Tightening feeling in lower abdomen
Tight stomach or abdomen: Causes and treatments
A feeling of tightness in a person’s abdomen is usually the result of digestive or hormonal issues. The sensation often goes away on its own, but it can signal an underlying health issue.
This article will look at potential causes of a tight abdomen, which people often refer to as their stomach.
They include:
- gas
- constipation
- indigestion
- food poisoning
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- hiatal hernia
- gastritis
- premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- pregnancy
- ascites
It will also discuss symptoms, treatments, and ways to prevent a tight abdomen.
A tight abdomen can feel different for everyone. It may feel as if the abdominal muscles are contracting and creating pressure in the stomach or as if the abdomen is full, creating pressure.
Here are some possible sources of a feeling of tightness:
- contractions in the abdominal muscles
- problems with the organs in the abdomen
- problems inside the gastrointestinal tract
- fluid collecting in tissues, known as edema or ascites
The tight sensation is often a temporary discomfort caused by diet or hormones. However, it can also be a symptom of an underlying condition.
Here are some of the reasons a person might have a tight abdomen.
Gas
Gas commonly causes distension and tightness in the abdomen.
A person may also experience:
- belching
- bloating
- passing gas
Here are some possible reasons for gas:
- swallowing air, for example by eating fast or drinking fizzy drinks
- the natural process of breaking down carbohydrates in the gut
- having a health condition, such as IBS or a food intolerance
- overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine
- obstructions, which can increase gas
There are many ways to prevent gas, such as:
- taking time when eating and drinking
- avoiding or quitting smoking
- limit consumption of fizzy drinks and drinking with a straw
- talking with a doctor about dietary changes
- taking medications to manage gas
- seeking treatment for health conditions such as IBS or a food intolerance
How can you get rid of trapped gas?
Constipation
When the stool is not passed through the colon quickly enough, it can cause a tight feeling in the abdomen.
Other symptoms of constipation include:
- fewer than 3 bowel movements a week
- unusually firm, lumpy, or dry stools
- difficulty emptying the bowels
- abdominal pain
Many factors increase the risk of constipation, including:
- a low fiber diet
- a low fluid intake
- some medications
- surgery, for example, to the colon
- medical conditions, such as IBS, celiac disease, and diabetes
- low activity levels
- pregnancy
Treatment options include:
- consuming more fiber
- drinking more water
- regular physical activity
- checking with a doctor about drugs and supplements that may cause constipation
- taking over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription medications
Which foods are good for people with constipation?
Indigestion
Indigestion or dyspepsia occurs when stomach acid irritates the stomach lining or the food pipe.
Indigestion can happen for many reasons, such as:
- eating too much or too quickly
- smoking
- certain medications
- stress
- alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods
Indigestion can cause bloating and a tight stomach, as well as:
- a burning feeling in the upper abdomen
- burping, possibly burping up food or liquid
- feeling too full soon after eating
- nausea
- gas
- growling in the digestive system
Here are some remedies that can help:
- reducing caffeine and alcohol intake
- limiting consumption of fizzy drinks
- avoiding rich, fatty, or spicy foods
- avoiding or quitting smoking
- managing stress
- using OTC or prescription medications
- seeking treatment for various health problems, including acid reflux, gallbladder inflammation, and lactose intolerance
What foods should you eat and avoid with acid reflux?
Food poisoning
Food poisoning occurs after eating contaminated foods.
It can cause a tight feeling and cramps in the abdomen, along with:
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- nausea
- fever
Depending on the cause of contamination, symptoms can take from 30 minutes to 2 weeks to appear.
People should see a doctor if they have severe symptoms, signs of dehydration, or blood in stools. Treatment will depend on the underlying pathogen.
What can you eat after food poisoning?
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) refers to a collection of symptoms that affect the digestive system.
IBS can cause a tight feeling in the abdomen, due to bloating. Other symptoms include:
- abdominal pain
- constipation, diarrhea, or both
- mucus in stool
- the feeling of not finishing a bowel movement
It is unclear what causes IBS, but it may be linked to stress, bacterial infections, or food sensitivities.
Treatment may involve:
- dietary changes
- managing stress
- exercise
- getting enough sleep
- probiotics
- OTC and prescription medications
Which diet can help with IBS?
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal or hiatus hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest. Tightness in the upper portion of the stomach can occur.
Tightness in the upper portion of the stomach can occur.
Other possible symptoms are:
- gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), with acid reflux
- heartburn
- cough
- asthma
- bad breath
- abdominal bloating
- gas
- nausea
- pain or difficulty with swallowing
Treatment aims to manage symptoms, usually with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Some people will need surgery.
Which foods should you eat or avoid with a hiatal hernia?
Gastritis
Gastritis is a common condition that involves inflammation of the stomach lining. Often, there are no symptoms. But, it can cause symptoms of indigestion, including pain, discomfort, and tightness in the upper abdomen.
It can also lead to:
- feeling too full during or soon after eating
- nausea and vomiting
- low appetite and weight loss
It may stem from a bacterial infection or an autoimmune reaction, where the body attacks healthy cells in the stomach. It can also occur with a number of health conditions and treatments, such as celiac disease, portal hypertension, and chemotherapy.
It can also occur with a number of health conditions and treatments, such as celiac disease, portal hypertension, and chemotherapy.
Treatment for gastritis will depend on the cause. Options include using a PPI, antibiotics, supplements, and dietary changes.
Which dietary choices are best for gastritis?
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome often occurs after ovulation and before a menstrual period.
PMS can cause fluid to build up, leading to bloating. This can make the abdomen feel tight.
Other symptoms can occur, such as:
- abdominal pain and cramping
- diarrhea or constipation
- headache
- back pain
- clumsiness
- increased sensitivity to light and sound
- fatigue
- irritability
- mood changes
- painful breasts
Various treatments can help manage PMS. Diuretics, sometimes called water pills, may help relieve bloating due to fluid retention.
Which foods can help relieve period cramps?
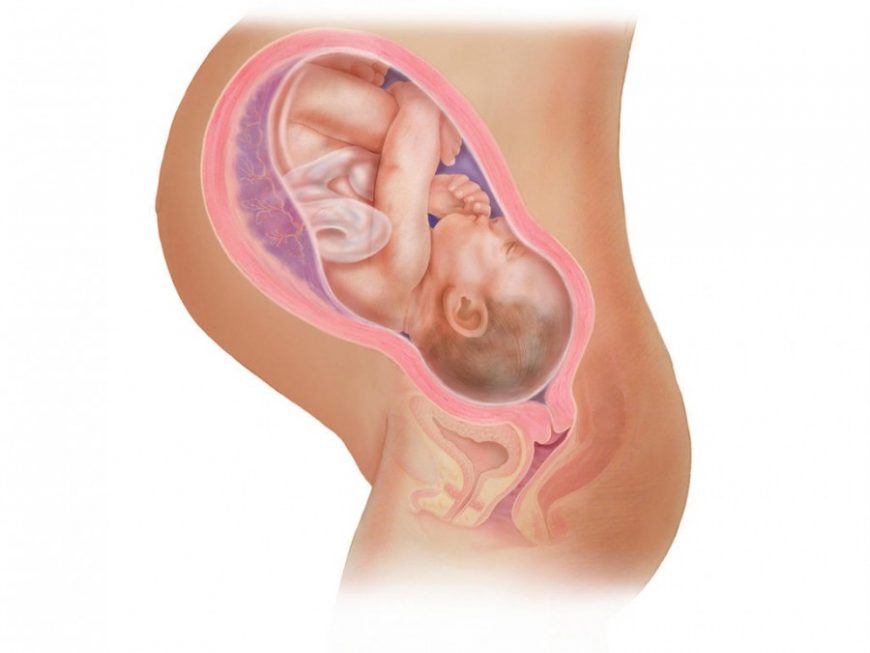
Pregnancy
Tightness can occur in the abdomen in the early stages of pregnancy as the womb or uterus stretches. If pain occurs too, the person should seek medical help as it may indicate something is wrong.
If pain occurs too, the person should seek medical help as it may indicate something is wrong.
In the second or third trimester, labor contractions or Braxton Hicks contractions can produce a sense of abdominal tightening. Both types of contractions are more common in the third trimester.
Braxton Hicks contractions can cause discomfort, but they pass. They do not mean labor is starting. Persistent contractions may be a sign that labor is beginning.
Braxton Hicks contractions last from less than 30 seconds up to 2 minutes. Labor contractions last from 30 to less than 90 seconds.
Changing sitting or lying positions or doing gentle activities, such as stretching or walking, can relieve abdominal tightness during pregnancy.
What should you eat and avoid during pregnancy?
Ascites
Ascites is when fluid collects in the abdominal cavity, causing the abdomen to appear swollen and feel tight.
Ascites can also lead to:
- weight gain
- abdominal pain or discomfort
- difficulty breathing
- fluid in the lung cavities
Ascites can occur with:
- liver disease
- blood clots in vessels around the liver
- heart failure
- kidney failure
- metastatic cancer
Treatment includes reducing sodium intake. Diuretics (water pills) may also help. In some cases, a person will need a doctor to remove fluid.
Diuretics (water pills) may also help. In some cases, a person will need a doctor to remove fluid.
Which foods protect the liver?
The best methods for preventing a tight abdomen will vary depending on the cause.
It is not always possible, but measures that can help a person stay healthy include:
- eating a balanced diet
- staying hydrated
- exercising regularly
- managing stress
- regular handwashing
What are 12 home remedies for stomach pain?
In many cases, a tight abdomen does not require medical attention. However, it can be an early sign of a more serious condition.
If the feeling persists, causes significant discomfort, or worsens, an individual should seek medical advice. A doctor will determine the cause and recommend suitable treatment.
People should seek immediate medical attention if they experience the following alongside distention and tightness:
- bloody stools
- severe nausea and vomiting
- weight loss
- severe abdominal pain
- difficulty breathing
- a fever
When should you see a doctor for stomach pain and nausea?
Here are some answers to questions about tightness in the abdomen.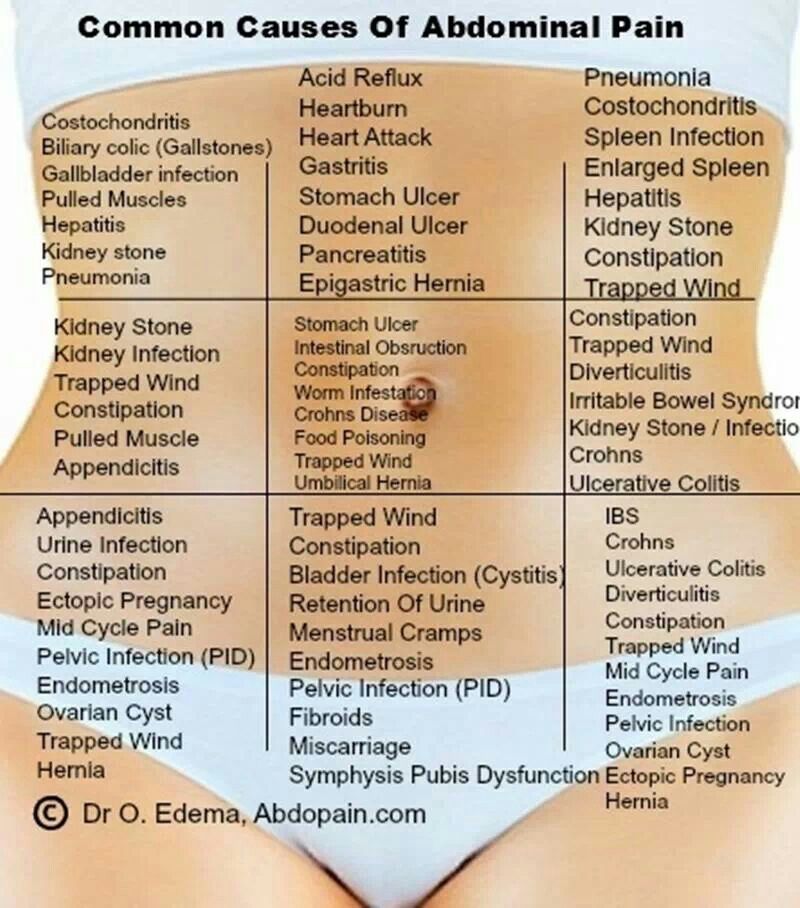
What causes stomach or abdominal tightness?
Common causes include gas, overeating, indigestion, IBS, and pregnancy. Fluid retention can lead to bloating in people with PMS or ascites, which occurs with liver disease and other chronic health issues.
How do you relieve stomach or abdominal tightness?
Tightness often passes with time, but if you have a condition such as GERD, a doctor may prescribe medication. Bloating that occurs with food poisoning may need urgent medical care.
How can I prevent stomach or abdominal tightness?
It is not always possible to prevent a feeling of tightness because it depends on the cause. However, eating a varied diet, getting enough exercise, drinking plenty of water, and managing stress may help keep the gut healthy. Anyone with severe, persistent, or recurring symptoms should seek medical advice. They may have an underlying condition that needs treatment.
There are many reasons why a person’s abdomen, including their stomach, might feel tight.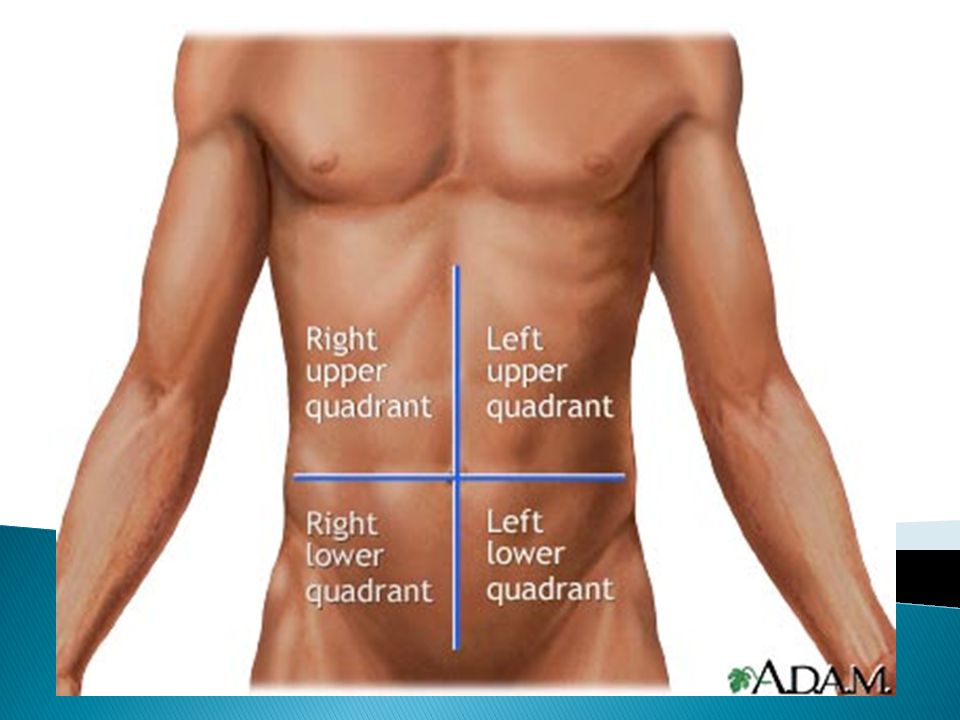 It is usually related to digestive or hormonal factors. There may be other symptoms, depending on the cause.
It is usually related to digestive or hormonal factors. There may be other symptoms, depending on the cause.
In most cases, a tight abdomen is not a cause for concern. However, if symptoms are severe or persistent, the person may need medical attention.
Tight stomach: Causes and treatments
A feeling of tightness in a person’s stomach is usually the result of digestive or hormonal issues. The sensation often goes away on its own, but it can also signal an underlying health issue.
This article will look at potential causes of a tight stomach, including:
- constipation
- indigestion
- food poisoning
- irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- hiatal hernia
- gastritis
- premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- pregnancy
It will also discuss symptoms, treatments, and ways to prevent a tight stomach.
Share on PinterestA tight stomach may have many different causes, including constipation, IBS, and food poisoning.A tight stomach can feel different for everyone. It may feel as if the abdominal muscles are contracting and creating pressure in the stomach.
It may feel as if the abdominal muscles are contracting and creating pressure in the stomach.
The feeling can come from the abdominal muscles, the stomach wall lining, or the organs surrounding the stomach.
The tight sensation is often a temporary discomfort caused by diet or hormones. However, it can also be a symptom of an underlying condition.
In most cases, a tight stomach is caused by physical factors, such as digestive issues or hormonal changes.
The feeling can also be caused by chronic stress. Stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness, may be helpful in such cases.
Physical causes for a tight stomach include:
Constipation
When the stool is not passed through the colon quickly enough, it can cause a tight feeling in the stomach. The normal range for bowel movements in adults is between 1 to 3 times per day and 2 to 3 times per week.
Other symptoms of constipation include:
- fewer than 3 bowel movements a week
- abdominal pain
- abnormally firm, lumpy, or dry stools
- difficulty emptying the bowels
Constipation is typically caused by a poor diet.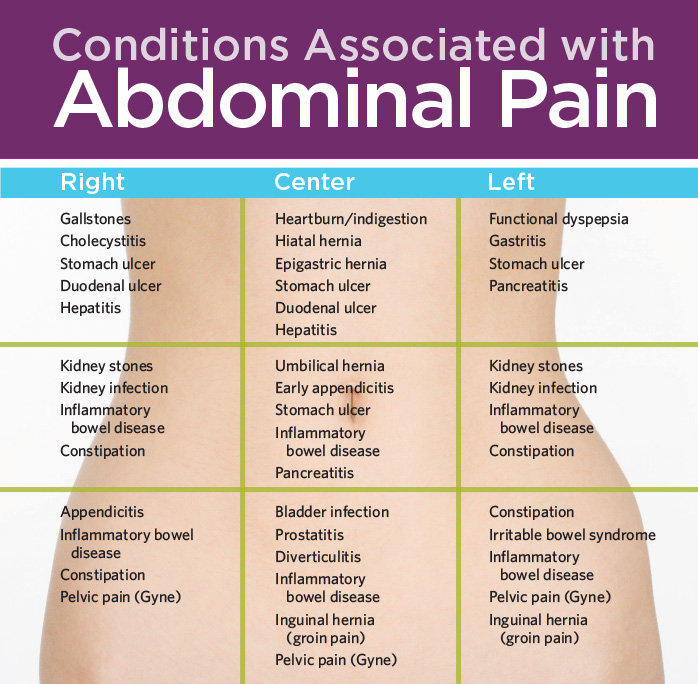 It can be relieved by eating high-fiber foods and drinking plenty of fluids.
It can be relieved by eating high-fiber foods and drinking plenty of fluids.
Indigestion
Indigestion occurs when stomach acid irritates the lining of the stomach or the food pipe.
Overeating, or eating too quickly, can lead to indigestion. Smoking, certain medications, stress, and alcohol can also trigger the condition.
Indigestion can cause a tight stomach, alongside:
- heartburn
- nausea
- gas
- abdominal bloating
- a bad taste in the mouth
Indigestion often resolves without treatment, but home remedies can help, including:
- avoiding caffeine and alcohol
- avoiding rich, fatty, or spicy foods
- cutting down on smoking
- losing weight
- propping the head and shoulders up when lying down
Food poisoning
Share on PinterestA tight feeling in the stomach may be caused by food poisoning.
Food poisoning occurs after eating contaminated foods. It can cause a tight feeling in the stomach, alongside other symptoms, such as:
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- nausea
- abdominal pain or cramps
- loss of appetite
- fever
- muscle aches
In most cases, food poisoning can be managed at home by resting, eating dry, bland food, and staying hydrated.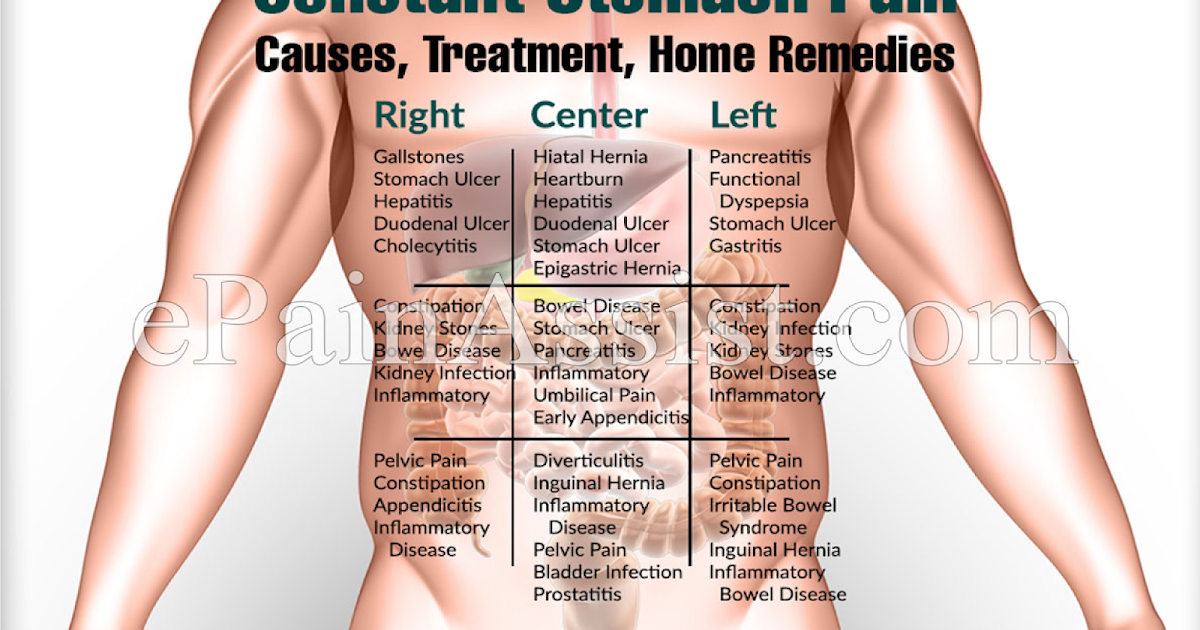 If food poisoning is severe, a person should consult a doctor.
If food poisoning is severe, a person should consult a doctor.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome is a chronic condition affecting the digestive system. Alongside a tight stomach, IBS symptoms can include:
- abdominal pain
- constipation
- abdominal bloating
- gas
- diarrhea
IBS is usually managed with medication and lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments.
Hiatal hernia
A hiatal or hiatus hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes into the chest. Tightness in the upper portion of the stomach can occur, along with other symptoms, including:
- heartburn
- bad breath
- abdominal bloating
- gas
- nausea
- acid reflux
- difficulty swallowing
A hiatal hernia does not usually require treatment. It can be addressed with dietary changes and medications, such as antacids. In severe cases, surgery may be an option.
Gastritis
Gastritis is a common condition that occurs when there is an inflammation of the stomach lining.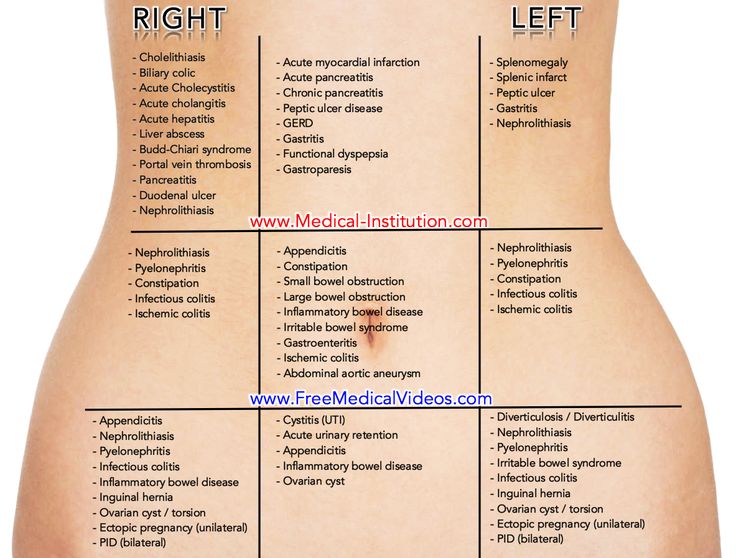 This can cause tightness in the upper region of the stomach.
This can cause tightness in the upper region of the stomach.
Other symptoms of gastritis include:
- indigestion
- nausea and vomiting
- feeling unusually full after food
- abdominal pain
Gastritis is treated with medications, including antacids, histamine blockers, and proton-pump inhibitors.
Premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
Premenstrual syndrome often occurs within 2 weeks of a person’s menstrual period. PMS can cause a tight stomach and other symptoms, such as:
- abdominal pain
- abdominal bloating
- fatigue
- irritability
- mood swings
- muscle aches
- painful breasts
Symptoms of PMS can be managed by:
- eating small, regular meals to reduce bloating
- avoiding salt to limit bloating
- eating fruits, vegetables, and fiber-rich foods
- exercising
- taking painkillers
Pregnancy
A person may feel tightness in their stomach in the early stages of pregnancy. This is caused by the womb or uterus stretching.
This is caused by the womb or uterus stretching.
A woman should seek medical help if severe pain also occurs, particularly in the first 20 weeks, as this can be a sign of miscarriage.
In the second or third trimester, stomach tightening can be caused by labor contractions or Braxton-Hicks contractions. Both types of contractions are more common in the third trimester, however.
Braxton-Hicks contractions can cause discomfort, but they will pass. If contractions do not pass and are becoming more persistent, this may be a sign that labor is beginning.
Changing sitting or lying positions or doing gentle activities, such as stretching or walking, can relieve stomach tightness during pregnancy.
Share on PinterestMinimizing stress may be recommended to help reduce the chance of developing a tight stomach.
The best methods for preventing a tight stomach will vary depending on the cause.
In some cases, it may not be possible to prevent a tight stomach, such as during pregnancy or food poisoning.
In other cases, the chances of developing the symptoms of a tight stomach can be reduced through:
- eating a healthful, balanced diet
- staying hydrated
- exercising regularly
- minimizing stress
In most cases, a tight stomach does not require medical attention. However, it can also be an early sign of a more serious condition.
If the feeling causes significant discomfort and persists for more than a few days, an individual should seek medical advice to determine the cause, and find out how to manage the feeling.
Immediate medical attention should be sought if the following symptoms occur alongside stomach tightness:
- bloody stools
- severe nausea and vomiting
- weight loss
- severe abdominal pain
- difficulty breathing
There are many reasons why a person’s stomach might feel tight. It is usually related to digestive or hormonal factors. A tight stomach may be accompanied by other symptoms that can be mild or severe, depending on the cause.
In most cases, a tight stomach is not a cause for concern. However, if symptoms persist for longer than a few days, or are severe, then medical attention may be required.
Heaviness in the lower abdomen - the causes of occurrence, under what diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. nine0003
Heaviness in the lower abdomen - the causes of occurrence, in what diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
The feeling of heaviness, fullness, pulling pain in the lower abdomen are subjective sensations and require detailed diagnosis. The abdomen is a concentration of vital organs that are located close to each other, which makes it difficult to determine the source of discomfort. The situation is aggravated by the fact that it is difficult for a person to describe the sensations experienced and indicate the exact localization of pain. nine0003
Varieties of
Often, heaviness in the lower abdomen is accompanied by pain, a feeling of fullness, and sometimes discharge from the genitals or rectum.
The pain can be acute, paroxysmal, pulling, have different localization (right, left or center) and give to the lower back, scrotum, rectum or vagina.
Possible causes of heaviness in the lower abdomen
Heaviness and pulling sensations in the lower abdomen are often physiological in nature and occur at pregnancy . Discomfort develops due to an increase in the uterus, which puts pressure on neighboring organs - the bladder, intestines. In addition, the enlarged uterus stretches the ligaments and abdominal muscles, causing mild pain. However, the combination of severity with severe pain may be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy or early placental abruption.
Discomfort develops due to an increase in the uterus, which puts pressure on neighboring organs - the bladder, intestines. In addition, the enlarged uterus stretches the ligaments and abdominal muscles, causing mild pain. However, the combination of severity with severe pain may be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy or early placental abruption.
Also common causes of heaviness in the lower abdomen include premenstrual syndrome and dysmenorrhea. Premenstrual syndrome occurs in more than half of women. There is no clear clinical picture for this condition. Often it is accompanied by heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen, mood swings, tearfulness, headache. These symptoms disappear after the onset of menstruation.
Premenstrual syndrome is based on hormonal changes.
With dysmenorrhea , the pain syndrome is more pronounced, and the cause may be a violation of blood circulation in the pelvic area. Vasospasm and venous congestion lead to irritation of the nerve endings, which is accompanied by pulling pain. Similar sensations are characteristic of perimenopausal period , which occurs from the moment of the first menopausal symptoms and lasts one to two years after the last menstruation. During this period, the level of estradiol in the blood fluctuates greatly, which can cause heaviness in the lower abdomen and back pain.
Similar sensations are characteristic of perimenopausal period , which occurs from the moment of the first menopausal symptoms and lasts one to two years after the last menstruation. During this period, the level of estradiol in the blood fluctuates greatly, which can cause heaviness in the lower abdomen and back pain.
Gynecological diseases are almost always accompanied by pain and heaviness in the lower abdomen. Most often, these are inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs: adnexitis, endometritis, salpingitis, parametritis , etc. As a rule, these pathologies develop as a result of an ascending infection. The main pathogens are sexually transmitted microorganisms, or microorganisms that live in the vulva and anus. Additional factors contribute to the development of inflammation: frequent change of sexual partners, previous infectious processes, abortion, use of intrauterine devices, etc. nine0003
Inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs are accompanied by pulling pain, radiating to the lower back and lower limbs, discharge (sometimes bloody) from the vagina, fever. Symptoms endometriosis , which often causes pulling pain, intensify before the onset of menstruation. Heaviness in the lower abdomen sometimes serves as the only manifestation of ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids .
Symptoms endometriosis , which often causes pulling pain, intensify before the onset of menstruation. Heaviness in the lower abdomen sometimes serves as the only manifestation of ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids .
A common problem was pelvic pain , which can be caused by urological, gynecological, proctological and vascular disorders.
Drawing and aching pains may appear with irritable bowel syndrome and be accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, bloating and flatulence. At night, the feeling of discomfort disappears.
In diseases of the genitourinary system, heaviness in the lower abdomen develops very often. When a stone blocks the ureter or urethra, the outflow of urine is disturbed and there are pulling pains in the groin. With complete obstruction, pain can acquire a sharp unbearable character. Violation of the outflow of urine can also be the result of other diseases: prostate hyperplasia or cancer, strictures of the urethra, etc. In these cases, pain appears in the perineum, in the sacrum or lower abdomen. Often they give to the groin and external genitalia. nine0003
In these cases, pain appears in the perineum, in the sacrum or lower abdomen. Often they give to the groin and external genitalia. nine0003
Often, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen can be a manifestation of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. Aching pain, as a rule, occurs while walking or in a sitting position. The pain subsides at night.
Diagnostics and examination
Diagnosis of pathologies associated with pain and a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen is difficult.
Since the clinical manifestations of diseases do not correspond to their severity, delay in the treatment of the abdominal organs is fraught with serious consequences. nine0003
After questioning and examining the patient, the doctor gives a referral for a clinical blood test and a general urine test.
In some cases, an X-ray examination of the kidneys and urinary tract is necessary. In this case, excretory urography is often used.
Which doctors to contact
With the appearance of heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen, you should contact therapist for referrals for tests and examinations. The therapist can refer to urologist and gastroenterologist. Women are encouraged to make an appointment with gynecologist, since often the cause of heaviness in the lower abdomen lies in diseases of the reproductive organs. If an X-ray examination reveals a disease of the spine, the patient is referred to a rheumatologist, traumatologist or neurologist. nine0003
The therapist can refer to urologist and gastroenterologist. Women are encouraged to make an appointment with gynecologist, since often the cause of heaviness in the lower abdomen lies in diseases of the reproductive organs. If an X-ray examination reveals a disease of the spine, the patient is referred to a rheumatologist, traumatologist or neurologist. nine0003
Treatment
Heaviness in the lower abdomen can be a manifestation of various diseases, so the treatment is determined by the diagnosis.
What to do
Heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen can be explained by physiological causes, but can also serve as symptoms of serious pathologies that require rapid diagnosis and treatment. If you experience discomfort, do not postpone a visit to the doctor.
With heaviness and pain in the lower abdomen, heating cannot be used - this can lead to irreparable consequences. Pain relievers should only be taken with a doctor's prescription.
Persistent acute pain, which may be accompanied by discharge from the genital organs, nausea, vomiting, urinary incontinence, requires immediate medical attention.
Sources:
- Clinical guidelines "Normal pregnancy". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. – 2020.
- Clinical guidelines "Amenorrhoea and oligomenorrhea". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. – 2021.
- Clinical guidelines "Endometriosis". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. – 2020.
- Clinical guidelines "Inflammatory diseases of the female pelvic organs". Developed by: Russian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. – 2021.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0005 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes over time, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
Diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles - symptoms, signs, degrees, causes and treatment in men and women in Moscow in the "SM-Clinic"
The surgeon deals with the treatment of this disease
Book online Request a call
- What is diastasis rectus abdominis?
- About disease
- Species
- Symptoms of diastasis recti
- Causes of diastasis recti
- Diagnostics of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
- Expert opinion
- Treatment of diastasis recti
- Surgical treatment of diastasis recti nine0104 Prevention
- Rehabilitation after surgery
- Questions and answers
- Sources
About the disease
The disease is based on stretching and expansion of the white line of the abdomen - a tendon that is located between the rectus muscles, connects and holds them. This is a strip of connective tissue, consisting of several layers, located in the middle of the abdomen vertically from the xiphoid process to the pubic joint. nine0003
This is a strip of connective tissue, consisting of several layers, located in the middle of the abdomen vertically from the xiphoid process to the pubic joint. nine0003
Due to an increase in intra-abdominal pressure or a violation of the properties of the connective fibers, the structure of the tendon changes, it weakens, becomes thinner and stretches. The trigger mechanism is prolonged pressure on the abdominal wall associated with pregnancy or visceral obesity. An aggravating factor is the loosening of the white line against the background of collagenopathy, the effects of relaxin, the immaturity of cellular structures, etc.
As a result, the white line becomes thinner and stretched. Normally, its dimensions are restored with a gradual decrease in the abdomen or as the properties of the connective tissue normalize. Thus, physiological diastasis is eliminated during the neonatal period or in women after childbirth. nine0003
If abdominal training is started early in the postpartum period, this leads to a contraction of the rectus muscles and a simultaneous increase in intra-abdominal pressure, and the white line is fixed in a stretched position and does not hold the internal organs well. As a result, unaesthetic vertical folds form on the abdomen, a rounded protrusion appears, dysfunction of the digestive tract occurs and the risk of hernia formation increases.
As a result, unaesthetic vertical folds form on the abdomen, a rounded protrusion appears, dysfunction of the digestive tract occurs and the risk of hernia formation increases.
Species
Depending on the magnitude of the stretching of the tendon ligament, there are 3 degrees of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles:
- first - the muscles move away from each other by 2.5-5 cm;
- second - ligaments diverge by 5-8 cm;
- third - the line is stretched more than 8 cm.
According to the localization of the place of maximum stretching, supra-umbilical, sub-umbilical and mixed forms of diastasis are distinguished.
According to the degree of involvement of other muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the pathology is classified into types:
- A - classical divergence of muscles after natural childbirth; nine0105
- B - relaxation of the lower lateral sections of the muscles;
- C - expansion affects the region of the ribs and the xiphoid process;
- D - diastasis is combined with a curvature of the waistline.
Symptoms of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
Manifestations of BPMD increase as the pathology progresses. In women, a vivid clinical picture manifests itself abruptly (shortly after childbirth), while in men the disease develops gradually.
At the onset of the disease, there may be no symptoms at all. The patient then notices a characteristic rounded vertical protrusion in the center of the abdomen. With deliberate tension of the press, the inner edges of the rectus muscles and the groove between them are clearly visible. Due to muscle dysfunction, pain in the spine, lower back, fatigue, and posture disorders are possible.
With the progression of the pathology, manifestations of dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract join:
- heartburn; nine0104 belching;
- flatulence;
- abdominal pain;
- constipation.
In the third stage of diastasis, patients are faced with the formation of hernias, which are formed due to structural defects in the white line. Possible ptosis (omission) of internal organs and serious disturbances in the work of the intestines (in severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops). Women often experience urinary incontinence, renal colic.
Possible ptosis (omission) of internal organs and serious disturbances in the work of the intestines (in severe cases, intestinal obstruction develops). Women often experience urinary incontinence, renal colic.
Causes of diastasis recti
Increase the risk of developing diastasis pathology of the connective tissue and increased pressure in the abdominal cavity. In different categories of patients, the causes of the development of PMSD are different.
Divergence of muscles in children is due to the failure of the musculature and tendons. After 2-12 months after birth, the muscles come into tone, the ligaments and tendons are strengthened - the process resolves itself. In premature babies and infants with intrauterine developmental pathologies, this may take longer. With Down syndrome, there is a risk of maintaining diastasis for life. nine0003
Pregnancy is the provocateur of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles in women. The growing uterus puts considerable pressure on the linea alba, stretching it. Under the action of hormones, the synthesis of collagen fibers is inhibited, the ligaments become looser. But a few months after the birth, the white line of the abdomen is normally restored.
Under the action of hormones, the synthesis of collagen fibers is inhibited, the ligaments become looser. But a few months after the birth, the white line of the abdomen is normally restored.
In men, BMD is often provoked by obesity, physical activity and hereditary collagenopathies. The risk of diastasis increases with a tendency to constipation, as well as with chronic respiratory diseases accompanied by coughing. nine0003
Treatment of pathology by conservative methods is possible with a small diastasis. At the later stages of development, the pathological divergence of muscles is eliminated with the help of abdominal plastic surgery.
Get advice
If you experience these symptoms, we recommend that you make an appointment with your doctor. Timely consultation will prevent negative consequences for your health.
You can find out more about the disease, prices for treatment and sign up for a consultation with a specialist by phone:
+7 (495) 292-39-72
Request a call back Book online
Why SM-Clinic?
1
Treatment is carried out in accordance with clinical recommendations
2
A comprehensive assessment of the nature of the disease and treatment prognosis
3
Modern diagnostic equipment and own laboratory
4
High level of service and a weighted price policy
Diagnosis of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
Identification of BPMD is not difficult, since the disease has characteristic clinical manifestations. With signs of diastasis, you should contact the surgeon.
An increase in the space between the rectus muscles is determined during palpation of the abdomen. To conduct the test, the patient is asked to lie on his back, legs slightly bent at the knees, and then tighten the abdominal muscles, raising his head and shoulder blades. In patients with obesity, the doctor is not always able to fully explore the width of the white line. nine0003
The exact size of the stretch is determined by ultrasound. This diagnostic method also allows you to detect complications (hernia, displacement of internal organs). In order to differentiate the symptoms of diastasis and manifestations of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or the genitourinary system, consultations of specialized specialists are prescribed.
Expert opinion
Surgeons warn that diastasis rectus abdominis is asymptomatic for a long time. Therefore, in the presence of predisposing factors (recent pregnancy and childbirth, chronic constipation, obesity) or non-specific complaints, you should independently feel the white line of the abdomen in the navel.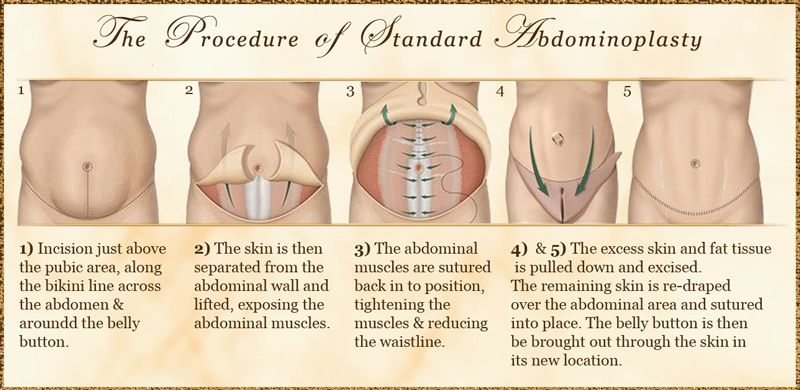 If the distance between the rectus muscles is more than 2.5 cm, contact the surgeon. Also, do not delay the visit in any doubtful cases. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis, self-examination does not exclude the need for an in-person consultation. nine0003
If the distance between the rectus muscles is more than 2.5 cm, contact the surgeon. Also, do not delay the visit in any doubtful cases. Only a doctor can establish the correct diagnosis, self-examination does not exclude the need for an in-person consultation. nine0003
Egiev Valery Nikolaevich, surgeon, oncologist, doctor of medical sciences, professor, head of the Department of Surgery and Oncology, FPC MR MI RUDN University
Treatment of diastasis recti
Functional diastasis in newborns and puerperas does not require treatment. Doctors use expectant tactics, recommend adhering to the principles of rational nutrition, doing massages, and doing gymnastics. The observation period can last up to 12 months. If after this time the problem persists, the surgeon decides on an operative method of correction. nine0003
Conservative treatment
Patients are prescribed a diet to prevent constipation and excessive gas formation, as well as to gradually reduce weight. In the postpartum period, incl. after a caesarean section, women are advised to wear a bandage, support the stomach during sneezing and coughing. The general strengthening of the muscles allows you to quickly restore the tone of the anterior abdominal wall, so patients are prescribed exercise therapy, swimming, yoga classes. It is important to exclude any training of the abdominal muscles. You can not perform exercises in the knee-elbow position, as well as in the emphasis (bar). Such loads can be resumed after the restoration of the size of the white line. Conservative treatment is effective only at the 1st stage of BPMD. nine0003
Surgical treatment of diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles
In case of complicated and uncomplicated diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles of the 2-3rd degree, surgical treatment is indicated. It is possible to use the following surgical techniques:
- Tension plasty using own tissues. It involves stitching the edges of the muscles with the removal of excess connective tissue.
 To date, it is not used due to the high risk of recurrence.
To date, it is not used due to the high risk of recurrence. - Tension-free repair with a mesh prosthesis. It implies the introduction of an endoprosthesis under the site of stretching. nine0105
- Tension plastic with prosthesis installation. It involves the removal of excess connective tissue, suturing the edges of the muscles and strengthening the zone with a polypropylene mesh.
- Combined technology. Includes muscle suturing, mesh strengthening, removal of excess adipose tissue and stretched skin.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of developing diastasis rectus abdominis, you should keep your body in shape - engage in regular exercise, train your muscles. However, do not overdo it: lifting weights can, on the contrary, become the main cause of muscle divergence. nine0003
It is also important to eat a complete and balanced diet - a lack of nutrients will lead to a decrease in the elasticity of the connective tissue.
It is necessary to control your weight - body mass index should not exceed 26 kg/m3. Obesity, especially of the abdominal type, is an important risk factor for BLV.
Obesity, especially of the abdominal type, is an important risk factor for BLV.
Prevention and timely treatment of chronic lung diseases accompanied by cough, pathologies of the digestive system, occurring with constipation, will reduce the possibility of increasing intra-abdominal pressure and, as a result, the likelihood of diastasis. nine0003
Rehabilitation after surgery
After surgery, the patient is under inpatient observation, receiving analgesic and antibiotic therapy. Full recovery lasts 1-3 months. During this period, the patient is prescribed a diet to normalize defecation, it is recommended to avoid significant physical exertion, weight lifting. To prevent excess tension, it is necessary to wear a bandage.
Questions and answers
A surgeon deals with the treatment of pathology. nine0003
In the stronger sex, obesity and connective tissue dysplasia are considered to be the main cause of BMD. Sharp weight loss or weight gain, excessive passion for power loads are capable of provoking muscle divergence. If a man or close relatives have hernias, varicose veins, valgus flat feet, hemorrhoids, this is regarded as an increased tendency to PMSD.
If a man or close relatives have hernias, varicose veins, valgus flat feet, hemorrhoids, this is regarded as an increased tendency to PMSD.
There is no need to rush in this matter. Just the desire to quickly get in shape is the main reason for the progression of diastasis in women. Physical activity can be resumed 1-2 months after birth. You can start with hiking or yoga. Abdominal exercises can be performed soon after the white line is reduced to 2 cm. It is advisable to pay attention to the diet. A smooth decrease in weight and volume of visceral fat will ensure gradual and timely muscle contraction. Sharp weight loss, on the contrary, can increase diastasis. nine0003
You can lie on a hard surface on your back, tense your abs. With gentle movements of the fingers, you should begin to probe the stomach in the middle in the navel. With a normal width of the white line and with diastasis, a depression will be found - this is the median ligament. If its width is equal to or greater than the width of two fingers, you should contact the surgeon. Constipation, bloating and abdominal pain should be alarming. If there are such symptoms, it is necessary to get to the surgeon in the near future.
Constipation, bloating and abdominal pain should be alarming. If there are such symptoms, it is necessary to get to the surgeon in the near future.
Pathogenesis and treatment of ventral hernias and diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles: Abstract of the thesis / Zagirov U.Z. - nineteen95.
Comparative aspects of methods for eliminating diastasis of the rectus abdominis muscles / Topchiev MA, Bondarev VA, Elderov S.Sh.// Astrakhan medical journal. - 2010.
Jessen M. L., Öberg S., Rosenberg J. Treatment Options for Abdominal Rectus Diastasis // Front Surg. - 2019. - No. 6. - R. 65
>
Surgeon Referral Diseases
Brodie's Abscess soft tissue abscess Appendicitis Ascites Atheroma femoral hernia Crohn's disease Bursitis Gangrene soft tissue hematoma Giant cell tumor of bone Hygroma Hernia Hernia of the white line of the abdomen hiatal hernia Cholelithiasis Keratoma salivary gland cyst Lipoma Mechanical jaundice Bowel obstruction Oleogranuloma kidney tumor Acute pancreatitis Inguinal hernia Peritonitis Barrett's esophagus Polycystic kidney disease Postoperative hernia Umbilical hernia Stomach cancer Reflux esophagitis (GERD) Thyroiditis Furuncle (boil) Furunculosis cholestasis Cholecystitis Chronic cholecystitis Erosive gastritis Esophageal ulcer Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
All doctors
VDNKh metro station
Belorusskaya metro station
Lesnaya, 57, pp.