Types of fertility treatments
Fertility Treatments For Infertility
In This Section
- Fertility Treatments
- What is IVF?
- What is IUI?
What fertility treatment options do I have?
If you’re struggling with infertility and need help getting pregnant, there are fertility treatments that can help increase your chances of having a baby.
What are the different types of fertility treatments?
Thanks to technology, there are lots of ways to help people with all kinds of fertility issues. The options that are best for you depend on your personal situation and what’s causing your infertility.
Sometimes only one person needs treatment, other times both partners will use a combination of treatments together.
Fertility treatments often include medications that help with hormones and ovulation, sometimes combined with minor surgical procedures. Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) describes several kinds of procedures that can help you have a baby. ART includes procedures that make it easier for sperm to fertilize an egg, and help the egg implant in your uterine lining.
Two of the most common fertility treatments are:
-
intrauterine insemination (IUI)
-
in vitro fertilization (IVF)
Cryopreservation (aka freezing your eggs, sperm, or embryos), egg or embryo donation, and gestational carriers (aka surrogacy) are also forms of ART.
Donor sperm, donor eggs, and surrogates are often used by same-sex couples or single people who want to have a baby. You can also use sperm and/or eggs from a donor if a problem with your own sperm cells or eggs is causing infertility issues.
Talking with a doctor who specializes in pregnancy and/or infertility can help you figure out which treatments are best for you. Your family doctor or gynecologist can refer you to a fertility specialist. You may also be able to get fertility treatments, or help finding a fertility specialist in your area, from your local Planned Parenthood health center.
Was this page helpful?- Yes
- No
Help us improve - how could this information be more helpful?
How did this information help you?
Please answer below.
Are you human? (Sorry, we have to ask!)
Please don't check this box if you are a human.
You’re the best! Thanks for your feedback.
Thanks for your feedback.
We couldn't access your location, please search for a location.
Zip, City, or State
Please enter a valid 5-digit zip code or city or state.
Please fill out this field.
Service All Services Abortion Abortion Referrals Birth Control COVID-19 Vaccine HIV Services Men's Health Care Mental Health Morning-After Pill (Emergency Contraception) Pregnancy Testing & Services Primary Care STD Testing, Treatment & Vaccines Transgender Hormone Therapy Women's Health Care
Filter By All Telehealth In-person
Please enter your age and the first day of your last period for more accurate abortion options. Your information is private and anonymous.
Your information is private and anonymous.
I'm not sure This field is required.
AGE This field is required.
Or call 1-800-230-7526
treatment for infertility - NHS
If you have fertility problems, the treatment you're offered will depend on what's causing the problem and what's available from your local integrated care board (ICB).
Find your local integrated care board (ICB).
There are 3 main types of fertility treatment:
- medicines
- surgical procedures
- assisted conception – including intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
Medicines
Common fertility medicines include:
- clomifene – encourages the monthly release of an egg (ovulation) in women who do not ovulate regularly or cannot ovulate at all
- tamoxifen – an alternative to clomifene that may be offered if you have ovulation problems
- metformin – is particularly beneficial for women who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- gonadotrophins – can help stimulate ovulation in women, and may also improve fertility in men
- gonadotrophin-releasing hormone and dopamine agonists – other types of medicine prescribed to encourage ovulation in women
Some of these medicines may cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, headaches and hot flushes.
Speak to your doctor for more information about the possible side effects of specific medicines.
Medicine that stimulates the ovaries is not recommended for women with unexplained infertility because it has not been found to increase their chances of getting pregnant.
Surgical procedures
There are several types of surgical procedures that may be used to investigate fertility problems and help with fertility.
Fallopian tube surgery
If your fallopian tubes have become blocked or scarred, you may need surgery to repair them.
Surgery can be used to break up the scar tissue in your fallopian tubes, making it easier for eggs to pass through them.
The success of surgery will depend on the extent of the damage to your fallopian tubes.
Possible complications from tubal surgery include an ectopic pregnancy, which is when the fertilised egg implants outside the womb.
Endometriosis, fibroids and PCOS
Endometriosis is when parts of the womb lining start growing outside the womb.
Laparoscopic surgery is often used to treat endometriosis by destroying or removing fluid-filled sacs called cysts.
It may also be used to remove submucosal fibroids, which are small growths in the womb.
If you have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a minor surgical procedure called laparoscopic ovarian drilling can be used if ovulation medicine has not worked.
This involves using either heat or a laser to destroy part of the ovary.
Read more about laparoscopy.
Correcting an epididymal blockage and surgery to retrieve sperm
The epididymis is a coil-like structure in the testicles that helps store and transport sperm.
Sometimes the epididymis becomes blocked, preventing sperm from being ejaculated normally. If this is causing infertility, surgery can be used to correct the blockage.
Surgical extraction of sperm may be an option if you:
- have an obstruction that prevents the release of sperm
- were born without the tube that drains the sperm from the testicle (vas deferens)
- have had a vasectomy or a failed vasectomy reversal
Both operations take a few hours and are done under local anaesthetic as outpatient procedures.
You'll be advised on the same day about the quality of the tissue or sperm collected.
Any sperm will be frozen and placed in storage for use at a later stage.
Assisted conception
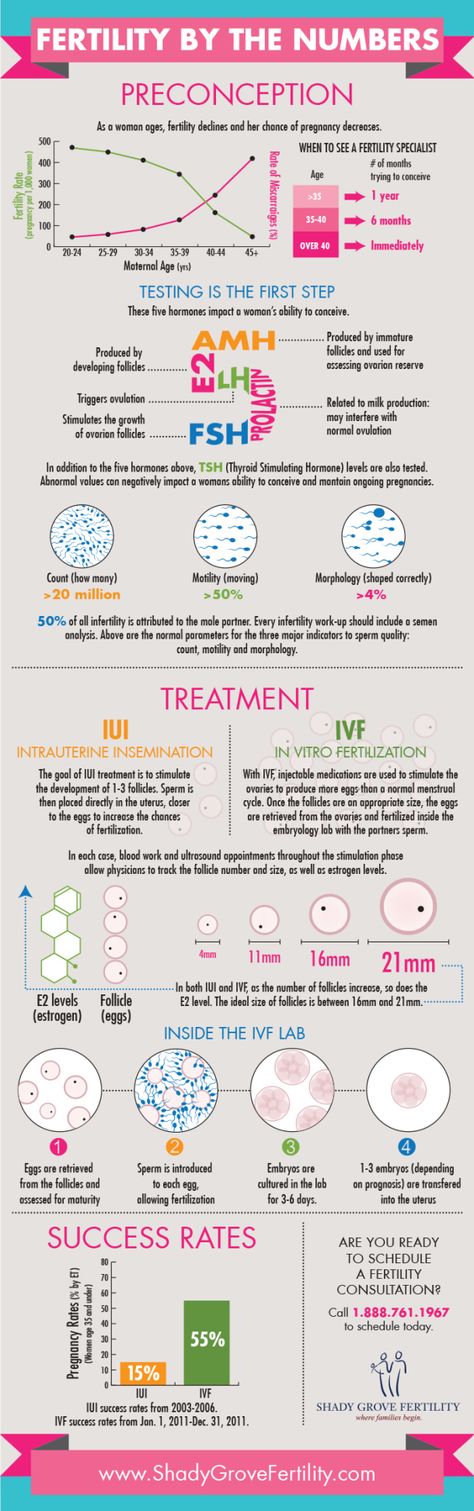
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI), also known as artificial insemination, involves inserting sperm into the womb via a thin plastic tube passed through the cervix.
Sperm is first collected and washed in a fluid. The best quality specimens (the fastest moving) are selected.
Read more about IUI.
In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
In vitro fertilisation (IVF), is when an egg is fertilised outside the body. Fertility medicine is taken to encourage the ovaries to produce more eggs than usual.
Eggs are removed from the ovaries and fertilised with sperm in a laboratory. A fertilised egg (embryo) is then returned to the womb to grow and develop.
Read more about IVF.
Egg and sperm donation
If you or your partner has an infertility problem, you may be able to receive eggs or sperm from a donor to help you conceive. Treatment with donor eggs is usually done using IVF.
Anyone who registered to donate eggs or sperm after 1 April 2005 can no longer remain anonymous and must provide information about their identity.
This is because a child born as a result of donated eggs or sperm is legally entitled to find out the identity of the donor when they become an adult (at age 18).
Further information
Get more information about fertility treatment options from the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) website.
Eligibility for fertility treatment on the NHS
Fertility treatment funded by the NHS varies across the UK. Waiting lists for treatment can be very long in some areas.
The eligibility criteria can also vary. A GP will be able to advise about your eligibility for treatment, or you can contact your local integrated care board (ICB).
If the GP refers you to a specialist for further tests, the NHS will pay for this. All patients have the right to be referred to an NHS clinic for the initial investigation.
Going private
If you have an infertility problem you may want to consider private treatment. This can be expensive, and there's no guarantee of success.
It's important to choose a private clinic carefully.
You should find out:
- which clinics are available
- which treatments are offered
- the success rates of treatments
- the length of the waiting list
- the costs
Ask for a personalised, fully costed treatment plan that explains exactly what's included, such as fees, scans and any necessary medicine.
Choosing a clinic
If you decide to go private, you can ask a GP for advice. Make sure you choose a clinic licensed by the HFEA.
The HFEA is a government organisation that regulates and inspects all UK clinics that provide fertility treatment, including the storage of eggs, sperm or embryos.
Complementary therapy
There's no evidence to suggest complementary therapies for fertility problems are effective.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) states further research is needed before such interventions can be recommended.
Page last reviewed: 18 February 2020
Next review due: 18 February 2023
Treatment of infertility at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences at a bargain price, clinic for the treatment of infertility in women in Moscow
According to various sources, from 15% to 18% of married couples in Russia face the problem of infertility. These statistics would be more positive if men and women did not waste time on doubts and long expectations of pregnancy. Thanks to modern reproductive technologies, most infertile couples can become parents after treatment.
Thanks to modern reproductive technologies, most infertile couples can become parents after treatment.
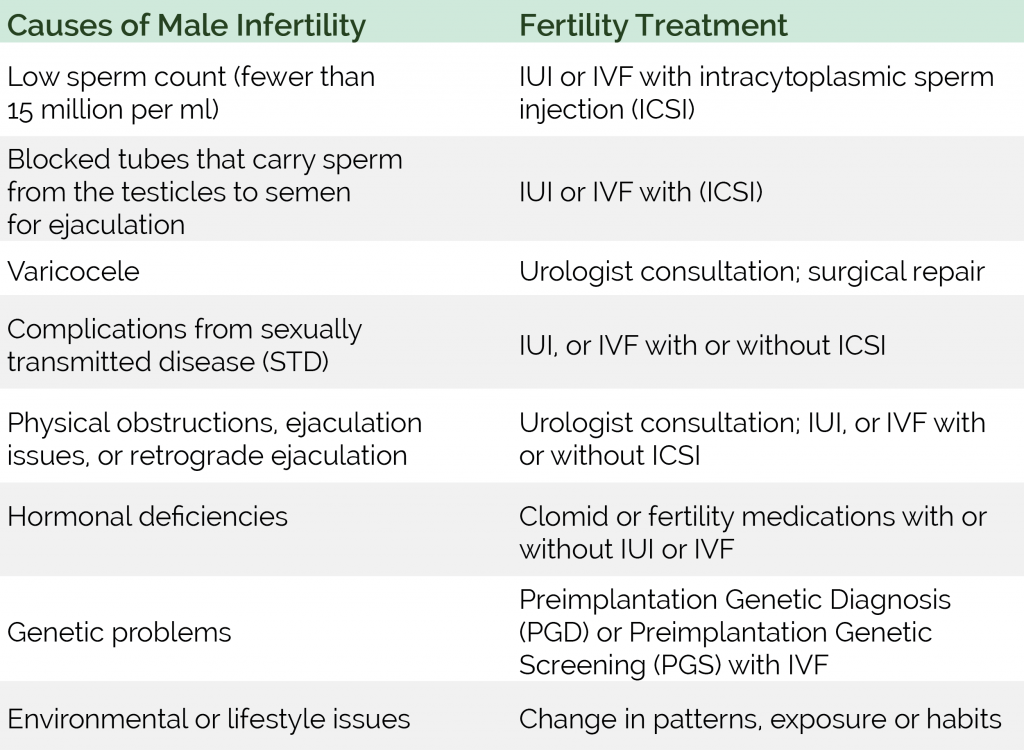
Causes of female and male infertility
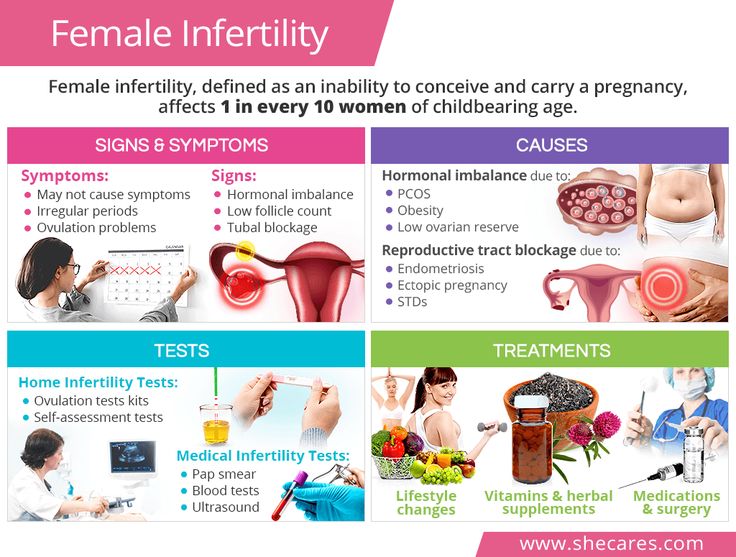
Doctors explain the inability to conceive a child with a violation of the reproductive function. Infertility can be female, male and combined (with incompatibility of partners). If a woman does not become pregnant within 8 to 12 months of regular intercourse without contraception, medical attention should be sought. The sooner doctors find out what is the reason for the failure of natural conception attempts, the more chances to solve the problem.
- Female infertility is most often associated with hormonal imbalance, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, endometriosis, adhesions in the pelvis, genetic abnormalities. Age matters a lot. After the age of 38, the number and quality of eggs produced decreases. This negatively affects the ability to conceive.
- Male infertility in most cases occurs due to insufficient production and low activity of spermatozoa.
 There is no connection between reproductive health and potency. The most common causes of deviations include congenital pathologies of the reproductive organs and sexually transmitted diseases.
There is no connection between reproductive health and potency. The most common causes of deviations include congenital pathologies of the reproductive organs and sexually transmitted diseases.
In more than 75% of cases, doctors manage to identify and eliminate the cause of infertility in a couple. Specialists are doing everything possible to restore the natural ability to conceive. If there is no chance of this, assisted reproductive technologies are used.
Infertility diagnostics
To restore reproductive abilities, both partners must undergo a comprehensive diagnosis.
As part of the diagnosis of infertility, the following types of studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the organs of the reproductive system;
- genetic tests;
- study of hormonal status;
- study of immunity;
- tests for infections;
- for men - urological examination, spermogram, biochemical analysis of semen;
- in women - gynecological examination, colposcopy, endometrial biopsy, hysterosalpingography (checking the patency of the fallopian tubes).
The diagnostic methods used in the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences allow in almost all cases (with the exception of the so-called idiopathic infertility, when a man and a woman are completely healthy and compatible, but not able to conceive a child) to accurately determine the cause of infertility in a couple. Treatment is prescribed based on the results of the examination.
Methods of treatment
To restore reproductive health, patients of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences are offered highly effective modern methods of treatment. They are prescribed strictly according to indications and in the absence of restrictions (contraindications).
- hormone therapy. In case of malfunctions in the endocrine system, high-quality medicines are used that do not cause side effects.
- ICSI is intracytoplasmic sperm injection. It is carried out in cases where there is no chance of fertilization of the egg in a natural way.
 Spermatozoa are isolated from the tissues of the testicles and injected into the uterus. The female egg is fertilized, the further development of the embryo proceeds in the usual way.
Spermatozoa are isolated from the tissues of the testicles and injected into the uterus. The female egg is fertilized, the further development of the embryo proceeds in the usual way. - Intrauterine insemination. In case of violation of ejaculation and low quality of sperm, sedentary spermatozoa are injected into the female reproductive organs with the help of special devices.
- Surgical intervention. Low-traumatic endoscopic interventions are indicated for women with pathologies in the structure of the genital organs, the presence of adhesions, cysts, and tumors.
- IVF (in vitro fertilization). Today it is one of the most popular and effective technologies. After drug therapy, which stimulates the readiness of the ovaries, mature male spermatozoa are planted in the woman's egg.
Benefits of infertility treatment at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences
It is impossible to solve the problem of infertility without professional medical help. The Department of Assisted Reproductive Technologies of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow is ready to offer you effective and safe options for restoring reproductive health using advanced technologies. Qualified doctors have sufficient experience and knowledge to treat all forms of infertility, including complex cases.
The Department of Assisted Reproductive Technologies of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow is ready to offer you effective and safe options for restoring reproductive health using advanced technologies. Qualified doctors have sufficient experience and knowledge to treat all forms of infertility, including complex cases.
To make an appointment at the clinic and clarify the cost of services, you can call +7 (499) 400 47 33 or use a special form on the website.
Methods of diagnosis and treatment of infertility in EMC
If a woman does not become pregnant within one year of regular intercourse without the use of contraceptives, we are talking about infertility.
However, the female factor is not always the cause of the problem. In almost half of the cases, infertility is associated with a violation in men.
Types of infertility
- Female infertility. Occurs in 40% of cases.
- Male infertility. Also detected in 40% of cases.
- Combined infertility. It accounts for 35% of cases.
In turn, these types are divided into primary and secondary infertility (secondary is exhibited if the woman has already had pregnancies).
Modern medicine has made such progress that today in most cases it is possible to successfully recover patients and give birth to a healthy baby.
Causes of infertility
Why female infertility occurs
Among the causes of infertility in women:
- Endocrine factor
- Diseases of the uterus (endometritis, endometrial hyperplasia, endometritis, etc.)
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes (tubal infertility)
- Immunological factor
- Endometriosis and others
Why male infertility occurs
In men, the most common causes of infertility are:
- Testicular disorders
- Urogenital infections
- Hormonal disorders
- Varicocele
- Impaired patency of the vas deferens
- Ejaculatory disorders (retrograde, premature or prolonged ejaculation), etc.
Fertility treatment
Treatment of female infertility
Before starting treatment for female infertility, doctors at the EMC Reproductive and Prenatal Medicine Clinic conduct a complete examination of the patient. Diagnostics may include an examination by a gynecologist, a reproductive specialist (if necessary, all the necessary specialists can join the examination process: an endocrinologist, geneticist, oncologist, etc.), laboratory tests (general blood and urine tests, hormonal tests, tests for the detection of STIs), instrumental methods research (ultrasound, MRI, hysteroscopy, laparoscopy, etc.).
Controlled ovulation induction
For women with good patency of the fallopian tubes, whose cause of infertility is problems with ovulation, the specialists of the EMC Reproduction Clinic offer controlled induction of ovulation. For this, a woman is prescribed medications, when taken, the follicle grows. In the process of stimulation, 1-3 follicles must grow in order to have a chance of pregnancy. Induction is performed under ultrasound, so that if necessary, you can change the dosage of the prescribed drugs. A prerequisite for pregnancy in this case is the good quality of the sperm of the spouse.
Induction is performed under ultrasound, so that if necessary, you can change the dosage of the prescribed drugs. A prerequisite for pregnancy in this case is the good quality of the sperm of the spouse.
However, in certain cases, conditions are diagnosed in which it is impossible to conceive a child on their own (for example, obstruction of the fallopian tubes, serious changes in the spermogram of the spouse, etc.) or the treatment is not effective. Then the only way to get pregnant is the use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
ECO
Artificial insemination is a salvation in almost all situations, even when a woman is diagnosed with complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes or their absence. IVF consists of several steps. First, ovulation is stimulated, then ovarian puncture is done. The husband donates sperm, it is carefully processed in the laboratory. To increase the chances of pregnancy, embryologists can use additional ART methods - ICSI, IMSI, PICSI, which involve manual selection of the healthiest spermatozoa in terms of morphology and speed. Next, the oocyte is fertilized in vitro and the subsequent growth of the embryo. On days 3-5, a healthy ready-made embryo is transferred into the uterine cavity. If the embryo takes root, then the normal development of the embryo occurs, which is no different from the process of a normal pregnancy. Transfer 1-2 embryos, if it turned out more, then they can be frozen.
Next, the oocyte is fertilized in vitro and the subsequent growth of the embryo. On days 3-5, a healthy ready-made embryo is transferred into the uterine cavity. If the embryo takes root, then the normal development of the embryo occurs, which is no different from the process of a normal pregnancy. Transfer 1-2 embryos, if it turned out more, then they can be frozen.
Treatment of male infertility
Tactics of treatment is also determined after a comprehensive examination.
Medical treatment
If urogenital infections or endocrine disorders are detected, medication is prescribed. After recovery, in the vast majority of cases, natural conception occurs.
Surgical treatment
In case of diagnosed impaired patency of the vas deferens, surgical methods of treatment are used.
Artificial insemination (AI)
Insertion of husband's or donor's sperm during ovulation into the woman's uterine cavity by means of a catheter. In this case, the process of fertilization occurs naturally. In the case of this ART technique, the chances of pregnancy are achieved through high-tech processing of sperm in the embryological laboratory. That is, only good quality sperm is used for AI. AI is effective in cases where a man is diagnosed with a reduced number of normal spermatozoa, the presence of antibodies in the semen, erectile dysfunction, abnormal development of the genital organs, etc. AI can also be used for women who do not have a sexual partner. In this case, reproductive specialists use donor sperm.
In this case, the process of fertilization occurs naturally. In the case of this ART technique, the chances of pregnancy are achieved through high-tech processing of sperm in the embryological laboratory. That is, only good quality sperm is used for AI. AI is effective in cases where a man is diagnosed with a reduced number of normal spermatozoa, the presence of antibodies in the semen, erectile dysfunction, abnormal development of the genital organs, etc. AI can also be used for women who do not have a sexual partner. In this case, reproductive specialists use donor sperm.
ECO
In vitro fertilization, especially in combination with additional ART methods - ICSI, IMSI and PICSI - significantly increases the chances of pregnancy even with a very poor quality of a man's sperm. Only in extreme cases, when it is impossible to obtain the spouse's spermatozoa in any way, the use of donor sperm is suggested.
Benefits of visiting the EMC Reproduction Clinic
- Competent specialists with experience in the world's leading clinics.