happens when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, about 10 to 14 days after conception.
 Usually occurs during the normal periods of the menstrual period. But not all women have such bleeding is a sign of a normal pregnancy. Therefore, in case of detection of deviations from the normal cycle, consult a gynecologist. nine0012
Usually occurs during the normal periods of the menstrual period. But not all women have such bleeding is a sign of a normal pregnancy. Therefore, in case of detection of deviations from the normal cycle, consult a gynecologist. nine0012 - Chair problems . Hormonal changes cause the digestive system to slow down, which can lead to constipation.
- Food aversions . When you are pregnant, you may become more sensitive to certain smells and your sense of taste may change. Like most other symptoms, these eating habits can be attributed to hormonal changes.
- Nasal congestion . An increase in hormone levels and blood production can lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa. This can cause congestion or runny nose, nosebleeds. nine0012
ᐈ Are you pregnant? What to do? — Reproductive medicine, gynecology, pregnancy monitoring, urology
Laser treatment and vaginal rejuvenation
Read more
Once again about hormones or a list of must-haves for the week
Read more
Visit to the urologist. For or Against?
For or Against?
More info
Reproductive health care
More info
Pregnancy with uterine fibroids
More info
Practical skills when examining barren couples
Read more
Pregnancy with endometriosis: Modern view
Read more
Breast cancer
Read more
Read more
Protocols for controlled ovarian stimulation (COS)
Read more
Miscarriage. What is the reason? nine0003
Read more
Hysteroscopy and its role in the treatment of infertility
Read more
Why you can’t get pregnant
more
How to calculate the gender of the child before the conception of
more details
Read more a look at the problem
More
Pregnancy with endometriosis - a modern view
More
Immunological infertility and the role of antisperm antibodies in it
More details
What is cervical pathology?
Read more
IVF in the natural cycle: pros and cons
Read more
Practical skills in examining infertile couples
Read more
Artificial insemination
Read more
Read more
Unable to get pregnant. Where to run? Where to begin? nine0003
Where to run? Where to begin? nine0003
Read more
What future parents need to know (most popular questions)
Read more
Endometriosis. Some important questions
Read more
Prolactin increase. Should I be afraid?
Read more
Obstruction of the fallopian tubes, what to do next?
More
Human papillomavirus. Basic information
Read more
KAMALIYA: “I consider Vladimir Kotlik the godfather of my children”
3
Read more
Infertility and cancer: why men should definitely visit a reproductologist
Read more
Sex, children, rock and roll: reproductive specialists about what can increase the chances of IVF
Read more
Portrait of a female doctor: 5 signs of a good gynecologist
Read more
Is sex during IVF a good idea?
Read more
Never say never. Why childfree is dangerous and why it is worth leaving a “part of yourself” in a cryobank
Why childfree is dangerous and why it is worth leaving a “part of yourself” in a cryobank
Learn more
How to plan for health, longevity and parenthood: practical advice from doctors for 2020
Learn more
From virus to cancer: hidden threats to women's health
Learn more
Threatened abortion
Reproductive health of teenage girls: what children and their parents need to knowRead more
Life is like magic: how to believe in a miracle if you are a pragmatist - a doctor's story
Read more
Beautiful skin in youth is the key to happy motherhood
Read more
Charged for success. What determines the effectiveness of ART
More
Why do not all eggs become embryos?
Read more
Maxim Gapchuk in "Mother and Child" ambitious future
Read more
Unsuccessful IVF, how to survive? Expert advice
Read more
What should an Rh-negative woman know? nine0003
Read more
9 tips for future parents
Read more
Eco: Modern methods and approaches in the treatment of female infertility
more
ICSI: Men's infertility is not a sentence
more
Laparoscopy: Advantages over traditional surgical
Read more
Uterine examination: what you need to know about hysteroscopy
Read more
Artificial intrauterine insemination: the essence of the method, stages and results
Read more
Infertility Diagnostics in men
Read more
10 reasons to contact a man to andrologist
Read more
Cryototechnology as a way of family planning
more details
How to become a mother: Psychological and physical training
Read more
9000 Monalisa Touch — what kind of technology is thisMore
Premature menopause in men: how to recognize and what is dangerous
More
Why visit a gynecologist for preventive examinations
More details
Laser therapy in gynecology: without anesthesia and pain
More details
Outpatient gynecology - timely seeking qualified help
More details
More details
Causes and prevention of female infertility
More details
One-day surgery: a modern approach to treatment
Read more
Pregnancy management: keep the baby healthy and mother feel good
Read more
Pregnancy after IVF: what future parents need to remember
Read more
Anomalies of the uterus and their impact on the onset and gestation of pregnancy.