Trimester during pregnancy
Everything you need to know
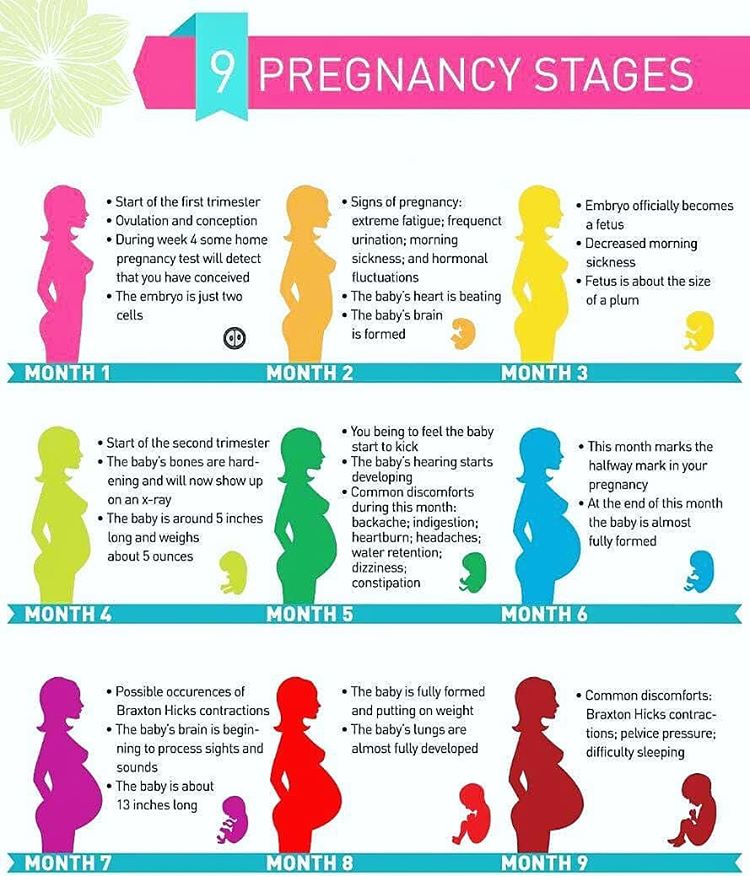
A full-term pregnancy has three trimesters and lasts around 40 weeks — starting from the first day of the last menstrual period. In each trimester, the fetus meets specific developmental milestones.
While 40 weeks is the usual time frame, a full-term baby can be born as early as 37 weeks and as late as 42 weeks.
The Office on Women’s Health defines the three trimesters as follows, though the timing can vary:
- first trimester: 1–12 weeks
- second trimester: 13–28 weeks
- third trimester: 29–40 weeks
Some people also talk about a fourth trimester, which is the 3-month transitional period after delivery.
Read on for more information about what to expect during each pregnancy trimester.
Image credit: Stephen Kelly, 2018
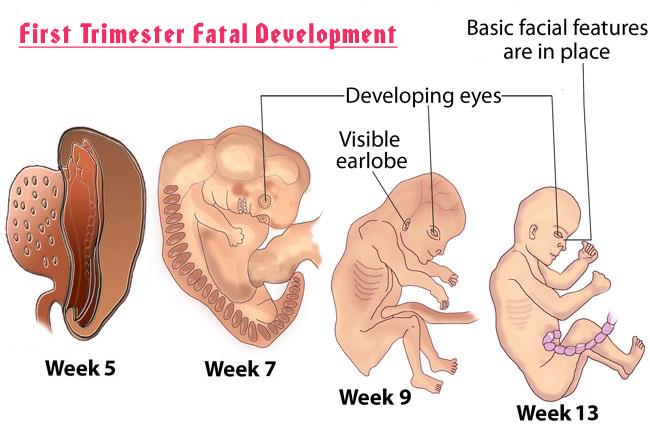
The first trimester is the first 12 weeks of the pregnancy, and it is a crucial time for fetal development.
The fetus
At conception, the egg and sperm combine to form a zygote, which implants in the wall of the uterus. The zygote becomes an embryo as its cells divide and grow.
By the end of the first 12 weeks:
- All the body’s major organs and structures have begun to develop.
- The heart is beating regularly.
- Fingers and toes have formed.
- The fetus is around 3 inches (in) long and weighs nearly 1 ounce.
- The nerves and muscles work together, and the fetus can make a fist.
- The eyelids have formed and will remain closed until around week 28, to protect the eyes.
The pregnant person
A person also experiences many changes during their first trimester of pregnancy.
These include:
- fatigue
- tender, swollen breasts
- mood changes
- cravings for certain foods
- headaches
- indigestion
- a need to urinate more often
- weight changes
- constipation
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting, known as morning sickness
Morning sickness can last throughout the first trimester and sometimes beyond. Despite its name, it does not occur only in the morning.
Despite its name, it does not occur only in the morning.
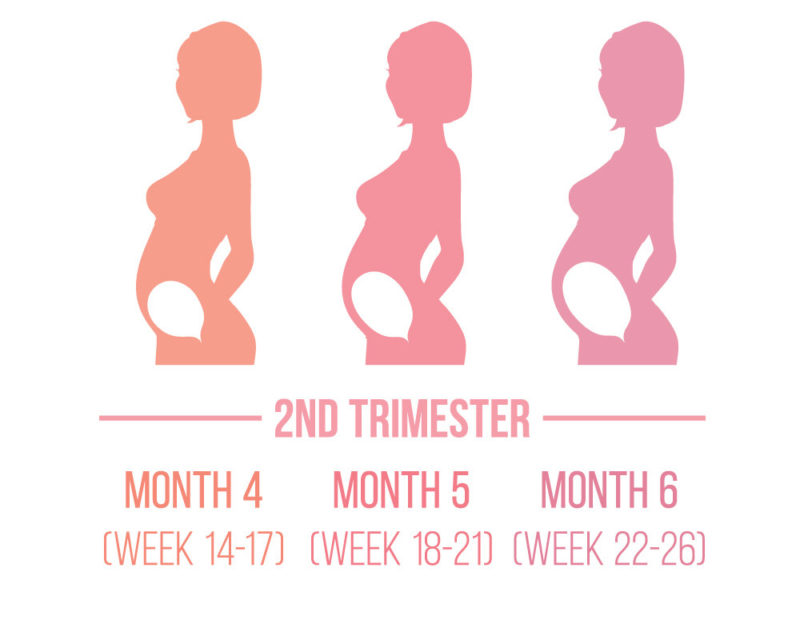
Weeks 14–27 are the second trimester. The fetus goes through many changes during this time, growing to be around 1 foot long and weighing 1.5 pounds.
The fetus
By the end of the second trimester, the following will have happened:
- Meconium, the first bowel movement, has developed in the intestines.
- The fetus can see, hear, make a sucking motion, and scratch itself.
- Skin, hair, and nails have formed.
- The lungs have formed but do not yet work.
- The fetus is sleeping and waking regularly.
- A male’s testicles will have moved to the scrotum, and a female’s eggs will have formed in the ovaries.
- Taste buds have formed.
- Bone marrow is making blood cells.
- Lanugo, which is fine hair, covers the body.
The pregnant person
Many people feel more comfortable during the second trimester of pregnancy. Morning sickness and fatigue often reduce or disappear.
Meanwhile, new changes take place:
- The abdomen expands as the fetus grows.
- Stretch marks may appear on the abdomen, thighs, breasts, and buttocks.
- The areola, the skin around the nipples, becomes darker.
- The skin on the face and may darken in patches.
- The ankles, fingers, and face may swell.
- Itching may occur. If it happens with vomiting or yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, known as jaundice, seek medical advice.
It becomes possible to feel the baby’s movements as this trimester progresses.
The third trimester lasts from week 29 until delivery, which is usually around week 40.
The fetus
Most organs and body systems have formed by now, and they will continue to grow and mature.
During this trimester:
- The bones are hardening.
- Movements become more noticeable.
- The eyes are open and can sense light.
- Lung formation becomes complete.
- Lanugo falls away, and a waxy coating, called vernix, develops.
Toward delivery, the fetus drops lower in the person’s abdomen and usually turns head-down.
The pregnant person
The growth of the fetus can cause new discomfort at this time.
A person might also experience:
- heartburn
- shortness of breath
- swelling in the ankles, face, and fingers
- insomnia
- mood changes
- leakage of milk from the breasts
- other breast and nipple changes
- frequent urination
- hemorrhoids
- Braxton-Hicks contractions, which do not indicate labor
- real contractions, which indicate labor
It is also normal to feel anxiety about the delivery and parenthood toward the end of a pregnancy.
The 3 months after delivery play a key role in the health of the person and their baby. Some people call this transitional period a fourth trimester.
While this can be an exciting time, the range of hormonal and environmental changes can pose challenges.
These challenges might involve:
- recovering after delivery, especially if there are stitches
- dealing with lochia, a discharge of blood and tissue, which may continue for several weeks
- cramping, which may feel like menstrual cramping, especially during breastfeeding
- adjusting to a new role of parenthood
- learning new skills
- having sore breasts and other difficulties related to breastfeeding
- having fatigue, due to a loss of sleep and other factors
- in some cases, experiencing postpartum depression
Some tips for managing include:
- limiting visitors, if this helps
- asking others for help
- reducing housekeeping duties
- resting when the baby does
- eating regularly, as far as possible
- raising any concerns about the baby, breastfeeding, or personal health
- attending all followup appointments
Anyone who experiences a persistent low mood, feelings of guilt or inadequacy, or thoughts of harming themselves or the baby should seek immediate medical care and guidance. These can be signs of postpartum depression.
These can be signs of postpartum depression.
Suicide prevention
If you know someone at immediate risk of self-harm, suicide, or hurting another person:
- Ask the tough question: “Are you considering suicide?”
- Listen to the person without judgment.
- Call 911 or the local emergency number, or text TALK to 741741 to communicate with a trained crisis counselor.
- Stay with the person until professional help arrives.
- Try to remove any weapons, medications, or other potentially harmful objects.
If you or someone you know is having thoughts of suicide, a prevention hotline can help. The 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline is available 24 hours a day at 988. During a crisis, people who are hard of hearing can use their preferred relay service or dial 711 then 988.
Click here for more links and local resources.
Pregnancy, childbirth, and the first few months with a newborn are unlike any other time in life. They are full of new experiences, great uncertainty, upheavals, and many new emotions.
Getting regular prenatal care is vital during each trimester. A doctor can help ensure that the fetus is meeting their developmental milestones and that the pregnant person is in good health. They can also provide guidance and resources for support.
Everything you need to know
A full-term pregnancy has three trimesters and lasts around 40 weeks — starting from the first day of the last menstrual period. In each trimester, the fetus meets specific developmental milestones.
While 40 weeks is the usual time frame, a full-term baby can be born as early as 37 weeks and as late as 42 weeks.
The Office on Women’s Health defines the three trimesters as follows, though the timing can vary:
- first trimester: 1–12 weeks
- second trimester: 13–28 weeks
- third trimester: 29–40 weeks
Some people also talk about a fourth trimester, which is the 3-month transitional period after delivery.
Read on for more information about what to expect during each pregnancy trimester.
Image credit: Stephen Kelly, 2018
The first trimester is the first 12 weeks of the pregnancy, and it is a crucial time for fetal development.
The fetus
At conception, the egg and sperm combine to form a zygote, which implants in the wall of the uterus. The zygote becomes an embryo as its cells divide and grow.
By the end of the first 12 weeks:
- All the body’s major organs and structures have begun to develop.
- The heart is beating regularly.
- Fingers and toes have formed.
- The fetus is around 3 inches (in) long and weighs nearly 1 ounce.
- The nerves and muscles work together, and the fetus can make a fist.
- The eyelids have formed and will remain closed until around week 28, to protect the eyes.
The pregnant person
A person also experiences many changes during their first trimester of pregnancy.
These include:
- fatigue
- tender, swollen breasts
- mood changes
- cravings for certain foods
- headaches
- indigestion
- a need to urinate more often
- weight changes
- constipation
- nausea, sometimes with vomiting, known as morning sickness
Morning sickness can last throughout the first trimester and sometimes beyond. Despite its name, it does not occur only in the morning.
Despite its name, it does not occur only in the morning.
Weeks 14–27 are the second trimester. The fetus goes through many changes during this time, growing to be around 1 foot long and weighing 1.5 pounds.
The fetus
By the end of the second trimester, the following will have happened:
- Meconium, the first bowel movement, has developed in the intestines.
- The fetus can see, hear, make a sucking motion, and scratch itself.
- Skin, hair, and nails have formed.
- The lungs have formed but do not yet work.
- The fetus is sleeping and waking regularly.
- A male’s testicles will have moved to the scrotum, and a female’s eggs will have formed in the ovaries.
- Taste buds have formed.
- Bone marrow is making blood cells.
- Lanugo, which is fine hair, covers the body.
The pregnant person
Many people feel more comfortable during the second trimester of pregnancy. Morning sickness and fatigue often reduce or disappear.
Meanwhile, new changes take place:
- The abdomen expands as the fetus grows.
- Stretch marks may appear on the abdomen, thighs, breasts, and buttocks.
- The areola, the skin around the nipples, becomes darker.
- The skin on the face and may darken in patches.
- The ankles, fingers, and face may swell.
- Itching may occur. If it happens with vomiting or yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, known as jaundice, seek medical advice.
It becomes possible to feel the baby’s movements as this trimester progresses.
The third trimester lasts from week 29 until delivery, which is usually around week 40.
The fetus
Most organs and body systems have formed by now, and they will continue to grow and mature.
During this trimester:
- The bones are hardening.
- Movements become more noticeable.
- The eyes are open and can sense light.
- Lung formation becomes complete.
- Lanugo falls away, and a waxy coating, called vernix, develops.
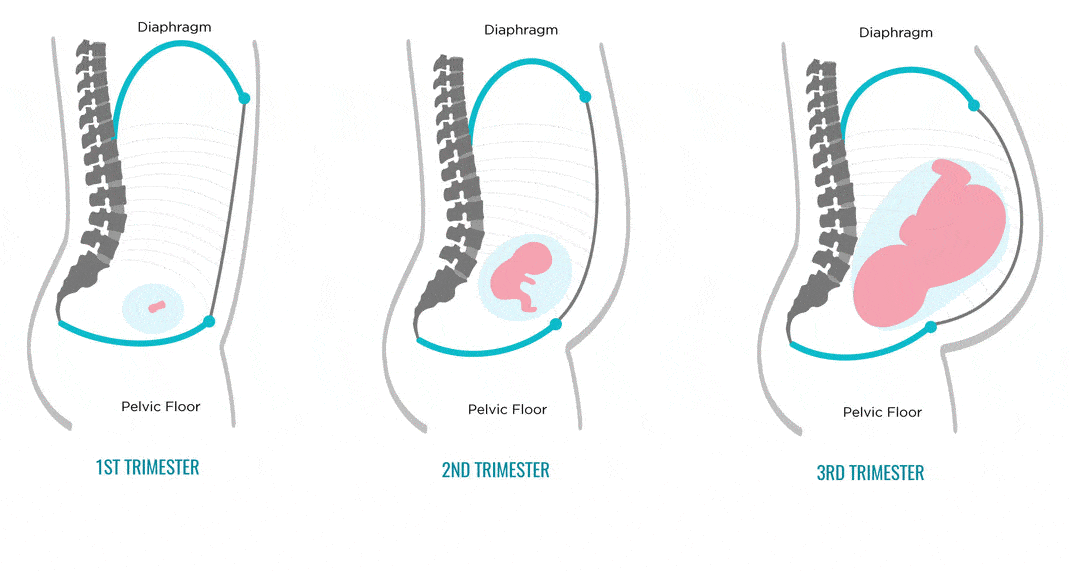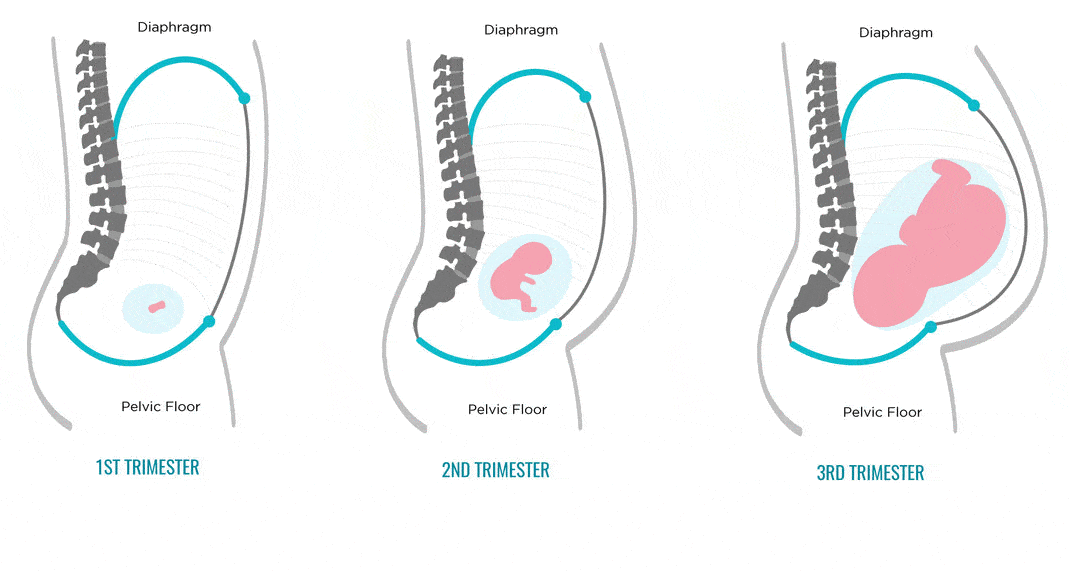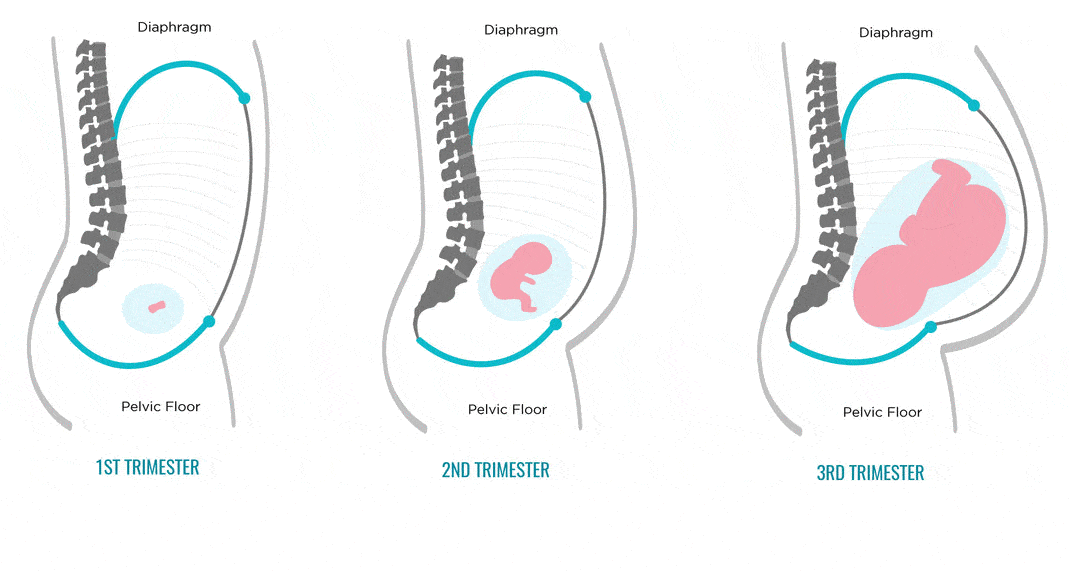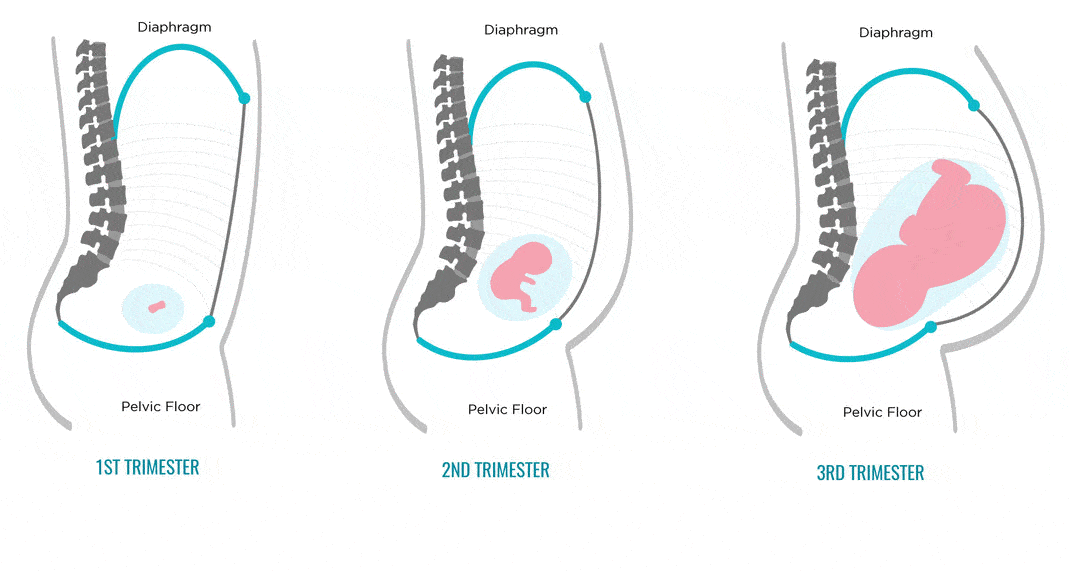
Toward delivery, the fetus drops lower in the person’s abdomen and usually turns head-down.
The pregnant person
The growth of the fetus can cause new discomfort at this time.
A person might also experience:
- heartburn
- shortness of breath
- swelling in the ankles, face, and fingers
- insomnia
- mood changes
- leakage of milk from the breasts
- other breast and nipple changes
- frequent urination
- hemorrhoids
- Braxton-Hicks contractions, which do not indicate labor
- real contractions, which indicate labor
It is also normal to feel anxiety about the delivery and parenthood toward the end of a pregnancy.
The 3 months after delivery play a key role in the health of the person and their baby. Some people call this transitional period a fourth trimester.
While this can be an exciting time, the range of hormonal and environmental changes can pose challenges.
These challenges might involve:
- recovering after delivery, especially if there are stitches
- dealing with lochia, a discharge of blood and tissue, which may continue for several weeks
- cramping, which may feel like menstrual cramping, especially during breastfeeding
- adjusting to a new role of parenthood
- learning new skills
- having sore breasts and other difficulties related to breastfeeding
- having fatigue, due to a loss of sleep and other factors
- in some cases, experiencing postpartum depression
Some tips for managing include:
- limiting visitors, if this helps
- asking others for help
- reducing housekeeping duties
- resting when the baby does
- eating regularly, as far as possible
- raising any concerns about the baby, breastfeeding, or personal health
- attending all followup appointments
Anyone who experiences a persistent low mood, feelings of guilt or inadequacy, or thoughts of harming themselves or the baby should seek immediate medical care and guidance. These can be signs of postpartum depression.
These can be signs of postpartum depression.
Suicide prevention
If you know someone at immediate risk of self-harm, suicide, or hurting another person:
- Ask the tough question: “Are you considering suicide?”
- Listen to the person without judgment.
- Call 911 or the local emergency number, or text TALK to 741741 to communicate with a trained crisis counselor.
- Stay with the person until professional help arrives.
- Try to remove any weapons, medications, or other potentially harmful objects.
If you or someone you know is having thoughts of suicide, a prevention hotline can help. The 988 Suicide and Crisis Lifeline is available 24 hours a day at 988. During a crisis, people who are hard of hearing can use their preferred relay service or dial 711 then 988.
Click here for more links and local resources.
Pregnancy, childbirth, and the first few months with a newborn are unlike any other time in life. They are full of new experiences, great uncertainty, upheavals, and many new emotions.
Getting regular prenatal care is vital during each trimester. A doctor can help ensure that the fetus is meeting their developmental milestones and that the pregnant person is in good health. They can also provide guidance and resources for support.
what happens in 1, 2, 3 months
Wise nature endowed a woman with everything she needs to bear and give birth to a child. But this does not prevent expectant mothers from being interested in what is connected with conception, pregnancy and childbirth - asking important questions and looking for answers to them. They want to know what happens in the first trimester of pregnancy, how the baby develops, what processes take place in the body, what can and cannot be done. Let's talk about this in more detail.
Excursion to obstetrics
First, let's define some terminology.
The entire pregnancy (gestation) of a woman lasts 40 weeks (280 days). These data are conditional, because normally, childbirth can begin at almost any time for a period of 37-42 weeks. This entire period is divided into three trimesters. The first trimester of pregnancy lasts from the first day of the last menstrual period until the end of the 13th week.
This entire period is divided into three trimesters. The first trimester of pregnancy lasts from the first day of the last menstrual period until the end of the 13th week.
The division of pregnancy into weeks and trimesters is accepted in obstetrics. But women more often measure this period by months. This is not entirely correct, because one month includes 4 or 5 weeks. Therefore, in the article we will focus specifically on the obstetric weeks of gestation, but we will also correlate them with the months familiar to many women. nine0003
What happens in the first trimester of pregnancy
Obstetricians calculate the gestational age from the first day of the last menstruation. This is convenient - after all, most women keep a calendar and know this date. However, there is still no fetus during this period. Conception happens later - during ovulation, after about two weeks. It would be possible to count the gestational age from the moment of conception, but this date is difficult to calculate. In addition, ovulation may not occur in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier or later - and then it will be even more difficult to calculate it. nine0003
In addition, ovulation may not occur in the middle of the cycle, but much earlier or later - and then it will be even more difficult to calculate it. nine0003
So, there are two stages of pregnancy:
- Obstetric - from the first day of the last menstruation.
- Embryonic - from the moment of conception.
We will focus on the obstetric period
In the article we will divide this period into weeks, not stages. Conventionally, the first trimester of pregnancy can also be divided into three months.
First month of pregnancy
The 1st month of pregnancy is the period from the 1st to the 4-5th week. nine0003
No baby in the first two weeks. During this period, the woman's body is preparing for a possible pregnancy. Follicles mature in the ovaries, one (rarely two or more) dominant follicles stand out among them. If ovulation occurs, the egg is released from the follicle. When it meets sperm, fertilization occurs and new life is born.
In the third week of gestation, the fertilized egg moves through the fallopian tubes. Its task is to get into the uterine cavity and attach to its wall. This happens on the 7-8th day after conception - by the beginning of the 4th week. After implantation, the development of the fetal egg, the new life in it, continues. By the way, a child in early pregnancy is called an embryo, and after a full 8 weeks it will be called a fetus. nine0003
At the 3rd week, the embryo is a multitude of cells that are constantly dividing and developing. By the end of the first month of pregnancy, it already begins to influence the hormonal background of a woman due to the production of its own hormone - hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). It is by the concentration of the hormone that it is possible to determine whether conception occurred in this menstrual cycle.
In the 1st month of gestation, the woman's well-being practically does not change. And only at the end of the 4th week toxicosis can develop. It is manifested by nausea, vomiting, increased salivation and weakness. Many women do not have toxicosis - and this is also a variant of the norm. The belly in the first month of pregnancy is not yet visible. nine0003
It is manifested by nausea, vomiting, increased salivation and weakness. Many women do not have toxicosis - and this is also a variant of the norm. The belly in the first month of pregnancy is not yet visible. nine0003
Second month of pregnancy
The 2nd month of gestation is the period from 4-5 to 8-9 weeks.
In the early stages of pregnancy, the active development of the embryo continues. It still has a C-shape. By the end of the 4th week, limb rudiments are formed, a circulatory system and a two-chamber heart rudiment appear. At the 6th week, the heart begins to beat - and it can be heard during an ultrasound.
At the beginning of the 5th week, further development of the nervous system of the embryo takes place. The rudiment of the brain is isolated, conditions are created for its further differentiation. nine0003
On the 6th week of the 1st trimester, the organs of vision develop, the rudiments of the genital organs appear. The heart becomes three-chambered. At the 8th week, the sex of the embryo is determined - but it cannot yet be seen on ultrasound. As a result of all these transformations, in the second month of pregnancy, the fetus acquires a clear human appearance.
At the 8th week, the sex of the embryo is determined - but it cannot yet be seen on ultrasound. As a result of all these transformations, in the second month of pregnancy, the fetus acquires a clear human appearance.
A woman's feelings change in the middle of the 1st trimester. Symptoms appear, which are usually called characteristic signs of pregnancy:
- Nausea, vomiting, increased salivation - this is how toxicosis manifests itself. nine0022
- General weakness, fatigue.
- Sudden mood swings.
- Frequent urination.
- Breast augmentation and enhancement of its sensitivity.
- Increased sensitivity to odors.
- Predilection or aversion to certain foods.
The belly is not yet visible in early pregnancy. The uterus is already growing, but so far it is completely in the pelvic cavity and does not go beyond the womb. But the breasts in the 2nd month of pregnancy already noticeably increase, become sensitive or even slightly painful. nine0003
nine0003
The third month of pregnancy
The 3rd month is the period from the 8th-9th to the 12th-13th week.
In the third month of pregnancy, the further development of the child continues. Now it is called fruit. Its head, rudiments of limbs, torso, rudiments of eyes, nose and mouth are clearly visible. The fruit reaches the size of a goose egg.
On the 9-10th week, the cerebral cortex differentiates in the fetus, and the development of the nervous system continues. By the 12th week, foci of hematopoiesis appear in the bone marrow, and the first cells appear in the blood. At the 13th week, the formation of all organs of the fetus is completed, and the placenta is formed. nine0003
The placenta in early pregnancy is usually low, near the cervix. It provides the baby with everything necessary - oxygen and nutrients, and removes metabolic products. It connects to the fetus through the umbilical cord, in which two arteries and one vein pass. Gradually, the placenta migrates and by the end of the second trimester, as a rule, takes the correct position.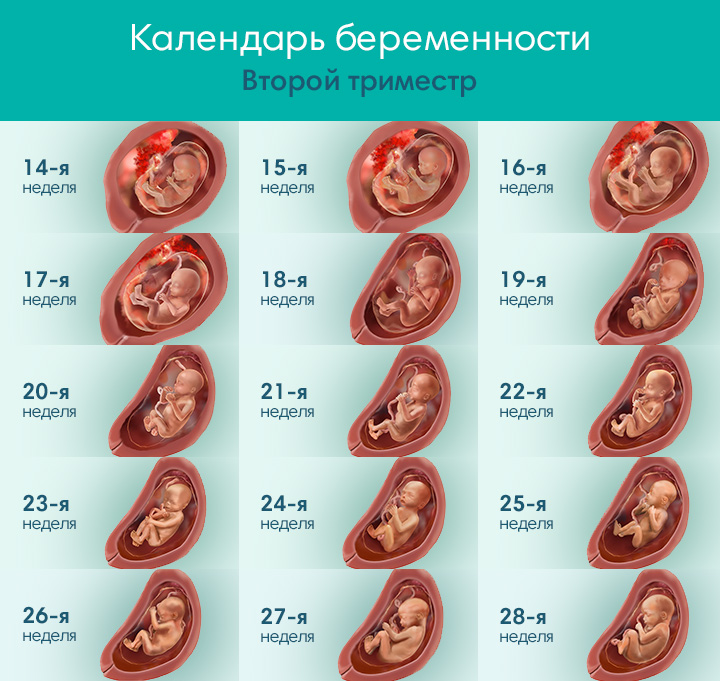
The feelings of a woman in the 3rd month of pregnancy remain the same. As before, she feels weakness, mood swings, changes in taste preferences. There may be signs of toxicity. But some women do not notice significant changes in their well-being - and this is also the norm. nine0003
The belly is not visible at the 3rd month. Only on the 12-13th week the uterus goes beyond the womb. A slight rounding of the abdomen will be visible only at the 14-16th week.
What problems can be in the first trimester of pregnancy
The expectant mother should be alerted by the appearance of such symptoms: There are no periods during pregnancy. Seek medical attention if bleeding occurs.
 nine0022
nine0022 If you experience any unusual sensations and symptoms, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible!
What examinations are needed in the early stages of pregnancy
To confirm the fact of pregnancy, you can donate blood for hCG as early as the 1st month. This hormone rises 8-10 days after conception - after the implantation of the embryo. It is recommended to donate blood for hCG immediately after a missed period. nine0003
If hCG is positive, you need to contact a gynecologist and get registered. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may refer you to an ultrasound scan. With ultrasound in the 1st trimester, from the 3rd-4th week, you can see the fetal egg, from the 6th week, you can hear the fetal heartbeat. The next ultrasound, if there are no other indications, is carried out for a period of 11-14 weeks. This will be the first screening where you can assess the condition of the fetus and placenta, make sure that there are no malformations and other complications.
This will be the first screening where you can assess the condition of the fetus and placenta, make sure that there are no malformations and other complications.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, all women are recommended to be screened:
- Pass blood and urine tests (the list will be issued by the attending physician).
- Get checked out by a dentist and an ophthalmologist.
- If necessary, visit other specialists (for example, an endocrinologist - if there is a thyroid disease).
- Make an ECG and consult a therapist.
All this is necessary in order to make sure that the expectant mother is healthy, can bear and give birth to a child.
Many women wonder how to behave if the pregnancy is less than a month old. Here are some recommendations:
In the first trimester of pregnancy, all women are advised to be screened:
- Give up alcohol and quit smoking if you did not do so before conception.

- Do not take medicines without a doctor's prescription.
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia.
- Do not take X-rays, MRIs, or similar procedures unless you have a strong indication and a referral from a doctor.
- Do not overexert yourself, reduce physical activity, including in sports. nine0022
- Avoid stressful situations.
In the following weeks of the first trimester, the recommendations remain the same, and nutritional advice is added:
- Eat often, in small portions, 5-6 times a day.
- Eat only fresh produce.
- Avoid foods that increase the symptoms of toxicosis and provoke constipation.
- Avoid feeling hungry, but don't overeat either.
It is worth noting that the nutrition of the expectant mother affects not only her, but also the baby, and it is worth taking a responsible approach to this. Yes, a special universal diet has not been developed, but the doctor may recommend that the expectant mother adhere to a certain diet after the examination (add certain foods to the diet if any elements are missing, etc. ). nine0003
). nine0003
It is recommended to follow the general principles of a healthy diet:
- Eat more fresh vegetables, fruits and greens - up to 5 servings per day.
- Limit salt and added sugar intake.
- Reduce the proportion of animal fats in the diet.
- Refuse fried, spicy, salty foods, sausages and smoked meats.
- Prefer whole grains.
If you need to follow a special diet for health reasons, you should discuss this with your doctor. nine0003
Most of the questions in the early stages arise in women during their first pregnancy. Everything is unusual and incomprehensible, what can and cannot be done, and how to maintain health - one's own and the child's. If you have any questions, you can consult with a gynecologist. A doctor observing a woman knows all the nuances and will tell you how to behave in the first trimester of pregnancy.
1. Normal pregnancy. Clinical recommendations, 2019.
2. Obstetrics: national guidance.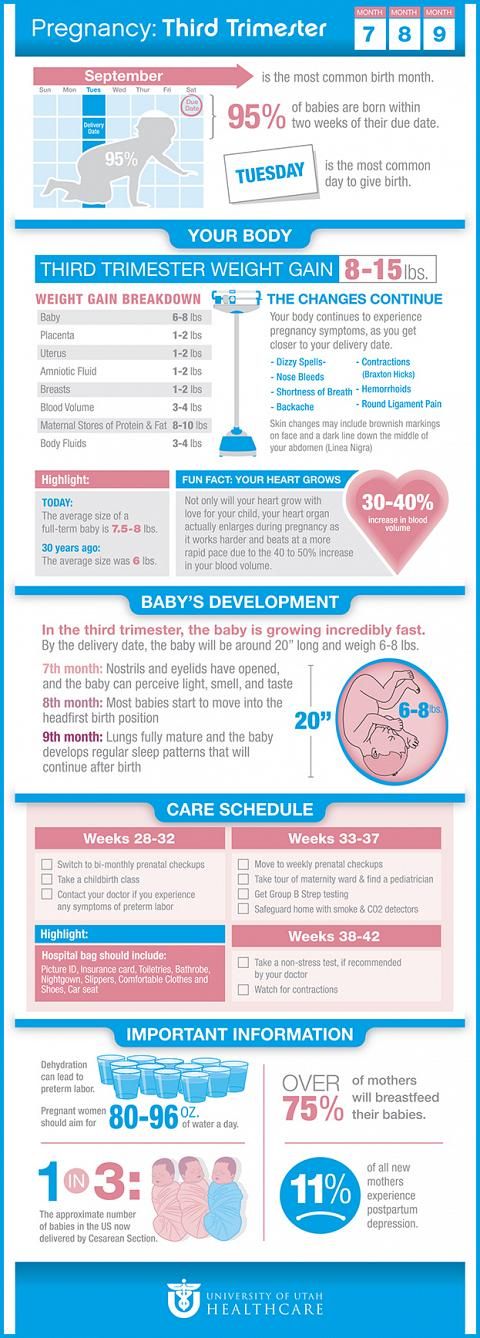 : Ailamazyan E.K., Savelyeva G.M., Radzinsky V.E.
: Ailamazyan E.K., Savelyeva G.M., Radzinsky V.E.
3. S. Yu. Vinogradov, S. V. Dindiaev. Introduction to embryology and human embryonic histogenesis..
Women and men of reproductive age | Pregnancy
If a woman's body fertilizes an egg with a sperm, pregnancy occurs. A normal pregnancy lasts about 37-42 weeks (average 40 weeks) and is measured in trimesters from the first day of your last period. The trimesters of pregnancy are a convenient method for observing the changes that occur during the entire period of bearing a baby. The entire period of pregnancy is usually divided into three trimesters, each of which has its own symptoms and signs. nine0003
First trimester:
1-12 weeks pregnant
Mother
During the first trimester of pregnancy, a woman's body goes through many changes. Hormonal changes affect the functioning of almost all body systems and provoke symptoms that can be noticed already in the first week of pregnancy. In particular, one of the early symptoms of pregnancy, caused just by hormonal fluctuations, is the absence of menstruation.
In particular, one of the early symptoms of pregnancy, caused just by hormonal fluctuations, is the absence of menstruation.
Changes that can be noticed during the first trimester of pregnancy include:
- Increased fatigue
- Very sensitive, swollen breasts. The nipples and surrounding areolas enlarge and darken.
- Toxicosis of pregnancy (nausea in the morning, sometimes vomiting)
- Change in eating habits (addiction to certain foods)
- Mood swings
- Constipation
- Increased urge to urinate
- Headaches
- Heartburn nine0021 Fluctuations in body weight (increase or, conversely, decrease in weight)
With the changes that occur in the body in the first trimester of pregnancy, the expectant mother is usually forced to make changes in her daily routine - for example, go to bed earlier or eat less, but more often. Fortunately, most of the uncomfortable early signs of pregnancy disappear over time. And some women during the first trimester of pregnancy do not experience any unpleasant symptoms at all. nine0003
And some women during the first trimester of pregnancy do not experience any unpleasant symptoms at all. nine0003
Baby
Your baby will grow and develop rapidly during the first trimester of pregnancy. By the 10th week of pregnancy (8 weeks after fertilization), all parts of the baby's body are already present, and the placenta is fully formed. During this period, the embryo is called a fetus. Nutrients are passed from you to your baby through the placenta. By the 12th week of pregnancy (10 weeks after fertilization), the baby is about 60 mm long. At this stage, his brain and nervous system are actively developing, his eyelids are still closed, his ears are being formed. nine0003
1-10 weeks of development:
from embryo to fetus
Second trimester:
13-28 weeks of pregnancy
Mother
Most women find that the second trimester of pregnancy is much easier than the first. In the second trimester, by 16-20 weeks of pregnancy, many ailments, including nausea, usually disappear or decrease in intensity.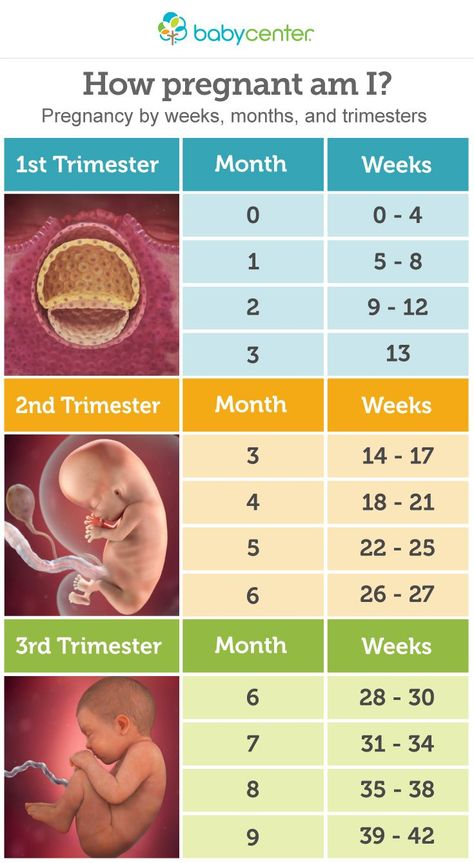 However, pain in the back, hip, or hip joint may occur because pregnancy hormones cause the ligaments and tendons to relax. Posture may change as the child grows and their weight increases. nine0003
However, pain in the back, hip, or hip joint may occur because pregnancy hormones cause the ligaments and tendons to relax. Posture may change as the child grows and their weight increases. nine0003
The first movements of the baby are felt at 18-20 weeks of pregnancy, but this is individual and can occur a few weeks earlier. The movements of the child become more energetic over time, as he becomes larger and stronger.
During the second trimester, the following signs of pregnancy may be noticed:
- Aching pain in the back, abdomen, groin or thighs
- Appearance of stretch marks on the skin of the abdomen, chest, thighs, buttocks
- Appearance of a dark line on the skin starting at the navel and ending at the groin
- The appearance of separate areas of dark skin on the cheeks, forehead, nose, above the upper lip (most often such dark spots are located symmetrically). This type of hyperpigmentation of the skin is called melasma (“mask of pregnancy”) and is caused by a change in the level of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman
- Numbness of hands or tingling sensation in hands
- Itching of the abdomen, palms, soles (if itching is accompanied by loss of appetite, nausea, jaundice or increased fatigue, you should immediately consult a doctor - this may be a sign of serious problems with the liver)
- Swollen ankles, fingers, face (if swelling of certain parts of the body occurs suddenly and very sharply or is accompanied by a rapid increase in body weight, you need to see a doctor - this may be a sign of preeclampsia, late pregnancy toxicosis)
Baby
In the second trimester of pregnancy, the baby's organs become more mature and the skeleton begins to harden.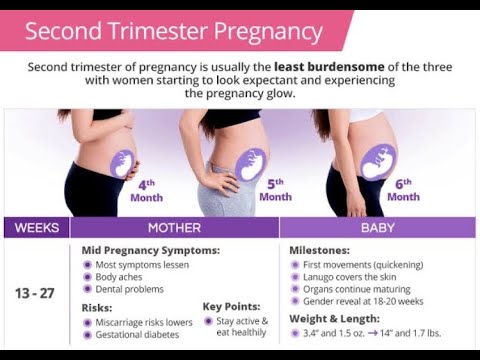 The baby receives nutrients through the amniotic fluid. The kidneys begin to work and pass a small amount of urine. K 19In the 3rd week, the baby is already able to hear and is covered with fine hairs called lanugo.
The baby receives nutrients through the amniotic fluid. The kidneys begin to work and pass a small amount of urine. K 19In the 3rd week, the baby is already able to hear and is covered with fine hairs called lanugo.
An ultrasound scan (ultrasound examination) at this stage can often determine the sex of the baby. By the end of the second trimester, the baby has a chance of survival if it is born prematurely. However, he will need intensive care.
by the 19th week of development it is already possible
to determine the sex of the unborn child
Third trimester:
29-40 weeks of pregnancy nine0184
Mom
The third trimester is the final stage of pregnancy, which, however, is accompanied by significant discomfort for many women. In the third trimester, most of the unpleasant symptoms observed during the second trimester of pregnancy are accompanied by increased urge to urinate and difficulty breathing. This is due to the fact that the rapid growth of the fetus causes additional pressure on the organs.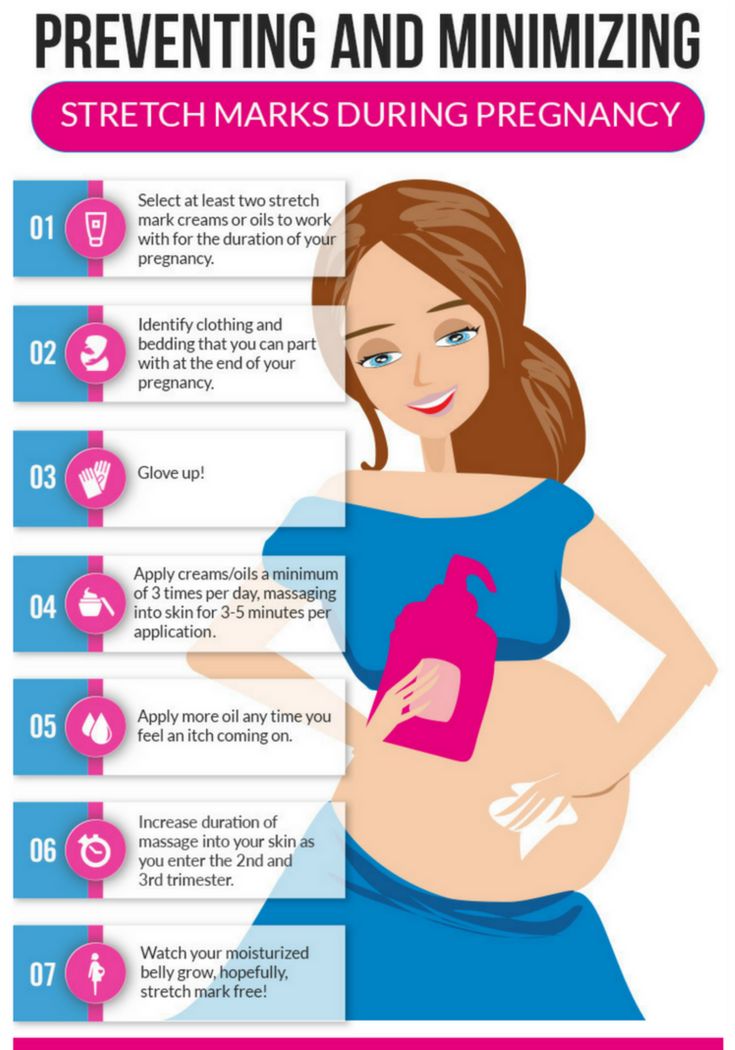 After childbirth, such problems disappear on their own. nine0003
After childbirth, such problems disappear on their own. nine0003
In the third trimester of pregnancy you may notice:
- Shortness of breath, shortness of breath
- Heartburn
- Swelling of ankles, fingers, face
- Hemorrhoids
- Breast tenderness, discharge of watery fluid from the nipples (colostrum - primary breast milk)
- Navel protrusion
- Sleep disorders
In the second trimester, false contractions may begin, but they are more likely in the last - third. False contractions can be mistaken for the onset of labor, but you should be aware that real uterine contractions are regular. False contractions last only about 25 seconds. nine0003
Baby
During the third trimester of pregnancy, the baby's lungs fully mature and at 32 weeks the baby is much more likely to survive if born prematurely. The child is already breathing even if the lungs are not working properly. The baby grows thin hair and nails, eyes open and close, and teeth may begin to grow.
The baby grows thin hair and nails, eyes open and close, and teeth may begin to grow.
The birth of a new life
I month
II month
III month
IV month
V month
VI month
VII month
VIII month
IX month
9000 9000 9000
Changes in the mother's body by months
possible physical feelings possible
- Delayed menses;
- Increased fatigue in the morning;
- Chest changes; heaviness, pain; an increase in size, the nipples and areola around them darken; nine0022
- Hypersensitivity to the taste of food and any smells; it is possible that there will be preferences for some products, and disgust for others, familiar earlier;
- More frequent urination;
- Unexplained mood changes, irritability, tearfulness;
- Possible nausea, vomiting in the morning - typical signs of toxicosis of the 1st half of pregnancy.
Medical information
The first visit to the doctor is extremely important. It should be carried out no later than the 12th week of pregnancy, since this period is decisive for the development and health of your child. nine0003
Every pregnancy is unique, so medical supervision is necessary, even if you have already experienced pregnancy.
Visiting a doctor is your responsible attitude towards your health and the health of your unborn child.
During the first visit to the doctor:
- Confirmation of pregnancy;
- Filling out a medical record of a pregnant woman, a detailed survey regarding health, previous or existing diseases, etc.; nine0021 Determination of height, body weight and blood pressure, examination of the mammary glands;
- Vaginal examination;
- Review of the abdomen, determining the size of the pelvis and the height of the fundus of the uterus;
- Advice on nutrition, behavior, the opportunity to discuss issues that interest and concern you;
- Referral for laboratory research;
- Referral to specialists: general practitioner, ophthalmologist, dentist, otolaryngologist, ultrasound, etc.
Child development
The egg meets the sperm and fertilization takes place. A cell (zygote) is formed containing a complete genetic set: 23 chromosomes each from the father and mother. At this moment, the sex of the child is already laid (by the way, it is the father's chromosomes).
The cell begins to actively divide and move towards the uterus, where it is implanted somewhere on the 7th day. The formation of the placenta begins, through which nutrients will be transferred from mother to child and waste products will be excreted, the umbilical cord is laid. nine0003
The baby is gradually growing: at the end of the 1st month, the baby is already the size of a grain of rice (5-8 mm, 2-3 g). The newly formed heart begins to contract, the rudiments of future eyes, spine, brain, and internal organs appear.
In preparing this section, the materials of the brochure for pregnant women "My Pregnancy Diary", developed by a group of experts of the Ukrainian-Swiss program "Maternal and Child Health", reviewed and recommended for printing by the Ministry of Health of Ukraine, were used.