Traces of blood in urine pregnant
Blood in Urine During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Blood in Urine During Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph. D., MSN — By Scott Frothingham on May 10, 2019
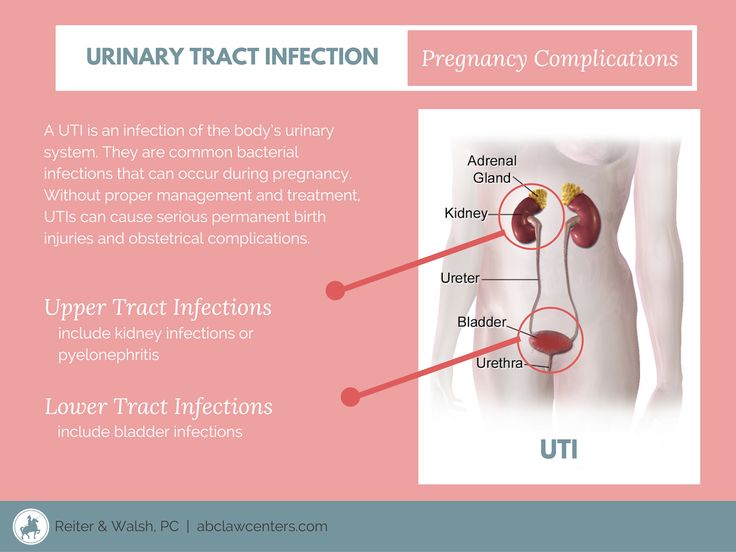
If you’re pregnant and see blood in your urine, or your doctor detects blood during a routine urine test, it could be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
A UTI is an infection in the urinary tract typically caused by bacteria. UTIs are more common during pregnancy because the growing fetus can put pressure on the bladder and urinary tract. This can trap bacteria or cause urine to leak.
Read on to learn more about the symptoms and treatment of UTIs, and other causes of blood in the urine.
Symptoms of a UTI may include:
- persistent urge to urinate
- frequently passing small amounts of urine
- burning sensation when urinating
- fever
- discomfort in the center of the pelvis
- back pain
- unpleasant smelling urine
- bloody urine (hematuria)
- cloudy urine
There are three major types of UTI during pregnancy, each with distinct causes:
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often caused by bacteria present in a woman’s body before she became pregnant. This type of UTI doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms.
This type of UTI doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms.
If left untreated, asymptomatic bacteriuria may lead to kidney infection or acute bladder infection.
This infection occurs in about 1.9 to 9.5 percent of pregnant women.
Acute urethritis or cystitisUrethritis is an inflammation of the urethra. Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder.
Both of these conditions are caused by bacterial infection. They’re often caused by a type of Escherichia coli (E. coli).
PyelonephritisPyelonephritis is a kidney infection. It can be the result of bacteria entering your kidneys from your bloodstream or from elsewhere in your urinary tract, such as your ureters.
Along with blood in your urine, symptoms may include fever, pain when urinating, and pain in your back, side, groin, or abdomen.
Doctors commonly use antibiotics to treat UTIs during pregnancy. Your doctor will prescribe an antibiotic that is safe for use during pregnancy but still effective in killing bacteria in your body. These antibiotics include:
These antibiotics include:
- amoxicillin
- cefuroxime
- azithromycin
- erythromycin
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends avoiding nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, as they have been linked to birth defects.
Blood leaking into your urine could be caused by a number of conditions, whether you are pregnant or not. This may include:
- bladder or kidney stones
- glomerulonephritis, an inflammation of the kidneys’ filtering system
- bladder or kidney cancer
- kidney injury, such as from a fall or vehicle accident
- inherited disorders, such as Alport syndrome or sickle cell anemia
The cause of hematuria cannot always be identified.
Although hematuria is often harmless, it can indicate a serious disorder. If you’re pregnant and you see blood in your urine, make an appointment with your doctor.
Screening for UTI should be part of routine prenatal care.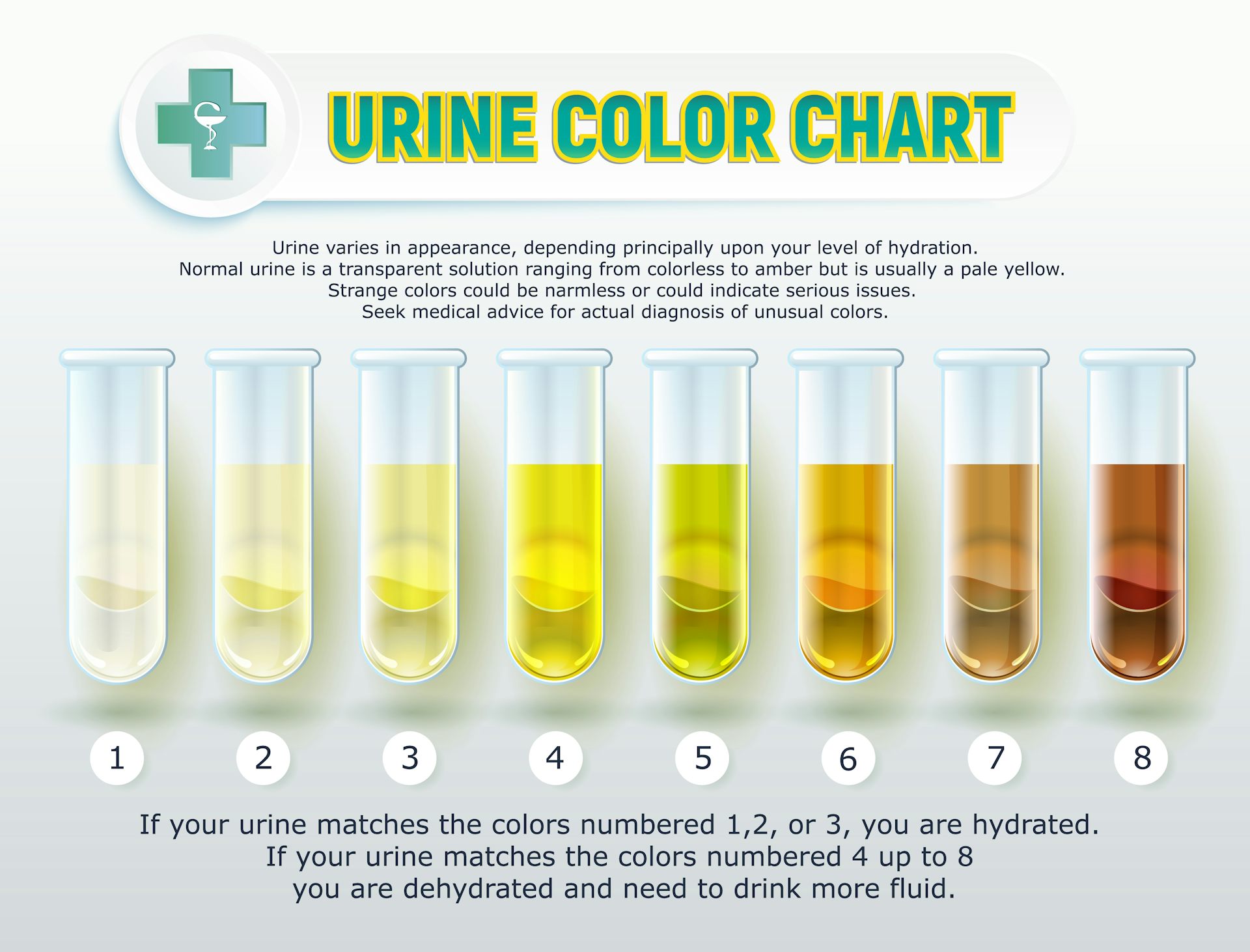 Talk with your doctor or gynecologist to make sure that they’ve done a urinalysis or a urine culture test.
Talk with your doctor or gynecologist to make sure that they’ve done a urinalysis or a urine culture test.
Last medically reviewed on May 10, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
- Cat 1
- urinaryhealth
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN — By Scott Frothingham on May 10, 2019
Read this next
Is it Normal for a UTI to Cause Urinary Bleeding?
Medically reviewed by Stacy Sampson, D.O.
A urinary tract infection can cause bloody urine. But once your UTI is treated, bleeding from a UTI should go away. Learn how UTIs cause bleeding…
READ MORE
Why Is There Blood in My Urine?
Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R.N., CCRN, CPN
Hematuria is the medical term for blood in urine.
 Discover possible causes, the types of hematuria, when to see a doctor, and more.
Discover possible causes, the types of hematuria, when to see a doctor, and more.READ MORE
What Causes Painful Urination?
Medically reviewed by Kevin Martinez, M.D.
Painful urination may be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI), sexually transmitted infection (STI), or other cause. Learn more about relieving…
READ MORE
Why Are There Red Blood Cells in My Urine?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
Red blood cells (RBCs) might show up in a urine sample. We’ll go over what’s normal, what’s not, and what can cause RBCs in your urine.
READ MORE
Is Foul-Smelling Urine a Sign of Cancer?
Medically reviewed by Alana Biggers, M.D., MPH
Foul-smelling urine is not a symptom or sign of cancer.
 It can, however, indicate other conditions, such as urinary tract infections or STIs. Learn…
It can, however, indicate other conditions, such as urinary tract infections or STIs. Learn…READ MORE
Exercise May Be as Beneficial as Drugs in Treating Premature Ejaculation, Study Finds
Researchers say exercise such as running and yoga can be as effective as medication in treating premature ejaculation
READ MORE
'Grower' or 'Shower': Scientists Define Categories for Penis Erections
Researchers say the amount a penis grows during an erection has nothing to do with sexual performance, but it could be useful information in some…
READ MORE
8 Ways to Keep Your Kidneys Healthy
Kidneys perform essential functions in your body, filtering waste and producing hormones. Read more on how to maintain good kidney health.
READ MORE
Why Are There Nitrites in My Urine?
Medically reviewed by Meredith Goodwin, MD, FAAFP
When a urinalysis comes back positive for nitrites, it usually means you have a bacterial infection.
 Find out why you can test negative and still have…
Find out why you can test negative and still have…READ MORE
Urinary Tract Infections: A New Antibiotic May Be on the Way to Treat UTIs
Officials say the antibiotic gepotidacin is performing so well in trials that it may be available sooner than expected for treatment of UTIs
READ MORE
Bloody urine in Pregnancy- What can be the cause?
Views: 27,025
If you are pregnant and notice blood in your urine, or the doctor detects blood in a routine urine test, it can be a sign of a urinary tract infection (UTI).
A UTI is the infection in the urinary tract and is typically caused by bacteria. UTIs are more common in pregnancy because the growing baby can put pressure on the urinary bladder and urinary tract, which can trap the bacteria or may also cause urinary leakage.
Read ahead to learn more about the causes, symptoms and treatment of Urinary Tract Infections in pregnancy, and other causes of blood in the urine during pregnancy.
Table of Contents
What are the symptoms of UTI in pregnancy?Symptoms of a UTI during pregnancy may include-
- Strong urge to urinate
- Frequently urinating small amounts of urine
- Burning sensation while urinating
- Discomfort in the center of pelvis
- Back pain
- Smelly urine
- Blood in urine (also known as hematuria)
- Cloudy urine
- Fever
What can cause UTI during pregnancy?
There are 3 major types of UTI in pregnancy, each with distinctive causes-
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria – Asymptomatic bacteriuria is often caused due to bacteria present in a female’s body before she becomes pregnant. This type of UTI does not cause any noticeable or uncomfortable symptoms. If left untreated, this infection can lead to acute bladder infection or kidney infection. Asymptomatic bacteriuria occurs in about 1.9 to 9.5 % of pregnant females.
- Acute urethritis or cystitis- Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra while cystitis is known as the inflammation of the bladder.
 Both of these infections are caused due to bacterial infection. They are often caused by a type of E. coli (Escherichia coli).
Both of these infections are caused due to bacterial infection. They are often caused by a type of E. coli (Escherichia coli).
- Pyelonephritis- Pyelonephritis is a type of kidney infection which can be the result of bacteria entering the female’s kidneys from her bloodstream or from elsewhere in her urinary tract, such as the ureters. Along with blood in urine, symptoms of pyelonephritis may include fever, pain or burning when urinating, and pain in the back, sides, groin, or abdomen.
Also Read- Causes and Symptoms of UTIs
Treatment for UTI during pregnancyDoctors commonly recommend antibiotics to treat UTIs in pregnancy. Not all antibiotics and other medicines are safe during pregnancy.
Also Read- Are antibiotics safe in pregnancy?
So, your doctor will prescribe you an antibiotic which is safe for use in pregnancy and is still effective in killing bacteria in the body. Such antibiotics for UTIs in pregnancy can include-
- Amoxicillin
- Erythromycin
- Cefuroxime
- Azithromycin
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) recommends avoiding nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for UTIs in pregnancy, as use of these medicines during pregnancy has been linked to birth defects in infants.
Also Read- Pregnancy Drug Category and Unsafe Drugs in Pregnancy
Other causes of blood in the urine in pregnancy?Blood leaking into the urine can be caused due to a number of conditions, whether the female is pregnant or not. Such causes can include:
- Kidney stones
- Bladder stones
- Glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the filtering system of the kidneys)
- Cancer of bladder or kidney
- Kidney injury
- Inherited disorders (like Alport syndrome or sickle cell anemia)
The cause of hematuria or bloody urine cannot always be identified.
Also Read- Why is there pain near belly button during pregnancy?
TakeawayAlthough blood in urine is often harmless, it can at times indicate a serious disorder. If you are pregnant and you see blood in urine, make an appointment with a doctor right away. You can also consult a doctor right now by simply clicking here!
- Gynaecology
- Pregnancy
×
- please enter 10 digit number.
- Select City
Urinalysis during pregnancy - what to watch
- Why take a urine test during pregnancy
- How to properly pass urine for analysis
- What a urine test shows and how it is assessed
- Special urine tests
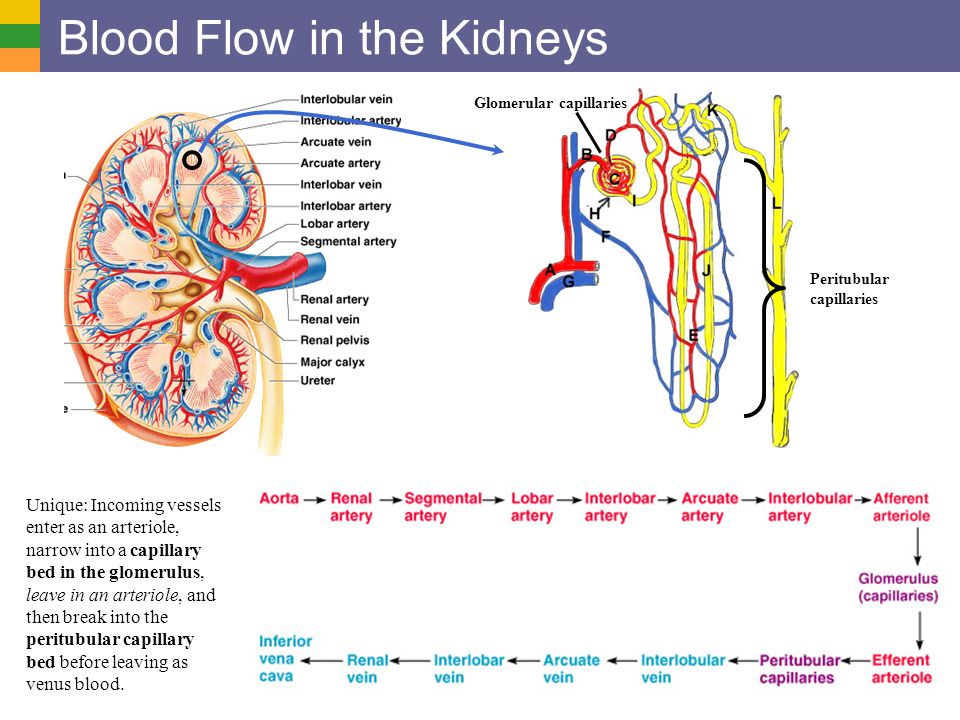
During pregnancy, a woman undergoes many different tests. The most frequent, and at the same time the simplest study is a urinalysis. It is taken regularly, before each visit to the doctor of the antenatal clinic, that is, at least 12 times during pregnancy.
Why take a urine test during pregnancy
Urine is formed in the kidneys during blood filtration, with it the decay products formed during metabolism, salts, vitamins, hormones are excreted from the body. Based on this analysis, one can judge the work of the kidneys and other organs. The main component of urine is water (92-99%). Approximately 50-70 dry substances are removed from the body with urine every day, most of which are urea and sodium chloride. The composition of urine varies significantly even in healthy people, depending on the diet, drinking regimen and medication. During pregnancy, a regular study of a general urine test allows you to suspect in time the initial pathological processes in the body of a future mother, for example, the development of a urinary tract infection or toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy. For a correct assessment of the results of the analysis, urine must be collected correctly.
The composition of urine varies significantly even in healthy people, depending on the diet, drinking regimen and medication. During pregnancy, a regular study of a general urine test allows you to suspect in time the initial pathological processes in the body of a future mother, for example, the development of a urinary tract infection or toxicosis in the second half of pregnancy. For a correct assessment of the results of the analysis, urine must be collected correctly.
How to donate urine for analysis
On the eve of the test, it is recommended to refrain from intense physical activity, do not eat a lot of meat products, salty, sour and spicy foods, as well as coloring foods (beets, carrots, etc.). This can lead to a distortion of the result - the appearance of protein and salts in the urine. For a general urinalysis, it is preferable to collect the morning portion of urine.
Preliminary thorough toileting of the external genitalia with warm water and soap. It is better to close the vagina with a cotton swab to prevent secretions from entering the urine sample. Urine is collected in a clean, dry container. For analysis, an average portion of urine is used, that is, for the first few seconds you need to urinate into the toilet, then into a jar, and the remains again into the toilet.
It is better to close the vagina with a cotton swab to prevent secretions from entering the urine sample. Urine is collected in a clean, dry container. For analysis, an average portion of urine is used, that is, for the first few seconds you need to urinate into the toilet, then into a jar, and the remains again into the toilet.
Urine must be delivered to the laboratory within two hours of collection and it is advisable to try not to subject it to strong shaking during transport. It is allowed to store urine in the refrigerator at a temperature of +2-+4 degrees, but not more than 1.5 hours. It is desirable that the amount of material collected for the study be at least 70 ml.
What a urinalysis shows and how it is evaluated
In a urinalysis, many parameters are evaluated.
Color
Normal urine has a yellow color of various shades. The shade depends on the degree of saturation of urine with a special pigment - urochrome. A change in the color of urine can occur when taking certain medications (for example, vitamins can give a bright yellow color, aspirin - pink).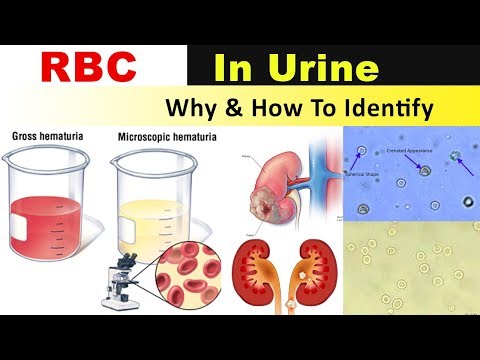 However, much more often a change in the color of urine indicates the presence of any pathological processes in the body. When blood appears in the urine, which occurs in diseases of the kidneys and bladder, the urine becomes bright red (with renal colic, cystitis) or the so-called “color of meat slops” (with acute inflammatory kidney damage). With increased destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes), urine acquires a reddish-brown hue. Yellow-brown (or beer-colored) urine occurs with liver diseases.
However, much more often a change in the color of urine indicates the presence of any pathological processes in the body. When blood appears in the urine, which occurs in diseases of the kidneys and bladder, the urine becomes bright red (with renal colic, cystitis) or the so-called “color of meat slops” (with acute inflammatory kidney damage). With increased destruction of red blood cells (erythrocytes), urine acquires a reddish-brown hue. Yellow-brown (or beer-colored) urine occurs with liver diseases.
Transparency
Transparency should normally be complete. Turbidity of urine can be the result of the presence in the urine of erythrocytes, leukocytes, epithelium, bacteria, fat droplets, precipitation of salts.
Relative density (specific gravity)
This is an indicator that characterizes the amount of trace elements, salts, various compounds. Normally, the specific gravity is 1003 - 1035 g / l. This indicator may decrease in the presence of glucose or protein in the urine, with toxicosis of the first half of pregnancy, dehydration. An increase in specific gravity occurs in chronic renal failure, diabetes insipidus, and heavy drinking.
An increase in specific gravity occurs in chronic renal failure, diabetes insipidus, and heavy drinking.
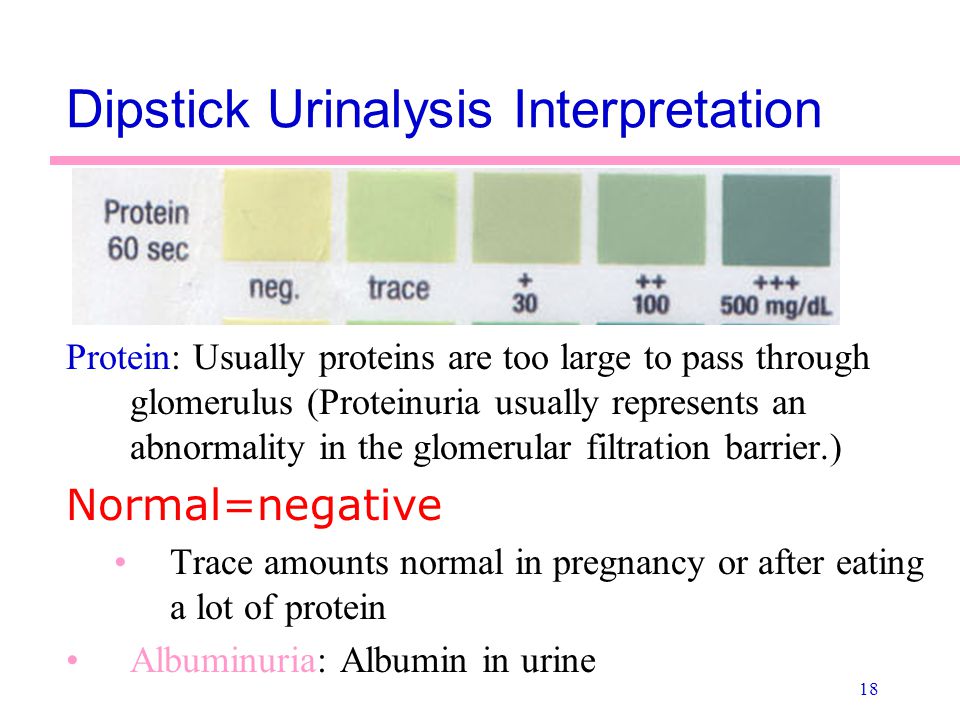
Protein
Protein content in urine is one of the most important indicators of kidney function. Normally, it shouldn't be. A small amount of protein in the urine (physiological proteinuria) can also be found in healthy people, while the protein concentration does not exceed 0.033 g / l, in modern laboratories with more sensitive equipment - 0.14 g / l. The appearance of protein in the urine is noted in diseases of the kidneys, inflammatory diseases of the bladder and urinary tract. The presence of protein in the urine, combined with increased blood pressure and edema, is a sign of a serious complication of pregnancy - late preeclampsia, which can lead to seizures and even death of a pregnant woman and fetus.
Glucose
Normally, there is no glucose in the general urine test. However, in the second half of pregnancy, the presence of glucose in the urine (glucosuria) can normally be detected. This is due to increased filtration of glucose in the kidneys. Since the appearance of glucose in the urine can be a sign of a serious illness - diabetes mellitus, acute inflammation of the pancreas, all patients with glucosuria need an additional examination - blood glucose control, sometimes even a glucose tolerance test with a sugar load - determination of blood glucose on an empty stomach and 2 hours after taking 75 grams of glucose.
This is due to increased filtration of glucose in the kidneys. Since the appearance of glucose in the urine can be a sign of a serious illness - diabetes mellitus, acute inflammation of the pancreas, all patients with glucosuria need an additional examination - blood glucose control, sometimes even a glucose tolerance test with a sugar load - determination of blood glucose on an empty stomach and 2 hours after taking 75 grams of glucose.
Bilirubin
This is a blood pigment that is formed as a result of metabolic processes in the body and is excreted with bile into the gastrointestinal tract. With an increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood, it begins to be excreted by the kidneys and found in the urine. This occurs mainly with liver damage or mechanical obstruction of the outflow of bile.
Urobilinogen
This is a conversion product of bilirubin. Normally, it is excreted in the bile and practically does not enter the urine. The appearance of urobilinogen in the urine occurs in liver diseases, poisoning, increased decay of red blood cells - erythrocytes.
Ketone bodies
These are products formed during the breakdown of fatty acids in the body. Normally, there are no ketone bodies in the urine test. Determining them is very important in diagnosing the adequacy of diabetes therapy. The appearance of ketones can occur in the first trimester of pregnancy with early toxicosis and indicate dehydration.
Nitrites
These are salts of nitrous acid and are not normally found in urine. Their appearance indicates the presence of a urinary tract infection.
Leukocytes
These are white blood cells. Normally, in the general analysis of urine, leukocytes are found up to 5 in the field of view. If the number of leukocytes is increased, this indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, bladder or urethra, while the higher the number of leukocytes, the more pronounced the inflammation. A slight increase in the number of leukocytes can be observed if vaginal discharge enters the urine with a poor toilet of the external genitalia.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells. Normally, in the general analysis of urine there should be no more than 2 erythrocytes in the field of view. An increase in their number occurs in the presence of stones in the kidneys or urinary tract, inflammation of the kidneys, injuries.
Cylinders
Cylindrical elements of urine sediment, consisting of protein or cells, may also contain various inclusions. Normally absent. They are found mainly in diseases of the kidneys.
Salts
These are inorganic substances which may precipitate on standing urine. Normally, there are no salts in the urine. The appearance of urates in the urine occurs with kidney diseases, as well as in the first trimester of pregnancy with vomiting of pregnant women.
Amorphous phosphates
Also found in vomiting of pregnant women, in inflammation of the bladder, and can occur normally with a predominance of vegetable and dairy foods in the diet.
Oxalates
Occurs in inflammation of the kidneys, diabetes mellitus, as well as in the predominance of foods rich in oxalic acid in the diet (spinach, sorrel, tomatoes, asparagus).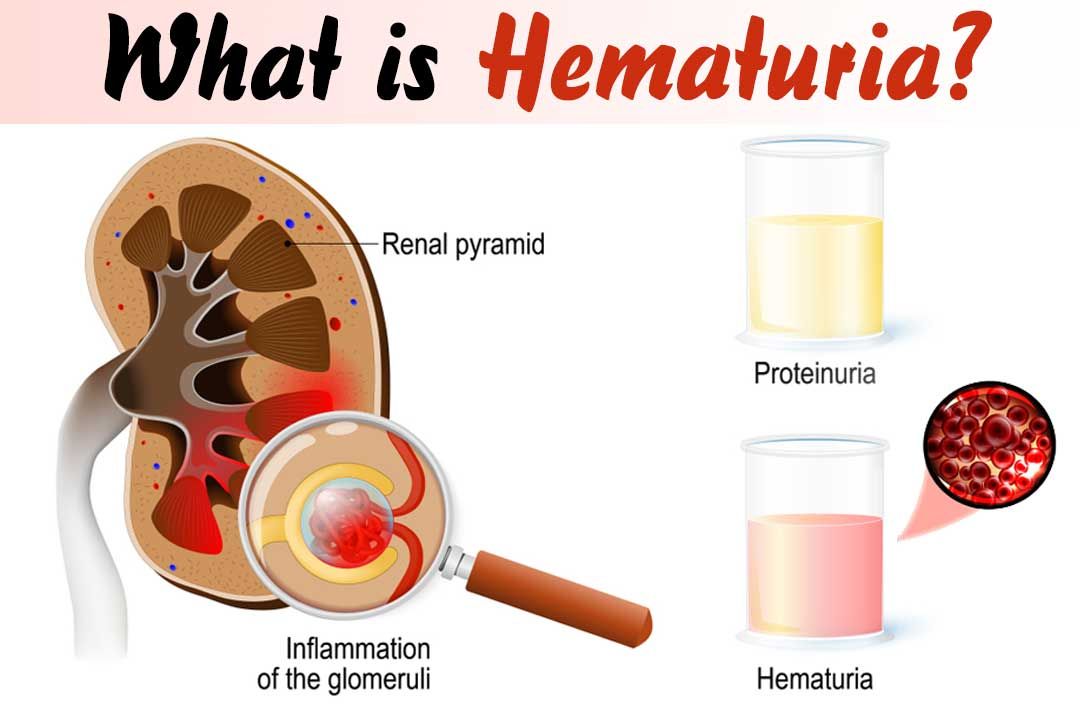
Bacteria
Isolation of bacteria in the urine is of significant diagnostic value in pregnancy. The appearance of bacteria in the urine indicates the presence of an inflammatory process in the kidneys, bladder or urethra and requires mandatory treatment, even if the expectant mother is not worried about anything. Bacteria can also enter the urine from the vagina when the toilet of the external genitalia is poor. To determine the number of bacteria, their type and sensitivity to antibiotic therapy, an additional urine culture for flora is mandatory. To obtain the correct result of this analysis, after a thorough toilet of the external genital organs, close the vagina with a cotton swab, collect the middle portion of urine in a sterile container, tighten the lid tightly and deliver it to the laboratory within one and a half to two hours. Urine culture is prepared on average from 7 to 10 days and allows the doctor to decide whether it is necessary to carry out antibacterial treatment, and with what drugs.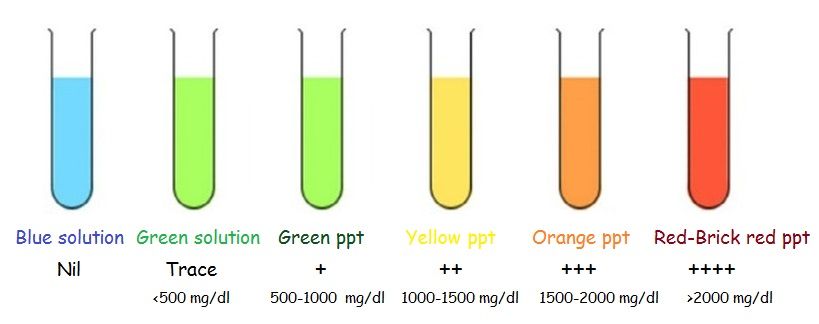
Find out more about the services:
- Tests for pregnant women
Special urinalysis
Urine culture
Mandatory if bacteria are detected in the general urinalysis.
The purpose of the study. Performed to determine the number of bacteria, their type and sensitivity to antibacterial drugs.
Rules for collecting urine for analysis. To obtain a correct result from this test, urine must be collected after thorough toileting of the vulva, covering the vagina with a cotton swab. It is necessary to collect an average portion of urine in a sterile container, screw the lid tightly and deliver it to the laboratory within one and a half to two hours.
Urine culture is prepared on average from 7 to 10 days and allows the doctor to decide whether to carry out antibacterial treatment and with what drugs. If there is a clinical picture of inflammation, before the results of the culture are obtained, antibacterial treatment with a broad-spectrum antibiotic (acts on a large range of bacteria) is carried out, and in case of asymptomatic course of the disease or mild inflammation, treatment is not carried out until the results of the analysis are obtained.
Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko
This is a special urine test that shows the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes and cylinders in 1 ml of urine.
The purpose of the study. This analysis is prescribed if there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process in the organs of the urinary system in a pregnant woman, if there are changes in the general analysis of urine. It gives more accurate results than a general urinalysis, and also allows you to control the ongoing treatment in dynamics.
Urine collection rules. Urine for analysis according to Nechiporenko is collected in the same way as for a general urine test.
Parameters under investigation
- The number of leukocytes - normally they should be less than 2 thousand in 1 ml . An increase of in the number of leukocytes indicates the presence of pyelonephritis (an inflammatory disease of the pelvis and calices of the kidneys).
- The number of erythrocytes is normally less than 1 thousand per 1 ml. An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the development of glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the renal glomeruli).
- The number of cylinders is normally less than 20 in 1 ml. The detection of an increased content of cylinders indicates arterial hypertension, diseases of the cardiovascular system, and can occur with early toxicosis of pregnant women.
Urinalysis according to Zimnitsky
Purpose of the study. This analysis is prescribed to clarify the ability of the kidneys to concentrate and dilute urine, to identify latent edema. The study may be needed if you suspect the development of preeclampsia, renal failure, infections of the urinary system, as well as diabetes.
Urine collection rules. For urinalysis according to Zimnitsky, urine is collected during the day (24 hours) in 8 containers (jars), while the amount of liquid drunk is necessarily taken into account (the pregnant woman writes down how much liquid she drinks during the day, taking into account soups, fruits and vegetables). At 6 am, a woman urinates into the toilet, then all subsequent urine is collected in jars.
At 6 am, a woman urinates into the toilet, then all subsequent urine is collected in jars.
Total 8 servings:
- 1 serving - 6:00 a.m. to 9:00 a.m.,
- 2 portion - from 9-00 to 12-00 hours,
- 3 portion - from 12-00 to 15-00 hours,
- 4 portion - from 15-00 to 18-00 hours,
- 5 portion - from 18-00 to 21-00 hours,
- 6 portion - from 21-00 to 24-00 hours,
- 7 portion - from 24-00 to 3-00 hours,
- 8 portion - from 3-00 to 6-00 hours.
Jars are signed and delivered to the laboratory.
Test parameters. The amount and specific gravity of urine in each portion is estimated. Normal kidney function is characterized by:
- daily urine volume about 1.5 liters;
- predominance of daytime urination over nighttime;
- urinary excretion of approximately 70--80% of the liquid drunk per day;
- the specific gravity of urine in at least one of the portions is not lower than 1.
 020--1.022;
020--1.022; - significant fluctuations during the day the amount of urine in individual portions (from 50 to 400 ml) and the specific gravity of urine (from 1.003 to 1.028).
Deviations from these standards indicate a violation in the work of the kidneys.
Rehberg's test
Purpose of the study. This test is used to determine the ability of the kidneys to filter urine. It must be carried out for all pregnant women with preeclampsia, with urinary tract infections, with kidney diseases, and with diabetes.
Urine collection rules. Before the test, intense physical activity, strong tea and coffee are excluded. Urine is collected during the day in one container, which is stored in the refrigerator during the entire collection time. After completing the collection of urine, measure the contents of the container, be sure to mix and immediately pour 70-100 ml into a special container or jar and deliver it to the laboratory, reporting the total volume of urine collected per day.
At the time of delivery of urine to the laboratory, blood is taken for creatinine from a vein.
Test parameters. The method is based on the assessment of glomerular filtration by the rate of purification of blood plasma from creatinine, a special product of protein breakdown. This indicator can be determined if you know the concentration of creatinine in the blood, in the urine and the daily volume of urine. This indicator is calculated using a special formula and is called creatinine clearance. Normally, the value of this indicator ranges from 75 to 134 ml / min / 1.7 m2. A decrease in the level of renal filtration indicates kidney damage and occurs with severe complications of pregnancy - gestosis, kidney diseases (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis), diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, urolithiasis.
Urine for 17-KC
This test was previously widely prescribed to pregnant women to determine the hormones produced by the adrenal cortex.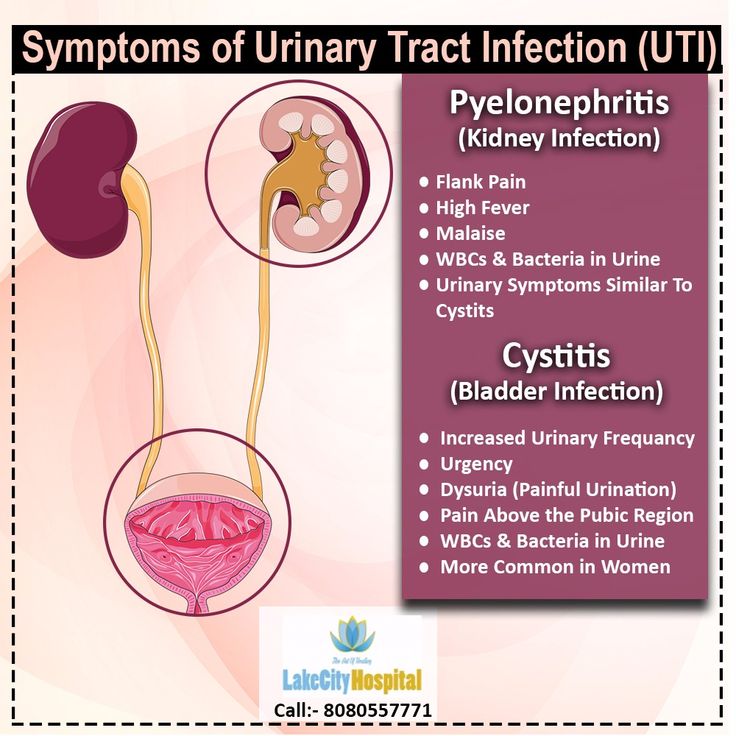 For analysis, urine was collected during the day, mixed, a small part of it was poured, which was delivered to the laboratory with an indication of the total amount of urine collected. An increase in the concentration of 17-ketosteroids in the urine indicated an excess production of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman, on the basis of which the doctor prescribed hormonal drugs. However, at present, the determination of these substances in urine is considered uninformative and is not used during pregnancy.
For analysis, urine was collected during the day, mixed, a small part of it was poured, which was delivered to the laboratory with an indication of the total amount of urine collected. An increase in the concentration of 17-ketosteroids in the urine indicated an excess production of hormones in the body of a pregnant woman, on the basis of which the doctor prescribed hormonal drugs. However, at present, the determination of these substances in urine is considered uninformative and is not used during pregnancy.
Urine tests are very easy to perform and very informative for the doctor, they allow you to timely detect the slightest changes in the body of the expectant mother and start treatment in a timely manner, which helps prevent serious complications from the pregnant woman and the unborn baby.
Blood in the urine (hematuria). Causes of hematuria
Author
Shenker Maria Olegovna
Deputy Director of the Medical Department
Leading physician
Therapist
Cashback 1000 rub for all services for a visit in March More All promotions
Blood in the urine is a warning sign.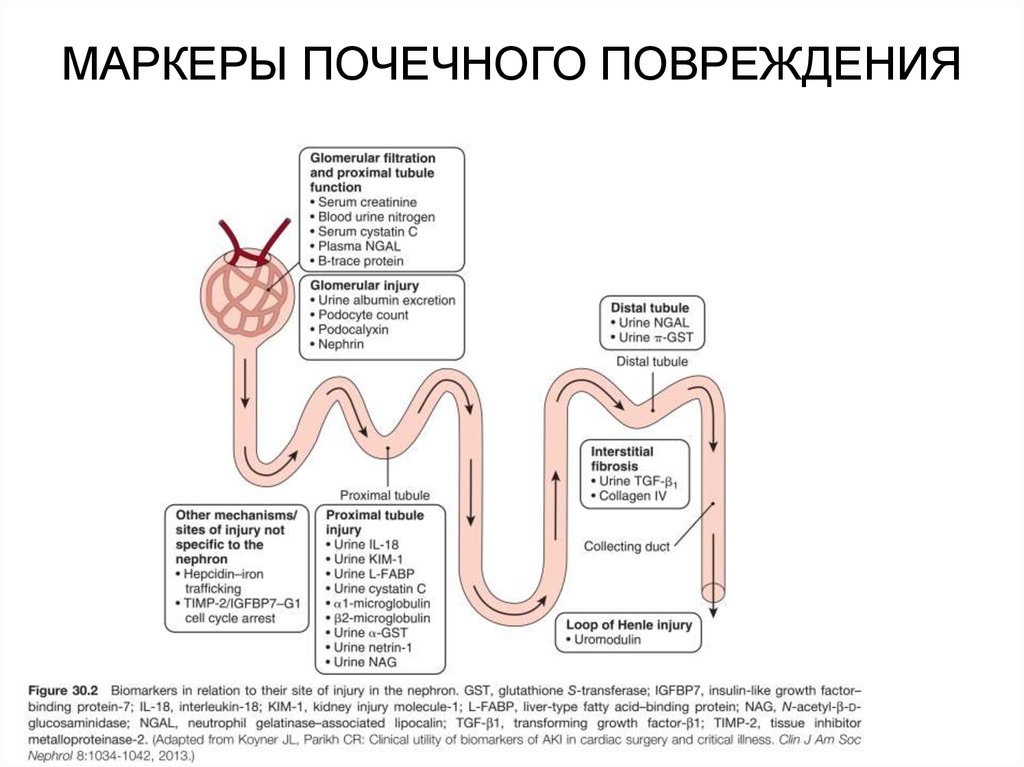 In the language of medicine, blood in the urine is called hematuria . There are gross hematuria when the presence of blood in the urine can be detected with the naked eye, and microhematuria when blood can only be detected during a laboratory test.
In the language of medicine, blood in the urine is called hematuria . There are gross hematuria when the presence of blood in the urine can be detected with the naked eye, and microhematuria when blood can only be detected during a laboratory test.
Causes of hematuria
Blood can enter the urine at any stage of the formation and excretion of urine, so hematuria can be a sign of damage to any organ of the urinary system - the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra. An indication of exactly where the problem is localized can be in which portion of the urine there is blood. If blood is detected at the beginning of urination (in the first portion of urine), then the source of bleeding is most likely in the urethra. If blood is present in the last portion (detected already at the end of urination), then the most likely location of the source of bleeding is in the bladder neck or in the upper part of the urethra or (in men) in the prostate gland.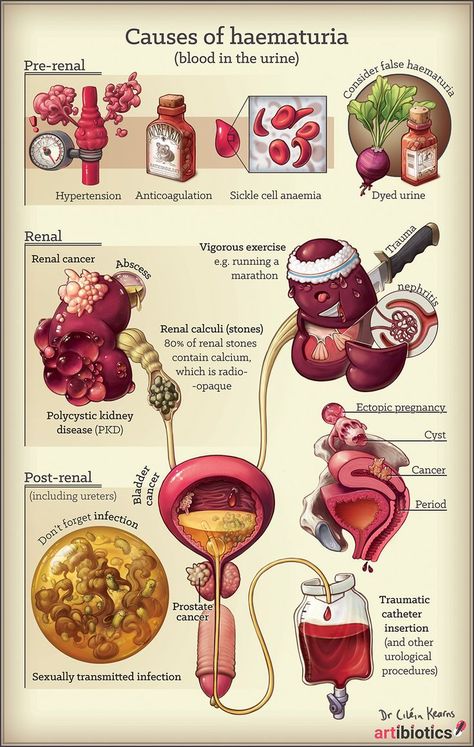 If blood is present throughout the entire act of urination, then we should expect that the source of blood is higher - in the kidneys, ureters or bladder.
If blood is present throughout the entire act of urination, then we should expect that the source of blood is higher - in the kidneys, ureters or bladder.
The main causes of blood in the urine are:
- infectious diseases. Inflammatory processes lead to circulatory disorders. With inflammatory processes in the kidneys and other organs of the urinary system, a small amount of red blood cells (erythrocytes) may be in the urine. As a rule, in this case we are talking about microhematuria. However, in women, one of the most common causes of blood in the urine is cystitis, one of the varieties of which - hemorrhagic cystitis - is characterized precisely by the visible presence of blood in the urine (that is, gross hematuria);
- injuries;
- urolithiasis. The resulting stones injure the organs of the urinary system. In some cases, the appearance of blood in the urine is the reason for the examination and detection of the disease;
- neoplasms;
- glomerulonephritis.
 With this disease, the functioning of the renal filtration barrier is disrupted. Normally, it should allow water and relatively small molecules of solutes to pass through, preventing blood cells from entering the urine. Glomerulonephritis causes red blood cells to enter the urine. At the same time, microscopy reveals deformation and discoloration of erythrocytes in the urine. This allows you to establish that the cause of the appearance of blood in the urine is precisely glomerulonephritis.
With this disease, the functioning of the renal filtration barrier is disrupted. Normally, it should allow water and relatively small molecules of solutes to pass through, preventing blood cells from entering the urine. Glomerulonephritis causes red blood cells to enter the urine. At the same time, microscopy reveals deformation and discoloration of erythrocytes in the urine. This allows you to establish that the cause of the appearance of blood in the urine is precisely glomerulonephritis.
Pregnant women often have idiopathic hematuria (i.e., hematuria whose cause cannot be determined). Such hematuria usually stops after childbirth.
Any questions?
Leave the phone -
and we will call you back
Blood in the urine: when to see a doctor
When blood appears in the urine, you should definitely consult a doctor. Don't wait for it to "go away". Blood in the urine is a fairly serious symptom that may indicate diseases that cannot go away on their own.